KIN 312 Midterm
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Winter 2025 with Bill McIlroy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Neurological Disorder
a disease or injury to the central or peripheral NS which could include:
brain or brainstem
spinal cord
peripheral nerves
neuromuscular junctions
Neurological disorders may be the result of:
injury/trauma/autoimmunity
structural abnormalities
biochemical imbalances
electrical conduction/impulse problems
Levels of Burden
there are 4 main ones
financial
health care
personal
caregiver
Financial Burden
cost of treatment
loss of work potential
assistance cost
ODSP (disability)
Health Care Burden
time it takes to diagnose
diagnostic/personnel resources
long term medical needs (e.g. infrastructure)
Personal Burden
losing years of healthy living
impairment
functional limitation
disability
financial
mental health
Caregiver Burden
physical, mental, emotional burden
financial/work impact
social disengagement
Prevalence
proportion of people who have X condition at a specific point in time (e.g. everyone who has it right now)
Incidence
the rate or proportion of people who will develop condition X during a particular time period (e.g. stroke is 0.14% per year)
Control of Movement
it is the process by which the human nervous system controls muscles to produce movement
interactions of muscles, joints, NS
needs planning, coordination, action, feedback, and adaptation
requires the control of posture from many systems and many levels in the CNS
Criteria of Healthy Movement
successful in space and time
smooth and coordinated
efficient (minimal energy needed)
adaptable
avoid injury
Postural Control in Movement
movement often have a clear purpose
some muscles contribute directly to the purpose
postural muscles are needed to control body position and stability
Adaptability
real capacity of the healthy motor control system to adapt to environmental demands
quick for solving immediate challenges (min or less)
long-term adaptations like learning a new skill (hours to months)
Building Blocks of NS
neurons and glial cells linked together in an organized manor needed for sensation, movement, cognition, regulating body systems
Neuron
for structure and for function, specialized for rapid communication
cell body with dendrites
axon and axon terminals (tracts in CNS, nerves in PNS)
dendrites for input
axon hillock for firing
myelin sheath for insulation and conduction (schwann cells in PNS, oligodendrocytes in CNS)
Functional Classification of Neurons
sensory (afferent): input from special endings to sense stimuli → output to neuron
motor (efferent): input from neuron → output to muscle
interneuron: input from neuron → output to neuron
Neuroglia
used for:
physical support
regulation (growth, development, repair, metabolic support)
insulation - myelin
homeostasis - nutrients, O2, chemical gradients
pathogen removal
synaptogenesis and plasticity
CNS Neuroglia
astrocytes (regulation of neuronal excitability, homeostasis, repair + plasticity)
oligodendrocytes (myelinated and insulate + propagate signals)
PNS Neuroglia
Schwann cells (glial cells that make myelin for a single neuron)
satellite cells (non-myelinating cells that make a supportive capsule around nerve soma in the ganglia)
Saltatory Conduction (within neuron)
myelin sheath on axon doesn’t have ion pumps or channels; nodes of Ranvier have concentrated Na/K pump and channels
action potential jumps between nodes and refreshes after the jump because of voltage decay
without myelin the signal wouldn’t go through even with firing → nerve block
Conducting Information Between Neurons
synaptic transmission (chemical signals)
action potential at synapse → calcium channels open + enters cell → vesicles release neurotransmitter into synapse → neurotransmitter reaches post-synaptic cell
CNS Terminology
nuclei - bundle of cell bodies
tract - bundle of axons that connect nuclei
cell bodies - grey matter (unmyelinated)
axons - white matter (myelinated)
Spinal Cord
entry + exit to PNS with ascending (towards brain) and descending (away from brain) fibre tracts
interneurons - found in spinal cord and brain to relay signals between sensory and motor nerves
cervical spinal cord - 7 vertebrae, 8 spinal nerves
thoracic spinal cord - 12 vertebrae, 12 spinal nerves
lumbar spine - 5 vertebrae, 5 spinal nerves, conus medularis
sacral spine - 5 fused segments, 5 spinal nerve roots
Basal Ganglia
group of subcortical nuclei that is connected to cortex, thalamus, and brain stem
includes:
putamen
caudate
globus pallidus
subthalamic nucleus
substantia nigra
controls action selection and procedural learning and plays a role in cognition and emotions
Cerebral Cortex
frontal lobe - decision-making, attention + impulse control, action selection, motor control
parietal lobe - somatosensory processing, visuospatial map → primary somatosensory cortex, motor control
temporal lobe - memory, auditory and language processing, emotions → primary auditory cortex
occipital lobe - visual processing → primary visual cortex
Functional Division of NS
somatic NS - afferent and efferent nerves
Structural Division of NS
autonomic - sympathetic (fight or flight) and parasympathetic (rest and digest) systems
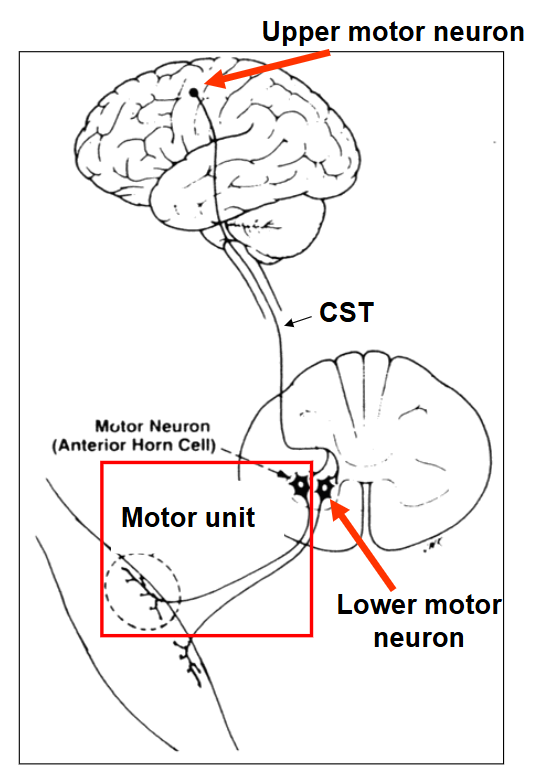
Motor Unit
consists of the alpha motor neuron and all of the muscle cells it connects to
motor neuron - nerve that activates muscle fibres (damage here allows for neurogenesis)
all or none rule applies here and more motor units recruited = bigger contraction
Upper Motor Neuron
cell body in cortex, synapses onto motor neuron
axon travels in the corticospinal tract to synapse on lower motor neuron
Lower Motor Neuron
cell body in spinal cord or brain stem and has axon that directly innervates muscle fibres
Akinesia
inability to initaite movement
dyskinesia
abnormal movement. difficulty controlling movement
Hypokinesia
decreased or weirdly diminished movements
Hyperkinesia
exaggerated or increase in movement
Bradykinesia
abnormal slowness of movement (note the difference between abnormal and compensatory)
Types of Hyperkinesia
could also be categorized as dyskinesias
chorea: ongoing, brief, irregular, asymmetrical, involuntary movement (looks dance-like, discussed in Huntington’s)
athetosis: slow continuous writhing/wringing that often involves distal limbs (e.g. hands and feet)
tics: sudden. repetitive, non-rhythmic, stereotyped movement including vocalizations
myoclonus: sequence of repeated, brief, involuntary shock-like jerks from involuntary muscle contraction/relaxation
Reflexes
hyperreflexia: exaggerated reflexes
hyporeflexia: diminished reflexes
areflexia: no reflexes
note: you can have akinesia but not areflexia and vice versa because reflexes are INvoluntary
Dystonia
abnormal muscle tone
symptoms: sustained contractions causing twisting, repetitive movements, abnormal posture
Hypertonia
abnormal increase in muscle tension at rest and reduced ability of a muscle to be stretched
spasticity
Hypotonia
abnormal decrease in muscle tone at rest - less muscle resistance
NOT the same as muscle weakness
Spasticity
excessive muscle tone whose magnitude is dependent on passive stretch velocity
Clonus
series of involuntary contractions from sudden stretching of the muscle (involuntary resistance when stretched) - common in ankle
form of hypertonia and hyperreflexia
Contractures
permanent shortening of muscle/tendon due to excessive tone
form of hypertonia
Hemiplegia
paralysis of one side of body
Paraplegia
paralysis of LOWER limbs
Quadriplegia/Tetraplegia
paralysis of four limbs
Hemiparesis
weakness on one side of body - affects ability to generate force
common symptom of stroke
Myopathy
muscular disease caused by primary defect within the muscle
could be neuromuscular or musculoskeletal
Neuropathy
damage to PNS like in sensory, motor, and/or autonomic fibres
Paresthesia
sensation of tingling, prickling, or numbness of skin (basically abnormal sensation)
Ataxia
lack of order of movement (coordination), movements characterized by discoordination that is not explained by loss of sensation or weakness
Apraxia
inability to do learned purposeful movements (work) that is not explained by loss of sensation, weakness, or coordination
basically can’t execute an intended, voluntary behaviour
Components of a Neurological Assessment
a combination of:
subjective report (what’s going on)
mental status/screening questions
objective exam
lab testing (blood work e.g.)
neuroimaging
electrophysical testing
Objective Assessment: Sensation
used to determine the type and location of sensory impairment
usually starts with a screen with multiple modalities - light touch, pain (sharp/dull) or temperature (hot/cold), proprioception (sense of body position) or vibration
dermatomal testing
area of skin supplied by a single nerve root tested to where the impairment comes from
Myotome Testing
a muscle/group of muscles supplied by a single nerve root
single nerve root lesion is usually associated with paresis of the myotome supplied by that nerve root