Physics A level: Module 1 - Development of Practical Skills in Physics
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Variable
Anything that has the potential to change in an experiment.
What is an independent variable?
The thing you change in an experiment
What is a dependent variable?
The thing you measure in an experiment
What is a control variable?
Things kept constant to ensure a fair test. Could be measured to check they are constant.
Give three examples of apparatus that could be used to measure length?
Metre ruler (Lowest resolution)
Micrometer (Highest resolution)
Vernier caliper
Give an example of apparatus that could be used to measure mass?
Top-pan balance (higher resolution than scales)
Give an example of apparatus that could be used to measure angle?
Protractor
Give an example of apparatus that could be used to measure time?
Stopwatch
Give an example of apparatus that could be used to measure temperature?
Thermometer
Give an example of apparatus that could be used to measure potential difference?
Voltmeter
Give an example of apparatus that could be used to measure current?
Ammeter
Give an example of apparatus that could be used to measure frequency?
Oscilloscope
Give an example of apparatus that could be used to measure extension?
Travelling microscope
“Describe how you can use this apparatus to determine…” Give three things to include in your answer.
The measurements to be taken. (Diameter, length, extension, mass, etc)
The equipment used to take the measurements. (and why - resolution, range)
How you would determine it from your measurements.
What is calibration?
The comparison between a known measurement and the measurement given on the reading. Check the accuracy and helps avoid zero errors.
What is an instrument’s sensitivity?
A measure of how much the quantity needs to change in order for the change to be detected.
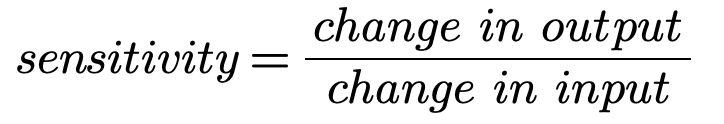
What is response time?
The time it takes for the output of an instrument to change after a change in input.
What happens if sensitivity and response time are too low?
The quality of the data will be poor.
Give 6 things needed in an answer to a Experimental Design evaluation question
Does it test what it sets out to test?
Is the method clear enough to be followed?
Are control variables controlled?
Is the apparatus appropriate?
Have enough repeated measurements been planned?
Is the experiment going to be conducted safely?
What axis does the independent variable go?
The x-axis
What axis does the dependent variable go?
The y-axis
How to find the gradient at a given point on a curved line?
Draw a tangent and calculate its gradient (Δy/Δx)
What should a “good” result be?
Precise, Valid, Accurate.
What is a precise result?
A result that is repeatable (you can repeat it to get the same results), and reproducible (someone else can recreate your experiment using different equipment OR methods and get the same results you do)
How can we increase precision?
Repeat measurement several times, they can be described as precise when the values are very similar to, or the same as, each other.
What is a valid result?
A result that answers the original question using precise data. (If control variable aren’t constant, not valid as independent variable effect isn’t tested in isolation)
What is an accurate result?
A result close to the true answer.
How can we increase accuracy of a result?
By repeating measurements and finding a mean average.
What also affects the precision of your data?
The experimental uncertainty (e.g caused by equipment resolution). The smaller the uncertainty, the more precise the results
What is the maximum different between your value and the true value called?
The margin of error
What is absolute uncertainty?
The total uncertainty for a measurement.
What is percentage error?
The uncertainty given as a percentage of the measurement.
If a ruler has uncertainty of ±0.05cm how much uncertainty is there when measuring the length of a piece of string?
±0.1cm, we take two measurements of which we have uncertainty, one at each end of the string, so 0.05 × 2 = total uncertainty of the measurement
How can we assume uncertainty?
By taking half of one increment of the last significant figure the value is given to. (2.0 would have an uncertainty of ±0.05 half of 0.1)
What is a conclusion?
A statement that explains what the data shows.