AP Psychology Notes (Full Year)
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary terms + definitions and all concepts covered by CollgeBoard for AP Psychology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What is Hindsight Bias?
The tendency to believe that an outcome was predictable after it has already occurred, expressed as 'I knew it all along.'
What does overconfidence refer to in cognitive psychology?
Overestimating one's ability to do or make something.
Define Confirmation Bias.
The tendency to gather information that supports preexisting expectations.
What are the key elements of Experimental Design?
Hypothesis, Operational Definition, Reliability, Validity, Population, Sample Size, and Convenience Sampling.
What are the two types of Measurement Instruments in research?
Qualitative (non-numerical data) and Quantitative (numerical data).
What is a Case Study?
An in-depth investigation of an individual or a small group with unusual traits.
List one pro and one con of using a Case Study.
Pro: Provides detailed information; Con: No correlation data or generalization.
What is a Meta-Analysis?
Taking multiple studies and drawing one’s own conclusions from them.
What does Naturalistic Observation involve?
Observing subjects in their natural habitat without manipulation.
What is Reflex Arc?
The direct pathway from sensory organs to the spinal cord bypassing the brain.
What is the Autonomic Nervous System function?
It regulates involuntary movements like heart rate and digestion.
What is the role of the Pituitary Gland?
The master gland that sends signals to other glands in the body.
Define Action Potential.
The electrical signal that travels down the axon when enough neurotransmitters are received.
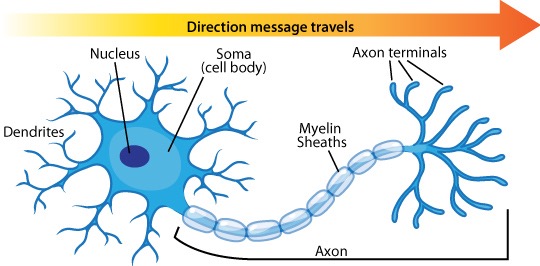
What is the function of Myelin Sheath?
It protects the axon and speeds up the electrical impulses traveling along the neuron.
What triggers the Firing of a Neuron?
The release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft when it reaches its threshold.
What is analytical transduction in audition?
The process of converting sound waves into neural impulses for interpretation.
What is the function of the Retina?
Sensory receptors for vision where transduction occurs.
Explain the concept of Depth Perception.
The ability to perceive the world in three dimensions and judge distance.
What does Color Constancy refer to?
The ability to perceive colors as constant despite changes in lighting.
What is the difference between Top-Down Processing and Bottom-Up Processing?
Top-Down Processing involves interpreting stimuli based on pre-existing knowledge; Bottom-Up Processing analyzes individual parts to form a whole.
What are Gestalt Principles?
Rules explaining how we organize visual information into meaningful wholes.
Top-Down Processing
When we observe the whole image first and apply existing knowledge to give it meaning (shorter time, less accurate).
Bottom-Up Processing
When we analyze the individual parts of a stimulus to gain meaning of the whole (takes longer, but more accurate).
Gestalt Principles
Rules of how we understand and organize information, including proximity, similarity, closure, and figure & ground.
Color Constancy
The perception that colors remain the same regardless of changes in lighting conditions.
Selective Attention
Focusing on one particular stimulus while ignoring others (e.g., cocktail party effect).
Availability Heuristic
Judging a situation based on similar situations that come to mind (most recent information).
Belief Perseverance
Maintaining a belief even after it has been proven wrong.
Functional Fixedness
The inability to see a new use for something
Adrenaline
comes from the adrenal glands and increases heart rate, blood pressure, and blood sugar. (Long-term adrenaline can cause diabetes and heart disease)
Ghrelin & Leptin (hunger hormones)
Ghrelin tells you you're hungry, and leptin tells you you're full
Testosterone & Estrogen (Sex Hormones)
Testosterone does human sex drive/aggression, and Estrogen is important for reproduction
Oxytocin (Love hormone)
plays a role in social acceptance needs and pregnancy/birth with baby bonding
Melatonin (sleep)
regulates circadian rhythms, helps you sleep, produces in response to darkness
What does the Endocrine System do?
Sends messages long-distance, circulates and regulates hormones, and transports hormones through the bloodstream.
Soma
The cell body
The life and support system of the cell
The nucleus
Determines if a neuron will fire or not
Dendrites
Branch-like structures that extend out of the cell body. Dendrites have receptors on the ends that receive neurotransmitters to start the chemical signaling process.
Terminal Branches
The root system of the neuron, where all the neurotransmitters are housed and sent out of, and vesicles are the sacks that hold the neurotransmitters.
Eugenics
Limiting reproduction to only the healthy and desirable genetics. There are negative and positive versions of eugenics.
Medulla (part of the brain stem)
Controls basic functions like breathing and heart rate
Reticular Activating System (part of the brain stem)
The brain’s reward system, learning cognition, etc.
Cerebellum (part of the brain stem)
Controls muscle movements and balance
Hypothalamus
The bridge between the endocrine and nervous systems and the 5Fs
Thalamus
directs traffic of senses (except smell)
Pituitary gland
master gland that holds, controls, and releases hormones
What are the four stages of language development in babies?
babbling
one word
two word
telegraphic sentences (full sentences)
An electrical signal through the brain can not effect what component of memory?
Longterm Potentiation
What study method best helps to retain learned information?
The spacing effect
What effect causes you to not remember where learned information is from?
Source Amnesia
During problem-solving what type of thinking narrows down information?
Convergent thinking
After typical methods of problem-solving don’t work we resort to using…
insight
What are the three measures of retention?
Recall, Relearning, and Recognition
Deriving meaning from specific sounds is an example of…
Semantics
We mentally group similar information into what? Example: holidays
concepts
A clear and easily recalled memory is most likely a…
Flashbulb memory
What are the three types of mental processing?
Chunking, Hierarchies, and Mnemonics
What are the smallest sound units in language?
Phonemes
Prospective Interfernece
When a person is trying to learn or recall a new memory while the old memory keeps interfering
Retrospective Interference
When new memories interfere with trying to remember old memories or information
What is Linguistic Determination?
A theory in psychology that suggests the structure and vocabulary of a language significantly influence how a person thinks and perceives the world. Proposed by Edward Sapir and Benjamin Lee Whorf.