Cell Diagram Matching
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
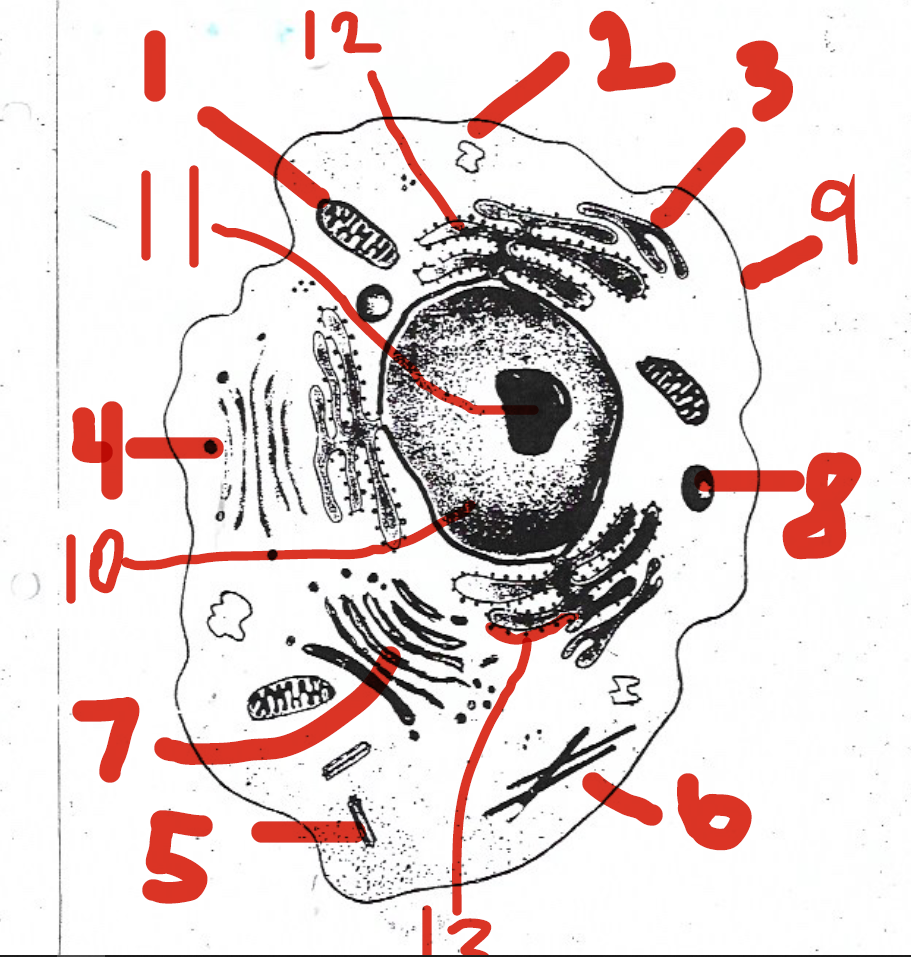
convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use
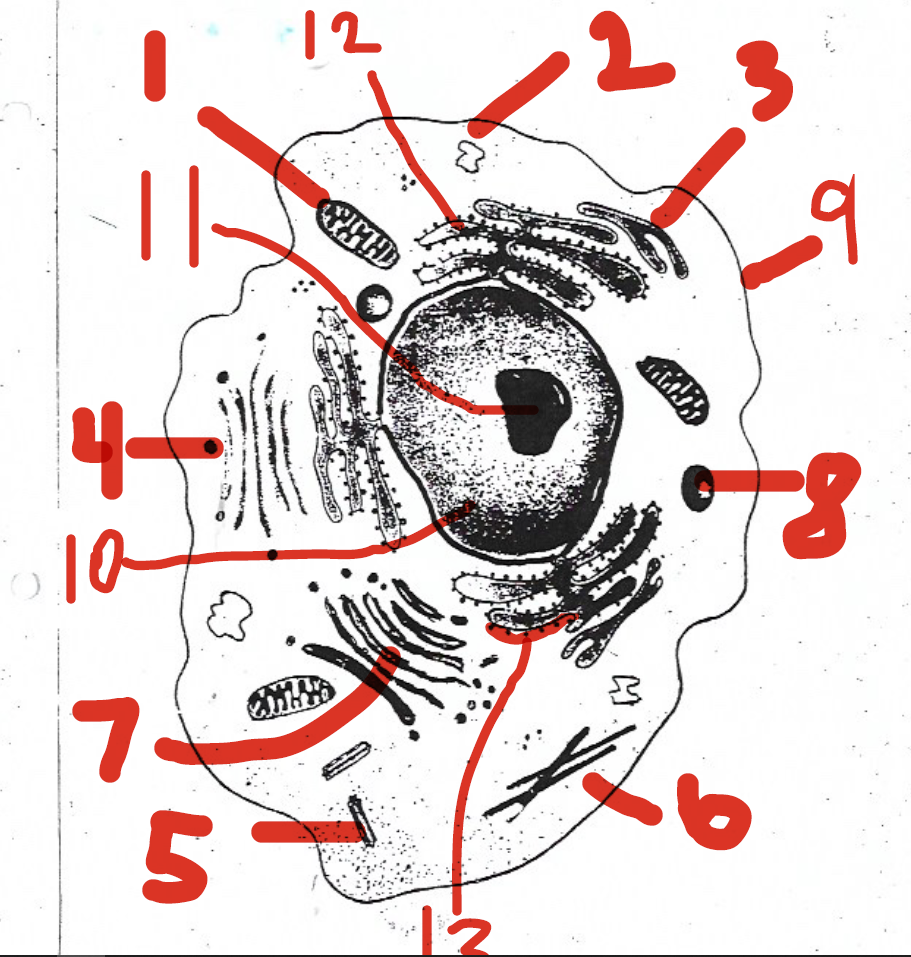
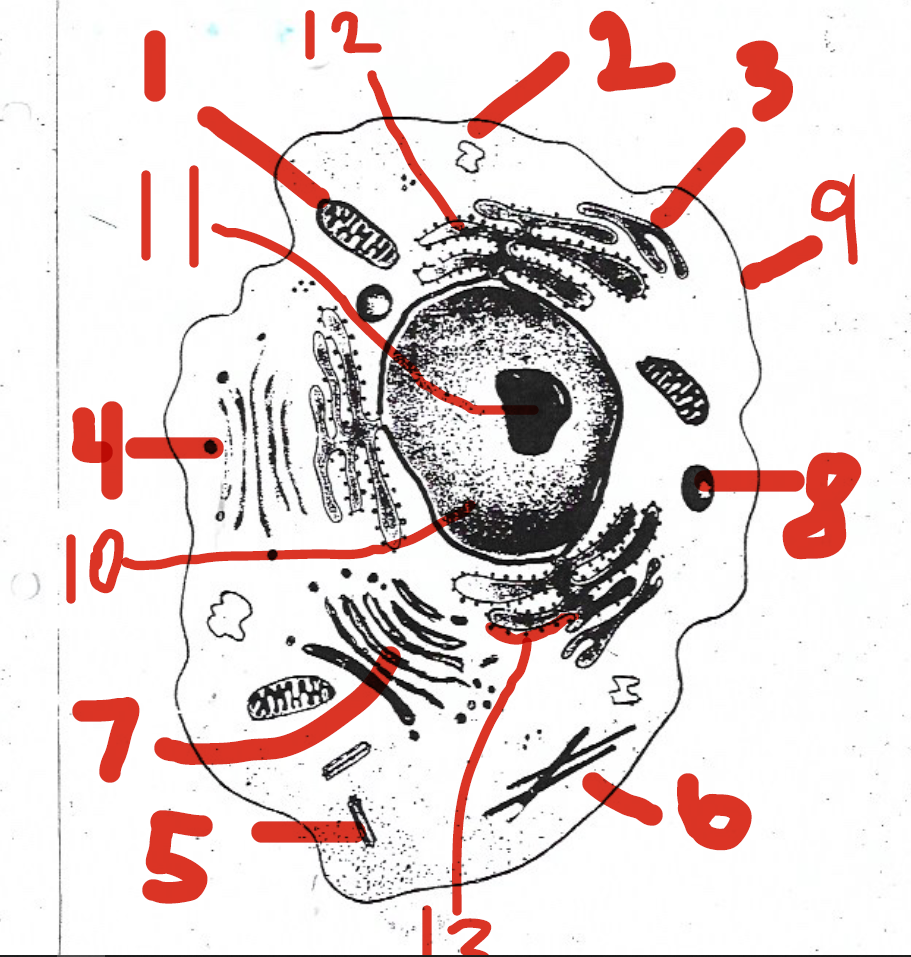
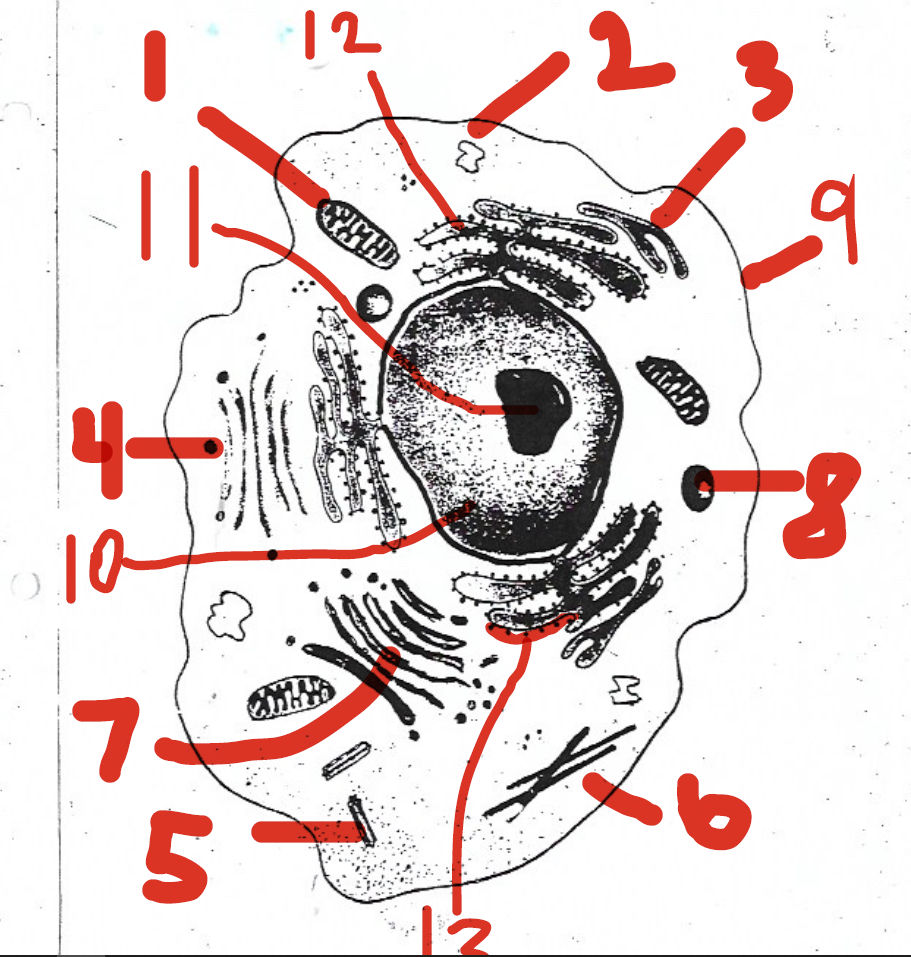
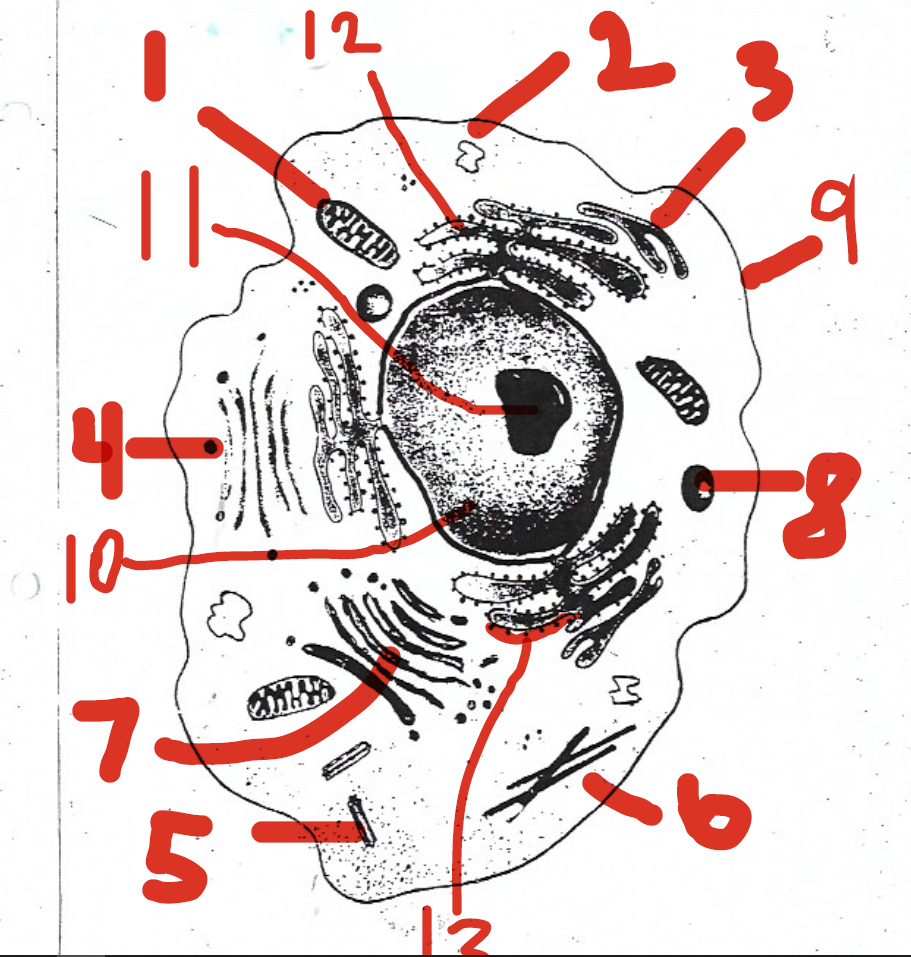
1 (mitochondria)
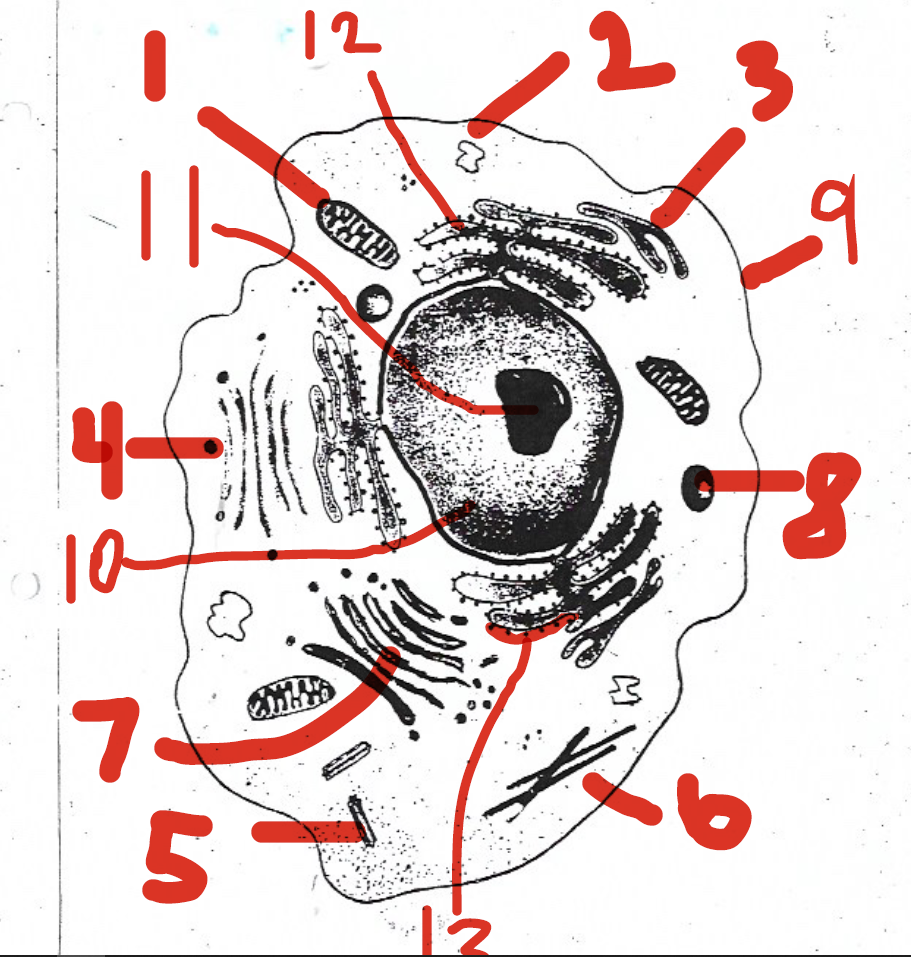
chemically modifies proteins
12 (rough endoplasmic reticulum)
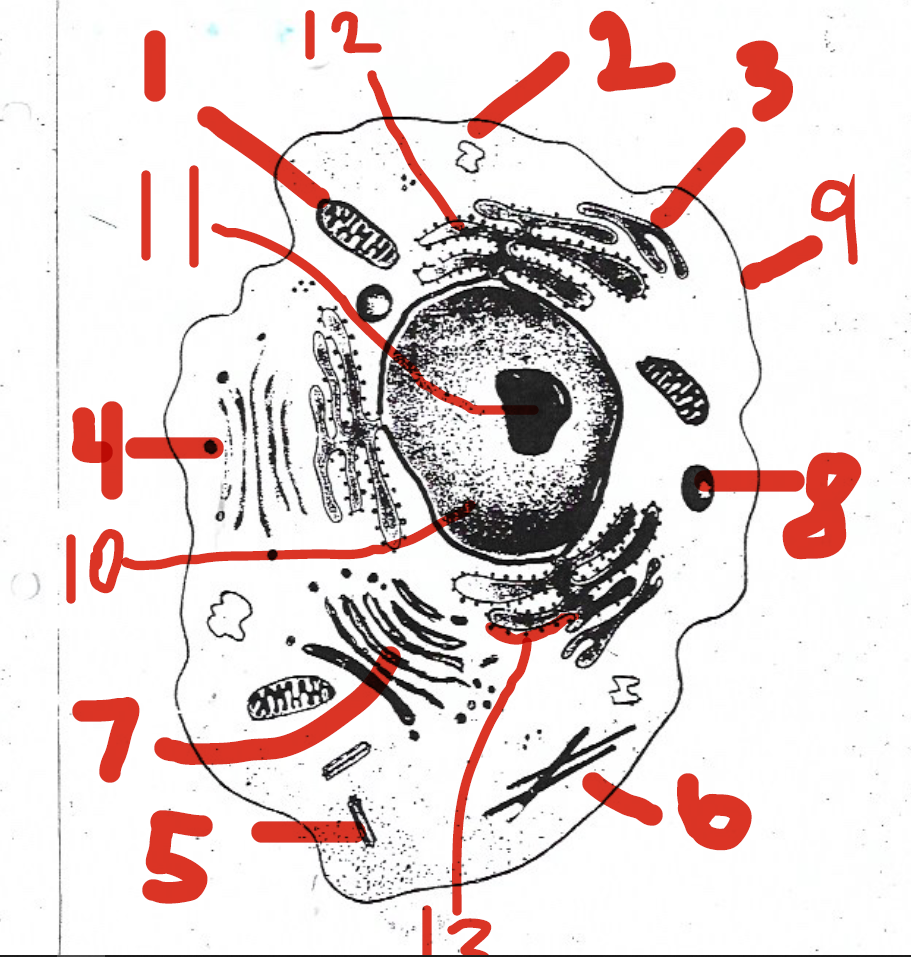
found only in animal cells
5 (centrioles)
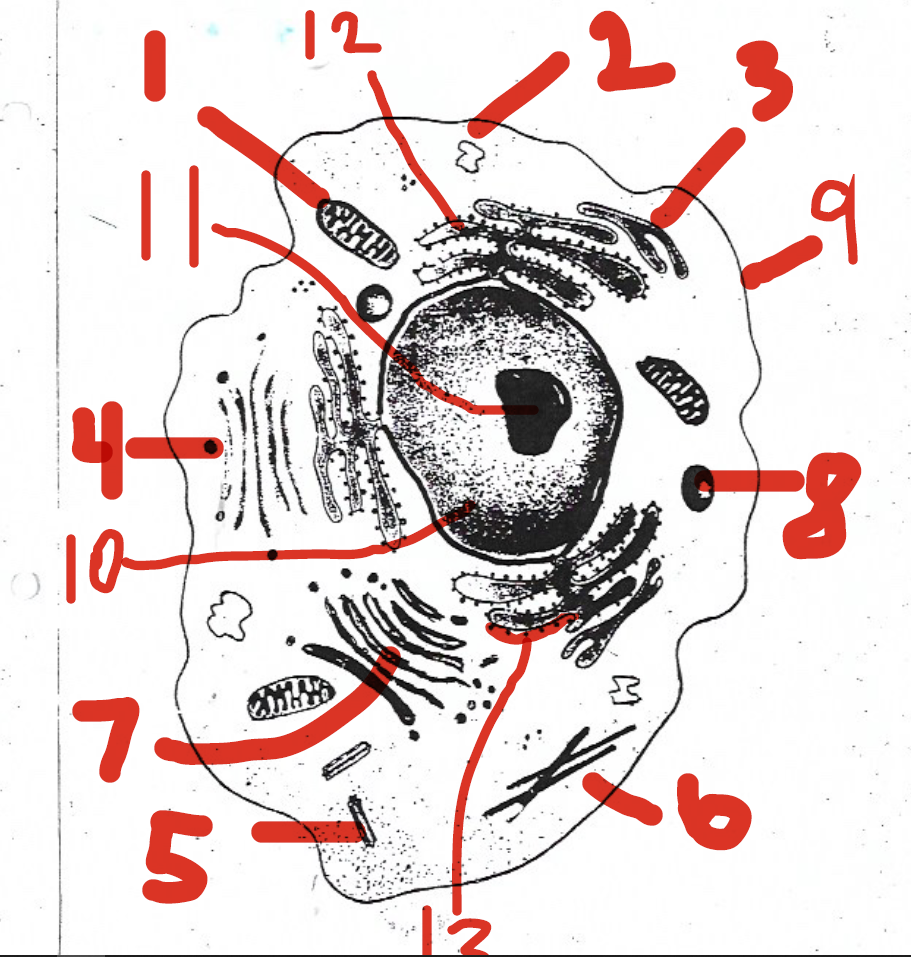
involved in ribosome synthesis
11 (nucleolus)
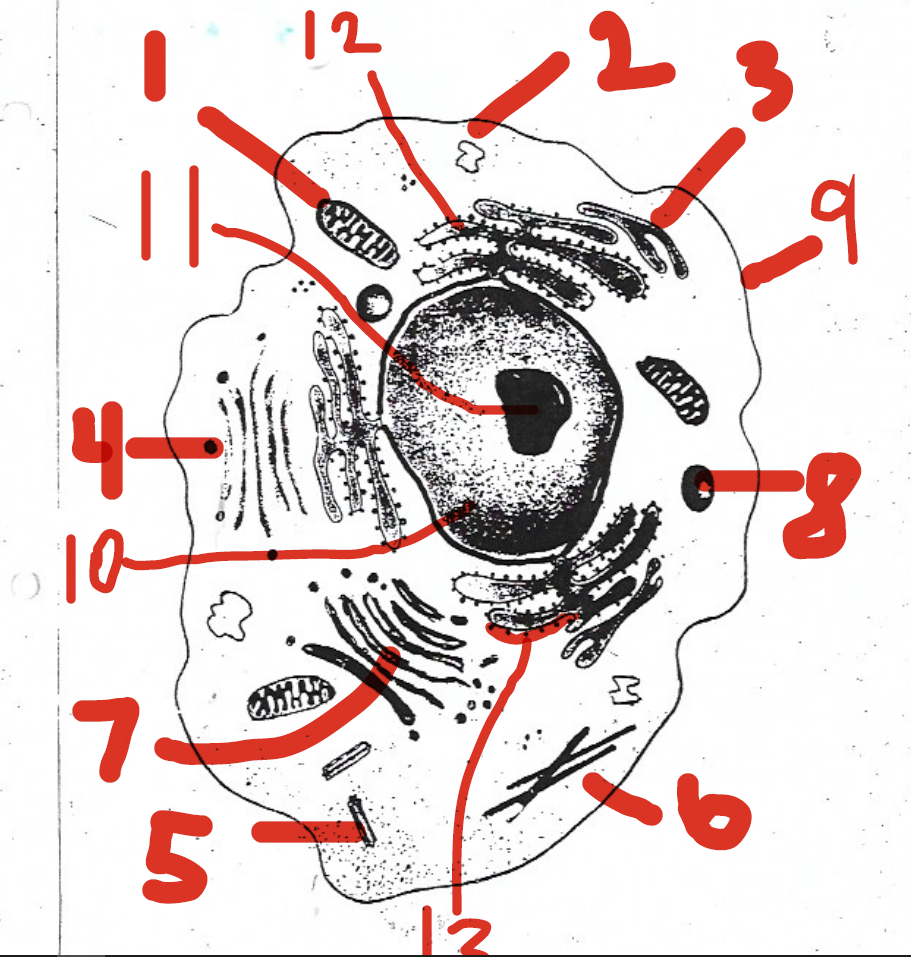
moves materials to and from the cell membrane
4 (vesicles)
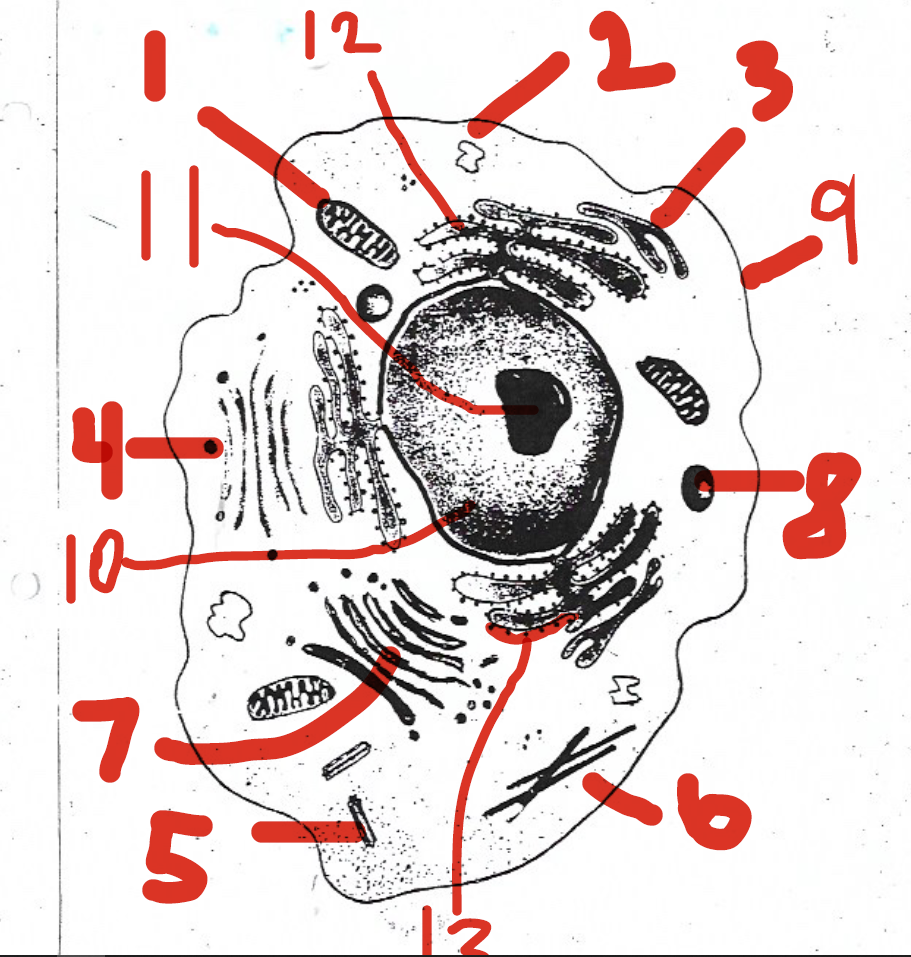
modifies, sorts, and packages proteins, etc. for storage and release
7 (Golgi apparatus)
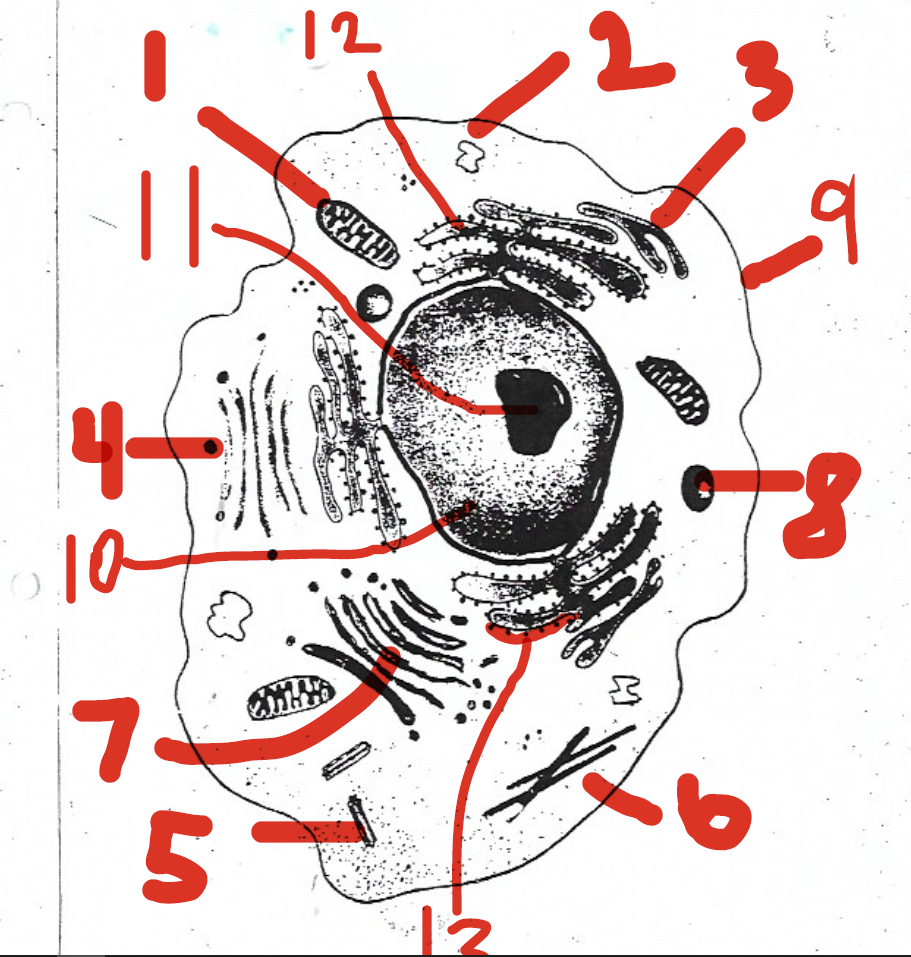
consists of a double layer called the lipid bilayer
9 (cell membrane)
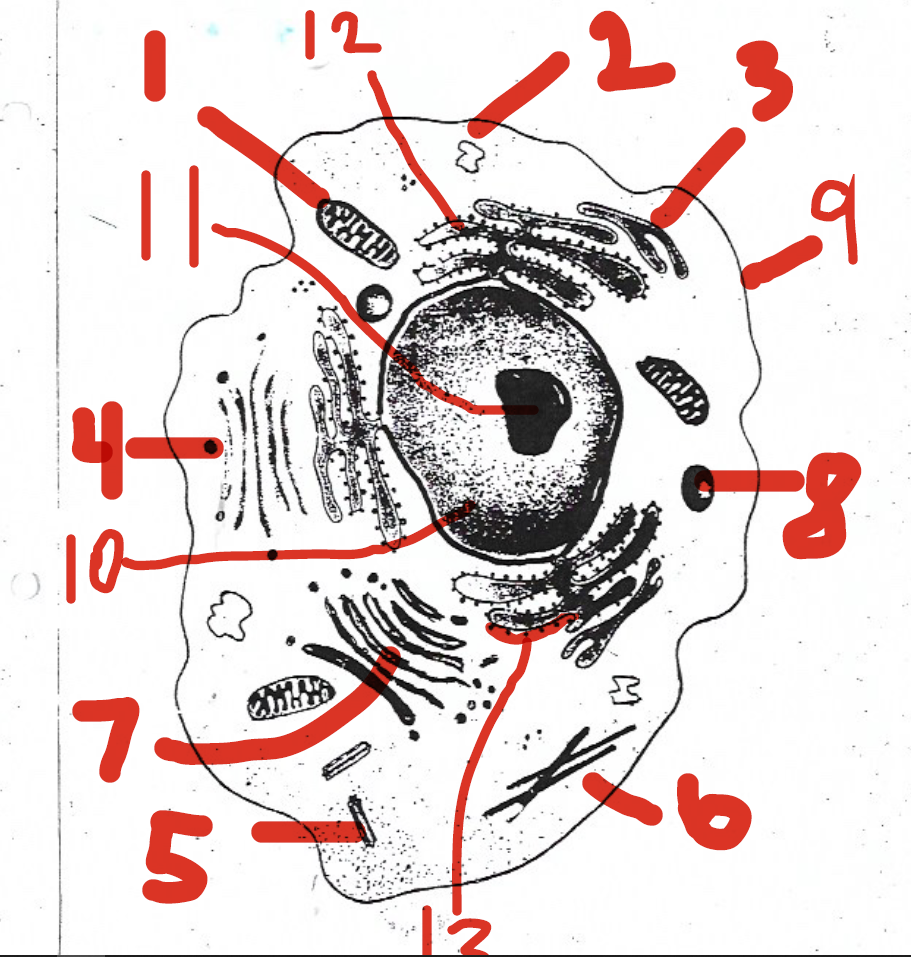
the site of protein assembly
13 (ribosomes)
maintains the shape and internal organization of the cell
6 (cytoskeleton)
breaks down organelles that have outlived their usefulness
8 (lysosomes)
store water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
2 (vacuoles)
control's the cell's activities
10 (nucleus)
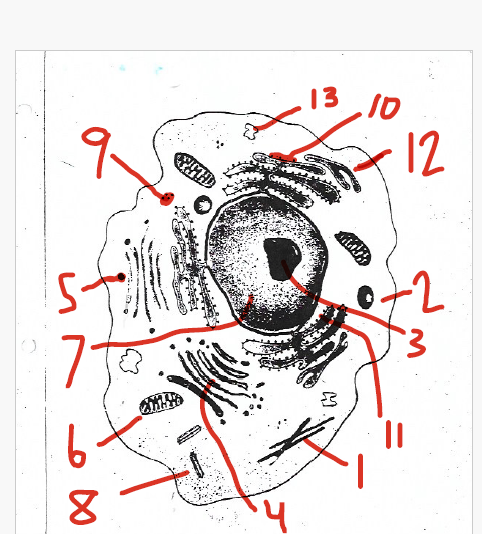
protects and supports the cell
14 (cell membrane)
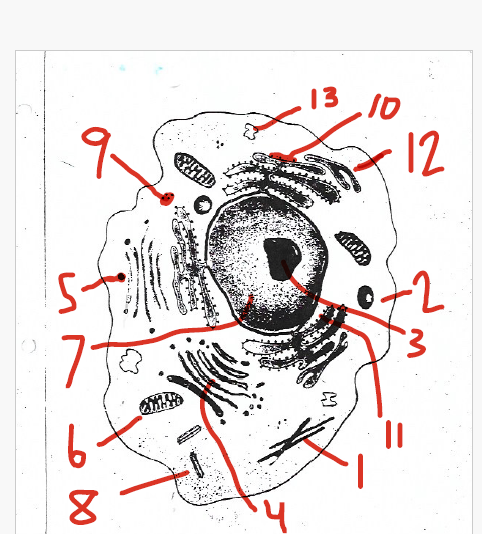
store water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
13 (vacuoles)
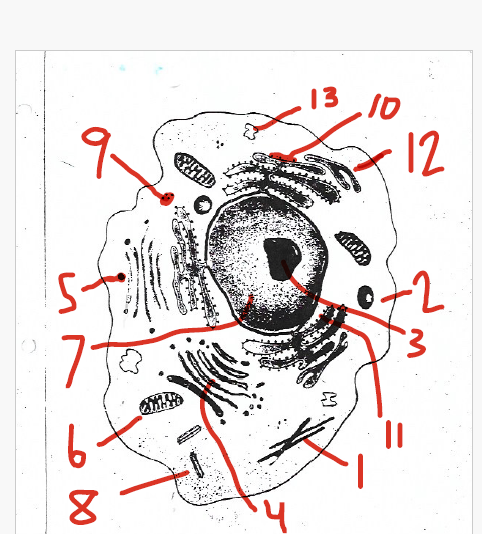
store and move materials between cell organelles
5 (vesicles)
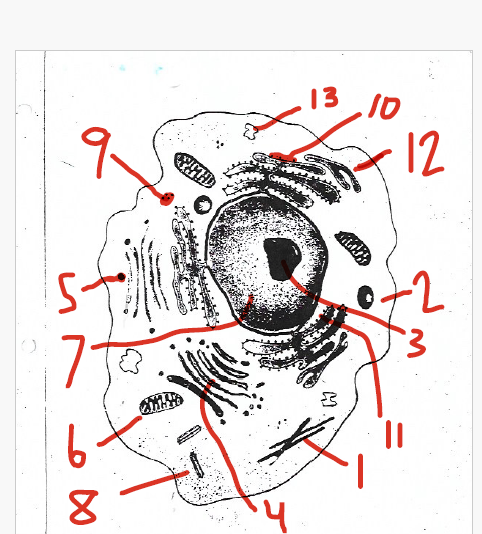
small and filled with enzymes
2 (lysosomes)
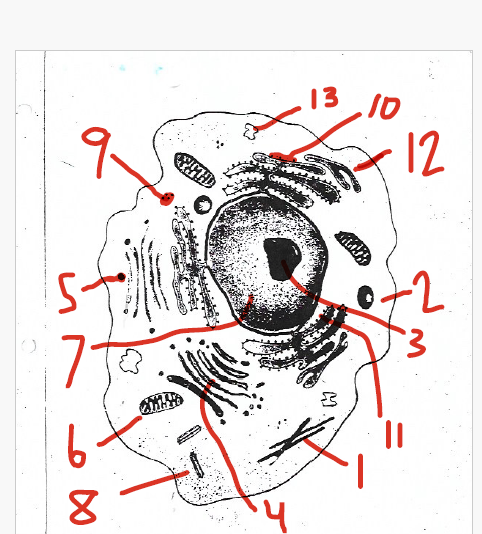
helps to transport materials between parts of the cell
1 (cytoskeleton)
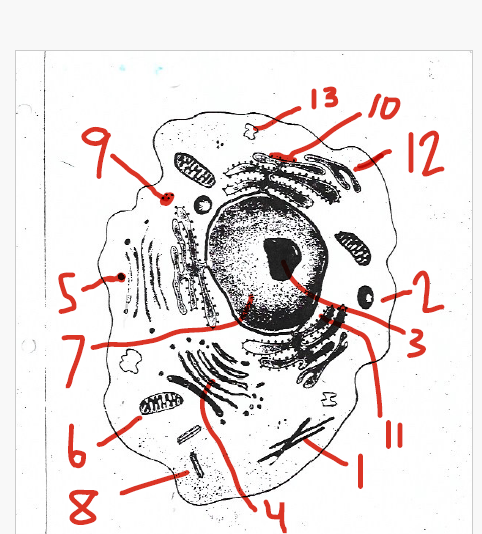
help organize cell division
8 (centrioles)
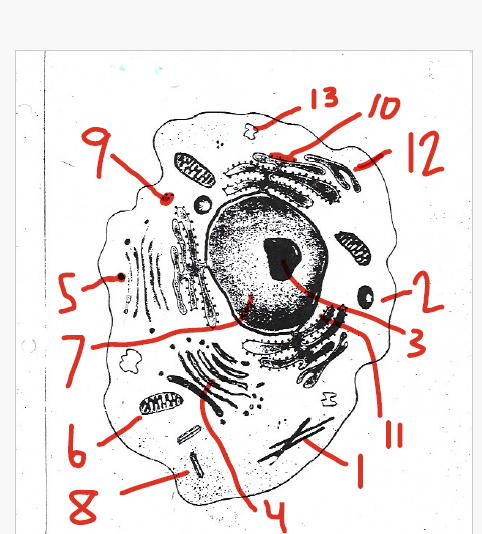
small particles of RNA and protein
9 / 10 (ribosomes)
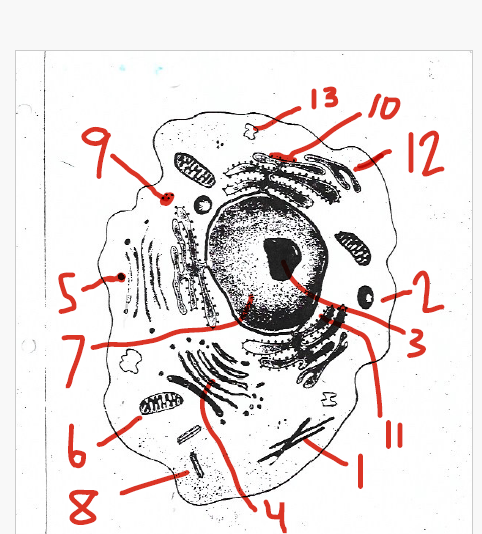
is abundant in cells that produce proteins for export
11 (rough endoplasmic reticulum)
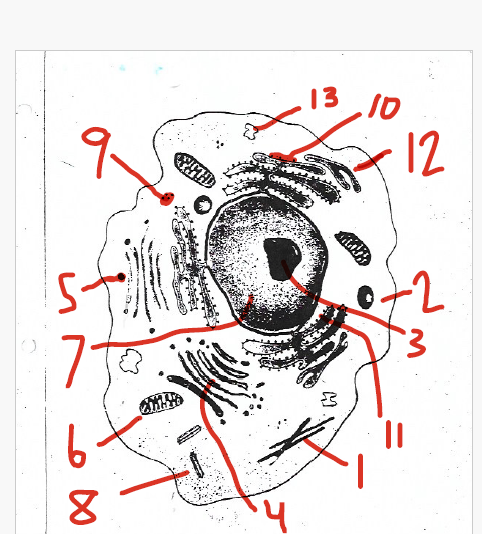
contains collections of enzymes that perform specialized tasks including membrane synthesis and detoxification of drugs
12 (smooth endoplasmic reticulum)
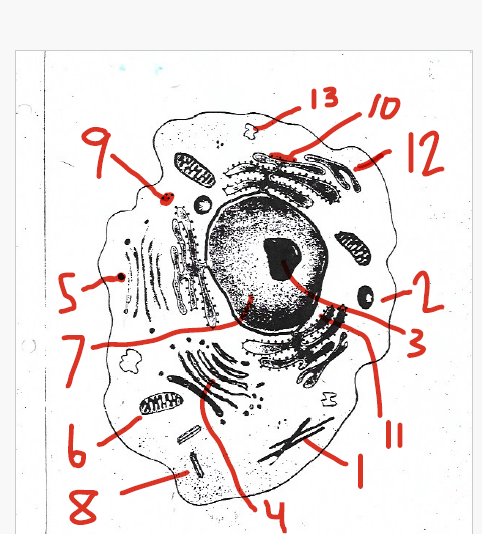
modifies, sorts, and packages proteins, etc. for storage and release
4 (Golgi apparatus)
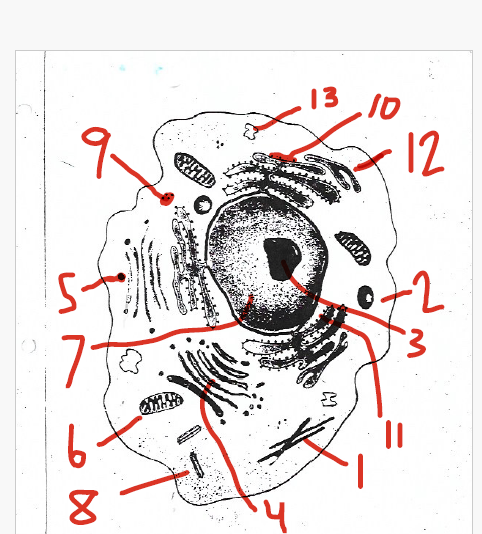
convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use
6 (mitochondria)
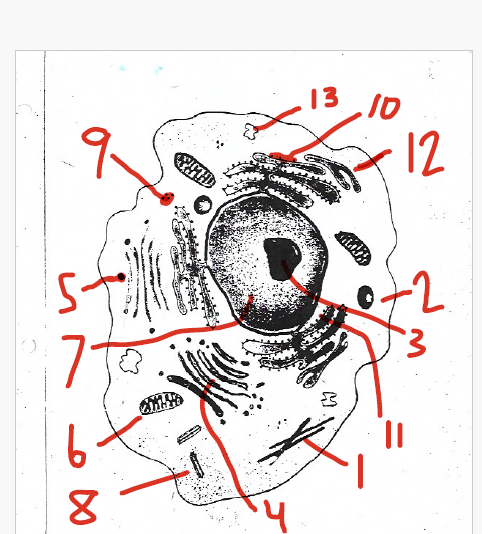
an area of chromatin
3 (nucleolus)
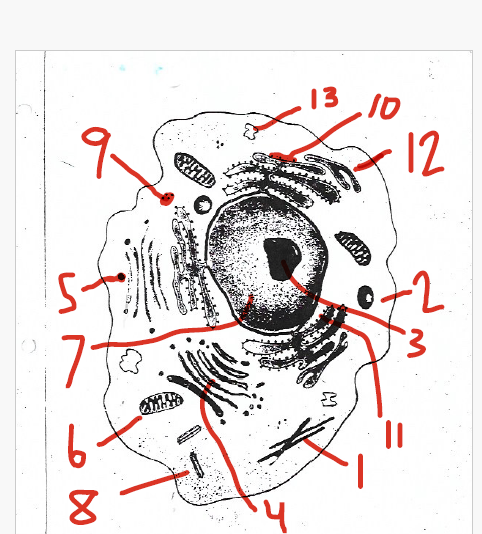
contains nearly all of the cell’s DNA
7 (nucleus)
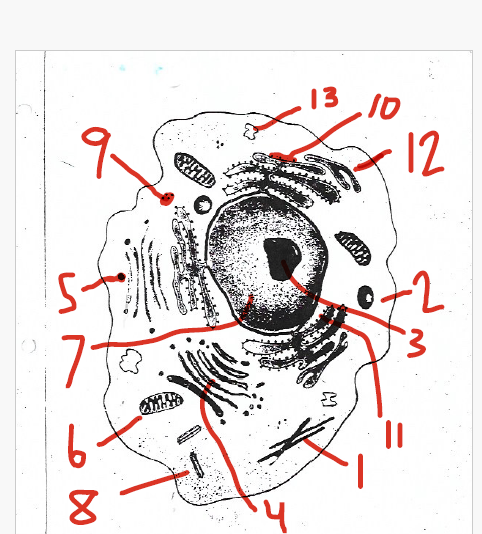
the site of protein assembly
9 / 10 (ribosomes)