AP Biology Unit 6
1/78
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
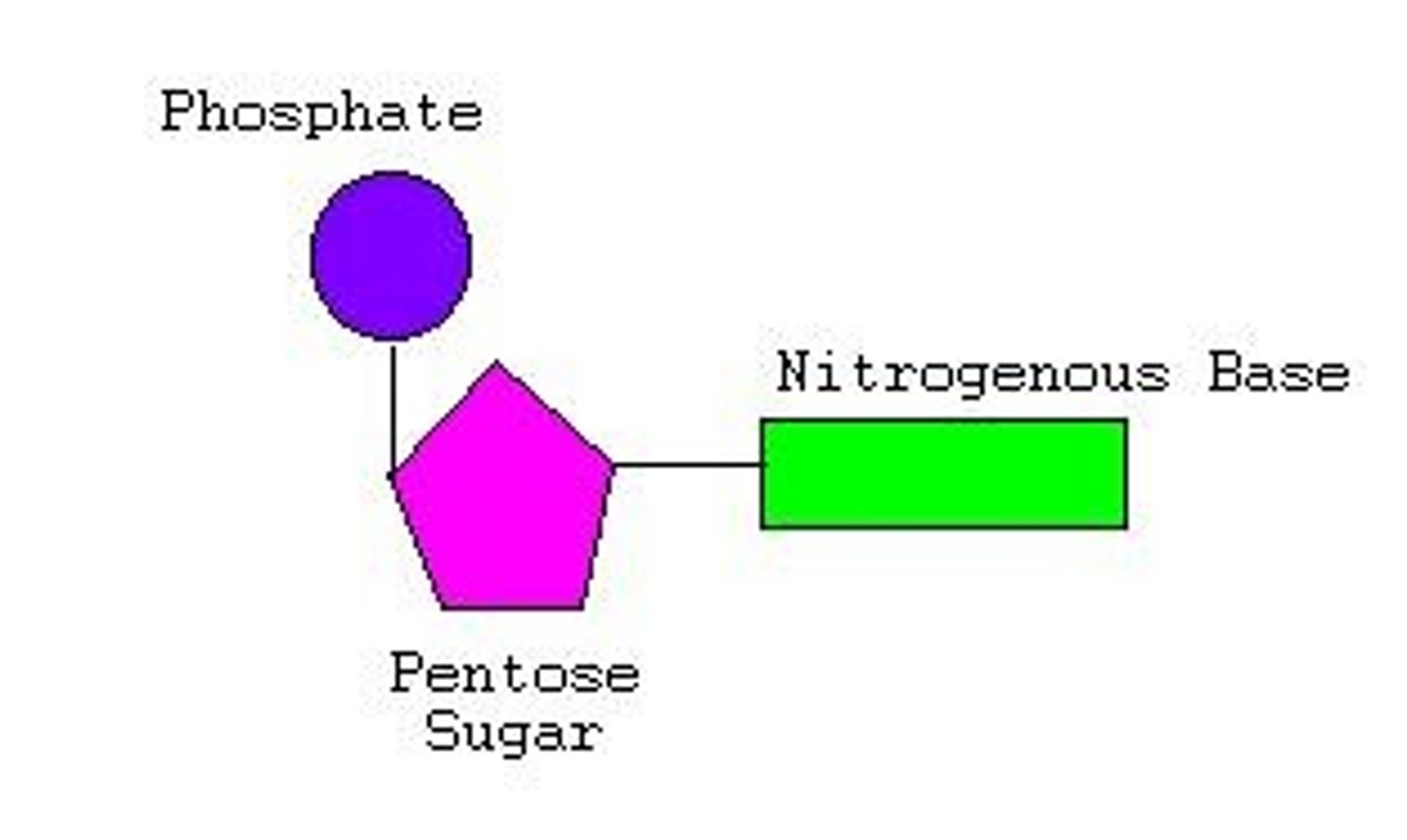
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
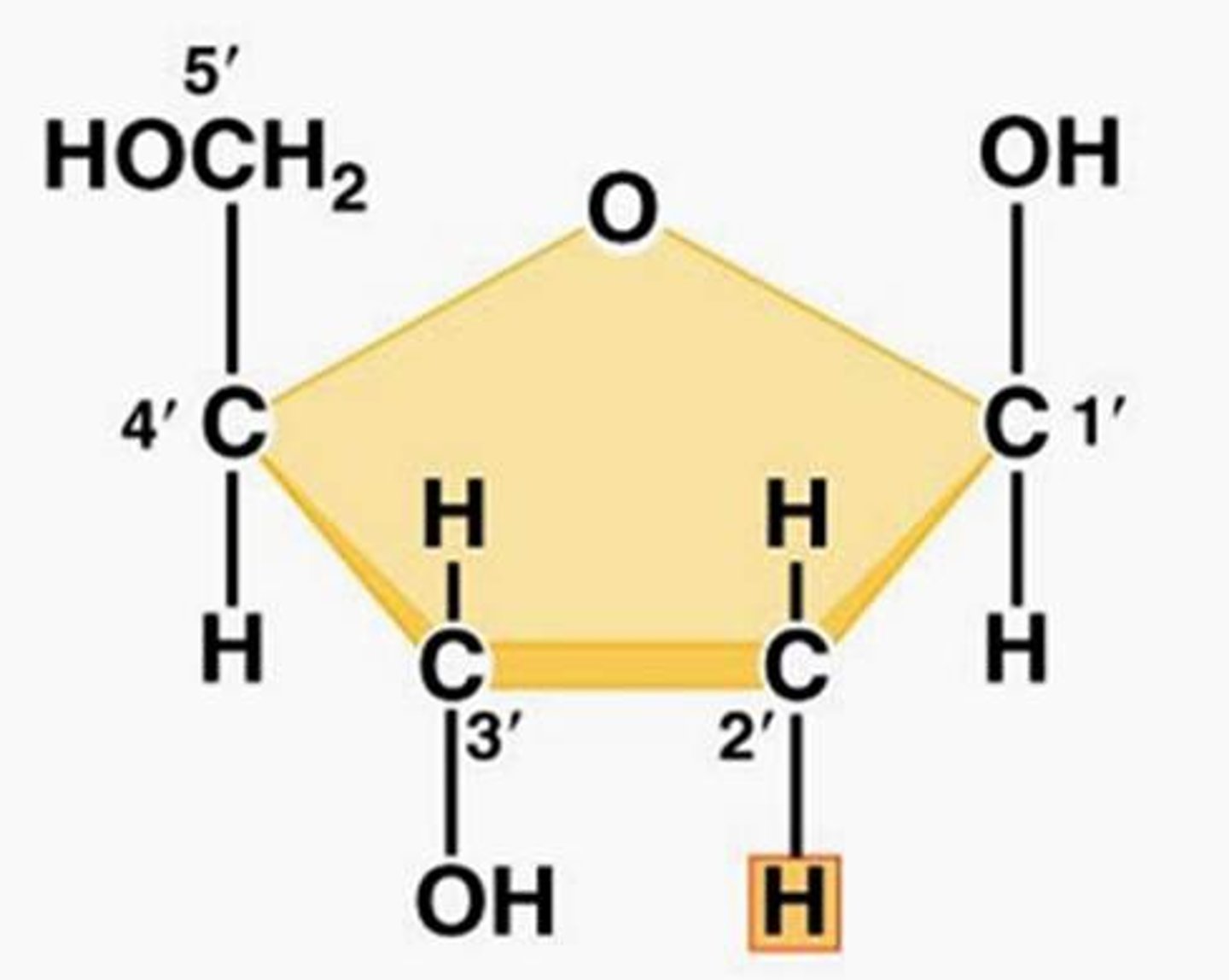
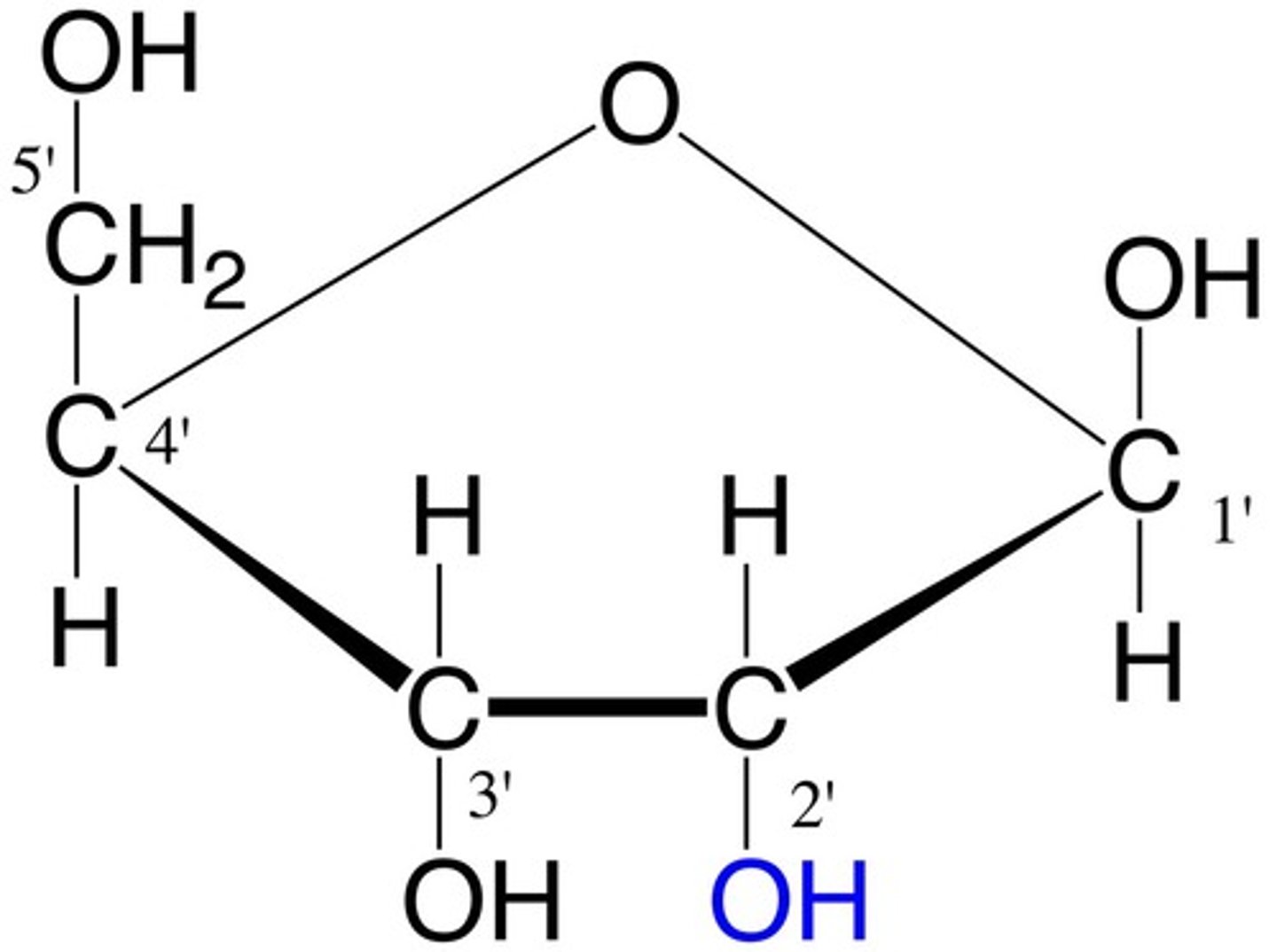
Deoxyribose
sugar found in DNA
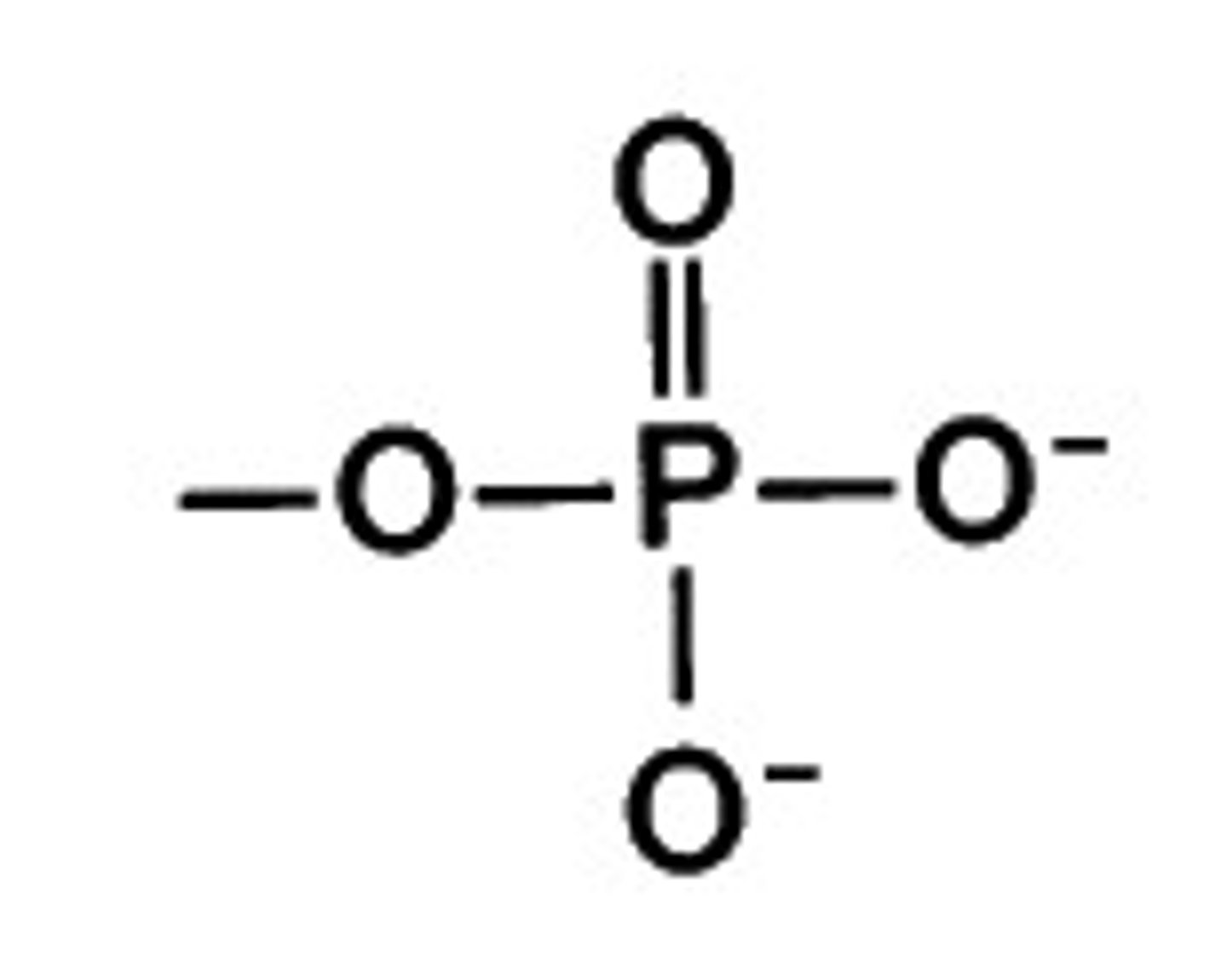
Phosphate
PO4 3-
Bases of DNA
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
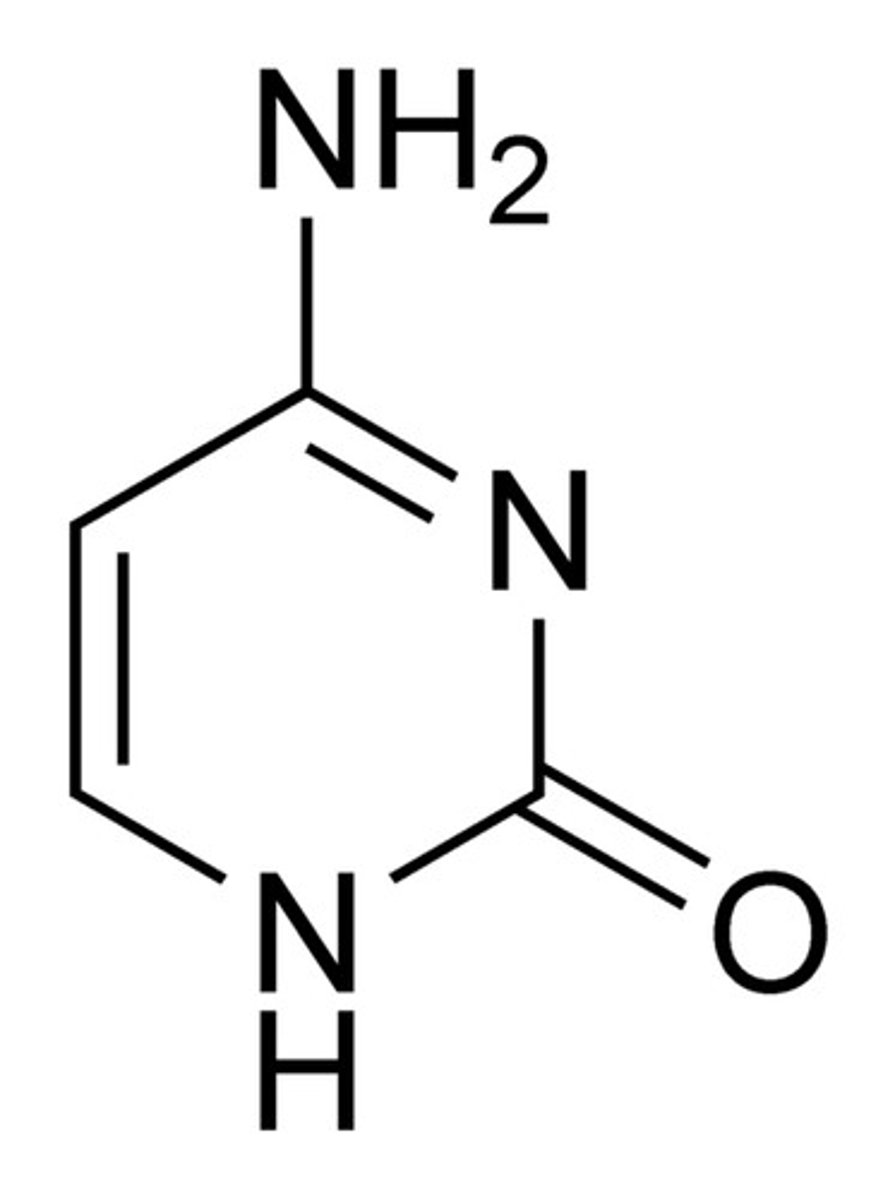
Adenine
The base that pairs with Thymine in DNA
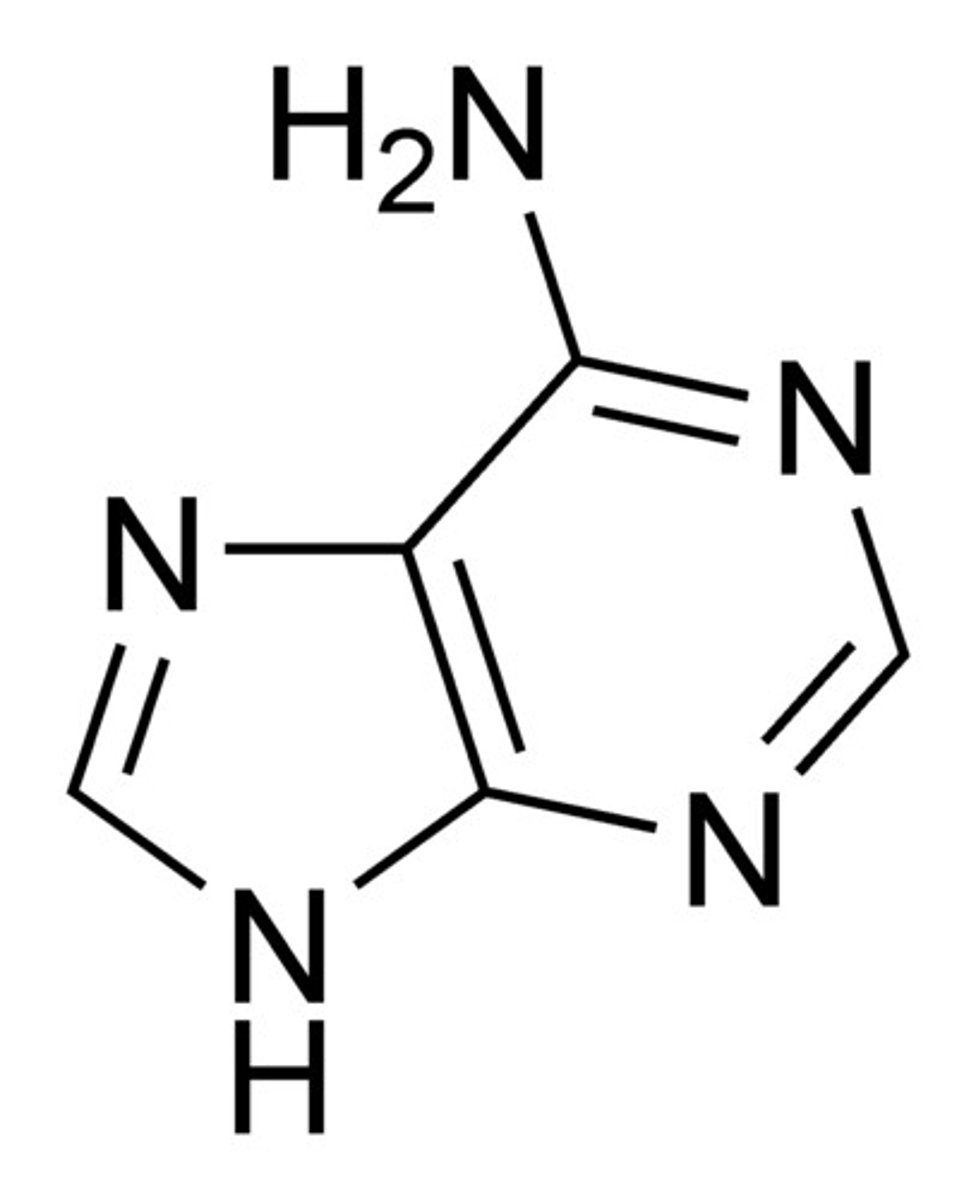
Thymine
The base that pairs with Adenine in DNA
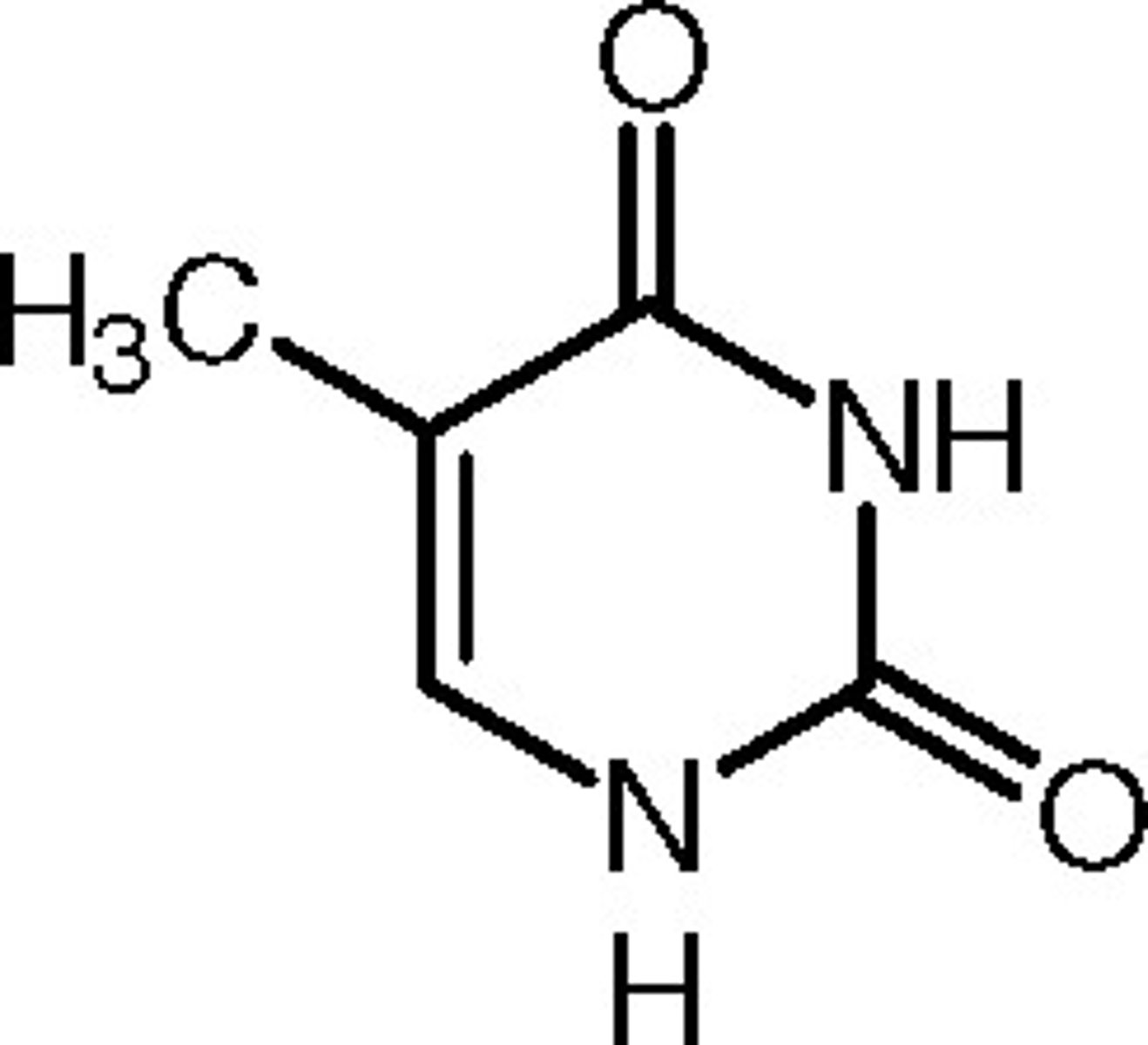
Guanine
The base that pairs with Cytosine in DNA
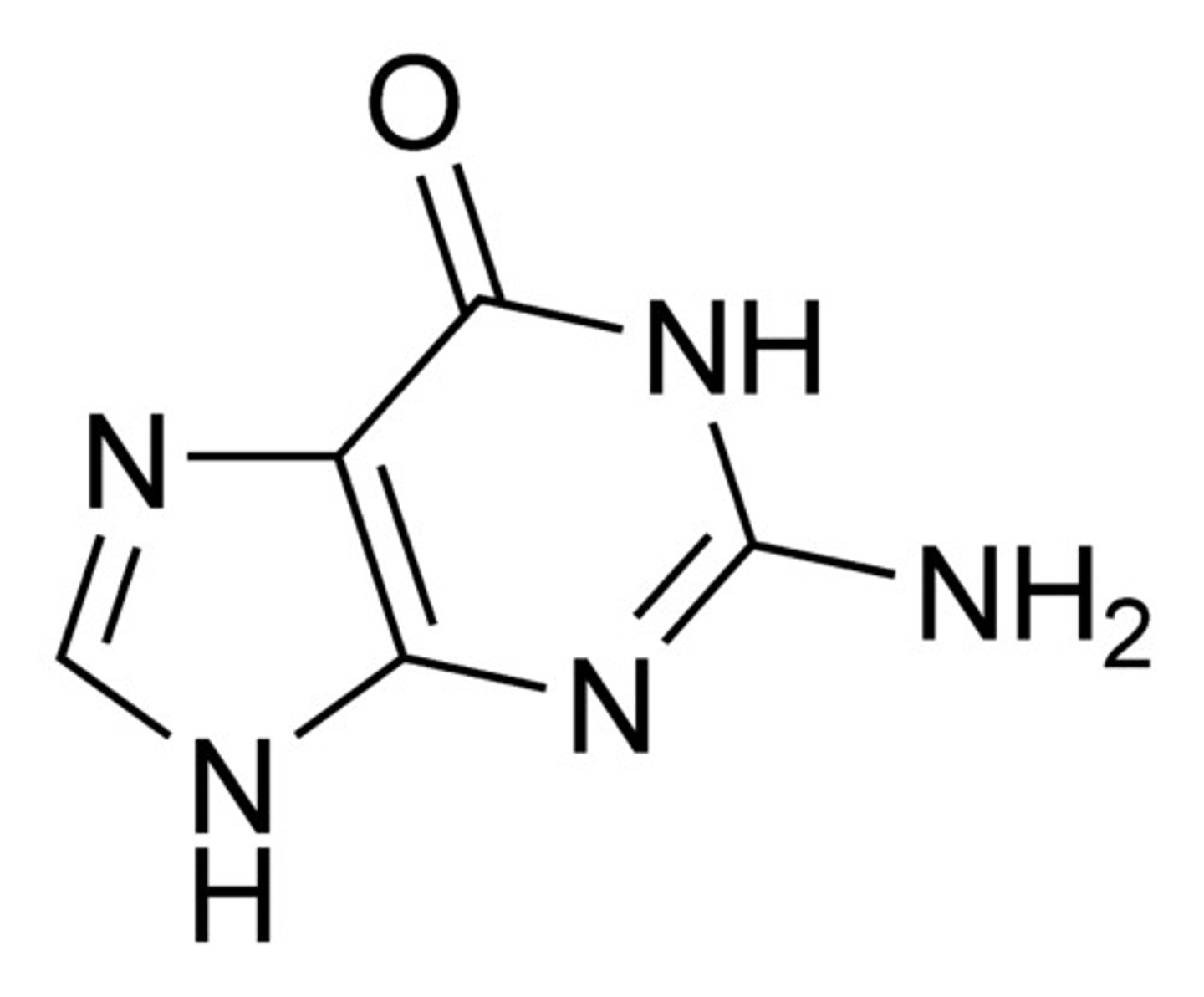
Cytosine
The base that pairs with Guanine with DNA
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
5' end
the end of a DNA strand that the phosphate is attached to
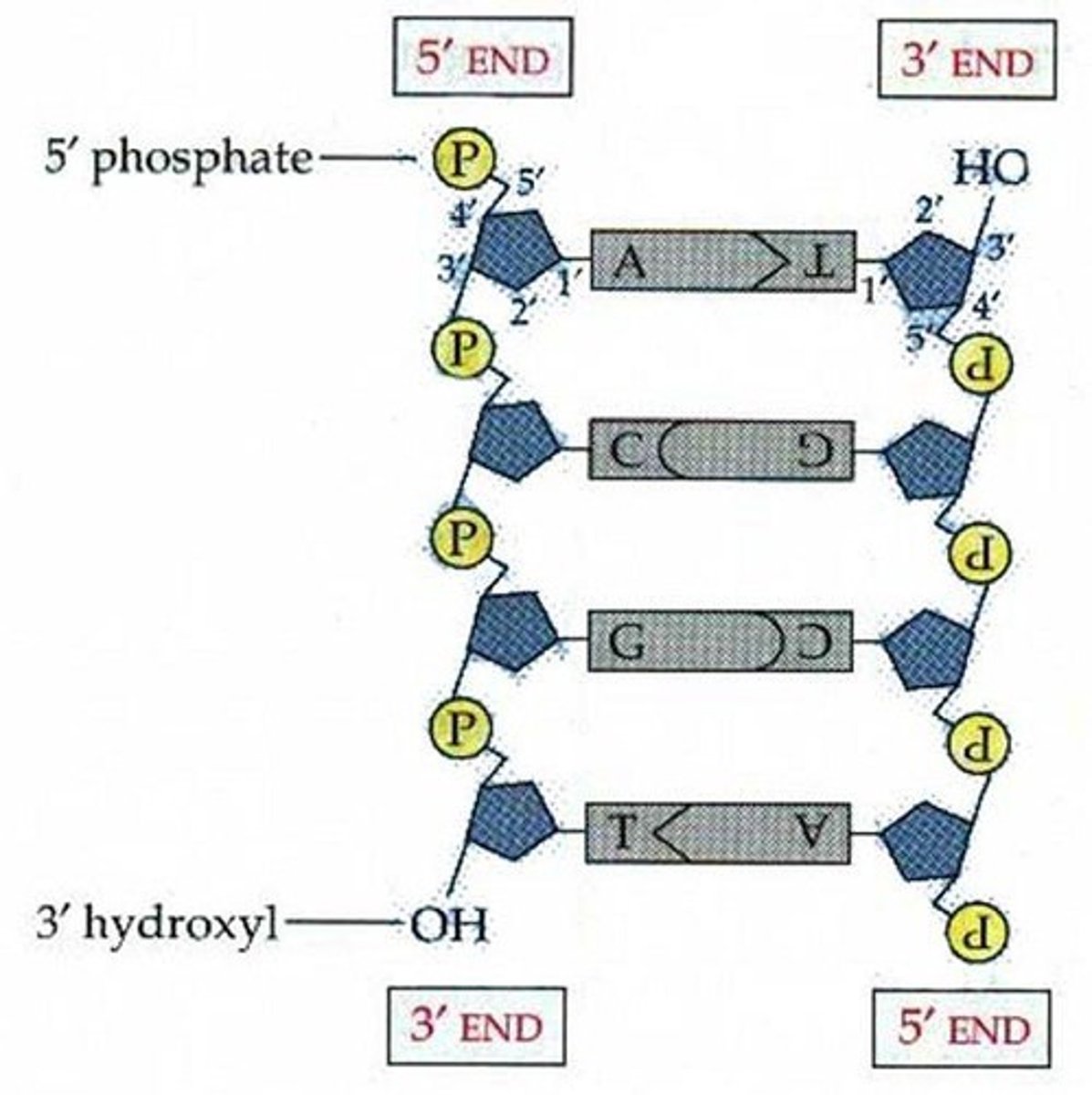
3' end
the end of a DNA strand that terminates with a hydroxyl group.
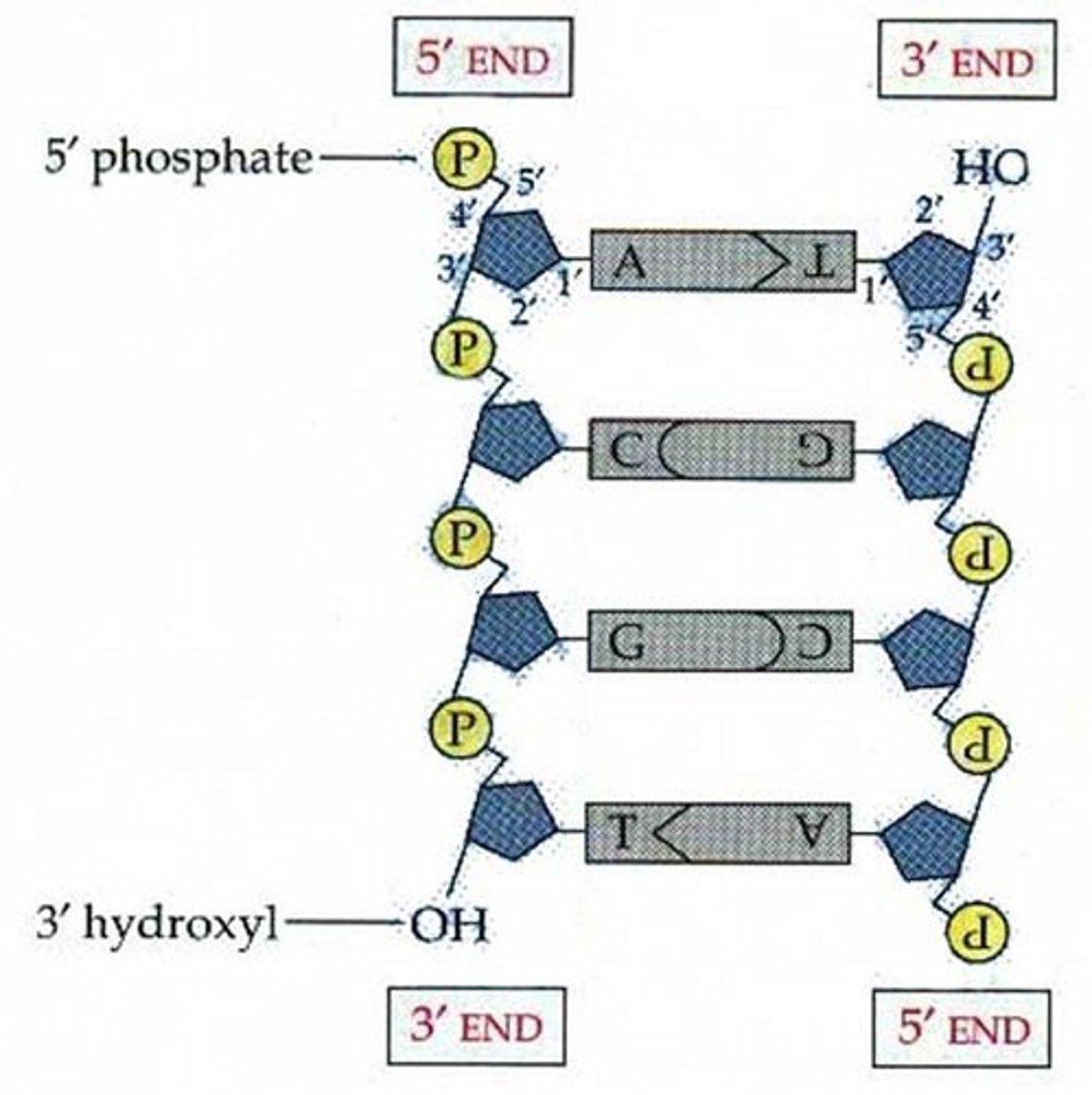
Antiparallel
Two strands of DNA in double helix oriented in opposite directions to each other
complementary
completing; fitting together well; filling mutual needs
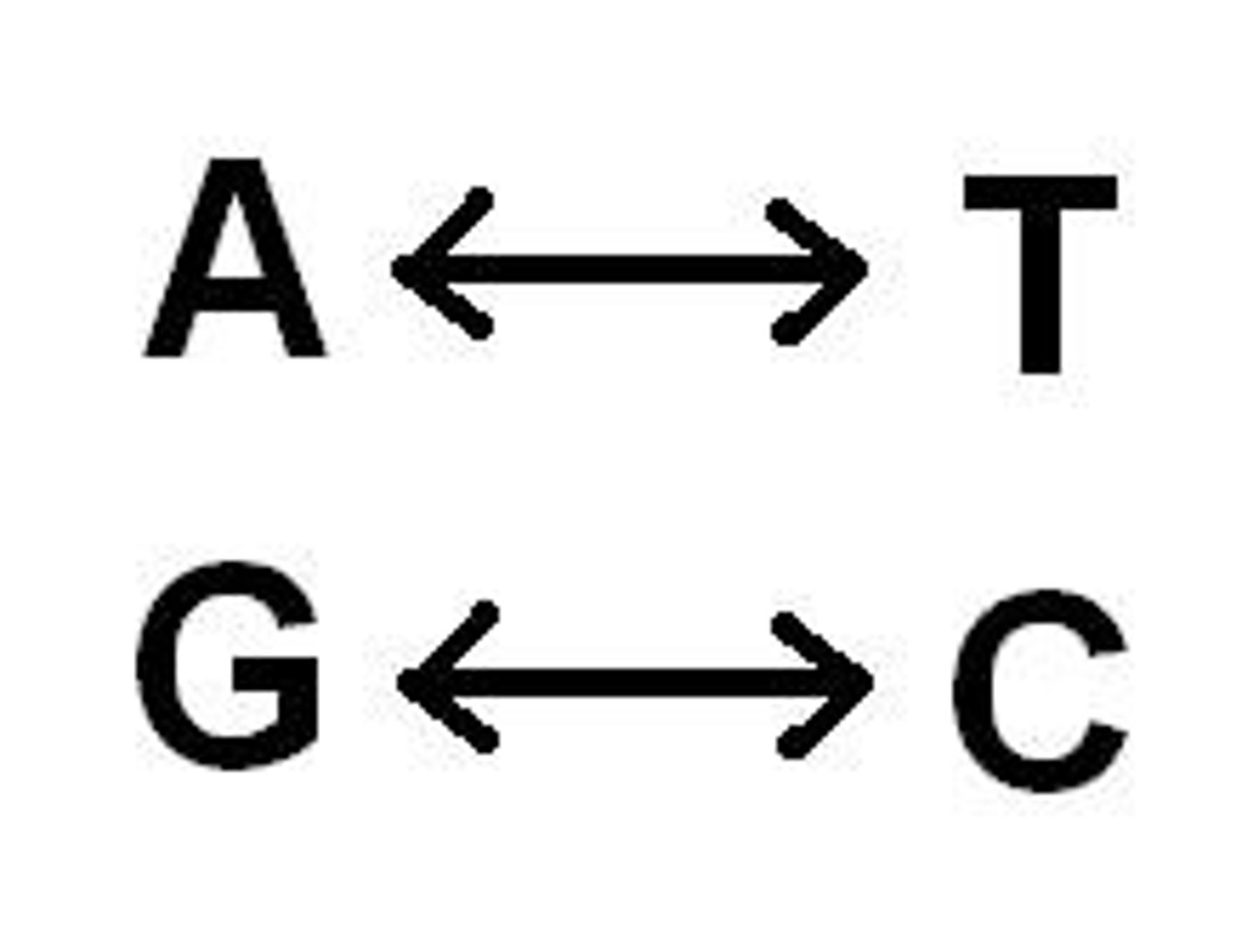
Ribose
sugar in RNA
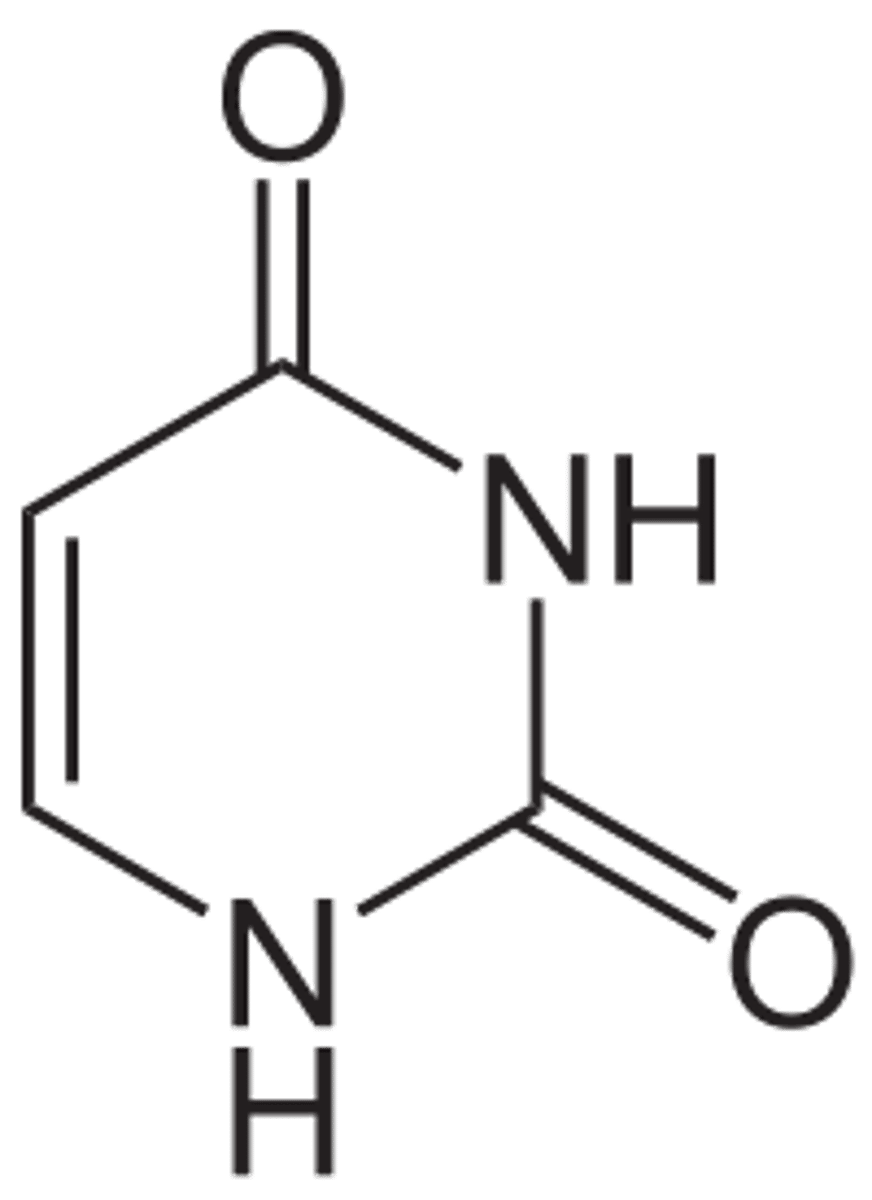
Uracil
a nitrogen-containing base found in RNA (but not in DNA) and derived from pyrimidine
doubleistranded
Two complementary strands of DNA hydrogen bound together
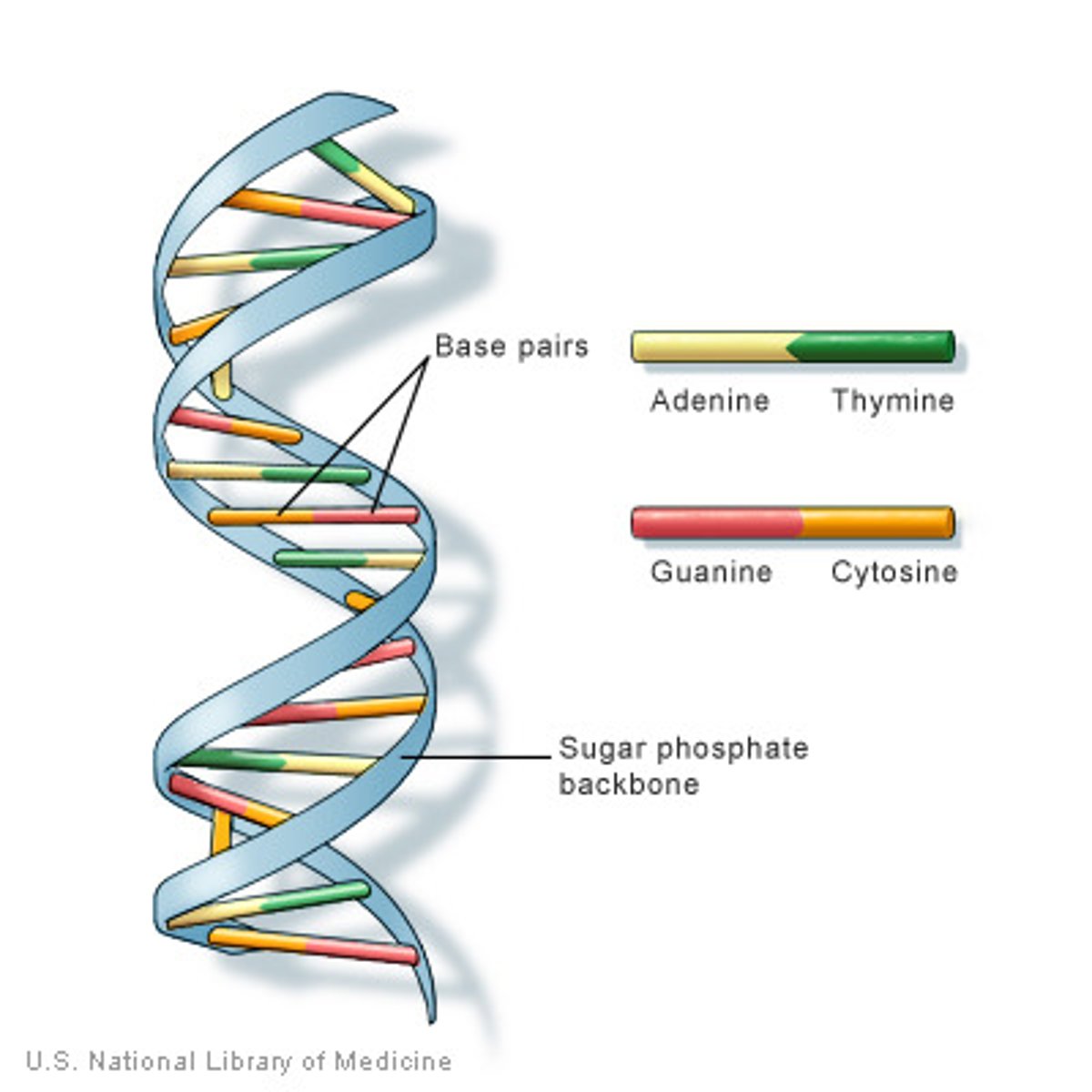
single-stranded
One strand of DNA or RNA
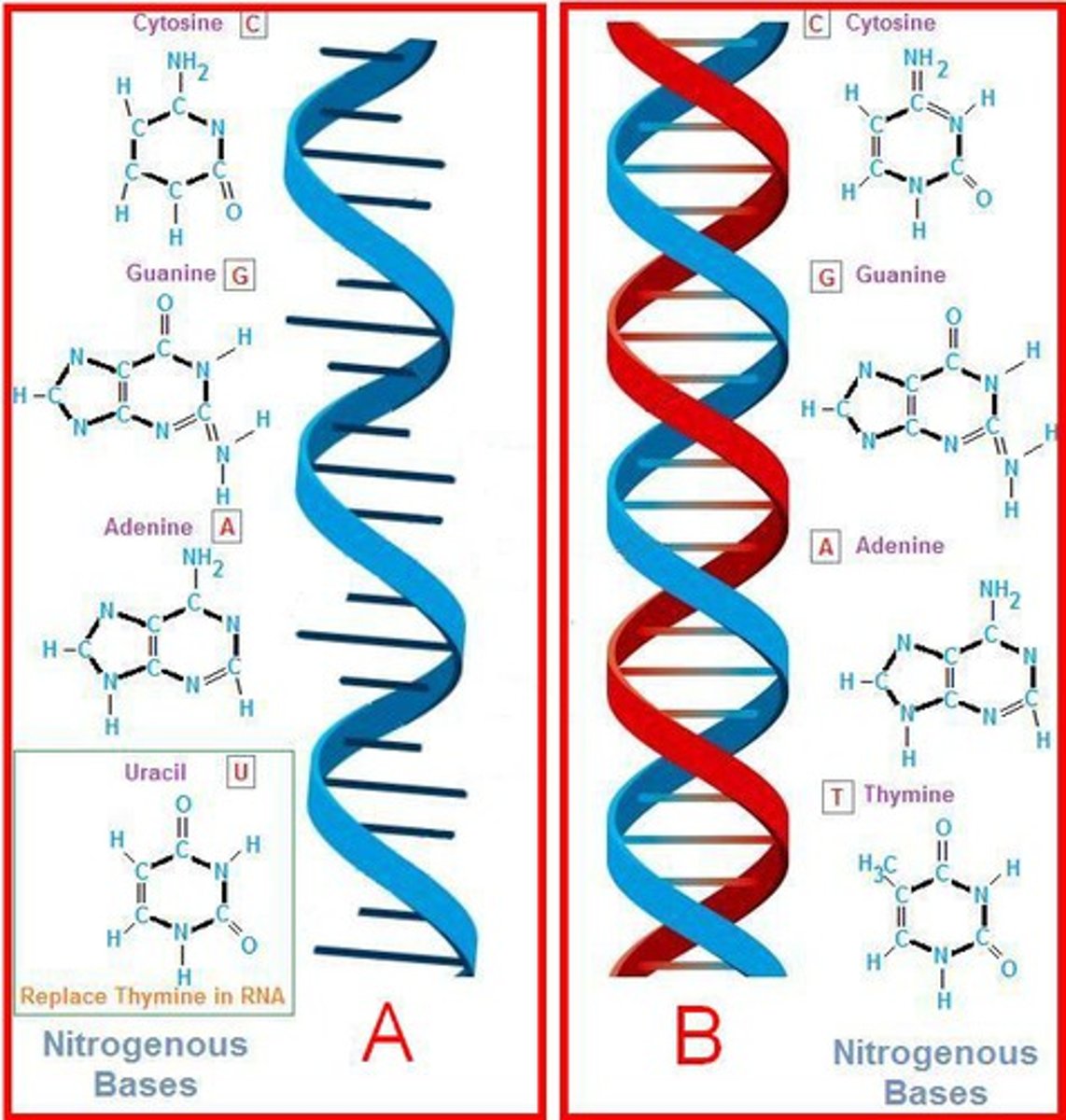
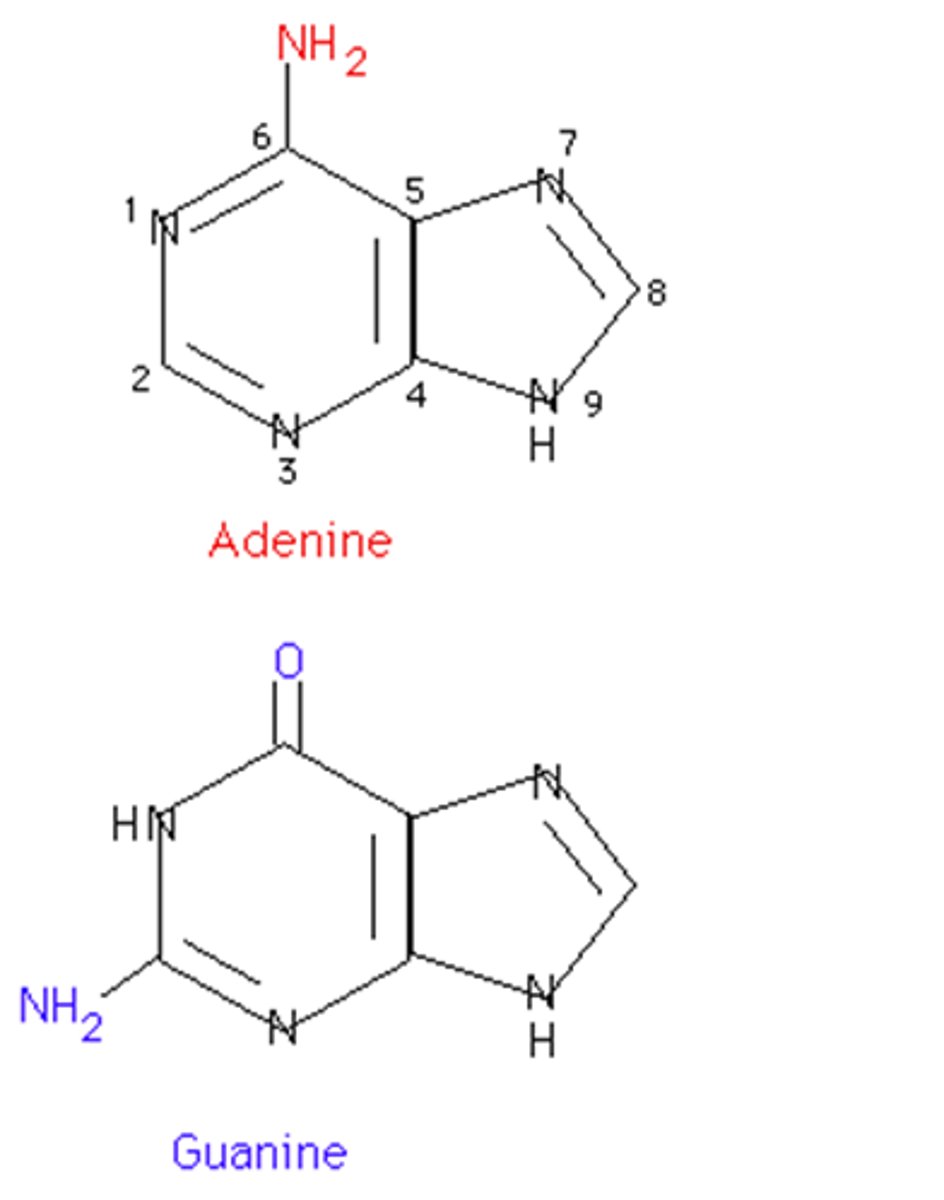
Purine
a nitrogenous base that has a double-ring structure; either adenine or guanine
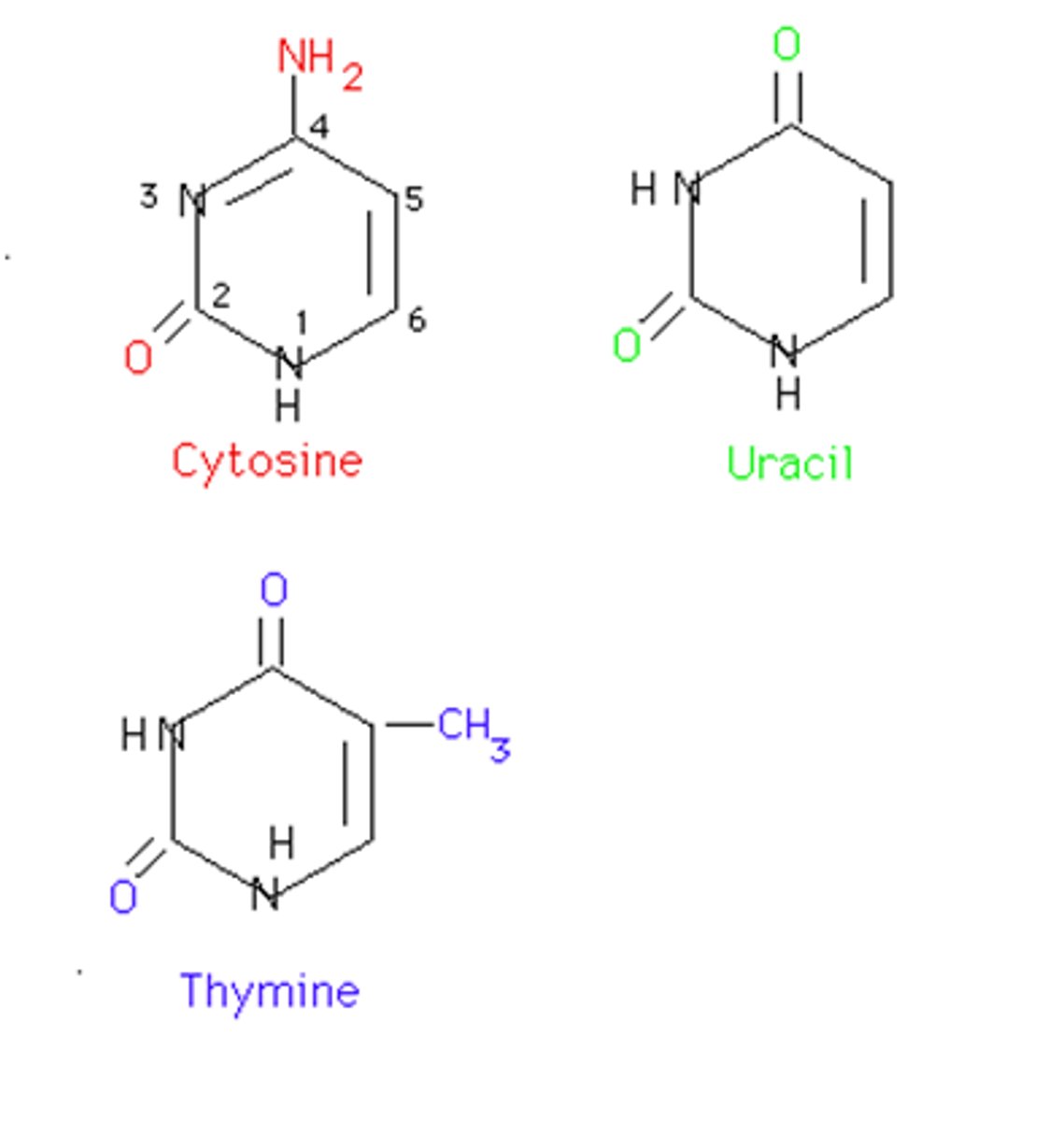
Pyrimidines
a nitrogenous base that has a single ring structure; either Thymine, Cytosine, or Uracil
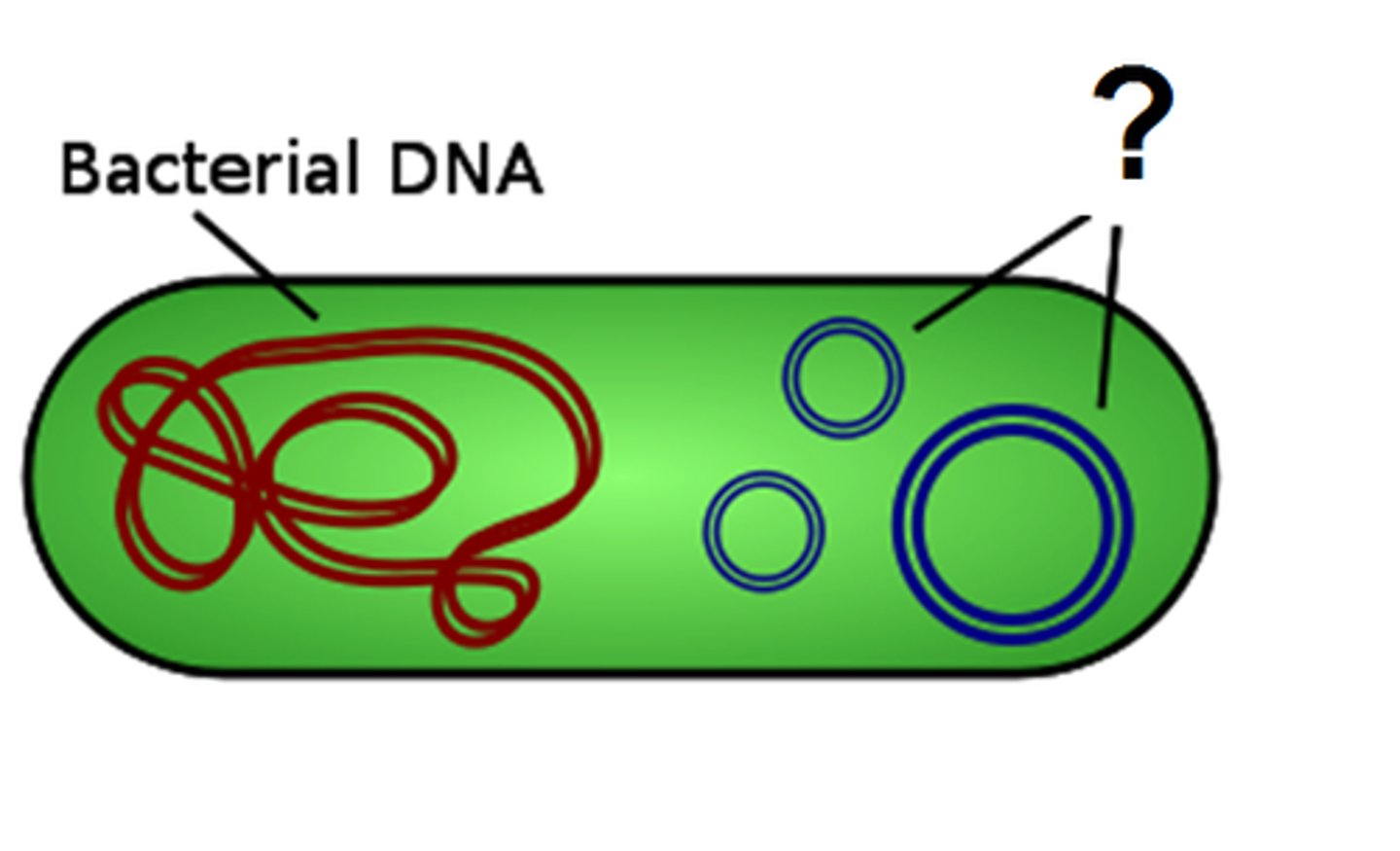
Plasmid
A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of the bacterial chromosome
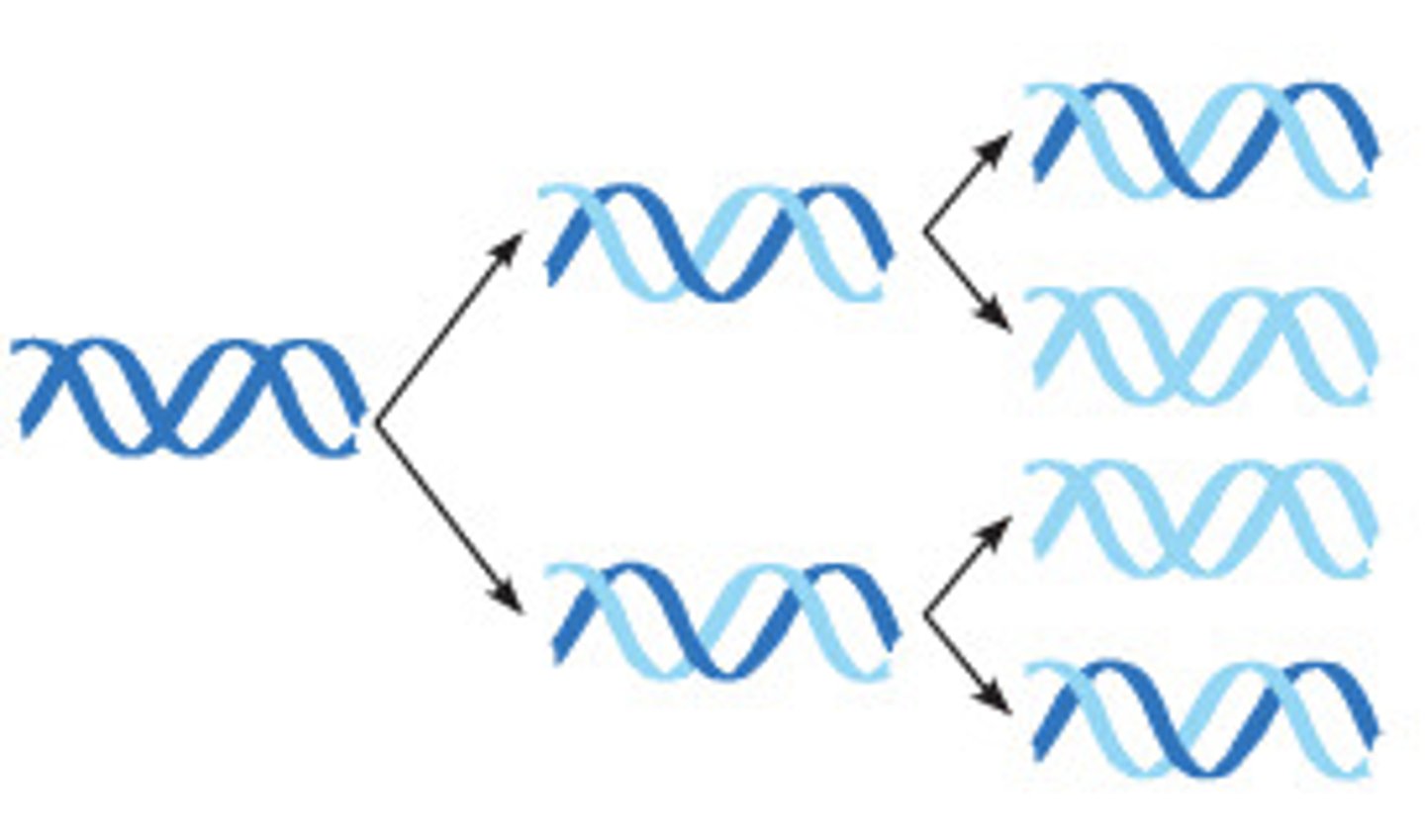
semiconservative replication
The process in which the DNA molecule uncoils and separates into two strands. Each original strand becomes a template on which a new strand is constructed, resulting in two DNA molecules identical to the original DNA molecule.
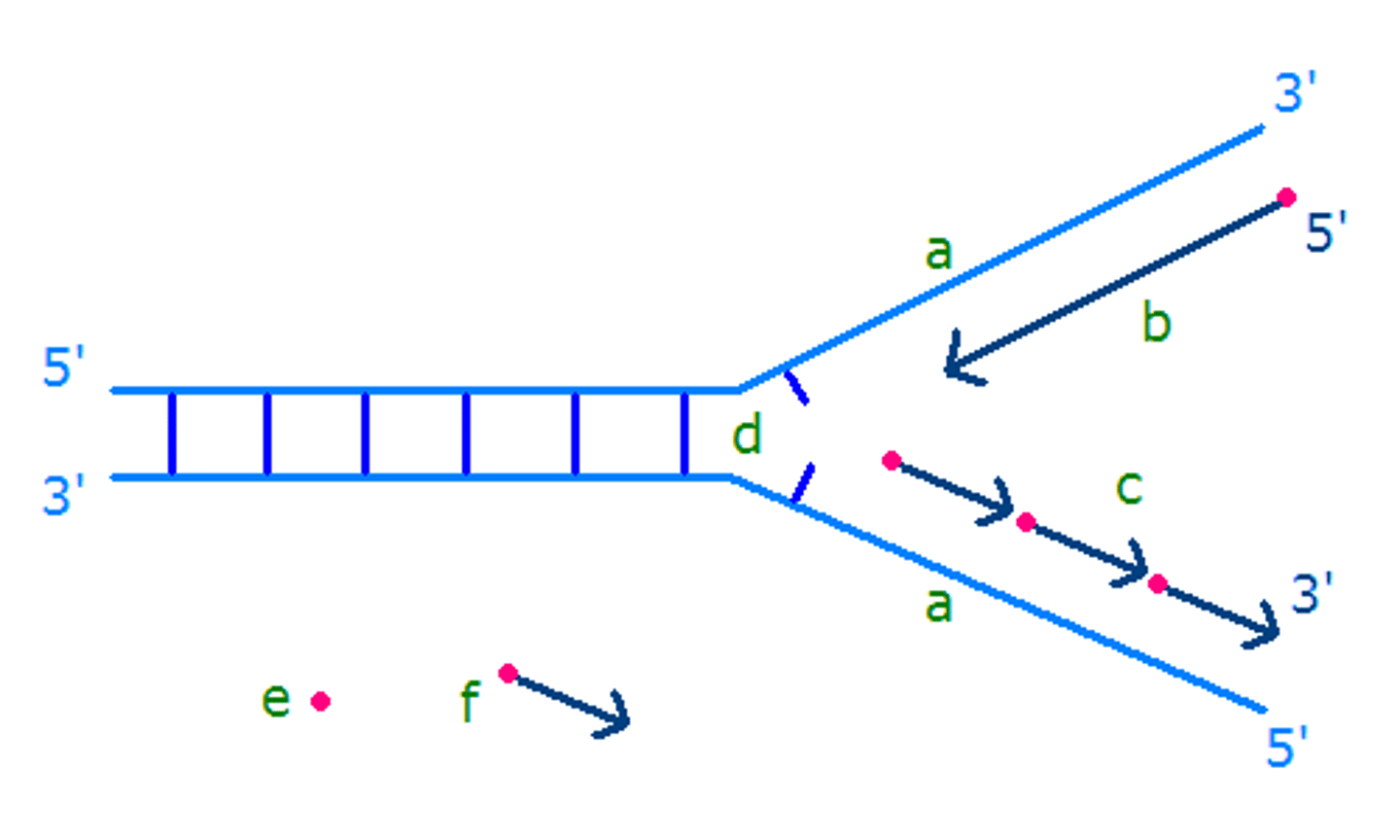
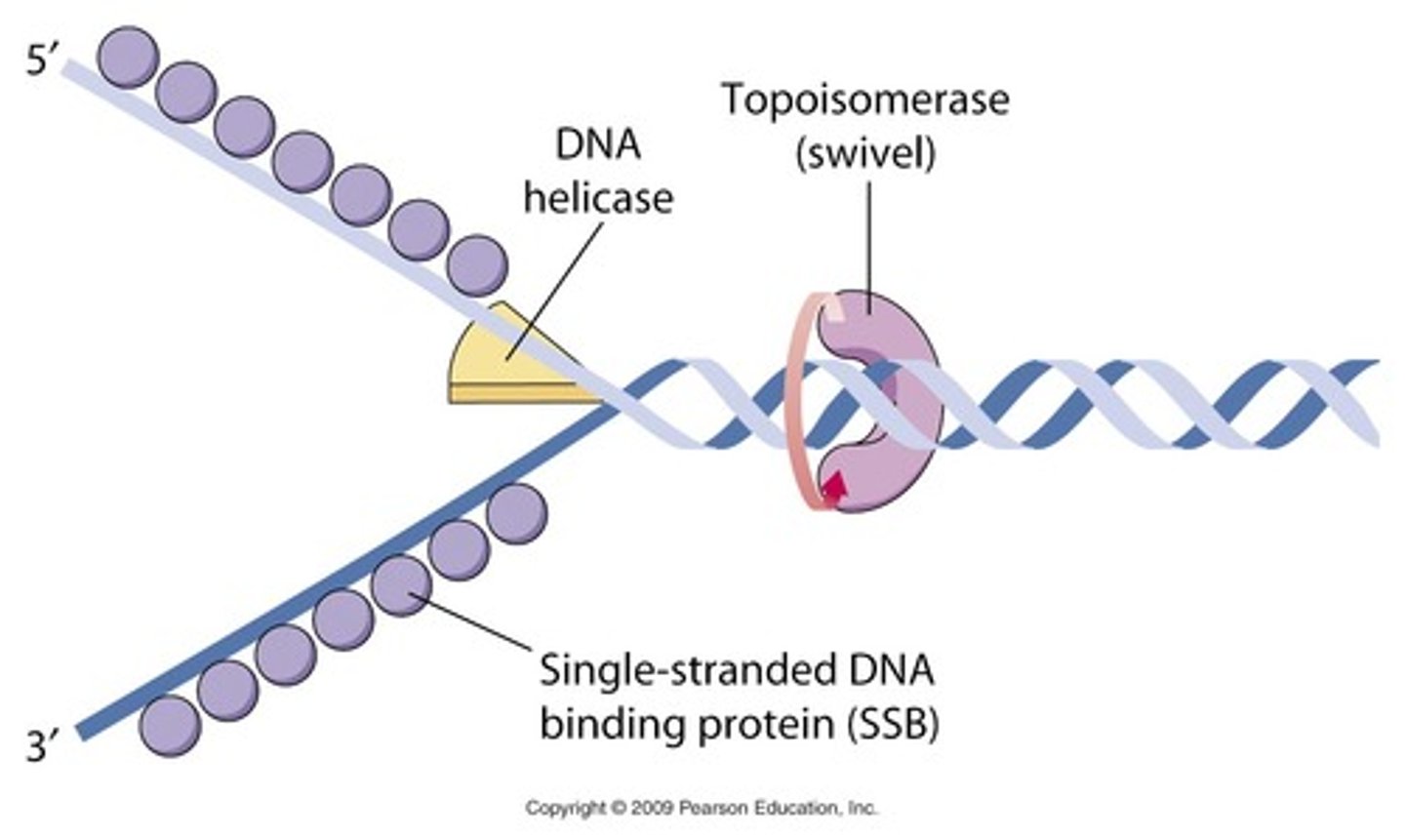
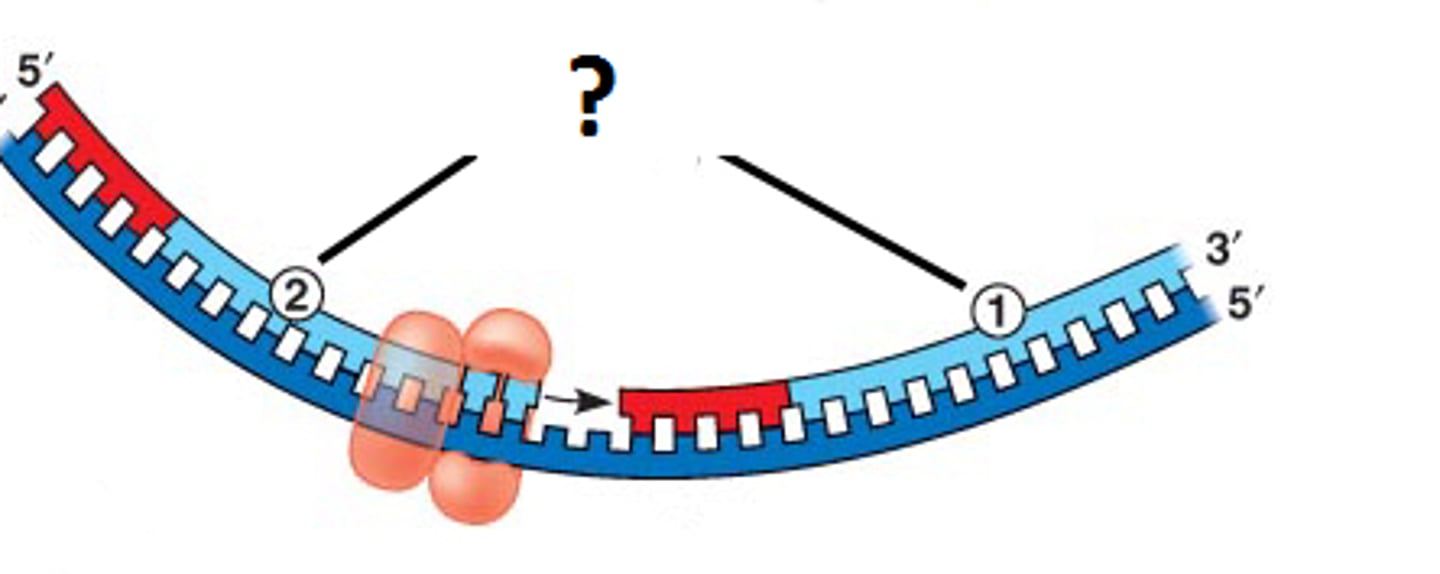
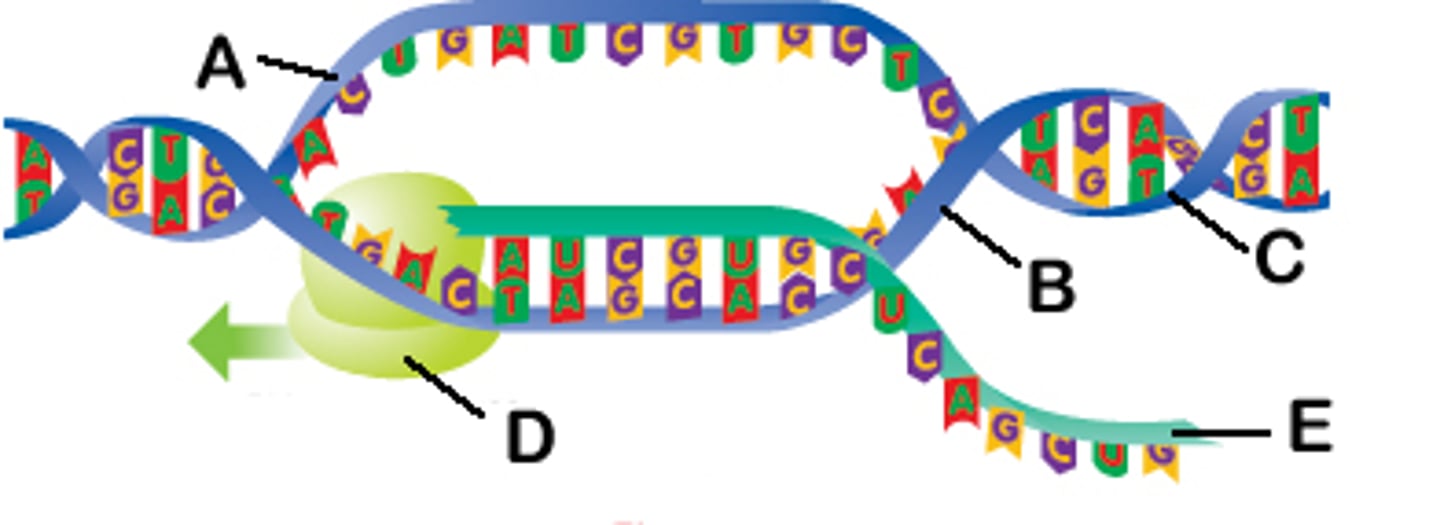
Helicase
An enzyme that untwists the double helix of DNA at the replication forks, separating the two parental strands

Topoisomerase
corrects "overwinding" ahead of replication forks by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands
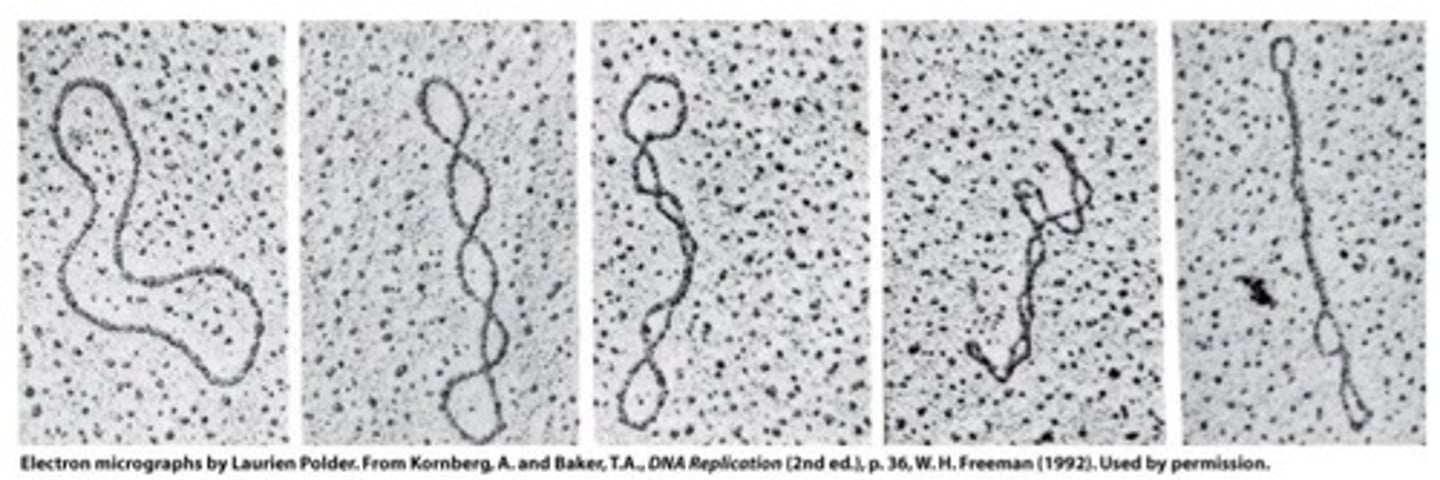
Supercoiling
twisting in the opposite direction to the turns of the double helix
DNA polymerase III
synthesizes new DNA only in the 5' to 3' direction
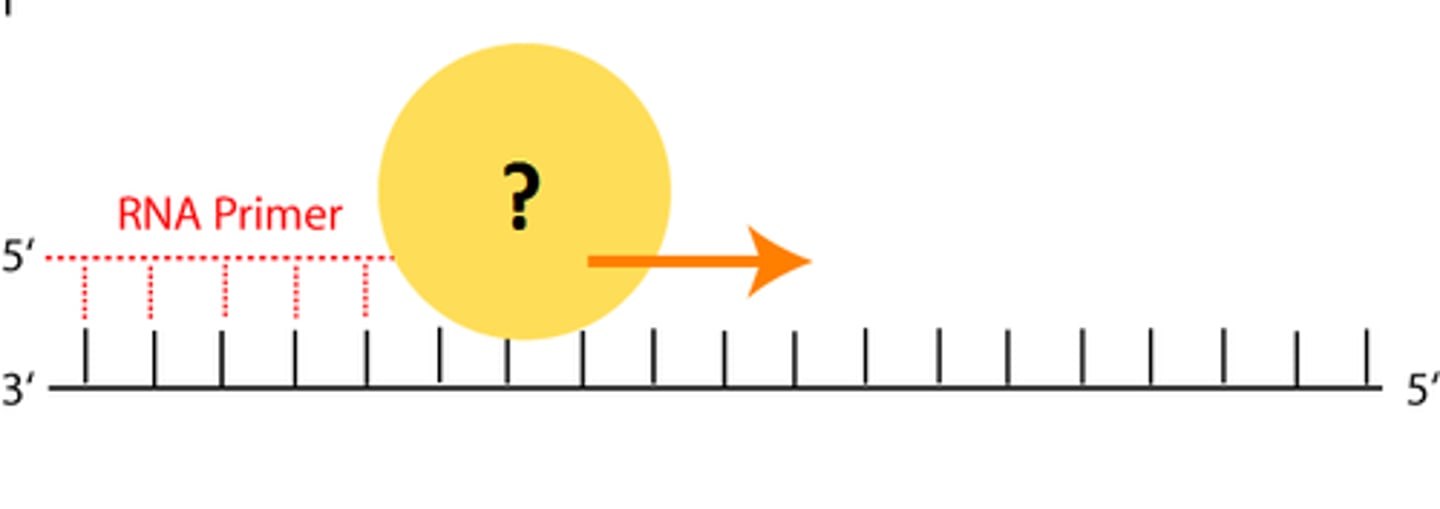
primer
A short strand of RNA that is synthesized by primase at the start of DNA replication
leading strand
The new continuous complementary DNA strand synthesized along the template strand in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction.
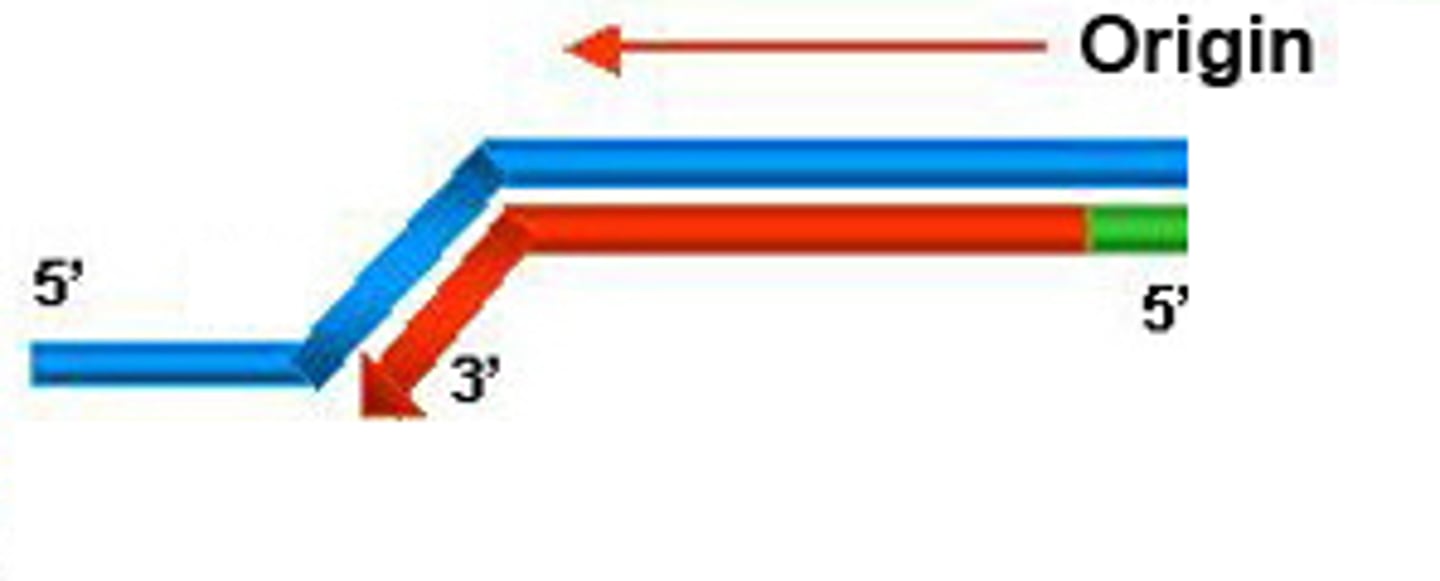
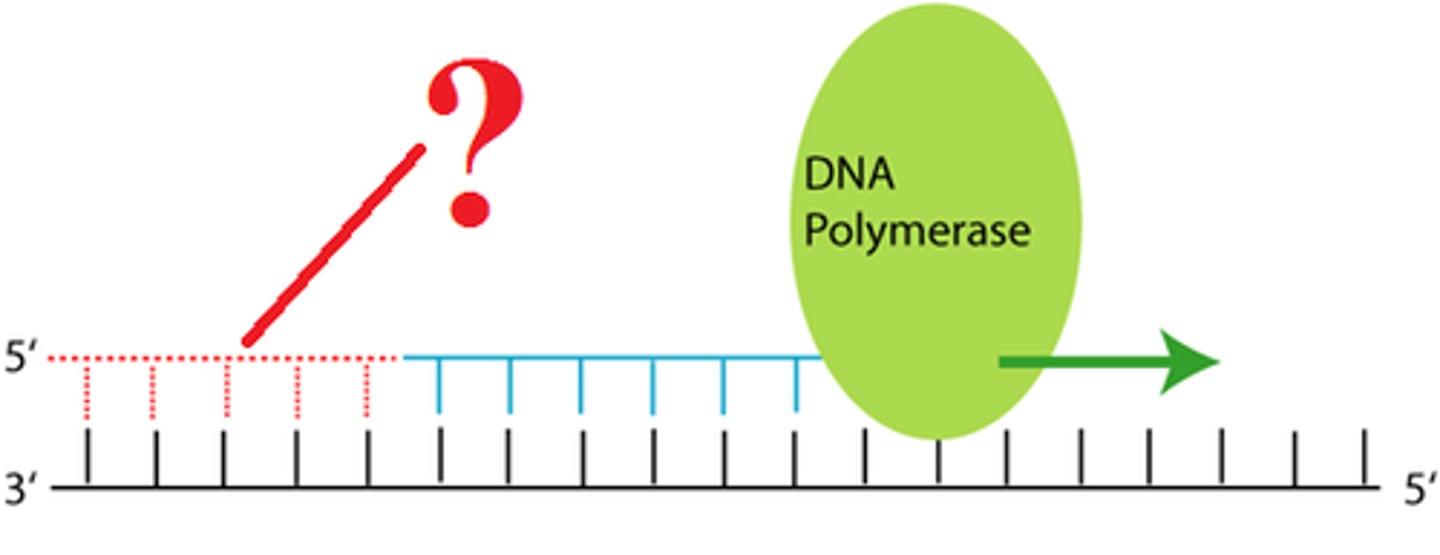
lagging strand
A discontinuously synthesized DNA strand that elongates by means of Okazaki fragments, each synthesized in a 5' to 3' direction away from the replication fork.
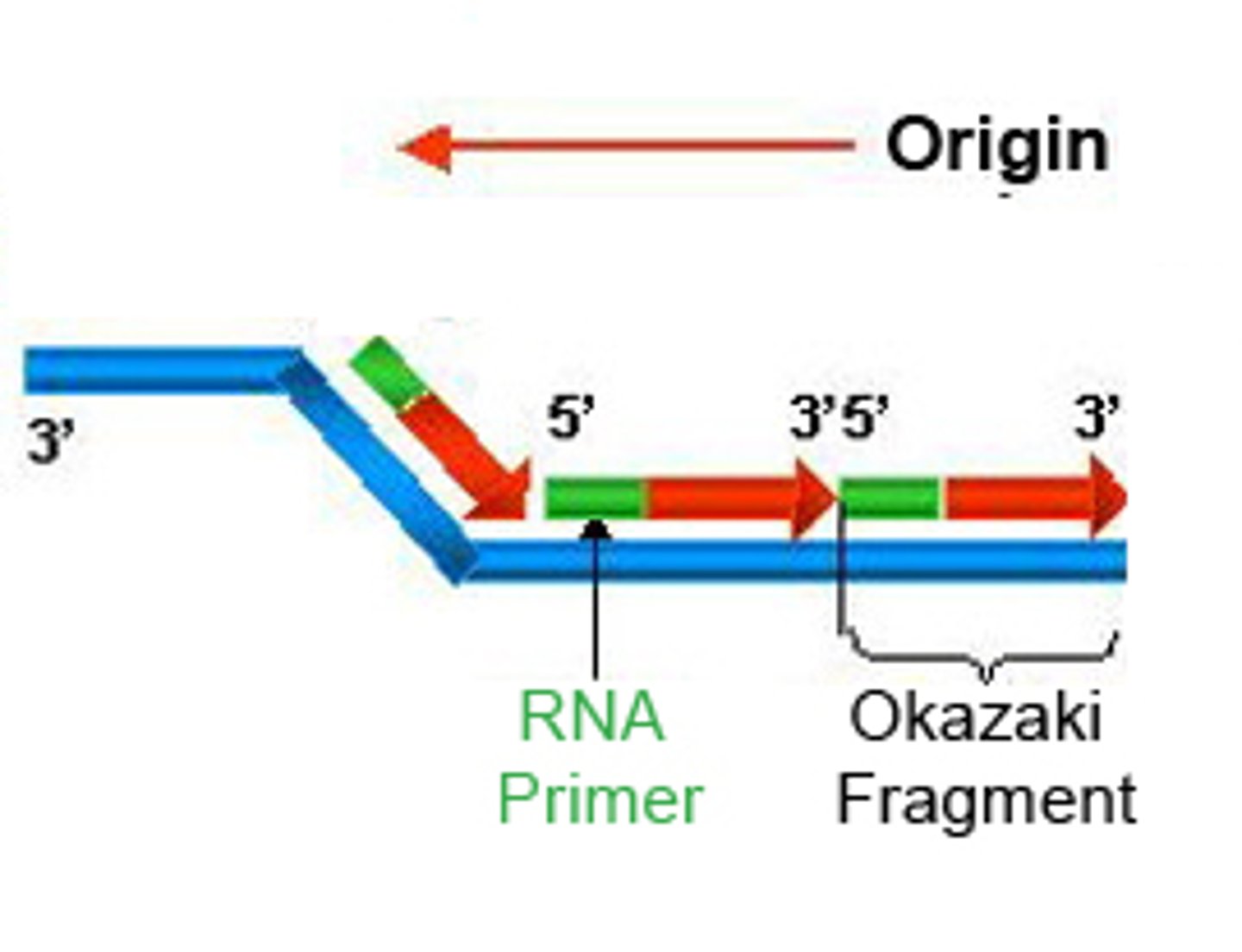
Okazaki fragments
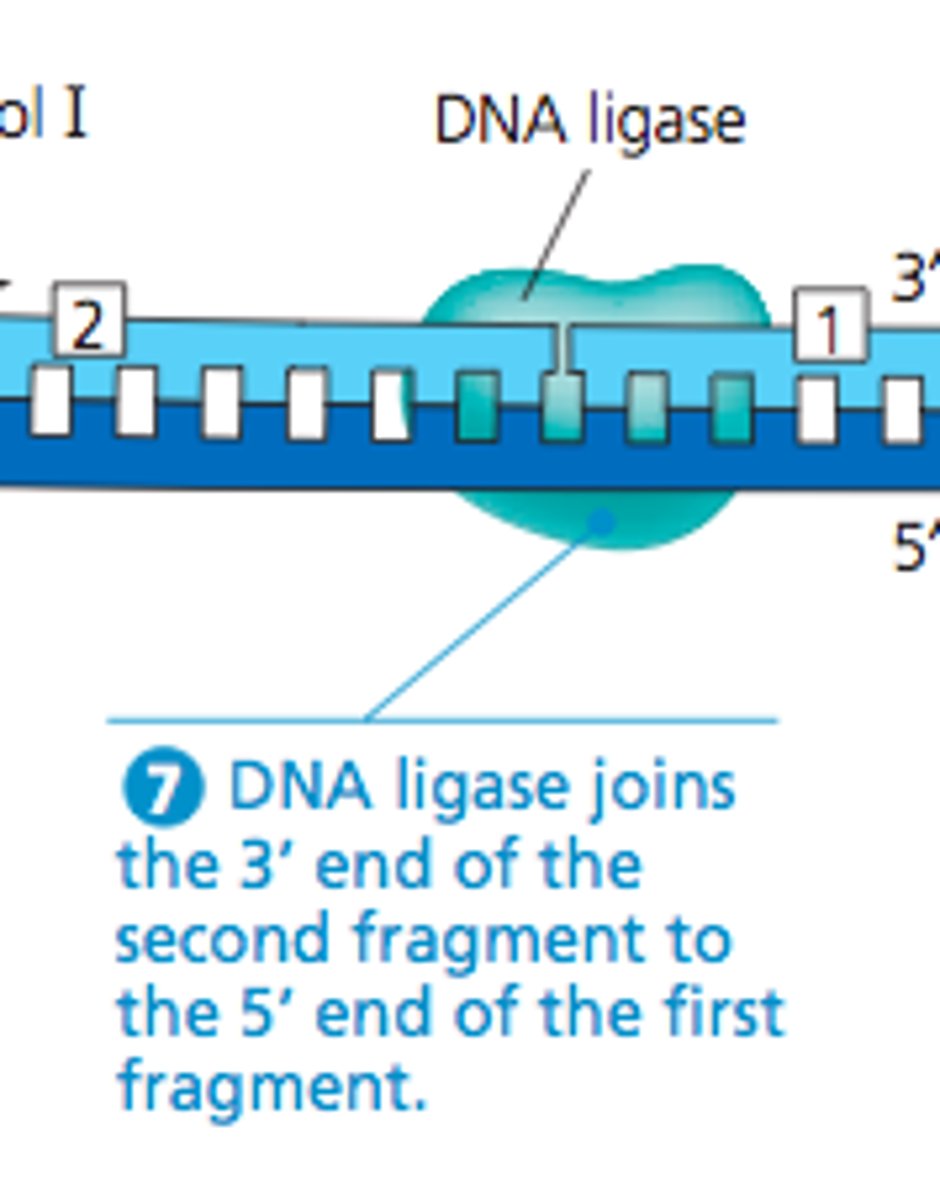
Small fragments of DNA produced on the lagging strand during DNA replication, joined later by DNA ligase to form a complete strand.
DNA Polymerase I
removes the RNA primer and replaces it with DNA
DNA Ligase
An enzyme that connects two fragments of DNA to make a single fragment
mRNA
messenger RNA; type of RNA that carries instructions from DNA in the nucleus to the ribosome
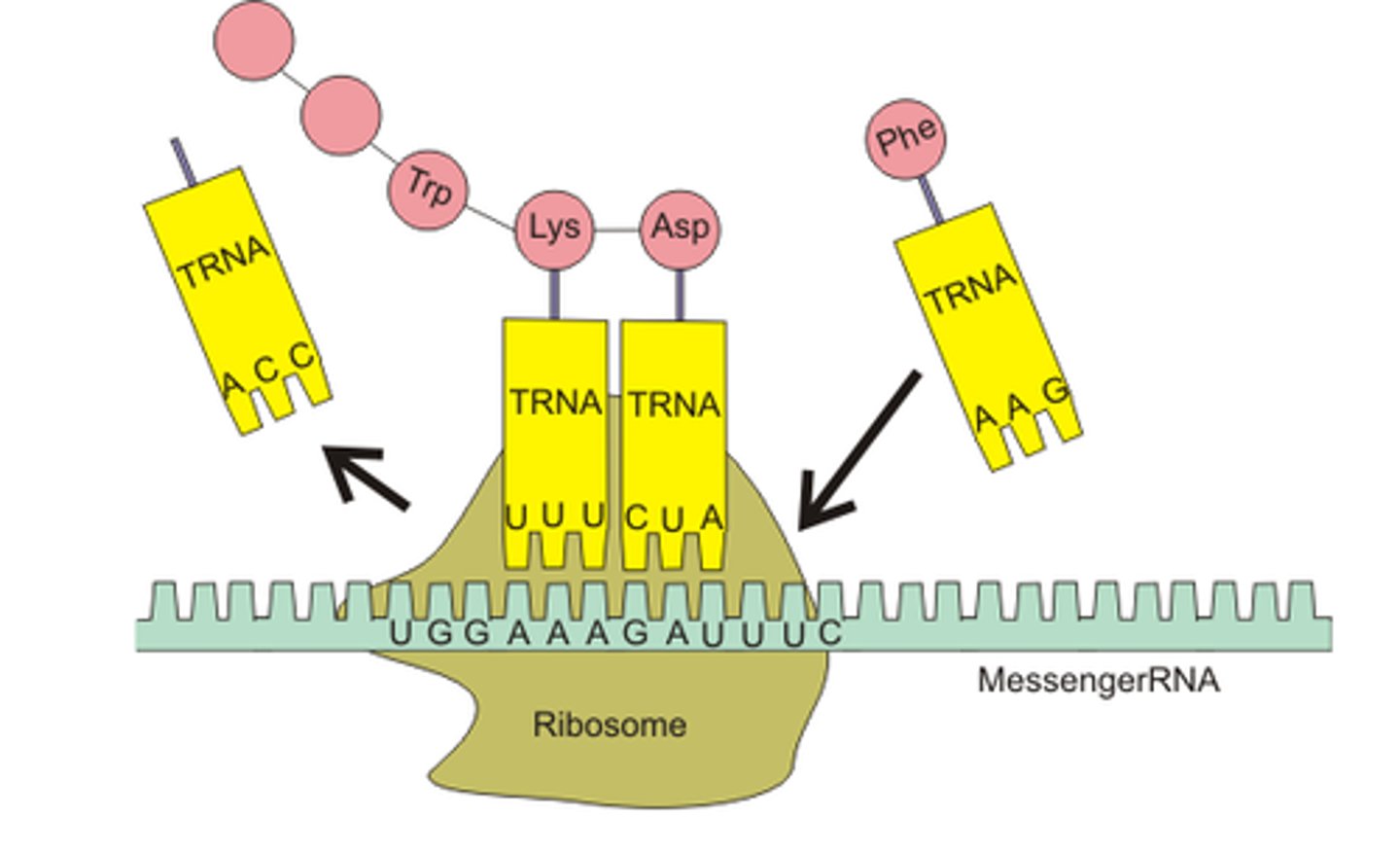
tRNA
transfer RNA; type of RNA that carries amino acids to the ribosome
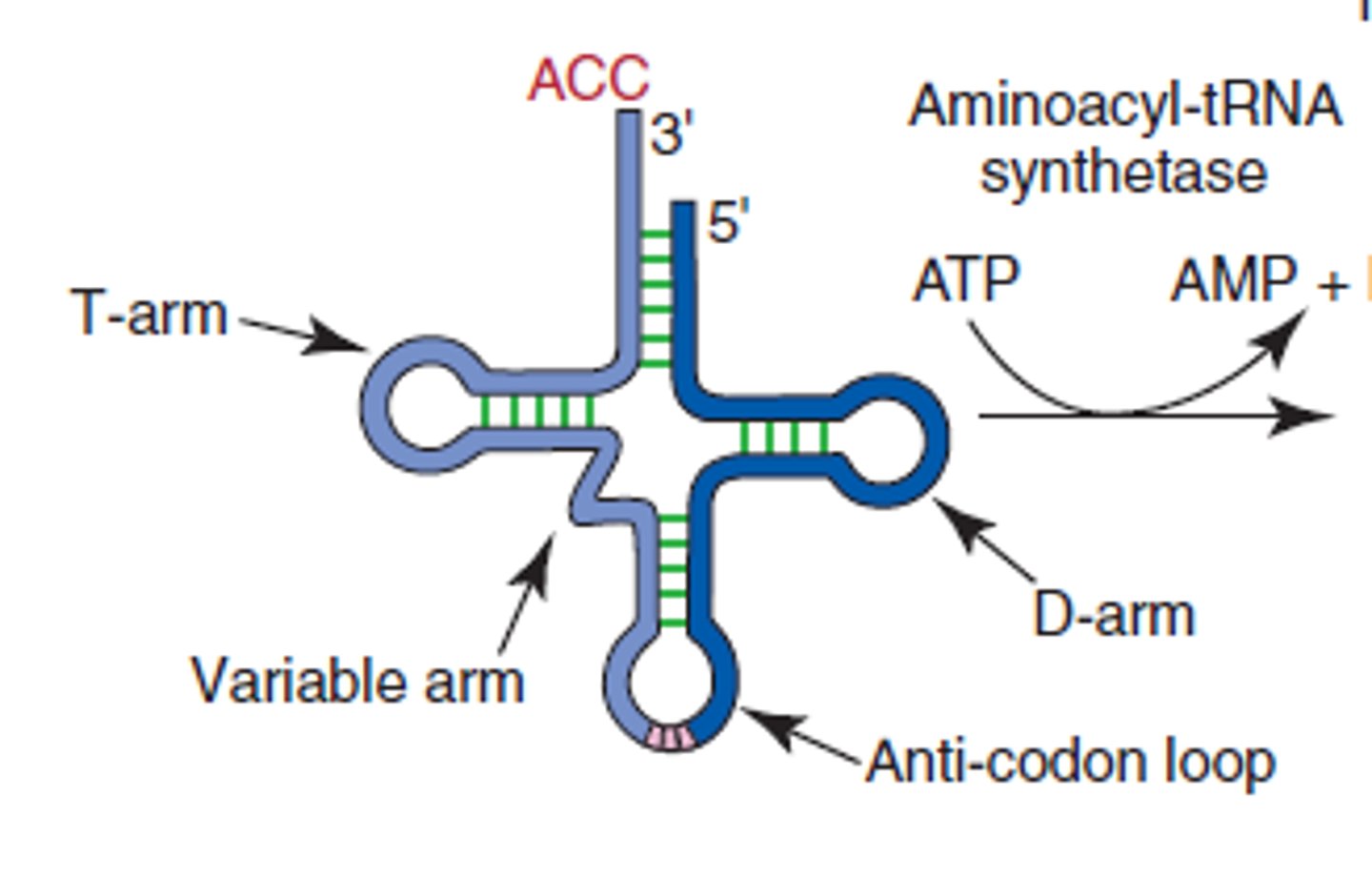
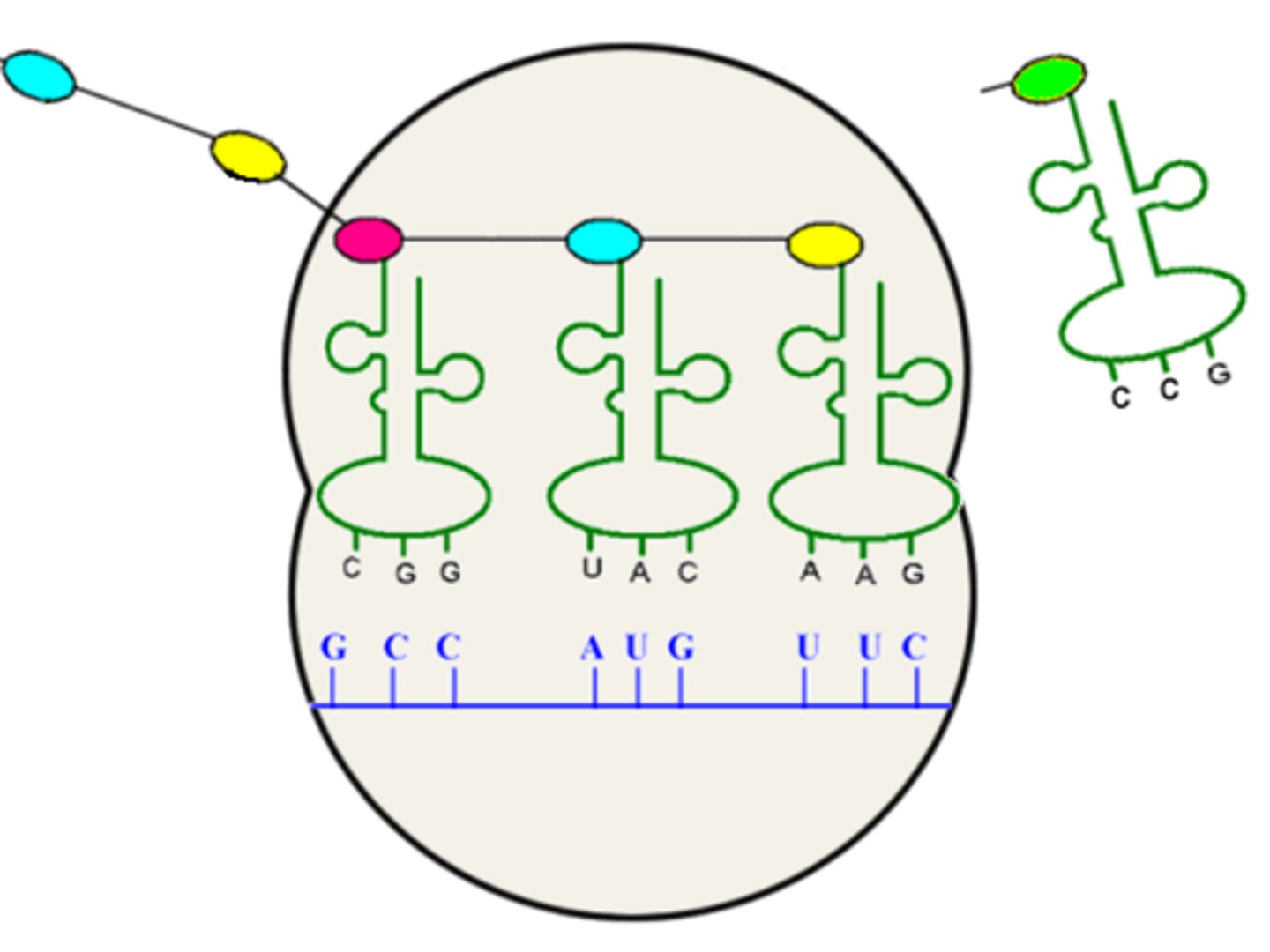
Anti-codon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
rRNA
ribosomal RNA; type of RNA that makes up part of the ribosome
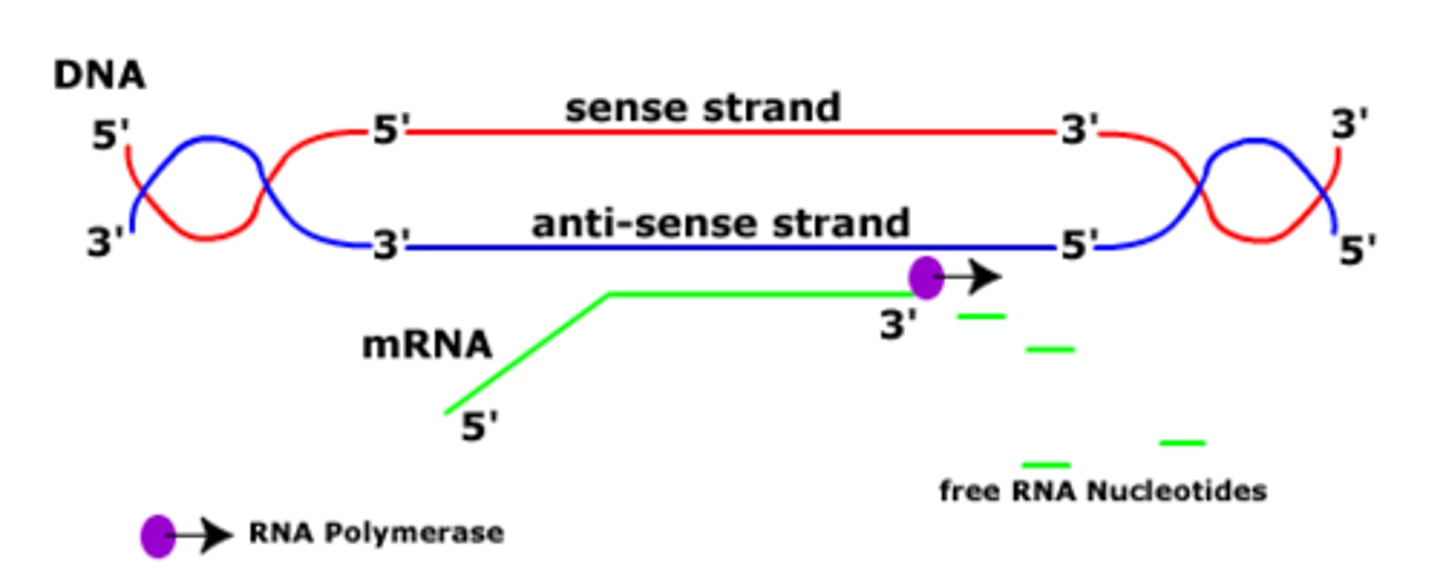
RNA polymerase
Enzyme similar to DNA polymerase that binds to DNA, separates the DNA strands, and synthesizes mRNA during transcription
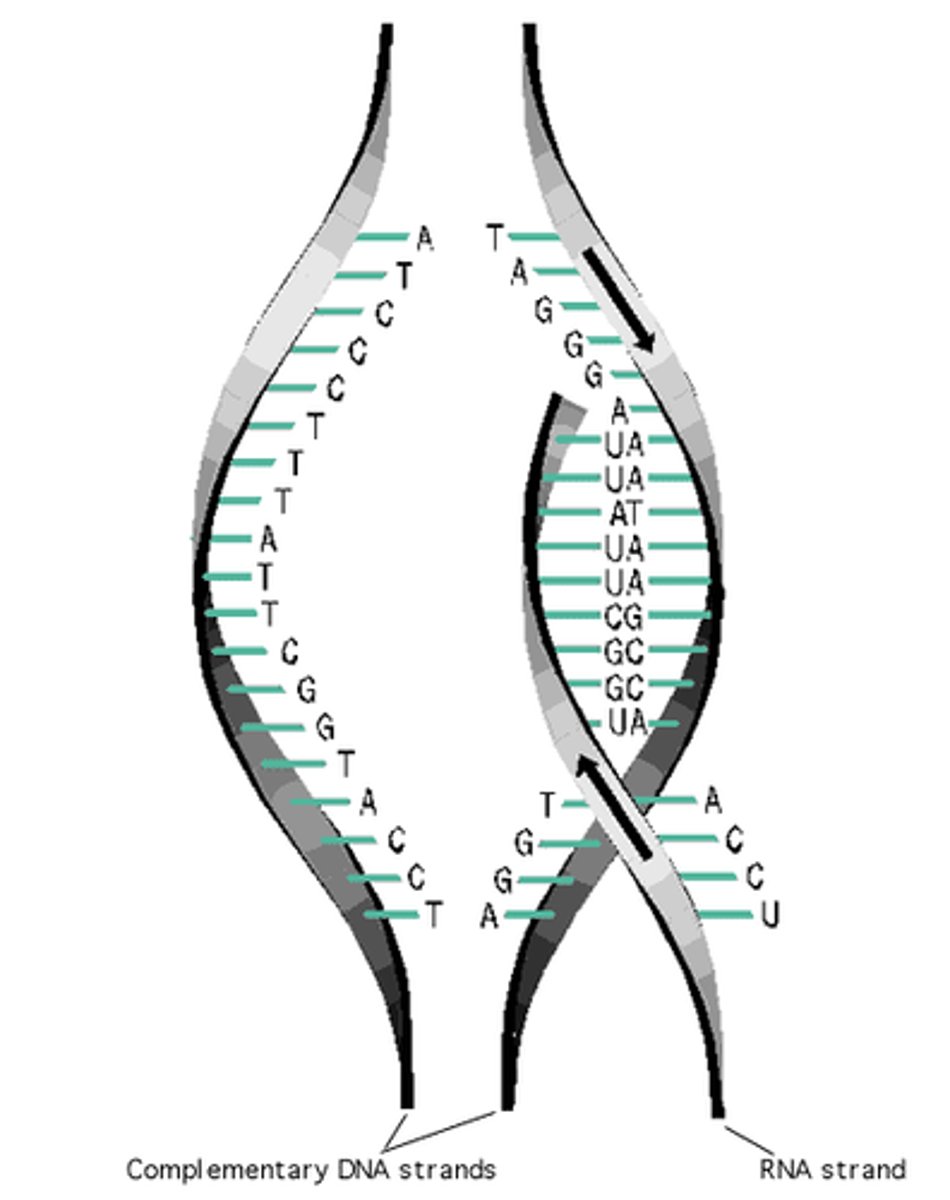
Transcription
synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template
Translation
Process by which mRNA is decoded and a protein is produced
Template Strand
The DNA strand that provides the template for ordering the sequence of nucleotides in an mRNA transcript.
noncoding strand
The strand of DNA within a structural gene that is complementary to the mRNA. The noncoding strand is used as a template to make mRNA.
minus strand
The DNA strand that serves as the template for transcription
antisense strand
the strand of DNA that runs 3' to 5' and is complementary to the sense strand. It acts as a template strand during transcription.
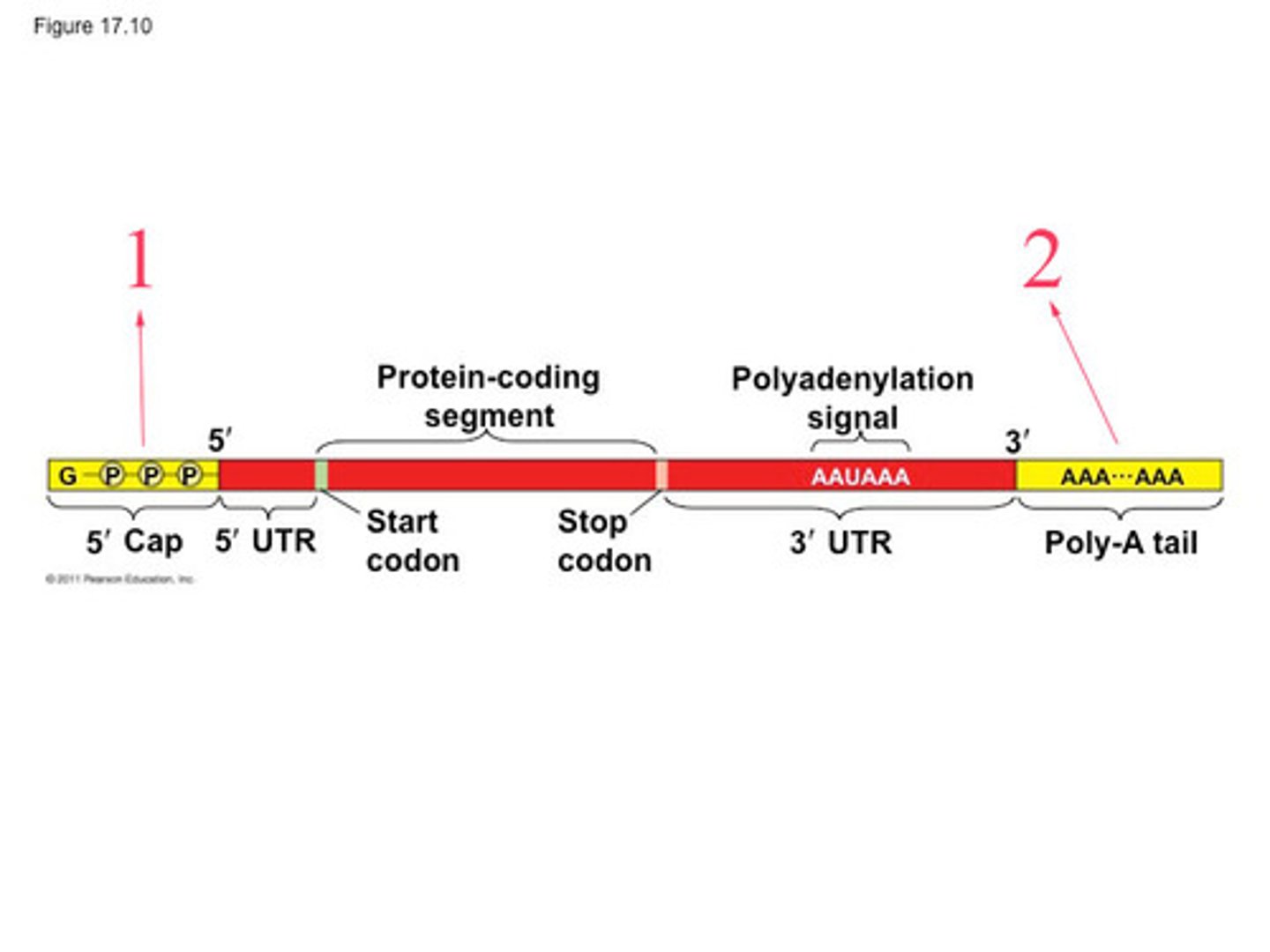
poly-A tail
Modified end of the 3' end of an mRNA molecule consisting of the addition of some 50 to 250 adenine nucleotides.
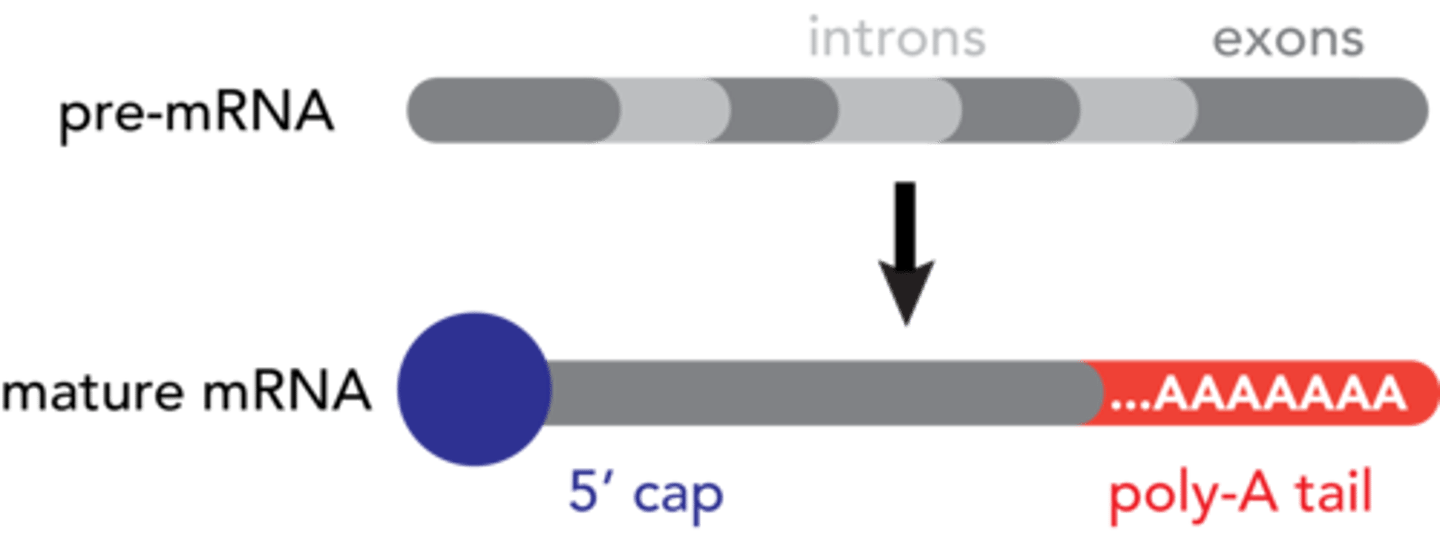
GTP cap
a molecule that is attached to the "head" of the mRNA after transcription
excision
removal by cutting

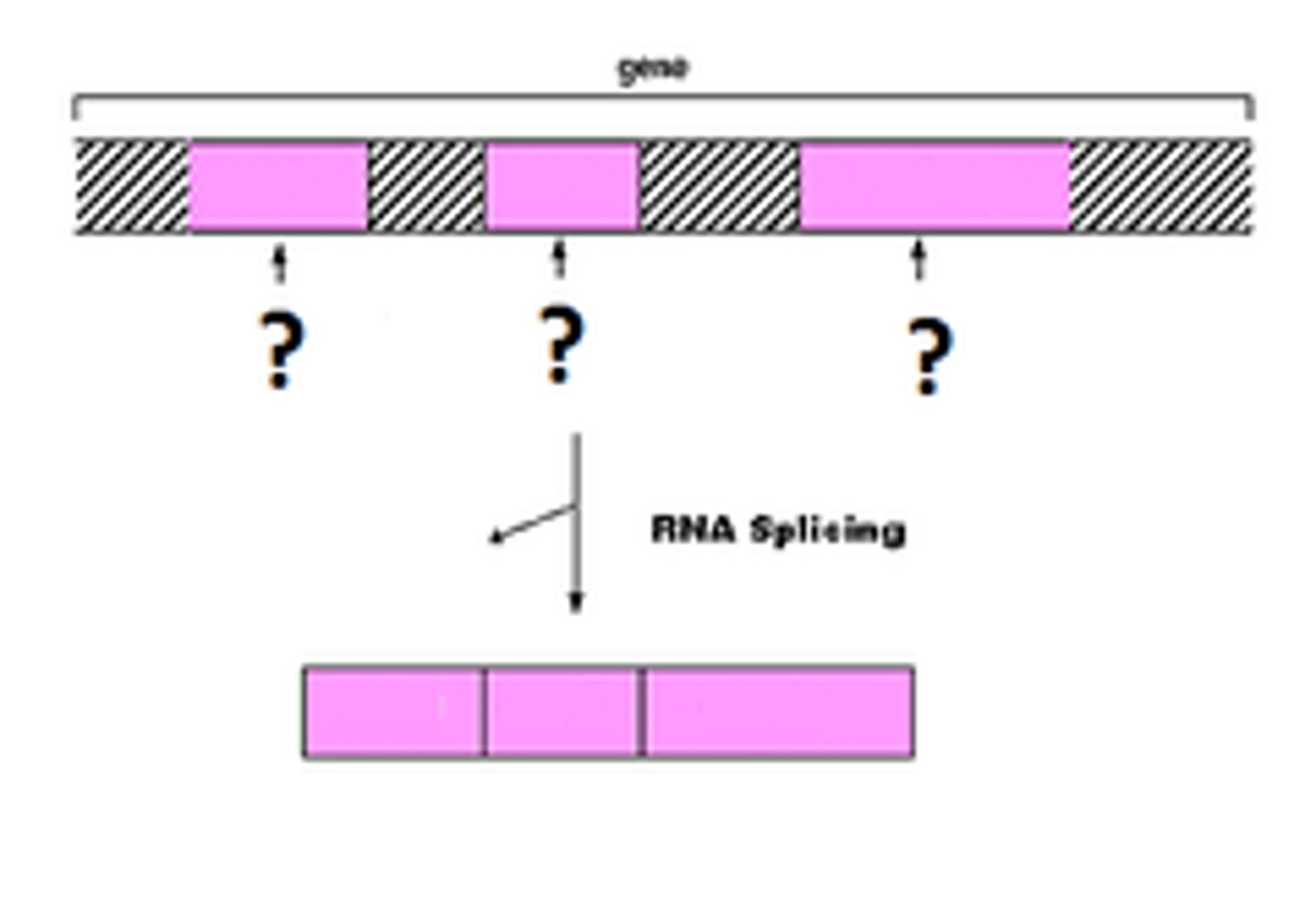
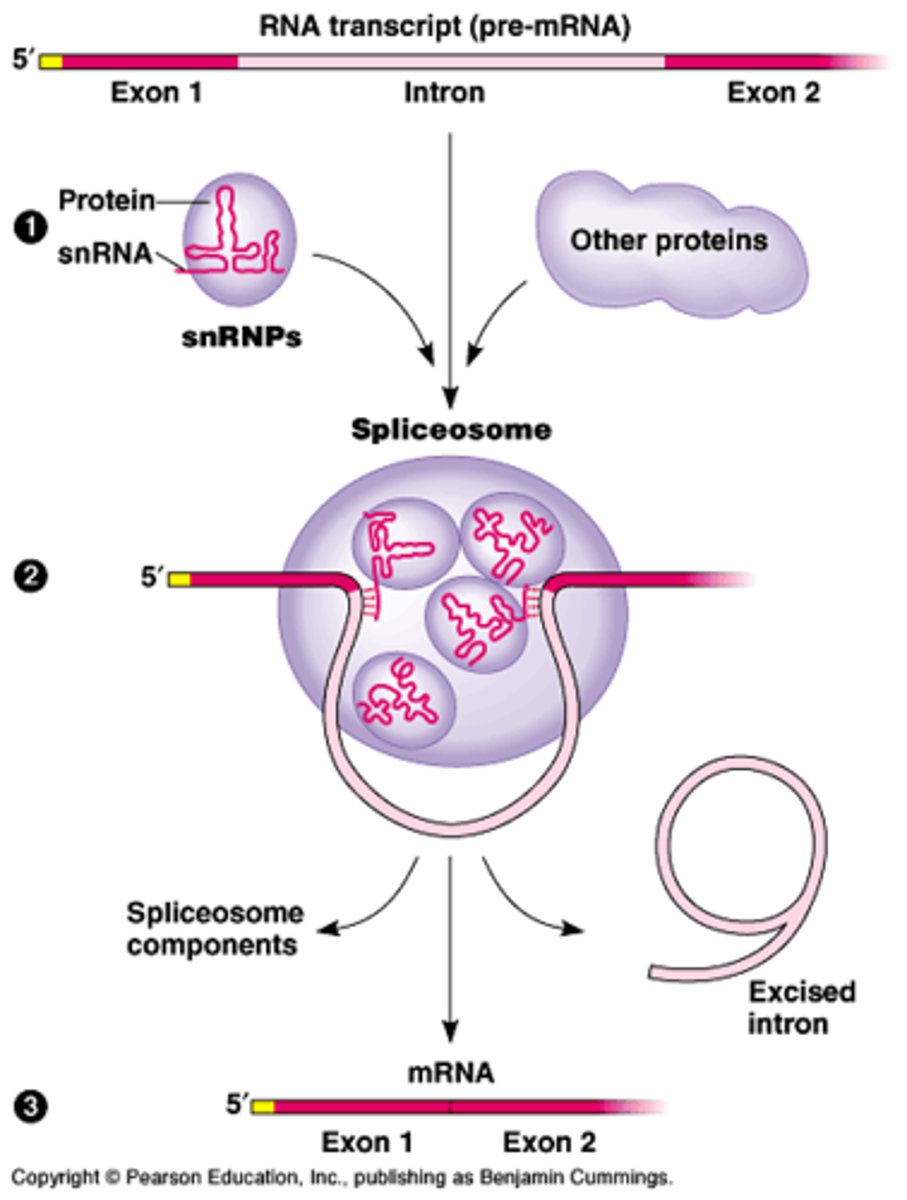
Splicing
the process of removing introns and reconnecting exons in a pre-mRNA
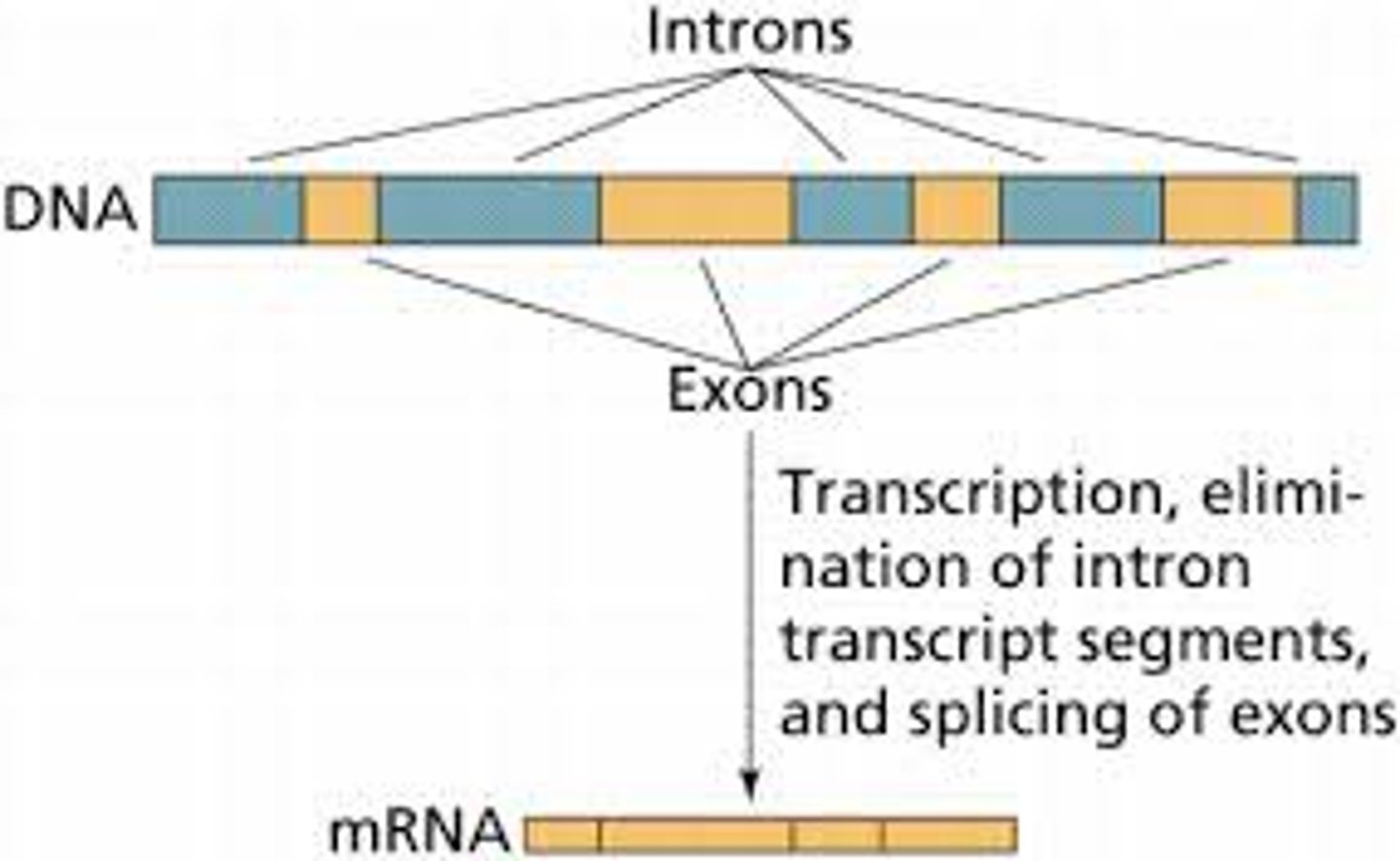
Introns
Noncoding segments of nucleic acid that lie between coding sequences.
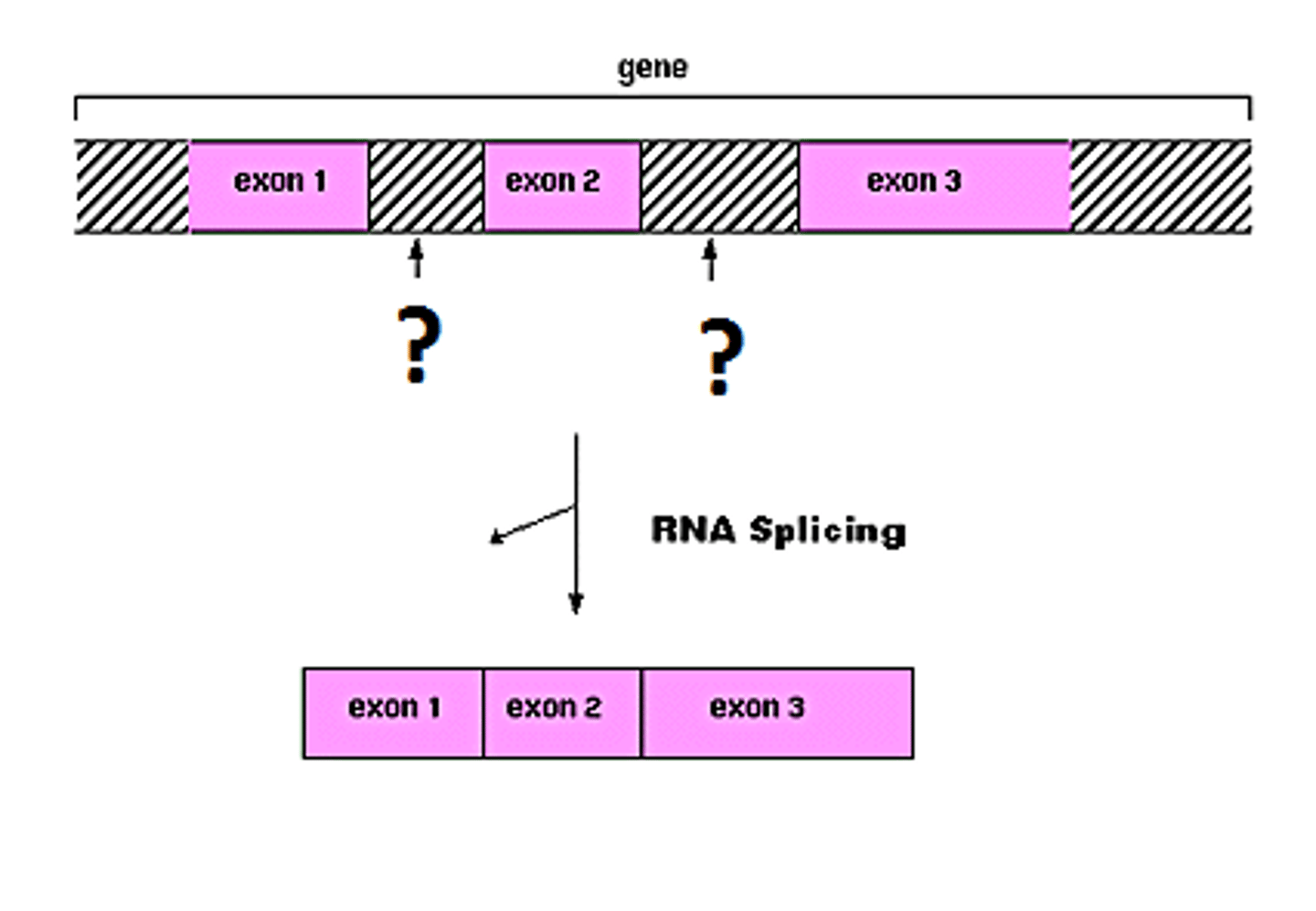
Exons
Coding segments of eukaryotic DNA.
spliceosome
A large complex made up of proteins and RNA molecules that splices RNA by interacting with the ends of an RNA intron, releasing the intron and joining the two adjacent exons.
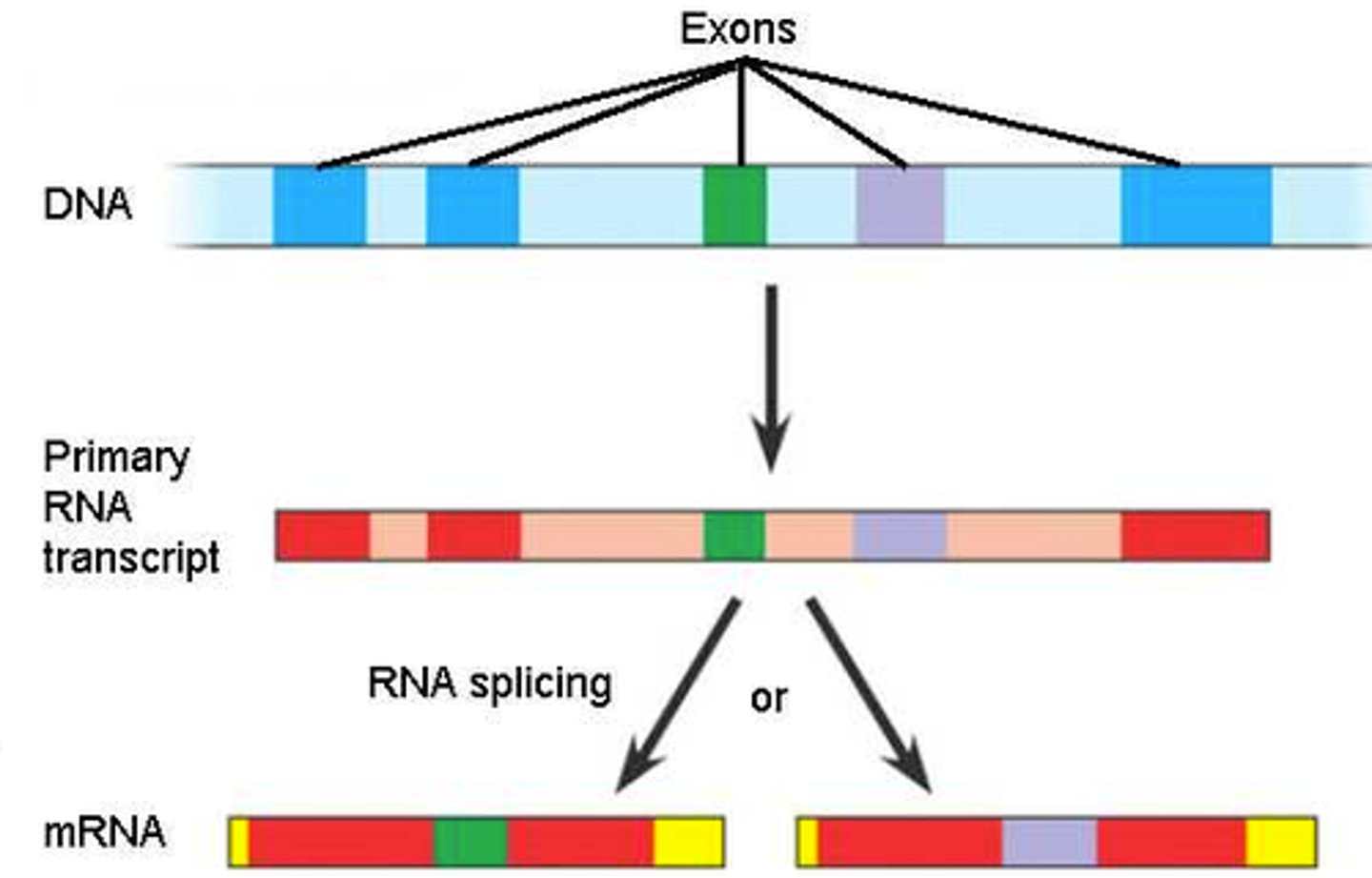
alternative splicing
Splicing of introns in a pre-mRNA that occurs in different ways, leading to different mRNAs that code for different proteins or protein isoforms. Increases the diversity of proteins.
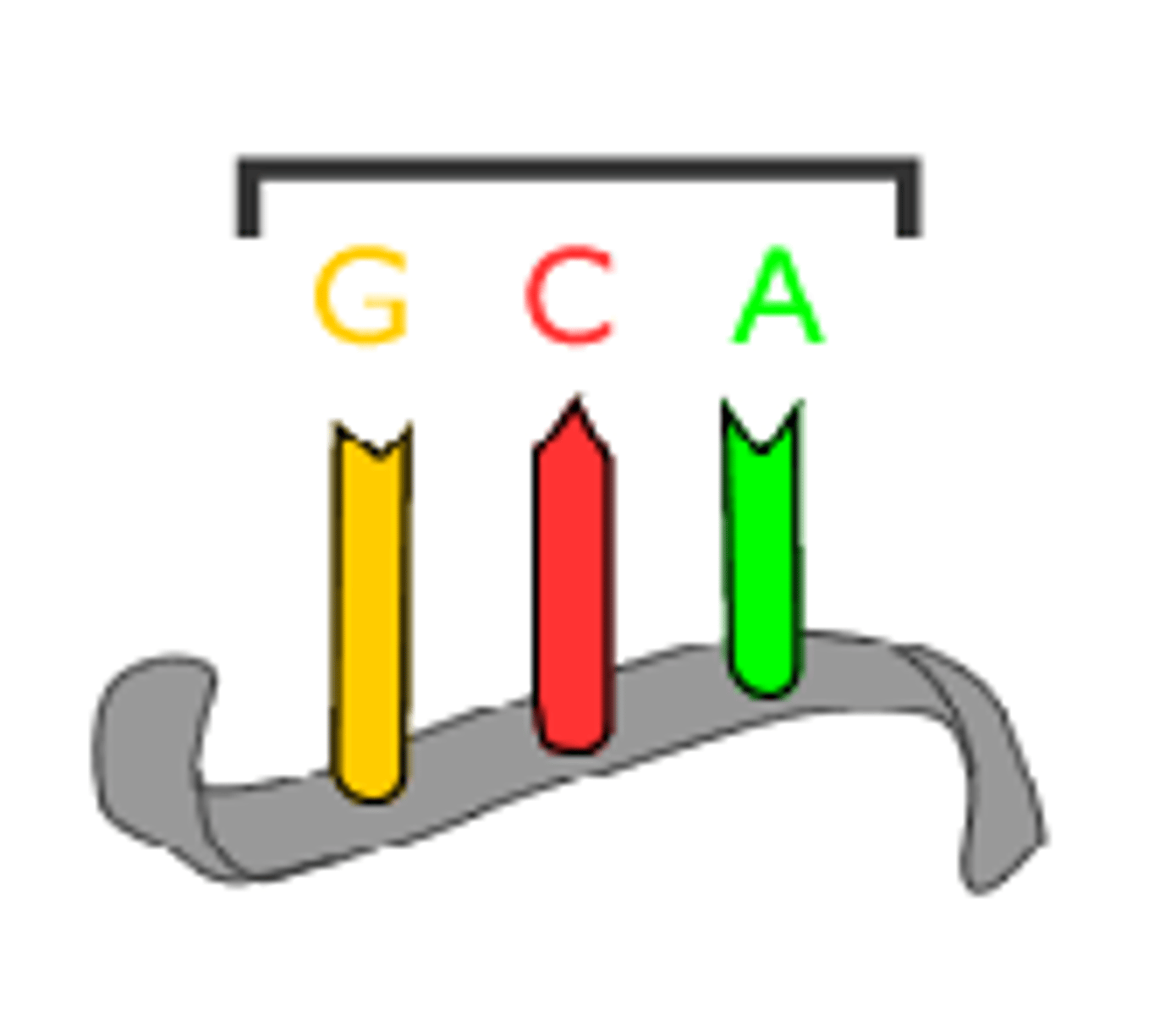
Codon
A specific sequence of three adjacent bases on a strand of DNA or RNA that provides genetic code information for a particular amino acid
Initiation
the mRNA, the tRNA, and the first amino acid all come together within the ribosome.
Elongation
a chain of amino acids grows longer and longer as more amino acids are added on.
Termination
the chain finally ends when a stop codon moves into the ribosome
start codon
codon that signals to ribosomes to begin translation; codes for the first amino acid in a protein
stop codon
codon that signals to ribosomes to stop translation

Retrovirus
An RNA virus that reproduces by transcribing its RNA into DNA and then inserting the DNA into a cellular chromosome
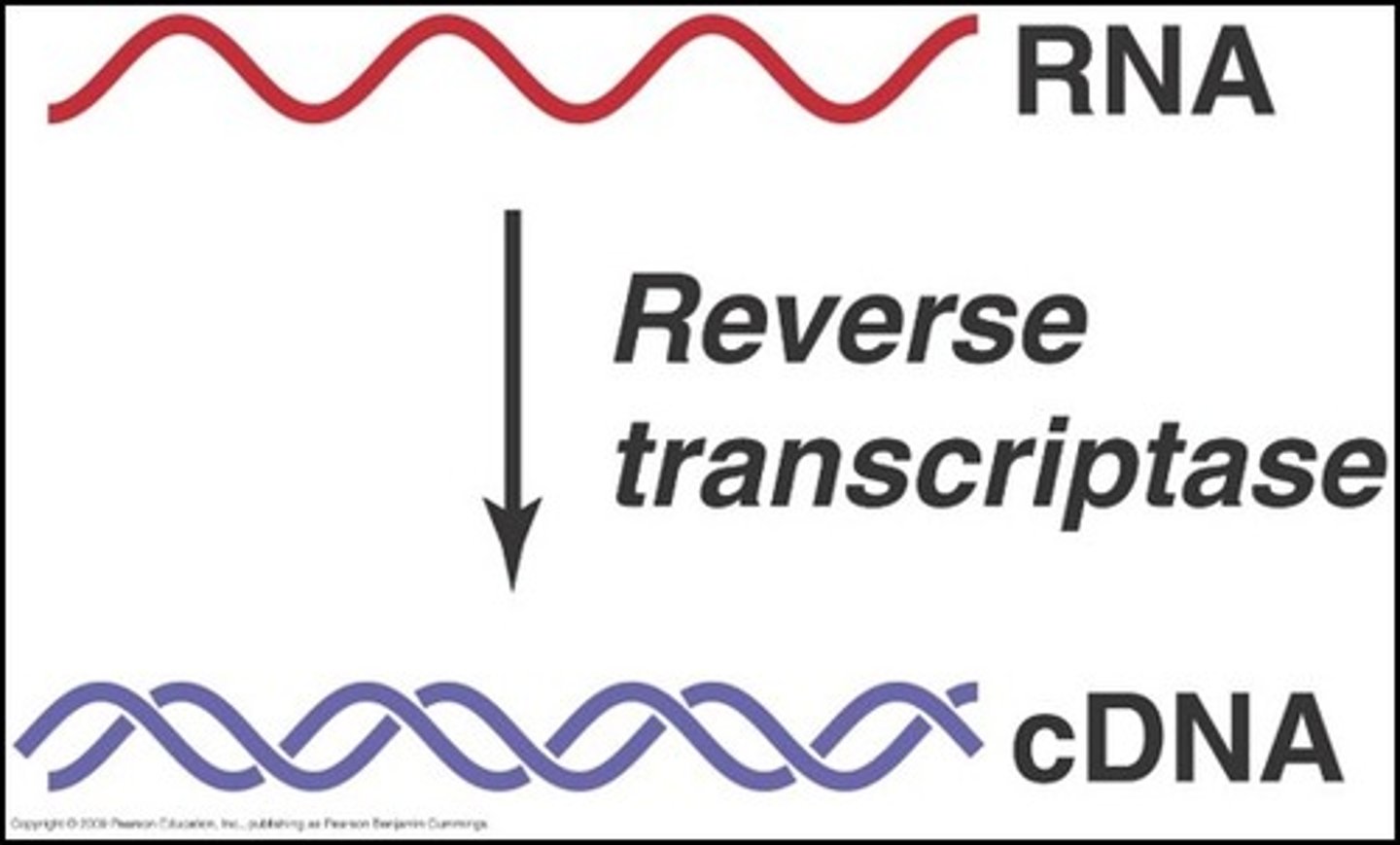
reverse transcriptase
An enzyme encoded by some certain viruses (retroviruses) that uses RNA as a template for DNA synthesis.
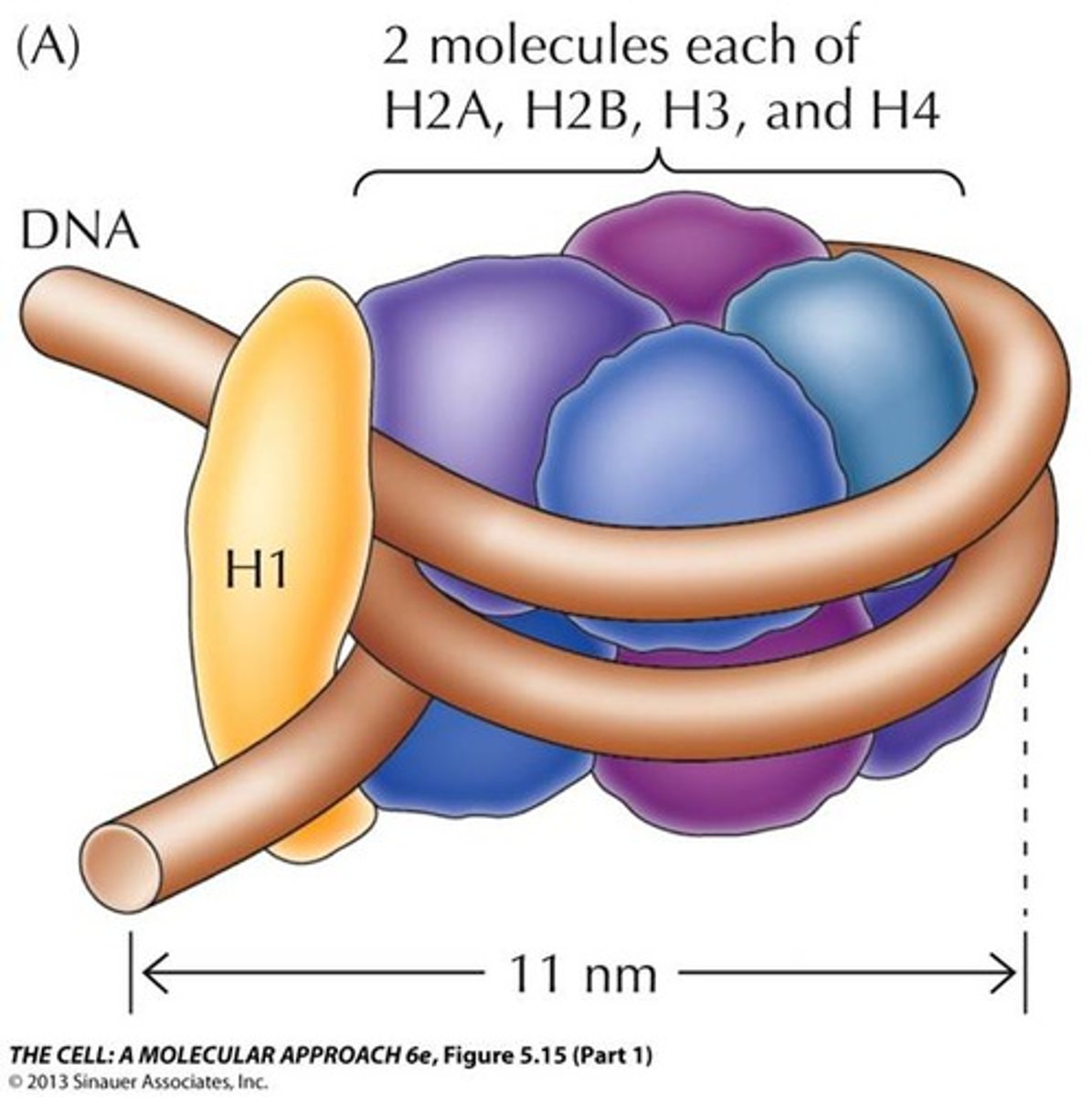
Histones
protein molecules around which DNA is tightly coiled in chromatin
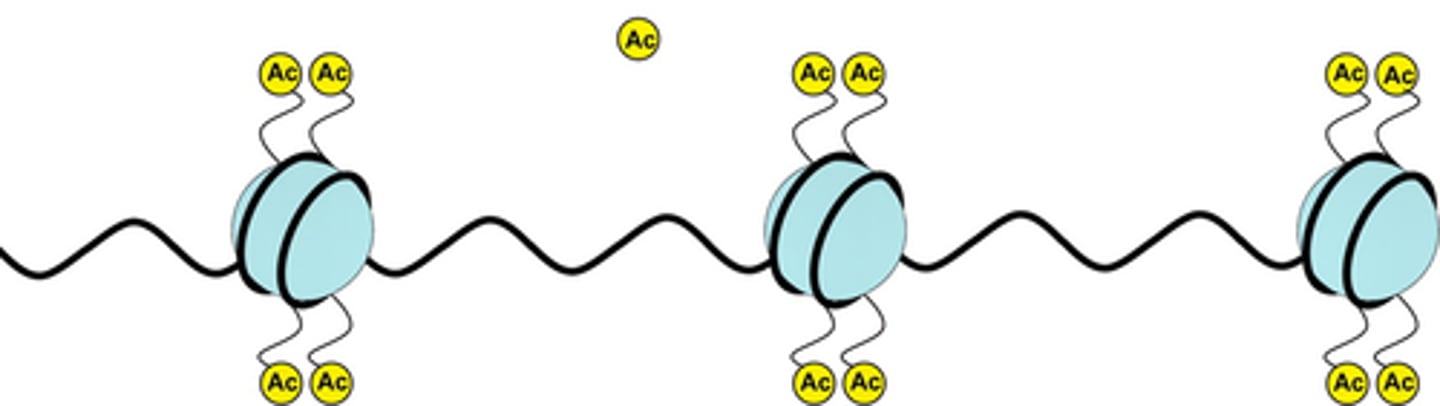
epigenetic
Referring to the effects of environmental forces on the expression of an individual's, or a species', genetic inheritance.
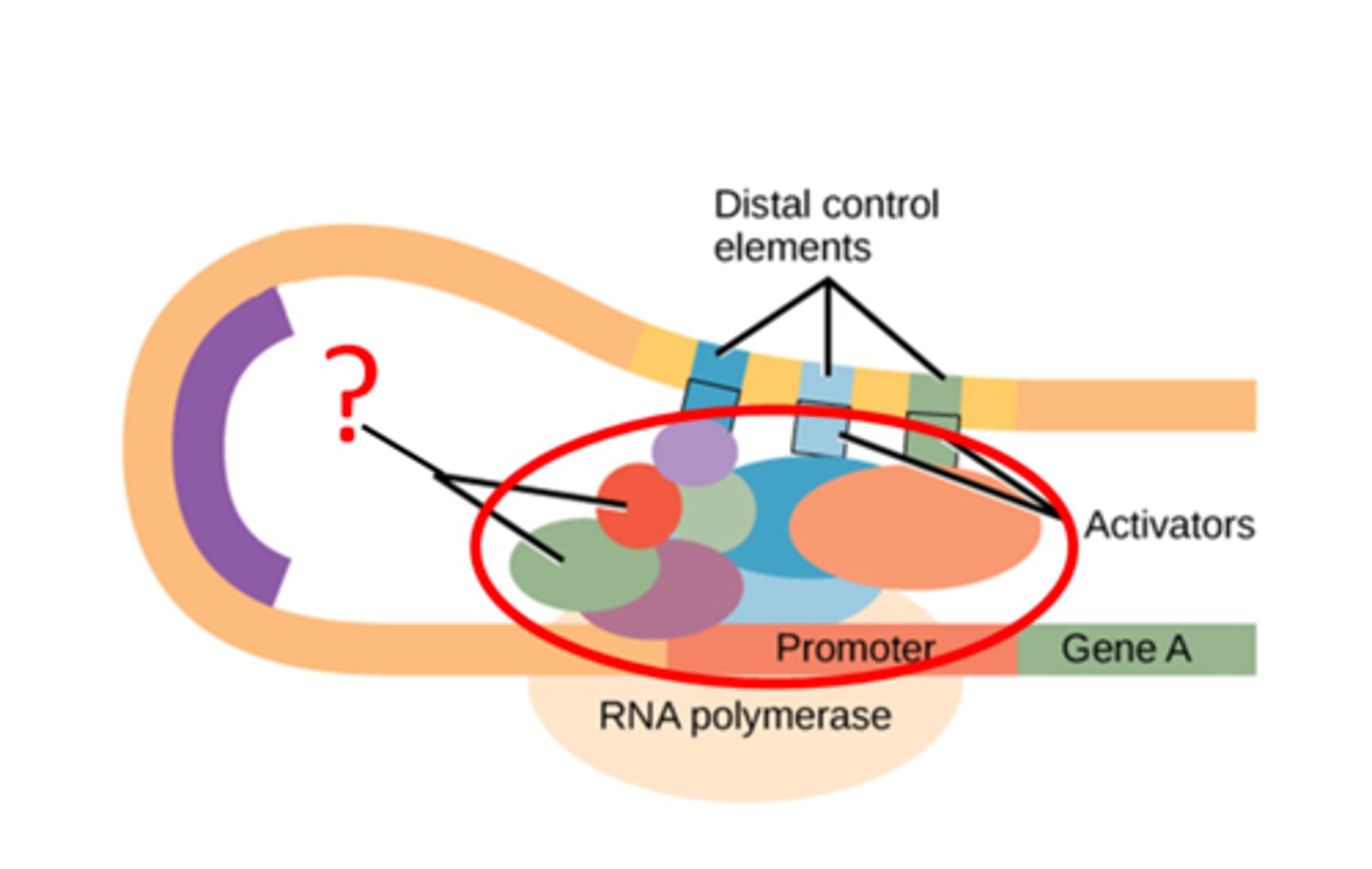
transcription factors
Collection of proteins that mediate the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription.
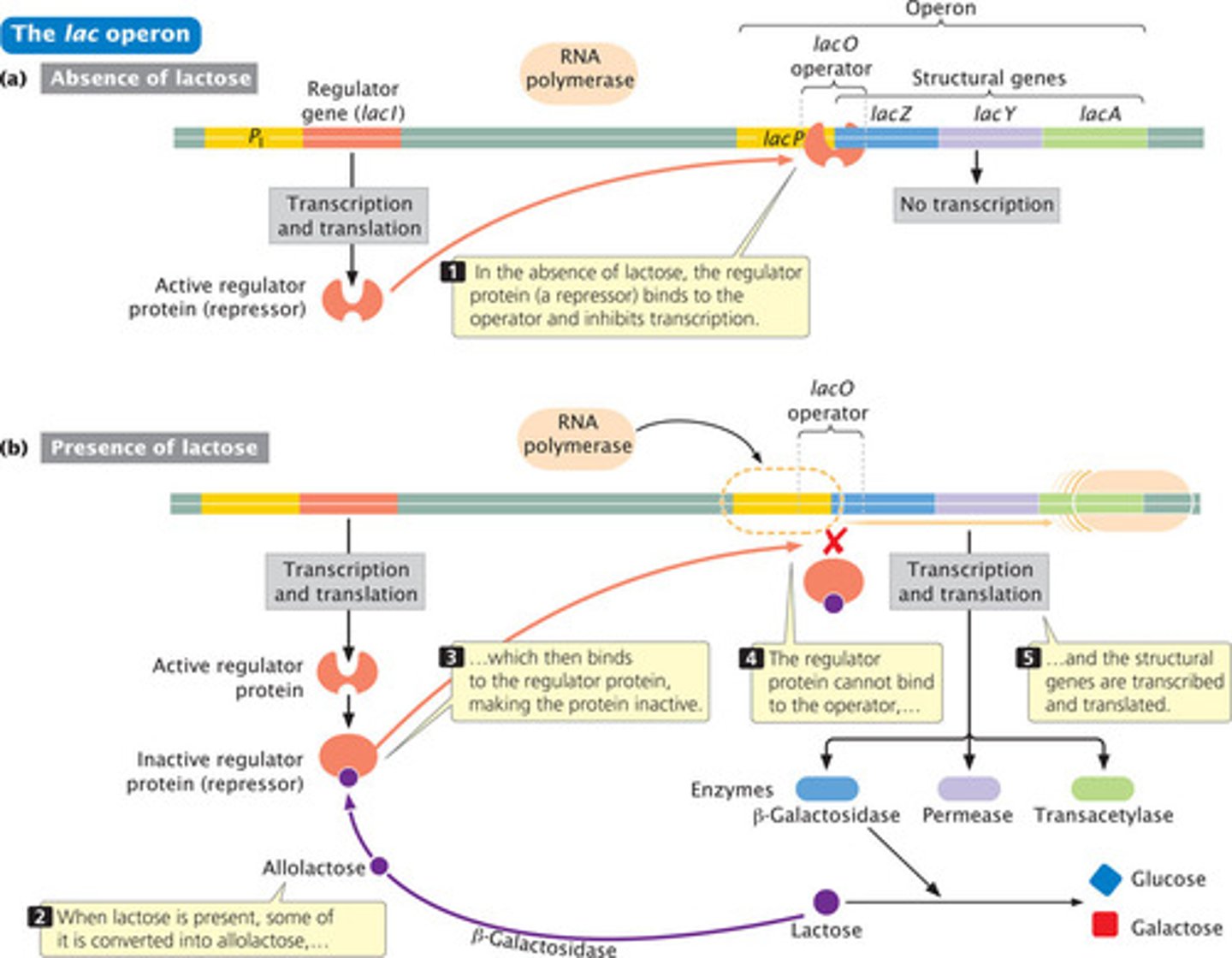
operon
group of genes operating together
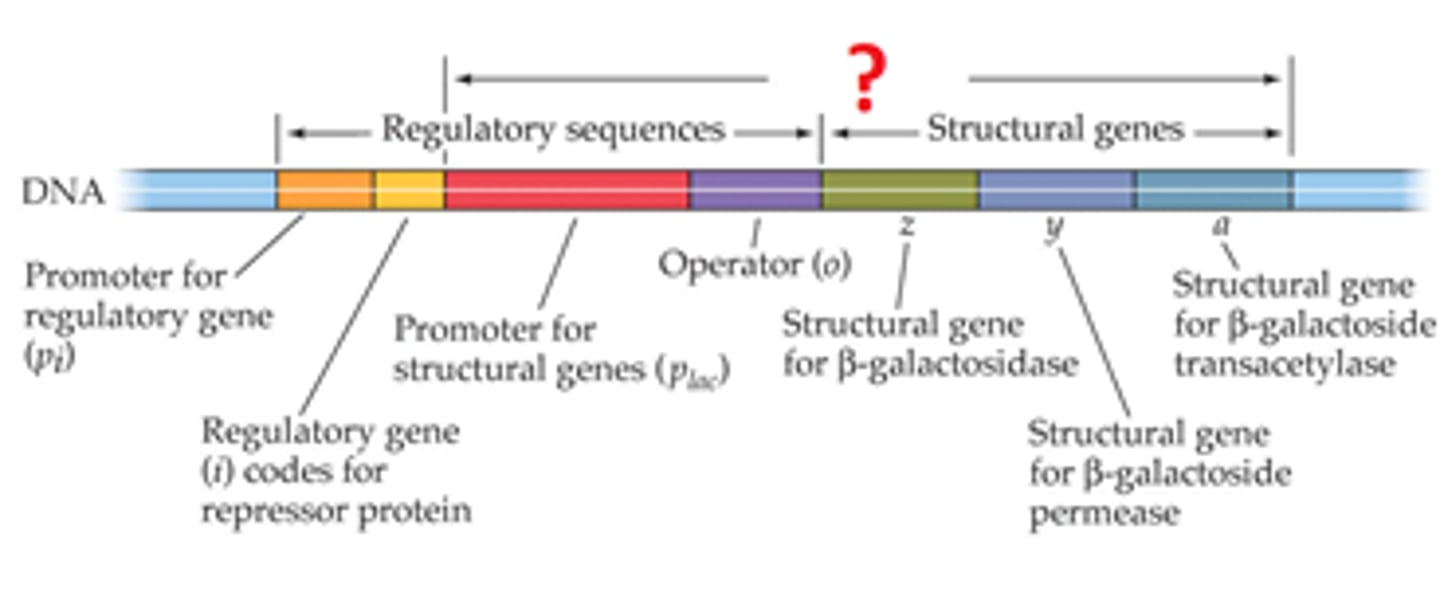
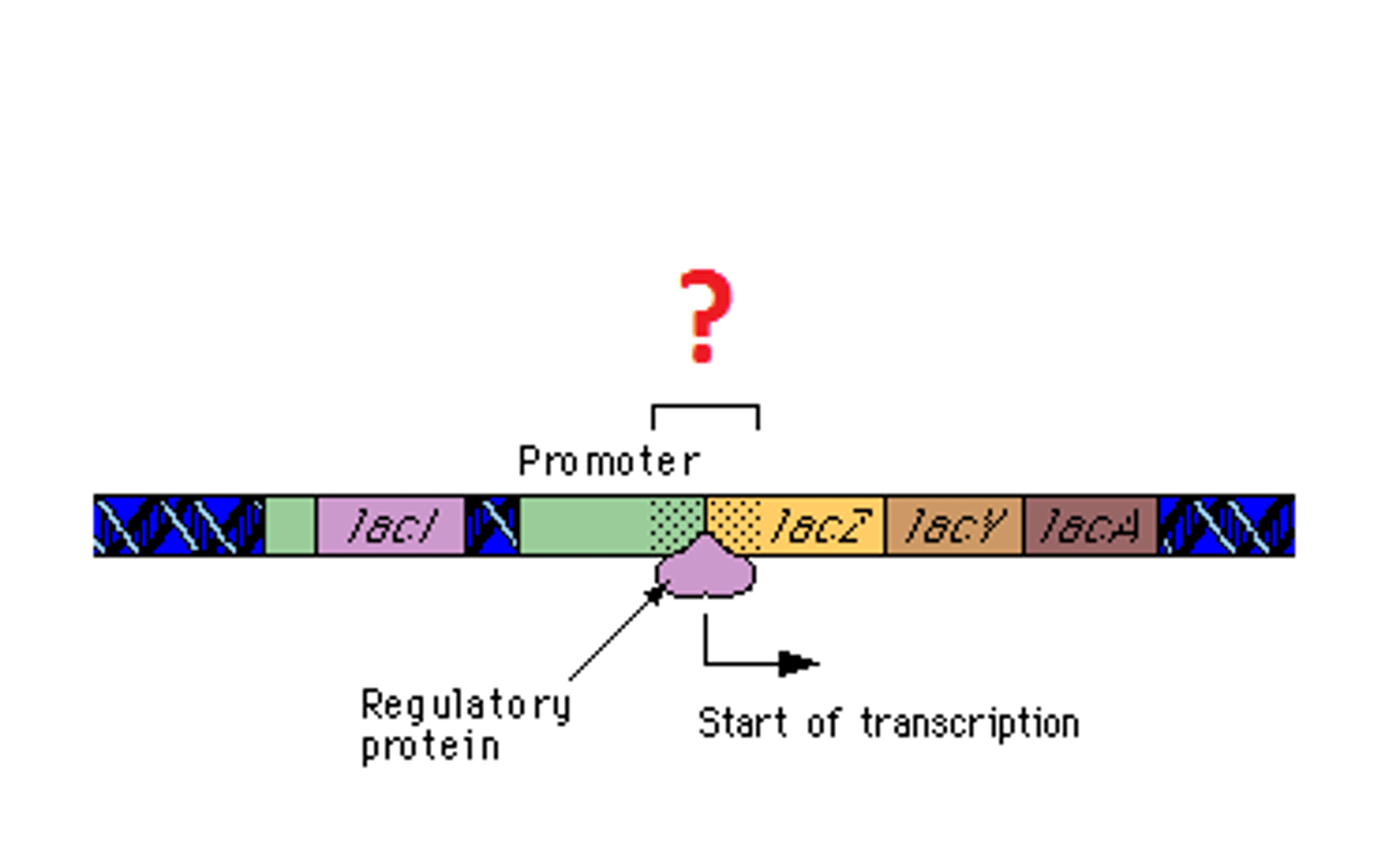
lac operon
a gene system whose operator gene and three structural genes control lactose metabolism in E. coli
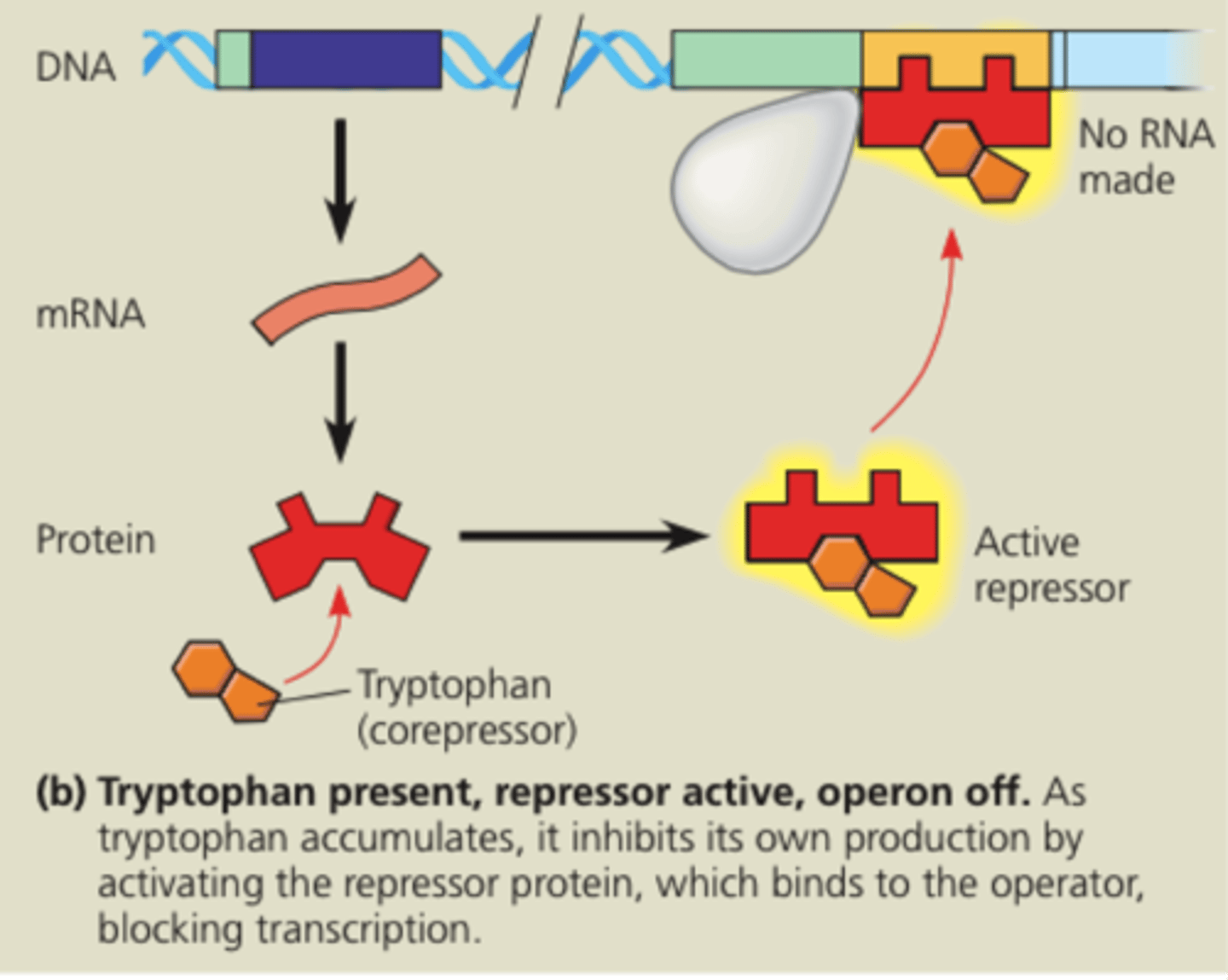
trp operon
tryptophan binds to the repressor protein and enables it to repress gene transcription.
Nucleosome
repeating subunit of chromatin fibers, consisting of DNA coiled around histones
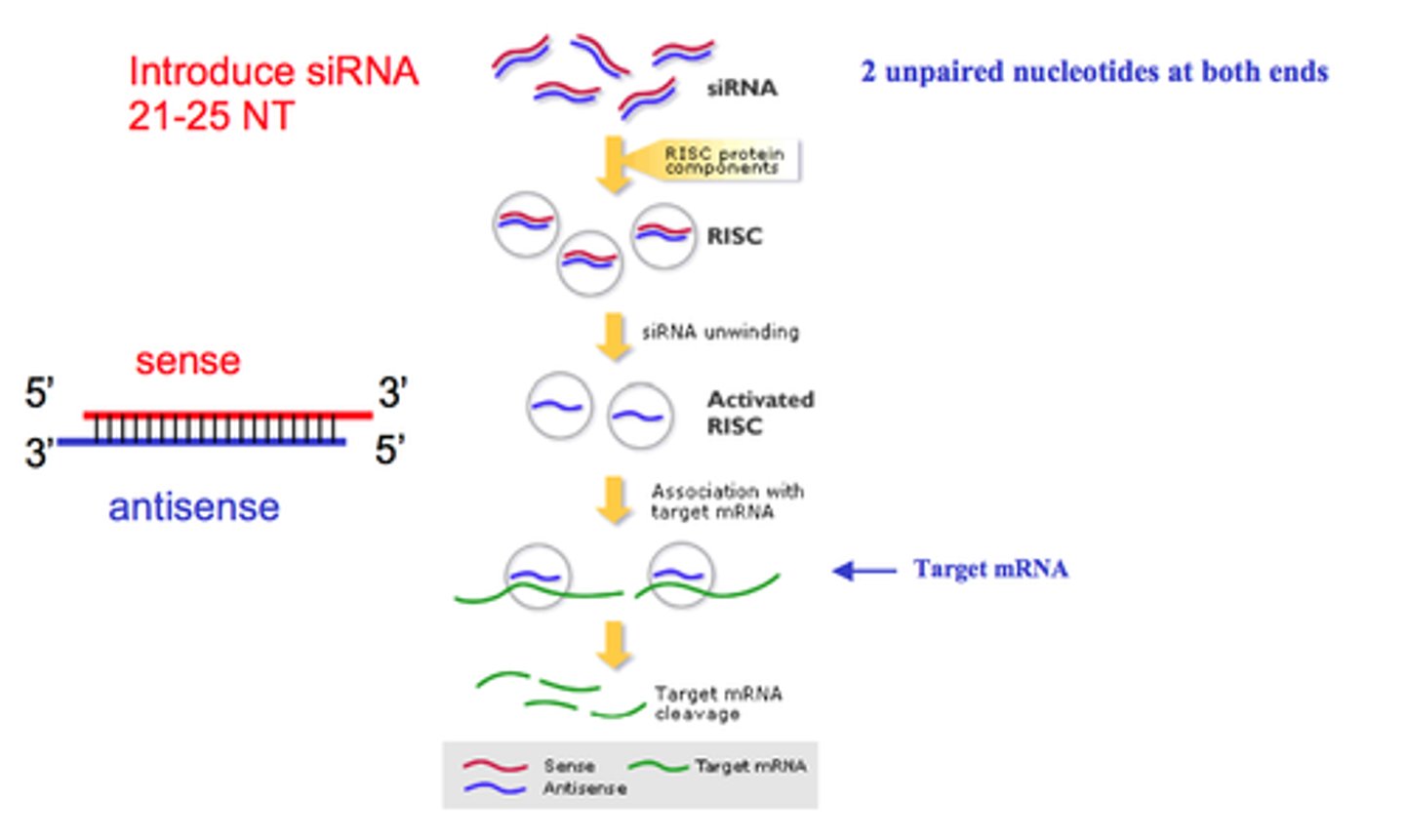
small RNAs
tiny pieces of nucleic material responsible for critical roles in regulating cell activities beyond a simple, primary protein sequence.
Promoter
specific region of a gene where RNA polymerase can bind and begin transcription
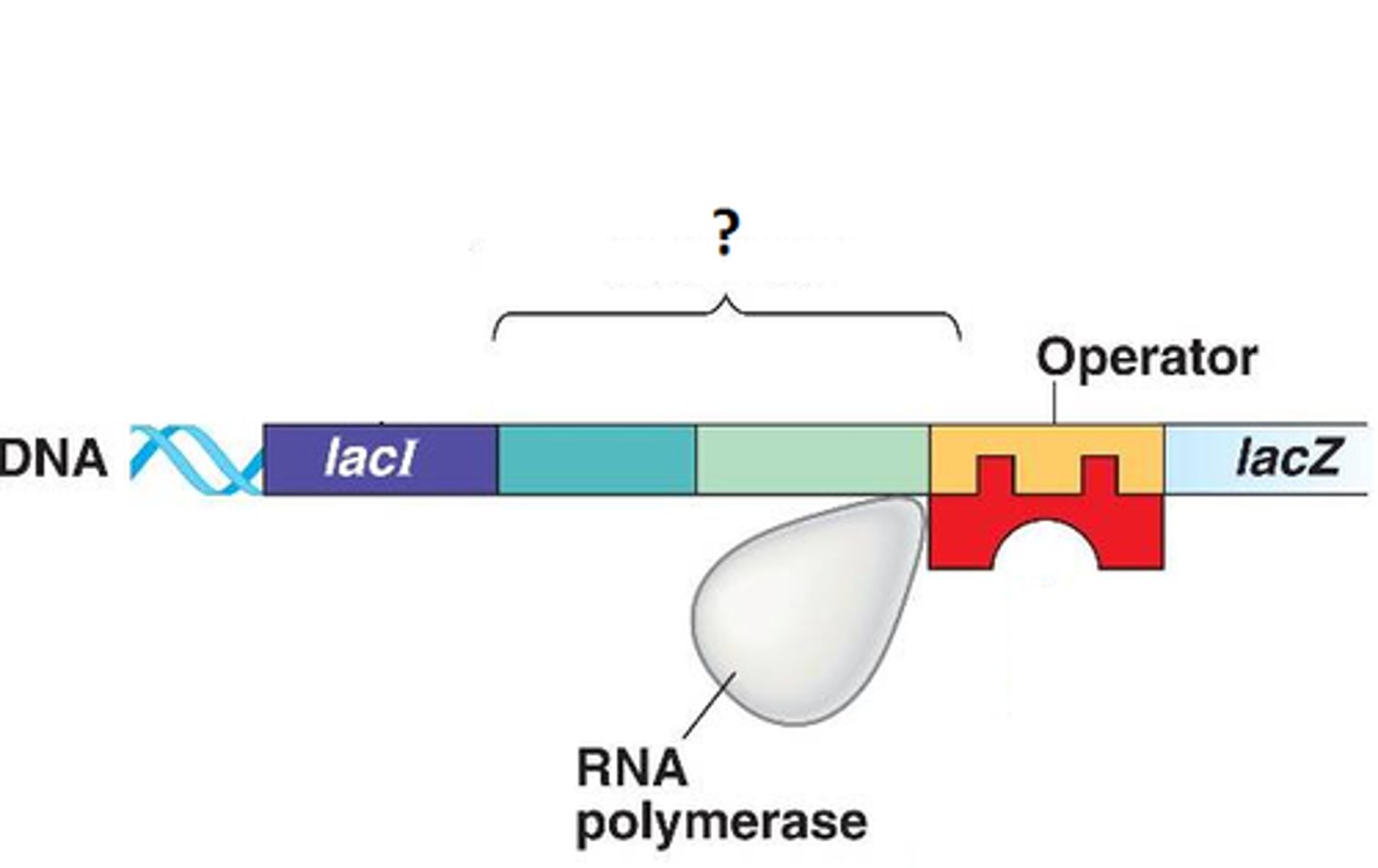
operator
Region of DNA that controls RNA polymerase's access to a set of genes with related functions.
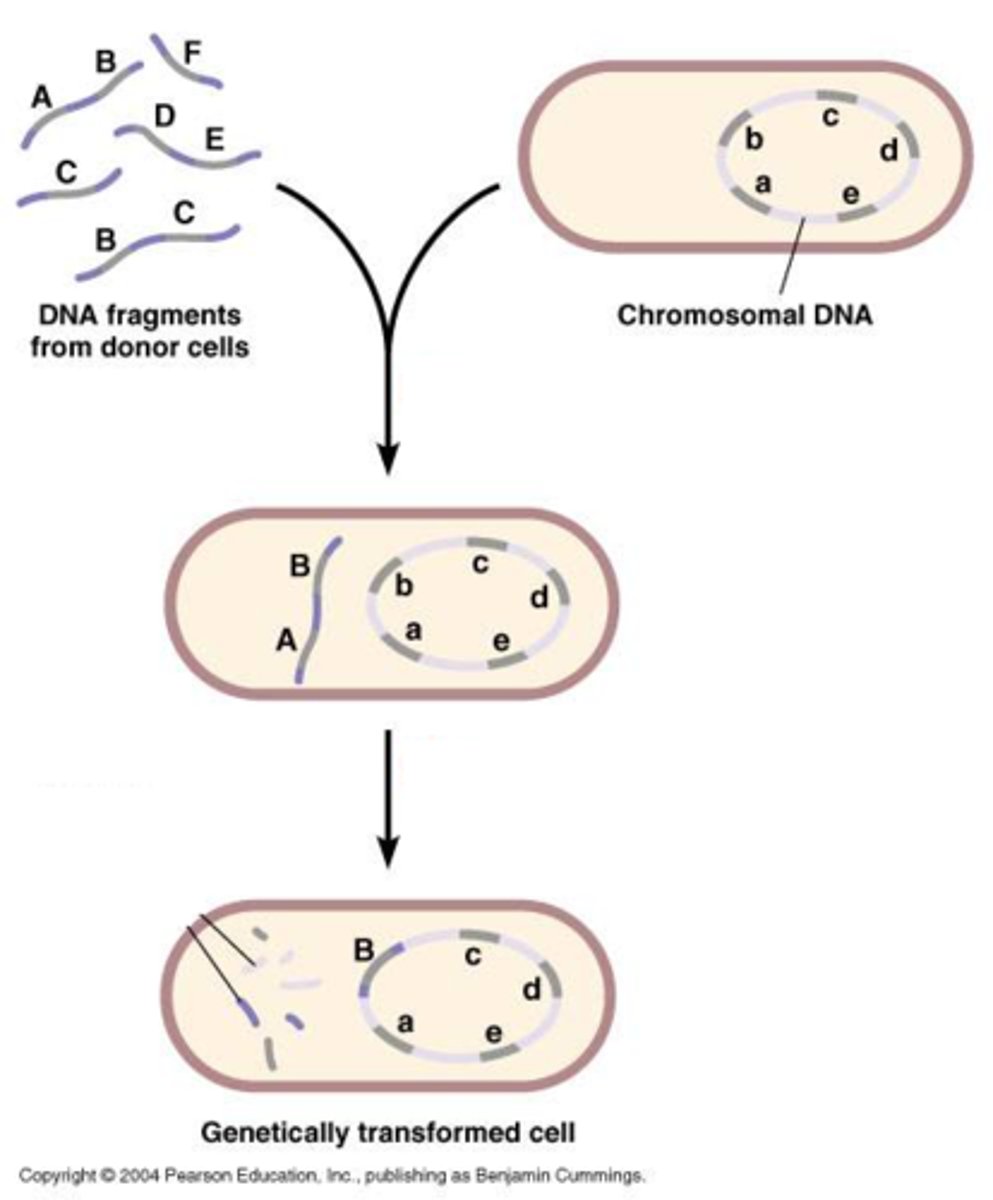
Transformation
A change in genotype and phenotype due to the assimilation of external DNA by a cell.
Transduction
DNA is transferred from one bacteria to another by a virus
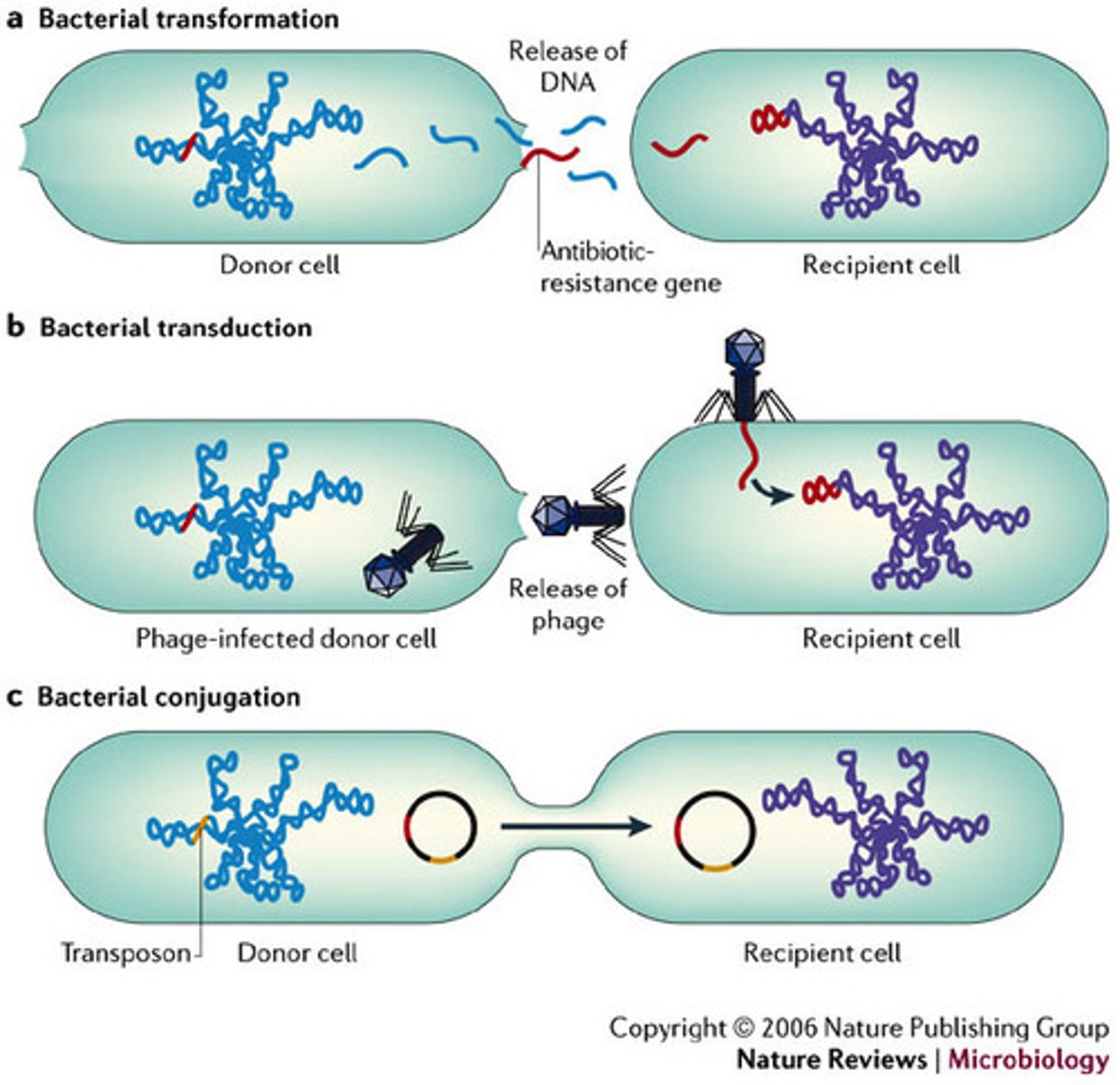
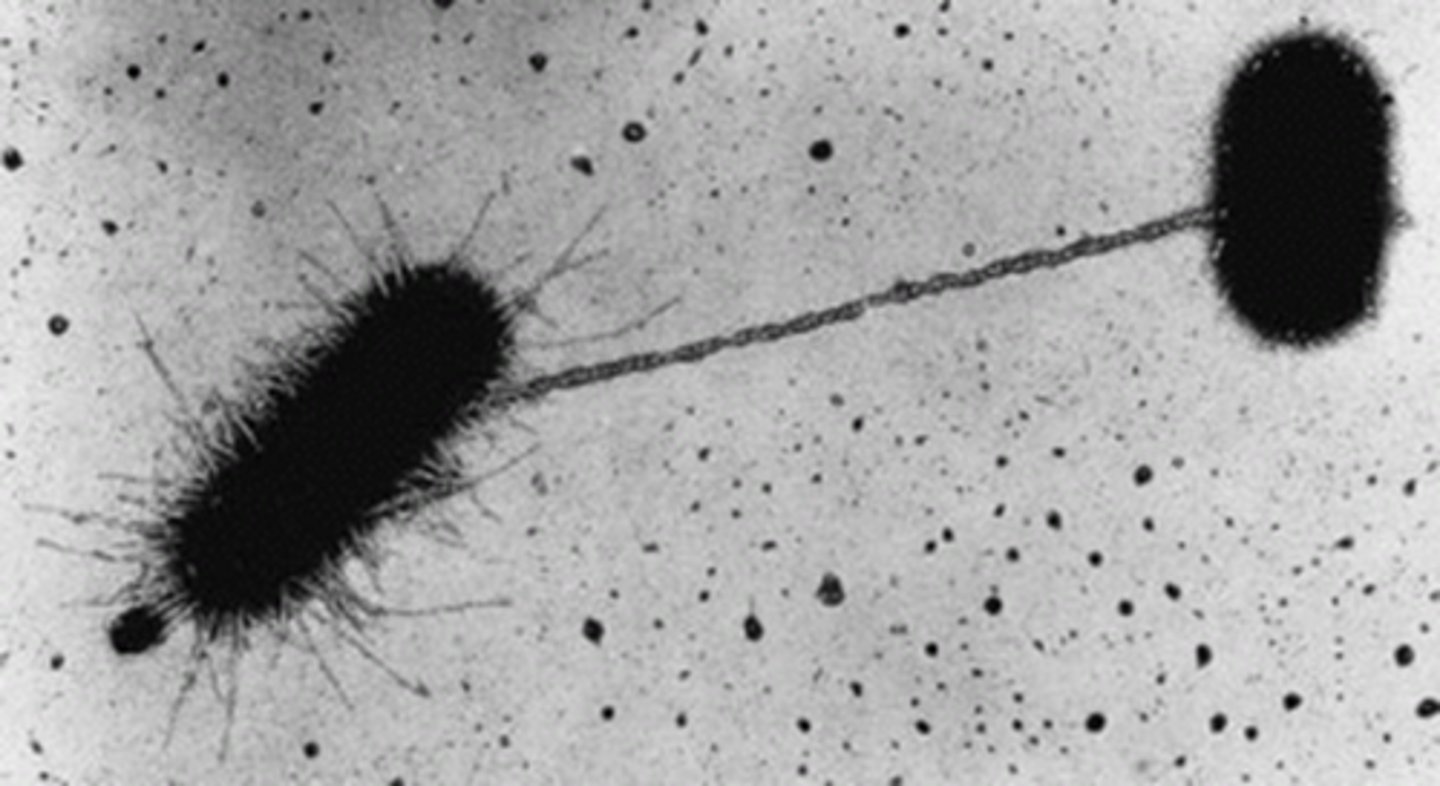
Conjugation
In bacteria, the direct transfer of DNA between two cells that are temporarily joined.
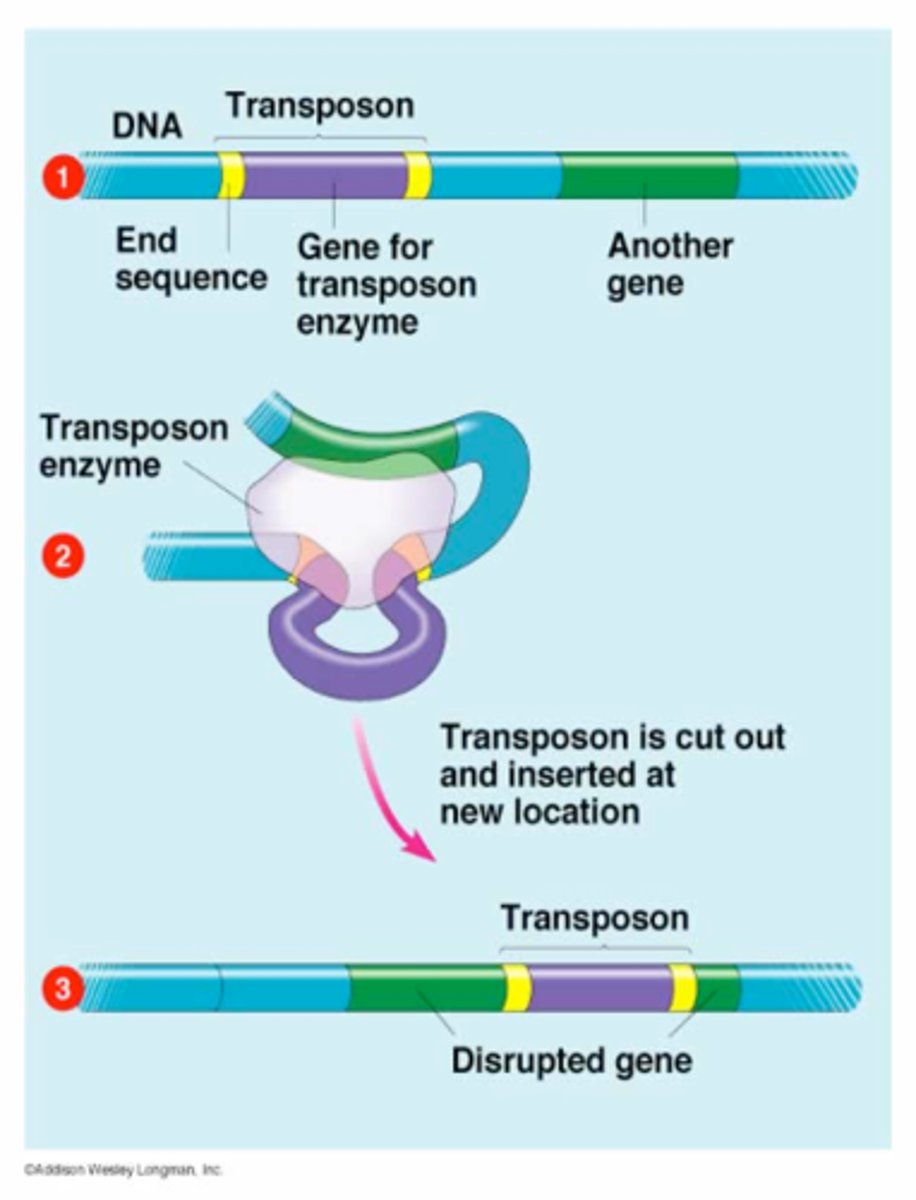
Transposition in bacteria
segment of DNA that can "jump" genome locations, can transfer genes to/from plasmid/chromosome
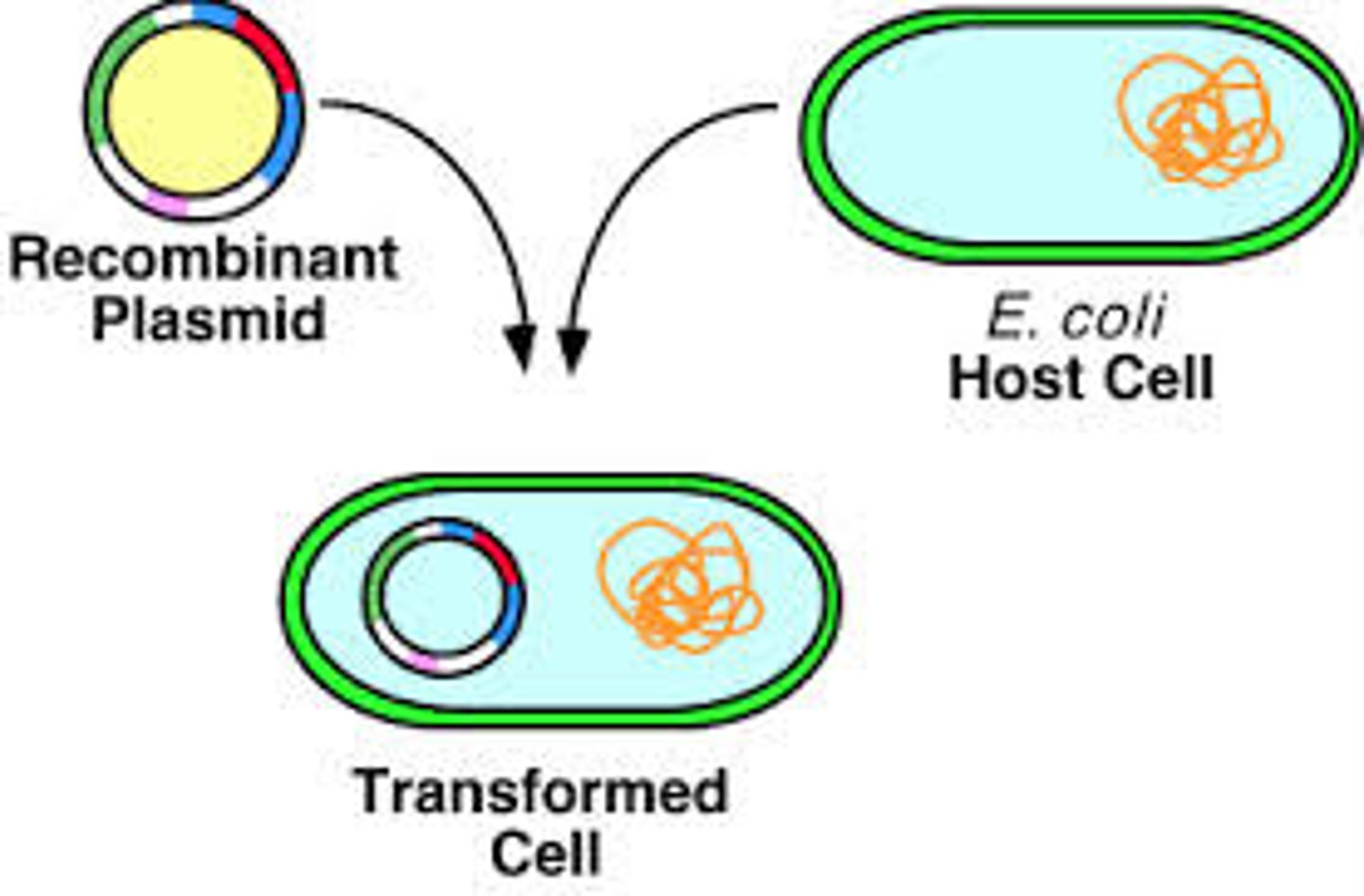
Recombinant DNA
DNA produced by combining DNA from different sources
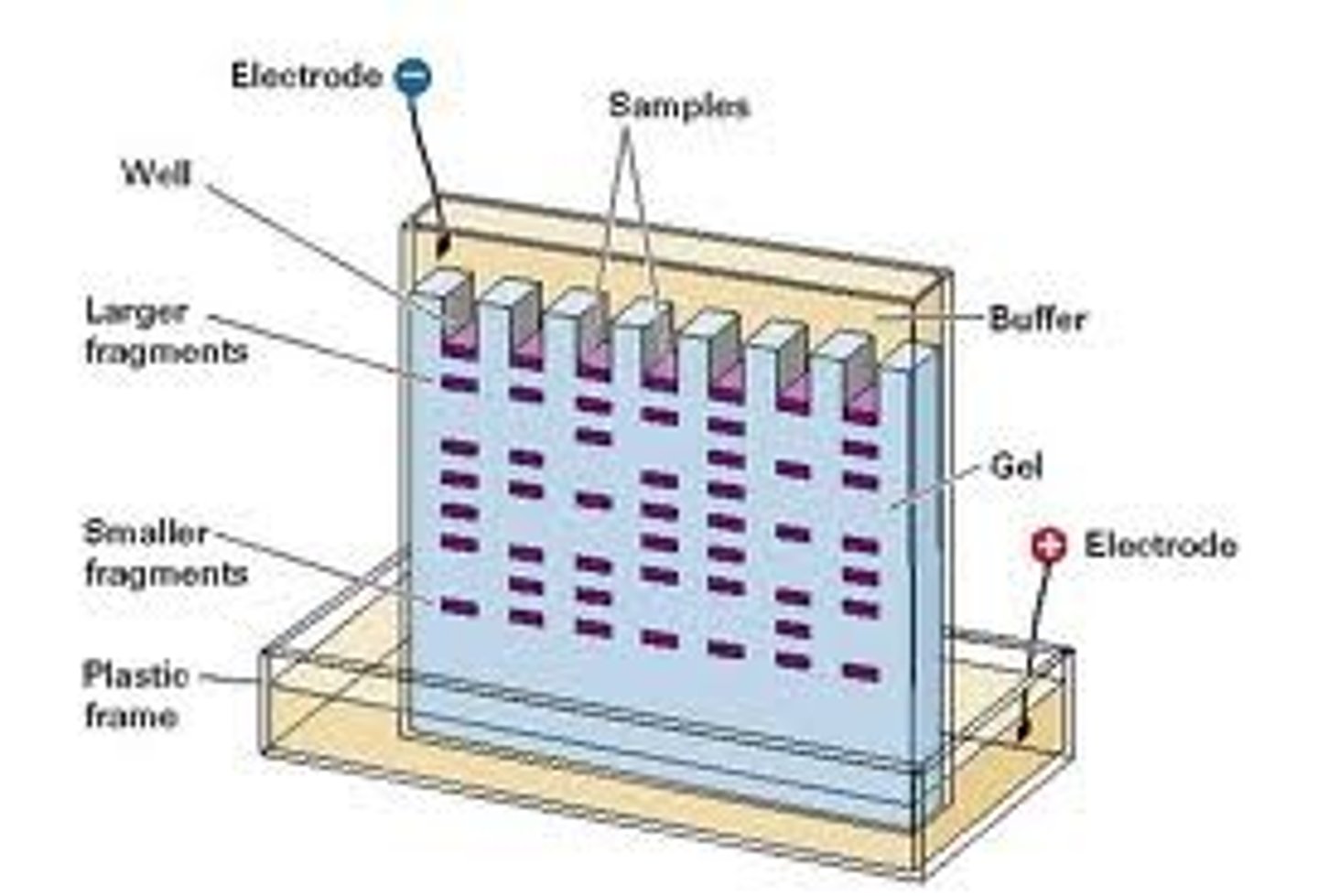
Electrophoresis
A process where DNA fragments are separated according to size using electrical charges
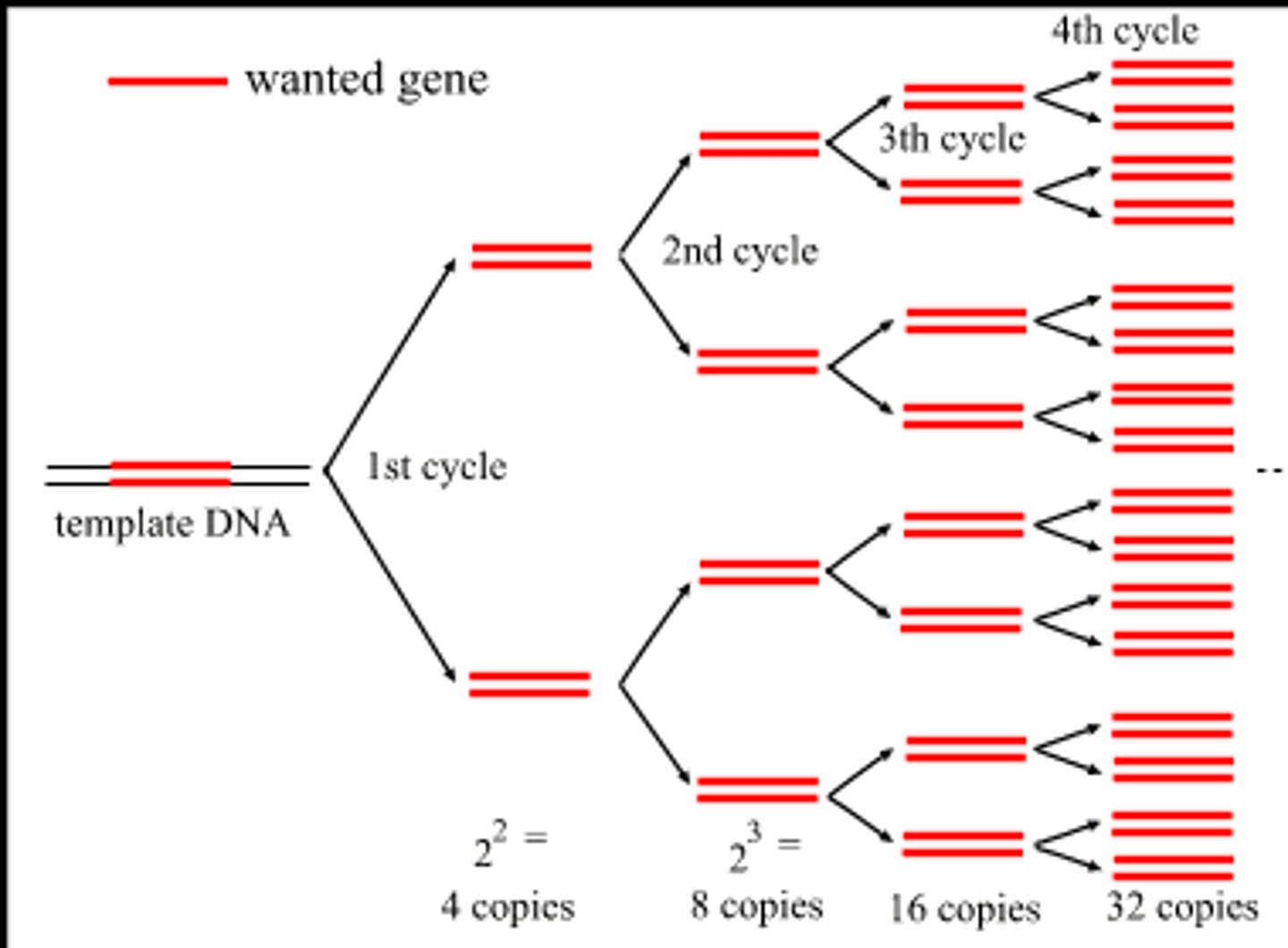
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
technique that allows molecular biologists to make many copies of a particular gene
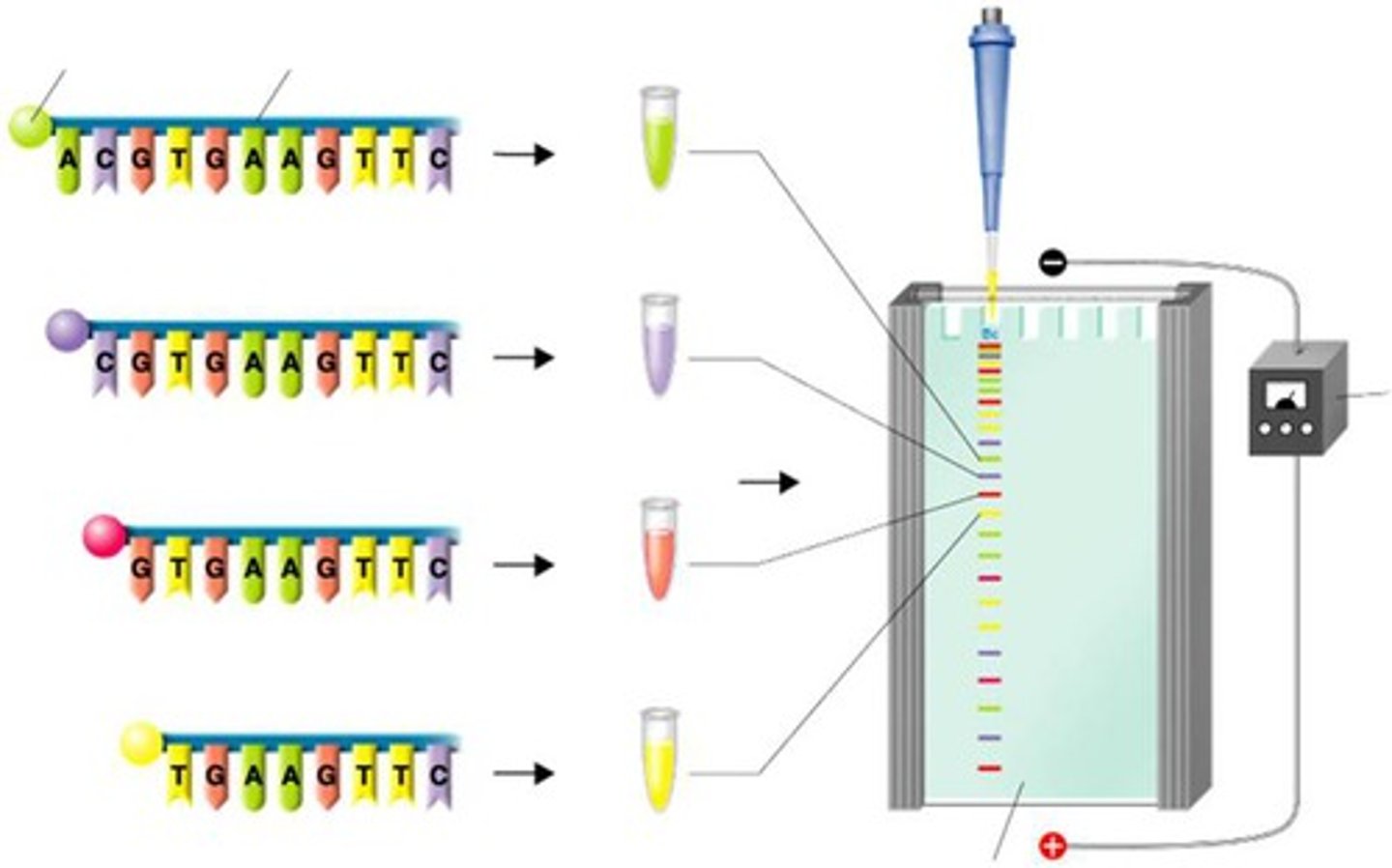
DNA sequencing
Determining the exact order of the base pairs in a segment of DNA.
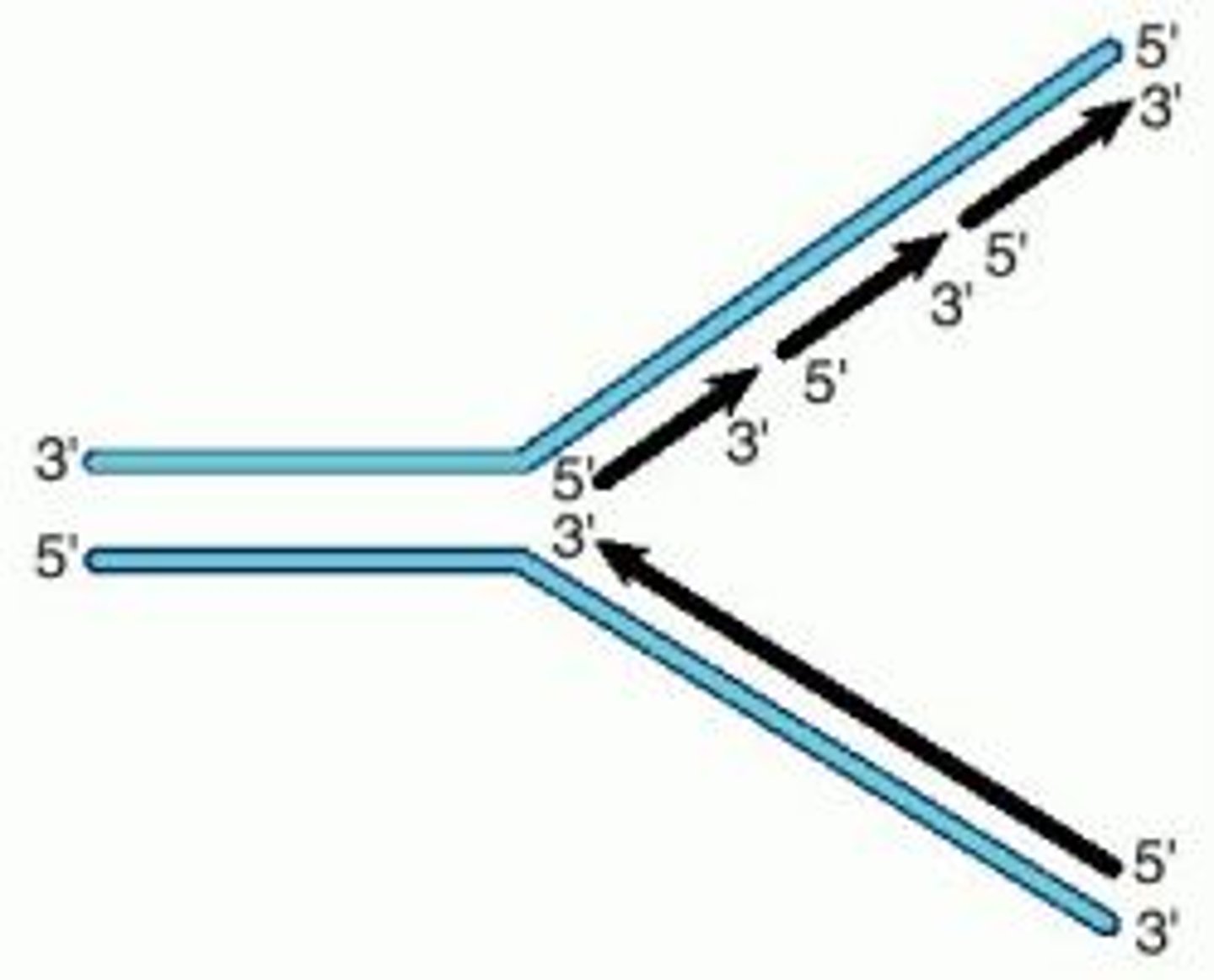
replication fork
A Y-shaped region on a replicating DNA molecule where new strands are growing.
Primase
An enzyme that joins RNA nucleotides to make the primer using the parental DNA strand as a template.