ch. 7 : cellular respiration
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration
C6 H12 O6 + 6O2 —> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Where does all energy ultimately come from?
The sun
energy flows into an ecosystem as ________ and leaves as ______. The chemical elements essential to life are ________.
Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat. The chemical elements essential to life are recycled.
Photosynthesis generates _____ and _________ / _______________, which are used in cellular respiration
O2 (oxygen) and glucose / organic molecules
Cells use ________ energy stored in _________ molecules to regenerate _____, which powers cellular work.
Cells use chemical energy stored in organic molecules to regenerate ATP, which powers cellular work
Catabolic pathways yield energy by ____________ _______ food into cellular building blocks of energy and monomers.
breaking down food
catabolic pathways yield energy by breaking down food (oxidizing / reducing organic fuels) into cellular building blocks of energy and monomers.
oxidizing
Why do catabolic pathways oxidize organic fuels?
Catabolic pathways oxidize organic fuels to release ________. During oxidation, organic molecules lose ________, which are transferred to electron carriers such as ________ and ________. The energy from these electrons is ultimately used to produce ________.
energy; electrons; NAD⁺; FAD; ATP
cellular respiration diagram
The breakdown of food / organic molecules is __________ - energy is ________.
exergonic, released
fermentation
partial degradation of sugars that occurs without oxygen / O2
aerobic respiration: uses ________ molecules and ________ to yield _______ with waste products of ____ and __________.
uses organic molecules and oxygen (O2) to yield ATP with waste products of CO2 and water
anaerobic respiration
similar to aerobic respiration but has an electron acceptor other than oxygen (such as sulfur)
cellular respiration includes both ________ and ________ respiration.
aerobic and anaerobic respiration
carbohydrates, fats, and proteins can all be used as fuel. but, cellular respiration is usually traced using _______.
glucose
During cellular respiration, _______ are transferred in chemical reactions, releasing stored energy in organic molecules. This energy is used to make ______.
electrons; atp
Glucose ______ electrons and is __________. Oxygen _______ electrons and is ________.
Glucose loses electrons and is oxidized. Oxygen gains electrons and is reduced.
Name the reactants and products of cellular respiration
Glucose and oxygen ——→ Carbon dioxide, water, ATP
What is the chemical formula for glucose
C6H12O6
How many oxygen molecules are used in cellular respiration?
6 molecules of O2
How many molecules of CO2 are released / produced in cellular respiration?
6 molecules of CO2 are produced
How many molecules of water are produced in cellular respiration?
6 water molecules.
How much ATP is produced per molecule of glucose?
38 ATP
__ ATP is made in ___________________
___ ATP is made in ___________________
_____ ATP is made per glucose molecule
4 ATP in substrate level phosphorylation
34 ATP in oxidative phosphorylation (making ATP by moving electrons)
38 ATP is made per glucose molecule
In cellular respiration, ________ and other molecules are broken down in a series of steps.
glucose
_________ from organic compounds are usually first transferred to ______ or _____.
NAD+ or FAD
NAD+ and FAD are coenzymes
they bind to enzymes during reactions and accept electrons as the reaction occurs (substrate is bound to enzyme while FAD/NAD+ is bound at same time)
leave as NADH or FADH2 and carry electrons to ETC, then drop off electrons to help make ATP.
After that, they’re recycled back into NAD+ or FAD
They help the enzyme work by oxidizing (removing electrons from) the molecule, making the molecule unstable
BIG IDEA : What molecules represent stored energy used to synthesize ATP later in the process?
NADH / FADH2 - The reduced for, of NAD+ / FAD
NADH/FADH2 passes the electrons to the ______ in a series of controlled steps.
ETC
NADH / FADH2 are known as carriers of what?
Energy
________ pulls the electrons down the chain in an energy yielding tumble.
O2 / oxygen
What molecule is the final electron acceptor?
Oxygen
The controlled release of energy in small steps from the electron transport chain is used to synthesize _____. The ETC “breaks the fall” of electrons.
ATP
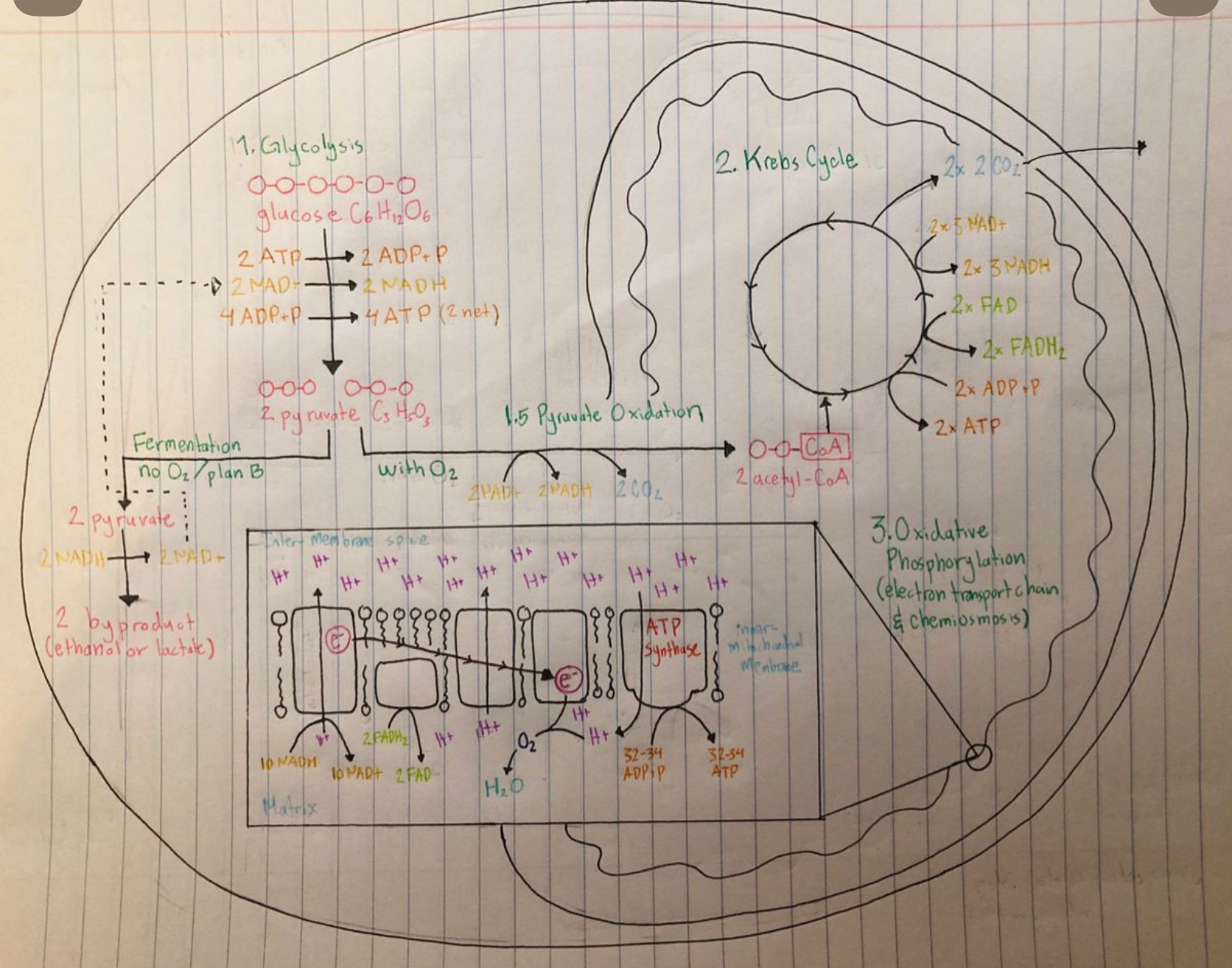
What are the 3 stages of cellular respiration?
1) Glycolysis
2) a. pyruvate oxidation
b. The Citric Acid cycle
3) Oxidative phosphorylation
oxidative phosphorylation is the _______ stage of cellular respiration and occurs in the _______ __________ of the mitochondria.
3rd, inner membrane
(the ETC is embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane)
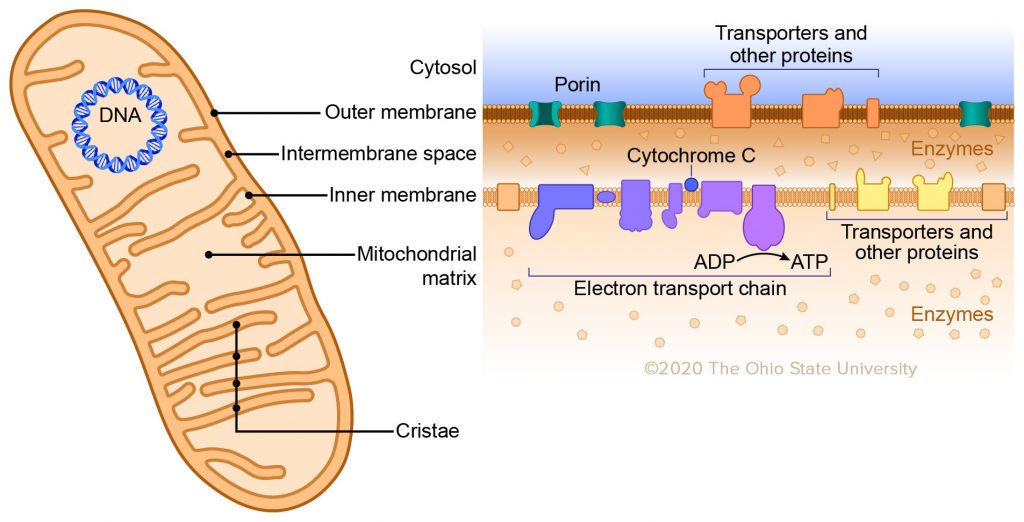
in oxidative phosphorylation, _______ reactions occur in the ______ and drive the production of ATP by c_____________. This accounts for ___% of the ATP made in cellular respiration.
redox; ETC (electron transport chain): chemiosmosis; 90%
substrate level phosphorylation
makes ATP with an enzyme.
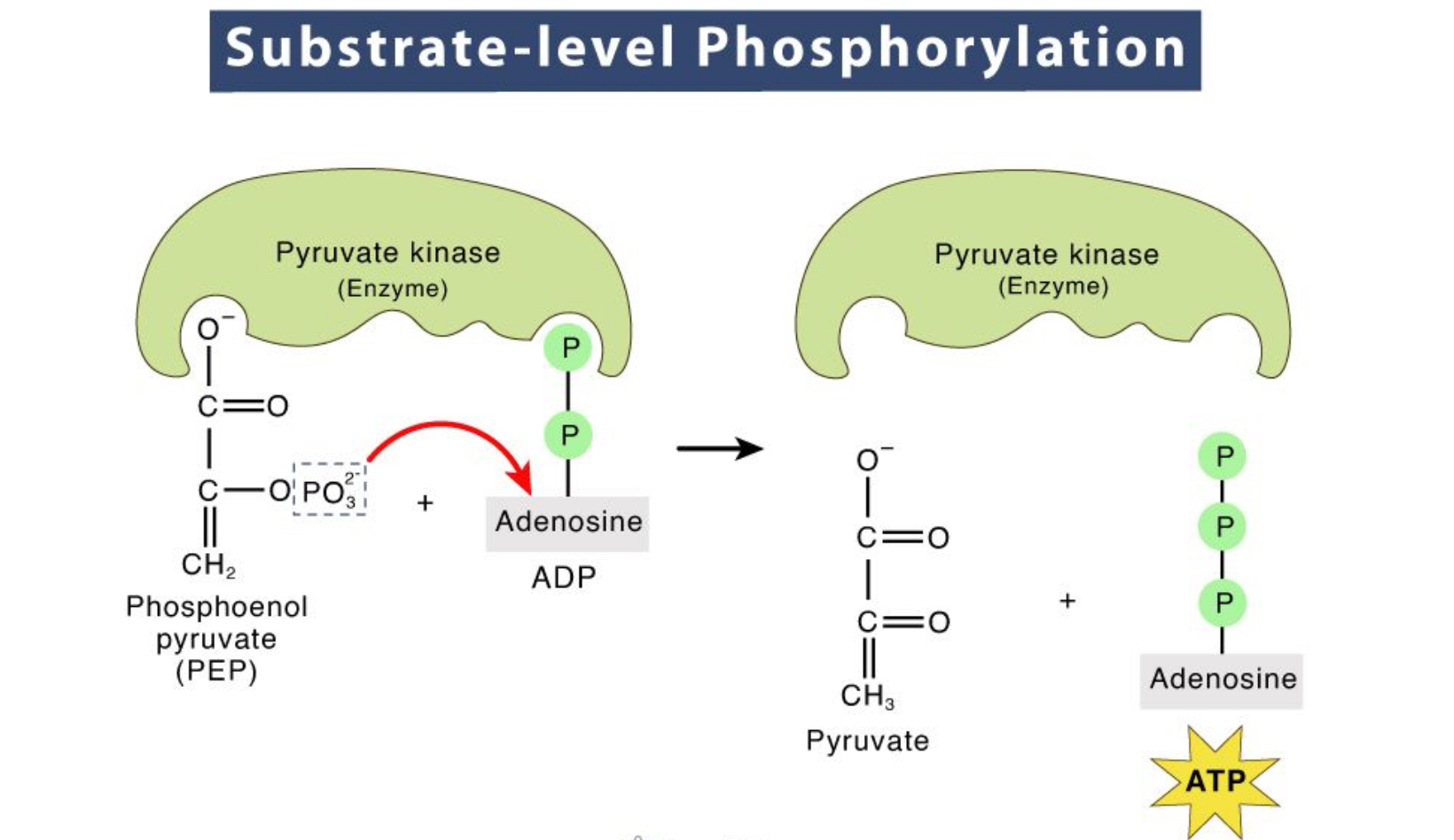
In substrate level phosphorylation, an enzyme transfers a phosphate group from a high-energy substrate molecule directly to ADP, forming ATP.
Glycolysis breaks down ________ into ______________.
Glycolysis breaks down glucose into 2 pyruvate
Glycolysis takes place in the _________ and does not require _________ (molecule). No ___________ (part of a cell) is required. Can all organisms complete this process?
cytoplasm; oxygen; mitochondria; yes
In the energy input phase, ___ ATP molecules are consumed, which helps destabilize ________ and make it more reactive.
2; glucose
In the energy payoff phase, ATP and NADH are produced from the energy in the G3P made in the first half.
2 NAD+ → 2 NADH (electrons are transferred)
4 ATP (2 net) are made via substrate level phosphorylation (ADP→ ATP)
What are the total products of glycolysis
2 pyruvate + 2H2O
2 ATP
2 (NADH+) + H+
________ occurs in nearly all organisms and probably evolved in ancient prokaryotes before there was oxygen in the atmosphere: it is an ancient process!
Total products of glycolysis
glucose → 2 pyruvate + (2H2O)
4 ATP formed - 2 ATP used → 2 ATP
(2 NAD+) + 4e + (4H+) → 2NADH + (2H+)