1️⃣ UE Orthotics
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
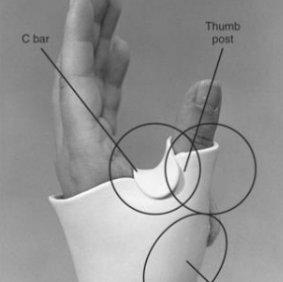
Name this static splint component. What’s its function?
C-bar
Holds the thumb in opposition
Positions the thumb in a way that preserves/and or increases the soft tissue length of the first web space
Should not block the movement of the 4th or 5th metacarpals
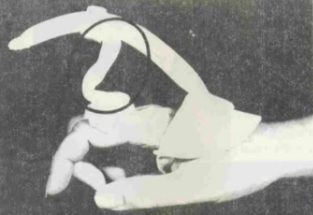
Name this static splint component. What’s its function?
Connector bar
Provides structural integrity for the orthosis.
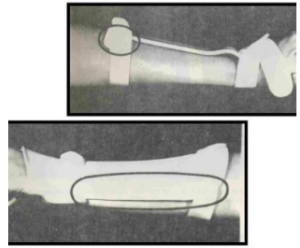
Name this static splint component. What’s its function?
Cross bar
Provides structural integrity for the orthosis
Point of attachment
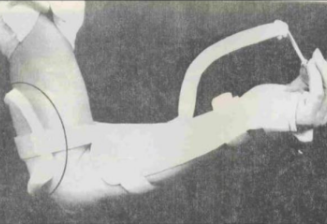
Name this static splint component. What’s its function?
Cuff or strap
Designed to hold the splint in place (usually made of soft, pliable material).

Name this static splint component.
Deviation bar
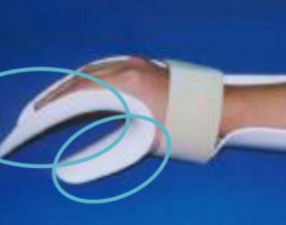
Name this static splint component. What’s its function?
Pan and thumb trough
Supports the fingers and the palm
Designed to conform to the arch of the hand to maintain hand functions such as grasping
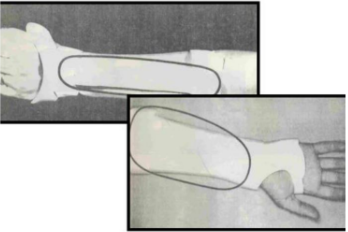
Name this static splint component. What’s its function?
Forearm trough
Provides support for the forearm (volar or dorsal depending on the condition it’s being used for).
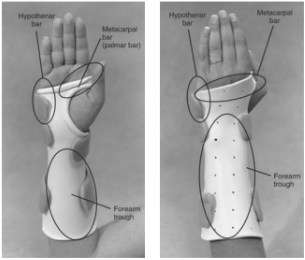
Name this static splint component. What’s its function?
Anatomic bar
It is placed over a joint to immobilize to achieve therapeutic goals
Provide connections to forearm trough
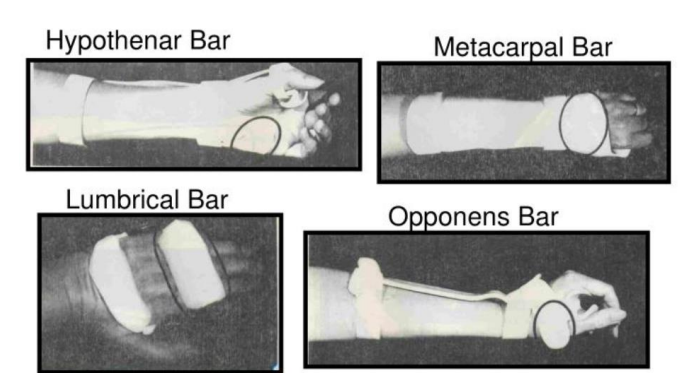
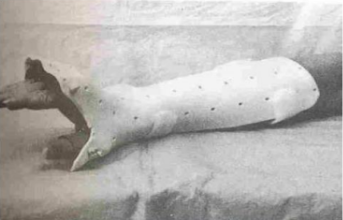
Name this static splint component. What’s its function?
Blocks
What is the classification of static orthoses?
FO | Finger orthosis |
HO | Hand orthosis |
WHO | Wrist-hand orthosis |
EO | Elbow orthosis |
SEO | Shoulder-elbow orthosis |
SEWO | Shoulder-elbow-wrist orthosis |
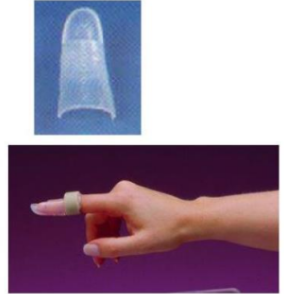
Name this orthosis.
Static volar DIP extension splint
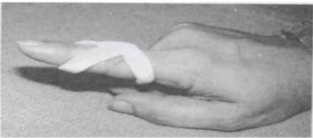
Name this orthosis. What deformity can it be used to treat?
Static three-point orthosis
Function:
Applies pressure at three specific points on a joint or limb to correct or support its position.
It’s used to correct boutonnière deformity (the PIP joint is flexed and the DIP joint is hyperextended). The splint applies pressure over the PIP joint to hold it in extension, while additional pressure at the proximal phalanx prevents the PIP joint from bending. Another point of pressure at the distal phalanx maintains DIP joint extension, stopping it from overextending.
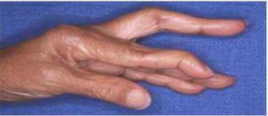
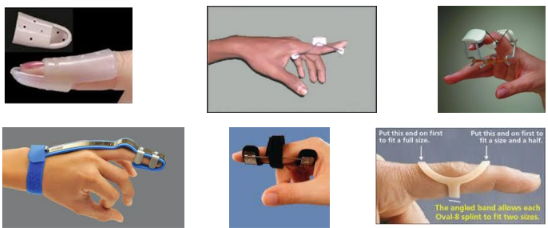
What classification of orthoses is this? Function? What are the indications to use them?
Finger orthosis
Function |
|
Indications |
|
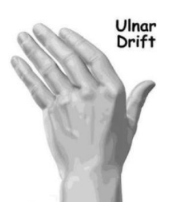
What type of orthosis can be used for ulnar drift? What classification does it fall under?
Static dorsal hand orthosis with an MCP block
Function:
It is a type of hand orthosis that immobilizes the hand while specifically blocking or restricting the movement of the MCP.
The MCP block in the orthosis stabilizes and prevents excessive ulnar deviation of the fingers by keeping the MCP joints in a neutral or aligned position.
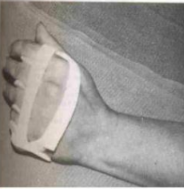
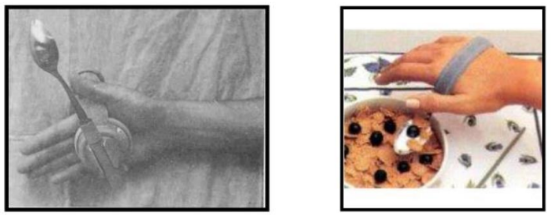
Name this hand orthosis?
Universal cuff
What is the function of a wrist hand orthosis? Give two examples.
Function:
Maintain the wrist in a neutral or mildly extended position.
Immobilizes the wrist while allowing full MCP flexion and thumb mobility.
Examples:
Wrist cock-up splint (image)
Dorsal wrist cock-up splint
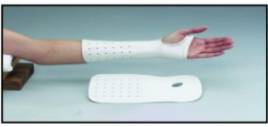
Why choose a dorsal wrist cock-up splint as opposed to a normal wrist cock-up splint?
Stronger mechanical support of the wrist and frees up some of the palmar surface for sensory input
Distributes pressure over the larger dorsal wrist surface area
Better tolerated by edematous hand
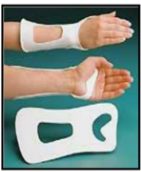
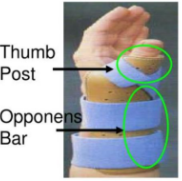
What is this? How is it placed? What materials are used to make the orthosis? Indications for use?
The thumb spica splint covers 2/3 of the distal radial forearm and surrounds the thumb to the IP joint. It should not restrict the motion of the other digits. The material consists of thermoplastics, metal, velcro, casting or padding.
Indications:
De-Quervain’s syndrome
Tenosynovitis
Thenar tendinitis
Thumb sprain
Scaphoid thumb fracture
Post-operative thumb
Median nerve lesion
Ulnar nerve lesion
Nerve Compression
What type of cast should be used? Suggested wearing schedule?
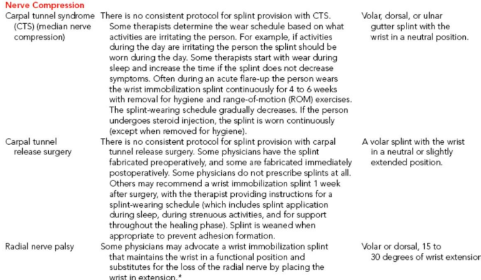
Tendinitis/Tenosynovitis
What type of cast should be used? Suggested wearing schedule?

Rheumatoid Arthritis
What type of cast should be used? Suggested wearing schedule?

Wrist Sprain
What type of cast should be used? Suggested wearing schedule?

Complex regional pain syndrome
What type of cast should be used? Suggested wearing schedule?

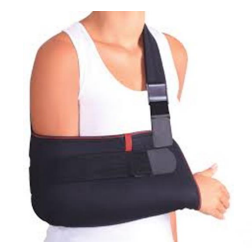
Name this orthosis. What classification does it fall under? Function and indications?
A humeral sling is a static elbow orthosis. It is used to support the forearm with the elbow flexed, the shoulder internally rotated and the arm adducted. The wrist should be supported by the sling to prevent wrist drop if there is a distal weakness. The hand should be higher than the elbow to decrease edema if any. The material consists of cloth, elastic, metal ring/fasteners and velcro.
Function:
Immobilize to promote tissue healing
Prevent overstretching of glenohumeral musculature/ligaments
Keeps forearm elevated to reduce edema
Indications:
AC joint injury
Scapular, humeral fractures
Rotator cuff injuries
Bicipital tendonitis
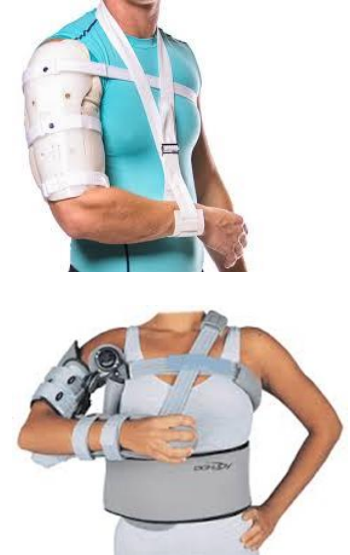
Name this static elbow orthosis.
Humeral fracture brace
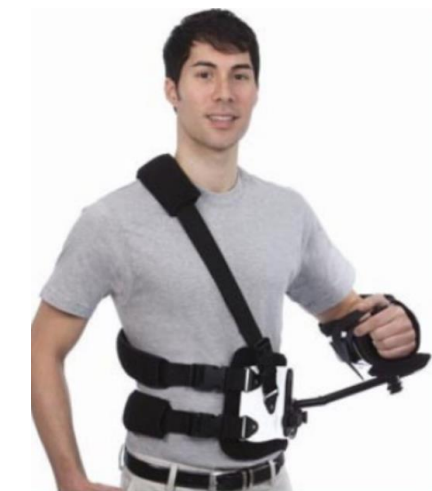

What classification of orthoses is this?
Static shoulder-elbow orthosis
Indications:
Painful or subluxated glenohumeral joint
Brachial plexus injury
*for long-term use as opposed to a simple sling
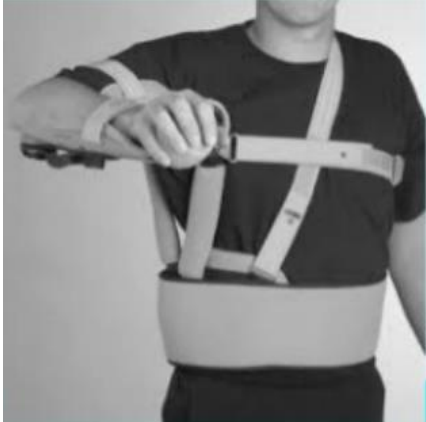
What classification of orthoses is this?
Shoulder-elbow-wrist orthosis (aka shoulder stabilizer or airplane splint)
Used to protect soft tissue injuries, prevent contractures or correct an existing deformity. The shoulder is positioned in abduction with the degree determined by pathology. Care is taken to avoid stretching the skin, nerves or vascular structures. The material of the orthosis consists of thermoplastic, metal, padding, strapping and velcro.
Indications:
Post-rotator cuff tear
Anteroposterior capsular repair
Axillary burns
What is the purpose of dynamic splinting? Physiological considerations?
Function:
Protect and assist weak musculature to perform selective tasks.
Used for patients with long-standing limitations who can benefit from increased function of the hand.
Considerations:
Stretch is too great - fatigue, injury, failure
Stretch is too little - atrophy and weaknesses, tendons and ligaments will shorten in the absence of habitual tensile forces
Stretch is enough - the patient should sense tension but feel no pain
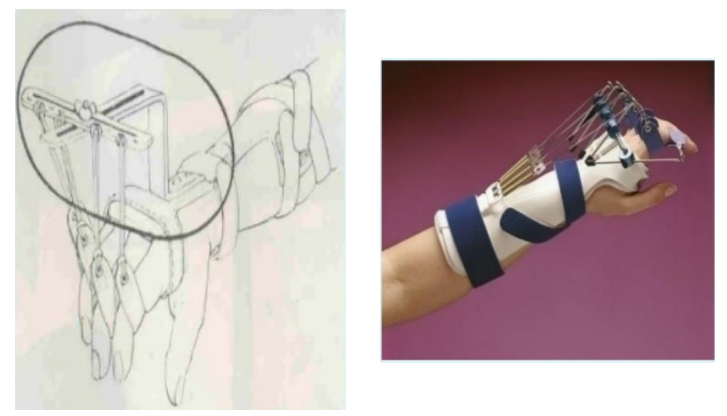
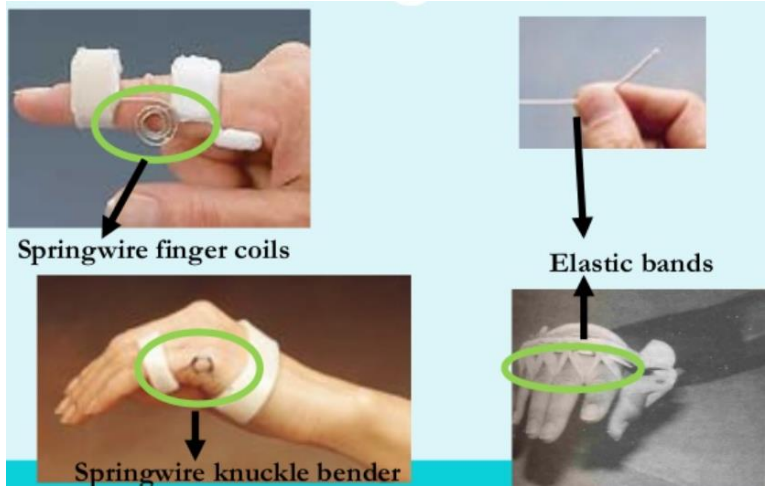
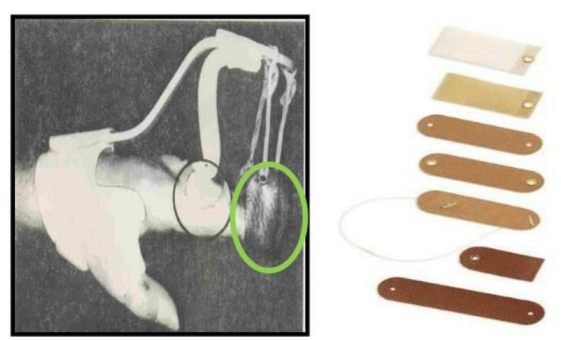
Name this component of a dynamic splint. What’s its function?
Outrigger
Provides a point of attachment for finger slings.
Name this component of a dynamic splint. What’s its function?
Dynamic assist
Assists weak musculature or substitutes for paralyzed muscles.
*Ideal for chronic conditions as it’s lightweight.
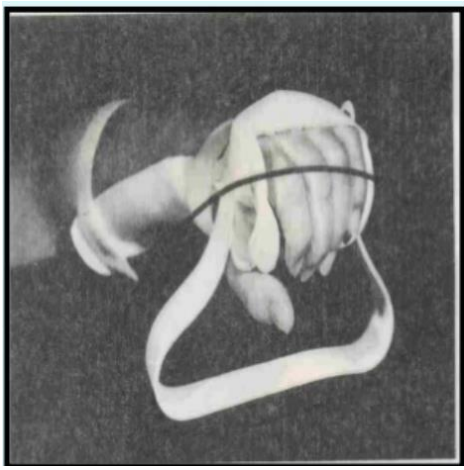
Name this component of a dynamic splint. What’s its function?
Finger cuff
Padding to distribute pressure.

Name this component of a dynamic splint. What’s its function?
Reinforcement bar
Provides structural integrity
Point of attachment
Name this component of a dynamic splint. What’s its function?
Phalangeal bar/finger pan
Supports the fingers.
What is the use of a dynamic finger extension splint (aka dynamic radial nerve splint)?
Function:
Immobilize the wrist in the functional position
Passively extend the MCP to 0
Permit full active MCP flexion and unrestricted IP motion
Indications:
Paralysis of the wrist, MCP or finger extensors
Advantage:
Less obtrusive design as compared to other splints such as an outrigger design.
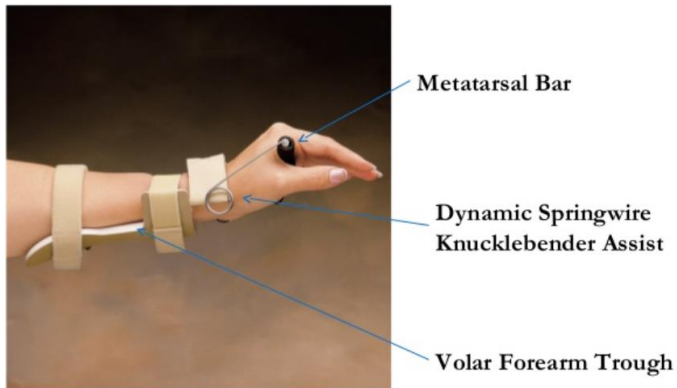
What is the use of a dynamic wrist extension splint?
Function:
Passively extends the wrist while allowing wrist flexion.
Prevent the contracture of unopposed, innervated wrist flexors.
Indications:
Weak or paralyzed wrist extensors
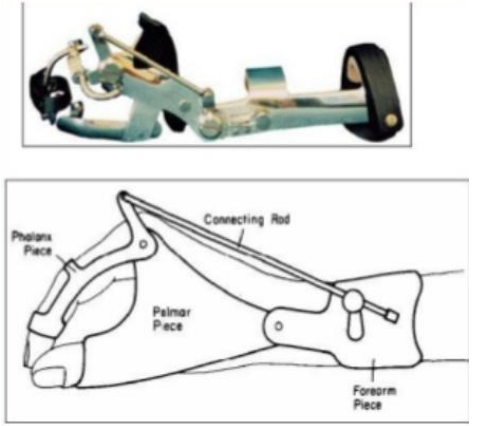
What type of dynamic splint is this? Function and indications?
Tenodesis splint
Function:
To train tenodesis grasp.
To promote a strong tripod pinch with wrist extension.
Allows finger opening with wrist flexion.
Indications:
C6 quadriplegia with Grade 3 strength of wrist extensors
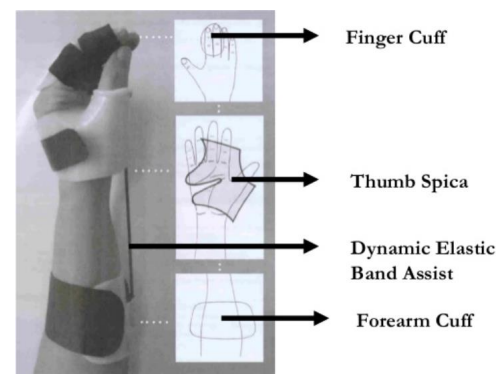
What is the use of a dynamic ulnar nerve splint (aka dynamic anti-claw deformity splint, Wynn Perry Splint)?
Function:
To passively flex the 4th and 5th MCP joints.
To prevent the shortening of the MCP collateral ligaments.
To promote active IP flexion.
Indications:
Ulnar nerve lesion
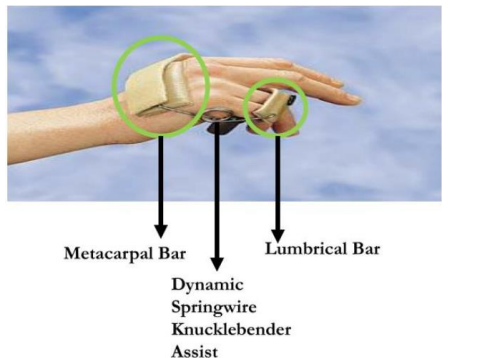
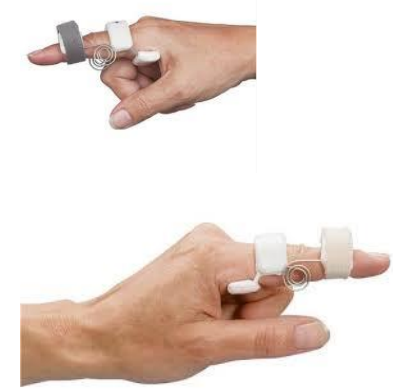
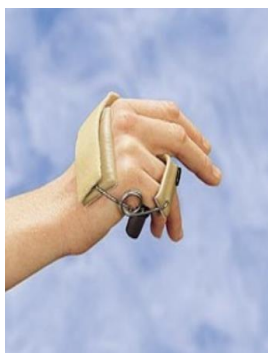
What is the use of a dynamic capener splint (aka dynamic spring wire splint for PIP extension)?
Function:
To passively extend the PIP
Allows active IP flexion
Provide stability to PIP
Indications:
PIP flexion contracture
PIP dorsal dislocation
Volar plate injury
Flexor tendon repair with resulting PIP flexion contracture
Partial or complete tear of the collateral ligament
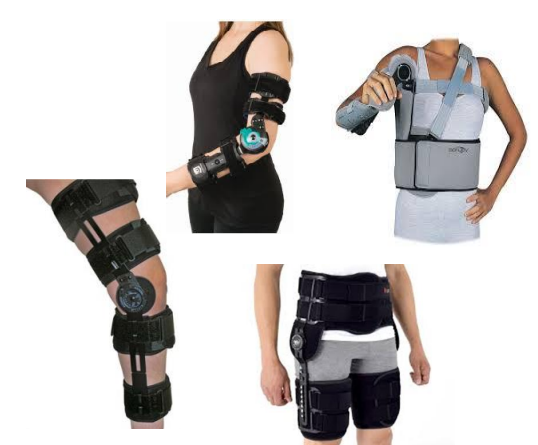
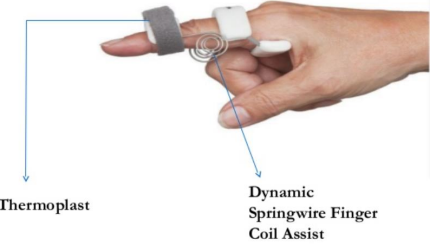

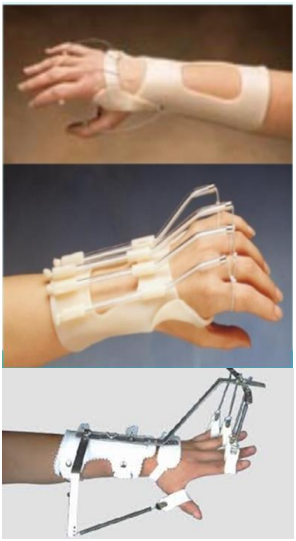
Name this orthosis? Function?
The ROM brace has metal hinges on both sides of the joint and fastens with Velcro straps over foam bands.
Function:
The brace restricts some movements to protect your joints during rehabilitation.
The joint can be locked to stop movement which is not recommended.
The brace provides some support.