BIO 1030 Lab exam Animals
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
Define Caudal
The tail region of an animal.
Define Posterior
The tail or hind end of an animal.
Define Anterior
The front or head end of an animal.
Define Cephalic
The head region of an animal.
Define Ventral
The underside of an animal.
Define Dorsal
The back or uppermost side of an animal.
Define Distal
A structure farthest from a reference point (e.g., wrist is distal to the shoulder).
Define Proximal
A structure closest to a reference point (e.g., elbow is proximal to the shoulder).
Define Oral
The mouth region of an animal.
Define Coelom
A fluid-filled body cavity completely lined with mesoderm.
Define Acoelomate
Animals lacking a coelom, such as flatworms.
Define Pseudocoelomate
Animals with a body cavity partially lined with mesoderm, such as nematodes.
Define Coelomate
Animals with a body cavity fully lined with mesoderm, such as annelids and mollusks.
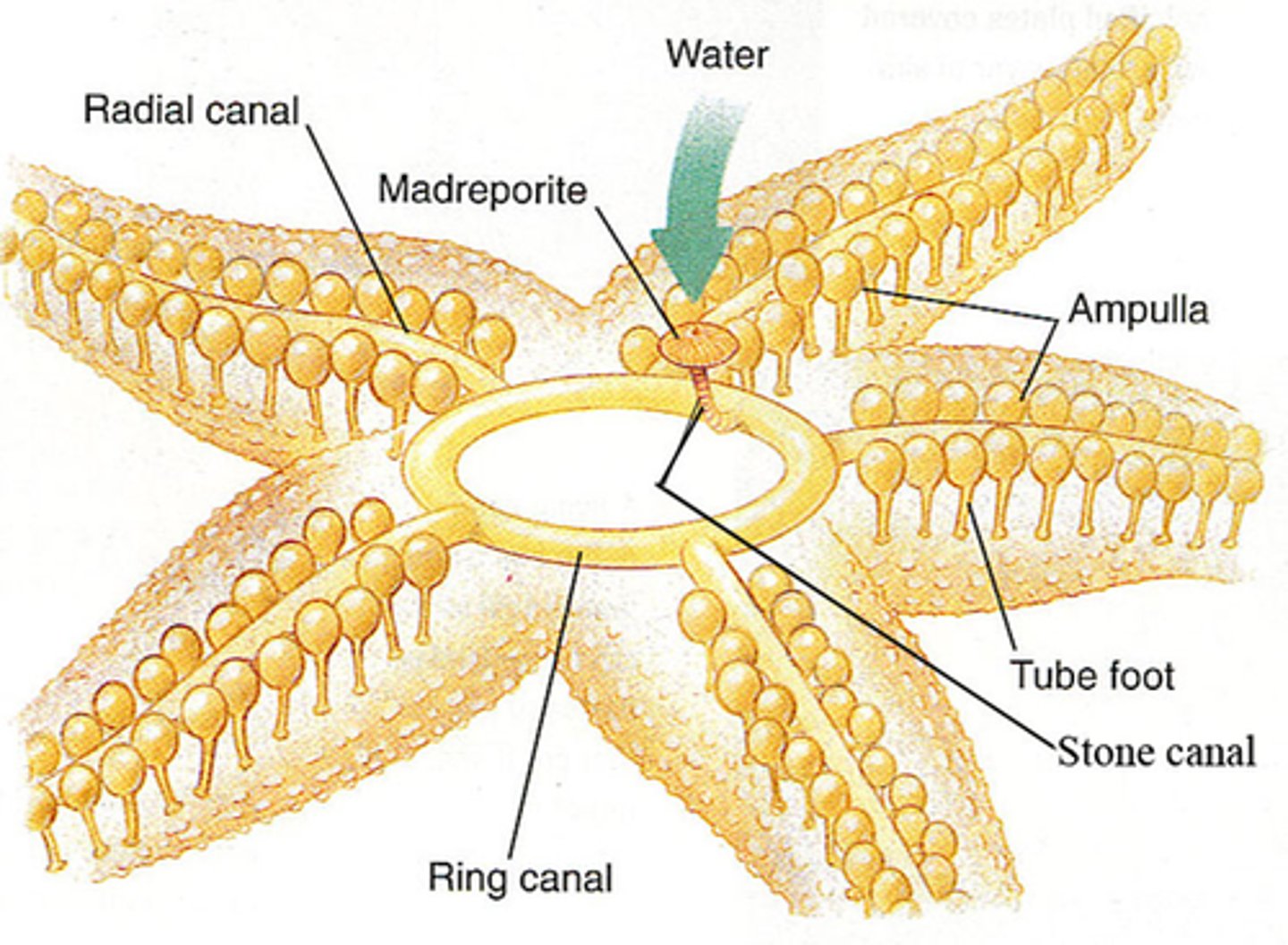
Describe the Water Vascular System in Echinoderms
A system of fluid-filled canals used for locomotion, feeding, and respiration.
What is the function of Tube Feet in Echinoderms?
Used for movement and feeding via suction created by ampullae.
What is the Madreporite?
A porous structure that regulates water entry into the water vascular system in echinoderms.
What is the function of the Hepatic Caeca in starfish?
Digestive glands that aid in digestion and nutrient absorption.
Describe the function of a Radial Canal in echinoderms
Transports water to tube feet for movement.
Define Cheliped
The large claws of a crayfish used for defense and capturing food.
Define Pereiopods
The walking legs of a crayfish.
Define Pleopods (Swimmerets)
Appendages on the abdomen of crayfish used for swimming and reproduction.
Define Uropods
Tail appendages of a crayfish that help in movement and stability.
Define Telson
The middle section of a crayfish tail used for propulsion.
Describe the function of the Crayfish Gills
Used for respiration, extracting oxygen from water.
What is the function of the Cardiac Stomach in a crayfish?
Grinds food before passing it to the pyloric stomach.
What is the function of the Pyloric Stomach in a crayfish?
Filters and digests food before it enters the intestine.
What type of circulatory system do arthropods have?
An open circulatory system, meaning blood flows into sinuses instead of being enclosed in vessels.
Define Notochord
A flexible rod that provides structural support in chordates.
Define Pharyngeal Gill Slits
Openings in the pharynx of chordates, used for filter-feeding or respiration.
Define Post-Anal Tail
A tail extending beyond the anus, present in chordate embryos.
Define Deuterostomia
A clade of animals where the blastopore becomes the anus (e.g., echinoderms and chordates).
Define Protostomia
A clade of animals where the blastopore becomes the mouth (e.g., mollusks, annelids, arthropods).
What is the function of the Malpighian Tubules in insects?
Excretory structures that remove waste from the blood.
How do arthropods grow?
Through ecdysis (molting), shedding their exoskeleton.
Describe the function of the Typhlosole in annelids
An internal fold in the intestine that increases surface area for nutrient absorption.
Define Lophophore
A ciliated feeding structure found in some Lophotrochozoa.
Define Trochophore
A ciliated larval stage found in mollusks and annelids.
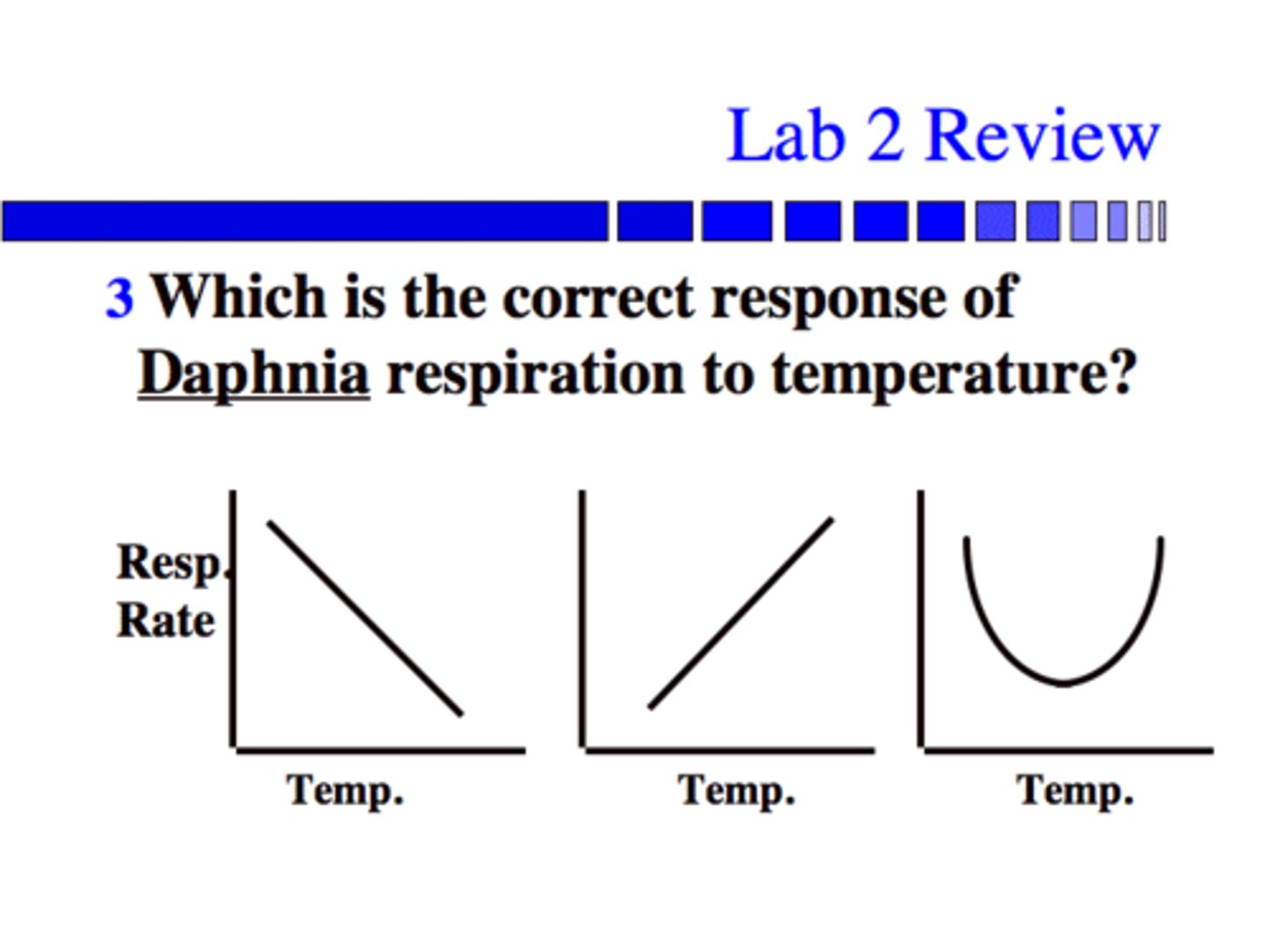
Describe the developmental and morphological traits discussed in Lab 2
After fertilization, cleavage forms a blastula, which undergoes gastrulation to form tissue layers.
Explain how developmental and morphological traits are used to create a phylogenetic tree
Traits such as symmetry, tissue layers, and blastopore fate determine evolutionary relationships.
Define True Tissues
Layers of cells separated by a thin protein membrane, allowing specialized functions.
Differentiate between Parazoa and Eumetazoa
Parazoa (sponges) lack true tissues, while Eumetazoa have distinct tissue layers.
Define Body Symmetry
The way an animal’s body can be divided into mirror-image halves.
Describe Asymmetry
No regular body shape or symmetry, seen in sponges.
Describe Radial Symmetry
Multiple planes of symmetry around a central axis, found in cnidarians.
Describe Bilateral Symmetry
A single plane divides the body into left and right halves, seen in most animals.
Explain Cephalization
The concentration of sensory organs at the anterior end, aiding in movement and coordination.
Define Diploblastic
Organisms with two germ layers (ectoderm and endoderm), found in cnidarians.
Define Triploblastic
Organisms with three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm), found in Bilateria.
Define Blastopore
The first opening that forms during gastrulation, leading to either the mouth or anus.
Differentiate between Protostomes and Deuterostomes
Protostomes develop the mouth first, while deuterostomes develop the anus first.
Define Lophotrochozoa
A clade of protostomes that grow continuously, including mollusks and annelids.
Define Ecdysozoa
A clade of protostomes that grow by molting (ecdysis), including arthropods and nematodes.
Explain Ecdysis
The process of shedding a hard outer covering to allow for growth, seen in ecdysozoans.
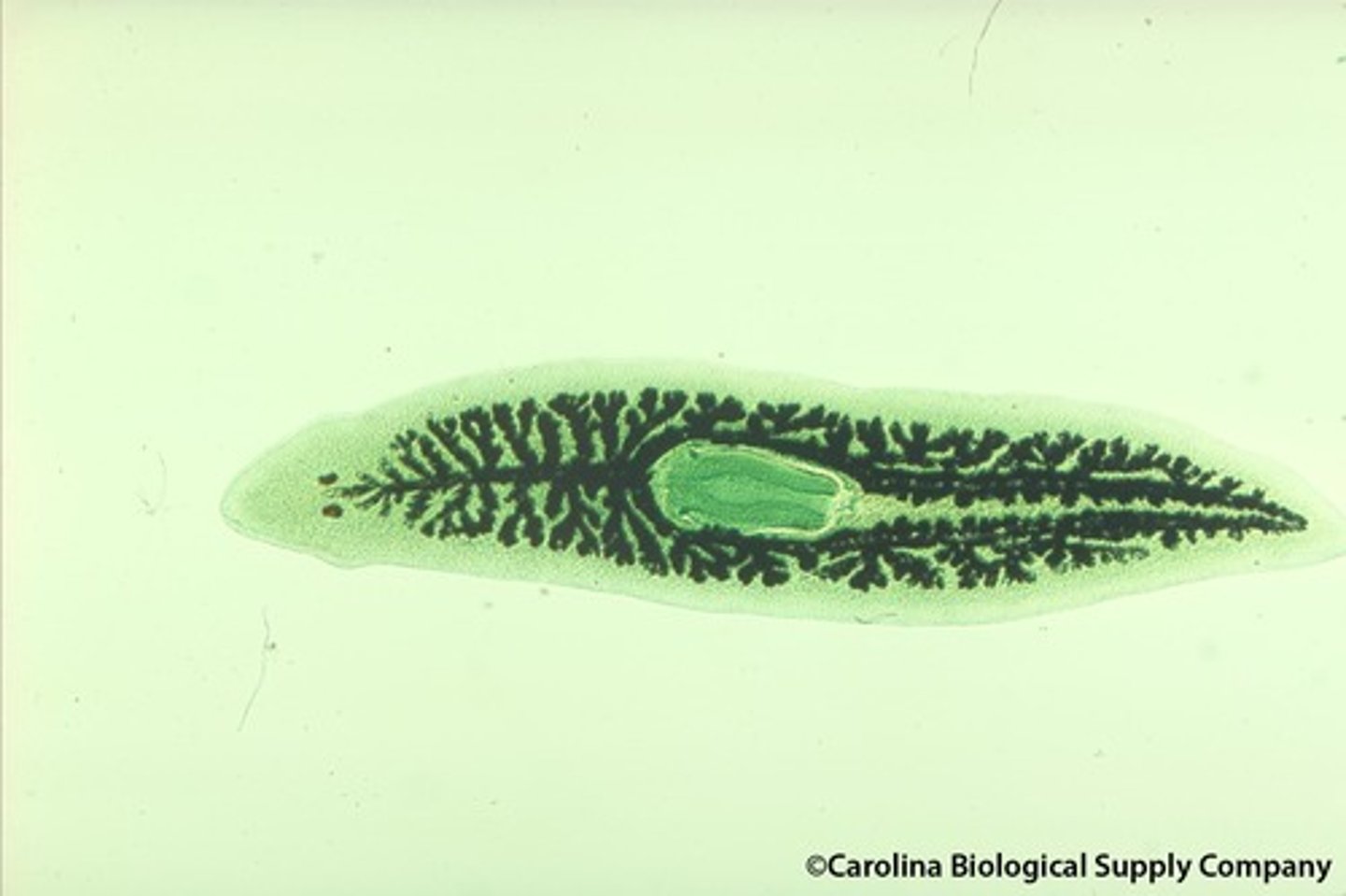
Tubellaria of the Platyhelminthes
Identify what organism this is
A) Turbellaria
B) Cestoda
C) Trematode

Enteron - Gastrovascular cavity
Identify the branched structure in this platyhelminthe
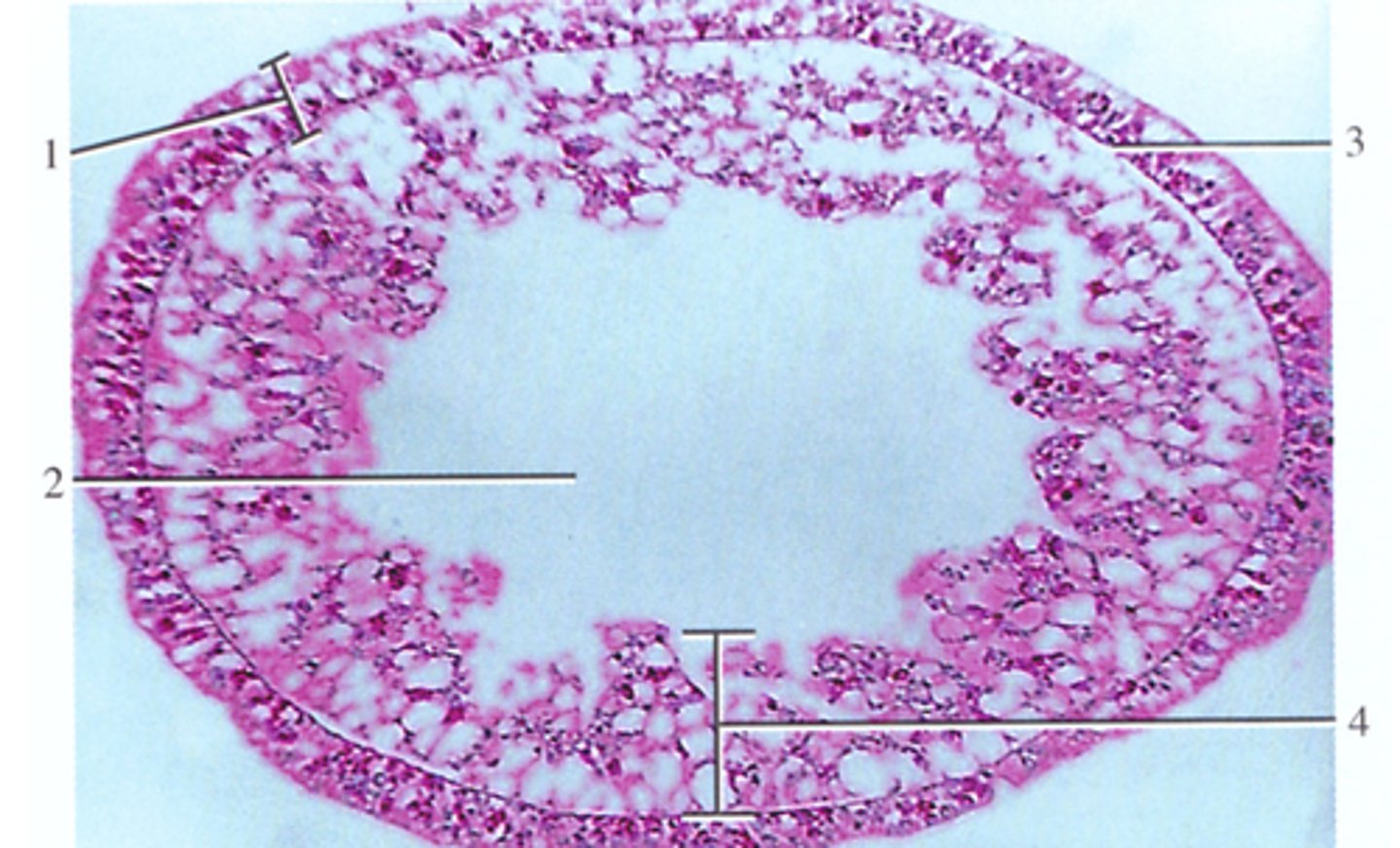
This is a cross section of a Hydra class Hydrozoa (dominant polyp stage), Phylum Cnidarian.
1. Epidermis
2. Gastrovascular Cavity
3. Mesoglea (just below)
4. Gastrodermis, just before the gastrovascular cavity
What is this cross section of? what organism does it belong to and name the numbered structures
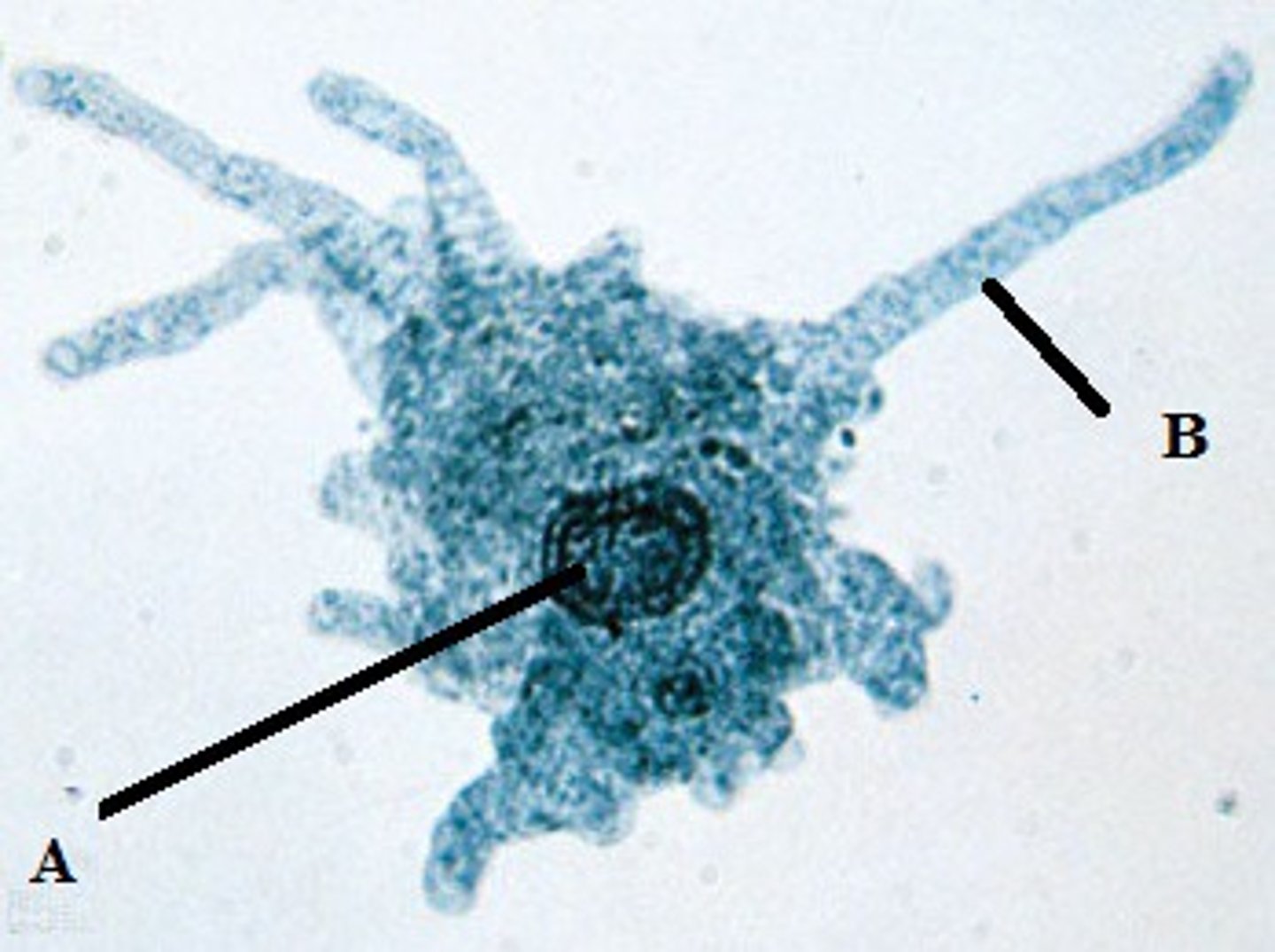
Kingdom protista, Phylum Cilliophora/Cilliates (SAR Clade of the 4 super groups) (a paramecium)
Identify the kingdom and phylum of this organism

This is an amoeba (a protist) belonging to the Kingdom Protista, Phylum Unikonta
Identify this organism, their kingdom and phylum.
B) Anthozoa belongs to Cnidarian Phylum
Which of the following is incorrectly matched with their phylum?
A) Platyheliminthes - Trematodes
B) Platyhelminthes - Anthozoa
C) Cnidaria - Schyphozoa
D) Cnidaria - Hydrozoa
E) Nematoda - tubatrix
D) Cilliophora (Cilliates) - Paramecium
Asexual reproduction in the Phylum Cnidaria, class Hydrozoa
What process is occuring in the image below and what Phylum and Class is this occuring in?
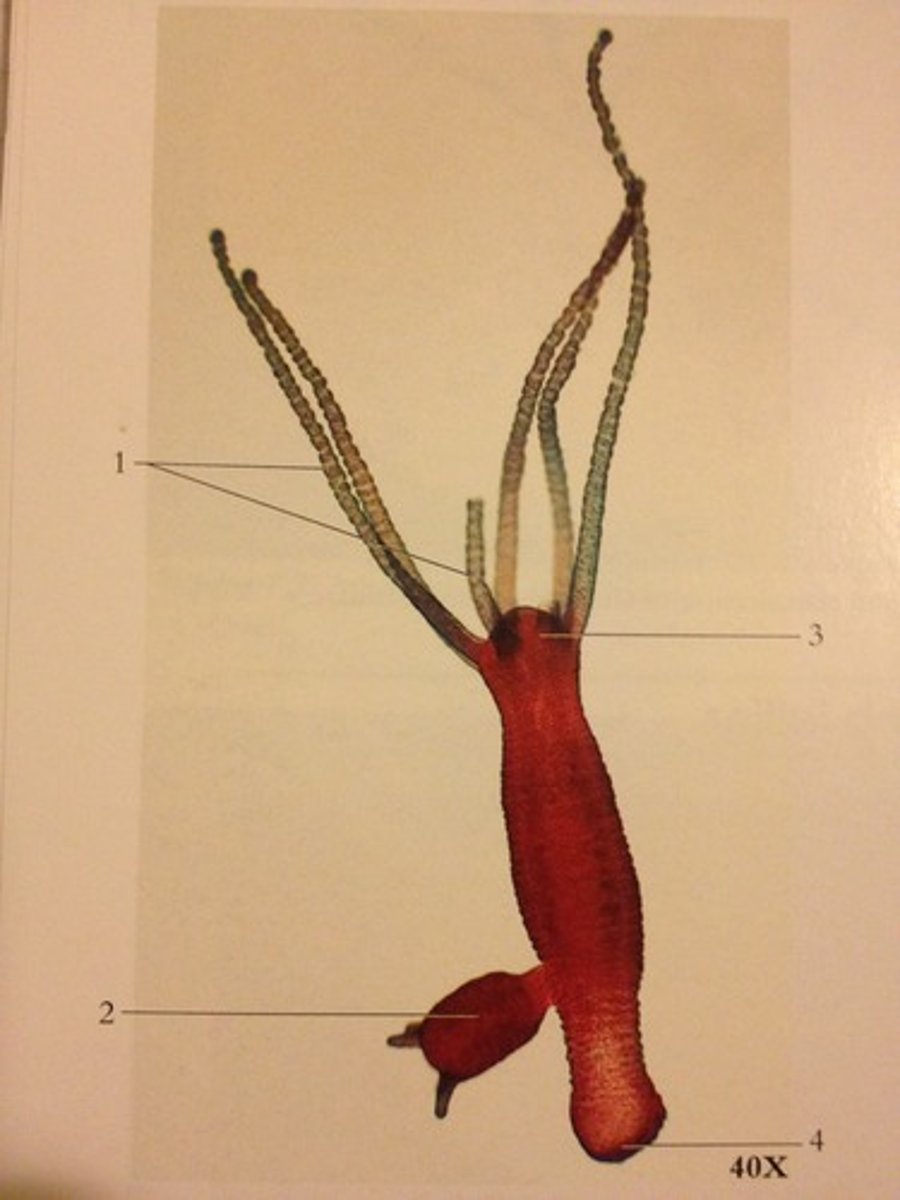
Hydrozoa have a dominant polyp lifecylcle, Schyphozoa has a dominant medusa stage (jellies) and Anthozoa lack a medusa stage (corals)
What are the differences between Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa and Anthozoa
Phylum Annelida, Oligochaeta (earthworms and leaches)
Identify the organism phyla and class below
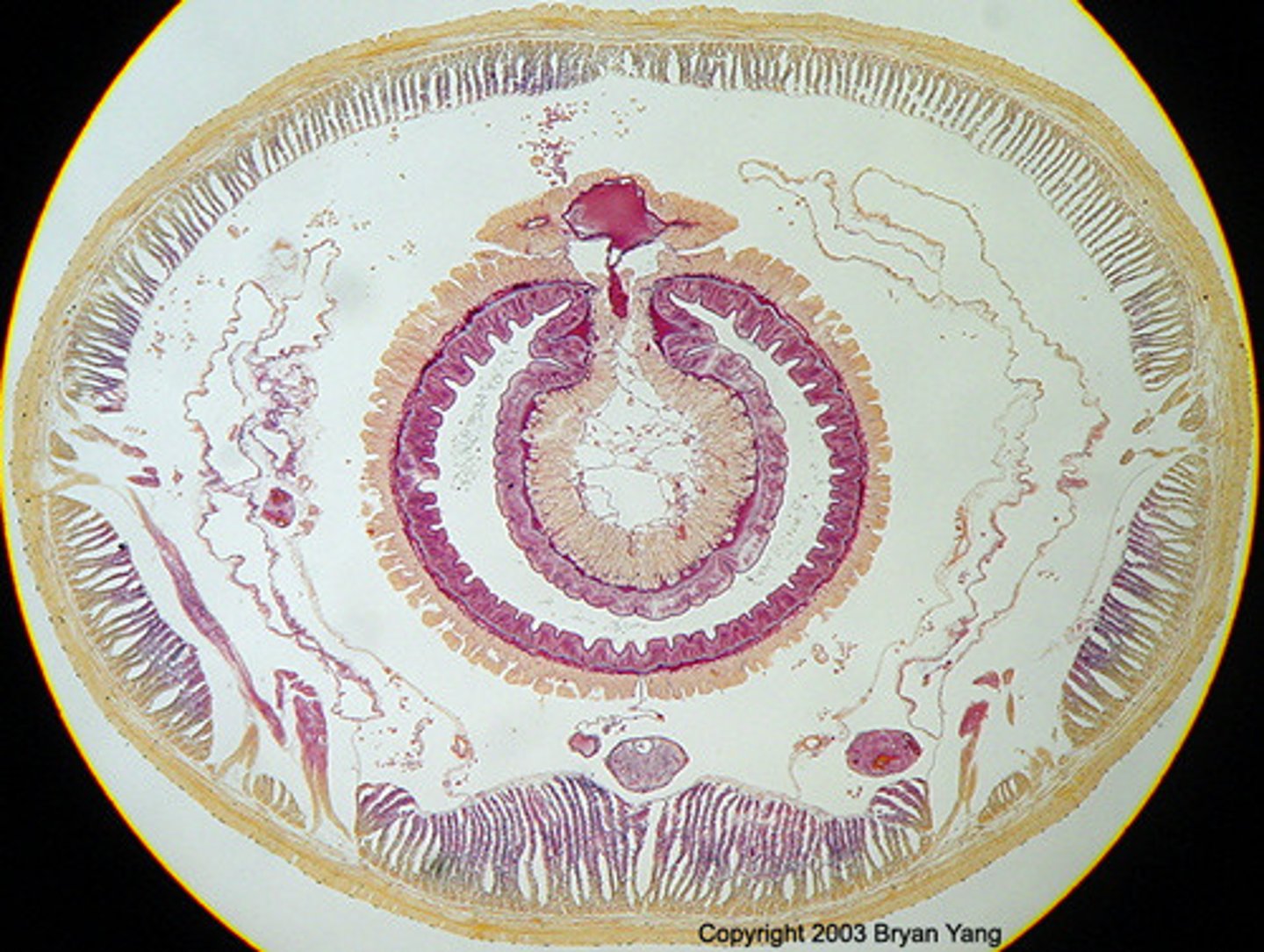
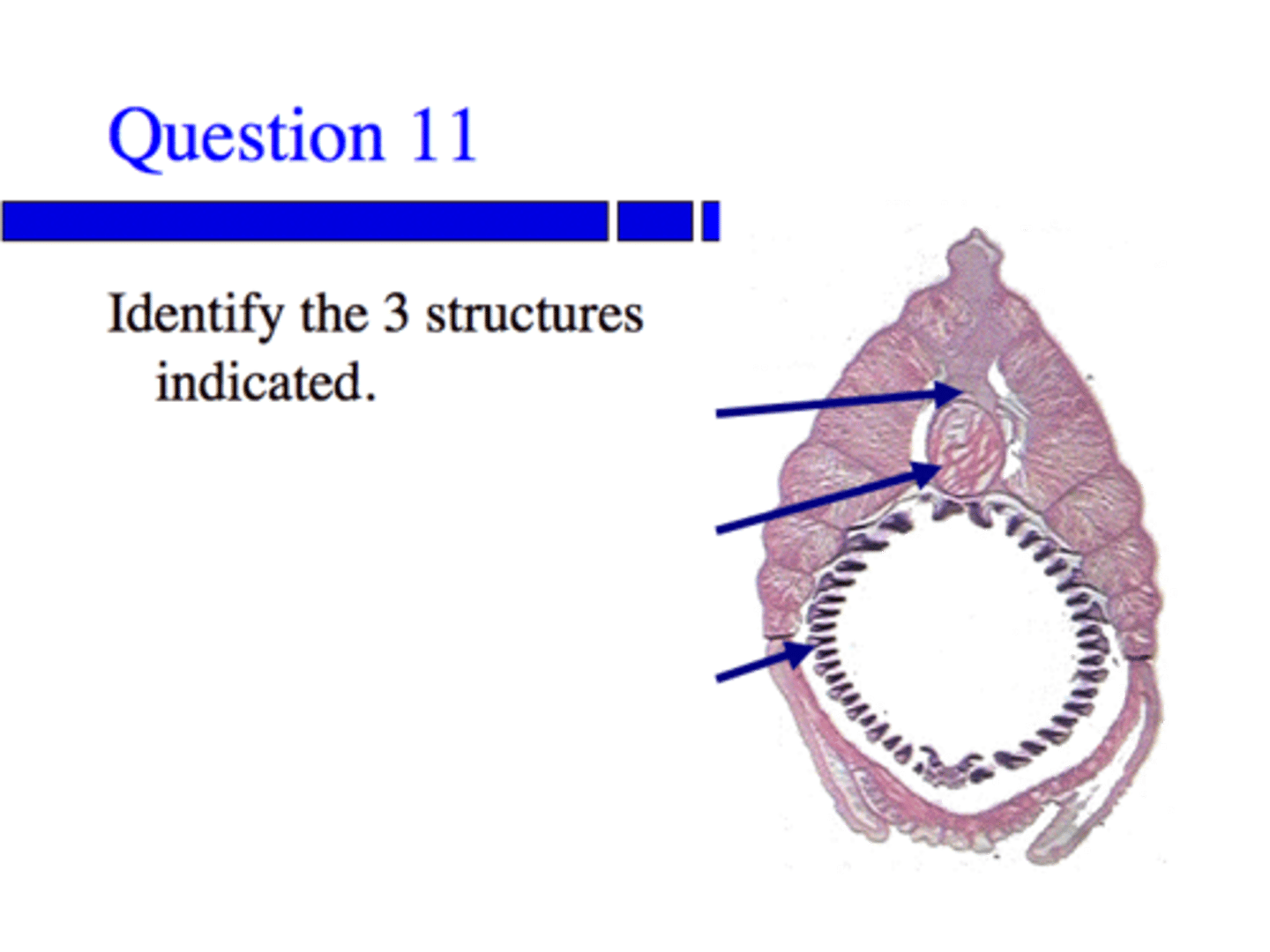
i) Coelom (true Coelom)
ii) Digestive cavity
Name the labels below of the Annelida (Lophotrochozoans) Oligochaetae (earthworm)
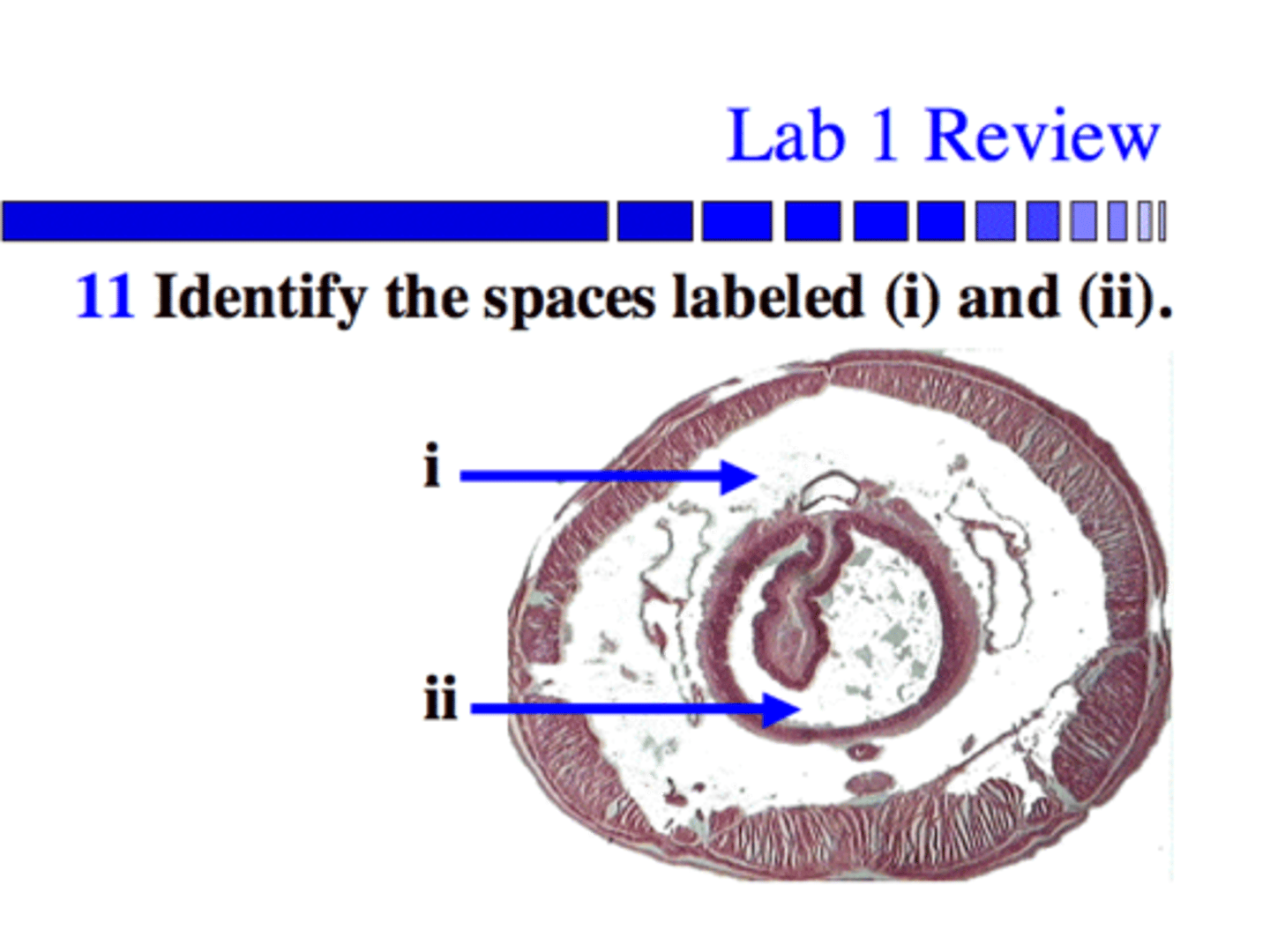
i) ventral blood vessel
ii) ventral nerve cord
iii) Longitudinal Muscle
Identify the labeled structures
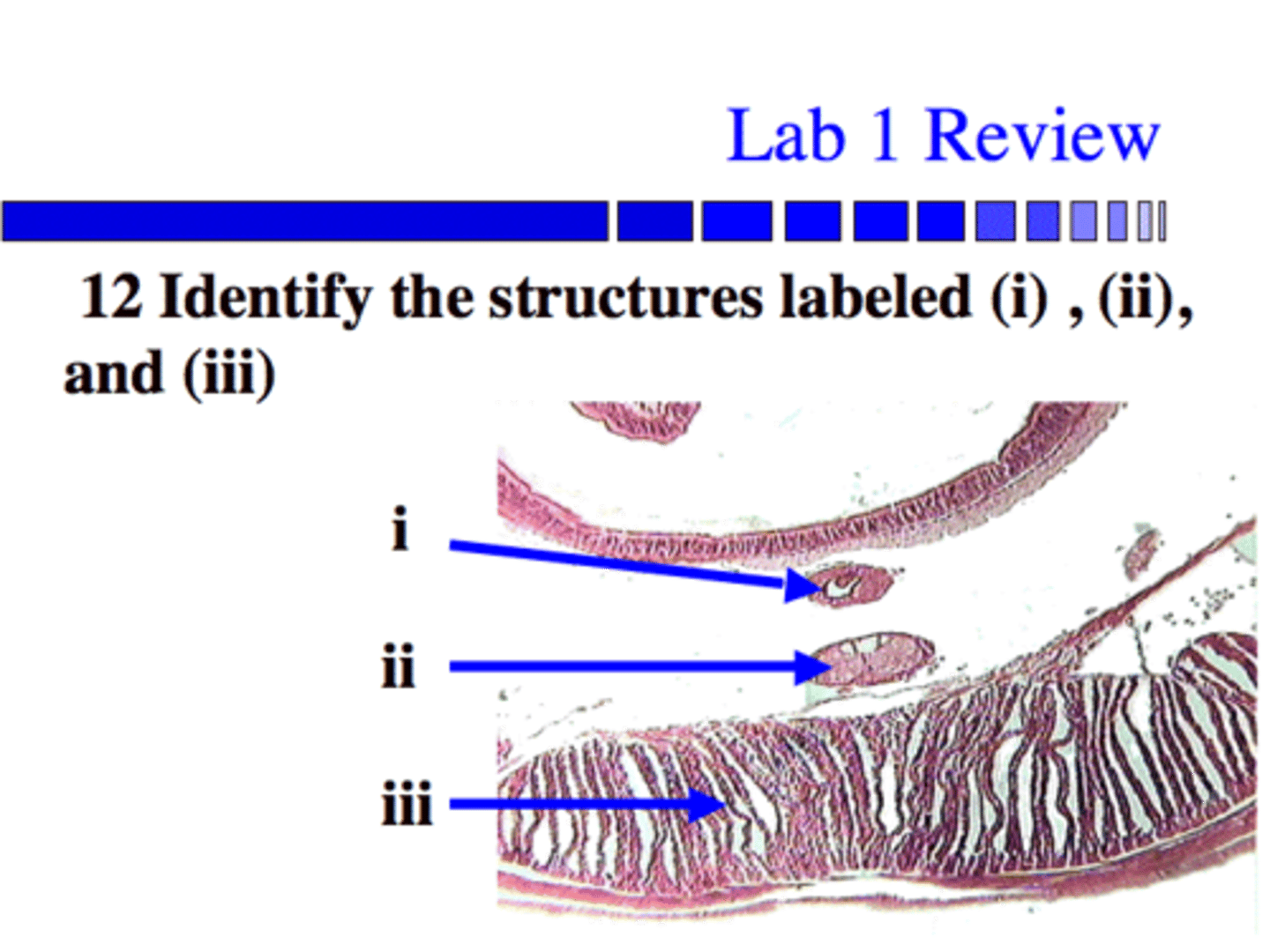
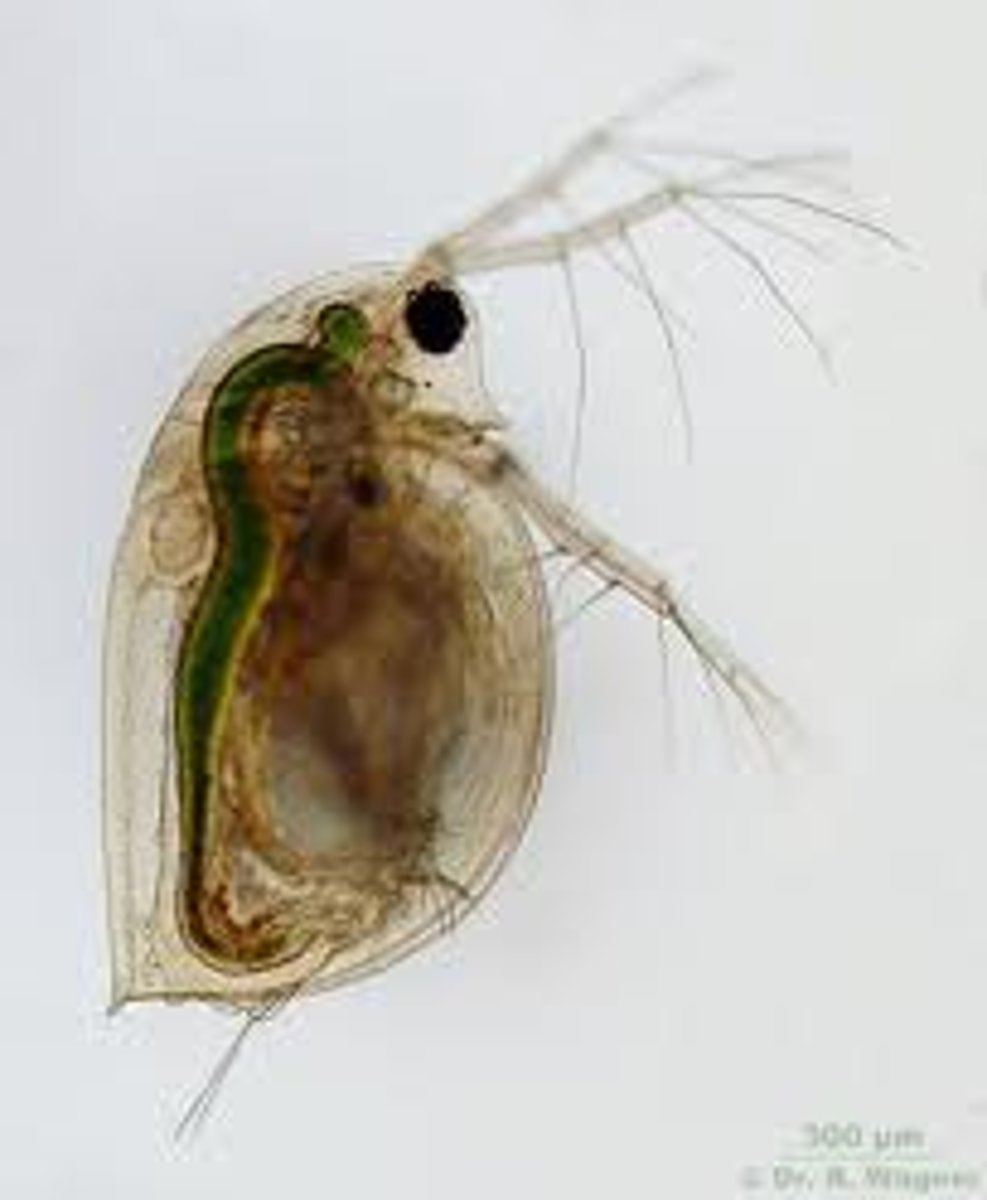
This is the Daphnia (water flea) which is an Arthropod, Crustacean. They have an Exoskeleton, Jointed Appendages, integrated nervous system and a hameocael
Identify the Phylum and the clade of this creature below. Why is it classified this way?
The middle one
C) Arthropod
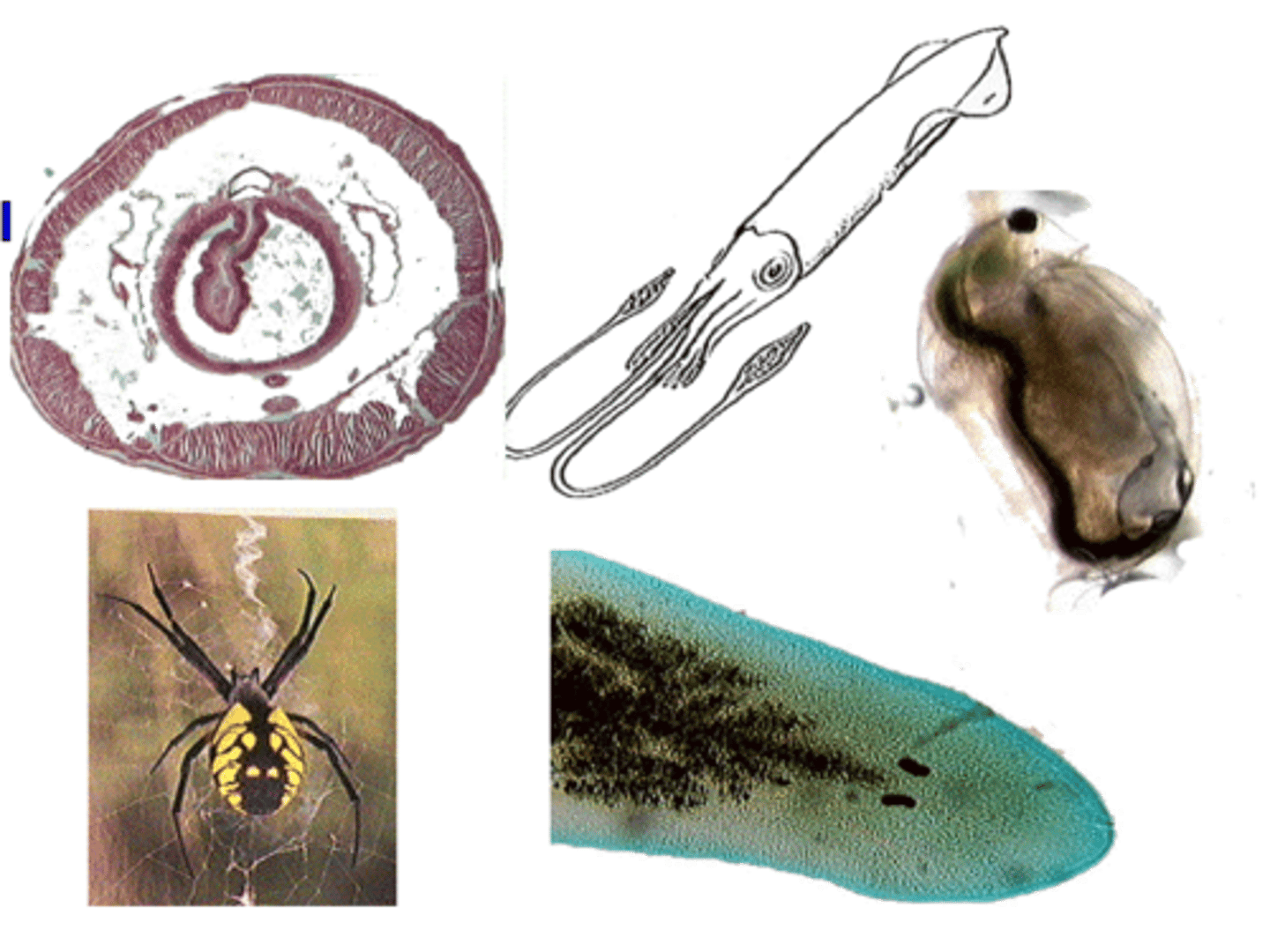
Identify the organism
A) Annelida
B) Mollusca
C) Arthropod

4. In Order it is
Annelida (Sedentaria/Oligochaeta)
Mollusca (cephalopoda)
Arthropoda (Crustacean, Chelicerates)
Platyheliminthes (tubelerria)
How many Phyla are shown in this image?
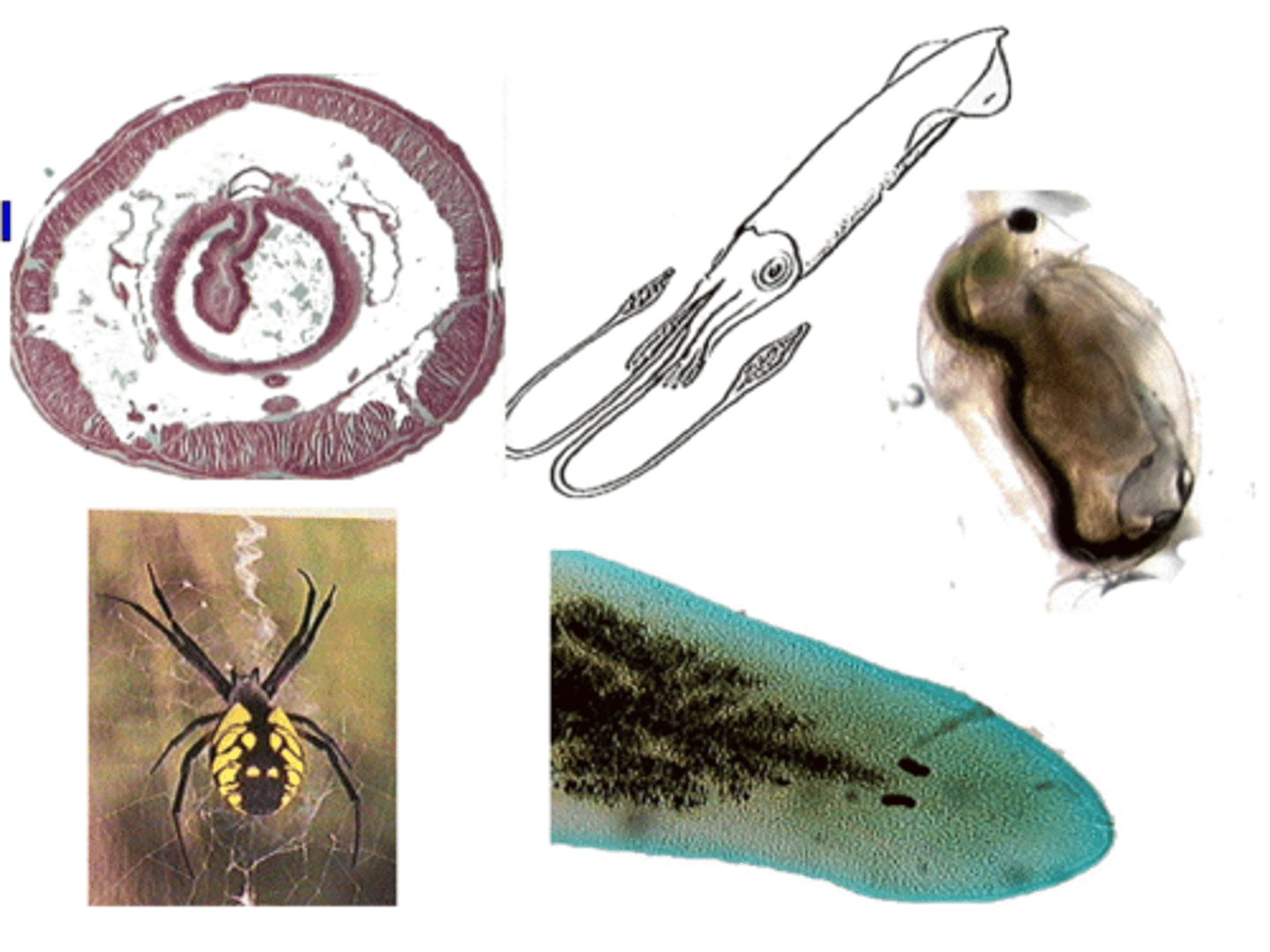
E) which includes - the presence of 3 germ layers, and showing bilateral symmetry
Which of the following features is common to all of these organisms?
A) Segmented Body
B) Three Germinal Layers
C) Bilateral Symmetry
D) Presence of some type of Coelom
E) Two of the above
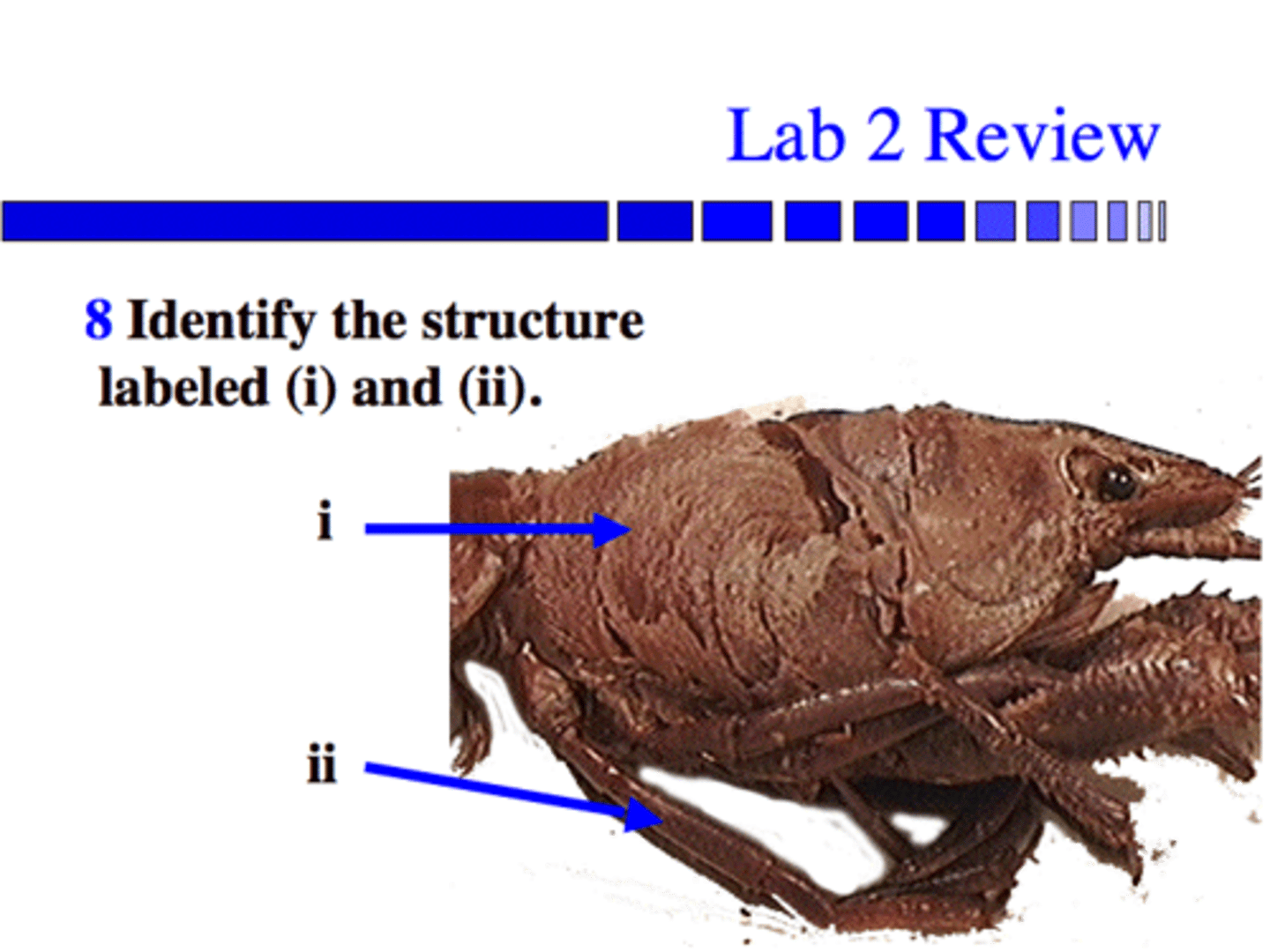
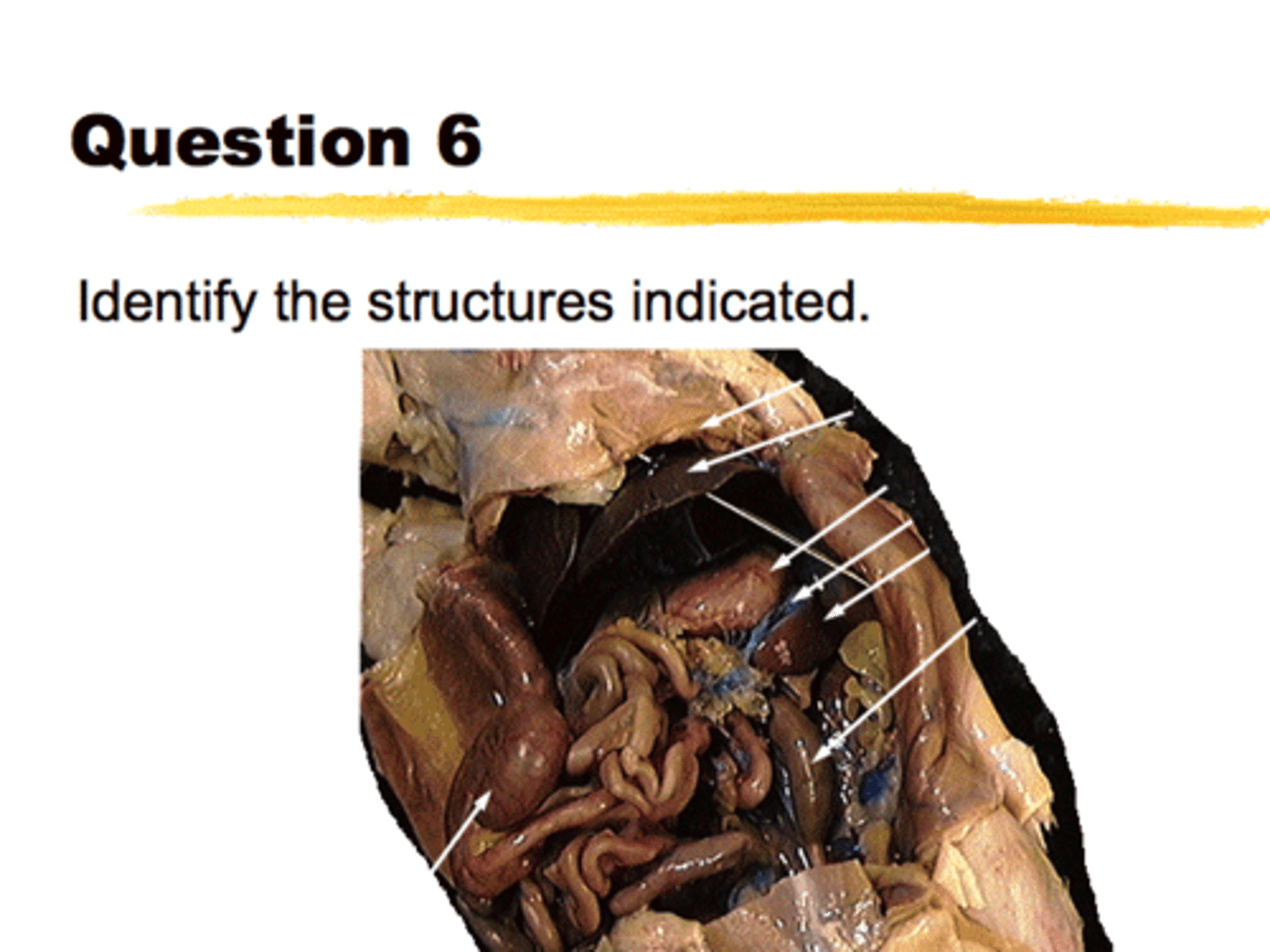
(i) The Carpace (hard protective covering)
ii) The heart
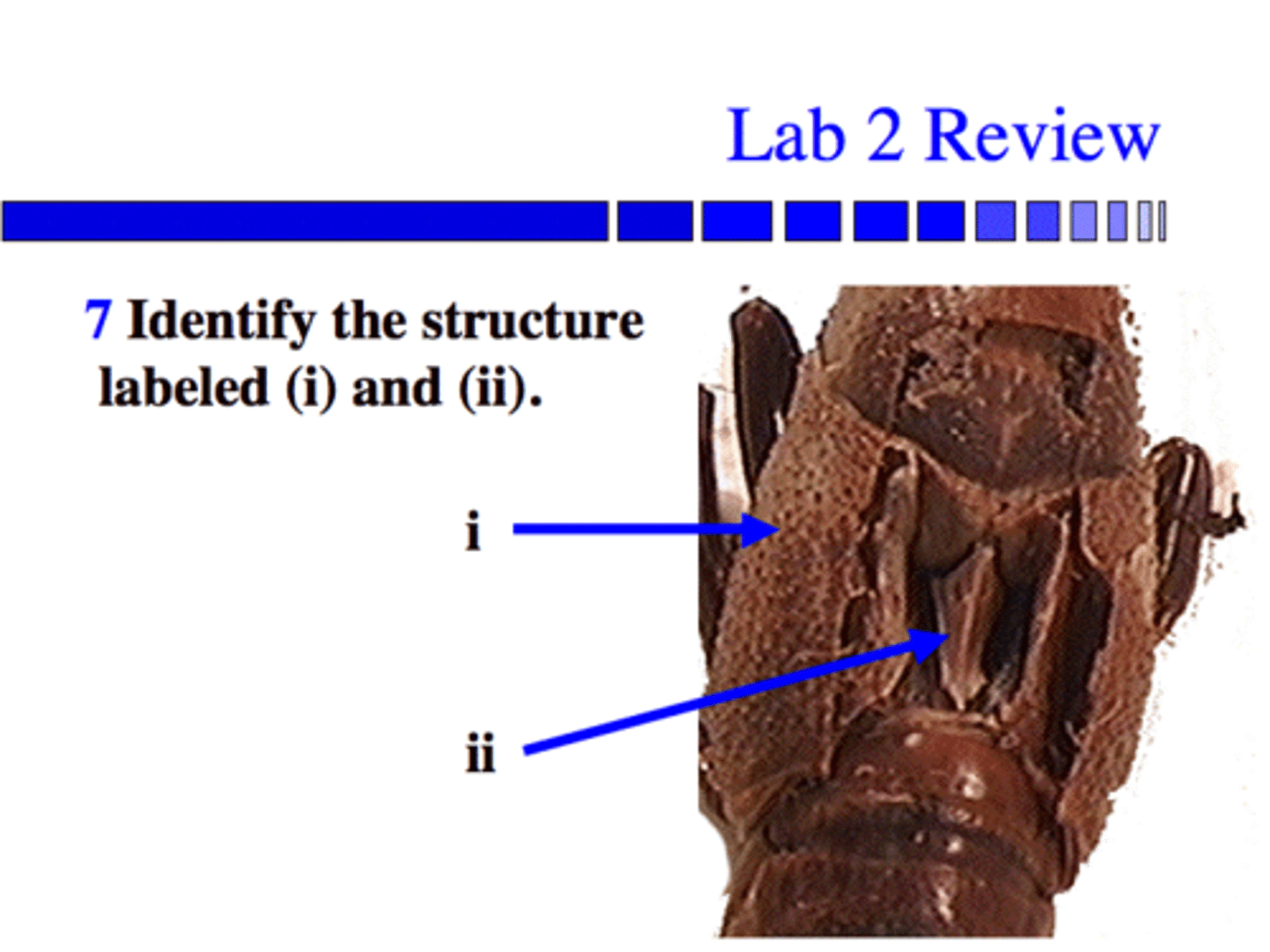
i) The gills in Branchial Chamber
ii) Periopod (Walking legs)
(Big claws are called chelipids, and little swimerettes are pleopods)
D) Median Sagittal Plane

C) Cephalic, Lateral and Ventral

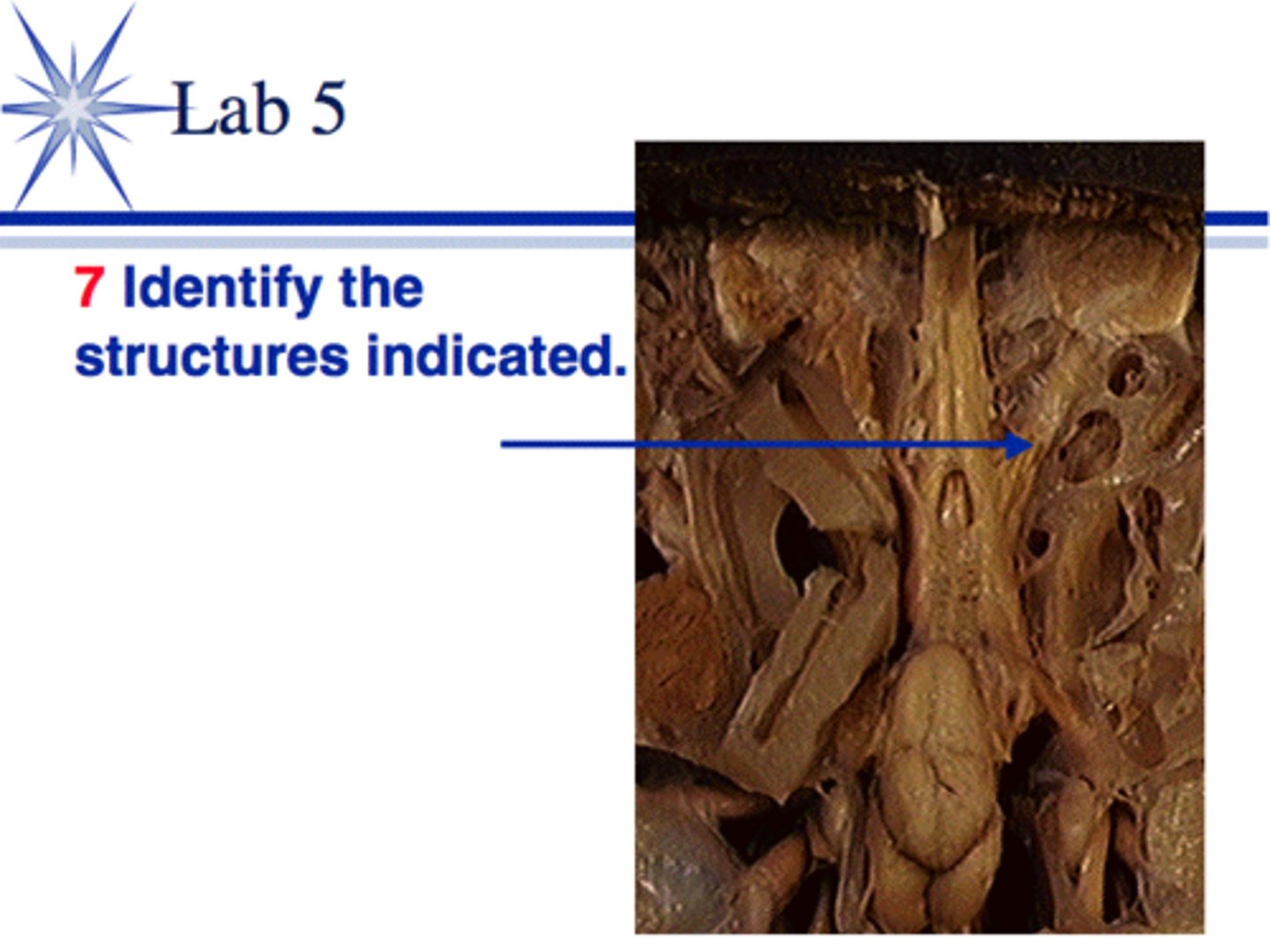
1. Dorsal Hollow nerve cord
2. Notochord
3. Pharyngeal Gill Slits
Chordate, cephalochordata, Amphixious (brachiostoma)
And what is this creature's phylum?
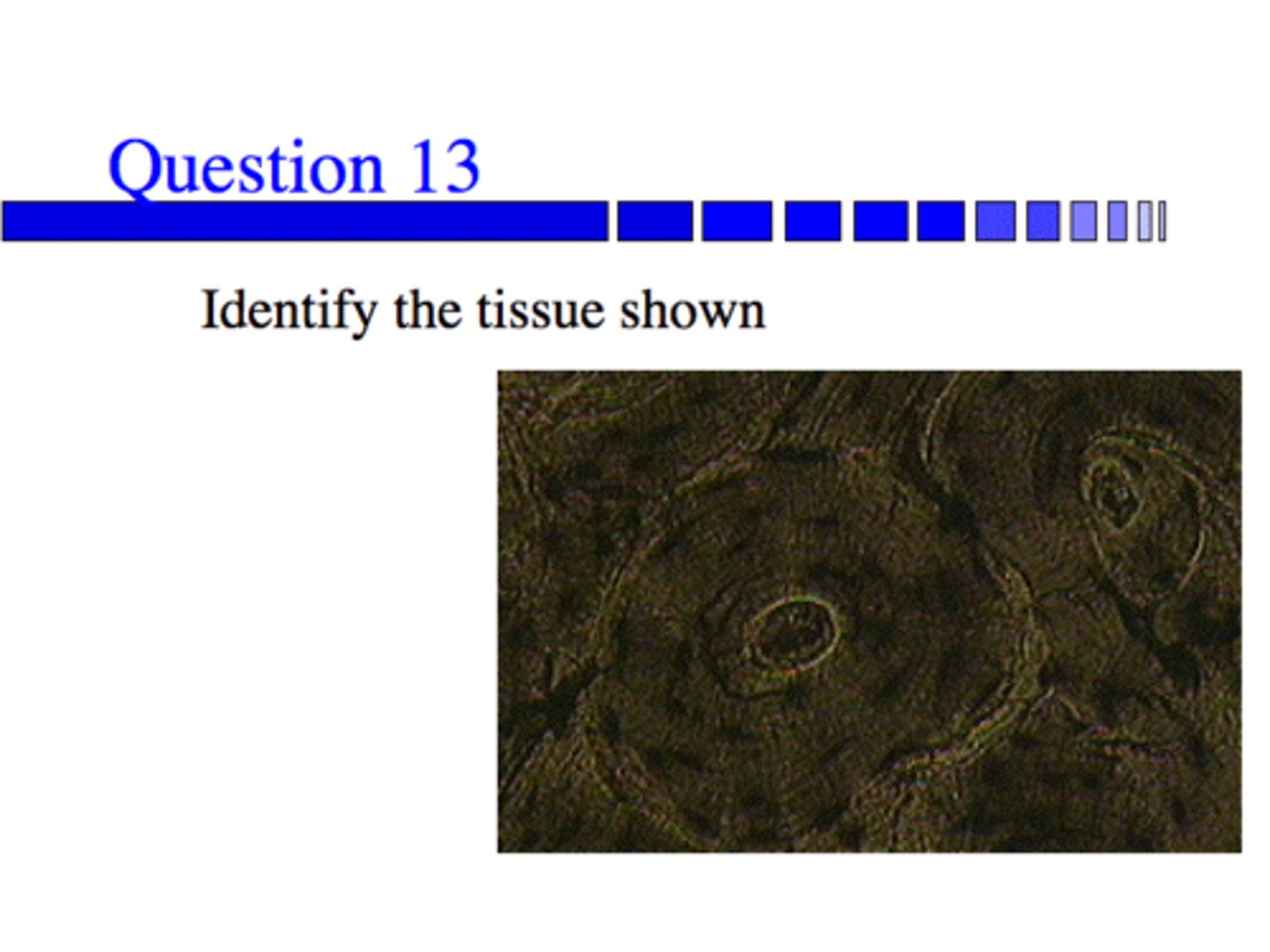
Bone Tissue with Haversian Canal in the middle
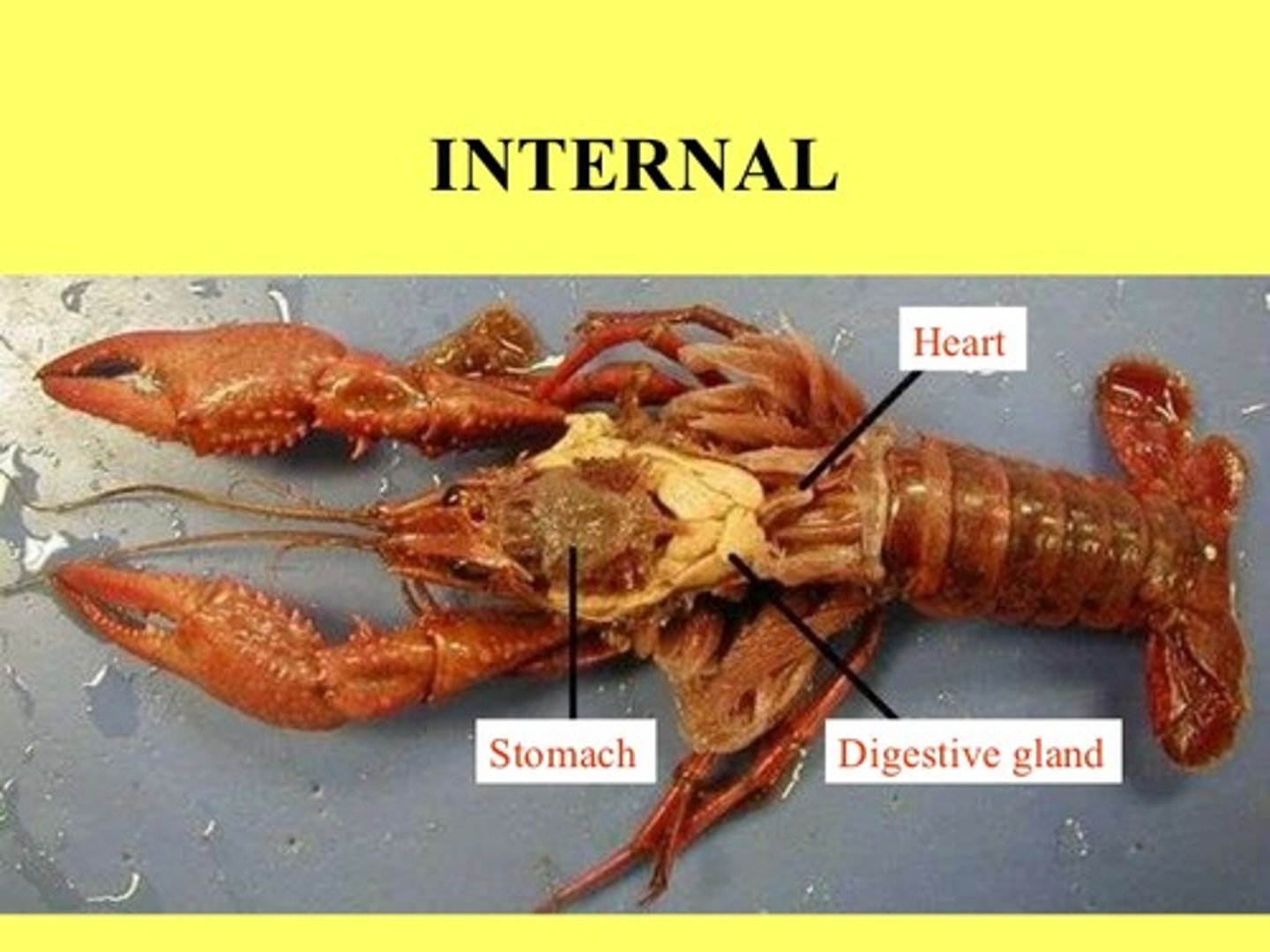
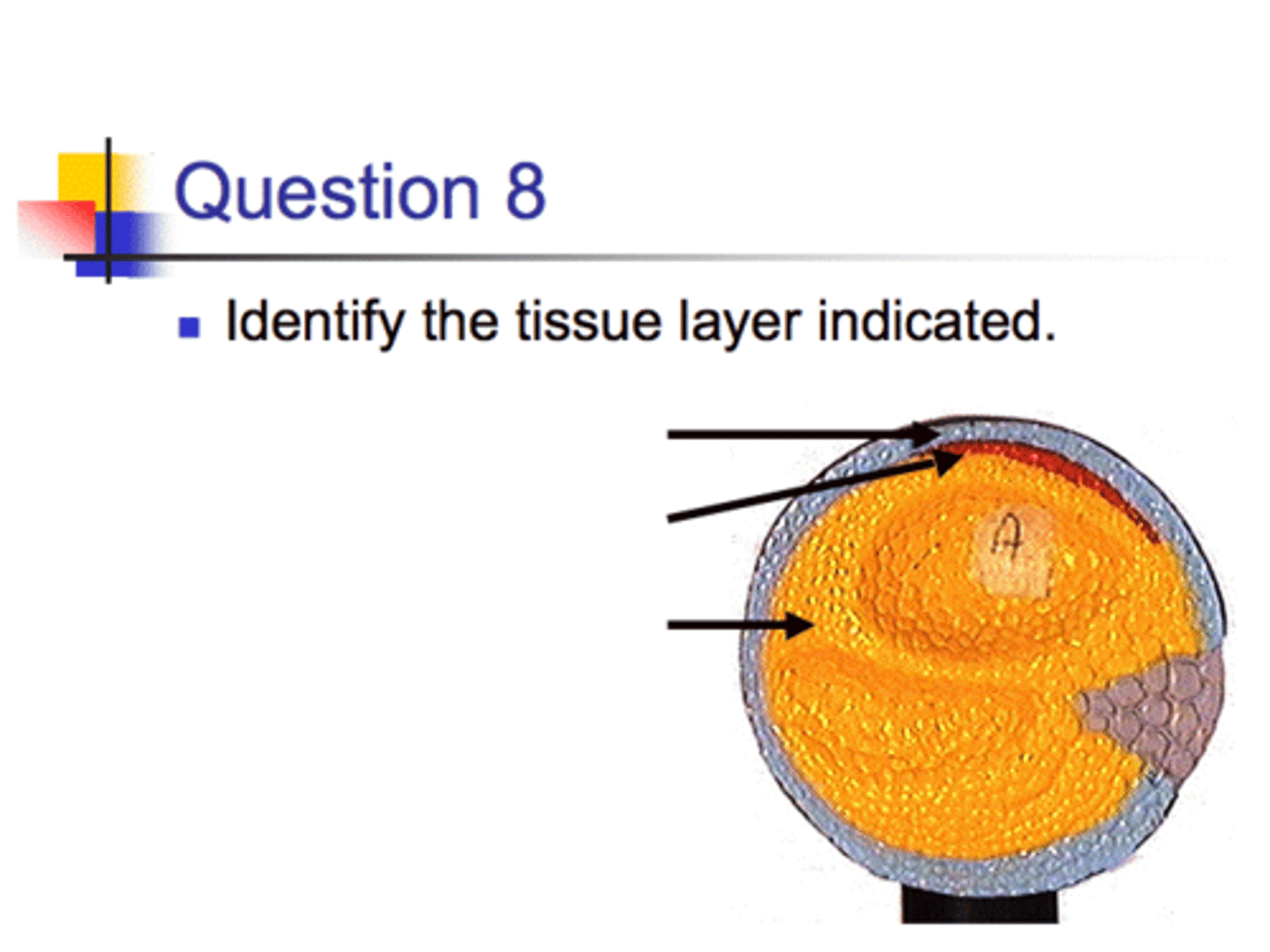
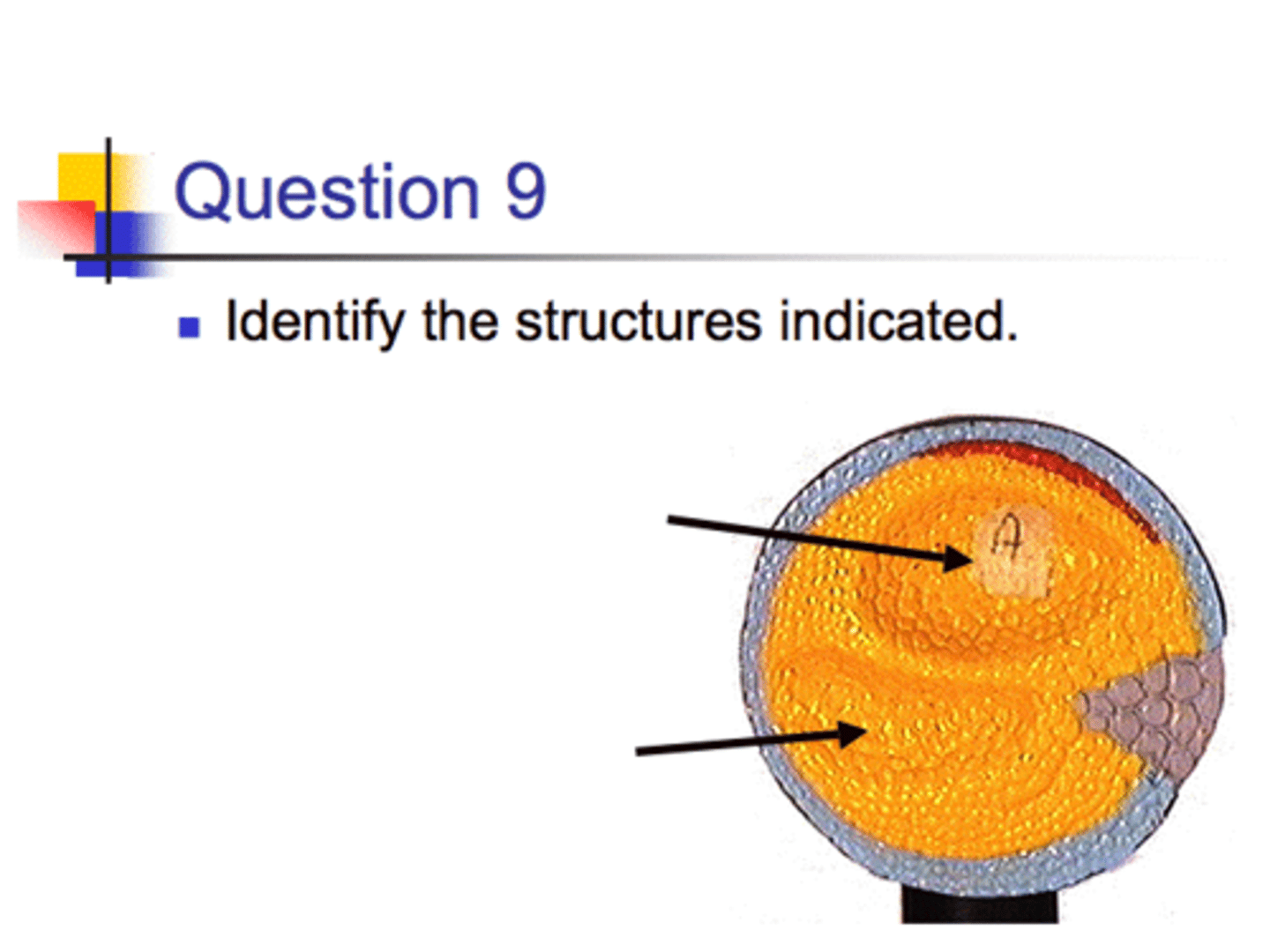
1. Hepatic Caecum
2. Gonads

Note the Gonads are just under the heart. Bilobed Ovary which is grainy. Or white ungrainy testis. Covered in pyloric stomach
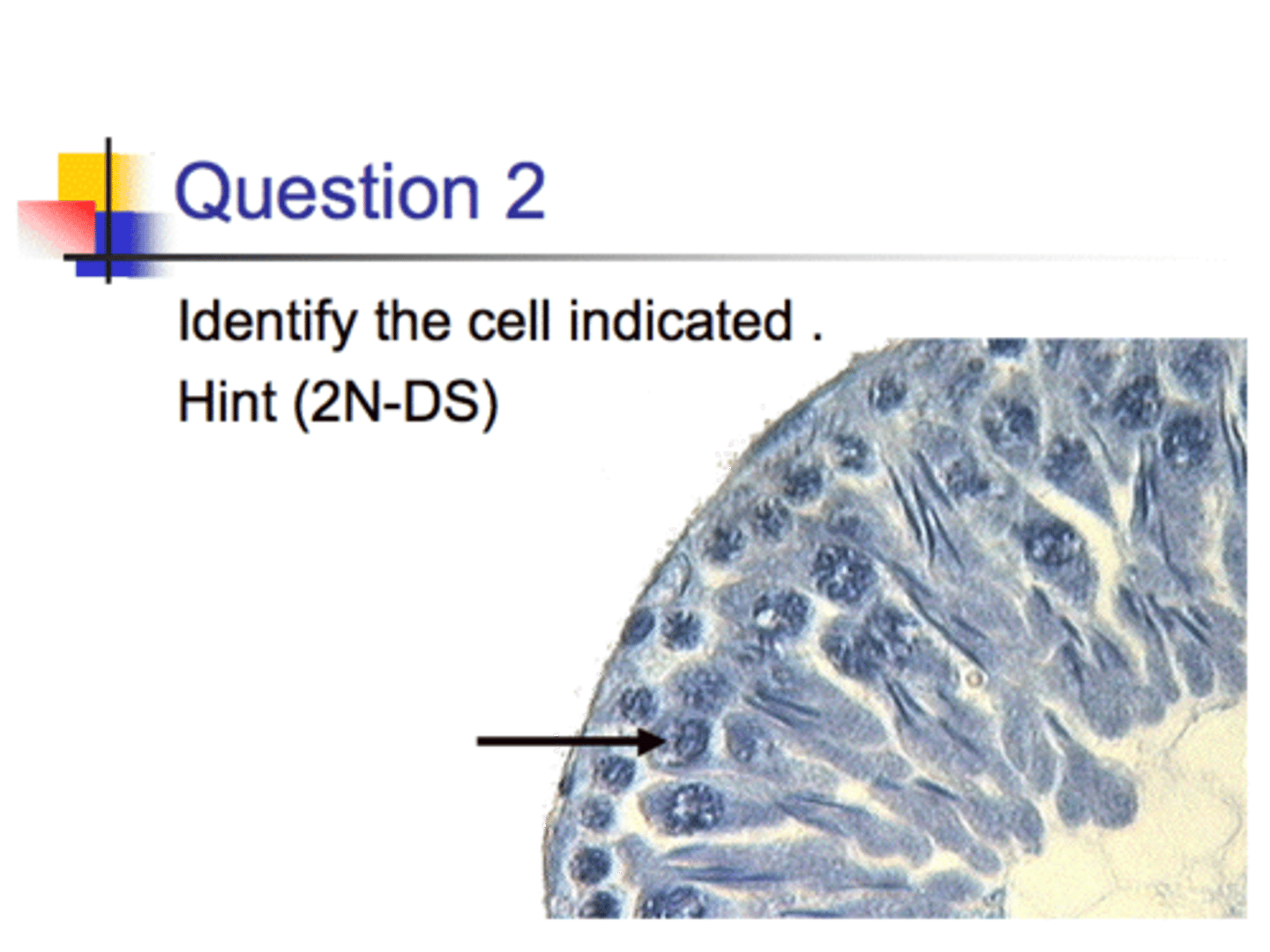
Seminferous Tubule ( a tube n the testis where spermatogonia are )

A primary spermatocyte (the spermatogonia diploid cells have differentiated - pre meiotic phase)
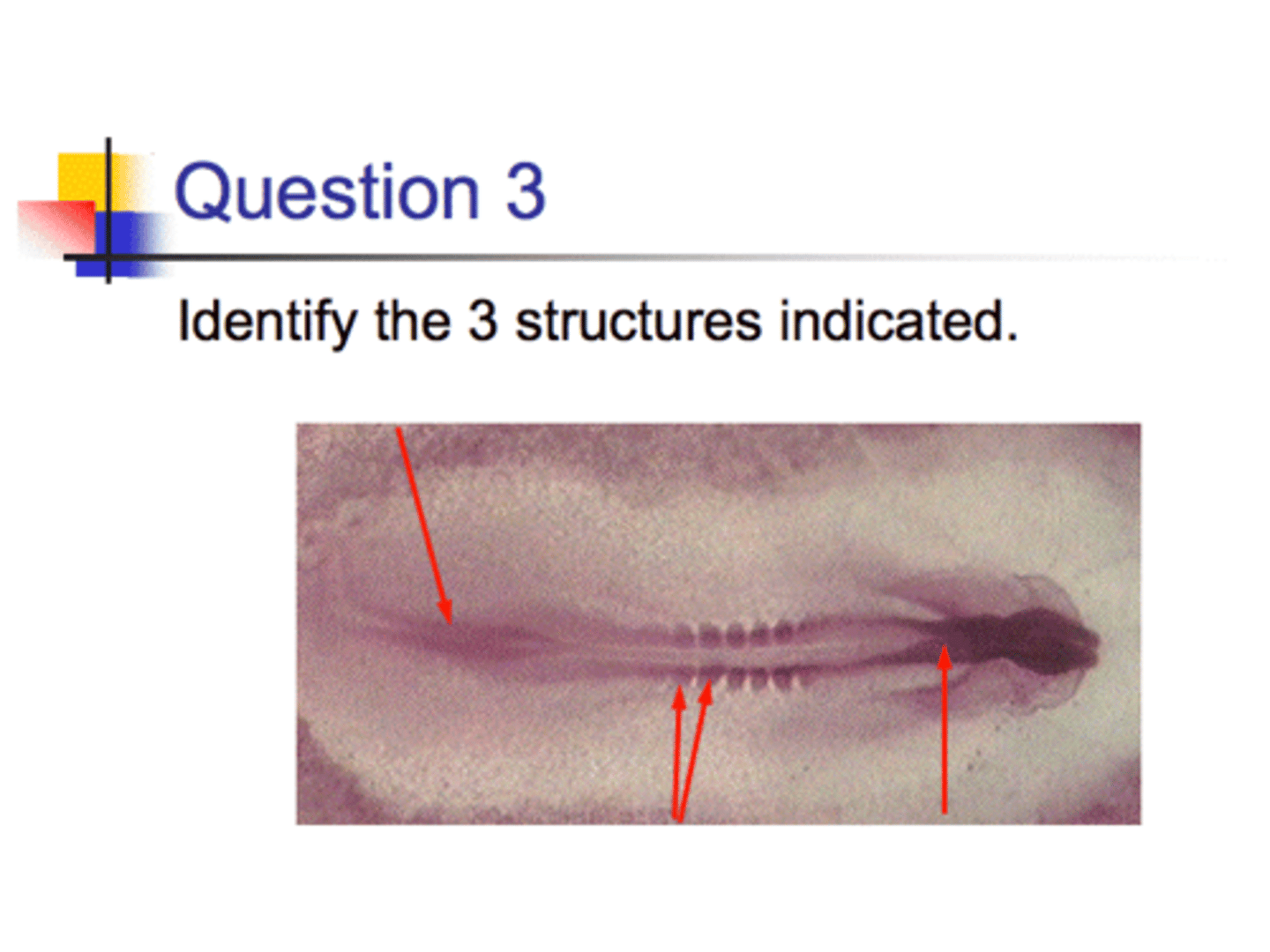
1. The primitive streak
2. Somites
3. The neural groove
Blastomere about to undergo cleavage

1. The Dorsal Lip of the blastopore
2. yolk cells

1. The animal pole
2. The vegetal pole

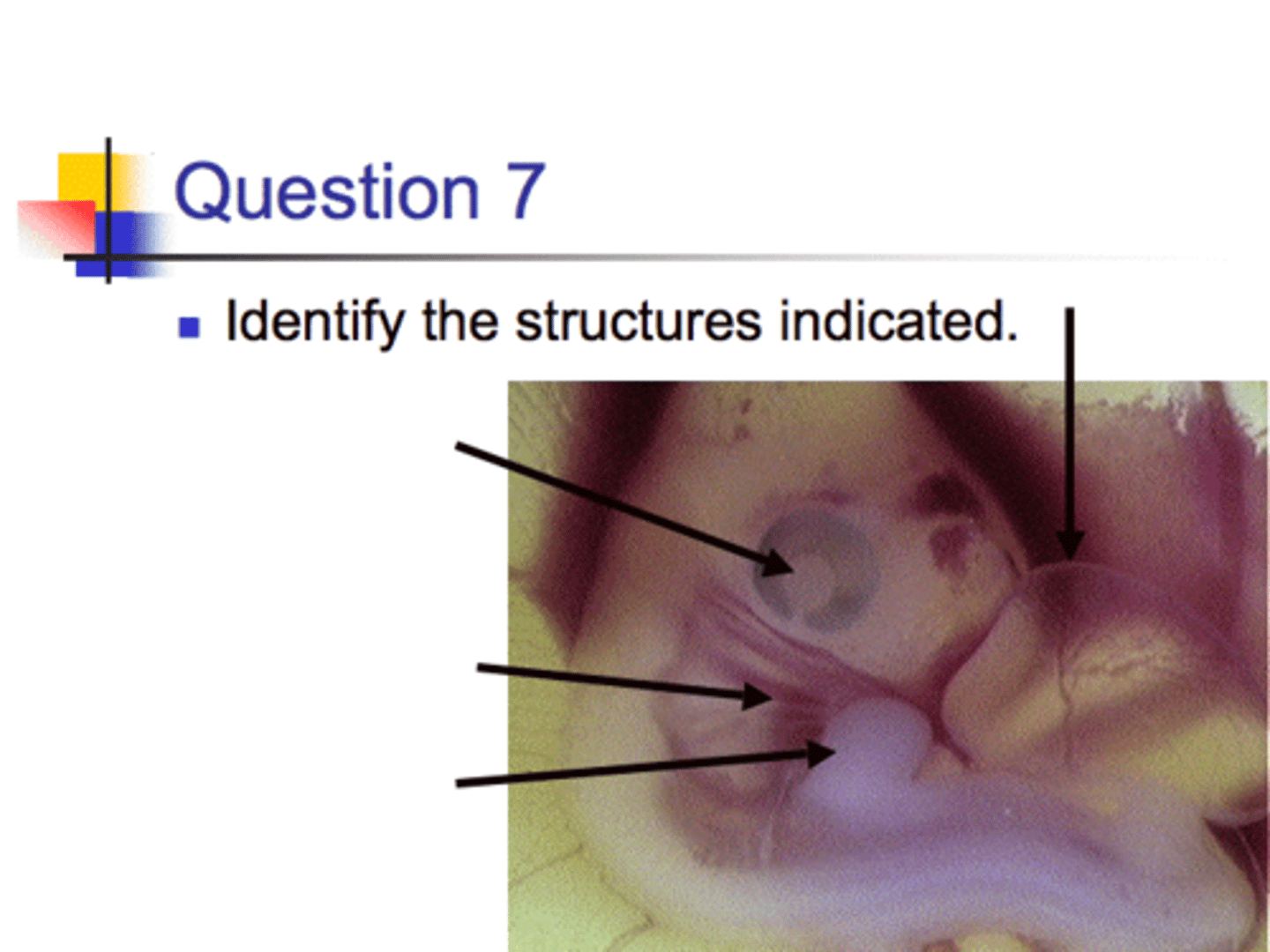
(Top to Bottom)
Eye,
Gill slits
Limb Bud
(Side right top)
Allantois
Ectoderm, Mesoderm, Endoderm
Archenteron (primitive gut formed during gastrulation)
Blastocoel (fluid filled cavity made during cleavage)
1. (left bottom) the Caecum
2. (top right) The Diaphragm
3. The liver (one of the 5 lobes)
4. The Stomach
5. The Omentum (connects stomach to spleen)
6. Spleen
7. Descending Colon (ascending, transverse and descending)
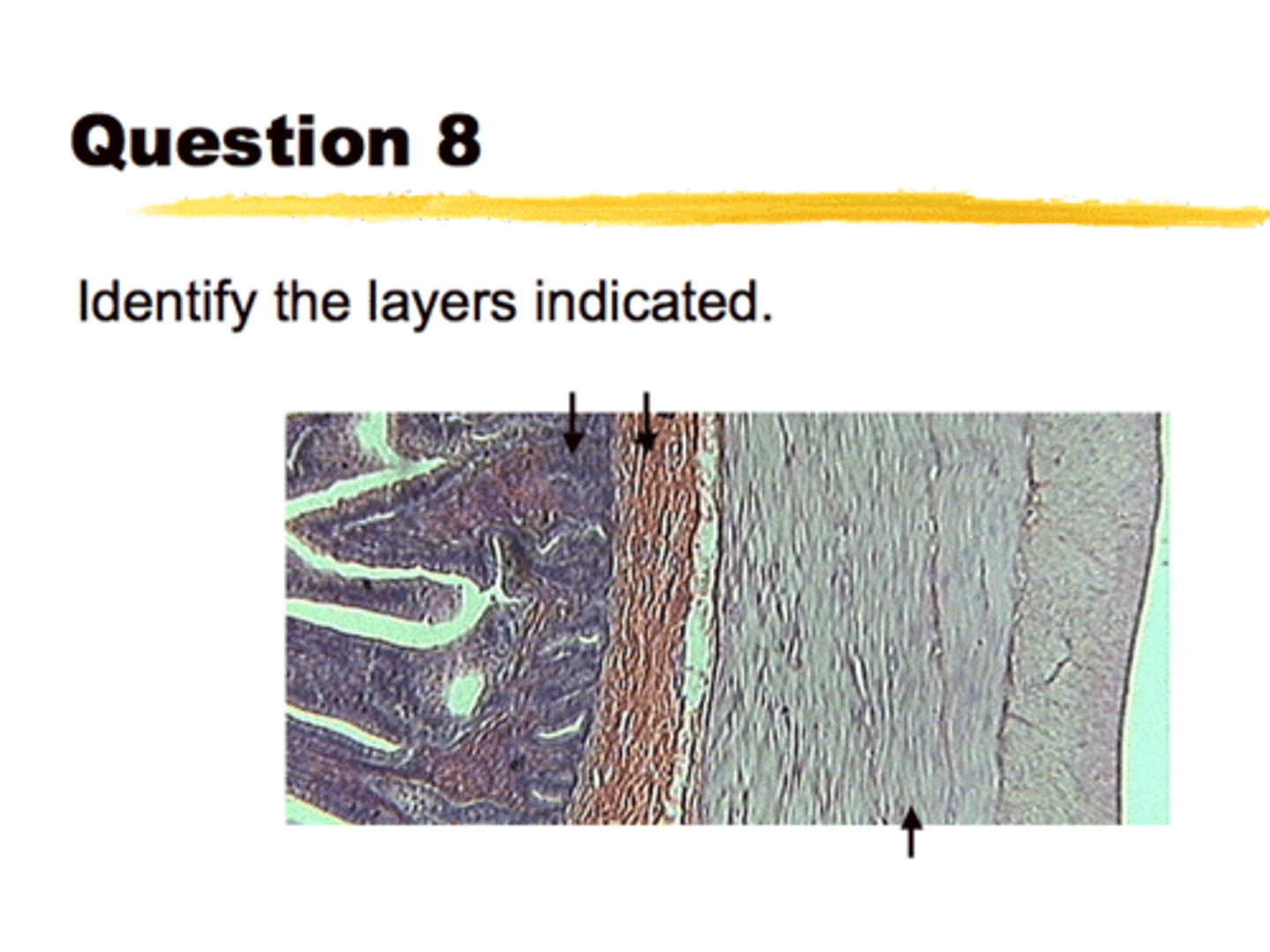
Layers of the small intestine
(left to right)
1. Mucosa (folded to form vili
2. Submucosa (region containing larger blood vessels and lymphatics of the gut)
3. Muscularis (smooth muscle layers inner circular, and outer longitudinal)
- Not shown - serosa - outer thin connective tissue layer of the intestine
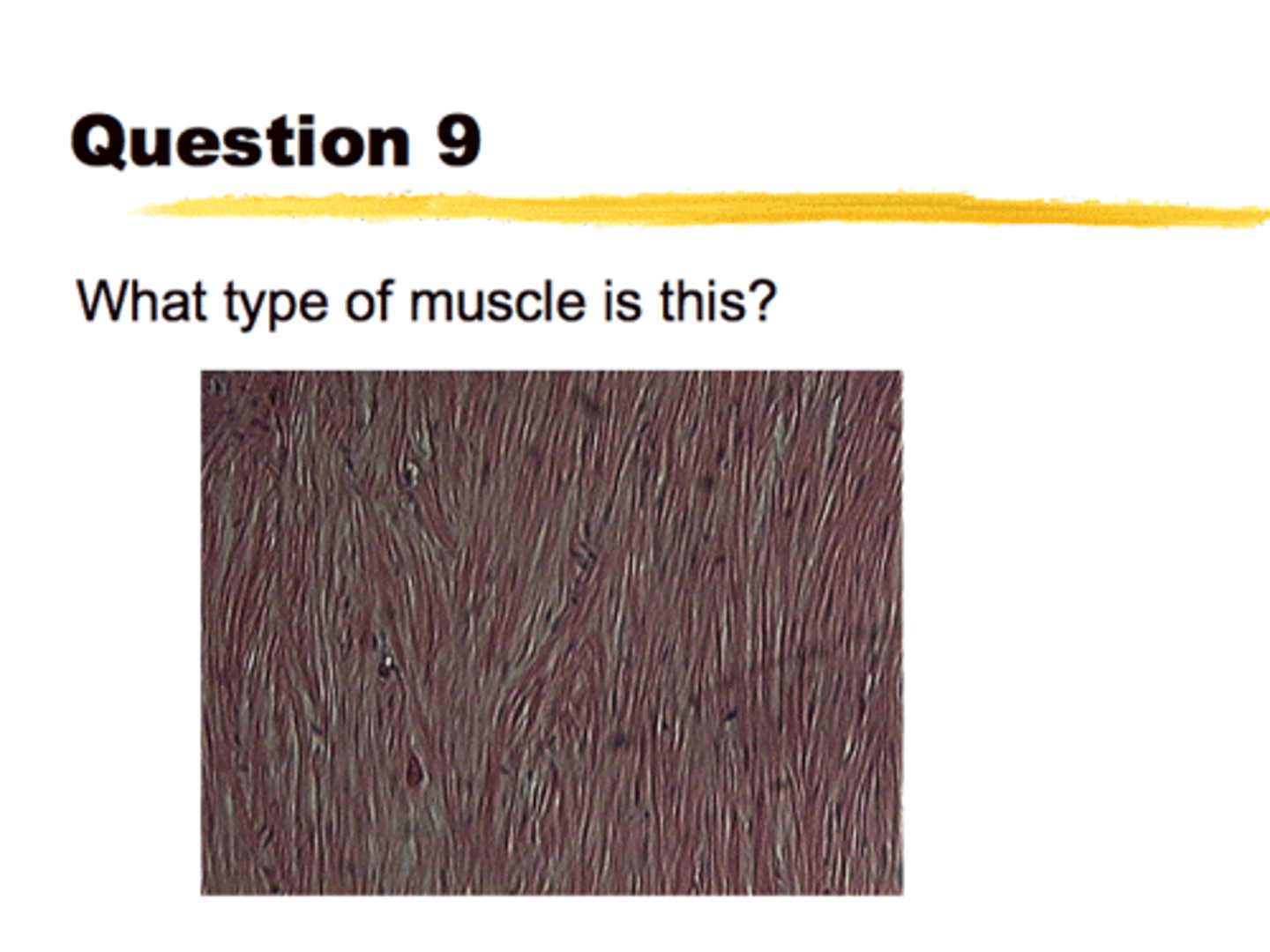
What is this slide a photo of?
Smooth Muscle
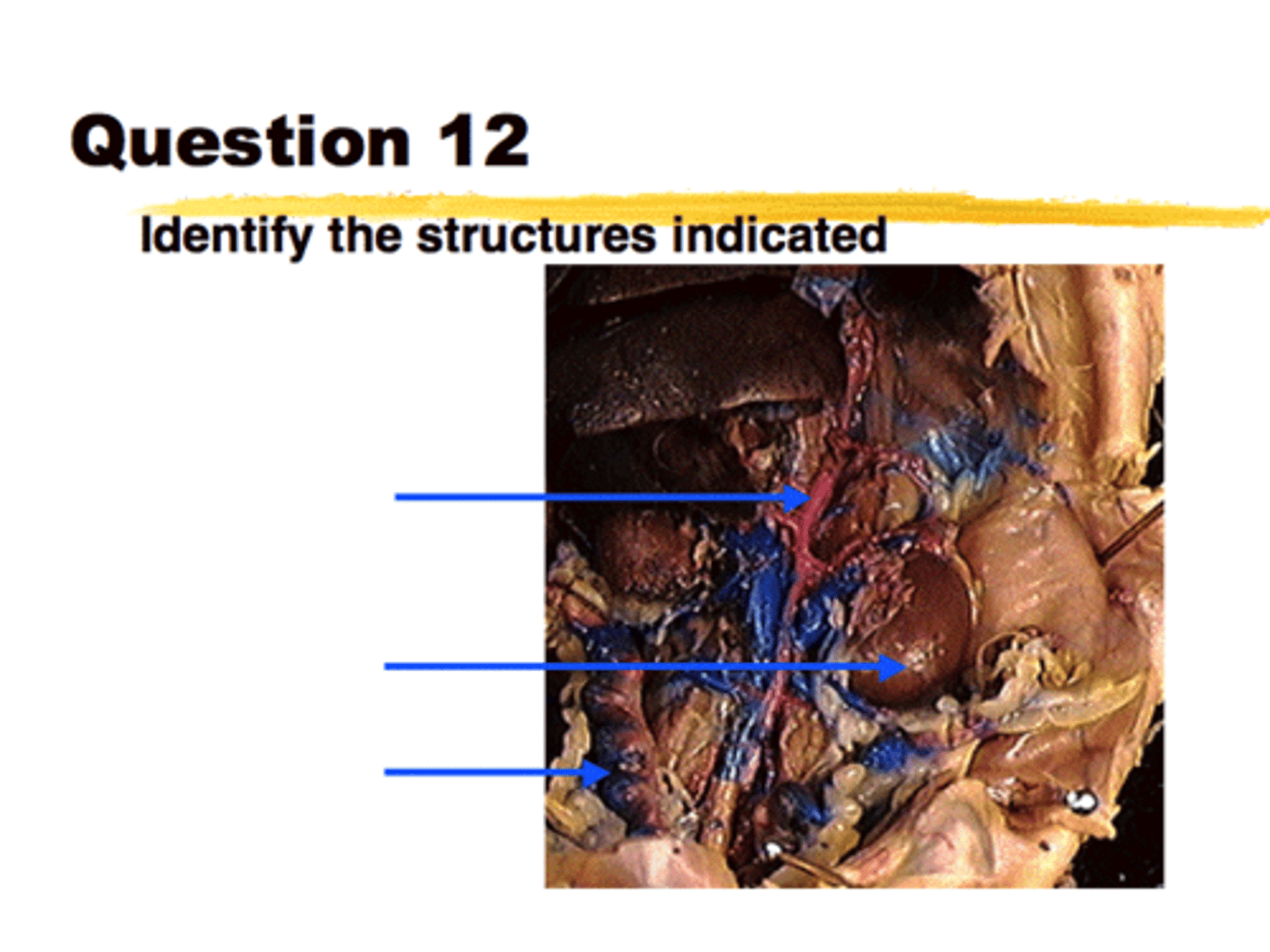
(top to bottom)
1. Dorsal Aorta
2. The Left Kidney
3. A uterine Horn
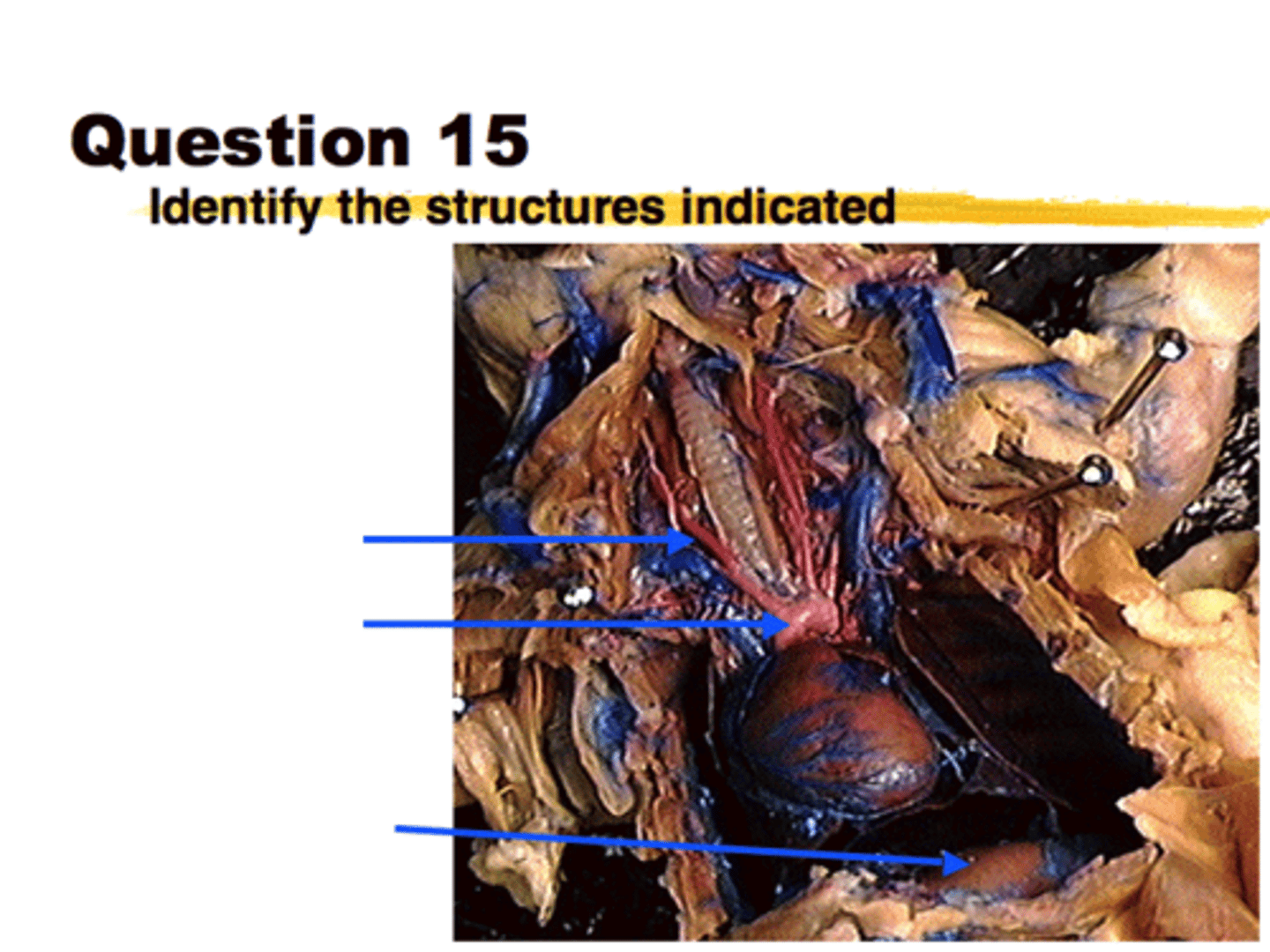
(top down)
Right Subclavian artery
Aorta
Diaphragm
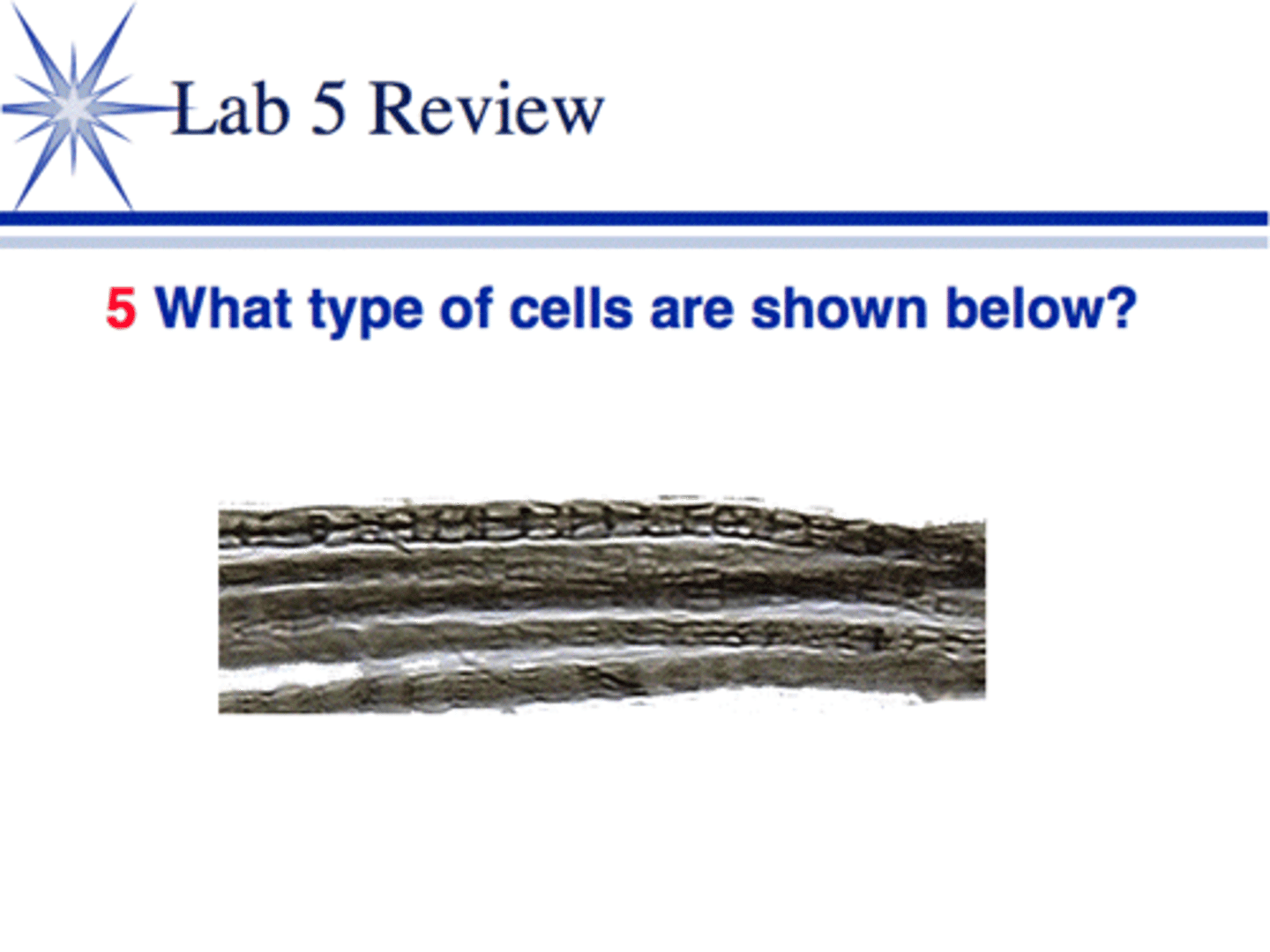
Nerve fibre cells
The Vagus nerve
Phylum Echinodermata
urchins, sea cucumbers, sea stars
marine, old
slow moving, sessile
thin epidermis covering endoskeleton of hard calcareous plates
unique water vascular system
large coelom, respiration
pentaradially symmetrical
Classes of Echinodermata
1. Crinoidea
2. Asteroidea
3. Ophiuroidea
4. Echinoidea
5. Holothuroidea
Class Asteroidea
sea stars, starfish
open groove runs along each arm bordered by rows of tube feet
1cm-1m across
sea daisies have no arms
- feed on bivalves
-attach to shell using tube feet
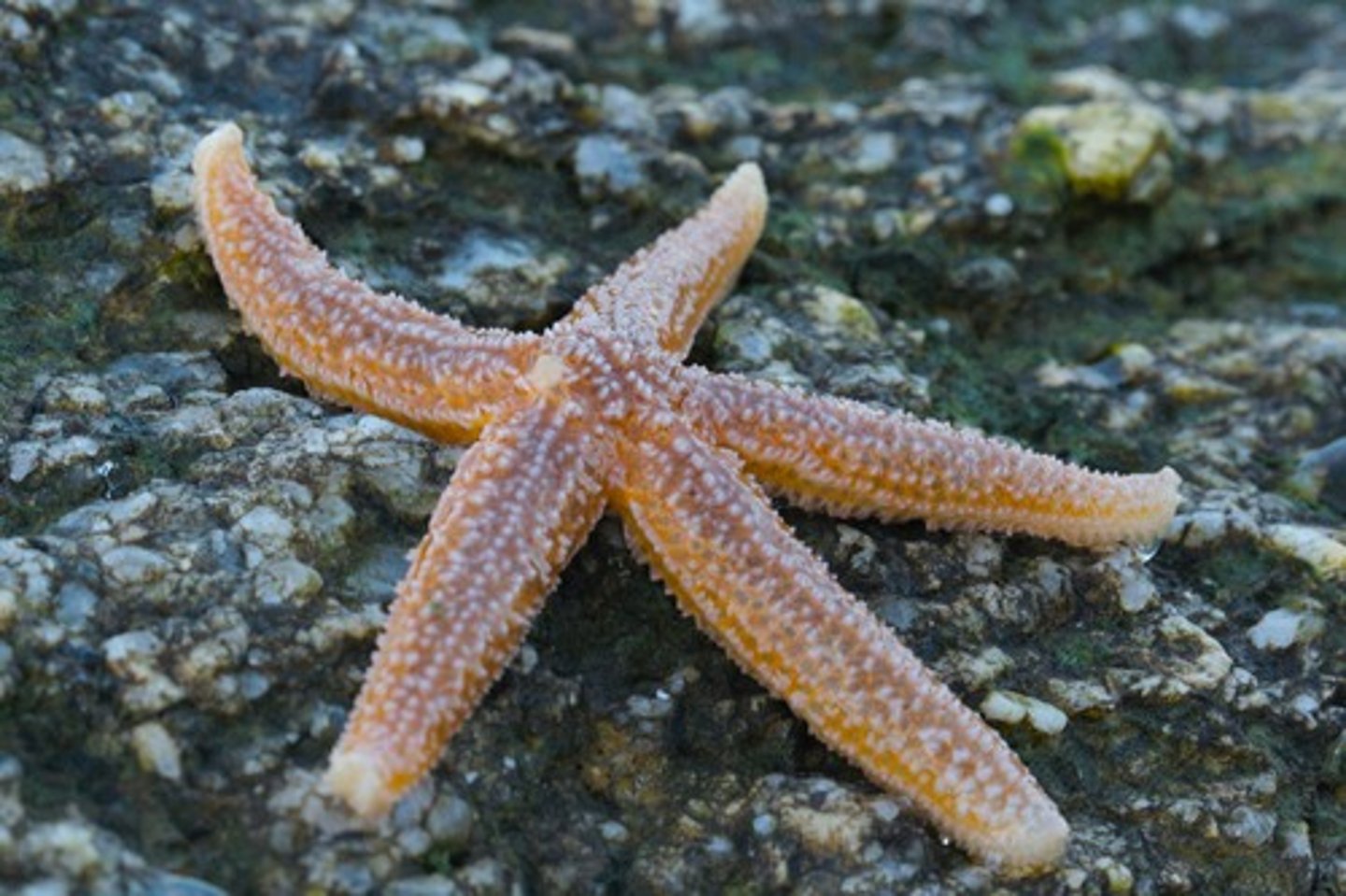

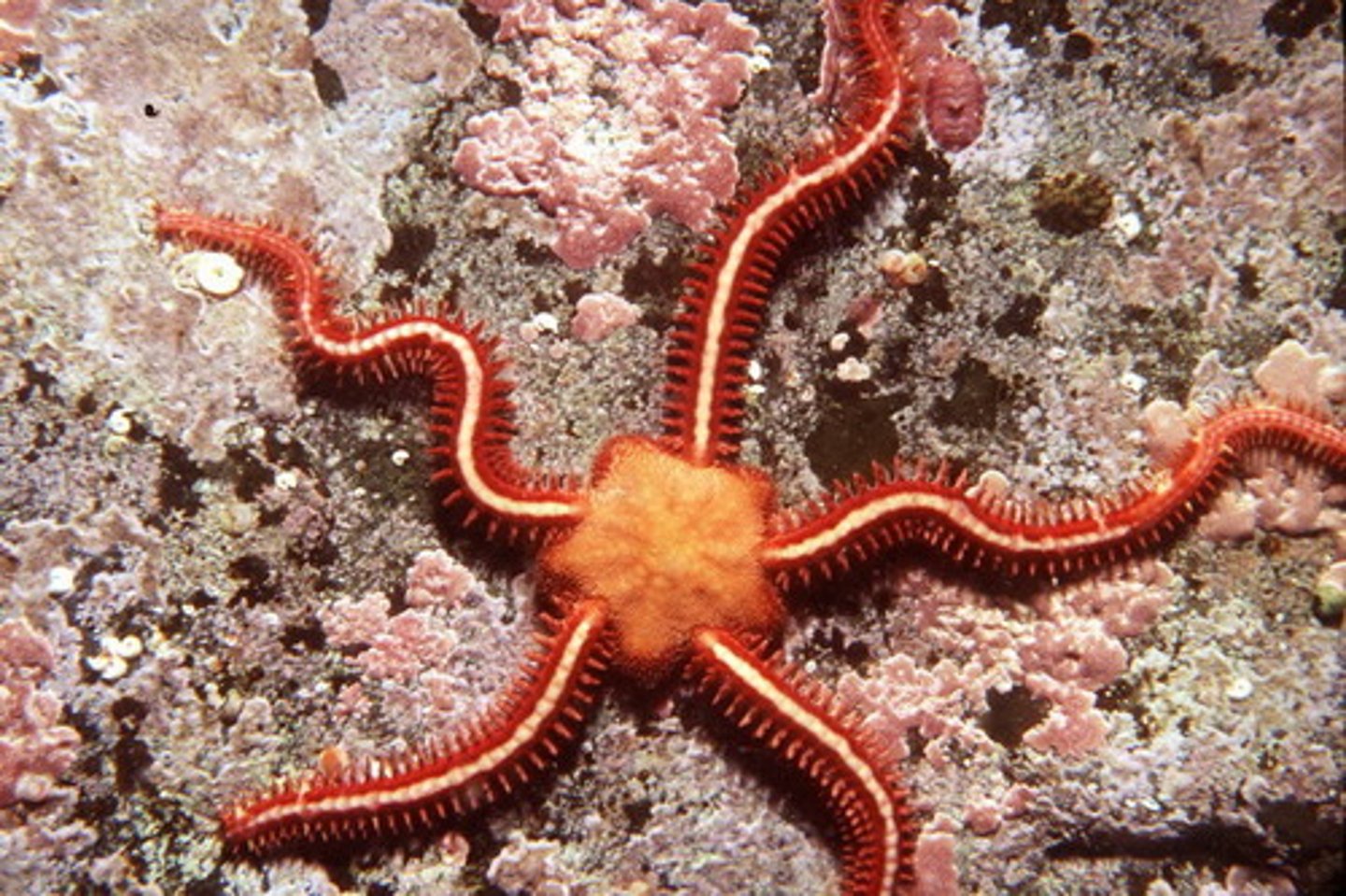
Class Ophioroidea
brittle stars
move via serpentine motion of arms
groove closed below arms
tube feet to capture small prey & sensory

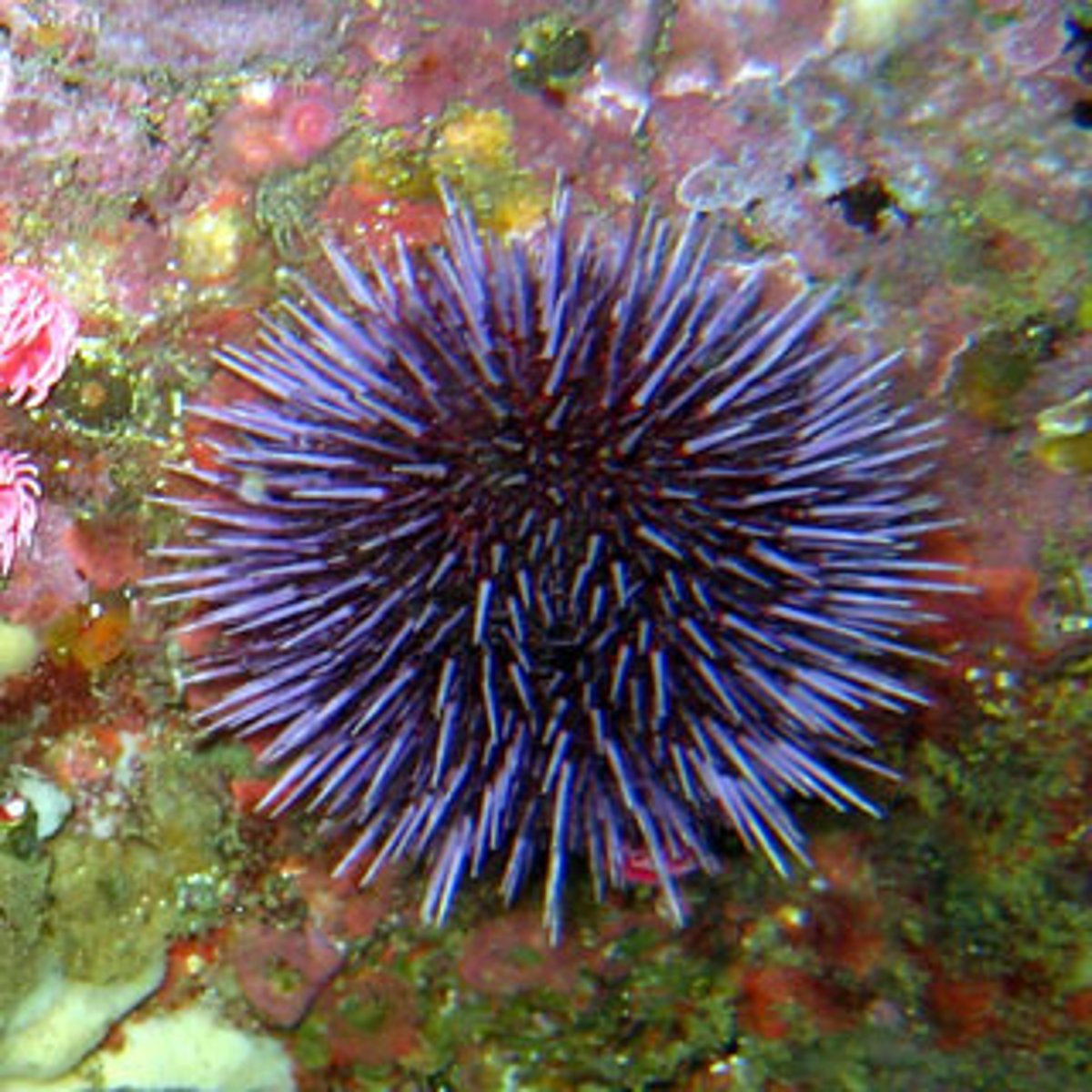
Class Echinoidea
sea urchins and sand dollars; no arms; usually move via spines operated by tube feet; vegetarians

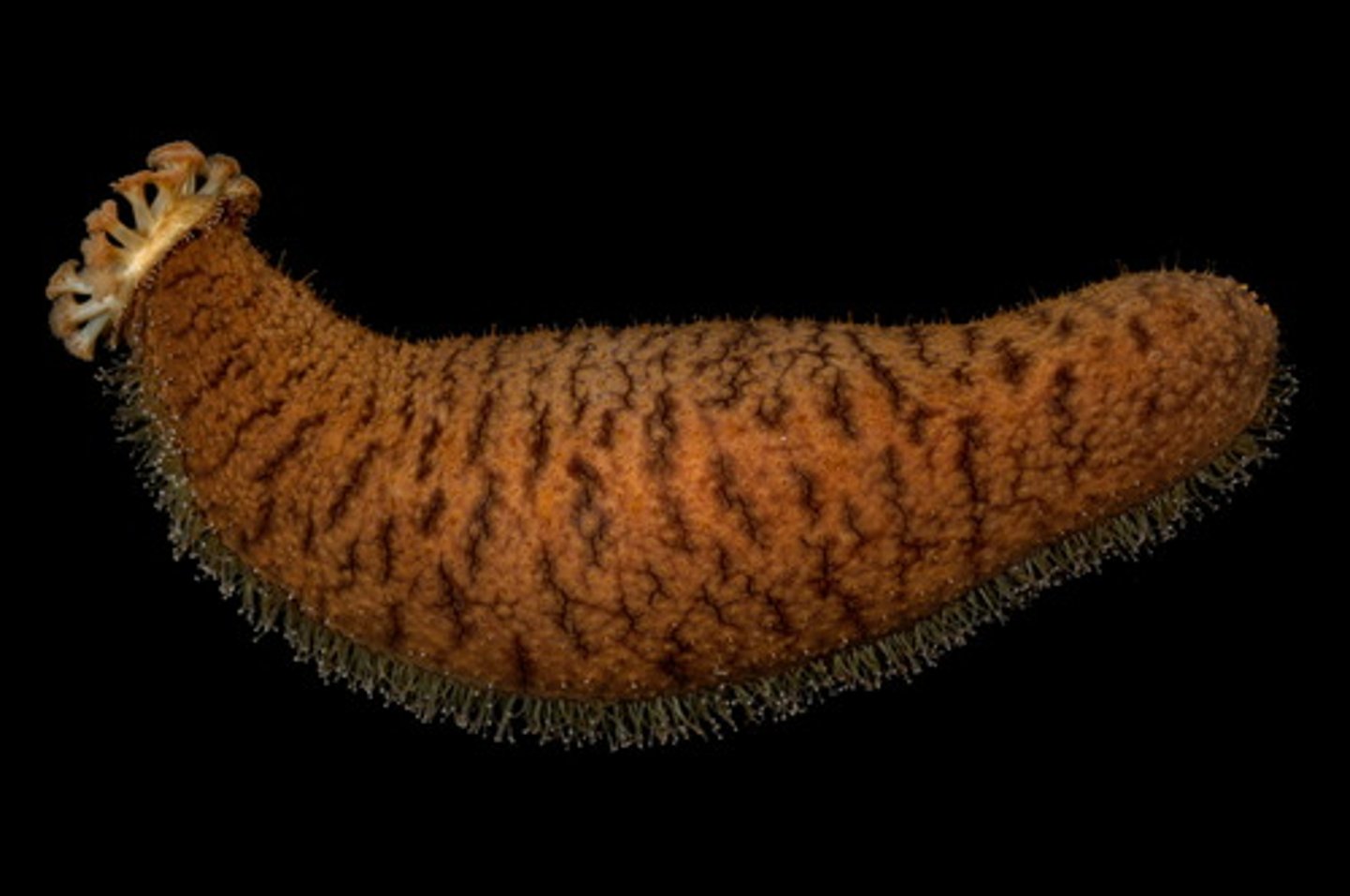
Class Holothuroidea
sea cucumbers
elongate
leathery skin
mouth surrounded by tube feet
tube feet move animal
extrude foul smelling stomach when frightened

water vascular system
A network of hydraulic canals unique to echinoderms that branches into extensions called tube feet, which function in locomotion, feeding, and gas exchange