Physiology Exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:44 PM on 10/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
1
New cards
Primary endocrine disorder
Problem in the last gland in the pathway
2
New cards
Secondary endocrine disorder
Problem in the anterior pituitary gland
3
New cards
Tertiary endocrine disorder
Problem in the hypothalamus
4
New cards
Explain how a misregulated hormone might produce different symptoms depending on age.
can impact secondary sex characteristics, growth hormones causing excessive growth
5
New cards
Long loop negative feedback
the hormone secreted by the peripheral endocrine gland “feeds back”
to suppress secretion of its anterior pituitary and hypothalamic
hormones
to suppress secretion of its anterior pituitary and hypothalamic
hormones
6
New cards
short-loop negative feedback
a pituitary hormone feeds back to decrease hormone secretion by the hypothalamus
7
New cards
ultra short-loop negative feedback
a hormone directly inhibits its own secretion via paracrine or autocrine effects
8
New cards
central nervous system (CNS)
consists of the brain and spinal cord
9
New cards
peripheral nervous system
(PNS)
(PNS)
consists of afferent and efferent neurons
10
New cards
What is the most common type of cell in the nervous system?
gilial cells
11
New cards
What is different about the
glial cells provide this support in the CNS vs. PNS?
glial cells provide this support in the CNS vs. PNS?
In the PNS, one Schwann cell forms a single myelin sheath. By contrast, in the CNS, the oligodendrocyte sends cell processes to myelinate multiple segments on many axons
12
New cards
Be able to label the parts of a neuron and understand the direction of electrical conduction
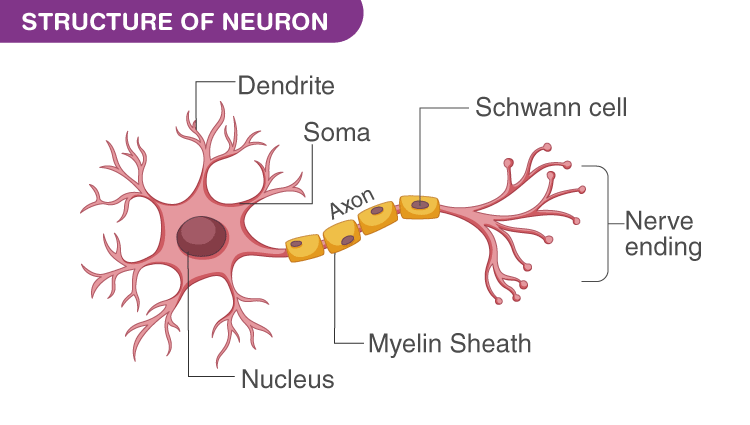
13
New cards
What are the three main processes necessary for neuronal signaling?
cell body, axon, dendrites
14
New cards
What is voltage?
difference in electric potiential
15
New cards
How does the Na+/K+ ATPase create the resting membrane potential of a neuron?
it creates a concentration gradient
16
New cards
What is a graded signal?
changes in membrane potential that vary in size
17
New cards
What is impulse dissipation and how might it relate to temporal summation?
over time the impulse gets weaker meaning it might not trigger an action potential, however another impulse can come along and add to the weaker impulse causing an action potential
18
New cards
What is the important event or functional role of the axon hillock?
sum incoming voltage changes and determine if an electrical signal called the action potential will be sent down the axon
19
New cards
graded potential
input signals at the dendrites and cell body; can use mechanically, chemically, or voltage gated channels; depolarizing or hyperpolarizing; can be summed; initiated by ions entering channels; no minimum level to initiate
20
New cards
action potential
regenerating conduction signal that starts at trigger zone and goes through axon; voltage-gated channels only; depolarizing only; all-or-nothing; cannot be summed; graded potential must be above threshold to initiate
21
New cards
Steps of action potential
1. Resting membrane potential
2. Depolarizing stimulus
3. Membrane depolarizes to threshold. Voltage-gated Na + and K + channels begin to open.
4. Rapid Na + entry depolarizes cell.
5. Na + channels close and slower K + channels open.
6. K + moves from cell to extracellular fluid.
7. K + channels remain open and additional K + leaves cell, hyperpolarizing it.
8. Voltage-gated K + channels close, less K + leaks out of the cell.
9. Cell returns to resting ion permeability and resting membrane potential.
2. Depolarizing stimulus
3. Membrane depolarizes to threshold. Voltage-gated Na + and K + channels begin to open.
4. Rapid Na + entry depolarizes cell.
5. Na + channels close and slower K + channels open.
6. K + moves from cell to extracellular fluid.
7. K + channels remain open and additional K + leaves cell, hyperpolarizing it.
8. Voltage-gated K + channels close, less K + leaks out of the cell.
9. Cell returns to resting ion permeability and resting membrane potential.
22
New cards
action potential proteins
channel proteins whose configuration switches between closed and open states as a function of the voltage difference between the interior and exterior of the cell
23
New cards
Why is an action potential unidirectional and/or what causes the refractory period?
inactivation of voltage-gated sodium channels, which occurs at the peak of the action potential and persists through most of the undershoot period. These inactivated sodium channels cannot open, even if the membrane potential goes above threshold.
24
New cards
How can a neuron communicate differences in stimulus intensity?
1) frequency coding, where the firing rate of sensory neurons increases with increased intensity and 2) population coding, where the number of primary afferents responding increases
25
New cards
How and why does axon diameter influence the speed/efficiency of neuronal signaling?
Larger diameter axons have a higher conduction velocity, which means they are able to send signals faster
26
New cards
How does myelination influence the speed/efficiency of neuronal signaling?
myelin can reduce the energy load needed and/or increase the speed of AP conduction
27
New cards
What is saltatory conduction?
describes the way an electrical impulse skips from node to node down the full length of an axon
28
New cards
What is the Babinski reflex and how does it involve myelination?
reflex is normal in infants and as the child grows, it should go away. if it does not, then it means that the myelin did not form correctly
29
New cards
Steps of synaptic transmission
1. action potential depolarizes an axon terminal
2. opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and Ca2+ enters cell
3. calcium entry triggers exocytosis of synaptic vesicle contents
4. neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds with receptors on the postsynaptic cell
5. neurotransmitter binding initiates a response in the postsynpatic cell
2. opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and Ca2+ enters cell
3. calcium entry triggers exocytosis of synaptic vesicle contents
4. neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds with receptors on the postsynaptic cell
5. neurotransmitter binding initiates a response in the postsynpatic cell
30
New cards
excititory neurotransmitter
depolarize their target cells, usually by opening ion channels that allow flow of positive ions into the cell
31
New cards
inhibitory neurotransmitter
hyperpolarize their target cells by opening Cl- channels and allowing
Cl- to enter the cell
Cl- to enter the cell
32
New cards
reuptake
reabsorption of excess back to pre-synaptic neuron terminal
33
New cards
Degradation
ezymatic breakdown of neurotransmitter
34
New cards
Name and describe three mechanisms of signal integration
Ion channel linked receptors, G protein–coupled receptors, and enzyme-linked receptors.
35
New cards
What is a nerve?
a bundle of fibers composed of neurons that uses electrical and chemical signals to transmit sensory and motor information
36
New cards
What is an afferent pathway?
A sensory pathway from a receptor to the central nervous system.
37
New cards
What is an efferent pathway?
A sensory pathway from the CNS to a receptor
38
New cards
Name three general types of structures used to protect the central nervous system
skull, spinal vertebrae, meninges, and cerebrospinal fluid
39
New cards
What cellular feature is used by ependymal cells in the choroid plexus AND by cells forming
the blood vessels delivering blood to the brain
the blood vessels delivering blood to the brain
tight junctions, which prevent the leakage of substances and fluids from the blood vessels into the CSF.
40
New cards
Why is the color of fluid from a spinal tap a potentially useful diagnostic for disease
Spinal fluid is normally clear and colorless. If the color is orange, yellow or pink, it might indicate abnormal bleeding. Spinal fluid that is green might indicate an infection or the presence of bilirubin
41
New cards
What is white v grey matter in the nervous system and how does their distribution differ
between the brain and spinal cord
between the brain and spinal cord
White matter is the whitish nerve tissue of the central nervous system that is mainly composed of myelinated nerve fibers (or axons). The central nervous system is the brain and spinal cord. And gray matter is grayish nerve tissue of the central nervous system mainly composed of nerve cell bodies and dendrites.
42
New cards
brainstem
connects brain to spinal cord
contains nuclei for many automatic functions and for cranial nerves
includes pons, medulla oblongata, cranial nerves
contains nuclei for many automatic functions and for cranial nerves
includes pons, medulla oblongata, cranial nerves
43
New cards
Cerebellum
"little brain"
processes sensory information to coordinate movement
input from body receptors, inner ears, cerebrum neurons that control motor output
processes sensory information to coordinate movement
input from body receptors, inner ears, cerebrum neurons that control motor output
44
New cards
Diencephalon
includes thalamus (integration, relay, filtering), hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and pineal gland
endocrine system
endocrine system
45
New cards
Cerebrum
sit of "higher" brain functions; sensory integration, motor output, language acquisition and use (mostly grey matter)
includes basal nuclei, limbic system, and cerebral cortex
includes basal nuclei, limbic system, and cerebral cortex
46
New cards
What is cerebral lateralization
the functional specialization of the two cerebral hemispheres
distribution of functional areas in cerebral hemispheres is not symmetrical
distribution of functional areas in cerebral hemispheres is not symmetrical
47
New cards
What are three basic methods to study specialization of the human brain?
1. use animal models
2. take advantage of accidents
3. brain imaging
2. take advantage of accidents
3. brain imaging
48
New cards
Describe how an EEG works
a test that detects abnormalities in your brain waves, or in the electrical activity of your brain
49
New cards
What is the autonomic nervous system?
controls involuntary actions, such as the beating of your heart and the widening or narrowing of your blood vessels
50
New cards
What are the main divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
sympathetic and parasympathetic
They both use acetylchloine and preganlionic neurons and both have a nicotine receptor
They have different points of origin and length of neurons. They use different neurotransmitters and have different effector targets
They both use acetylchloine and preganlionic neurons and both have a nicotine receptor
They have different points of origin and length of neurons. They use different neurotransmitters and have different effector targets
51
New cards
types of sensory input that may cause changes
monitor the levels of carbon dioxide, oxygen and sugar in the blood, arterial pressure and the chemical composition of the stomach and gut content
52
New cards
What is similar about sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways?
both originate from the spinal cord
both target smooth/cardiac muscles, endocrine and exocrine glands, and adipose tissures
Both use a preganglionic neuron, ACH, and have a nicotine receptor
both target smooth/cardiac muscles, endocrine and exocrine glands, and adipose tissures
Both use a preganglionic neuron, ACH, and have a nicotine receptor
53
New cards
What are three differences between sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways?
1. postganglion neurotransmitters and effector targets
2. point of origin from CNS
3. length of preganglionic vs postganglionic neurons
2. point of origin from CNS
3. length of preganglionic vs postganglionic neurons
54
New cards
How does the anatomical arrangement of sympathetic pathways facilitate “mass activation”
short preganglionic fibers with extensive branching
55
New cards
What is dual activation?
homeostasis with parasympathetic having rest and digest vs sympathetic fight or flight
56
New cards
Name an example of the antagonistic effects of sympathetic vs parasympathetic activation.
Sympathetic division induces dilation of the pupil while the parasympathetic division induces the pupil to constrict.
The sympathetic division speeds up heart rate while the parasympathetic division slows it down.
The sympathetic division speeds up heart rate while the parasympathetic division slows it down.
57
New cards
How is it possible that both the autonomic nervous system (involuntary control) and the
somatic nervous system (voluntary control) can target muscles using the same neurotransmitter
(i.e. acetycholine)?
somatic nervous system (voluntary control) can target muscles using the same neurotransmitter
(i.e. acetycholine)?
different receptors that control different processes
58
New cards
Why might sympathetic neurons not use breakdown enzymes to regulate synaptic
transmission?
transmission?