COMM 218Z Midterm
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
Why do we communicate?
Physical Needs (health)
Relational Needs
Identity Needs (how we learn who we are)
Practical Needs (allows us to complete tasks and successfully go through life)
Relational Rationale (Belongingness Hypothesis)
We need to maintain at least a minimum number of significant close relationships.
Relationships are needed for human wellbeing and development.
How are relationships beneficial?
Socially connected people live longer.
Isolated individuals are more susceptible to human cold.
Join easily, leave difficulty.
Definition of Interpersonal Communication
Communication that occurs between two people within the context of their relationship, helps us understand closeness, dominance, and intimacy.
What are the three modes of communication?
The Nature of Communication
Action model
Interaction model
Transactional model
What is the action model?
The action model treats communication as a one-way process (Ex: lecture)
A source formulates an idea
The source encodes the idea in a form of message
Message is sent through a channel
Receiver decodes the message
Interpretation is affected by noise (physical or psychological)
What is the interaction model?
The interaction model treats communication as a two-way process.
Includes all the elements of the action model, and also suggests that receivers provide feedback through verbal and nonverbal behavior
What is the transactional model?
Have a specific environment that changes the way two people talk to each other
Noise affects the way you are able to send and receive messages
Main difference is that in this model both people are constantly responding and decoding at the same time
Always communicating some meaning to each other
What are the characteristics of communication?
Communication is transactional (it is something we do WITH others not TO others
It’s irreversible
Sends messages, whether intentional or unintentional
Governed by rules
Explicit (grammatical, swear words)
Implicit (teacher isn’t supposed to yell at students)
What are communication myths?
Everyone is an expert at communication
Communication will solve any problem
More communication is always better
Communication is inherently good
What is communication competence?
Competent communicators are effective and appropriate
Effectiveness describes how well your communication achieves its goals
Appropriateness describes how well your communication complies with the rules and expectations of the social situation
How do you build communication competence?
Self-monitoring: Process of paying close attention to one’s behavior
Empathy/Perspective Taking: Process of paying close attention to the emotions and/or behaviors of others
Adaptability: Choose the right communication for the specific situation
Cognitive Complexity: Construct several different frameworks for viewing and issue
Ethics: Competence must be paired with morals
Involvement; Level of caring about the topic and person
What is mediated interpersonal communication?
Personal content
Personalized receivers
Mutual obligation
Expectation of privacy (not face to face, texting, conversation over text should be kept private)
Ex: telephone conversations, email
What is mass personal communication?
Personal content
Larger audience
Less mutual obligation
Low expectation of privacy (Instagram post, Facebook status update)
What is competence in mediated communication?
Consider the channel
Richness vs Leanness (fewer nonverbal communication)
Be aware of hyper personal communication
Synchronous vs Asynchronous communication
What is the difference between individualistic and collectivistic cultures?
Individualistic cultures believe their responsibility is to themselves.
Collectivistic cultures believe their responsibility is to their communities.
What is the difference between low-context and high-context cultures?
Low-context cultures are more direct, and you should say what you mean.
High-context cultures involve more subtle behaviors and contextual cues rather than verbal directness.
Achievement vs nurturing cultures
Achievement cultures place high value on material success and the task at hand
Nurturing cultures regard the support of relationship as primary goal
Difference in polychronic and monochronic cultures
Monochronic cultures view time as a finite commodity
Polychronic cultures view time as more holisitc, fluid, and less structured
Difference in uncertainty-avoiding and uncertainty-accepting cultures?
Avoiding cultures are drawn to the familiar and are relatively unlikely to take risks
Accepting cultures are open to novel situations and are accepting of people and ideas that are different from their own
What is intercultural communication?
Process when members of two or more cultures or co-cultures exchange messages in a manner that is influenced by their different cultural perceptions and symbol systems
What is intercultural communication competence?
Motivation and attitude: Do you care about the intercultural significance and/or salience in a given interpersonal encounter? Do you care about those differences? Are you motivated to learn about them?
Tolerance for ambiguity: Can you deal with some ambiguity in terms of the types of verbal/nonverbal norms for this encounter?
Open-mindedness: Can you encounter cultural differences without an ethnocentric mindset?
Knowledge and skill: Can you gain knowledge regarding verbal/nonverbal norms from other cultures and co-cultures? Ex: learning a new language
What is the self-concept?
The relatively stable set of perceptions you hold on yourself. Based largely on beliefs, attitudes, and values. Self-esteem is the positive or negative evaluation of that set of perceptions.
Development of self-concept
Biology
Family
Group memberships
Gender/culture
What is reflected appraisal?
Mirror of judgements you have received from the world around you
What is social comparison?
Comparing yourself to those around you (Ex: height, status, athleticism)
What are the characteristics of the self-concept?
Your self-concept is multi-faceted
You highlight different parts of yourself in different contexts
Your self-concept is mostly subjective
Think you’re a good singer when you’re not
Your self-concept resists change
Your self-concept strongly influences your behaviors
Idea of a self-fulfilling prophecy
See yourself as a better student, so you perform better in a classroom
What is image management?
I make sure you think about me in a certain way and you do the same
Collaborative
Multiple identities (chameleon)
Face: desired public image + face and - face
Facework: how we communicate that image to others
Communicating self (disclosure)
Act of intentionally giving others information about ourselves that believe to be true that we think they don’t already have
Intention and truthful
Varies in breadth and depth: social penetration theory
likely to disclose more in closer relationships or ones we are wanting to develop
disclosure is a gradual process and reciprocal
What are the benefits of self-disclosure?
Enhancing relationships and trust
Reciprocity (gives us information about the other person)
Catharsis (get a secret off your chest)
Self-clarification (clarify self-concept)
What are the risks of self-disclosure?
Rejection
Decrease relational satisfaction
Hurt to others
Loss of control
Alternative to self-disclosure: Deception
Speaker transmits information knowingly and intentionally for the purpose of creating a false belief in the receiver
What are the types of deception?
Falsification: communicating false information as thought it were true
Exaggeration: Overestimating something that is true in principle (I caught a 10 lb fish when it reality it was only 1 lb)
Omission: leaving out parts of a story to create a false impression (I built a playground for my kids, not telling people that my dad did most of the work)
Equivocation: making ambiguous statements to give 5e false impression that one has said something when one hasn’t
What is perception?
The process of making meaning from the people in our environment and our relationship with them
First order realities: physically observable qualities of thing/situation
Second order realities: attaching meaning to those first order realities
What is the perception process?
Selection: attention to stimulus (someone comes up to talk and you select them and you start organizing your perception
Organization: categorizing that information (categorize that person, determine their role like coworker or stranger)
Interpretation: assigning meaning to that information
Negotiation: influencing each other’s perception
What are influences in perception?
Physiological influences
health/fatigue
Hunger
Biological cycles
Psychological influences
mood
Self-concept
Social influences
occupation
Relationship
What are the fundamental forces in perception?
Stereotyping: identifying a group, recall a generalization about the group, apply generalization to that person
Primary effect
first paper changes gabe way the student is perceived for the rest of their papers
Recency effect
drastically change our perception (cheating)
Perceptual set
general predisposition to believe what we want to believe
Egocentrism
I want to protect my own identity/self image
Change perception (tribe)
Positivity bias
honeymoon stage, rose colored glasses
Negativity bias
only look at negative
Focus on bad characteristics
Halo effect
trust attractive people more
Horn effect
if one thing is wrong about the person, the entire person is terrible
Ex: wrong stance on pro life vs pro choice
Explaining what we perceive
Attribution: explanations we give for our own and other peoples behavior
Attributions vary according to their:
Locus
is it internal fault or external
Stability
generally flunk tests or first time
Controllability
did the person have a great deal of control over it
How we can fail in our attributions
Self-serving bias
our successes are earned and deserved (stable, controllable, internal)
Our failures are not our fault (unstable, uncontrollable, external)
Fundamental attribution error
other peoples behavior are due to internal, stable causes
Over attribution
identify one prominent characteristic of a person (sexual orientation, religious belief) attribute most of what that person says and does to that one characteristic
Nature of language
Definition: a structured system of symbols used for communication meaning
Symbolic: we use symbols that have no meaning in and of themselves to communicate meaning
Bound by context and culture
sapir-whorf hypothesis
Language is rule governed
phonological: how sounds are combined to form words
Syntatic: the way symbols are arranged (spelling)
Semantic: the meaning of statements
Pragmatic: what meaning is appropriate in a given context
Triangle of meaning
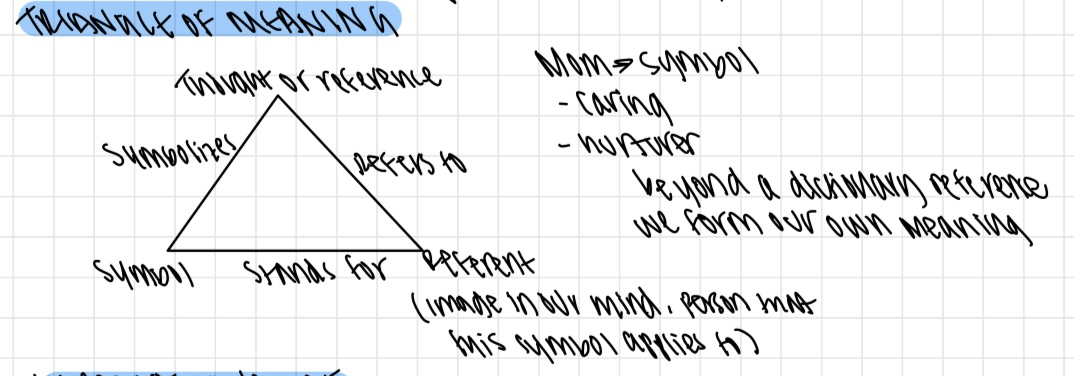
What is the impact of naming?
Names help shape the way we think about ourselves and how we perceive others
Ex: professor, husband or wife
What is the impact of affiliation?
Communication adaption —> convergence (sound like the person)
Highlight differences between two people —> divergence (talking to kids)
The image of credibility
Examples of dialects and swearing
The impact of PRECISION
Ambiguous language: words and phrases that have more than one correct definition (bass)
Abstraction: more specific to more abstract language
Euphemisms: innocuous terms substituted for blunt ones
Relative language: gains meaning by comparison (wealthy)
Static evaluation: pushes someone into a box (millennials are lazy)
The impact of responsibility
It language vs I language changes responsibility
But statements
I, you, and we language
I: during confrontations
You: praising or including others
We: group settings to enhance unity
Gender and communication
Expressive (F) vs instrumental talk (M)
More-powerful (M) vs less-powerful speech (F)
Either talking and interrupting more vs asking more questions and using hedges (sort of, might be)
Masculine vs feminine linguistic style
Either shorter sentences and more sentence fragments vs longer sentences with references to we and they (unity)
Gender differences
Touch
among adults, other-sex touch is more common than same-sex touch
In same-sex pairs, women touch each other more than men do
Emotional communication
women express more positive emotions, men express more negative emotions
Affection communication
among adults, women use more affection behaviors than men do
This is potential due to:
the amount of affection received in childhood
The perception that affection is feminine
Differences in hormonéis that promote affection behavior (women gave a more oxytocin)
Nonverbal communication
Definition: Include those behaviors and characteristics that convey meaning WITHOUT the use of words
Often conveys more meaning than verbal
Usually believed over verbal
Nonverbal communication characteristics
All nonverbal behavior can be communication
true wether conscious or unconscious
True wether intentional or unintentional
Primarily relational
demonstrates the relationship we have with other person
Ambiguous
higher abstraction (nonverbal cues have different meanings in different cultures)
Not a singular meaning for every action
Still present in mediated communication
for example avatars, emojis, font size, formatting
Influenced by culture and gender
emblems: culturally understood substitutes for verbal expressions
Usage of nonverbal cues (facial displays)
Functions of nonverbal communication
Creating and maintaining relationships
Regulate interactions
regulators: cues that help control verbal interactions (hand out - stop)
Influencing others (professional attire)
Primary method of emotional communication
Concealing/deceiving
Nonverbal leakage cues: speech errors, blinking, gaze, pupil dilation
Strategic deception behaviors: immediacy/nonimmediacy (leaning in/being far) channel selection (email instead of face to face)
Predictors of detection success: look for leakiest channels, familiarize yourself with the baseline
Are we good at this? No basically a coin flip
truth bias - believe people are telling the truth
To maintain relationships we need this element of shared trust
Impression management
manner: way we act (walk, posture, facial expression)
Appearance: way we dress, display of artifacts
Setting: physical items we surround ourselves with (posters, wall decor)
NONVERBAL CHANNELS
Kinesics, haptics, vocalics, proxemics, territoriality, chronemics, physical appearances, olfatics
What is kinesics?
Body movement!
facial displays (important for emotion, attractiveness)
Oculesis (eye behaviors like eye contact, pupil dilations)
Posture (confidence)
Gestures (illustrators, affect displays)
What is haptics?
TOUCH
affecitonate
Power/agression
Ritualistic
What is vocalics?
Aspects of voice that convey meaning
Pitch, inflection, volume, rate, filler words, accent, silence
What is proxemics?
Usage of space, such as how close we stand to each other
Intimate, personal, social, public
What is territoriality?
How you arrange yourself in comparison to those around you (classes, lunch tables)
What is chronemics?
Usage of time to communicate messages (value and power)
Physical appearance
Halo effect
Trust
Dark side of preference for beauty (ED)
What is olfatics?
Study of smell, including memory and sexual attraction
why do we communicate?
using messages to create meaning