ECO 201 exam 3
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
characteristics that define market structure (4)
number of firms
product differentiation (homogenous or differentiated)
can a firm influence price?
barriers to entry
firms want in perfect competition
to make the most profit possible through rational rule: Marginal Revenue (MR) = Marginal Cost (MC)
Perfectly competitive markets with lots of small buyers and sellers
There are many small buyers and sellers
No one can control the price (they're "price takers").
firms are restricted and can only charge the market price of the homogenous good being sold
Demand in a Competitive Market
Firms are price-takers: no control over market price
Firm demand: horizontal at market price (perfectly elastic)
Marginal Revenue = Price
Additional revenue from selling one more unit equals market price
Key for determining profit-maximizing output level
marginal cost
the additional cost incurred by producing one more unit of a good or service. It helps determine optimal production levels for a firm.
Marginal revenue
the additional revenue a firm earns by selling one more unit of a good or service.
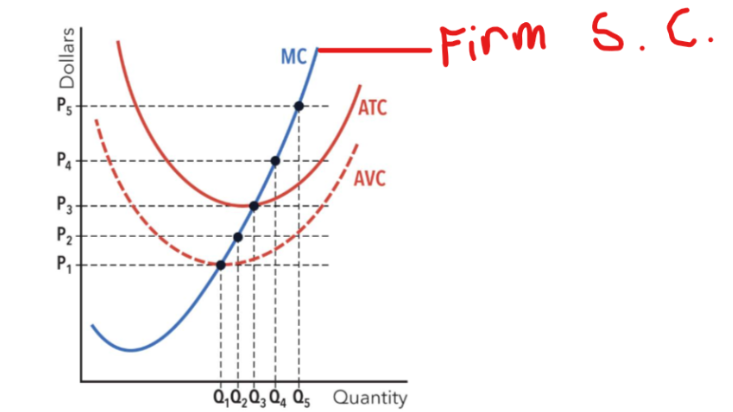
Firm Supply in a Perfectly Competitive Market
same as Marginal Cost (MC) curve. For any given market price, the firm consults its MC curve to determine the profit-maximizing quantity.
the firm always produces the quantity where what equals the market price to maximize profits.
marginal cost
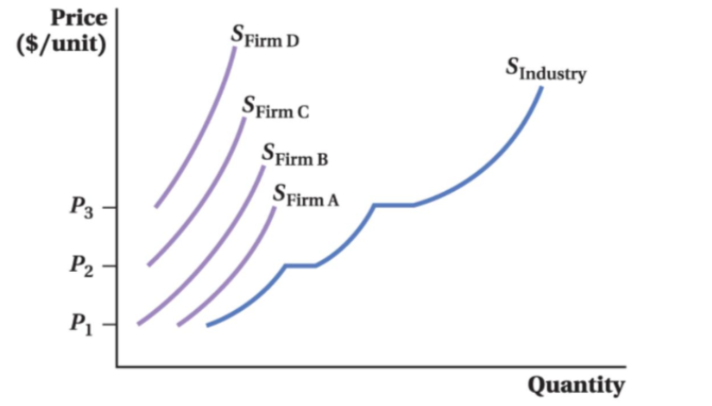
Market Supply in a Competitive Market
add up all the individual firm supply curves horizontally.
Short Run equilibrium
characterized by the absence of entry and exit. Because there are barriers, this allows firms to experience economic profits or losses in the short run. As a result, the number of firms in the market remains fixed in the short run.
Why are firms allowed to experience economic profits or losses in the short run?
there are barriers
As a result, the number of firms in the market remains _______ in the short run.
fixed
(P - AC) × Q, when P > AC
Calculating profits in the short run
Positive Economic Profits
If the market price is above the minimum of the average cost curve (P>min AC), the firm will earn this.
total economic profit
the difference between price and average cost (P-AC), multiplied by the quantity produced (Q).
(P - AC) × Q, when P = AC
formula for ZERO economic profit at minimum average cost
Zero Economic Profit
When the market price is equal to the minimum of the average cost curve (P=min AC).
In the case of what does the firm break even, as the price equals the average cost at the profit-maximizing output level?
0 Economic Profit
(AC - P) × Q, when P < AC
Calculating loss in the short run
Negative Economic Profit (Loss)
If the market price is below the minimum of the average cost curve (P<min AC).
In the short run, can a firm continue to operate even if it is incurring losses?
as long as the market price covers the average variable costs because the firm has already committed to fixed costs
Long-Run Equilibrium
Firms can enter and exit freely.
Why would a firm enter long run equilibrium?
They enter if experiencing short-run profits and exit if facing short-run losses, ultimately resulting in zero profits in long-run equilibrium.
conditions of Long-Run Equilibrium
Firms maximize profits (P = MC).
Market clears (Quantity supplied = quantity demanded).
Zero profits (Price = average cost). P = MC = AC. P = minimum average cost
Market power
extent to which a seller can charge a higher price without losing many sales to competing businesses
types of market structure
perfect competition - Lowest market power
monopolistic competition
oligopoly
Monopoly - Highest market power
To set price with market power, There's a trade-off between ________ and _______.
price, quantity
To set price with market power, it is a trade-off between _______________ versus making more money on each item.
selling a large quantity of items
firm demand curve and the marginal revenue curve
used to evaluate the trade-off between price & quantity
How does market power give firms profits?
Firms can raise prices and restrict quantity to get those profits
Problems with Market Power
Market power leads to higher prices.
Market power leads to inefficiently smaller
quantity.
Market power yields larger economic profits.
Businesses with market power can survive even with inefficiently high costs.
Deadweight loss equals what
What is the consequence of this failure?
market failure, room for government regulation
sophisticated pricing strategies?
Price Discrimination
Group Pricing
The Hurdle Method
profits
Price discrimination
Charging different prices for different people
Perfect price discrimination
Willingness To Pay = Pay = Marginal Cost
Requirements to Price Discriminate
Market Power
Different types of Willingness to Pay (WTP)
Ability to prevent resale
Market Power
Downward sloping firm demand (NO PC Firms)
Low WTP is ______ responsive to price changes
more
High WTP is ______ responsive to price changes
less
Ability to prevent resale
Low WTP getting low price can't resell to High WTP. ex: college spot
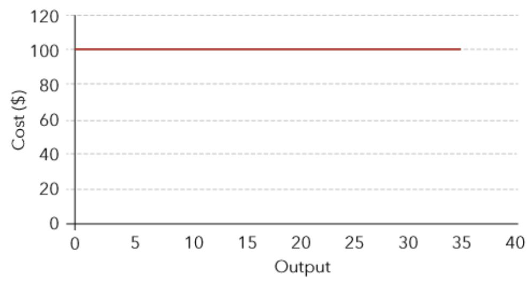
fixed costs
constant for any level of output
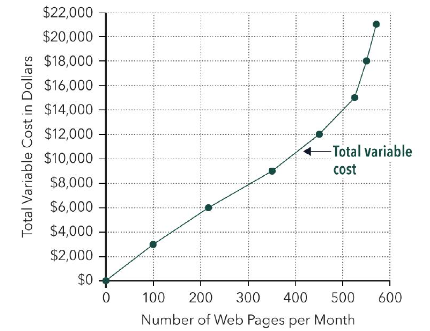
variable costs
change as output changes
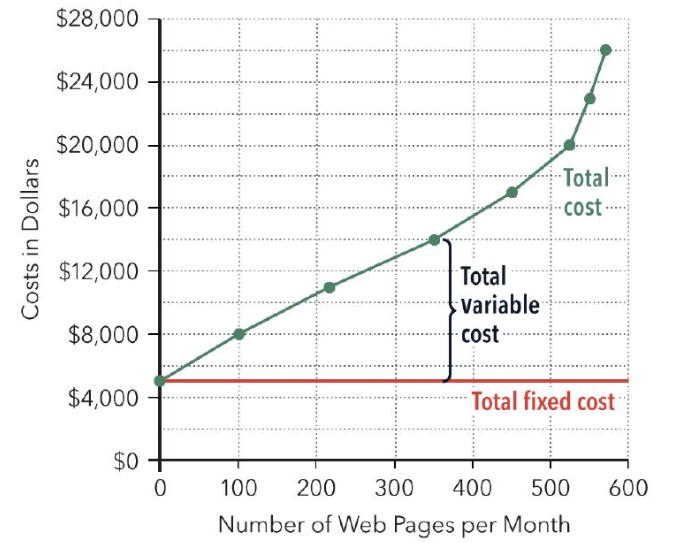
Total Cost
combines variable + fixed cost for each level of output
marginal cost
used to decide how much to produce
formula for marginal cost
Change in Variable Cost/Change in Output
average cost
total cost/total output
what does it mean if MC > AC
AC must be falling
what does it mean if MC < AC
AC must be rising
what does it mean if MC = AC
AC is at its minimum
economic profits
revenue minus all costs (implicit and explicit)
implicit costs
opportunity costs like:
what could the firm be doing instead?
where else could money have been invested?
what’s the owner’s time worth when they’re not getting paid?
normal profit
next best alternative’s accounting profit
accounting profit
revenue minus explicit costs
can a firm earn positive accounting profits, but negative or even zero economic profits?
yes
this type of profit means you could be doing better in another business route
negative economic profit’s
zero economic profit
accounting profits = opportunity costs
quantity choice to maximize profits
looking for quantity such that MR= MC or P = MC
The MC curve is described as the firm's __________ because it gives the quantities that maximize profits at any given market price.
supply curve
Market Power
extent to which a seller can charge a higher price without losing many sales to competing businesses
Different market _____ lead to different amounts of market _____
structures, power
types of market structure
perfect competition - lowest market power
monopolistic competition
oligopoly
monopoly - highest market power
marginal revenue is approximated by
P - ΔPxQ
output/quantity effect
the revenue increase from selling one more unit
output effect = P
equals the new price
discount effect
the revenue loss from cutting price on ALL units sold
discount effect = ΔPxQ
equals the change in price times the original quantity
problems with market power
leads to higher prices
leads to inefficiently smaller quantity
yields larger economic profits
businesses with MP can survive with inefficiently high costs
economic surplus
total benefits minus total costs flowing from a decision
economic surplus formula
= consumer surplus + producer surplus = marginal benefit - marginal cost
consumer surplus formula
= marginal benefit - price
( ½ x base x height)
producer surplus formula
= price - marginal cost
(½ x base x height)
producer surplus
difference between the minimum price a producer is willing to accept for a good or service and the actual price they receive
represented by the area above the supply curve and below the market price.
Consumer Surplus
difference between the maximum price a consumer is willing to pay for a good or service and the actual price they pay
represented by the area below the demand curve and above the market price.