practice questions
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
B. 150 bpm-tachycardia
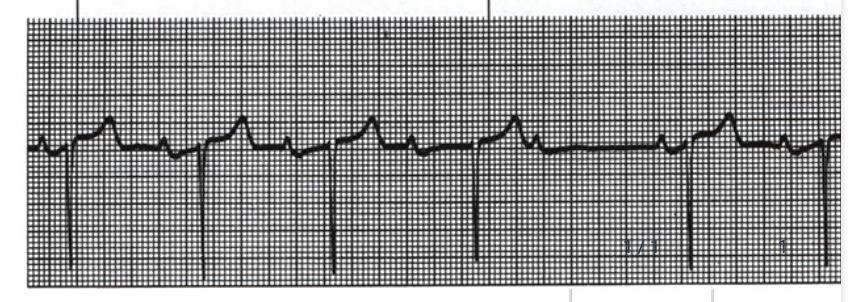
What is the HR displayed here and what would it be classified as?
A. 15 bpm-bradycardia
B. 150 bpm-tachycardia
C. 90 bpm-tachycardia
D. 150 bpm-bradycardia
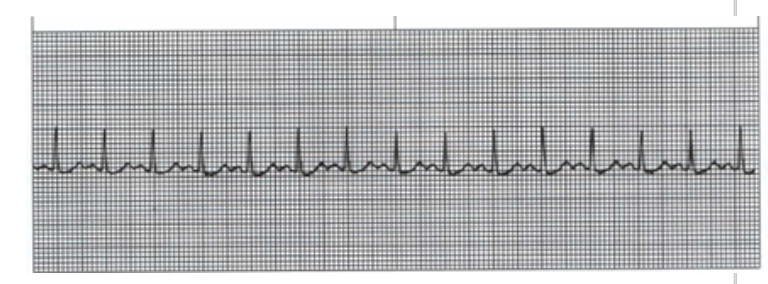
A
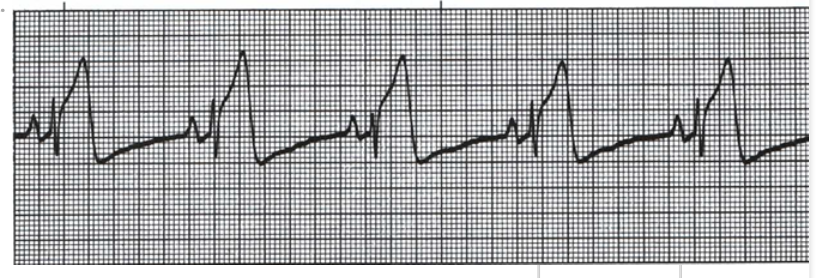
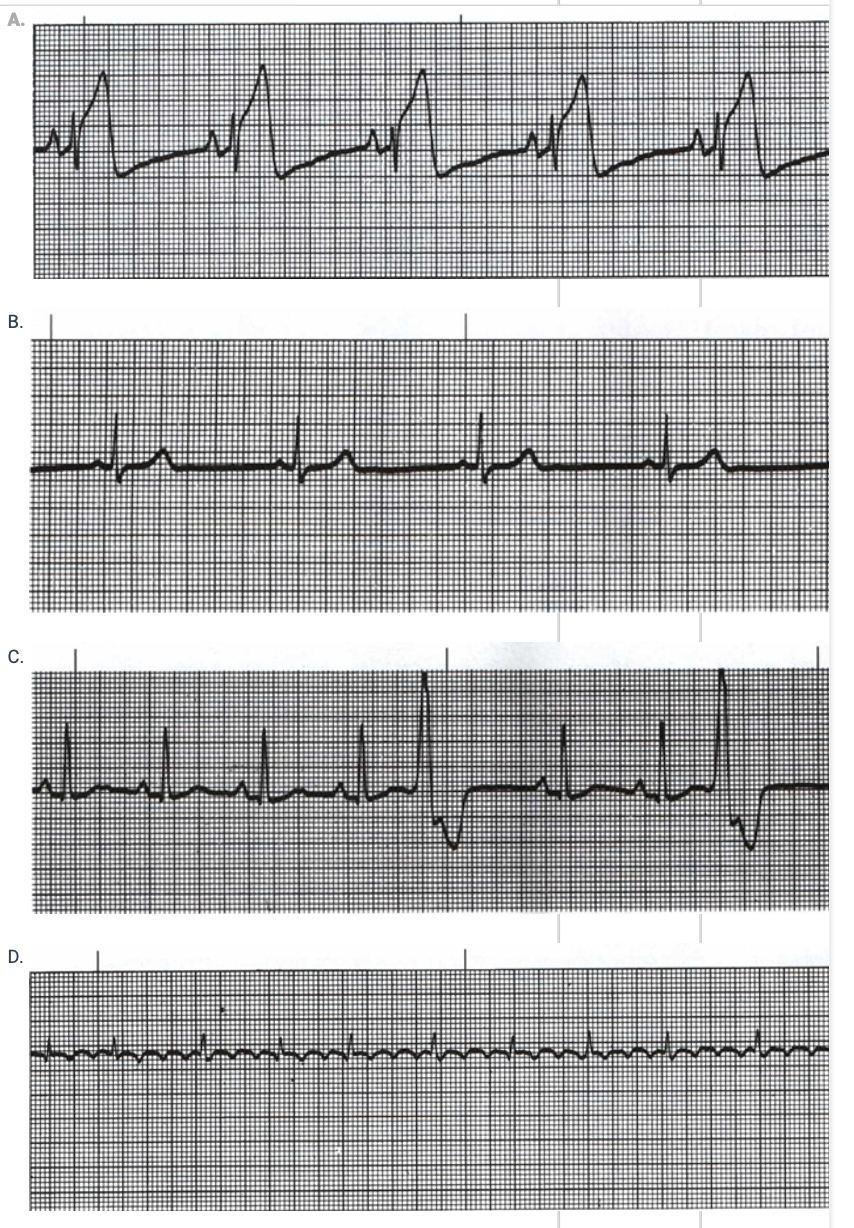
Choose the Rhythm Strip which would indicate a myocardial infarction as occurre
atrial depolarization
what happens at 1
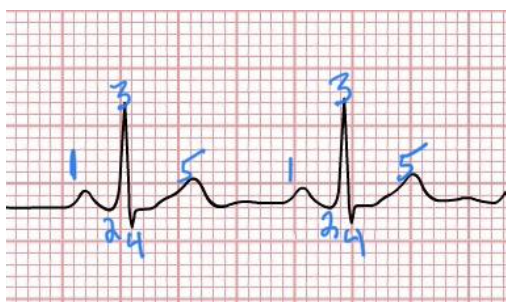
ventricular depolarization
what happens at 2,3,4
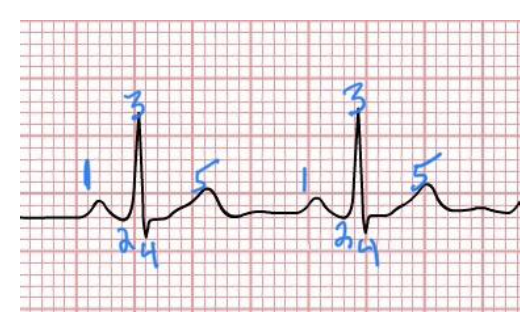
S-T segment
what happens at 4-5
ventricular repolarization
what is 5
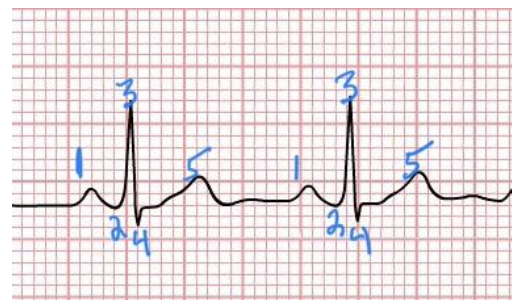
name the rhythm
A. 2nd Degree AV block:
Wenkebach/Mobitz 1
B. Ventricular Fibrillation
C. 3rd Degree AV Block/Complete
Heart Block
D. Atrial Flutter
an ECG…
A. displays the electrical fields created by the summation of action potentials in myocardial cells
B. shows the strength of the contraction of cardiac muscle cells
C. stands for electro-contraction graph
D. is representative of the opening and closing of the heart valves
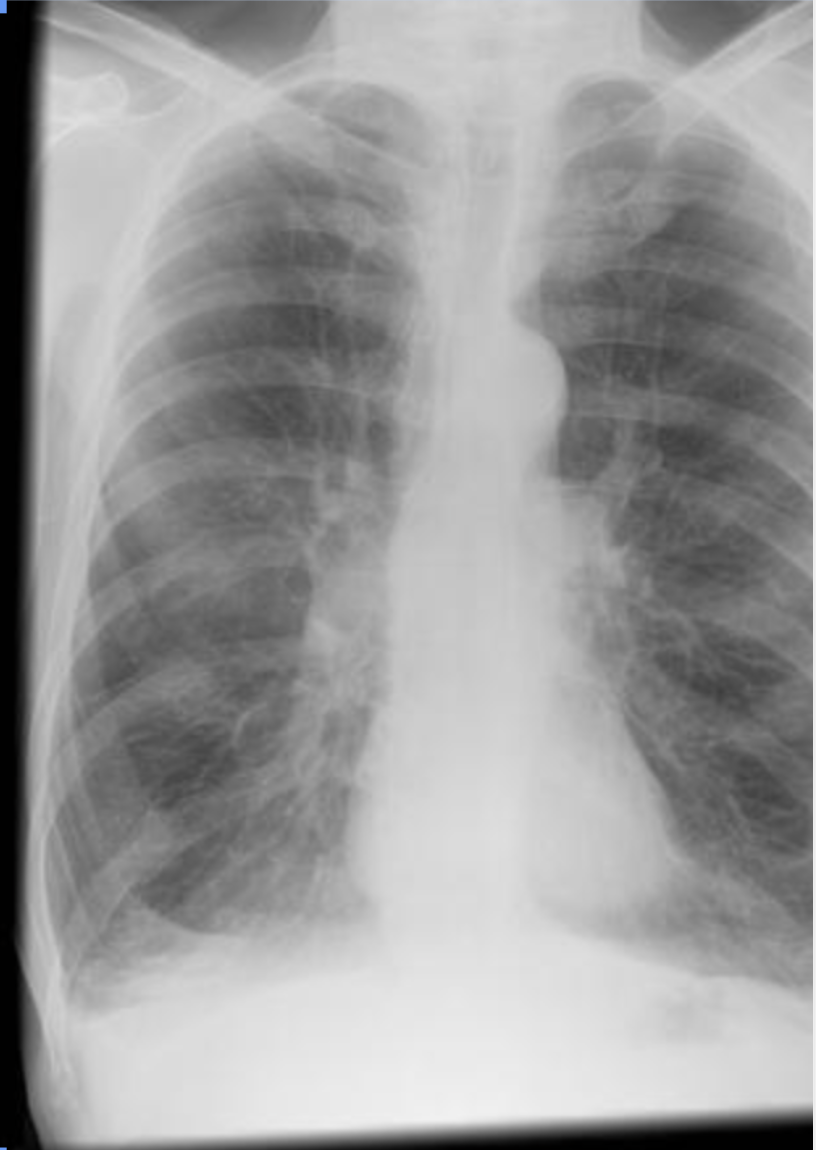
B. Flattened Diaphragm
This x-ray shows what deficit?
A. Ground-Glass Opacities
B. Flattened Diaphragm
C. Mediastinal Shift
D. Cardiomyopathy
A. Emphysema (Obstructive Disease)
In the accompanying picture, if graph "A" is considered healthy, "C" could be representative of
which disease?
A. Emphysema (Obstructive Disease)
B. Pulmonary Fibrosis (Restrictive disease)
C. Heart Failure
D. Atrial Fibrillation
A. Atelectasis: Get patient out of bed and mobilize.
thrown out: You see a patient at bedside following a right middle lobectomy. Auscultation of their lungs reveals decreased breath sounds and crackles over the posterior segment of the right upper lobe. What is likely occurring and what is your BEST plan of care?
A. Atelectasis: Get patient out of bed and mobilize.
B. Atelectasis: Lay back in bed with the head of bed raised.
C. Pneumothorax: Complete Chest Physiotherapy
D. Pneumothorax: Prescribe Acapella/Oscillating PEP
C. Pacing
A physical therapist instructs a patient with chronic pulmonary
dysfunction in energy conservation techniques. Which of the following techniques would be the MOST effective when assisting a patient to complete a selected activity without dyspnea?
A. Ventilatory muscle training
B. Pursed-lip breathing
C. Pacing
D. Diaphragmatic breathing
A. Respiratory Muscle Training
thrown out: Your patient presents with infiltrates in bilateral upper lobes and a weak cough. What would be the BEST , most direct treatment for this patient to improve both symptoms?
A. Respiratory Muscle Training
B. Breathing Techniques
C. Leg Strengthening
D. Using the incentive spiromete
D. Contact emergency services: the person likely is experiencing a PE due to a DVT
You walk into your patients home who is post-op day 4 from their right total knee replacement. They are sitting on their couch, look in distress, appear short of breath and report increased pain in their leg. Their heart rate is 110 bpm and have increased redness and swelling in their right calf. What is the BEST plan of action?
A. Continue with PT that day because these are normal symptoms following a total knee replacement.
B. Place a compression sleeve around the right calf and don't do PT for the day.
C. Tell the patient to relax, put their legs up on a pillow, ice the area and leave the phone in arms reach in case anything else happens and postpone PT for a few days.
D. Contact emergency services: the person likely is experiencing a PE due to a DVT
false
A Myocardial Infarction will cause scarring, but this scar eventually heals to become healthy myocardial cells and will not have an effect on the twisting motion of the heart's contraction.
true/ false?
A. is often reported by patients with myocardia ischemia
C. is thought to arise from the myocardium and stimulates free nerve endings in or near small coronary vessels
(Choose 2) Chest discomfort (heaviness, pressure, tightness,
pain):
A. is often reported by patients with myocardia ischemia
B. is considered STABLE when it occurs at rest.
C. is thought to arise from the myocardium and stimulates free nerve endings in or near small coronary vessels
D. is considered to be ASYMPTOMATIC myocardial ischemia
B. non-productive cough
Choose the sign/symptom that is NOT PRESENT in pneumonia.
A. Fever
B. non-productive cough
C. dyspnea
D. hypoxemia with desaturation on
exertion
B. chronic bronchitis
You are assessing the lungs of a patient and note the following: a productive cough, hyperinflation, flattened diaphragm, crackles (rales) and wheezes with prolonged expiration. What is the patients MOST LIKEL Y diagnosis?
A. pulmonary hypertension
B. chronic bronchitis
C. emphysema
D. pulmonary embolism
B. Weight Gain
D. Jugular Venous Distention
F . Pulmonary valve insufficiency
thrown out: Match the Clinical Manifestation to the diagnosis
(Left Hand Column will contain signs/symptoms of Left Ventricular Failure, Right Hand Column will contain signs/symptoms of Right Ventricular Failure)
A. Signs/Symptoms of Pulmonary Edema
B. Weight Gain
C. Dyspnea on Exertion
D. Jugular Venous Distention
E. Mitral regurgitation
F . Pulmonary valve insufficiency
G. Enlarged Heart
A. Occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficient cardiac output to meet the body’s metabolic demands
B. Reduces exercise capacity
D. Can cause bilateral pitting edema which may take greater than 15 seconds to return to normal
(Choose 3) Congestive Heart Failure:
A. Occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficient cardiac output to meet the body’s metabolic demands
B. Reduces exercise capacity
C. Results in transudation of fluid which “backs-up” and results in pitting edema on only one side of the body
D. Can cause bilateral pitting edema which may take greater than 15 seconds to return to normal
E. Increased stroke volume, resulting in decreased end- diastolic volume and pressure in the ventricles
true
true or false: Decreased Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second is a hallmark feature of pulmonary function tests in all pulmonary diseases.
B. 24 hours after the MI
Following an Acute MI, Creatine Kinase levels peak:
A. 4-8 hours after the MI
B. 24 hours after the MI
C. 2-3 days after the MI
D. Due to skeletal muscle death
A. crackles
You are completing your initial examination on a patient admitted to the hospital for a non-displaced hip fracture who is non-weight-bearing on the right LE. In your chart review, you notice their past medical history includes Emphysema. Being the thorough Binghamton Physical Therapist Alum you are and that patients with poor pulmonary status can quickly take a turn for the worse, you assess vital signs and lung auscultation. What symptoms are you UNLIKEL Y to hear?
A. crackles
B. diminished breath sounds
C. high pitched wheezing
D. prolonged expiratory phase
A. Dyspnea
B. Fatigue
C. Lightheadedness
Choose 3 appropriate signs and symptoms that a person may experience along with myocardial ischemia:
A. Dyspnea
B. Fatigue
C. Lightheadedness
D. Flatulence
E. Gastroc-Soleus pain
F. Loss of taste/smell
B. myocardial oxygen demand is not met by the supply
Myocardial Ischemia occurs when
A. myocardial oxygen supply decreases but the Myocardial demand is met.
B. myocardial oxygen demand is not met by the supply
C. myocardial oxygen supply increases to meet the myocardial demand
D. oxygen supply is low and myocardial cell death occurs
A. The patient has undiagnosed COPD.
Your patient arrives to their first physical therapy appointment
for back pain. When you greet them, you notice they have a barrel chest; they get dyspneic as you both walk back to the examination room. When they sit, they assume a tripod position and demonstrate a breathing technique similar to pursed lip breathing. They recover within 2 minutes. Nothing was in their chart regarding pulmonary disease. What is MOST LIKEL Y going on?
A. The patient has undiagnosed COPD.
B. The patient is experiencing a PE.
C. The patient is in acute respiratory failure.
D. The patient has undiagnosed interstitial lung disease.
False
thrown out: Neurological diseases can cause the patient to present with signs/symptoms consistent with pulmonary obstructive disorders.
True
False
C. Ribs 8,9,10
ONLY Bucket Handle Motion is seen in the following rib number/locations:
A. Ribs 2,3,4
B. Ribs 5,6,7
C. Ribs 8,9,10
D. Rib 1
A. of oxygen will increase from blood to tissue.
Unloading of O2 at the tissue occurs at a rate demanded by
the tissue mitochondria. Therefore, the more active the tissue is (such as during exercise), diffusion...
A. of oxygen will increase from blood to tissue.
B. of carbon dioxide will increase from blood to tissue.
C. of oxygen will stay the same.
D. of carbon dioxide will decrease.
B. Exercise
Dissociation of oxygen from hemoglobin is facilitated by conditions of increased temperature, increased partial pressure of CO2 and decreased pH in metabolically active tissue: Facilitation occurs during...
A. Seated Resting
B. Exercise
C. Sleeping
D. Colder weather.
A. Alveolar Membrane
In healthy conditions, PO2 is approximately 100 mmHg and PCO2 is approximately 45 mmHg at the/in the:
A. Alveolar Membrane
B. Mitochondria
C. Venous return
D. Trachea
A. Medulla
Receptors in the muscles of the chest wall as well as in the lung
and airways are sensitive to rate of breathing and stretch and relay this activity to the _____ to control ventilatory regulation.
A. Medulla
B. Cerebrum
C. Cerebellum
D. Vagus Nerve
A. increases the work of the heart
D. may cause hypertrophy of the myocardium
(Choose 2) An insufficient valve:
A. increases the work of the heart
B. closes completely but allows backward leakage of blood into the prior heart chamber
C. may cause hypotrophy of the myocardium
D. may cause hypertrophy of the myocardium
A. Forms due to scars and abnormal deposits
A stenotic valve:
A. Forms due to scars and abnormal deposits
B. Bulges backward into the prior chamber
C. Does not close fully
D. Is abnormal but does not affect forward blood flow through the heart
A. can be caused by elevated low density lipoproteins penetrating into arterial walls
B. can be caused by low density lipoproteins as they are toxic to endothelial cells and may cause injury and atherosclerotic build up
(Choose 2) Atherosclerosis:
A. can be caused by elevated low density lipoproteins penetrating into arterial walls
B. can be caused by low density lipoproteins as they are toxic to endothelial cells and may cause injury and atherosclerotic build up
C. can be caused by high density lipoproteins sticking together along the walls of the lumen in the vessels.
D. is caused due to low density lipoproteins growing quickly, unexpectedly causing an immediate blockage in vessels
true
A pneumothorax can occur due to blebs or bullae rupturing following a cough.
true or false?
D. The clinical presentation will be consistent with underlying cause of pulmonary edema
Which statement is FALSE regarding pulmonary edema.
A. It is important to diagnose the underlying cause of the edema because this determines prognosis and helps to identify a treatment.
B. the patient could present with acute or subacute onset of dyspnea, tachypnea, restlessness, pulmonary rales, and eventual peripheral cyanosis with hypoxemia
C. it is the breakdown of the capillary and alveolar endothelium that leads to an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the extravascular components of the lungs
D. The clinical presentation will be consistent with underlying cause of pulmonary edema
B. CVA (Stroke)
C. CHF (Congestive Heart Failure)
D. Aortic Aneurysm
(Choose 3) Hypertension is known as the silent killer due to its asymptomatic nature, which increases the risk for multiple complications, including:
A. Diabetes Mellitus
B. CVA (Stroke)
C. CHF (Congestive Heart Failure)
D. Aortic Aneurysm
E. Cardiac Arrhythmias
B. a condition with permanent, abnormal enlargement of the acini, resulting in an INCREASE in surface area for gas exchange
Choose the INCORREC T
statement about Emphysema
A. a condition with permanent, abnormal enlargement of the
acini, resulting in an DECREASE in surface area for gas exchange
B. a condition with permanent, abnormal enlargement of the acini, resulting in an INCREASE in surface area for gas exchange
C. Patients may become cachectic/emaciated and show symptoms that include bilateral
LE edema
D. Lung volume reduction surgery can be effective, removing up to 20% of dysfunctional lung, reducing the hyperinflated state and allowing more of the healthy lung to be actively utilized for gas exchange
B. is the portion of each breath that does not participate in gas exchange in the alveoli.
Dead space ventilation:
A. is the portion of each breath where gas is exchanged in the main bronchus
B. is the portion of each breath that does not participate in gas exchange in the alveoli.
C. is more than 50 percent of each breath we take
D. is NOT dependent on the pattern of breathing
D. Answers 1, 2 and 3.
The unpleasant perception of dyspnea happens...
A. 1. when the drive to breathe is excessive from feedback inputs from the chemoreceptors or feedfoward from the motor cortex
B. 2. when there is a discrepancy between the neural drive to breathe and the level of ventilation achieved.
C. 3. are reliant on mechanical impediments
D. Answers 1, 2 and 3.
E. none of the above
A. Intercostal muscles stiffen during inspiration to maintain a stiff thoracic cage against the negative, subatmospheric pressure created by the diaphragm
D. Maximal Inspiratory Pressure and Maximal Expiratory Pressure can be used to establish a respiratory muscle strengthening program to improve dyspnea on exertion
(Choose 2) 2 functions of the respiratory muscles include
A. Intercostal muscles stiffen during inspiration to maintain a stiff thoracic cage against the negative, subatmospheric pressure created by the diaphragm
B. The scalenes and sternocleidomastoid cause an increase in expiratory pressure to exhale during high levels of exertion.
C. Expiration is primarily caused by activation of the abdominal muscles, NOT by the elastic recoil of the lungs, thoracic cage, and inspiratory muscle relaxation.
D. Maximal Inspiratory Pressure and Maximal Expiratory Pressure can be used to establish a respiratory muscle strengthening program to improve dyspnea on exertion
A. Long Acting Beta-2 Agonist
Advair (fluticasone propionate/salmeterol) is in the drug class:
A. Long Acting Beta-2 Agonist
B. Short Acting Beta-2 Agonist
C. Anti-andrenergic agent
D. Angiotension II receptor blocker
C. myalgia/myopathy
A primary concern for physical therapists for a patient taking atorvastatin is:
A. digoxin toxicity
B. orthostatic hypotension
C. myalgia/myopathy
D. arrhythmia
B. Brawner's Formula (164 - (0.7 x age))
When creating an exercise program for a patient with COPD who is reporting dyspnea on exertion and is taking atenolol for their hypertension, what formula would you use to determine maximal heart rate?
A. Tanaka's Formula (208 - (0.7 x age))
B. Brawner's Formula (164 - (0.7 x age))
C. Karvonen's Formula [((HRpeak − HRresting) × Lowest % Intensity) + resting HR → ((HRpeak − resting HR) × Highest % Intensity) + resting HR]
D. Colonel's Formula
A. Heart Failure
D. Arrhythmia
(Choose 2) Digoxin is used to treat:
A. Heart Failure
B. Hypertension
C. Pulmonary Hypertension
D. Arrhythmia
E. Interstitial Pulmonary Fibrosis
F. Hypercholesterolemia
A. an increased risk of bone loss
D. an increased risk of bone fracture
(Choose 2) Physical Therapists need to be aware of their patients taking hydrocortisone due to 2 of the following reasons:
A. an increased risk of bone loss
B. an increased risk of hypertension
C. an increased risk for excessive bleeding/bruising
D. an increased risk of bone fracture
B. Hypertension
Lisinopril/Zestril is given to patients to address which disease?
A. Heart Failure
B. Hypertension
C. COPD
D. Diabetes Mellitus
A. angina
Nitroglycerin is given to patients who are experiencing:
A. angina
B. dyspnea
C. myalgia/myopathy
D. atrial fibrillation
A. Increase the body's sensitivity to insulin.
Metformin and Exercise have the same effect on the body's ability to do what?
A. Increase the body's sensitivity to insulin.
B. Utilize oxygen in metabolic processes.
C. Increase bronchodilation.
D. Improve vasodilation in skeletal muscle
A. O2 saturation dropping
A V/Q mismatch where V continues to drop and Q remains constant will present with what vital sign?
A. O2 saturation dropping
B. Heart Rate dropping
C. Blood Pressure dropping
D. O2 saturation rising
F. Oral
parenteral routes of medication administration include all of the following EXCEPT:
A. injections
B. inhalation
C. subcutaneous injection
D. transdermal
E. transmucosal
F. Oral
A.webMD
B. drugs.com
C. epocrates
choose the 3 free to use drug databases from the following line
A.webMD
B. drugs.com
C. epocrates
D. micromedex
E. Lexicomp
B. congestive heart failure
A note in the medical record indicates that a patient was recently prescribed Lasix furosemide). Which of the following medical conditions is MOST commonly associated with the use of this medication
A. hypelipidemia
B. congestive heart failure
c. DVT
D. atrial flutter
B. Orthostatic hypotension and dizziness
A patient with congestive heart failure (CHF) is on a regimen of diuretics (chlorothiazide). The PT should be alert for which adverse effects of this medication?
A. A Hyperkalemia and premature ventricular contractions (PVCs).
B. Orthostatic hypotension and dizziness
C. Myalgia and joint pains.
D. Reflex tachycardia and unstabl
B. are also known as adrenergic antagonists
C. stimulate the sympathetic system
choose 2 sympatholytics:
A. decrease sympathetic activity
B. are also known as adrenergic antagonists
C. stimulate the sympathetic system
B. hypoglycemia would be considered a toxic, unintended and unpredictable effect of insulin
choose the incorrect statement regarding drug reactions
A. side effects are unwanted effects of a drug at the therapeutic dose but are predictable
B. hypoglycemia would be considered a toxic, unintended and unpredictable effect of insulin
C. toxic effects are seen at higher doses of a drug and can be serious
D. adverse drug reactions are unexpected, unintended and may harm a patient but are predictable
B. exercise induced asthma
a physical therpaist reads in a patients medical chart that the patient has been prescribed albuterol. which of the following conditions would MOST likely require the use of this medication
A. angina pectoris
B. exercise induced asthma
C. spinal cord injury
D. breast cancer
A. osteoporosis
a patient with cancer has been taking oral corticosteroids along with chemotherapy for the past year what is an expected adverse effect of prologned use of corticosteroids?
A. osteoporosis
B. thickening of skin
C. flattening of the thoracic spine
D. low BP
D. HR to be low at rest and rise minimally with exercise
what is the expected hemodynamic response for a patient on a beta-adrenergic blocking agent during exercise?
A. HR to be low at rest and rise continuously to expected levels as exercise intensity increases
B. systolic BP to be within normal limits at rest and progressively fall as exercise intensity increases
C. systolic BP to be low at rest and not rise with exercise
D. HR to be low at rest and rise minimally with exercise
B. block reabsorpation of sodium and calcium in the ascending Loop of Henle
loop diuretics, including furosemide, are often called “water pills: by patients because of this mechanism of action:
A. Increases reabsorption of water into the blood for redistribution throughout the body block reabsorption of sodium and calcium in the ascending loop of henle
B. block reabsorpation of sodium and calcium in the ascending Loop of Henle
C. create water by accelerating the action of the Kreb’s cycle
increasing contractility of the heart, pushing fluid (blood) through the system , increasing BP
A. vasoconstrict
norepinephrine is an Alpha -1 receptor agonist which stimulates alpha-1 andrenergic receptors in vascular smooth muscle. what does norepinephrine do to the blood vessel?
A. vasoconstrict
B. vasodilate
B. corticosteroids
prolonged use of these drugs can lead to decreased bone mineral density
A. alpha -1 blockers
B. corticosteroids
C. statins
D.nitrates
C. bisoprolol
this drug works by selectively inhibiting beta 1 adrenergic receptors;
A. amlodipine
B. insulin
C. bisoprolol
D. spironolactone
steps for using inhaler
shake the inhaler well for 5 sec
exhale as much as possible
holding inhaler straight up, mouth firmly around the mouth piece
push the metal canister all the way down and simultaneously breath in
remove inhaler from mouth and hold breath as long as comfortable
slowly breathe out as long as you can
rinse mouth out with water. do not swallow water
A. when prolonged exposure of an medication may cause an increased removal of receptors
D. decreased receptor synthesis
choose 2: receptor down regulation occur in 2 of the following ways
A. when prolonged exposure of an medication may cause an increased removal of receptors
B. the cell undergoes an increase in responsiveness and sensitivity to the medication
C. a prolonged decrease in the stimulation of post synpatic receptors
D. decreased receptor synthesis
F. heart failure
E. hypertension
G. ACE inhibitor
lisinopril is a ___ which is commonly used to treat __
A. hypercholesterolemia
B. angina
C. thiazide diuretic
D. calcium channel blocker
E. statin
F. heart failure
E. hypertension
G. ACE inhibitor
A. stimulate the parasympathetic system
C. are also known as cholinergics
choose 2: parasympathomimetics
A. stimulate the parasympathetic system
B. decrease activity at acetylcholine synapses
C. are also known as cholinergics
C. reduces airway resistance by reducing bronchoconstriction
a patient with asthma is taking beta 2 agonist (sympathomimetic), albuterol (ventolin). what is. theMOST important effect of this medication?
A. increases HR and BP to enhance training effect during aerobic activity
B. increases airway resistance and decreases secretion production
C. reduces airway resistance by reducing bronchoconstriction
D. reduces bronchial constriction and high BP that accompanies exercise
C. extreme fatigue and arrhythmias
what are some common adverse effects that patients taking nitrates, diuretics, beta blockers, or calcium antagonists might experience?
A. hypotension and dizziness
B. arrhythmia and unstable BP
C. extreme fatigue and arrhythmias
D. hypotension and decreased electrolytes