Mitosis and Meiosis
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
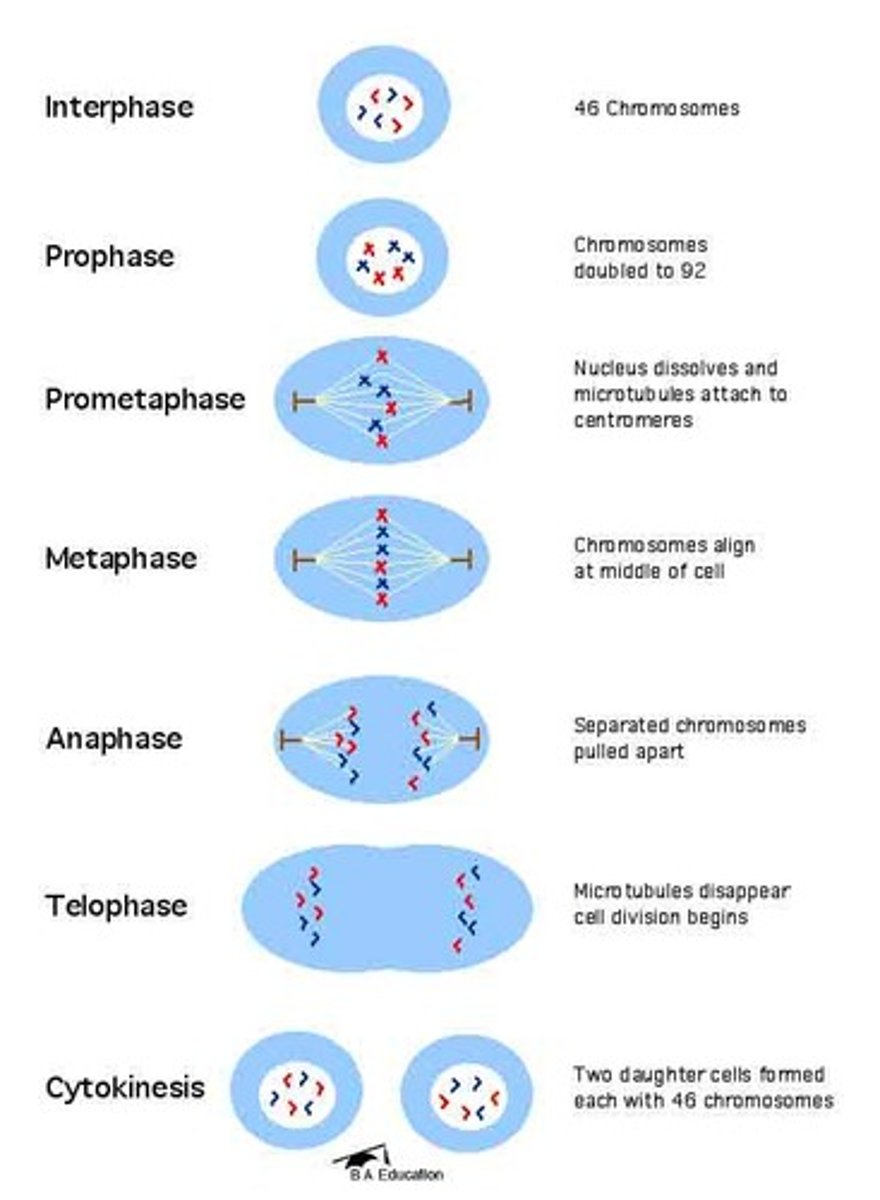
Mitosis
cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
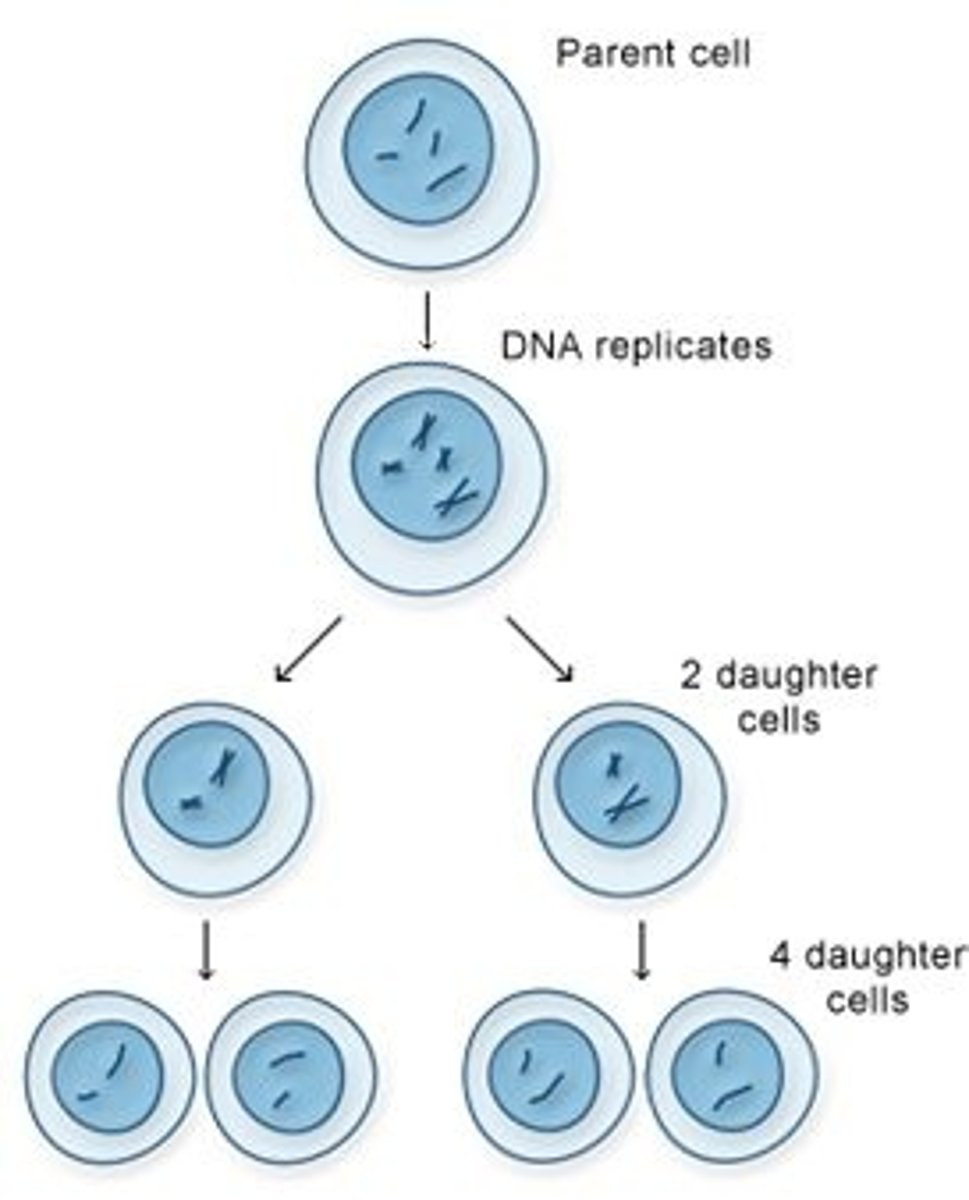
Meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
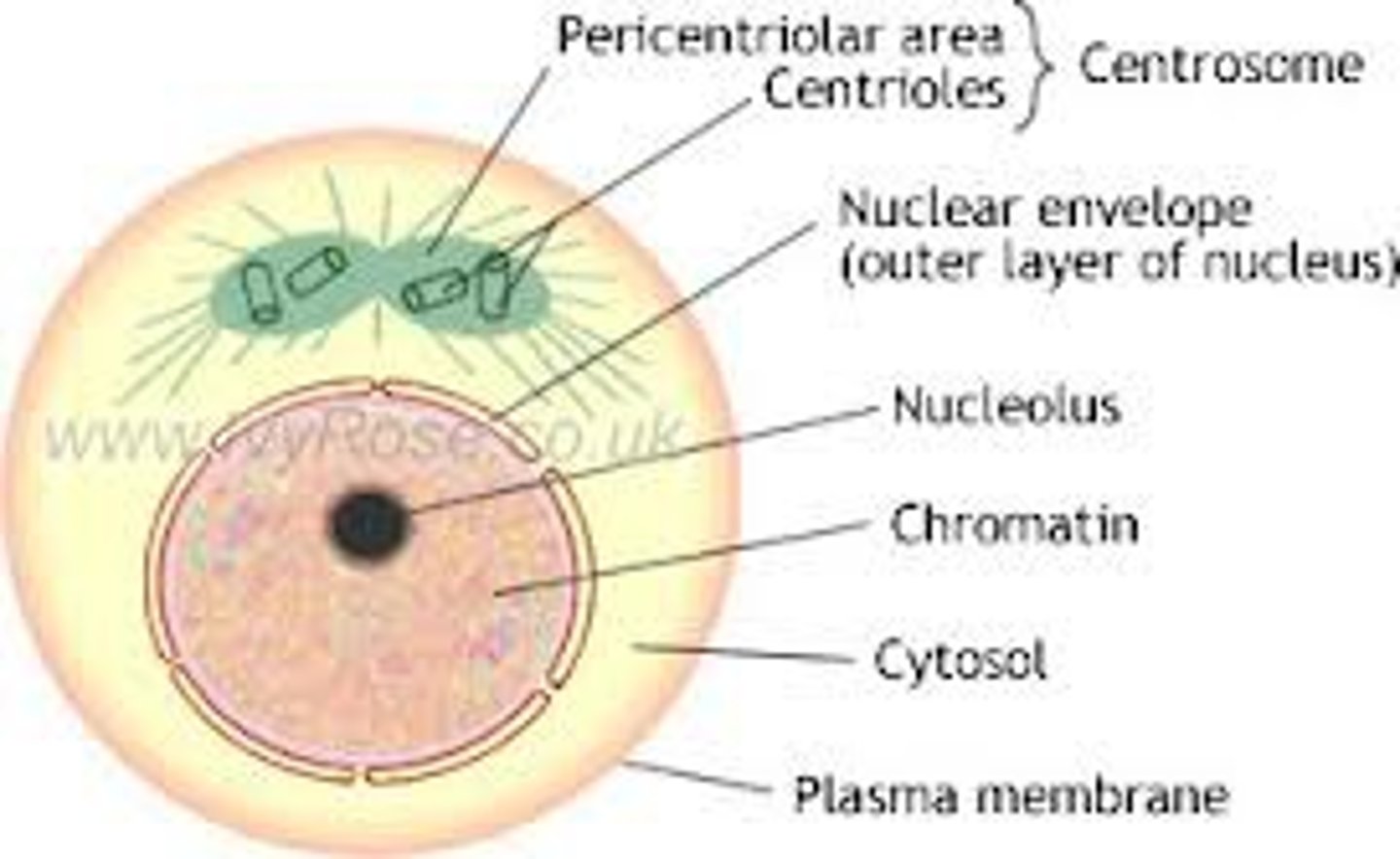
Interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
Prophase I (Meiosis)
homologous chromosomes pair up and crossing over occurs

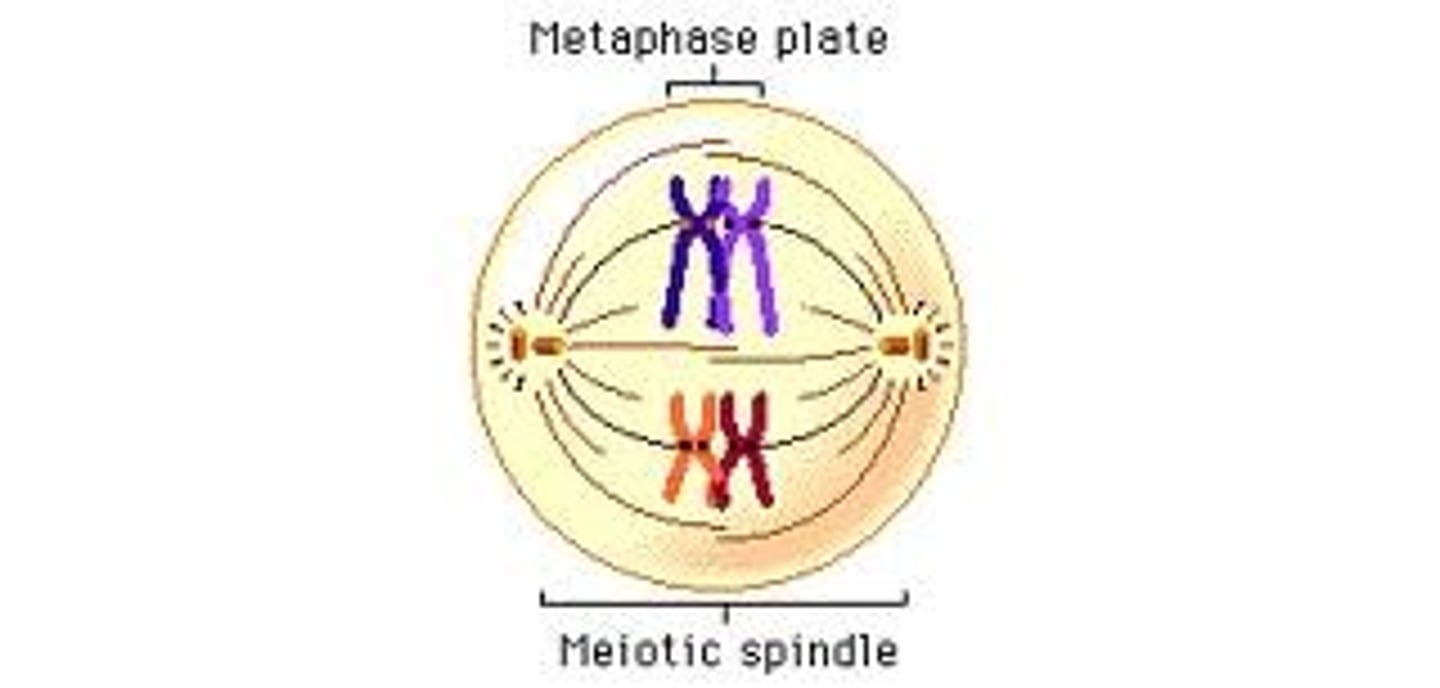
Metaphase I (Meiosis)
homologous pairs (tetrads) align at the equatorial plane and each pair attaches to a separate spindle fiber at the kinetochore
Anaphase I (Meiosis)
Homologous chromosomes separate
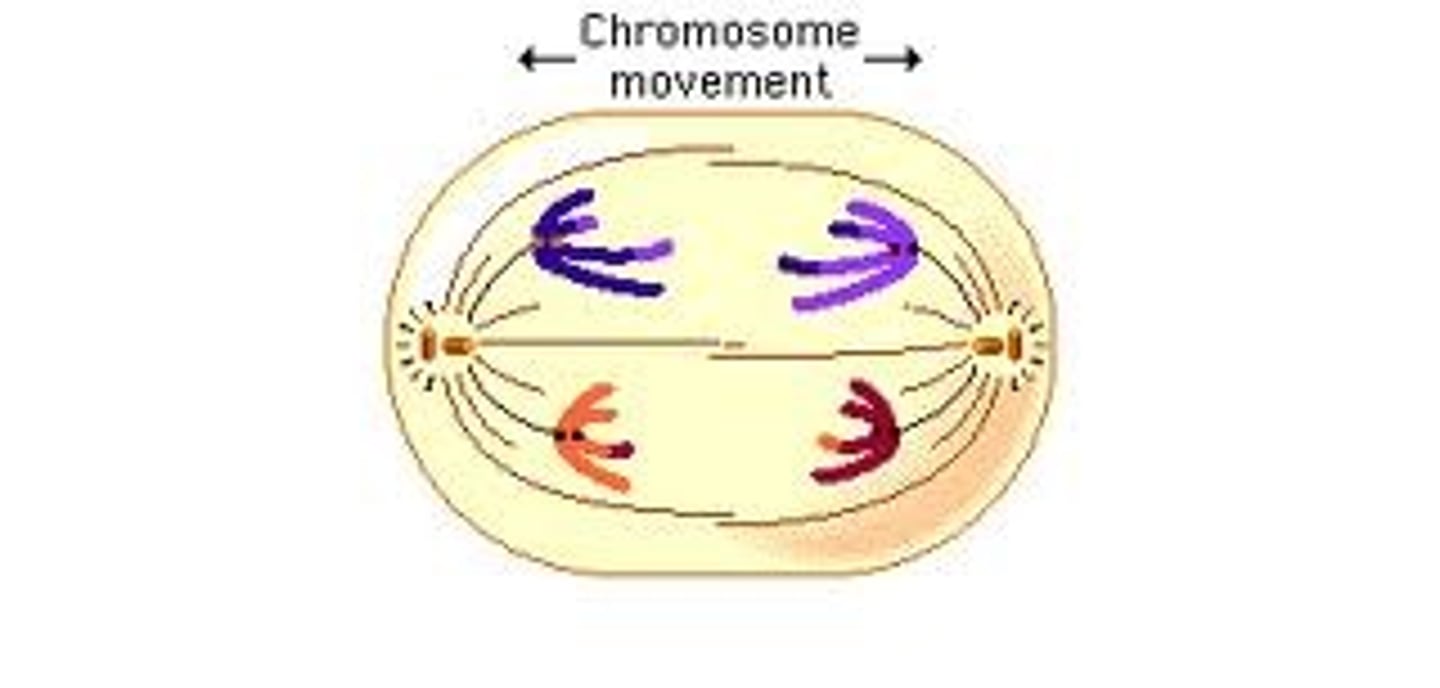
Telophase I (Meiosis)
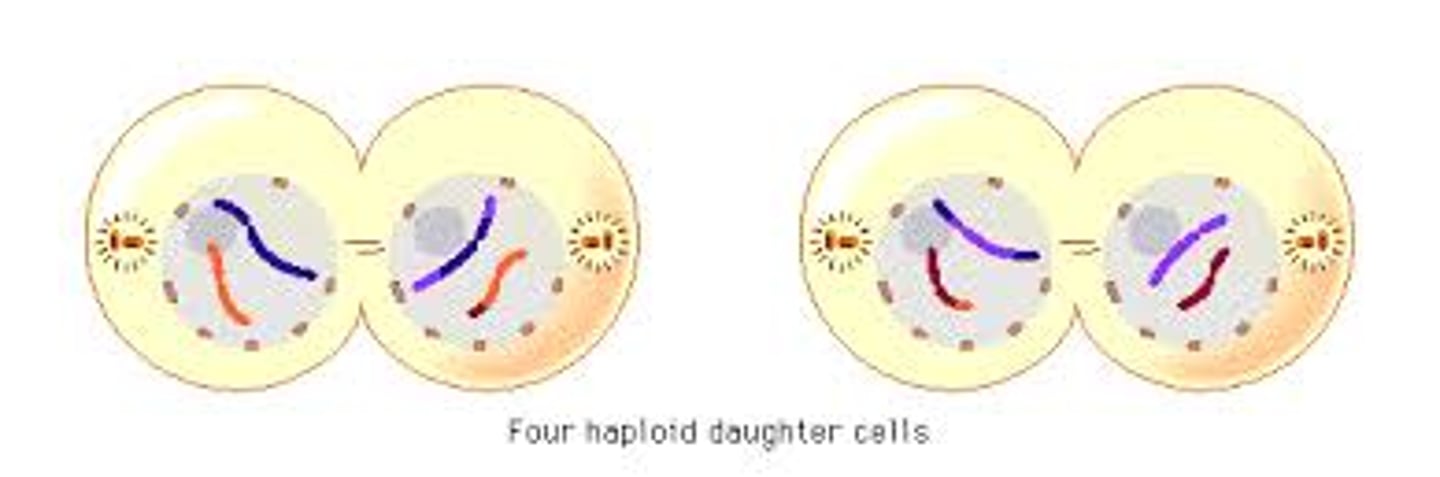
Cytokinesis occurs, the result are two haploid daughter cells
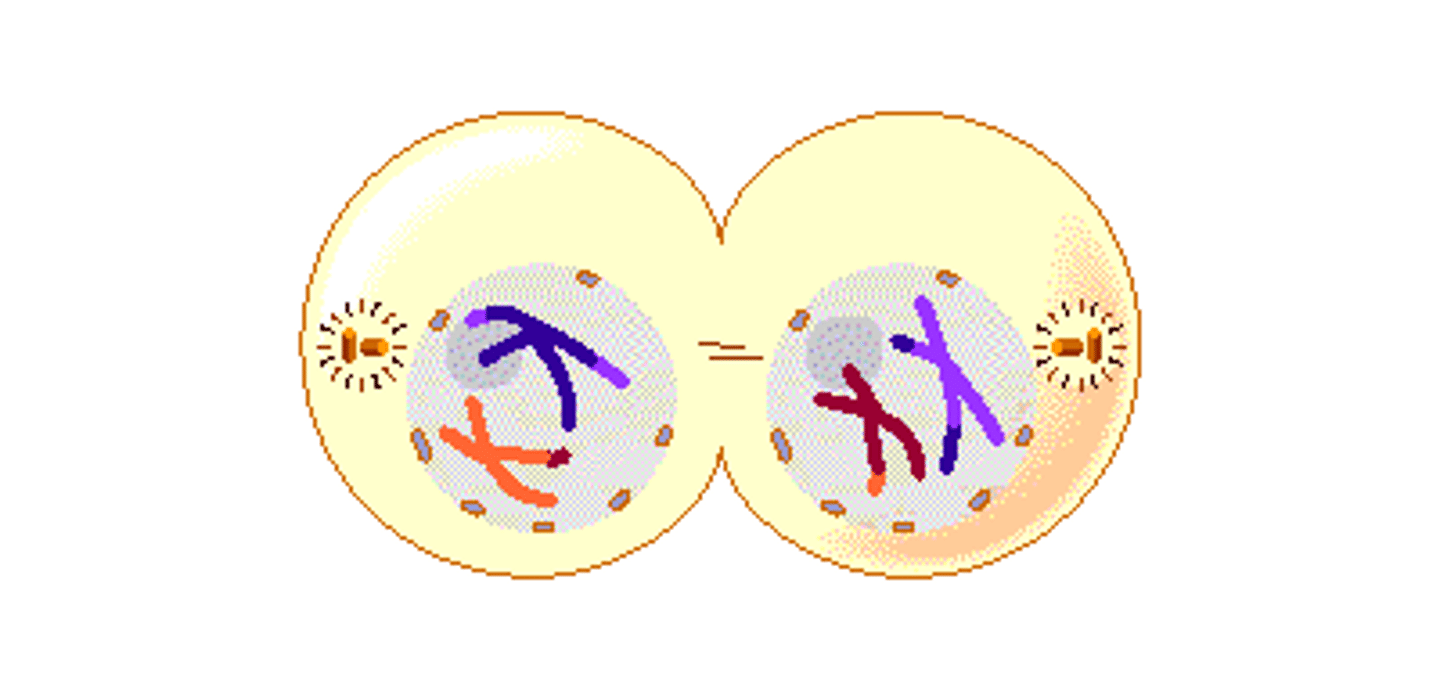
Prophase II
The duplicated chromosomes and spindle fibers reappear in each new cell.
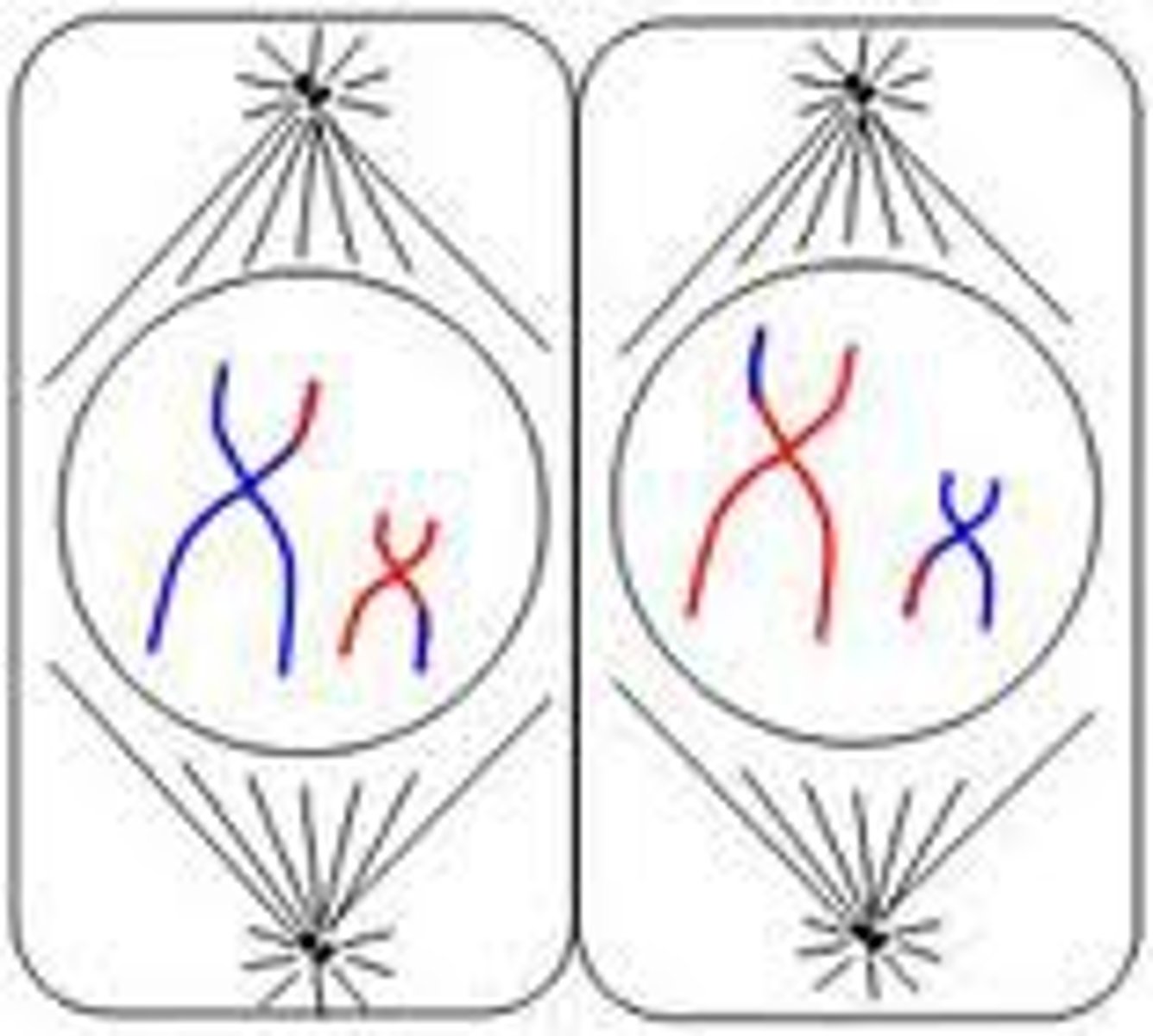
Metaphase II
The duplicated chromosomes move to the centre of the cell. Each centromere attaches to two spindle fibers instead of one.
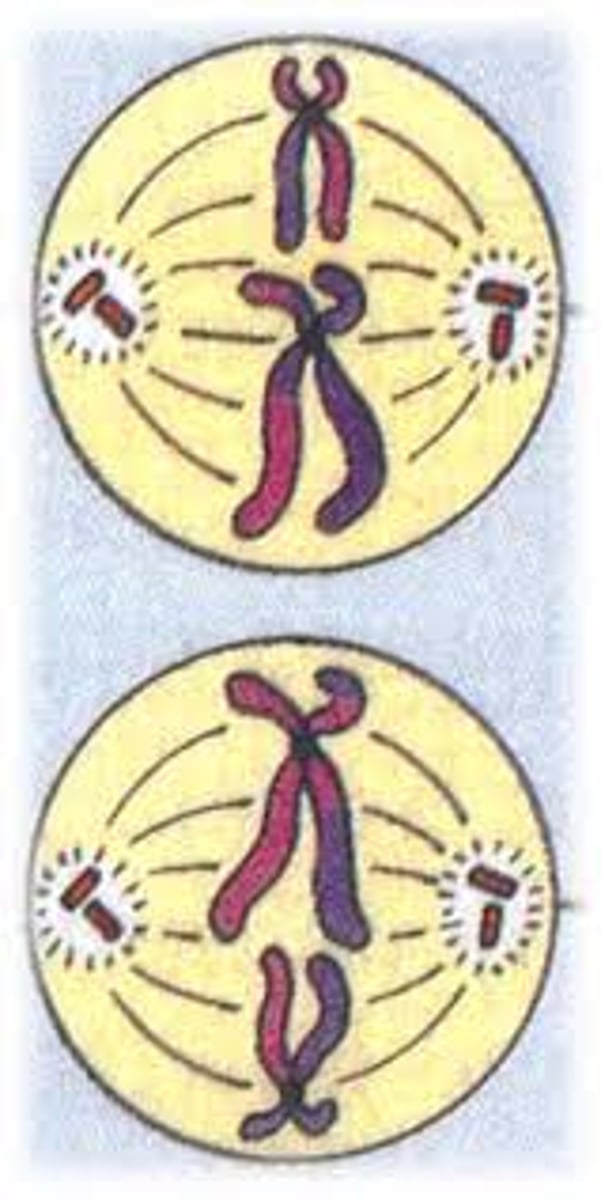
Anaphase II
Centromeres divides. chromatids move to the opposite poles of the cells.
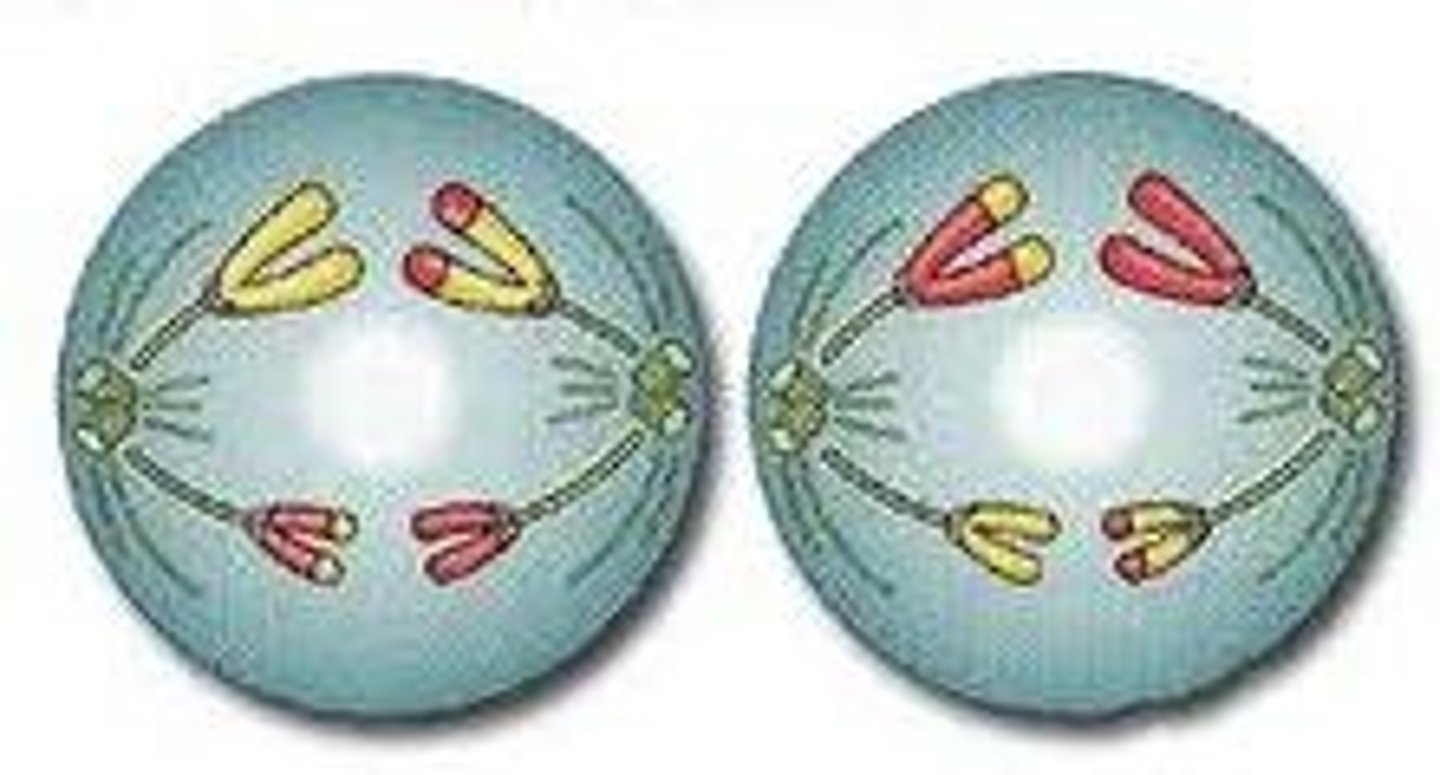

Telophase II
Nuclear membrane reforms, cytoplasm divides, 4 daughter cells formed
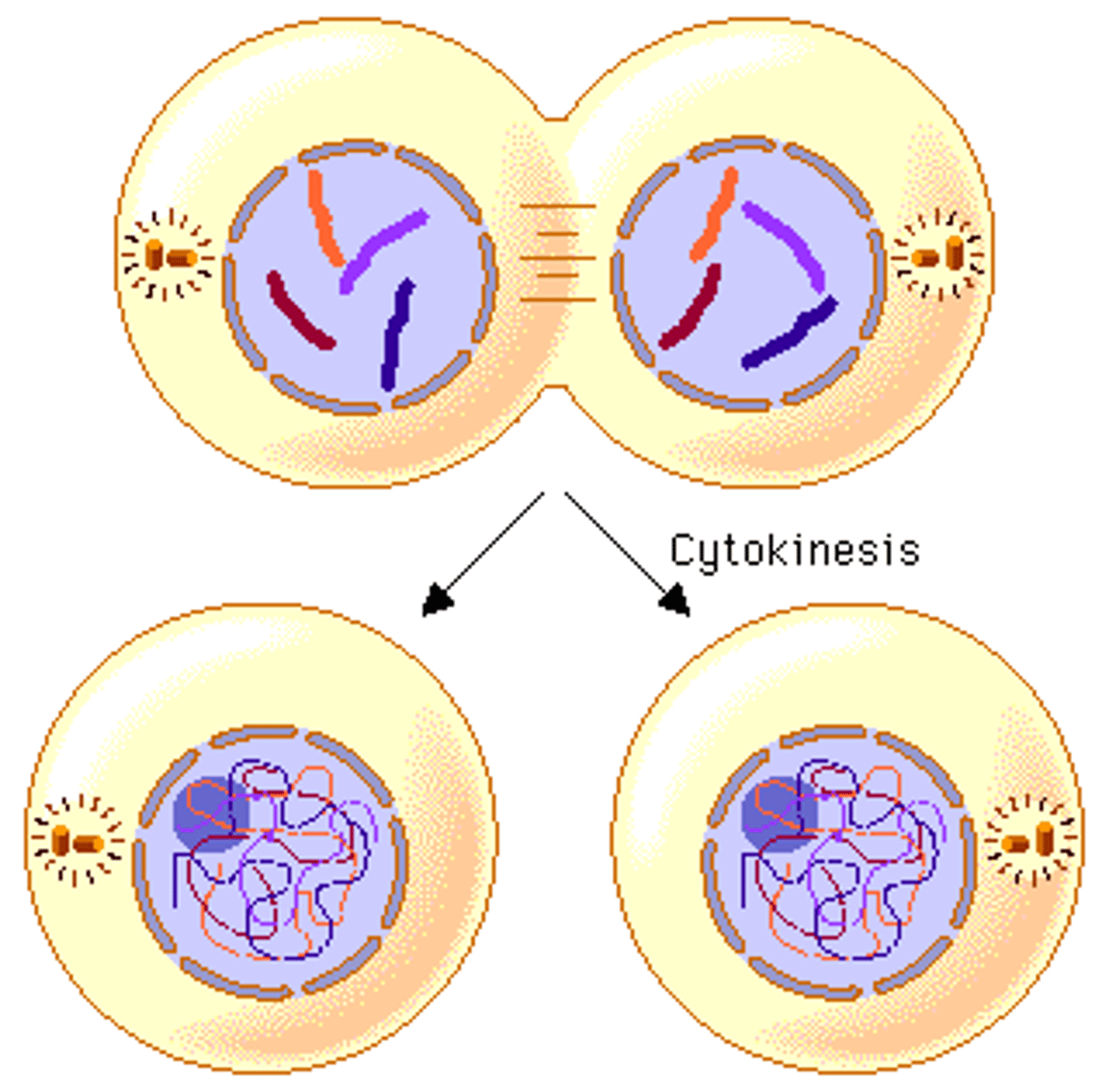
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
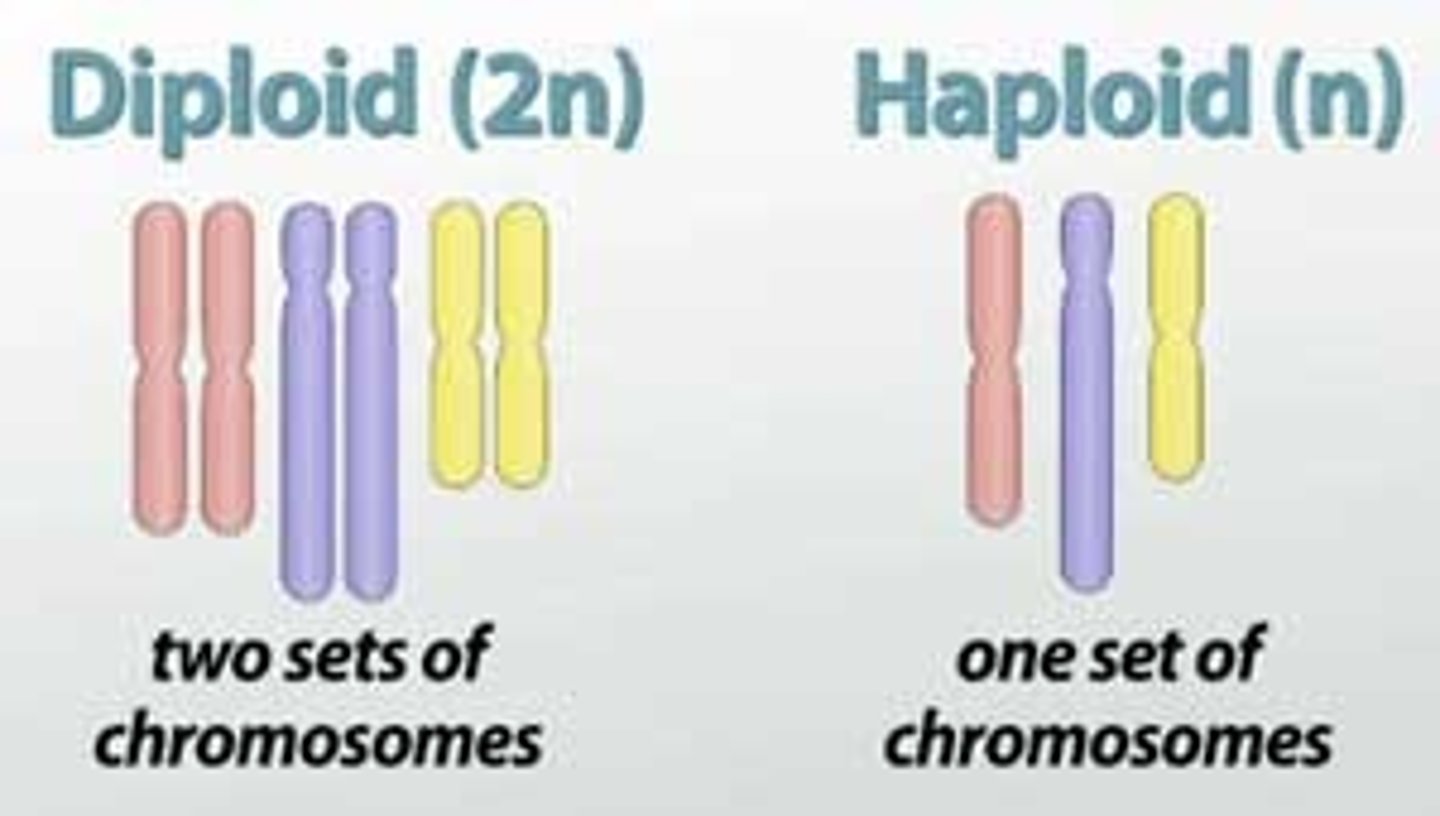
Diploid
containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.
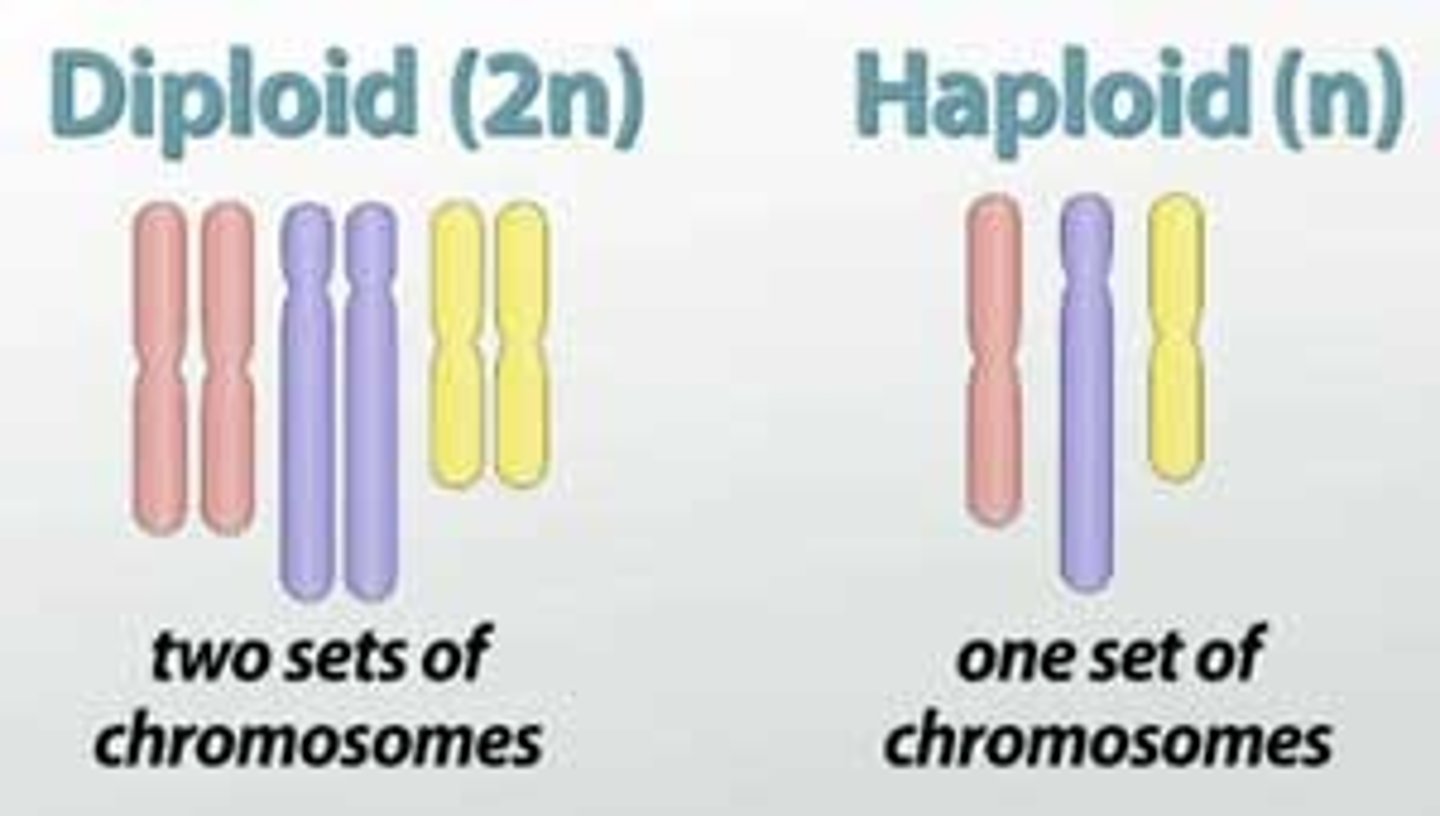
Haploid
An organism or cell having only one complete set of chromosomes.
Gamete
sex cell
somatic cells
Any cells in the body other than reproductive cells
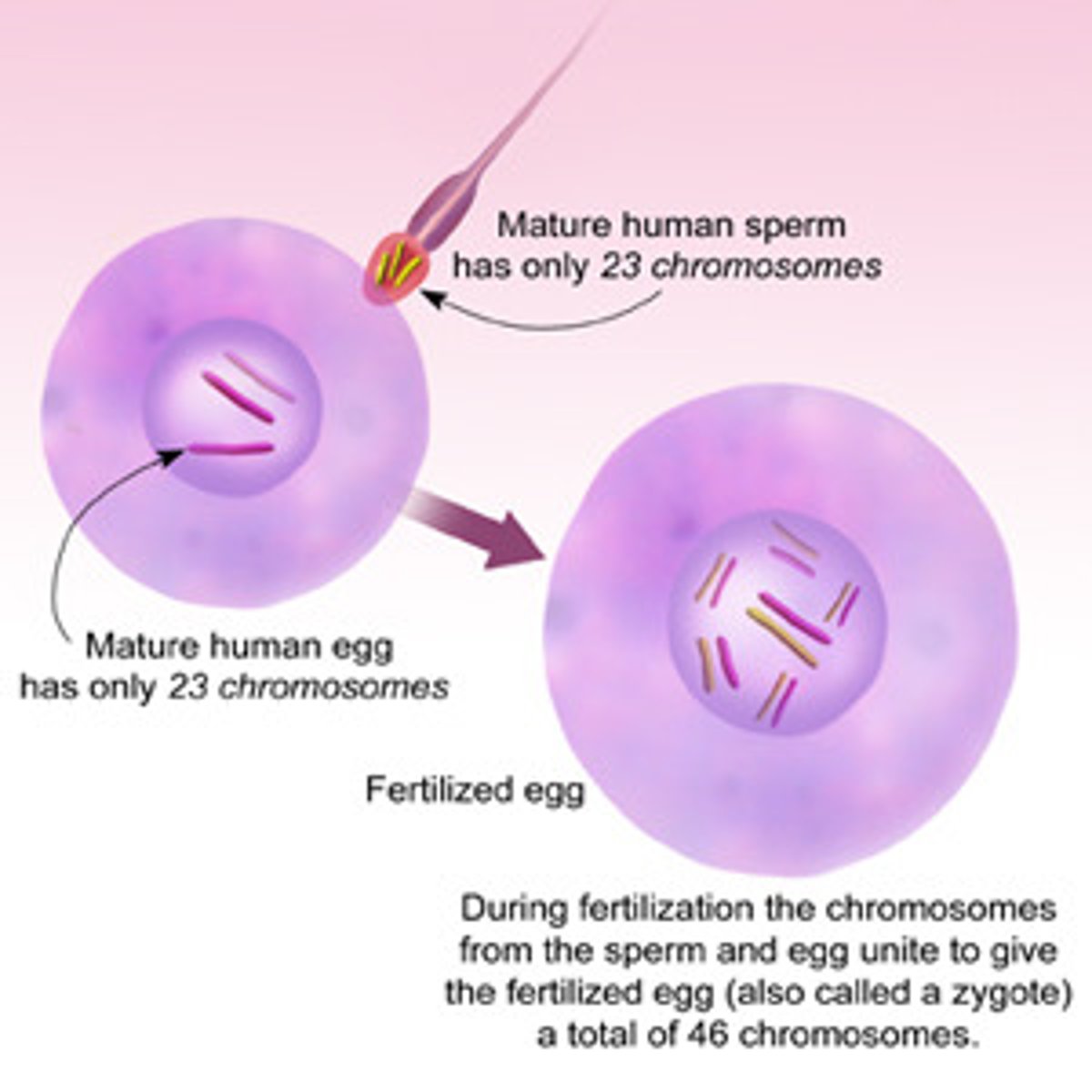
Zygote
a diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum.
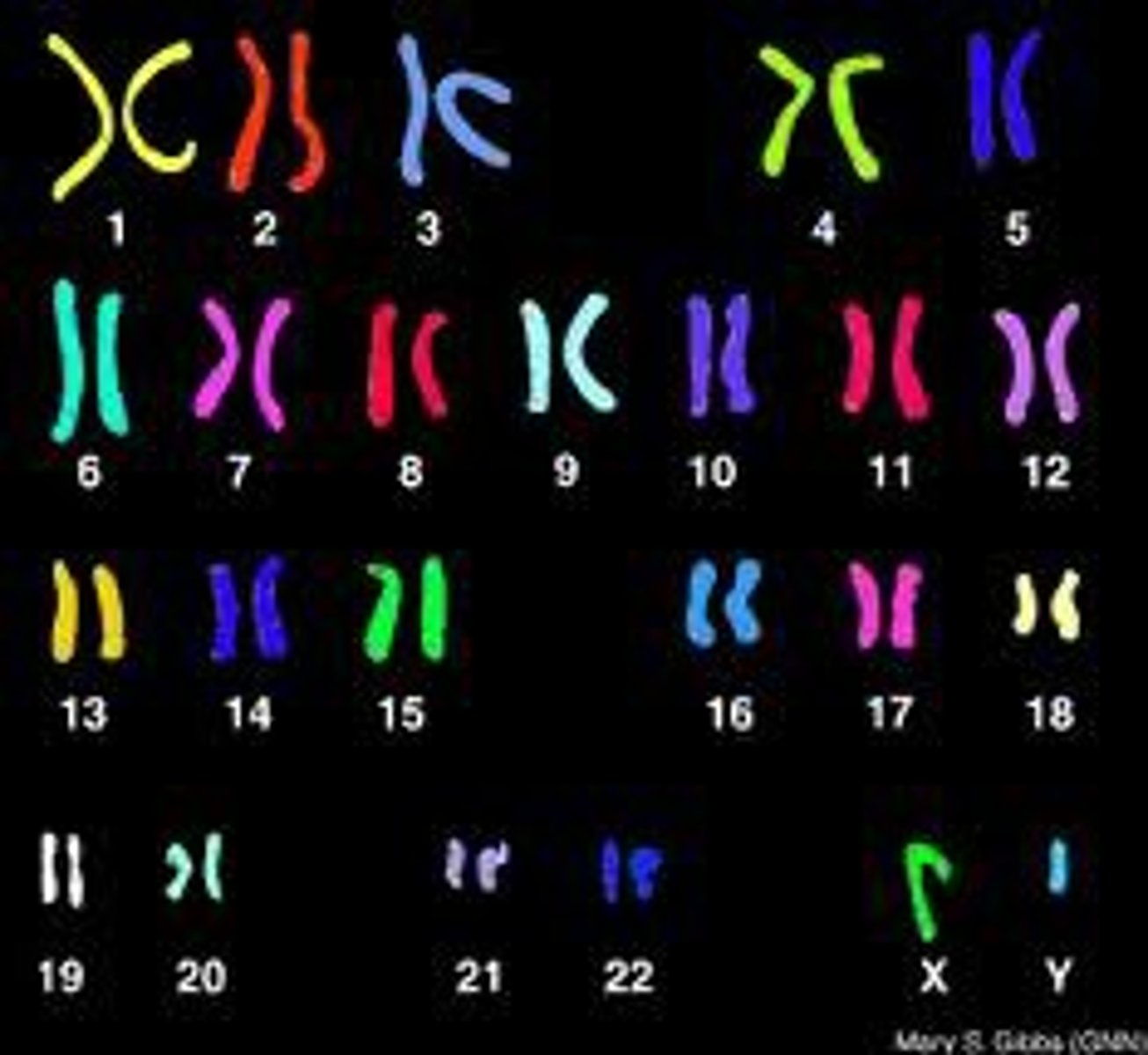
Karyotype
A picture of all the chromosomes in a cell arranged in pairs
homologous chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes that are the same size, same appearance and same genes.
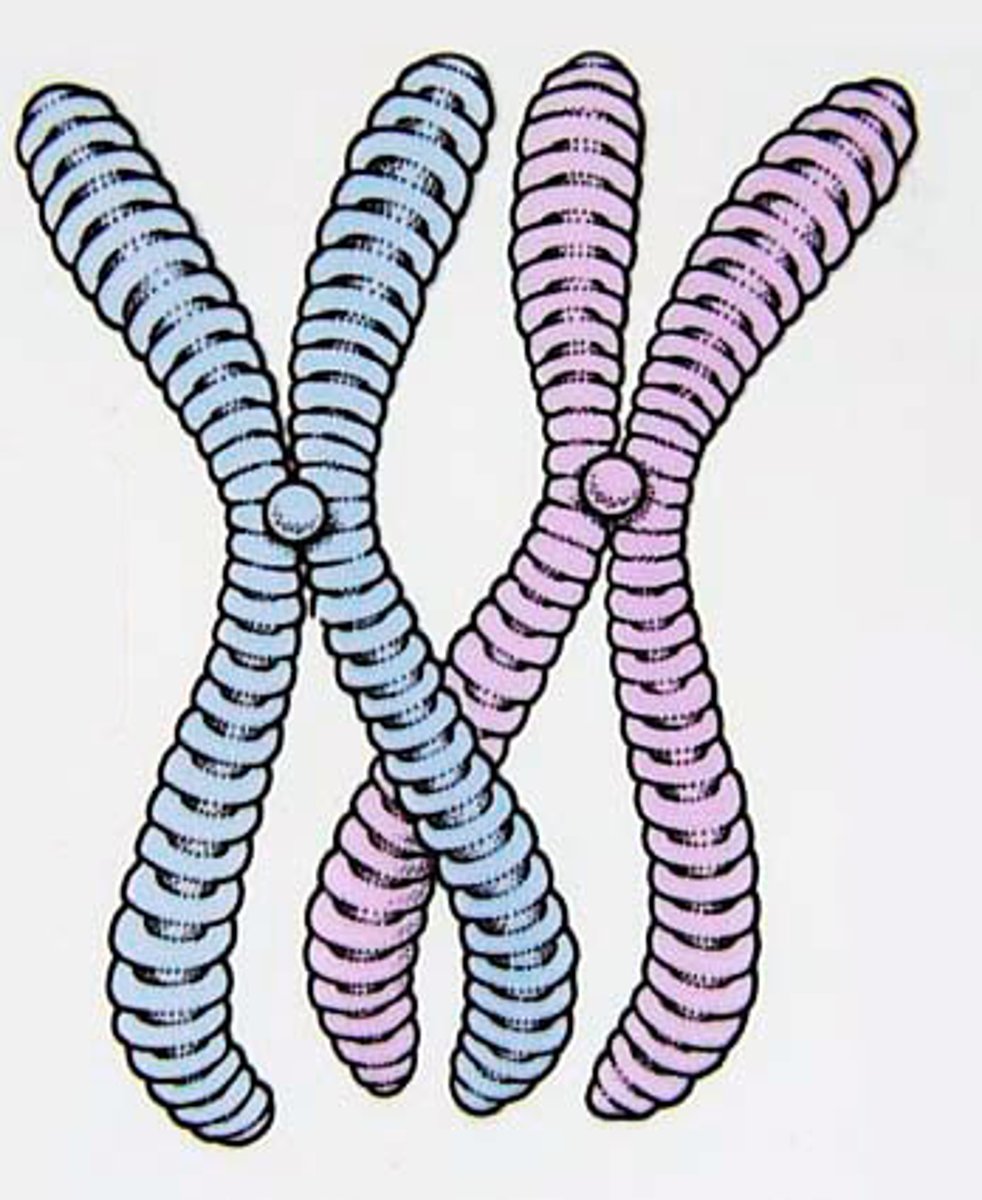
genetic variation in meiosis
Results in cells that are genetically different as the result of crossing over and independent assortment
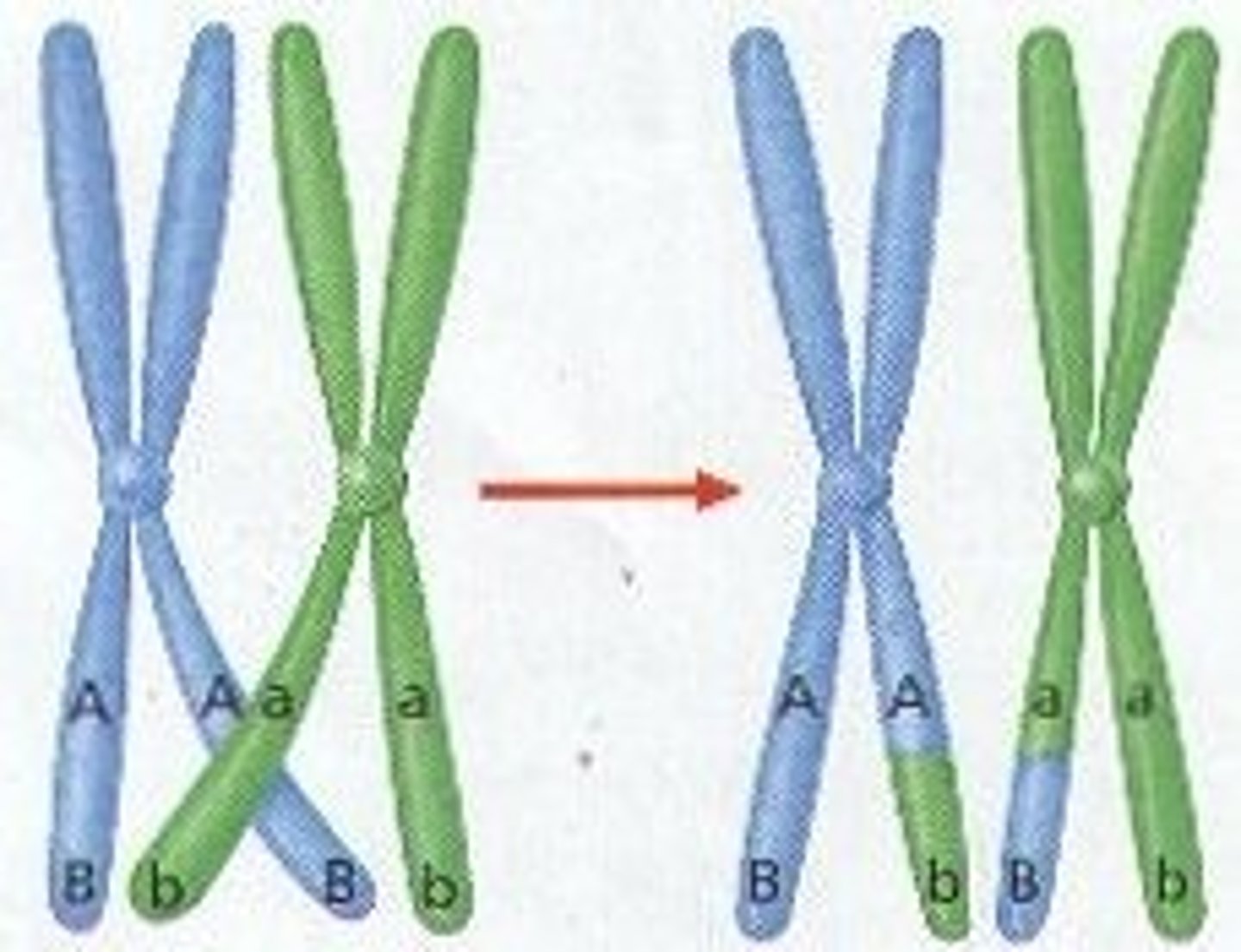
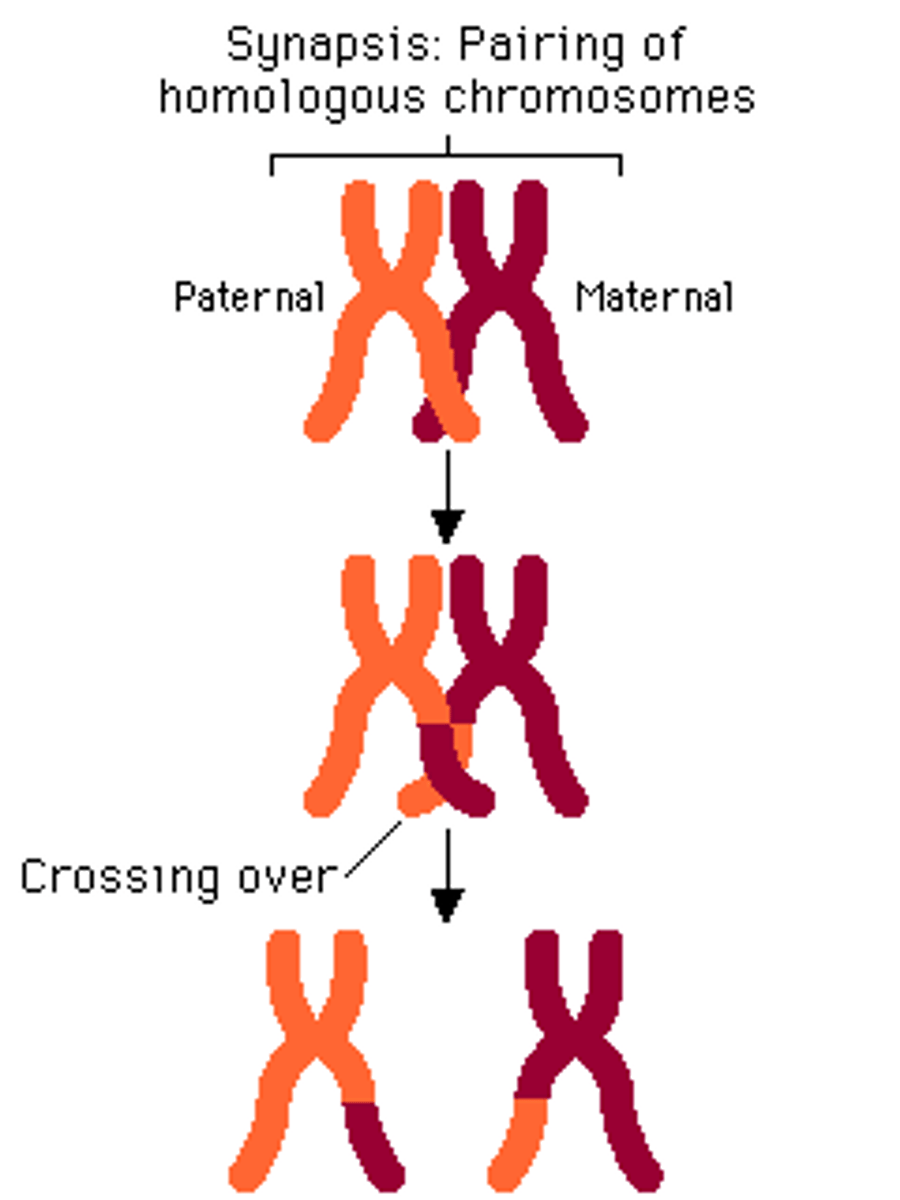
crossing over/recombination
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
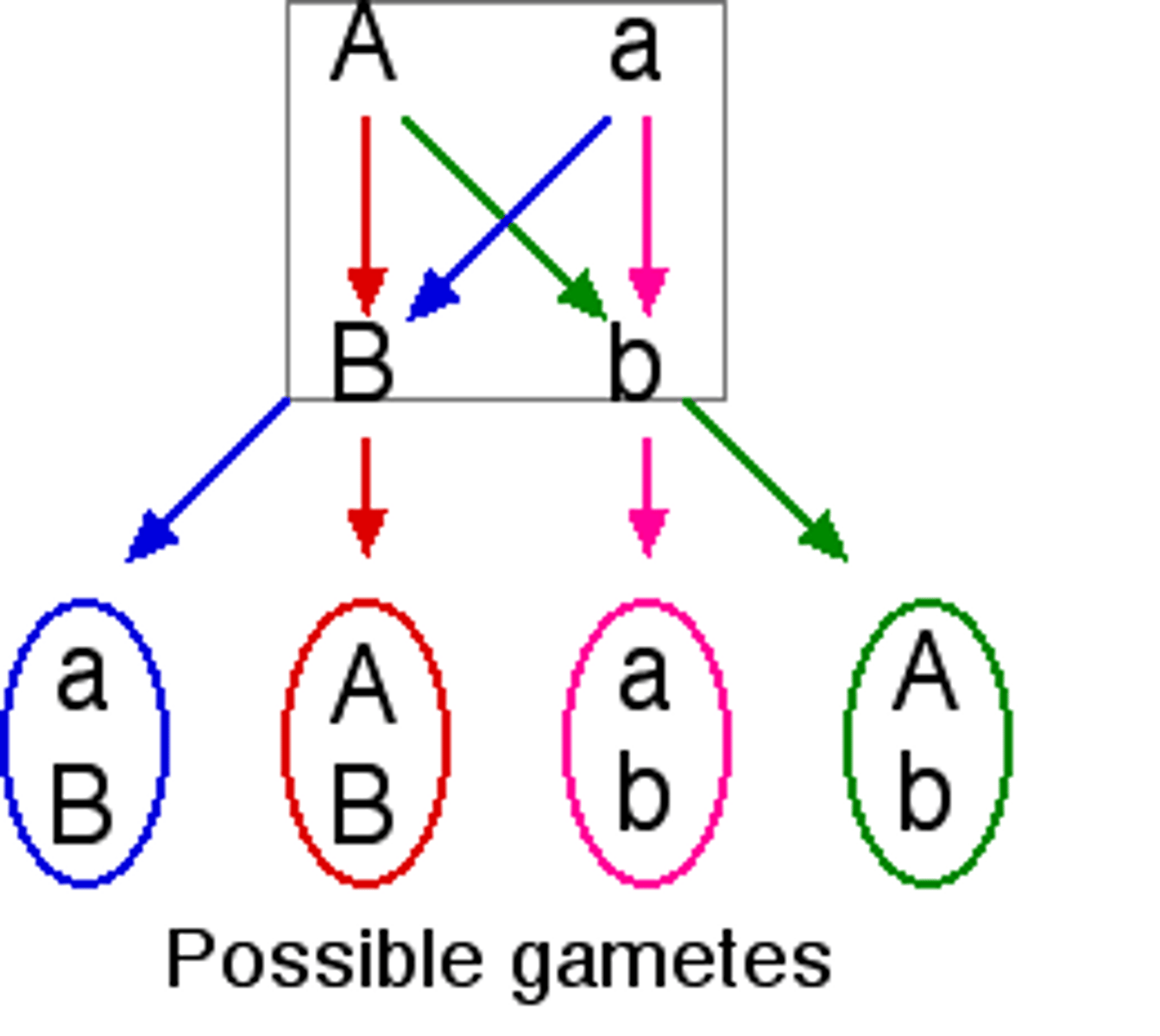
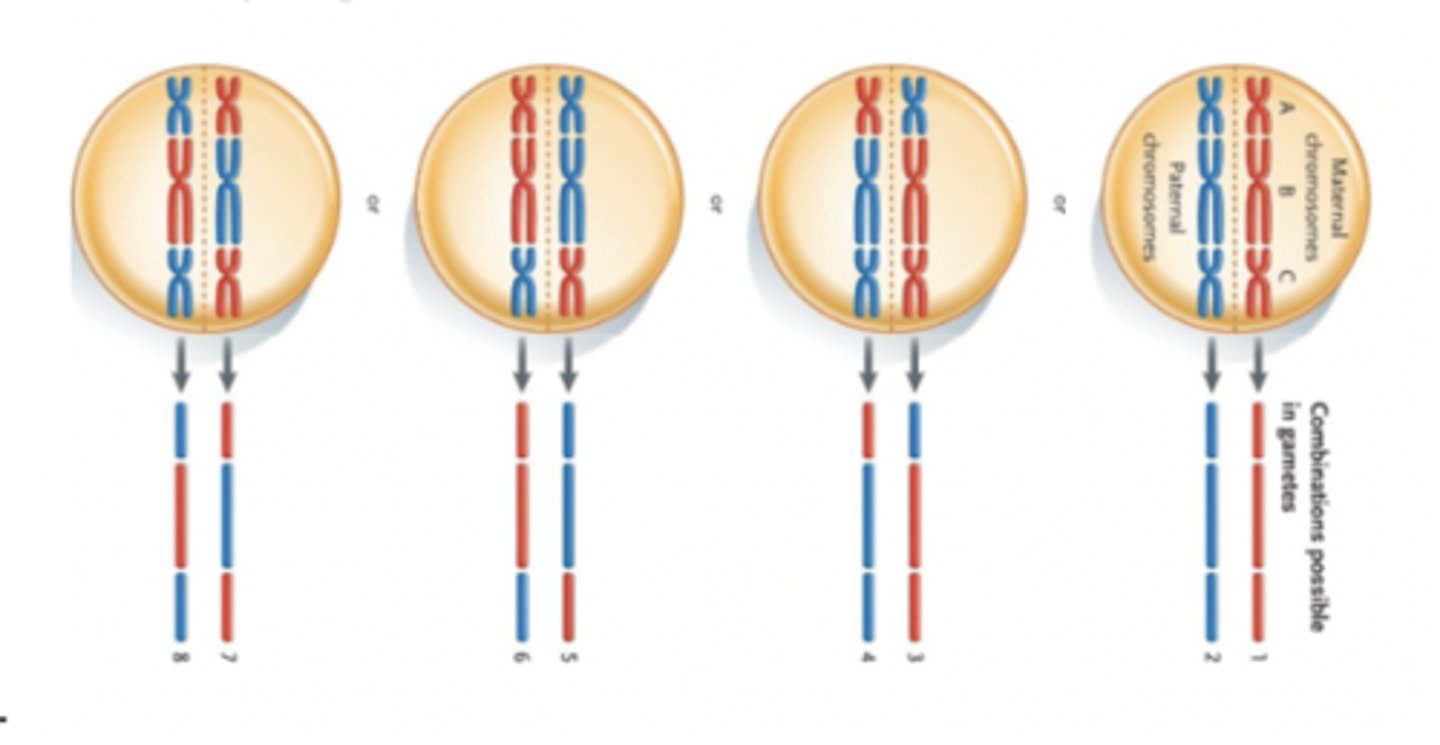
independent assortment of chromosomes
The random distribution of maternal and paternal chromosomes into gametes during meiosis.
Random segregation of chromosomes
chromosomes in meiosis are separated randomly to produce gametes
asexual reproduction
A reproductive process that involves only one parent and produces offspring that are identical to the parent.
binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in which one cell divides to form two identical cells.
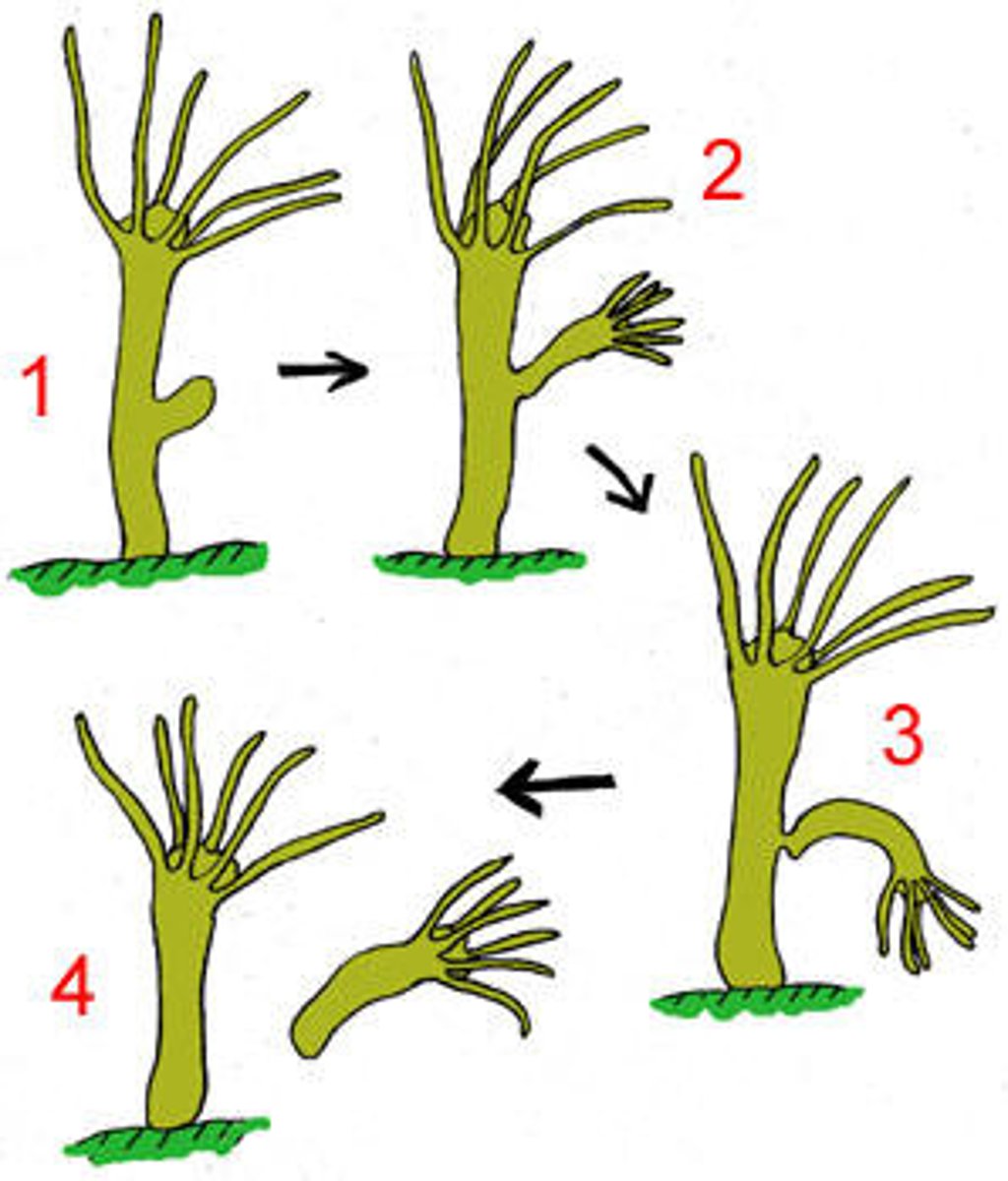
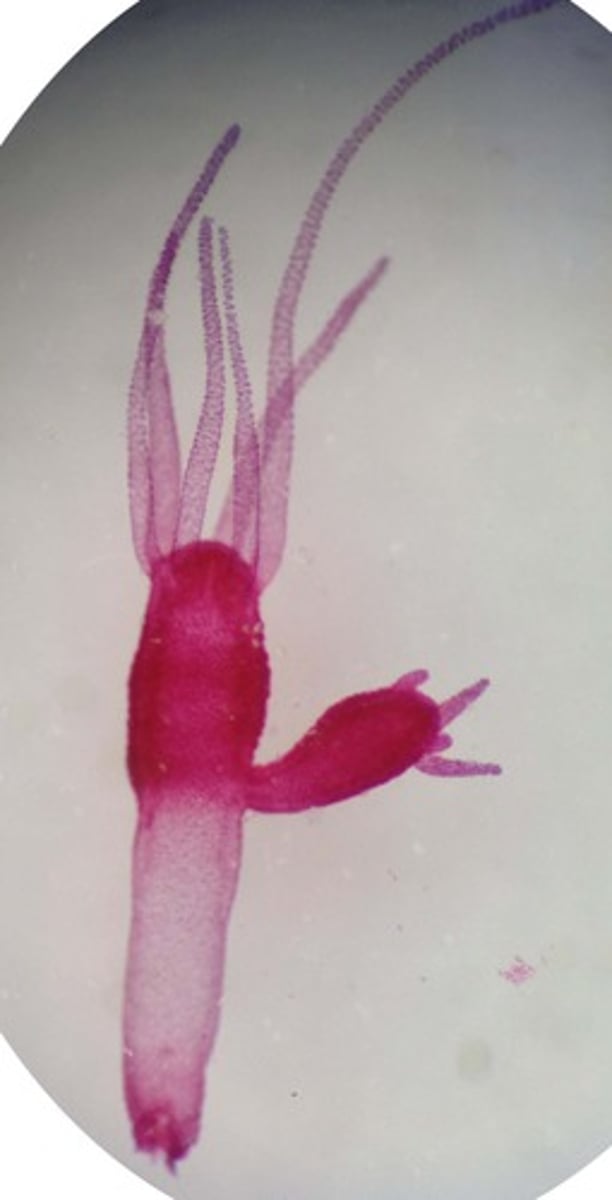
Budding (asexual)
when a new organism grows out of the parent's body
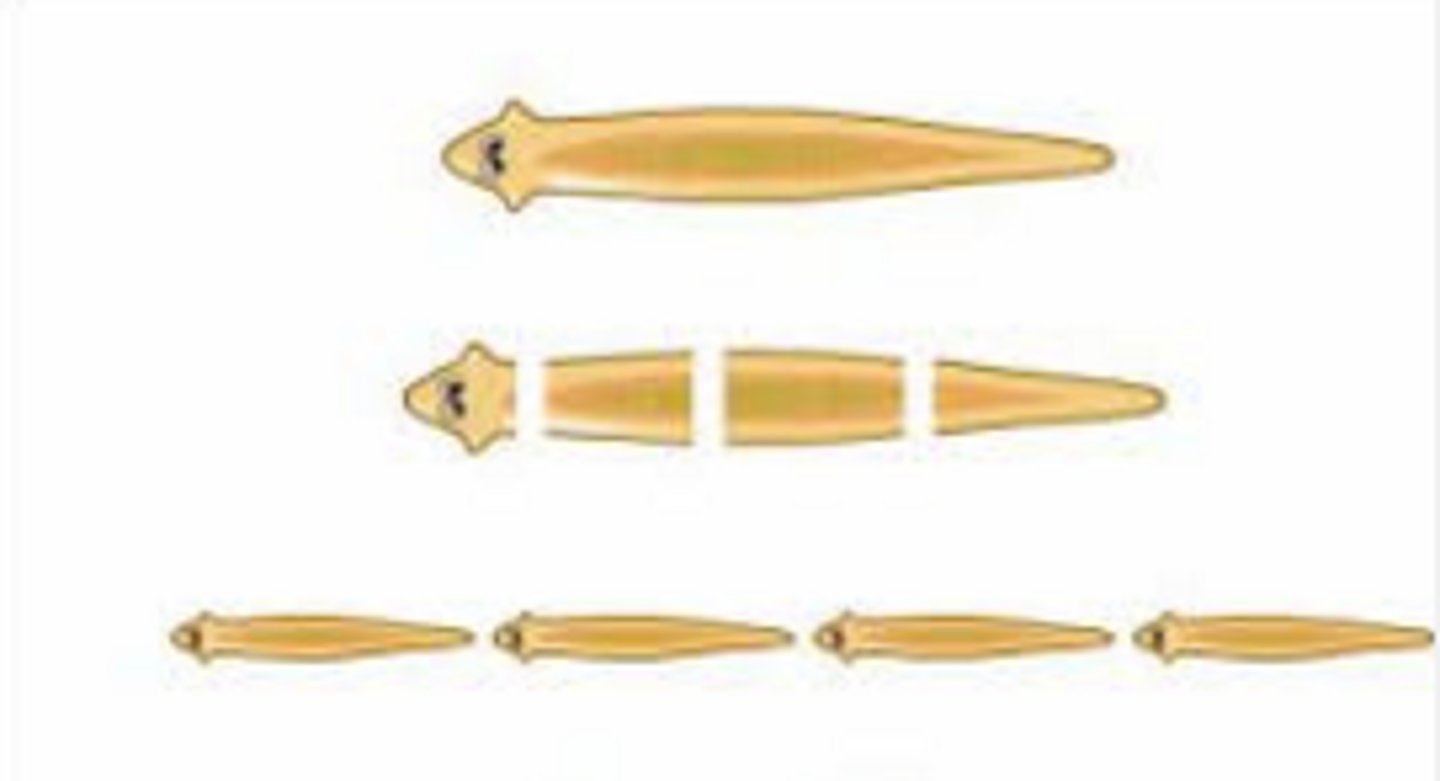
Fragmentation
A means of asexual reproduction whereby a single parent breaks into parts that regenerate into whole new individuals.

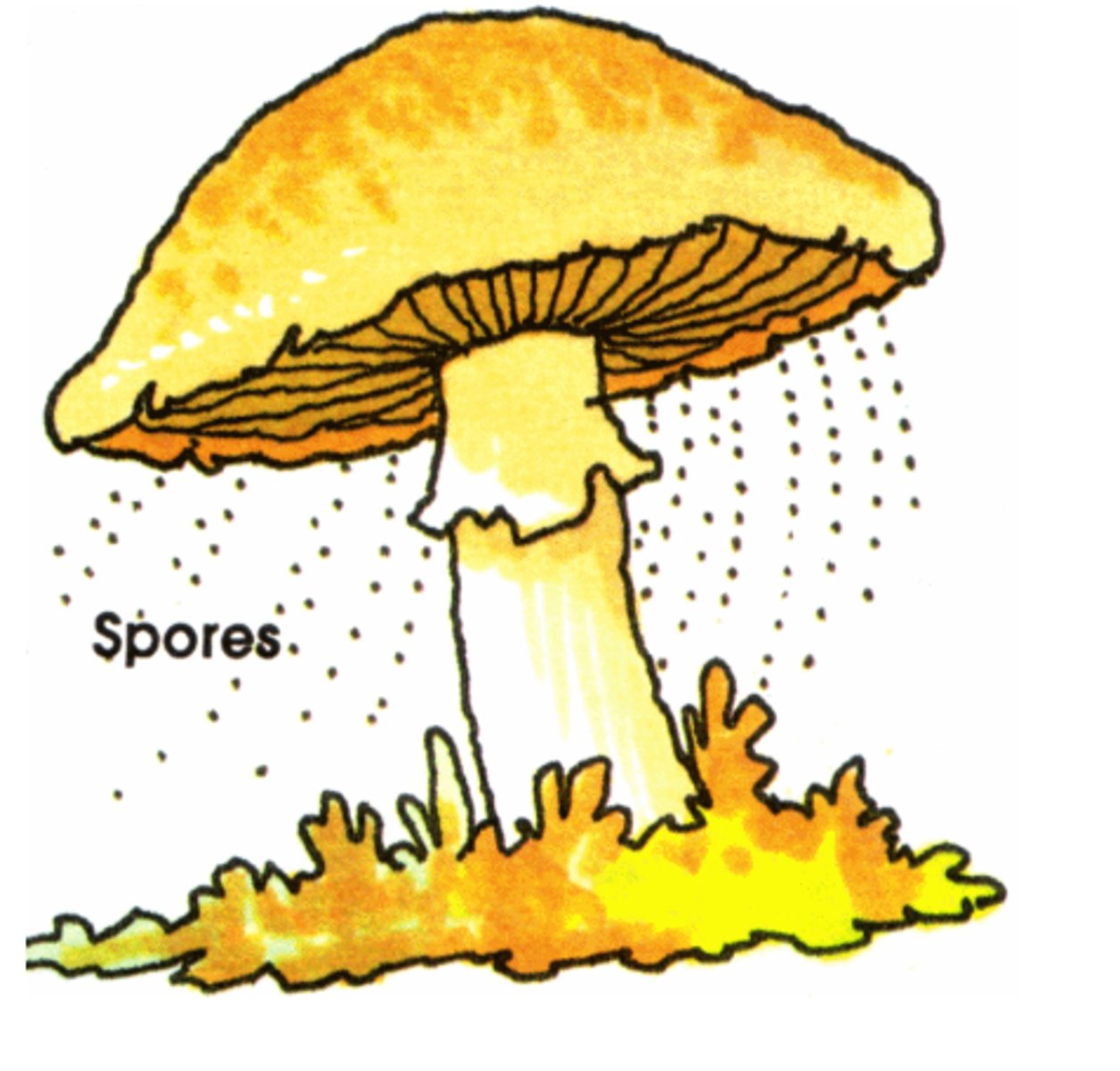
Spores
Asexual reproductive or resting cell capable of developing into a new organism without fusion with another cell, in contrast to a gamete

Vegetative
reproduction of plants by direct cloning from existing plants
