Anatomy LAB - Urinary Anatomy & Physiology
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
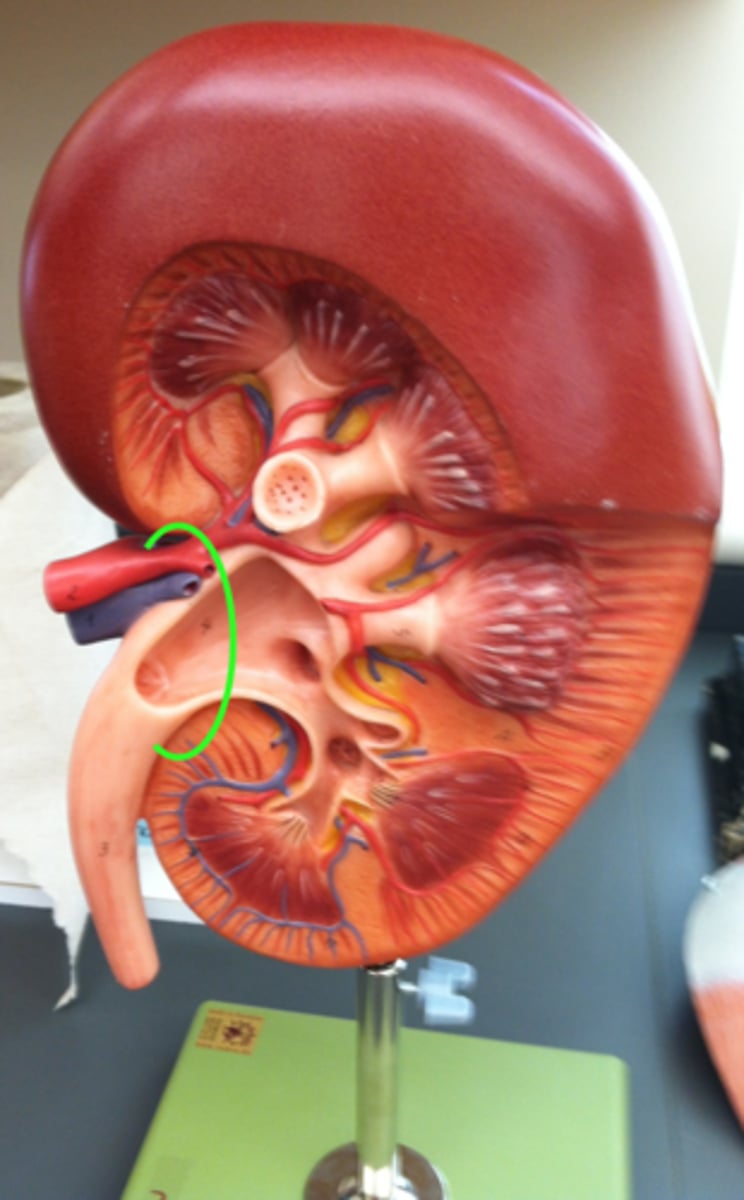
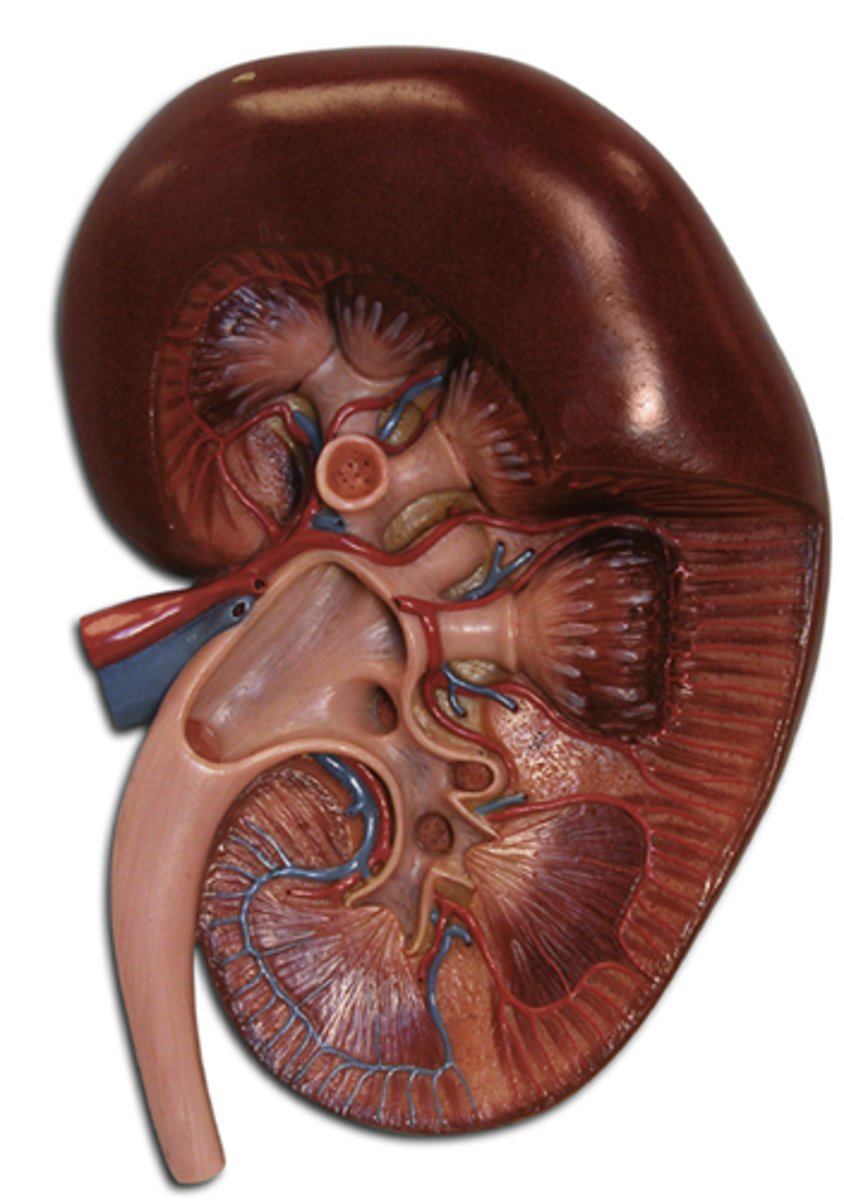
Renal hilus of kidney
allow for the passage of structures that service the kidney
Renal cortex of kidney
creates the hormone erythropoietin (EPO), which helps make red blood cells in your bone marrow
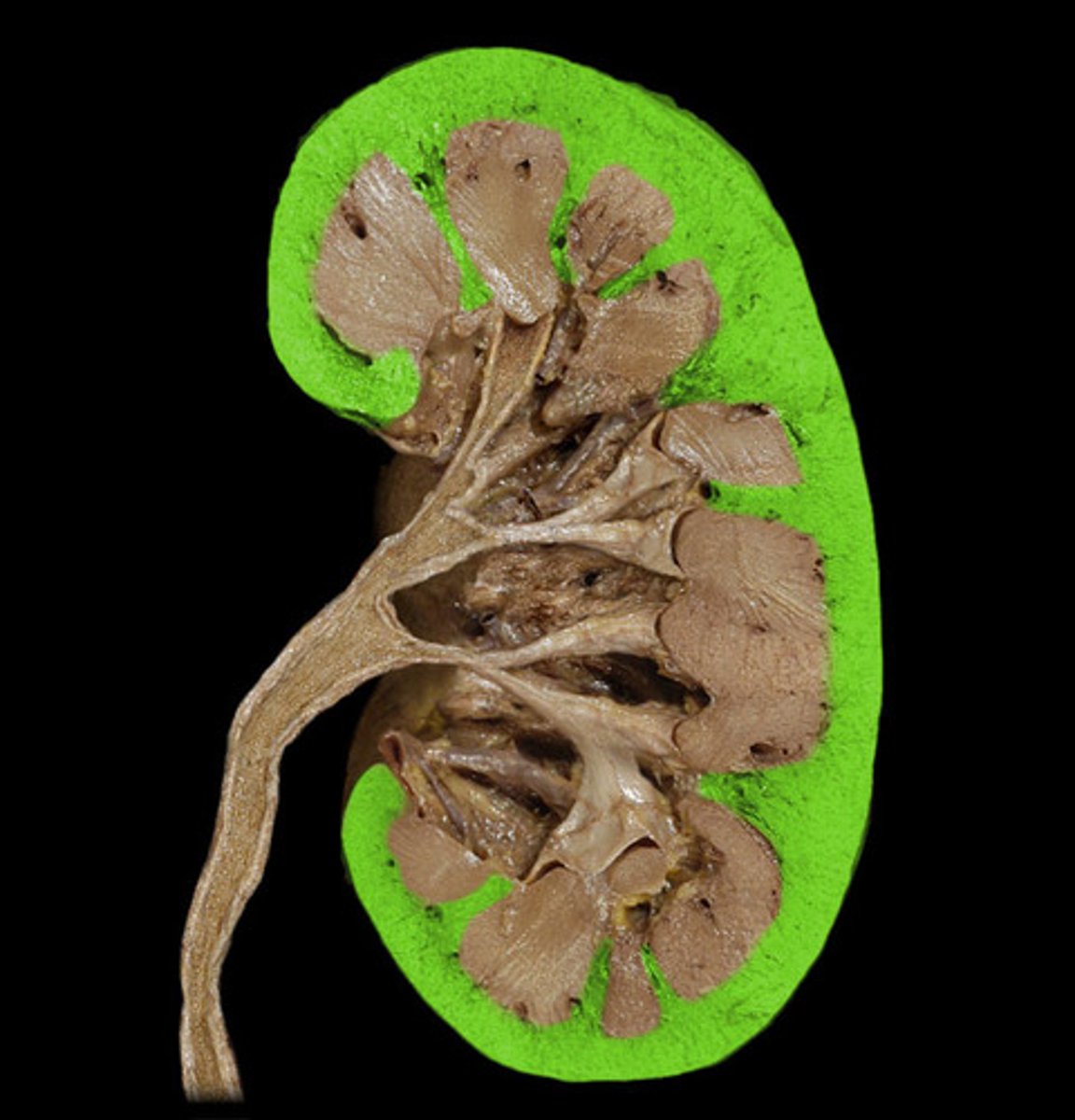
Renal medulla of kidney
regulate the concentration of urine by filtering out water, salts, and acid
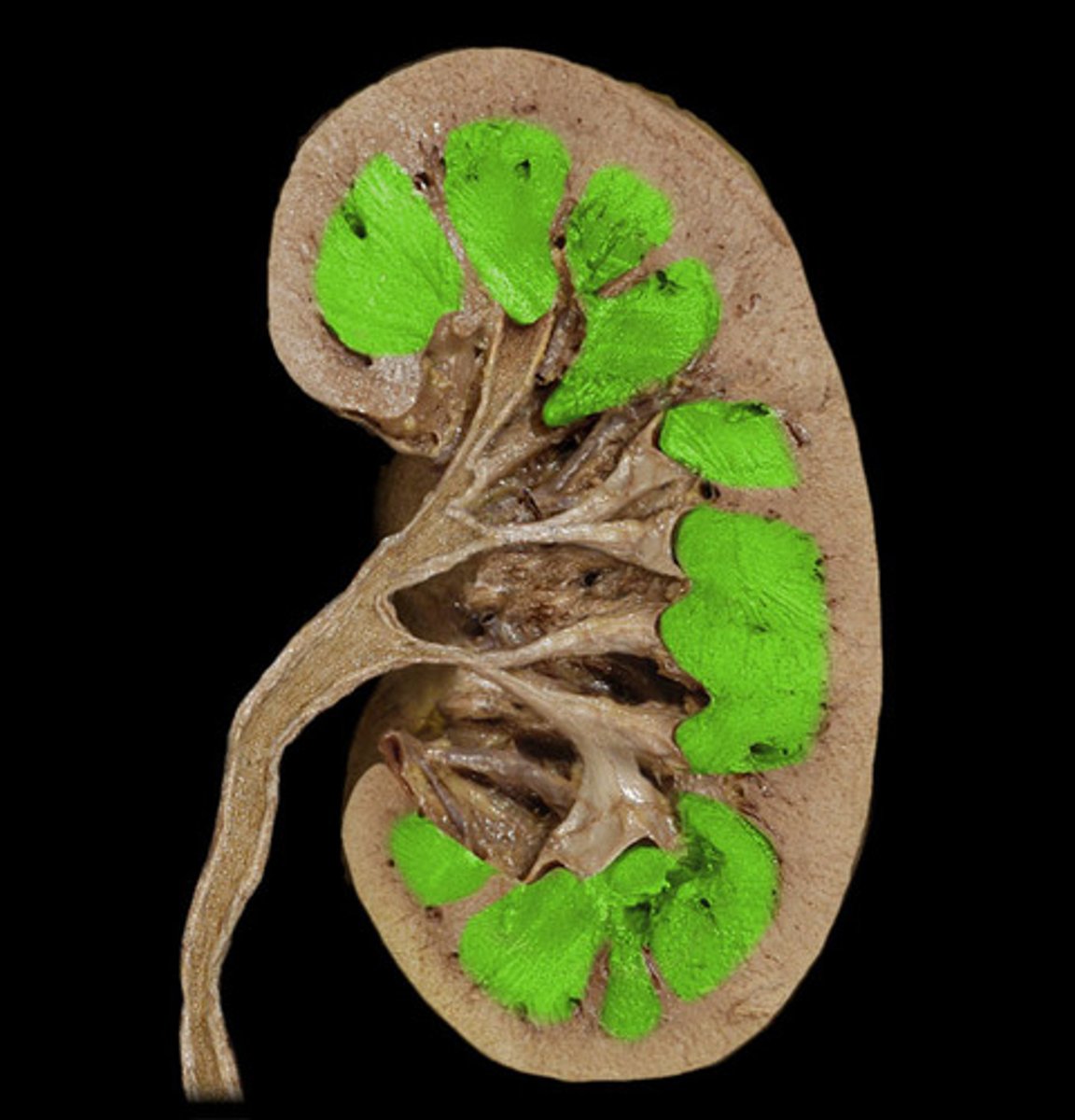
Renal pyramid of kidney
collect and transport urine produced by the nephrons within the kidney medulla
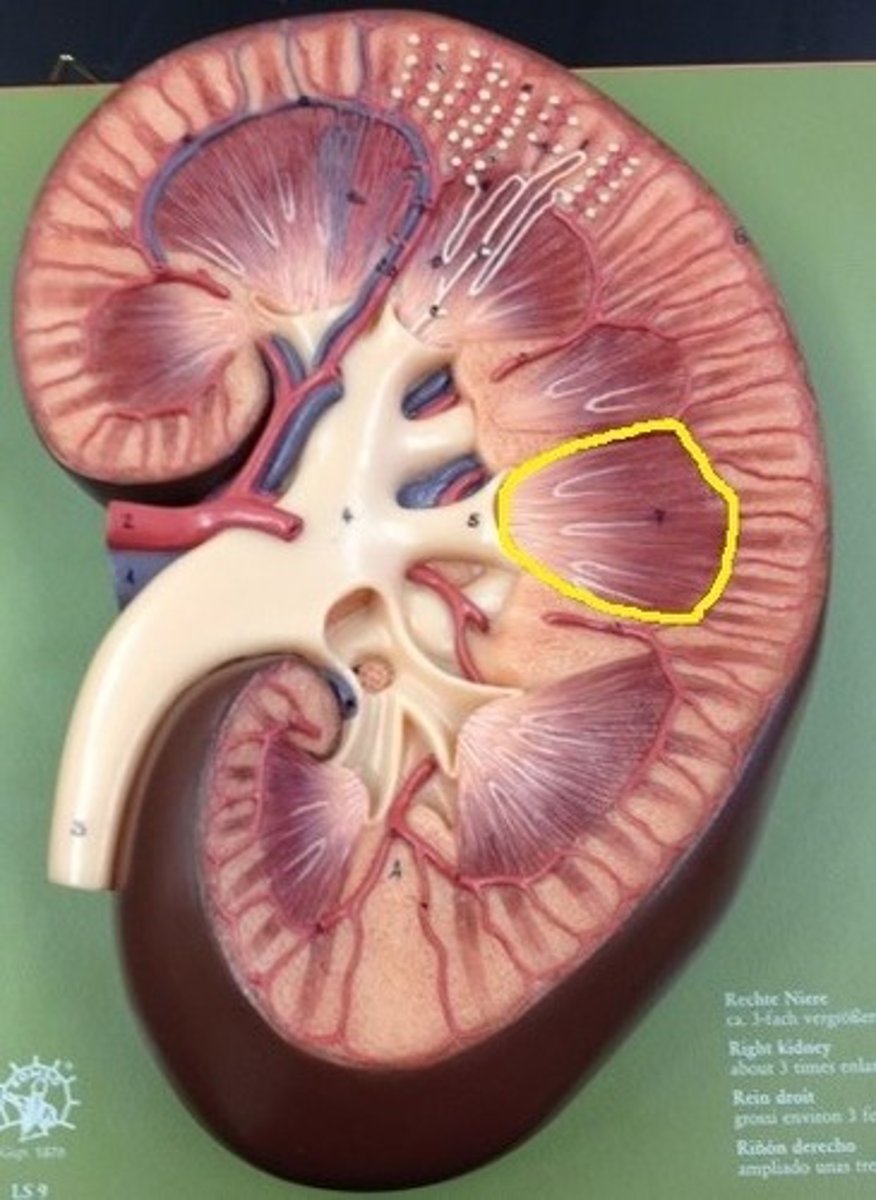
Renal column of kidney
divide the kidney into 6-8 lobes and provide a supportive framework for vessels that enter and exit the cortex
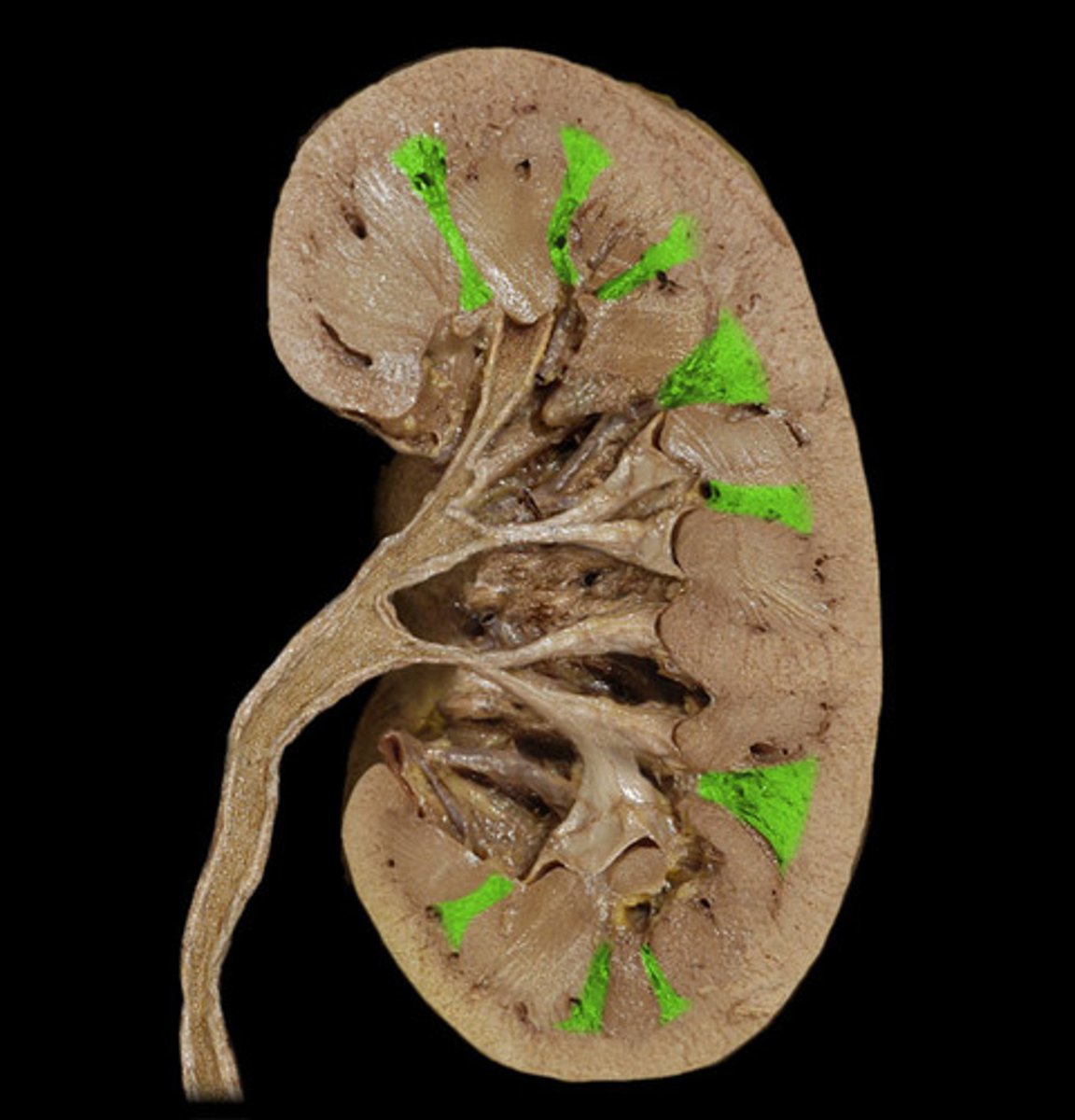
Major calyx of kidney
collect urine from the minor calyces and empty it into the renal pelvis
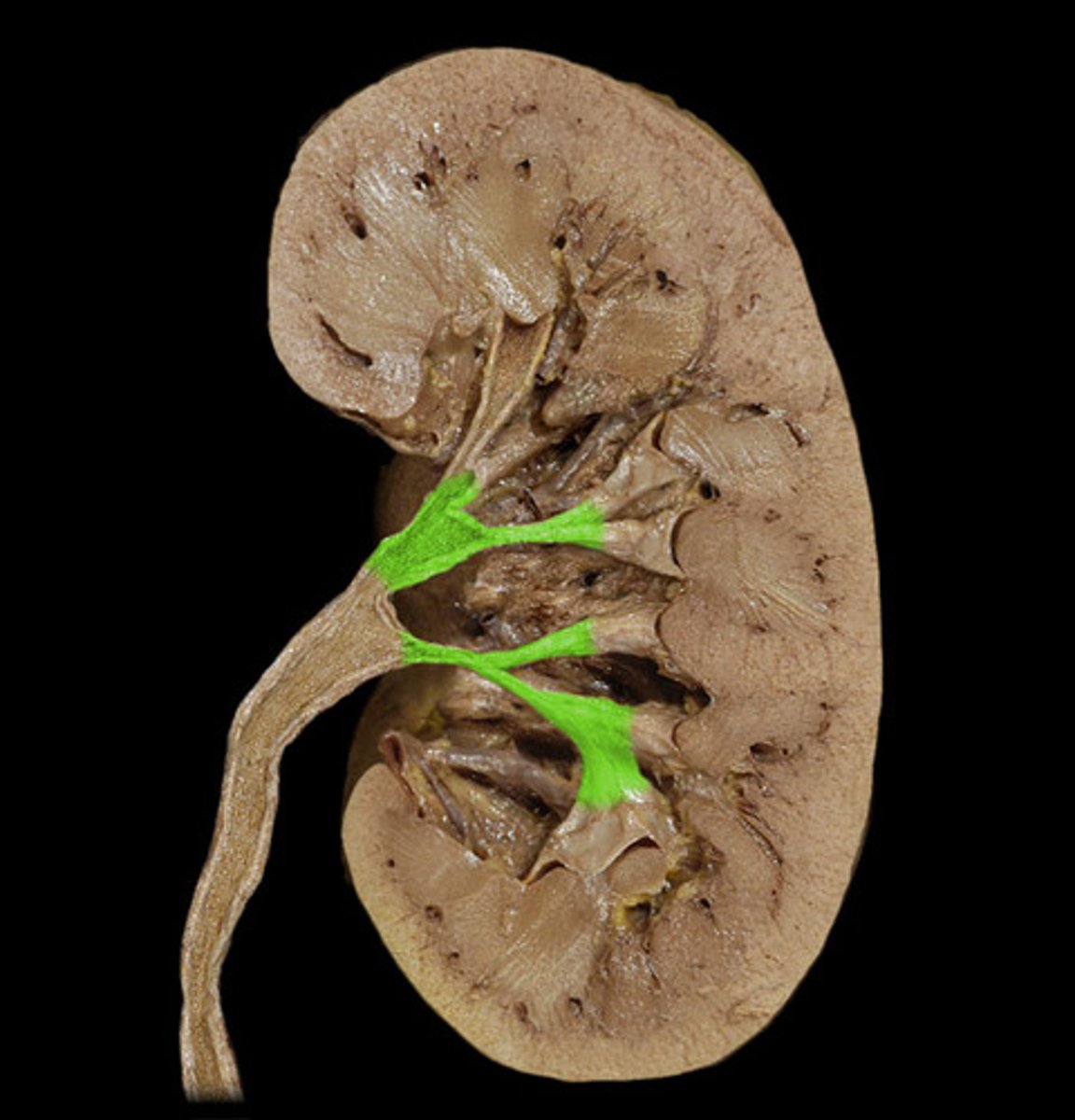
Minor calyx of kidney
collects urine directly from the renal papillae at the apex of each renal pyramid
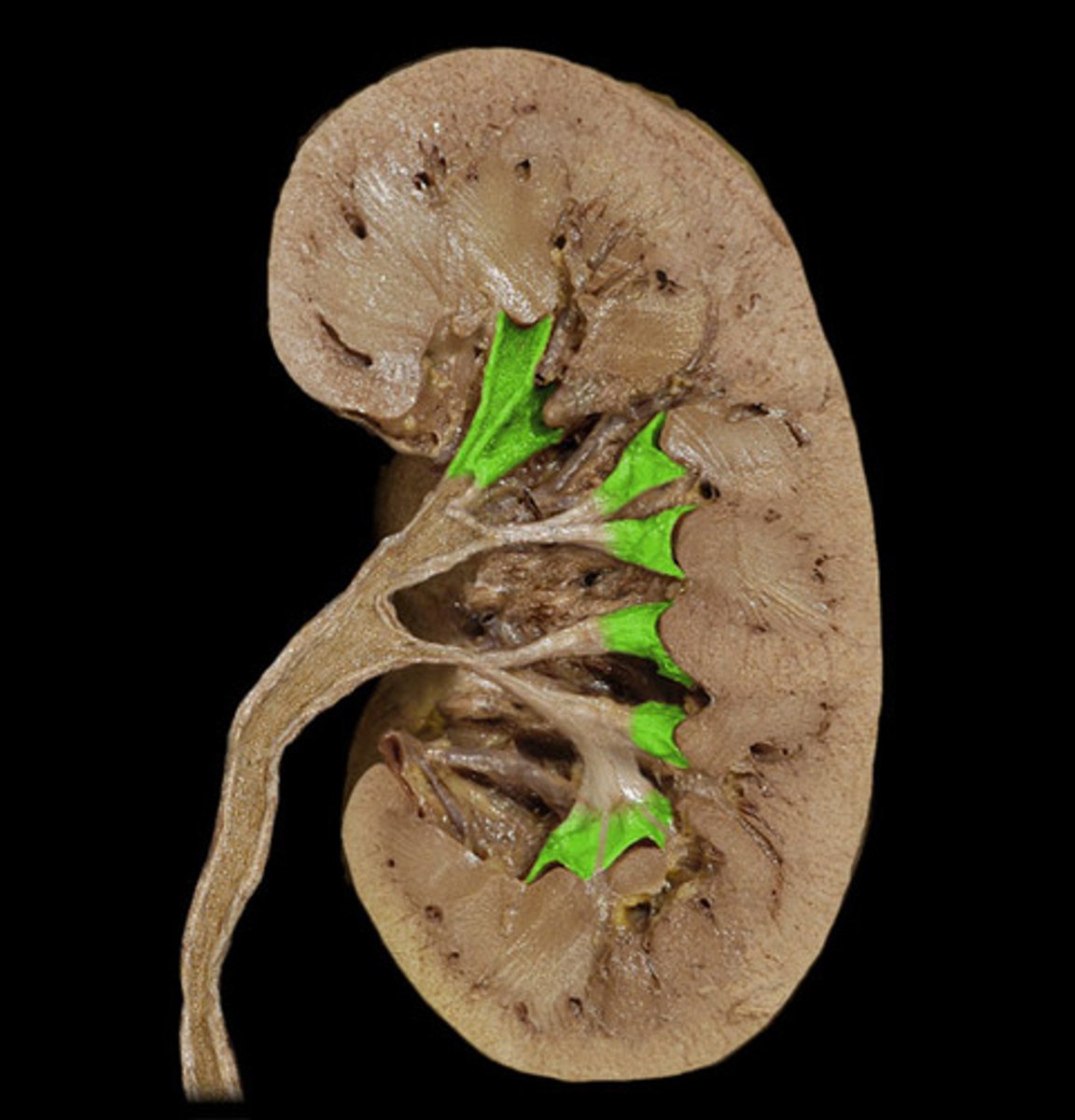
Renal papilla of kidney
The renal papilla is where urine drains from the collecting ducts into the ureters
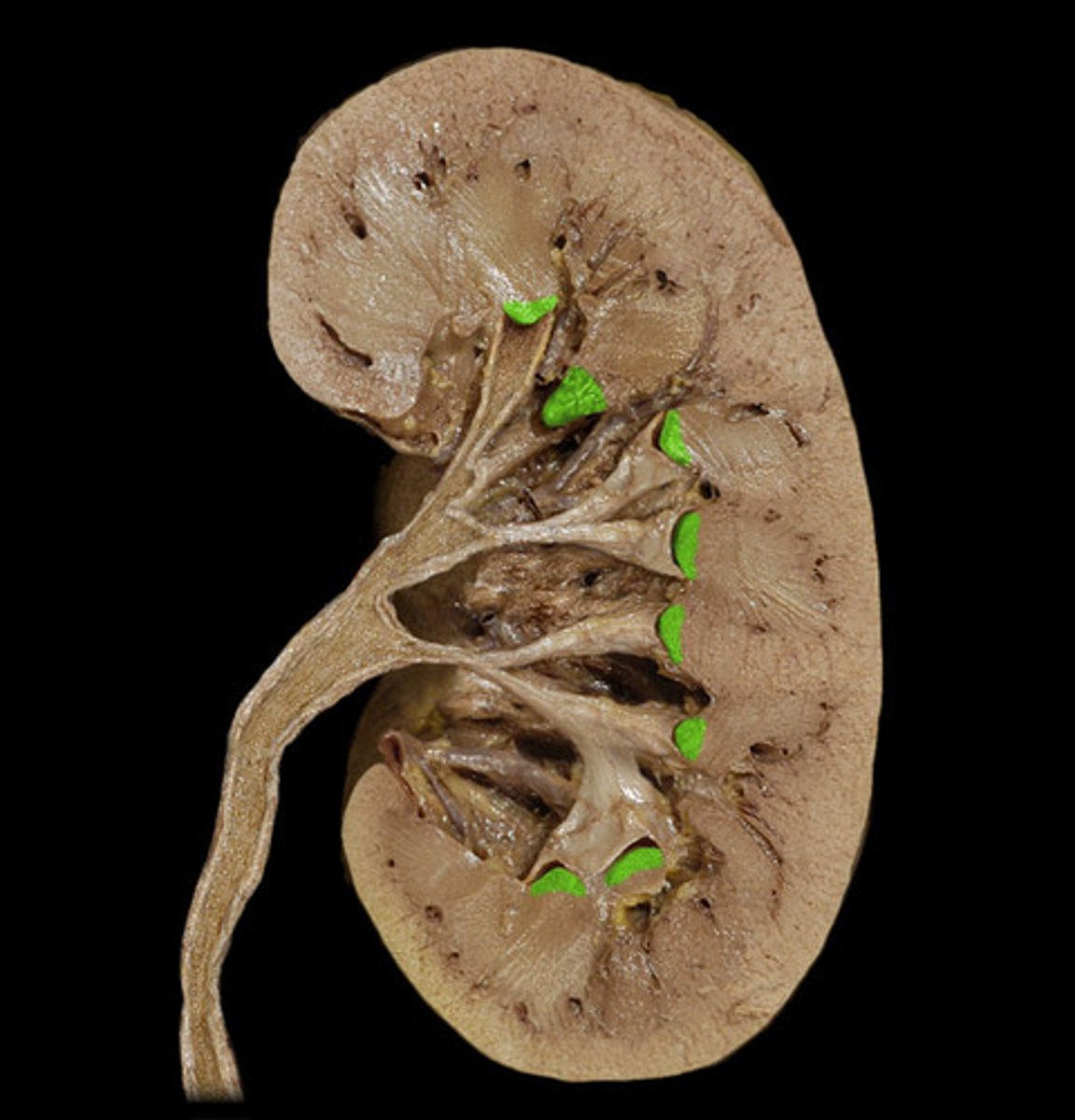
Renal pelvis of kidney
collects urine and directs it into the ureter
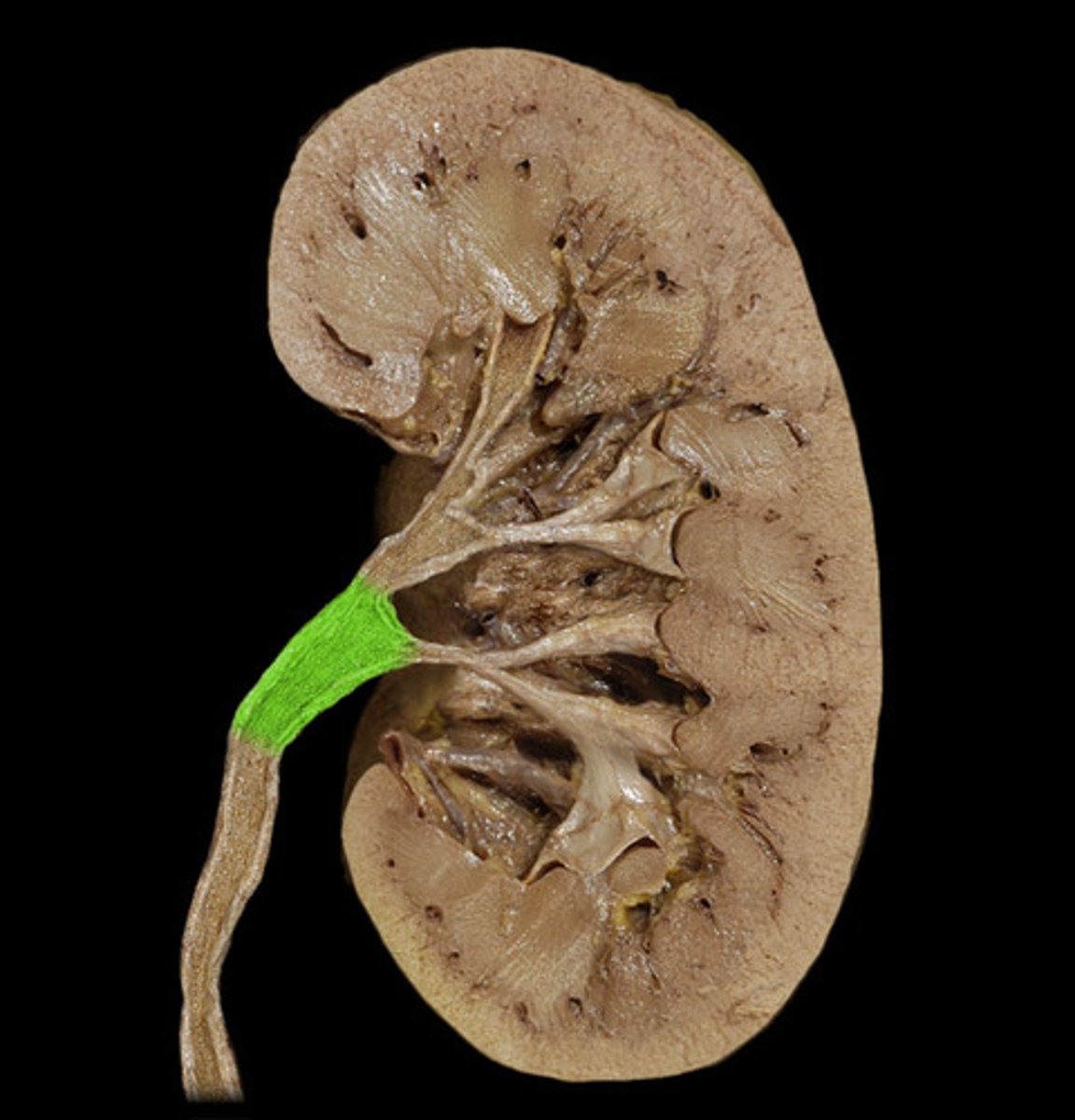
Distal convoluted tubule of kidney
salt and water reabsorption and plays a major role in acid-base balance
regulation
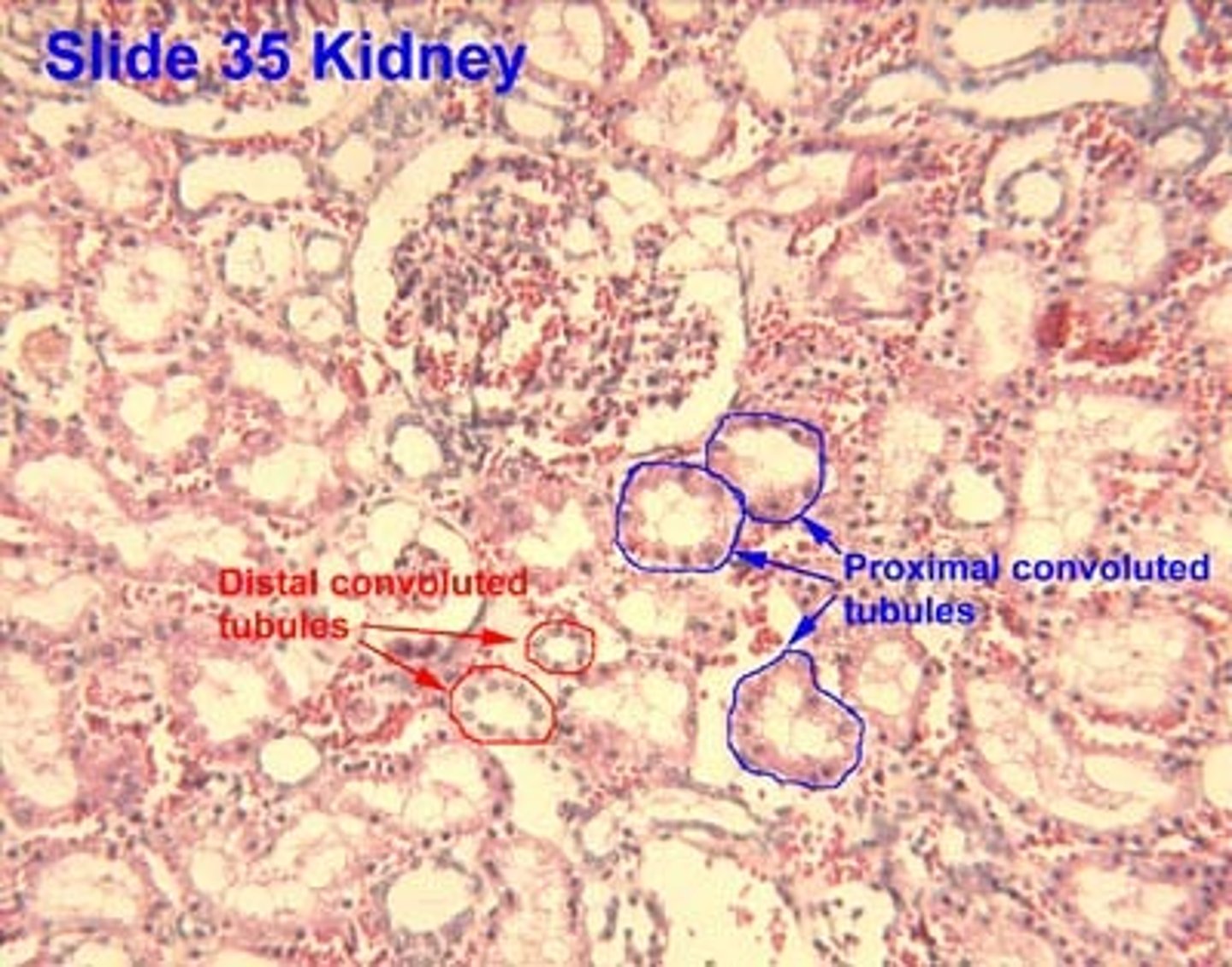
Renal corpuscle of kidney
filter waste from the blood
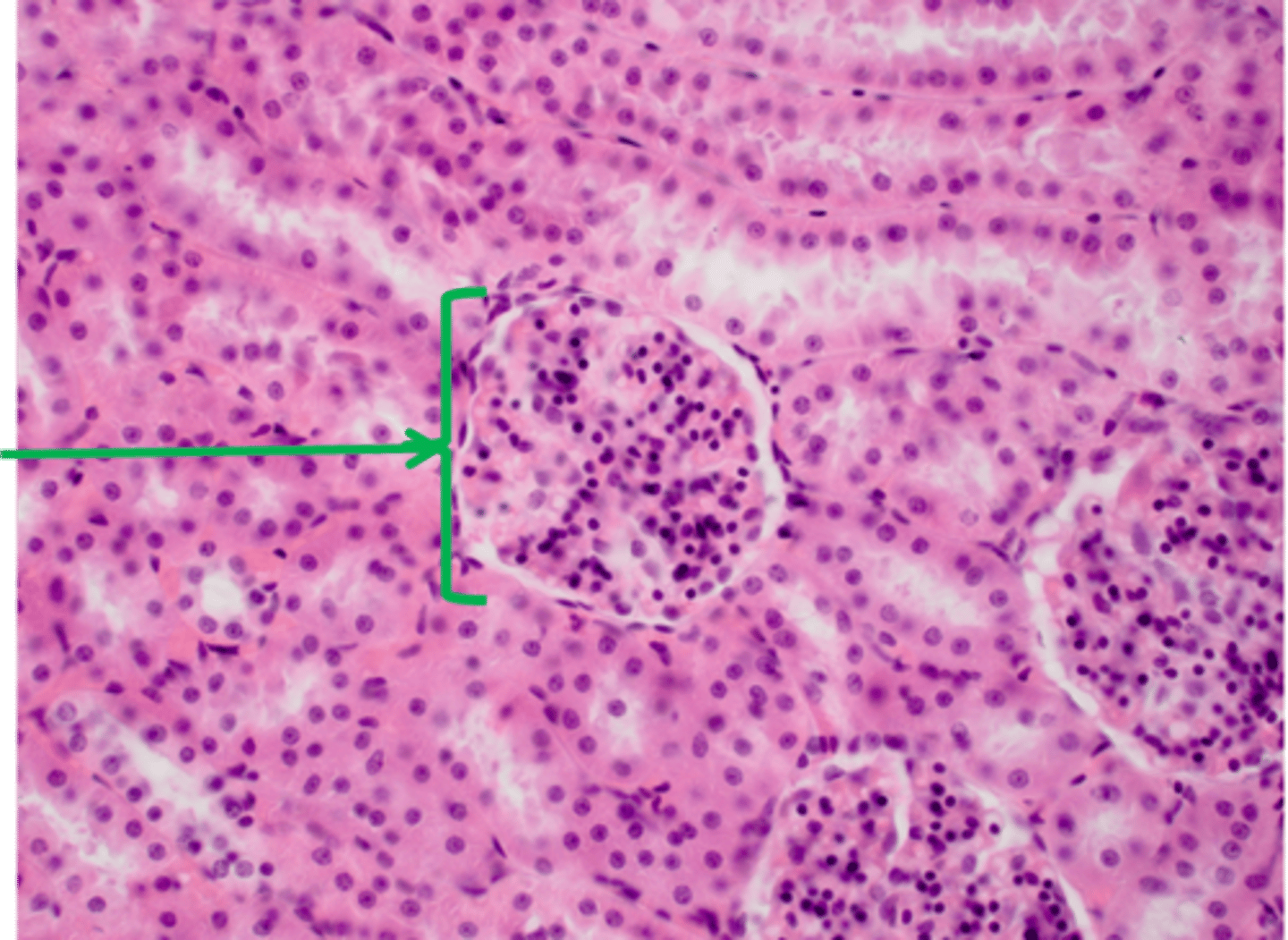
Bowman's capsule of kidney
participates in the filtration of blood from the glomerular capillaries
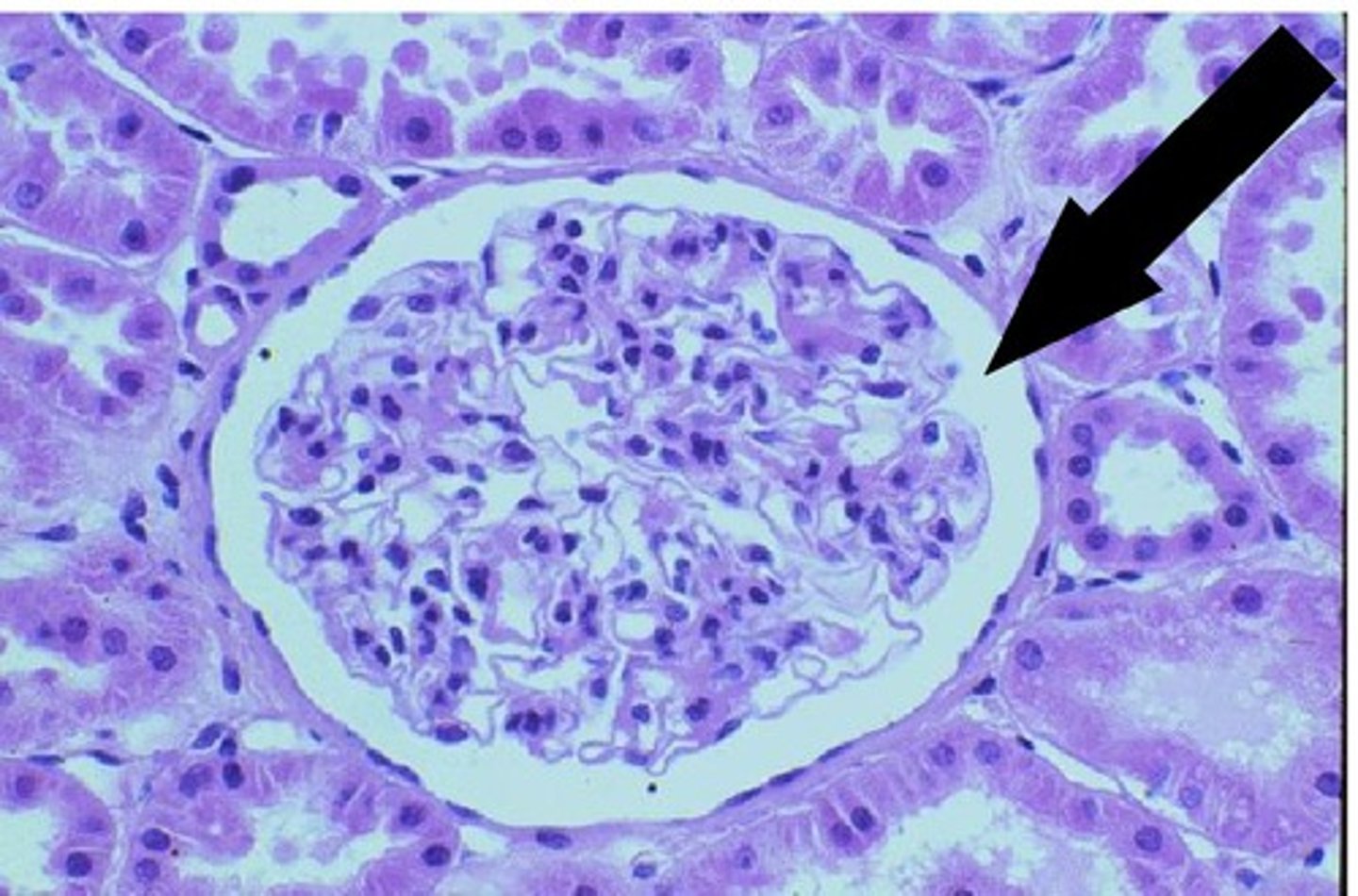
Glomerulus of kidney
removes waste and extra fluid from the blood
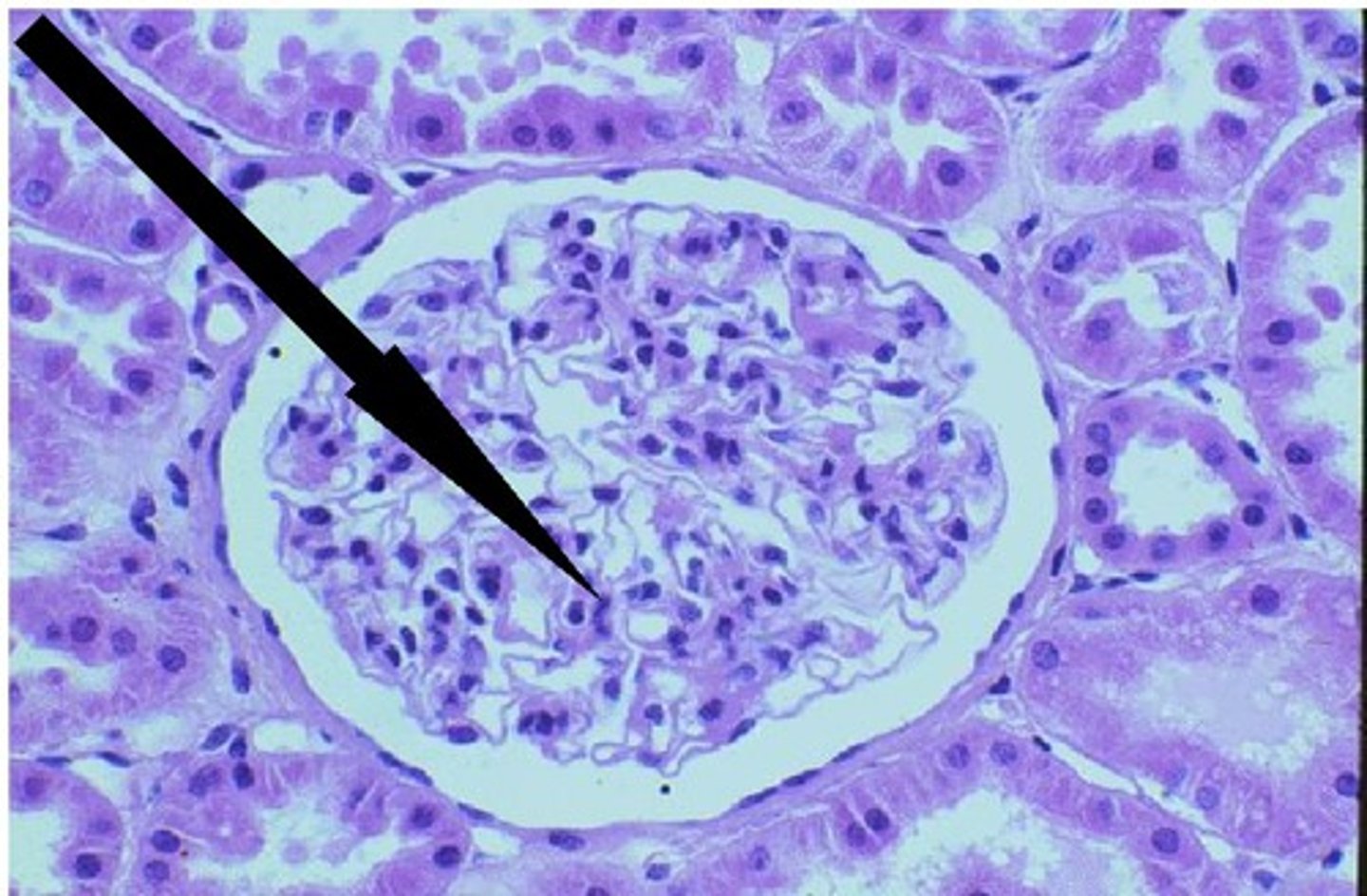
Ureter
carries urine from the kidney to the bladder
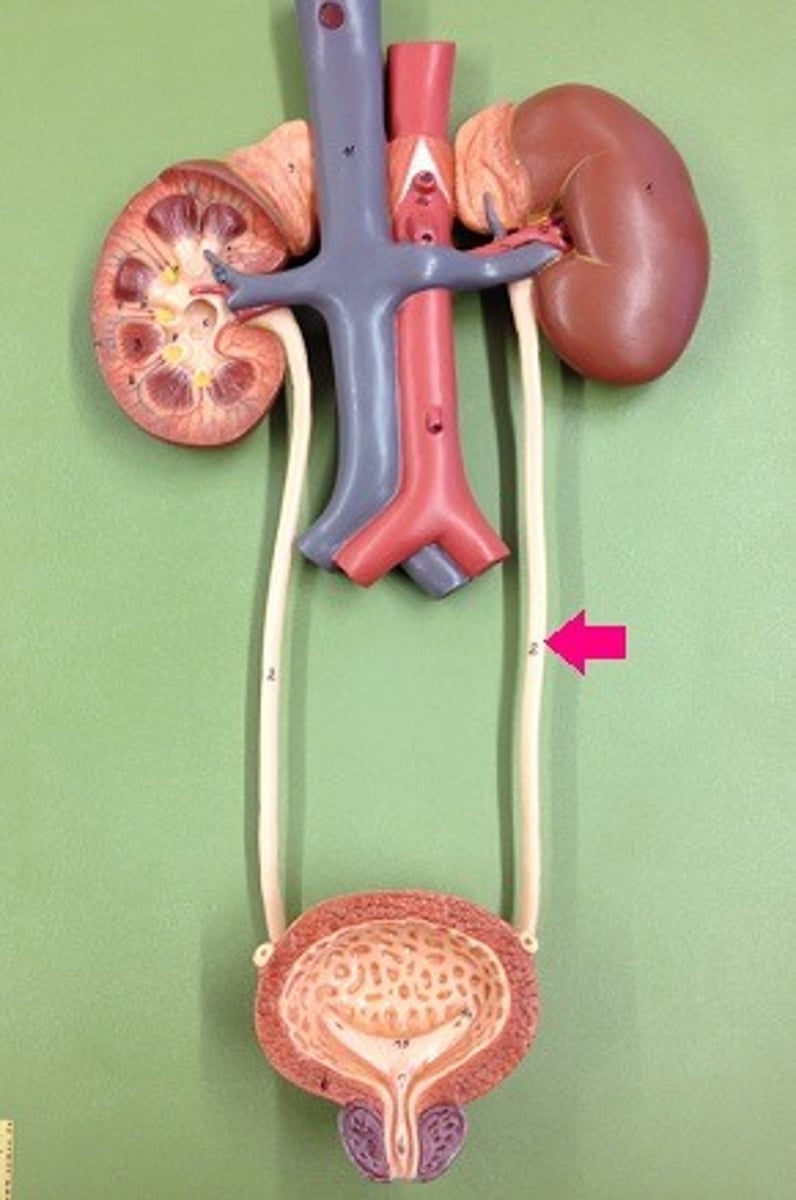
Kidney
filters blood to eliminate waste, acid balance, fluid and ion balance, maintain homeostasis
Detrusor muscle of bladder
responsible for contracting to expel urine from the bladder during urination
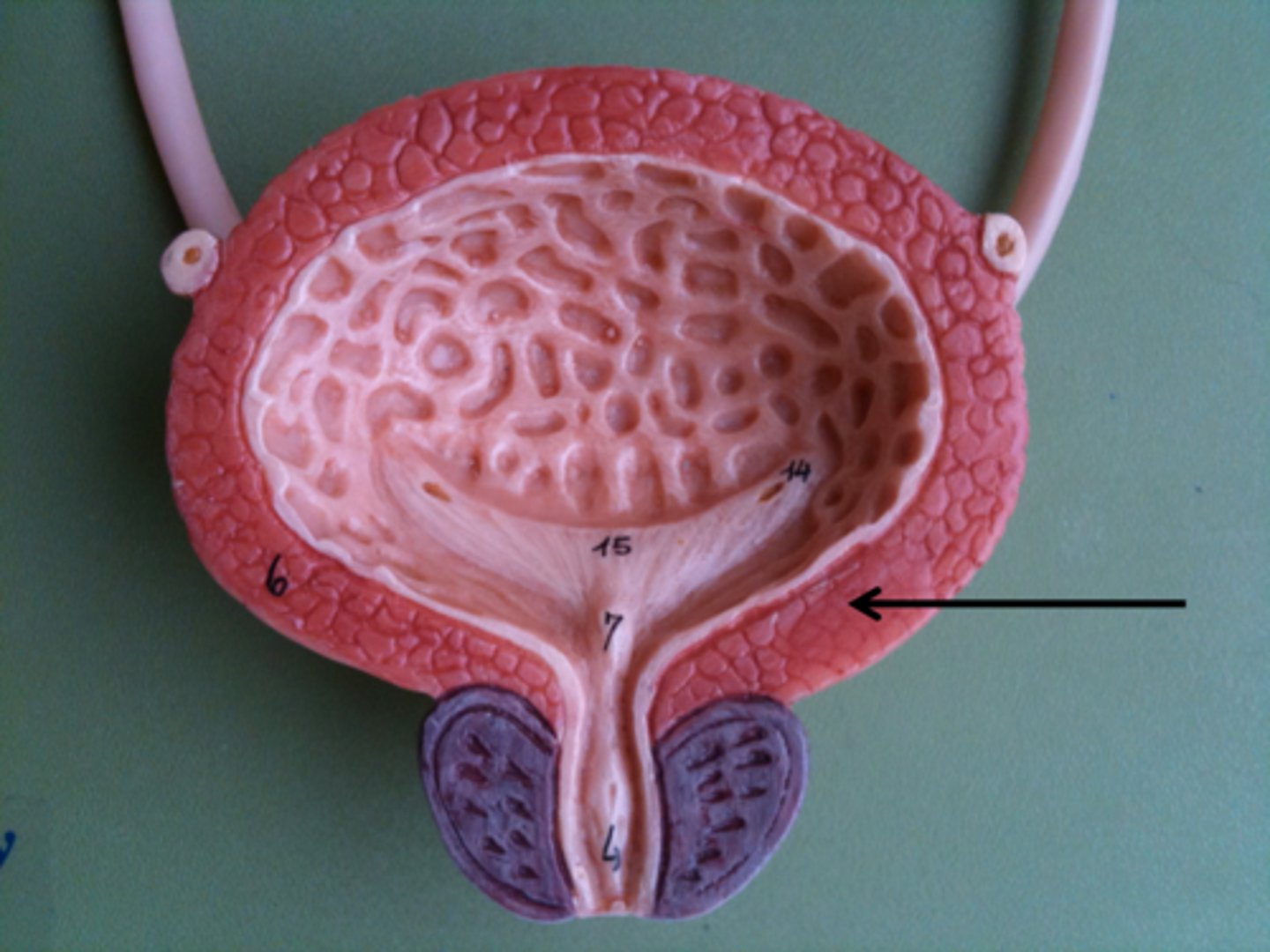
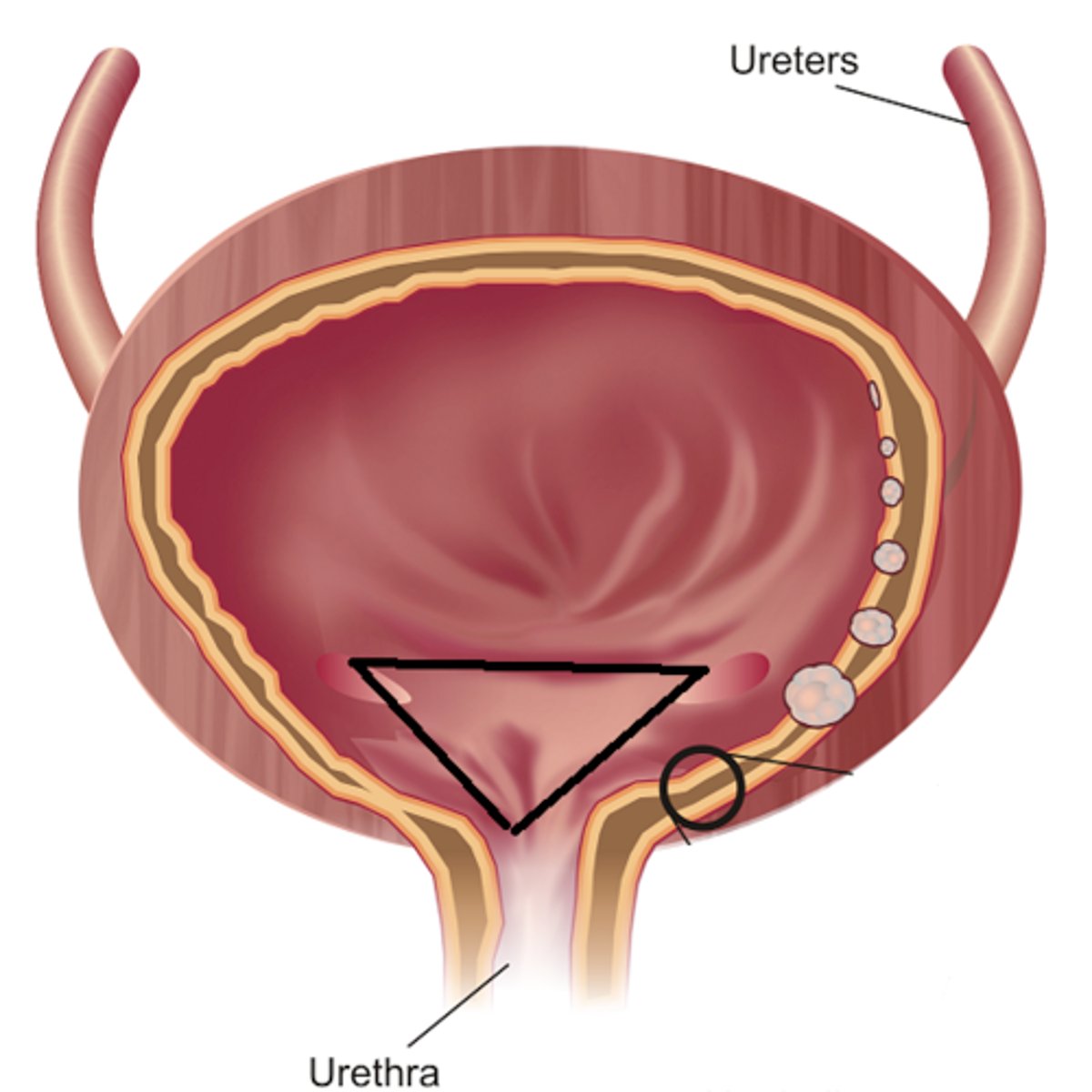
Ureteral opening of bladder
allows urine to pass outside the body
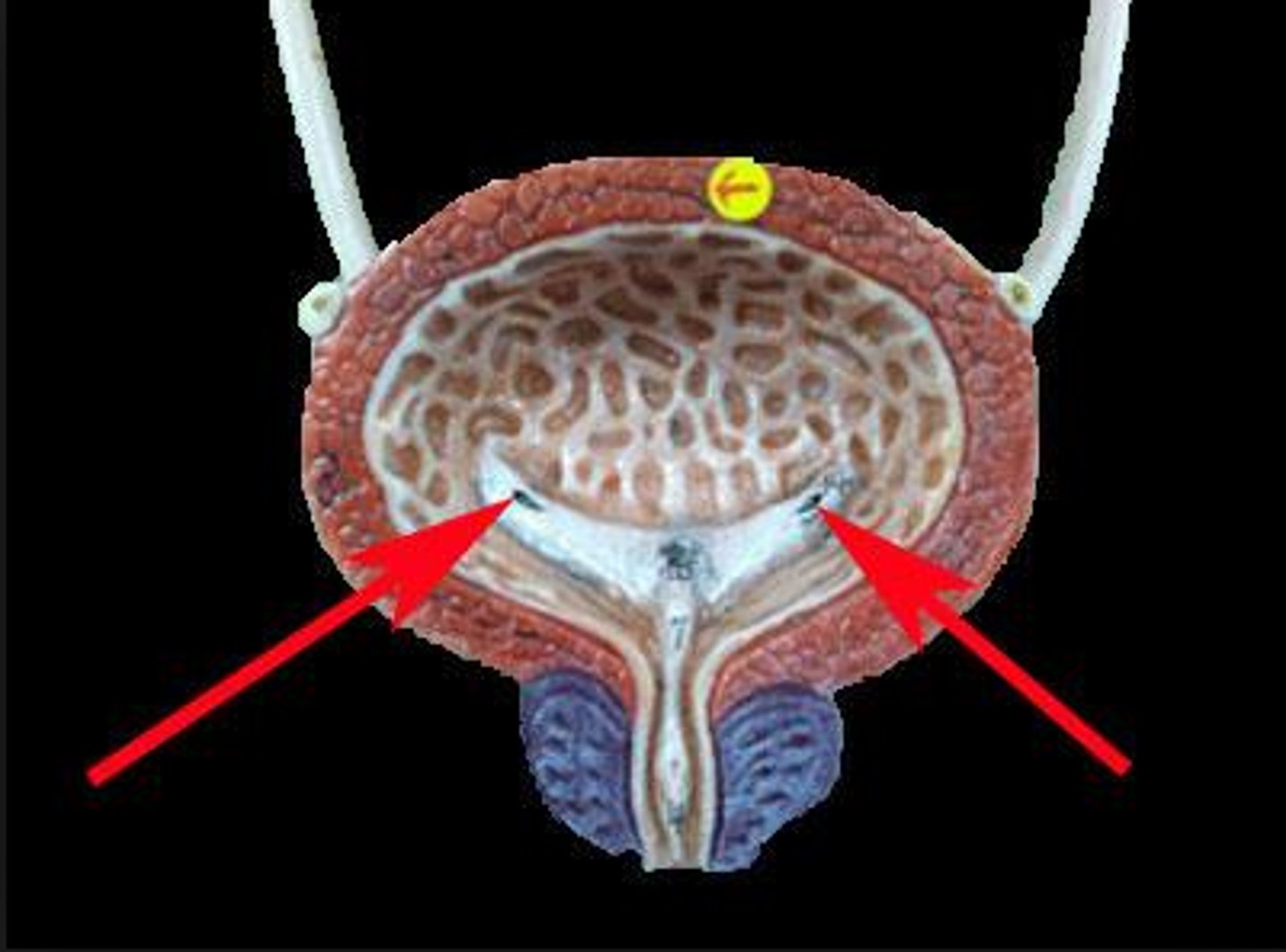
Trigone of bladder
The trigone stabilizes the attachment of the ureters to the bladder, and the bladder to the pelvic fascia
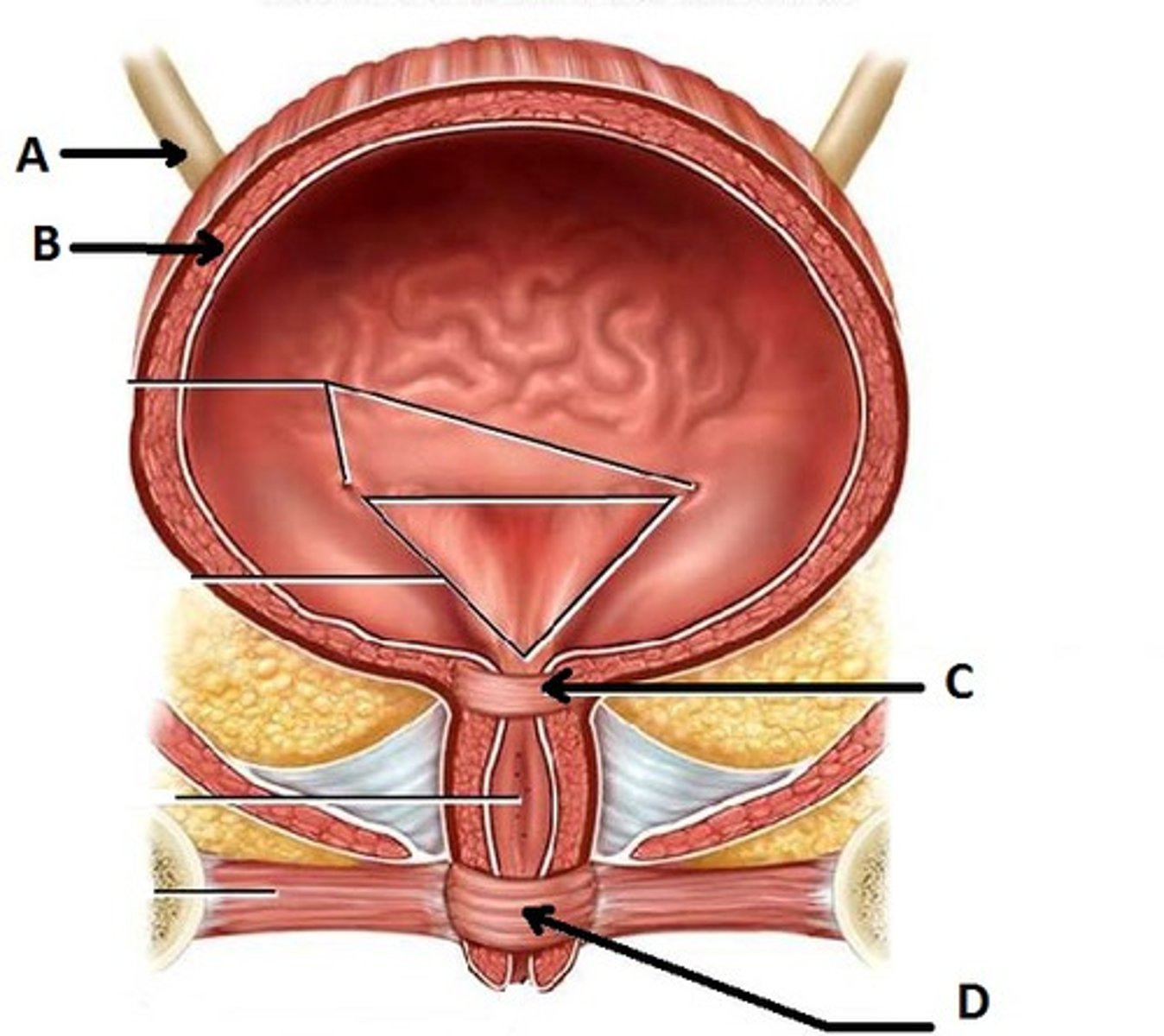
External urethral sphincter of bladder
D
a voluntary muscle that actively controls the flow of urine by contracting to prevent leakage and relaxing to allow urination
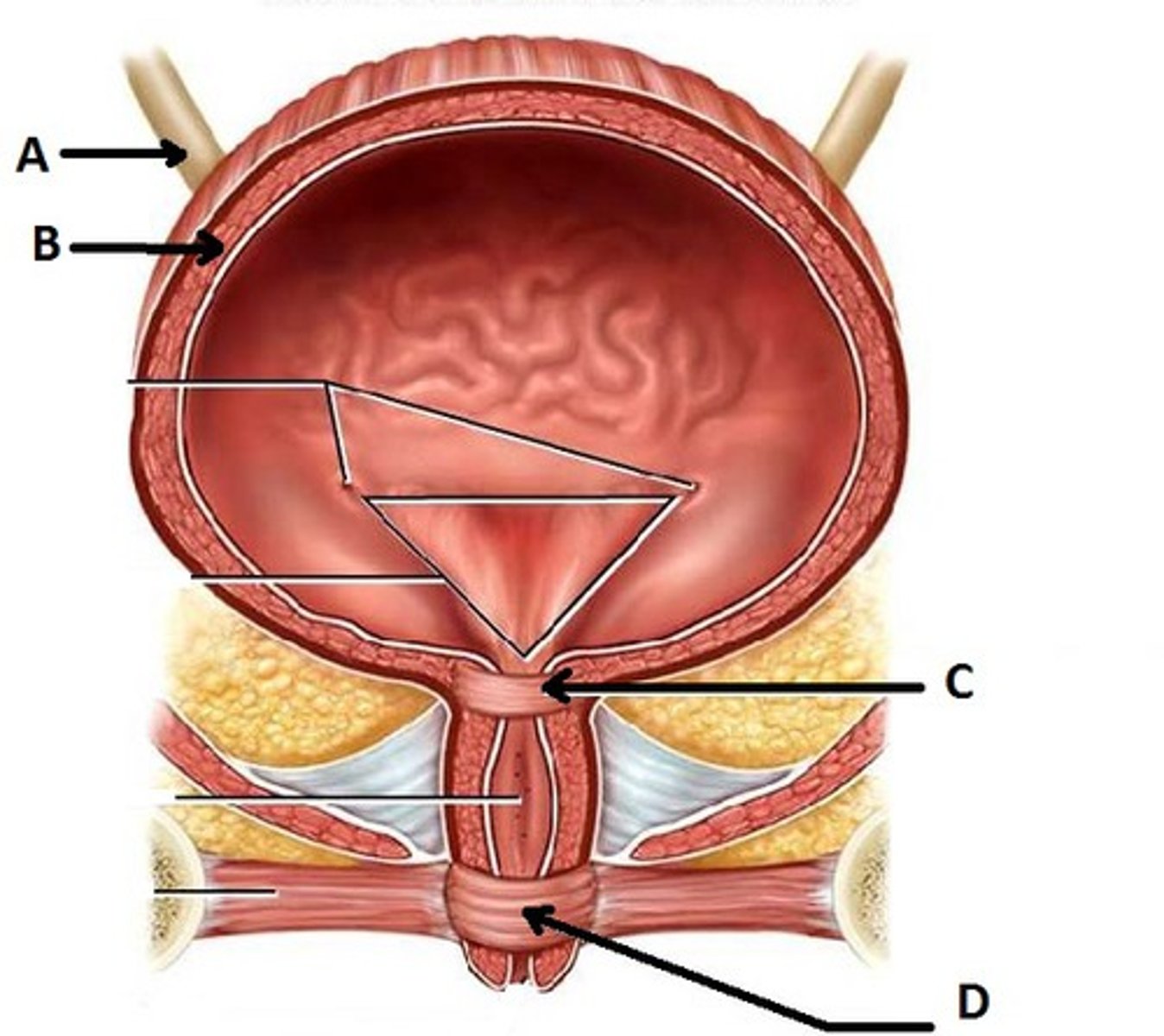
Internal urethral sphincter of bladder
C
to control the involuntary flow of urine from the bladder to the urethra
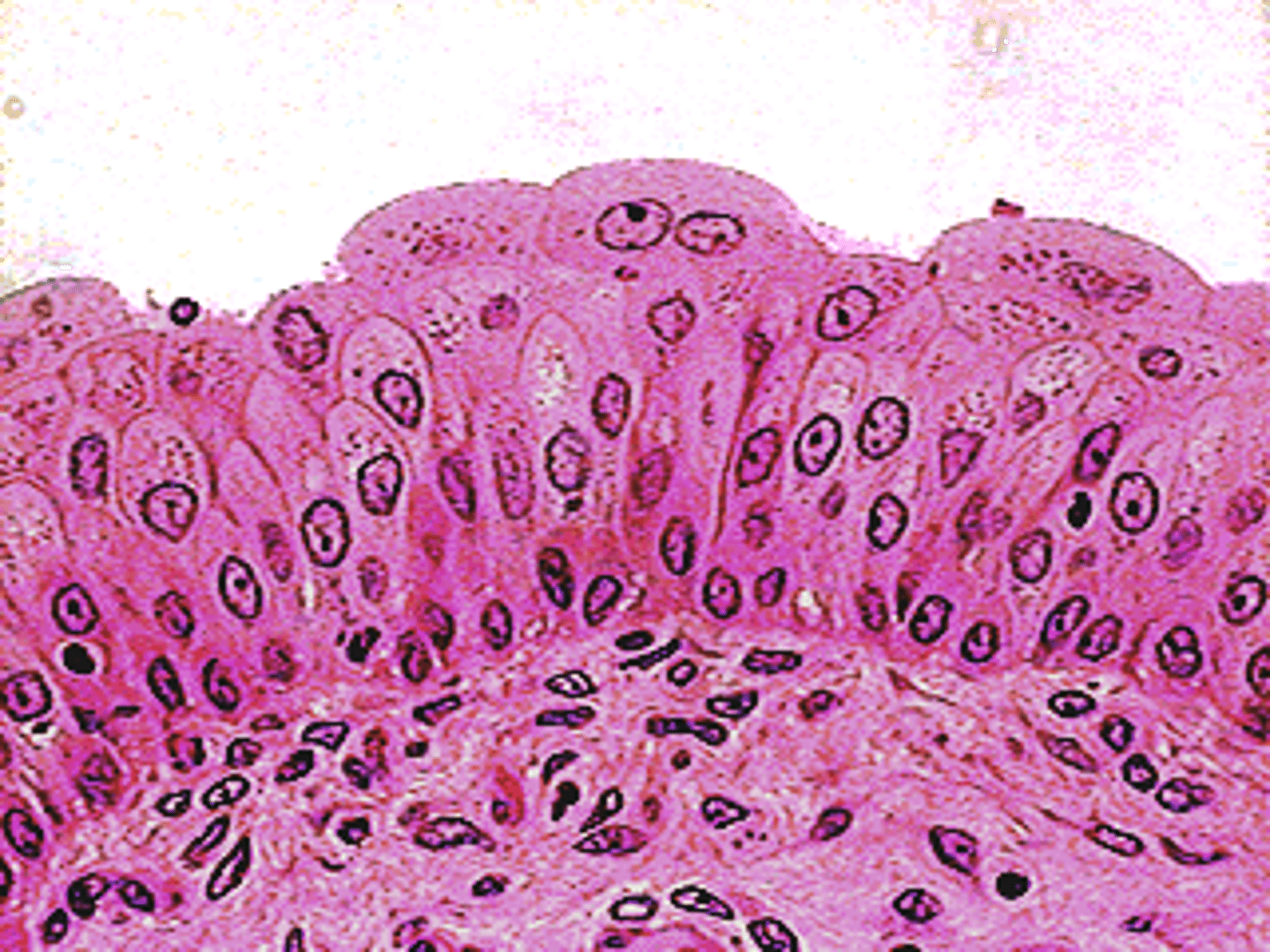
Transitional epithelial tissue of bladder
accommodate fluctuations in urine volume by expanding and contracting as the bladder fills and empties
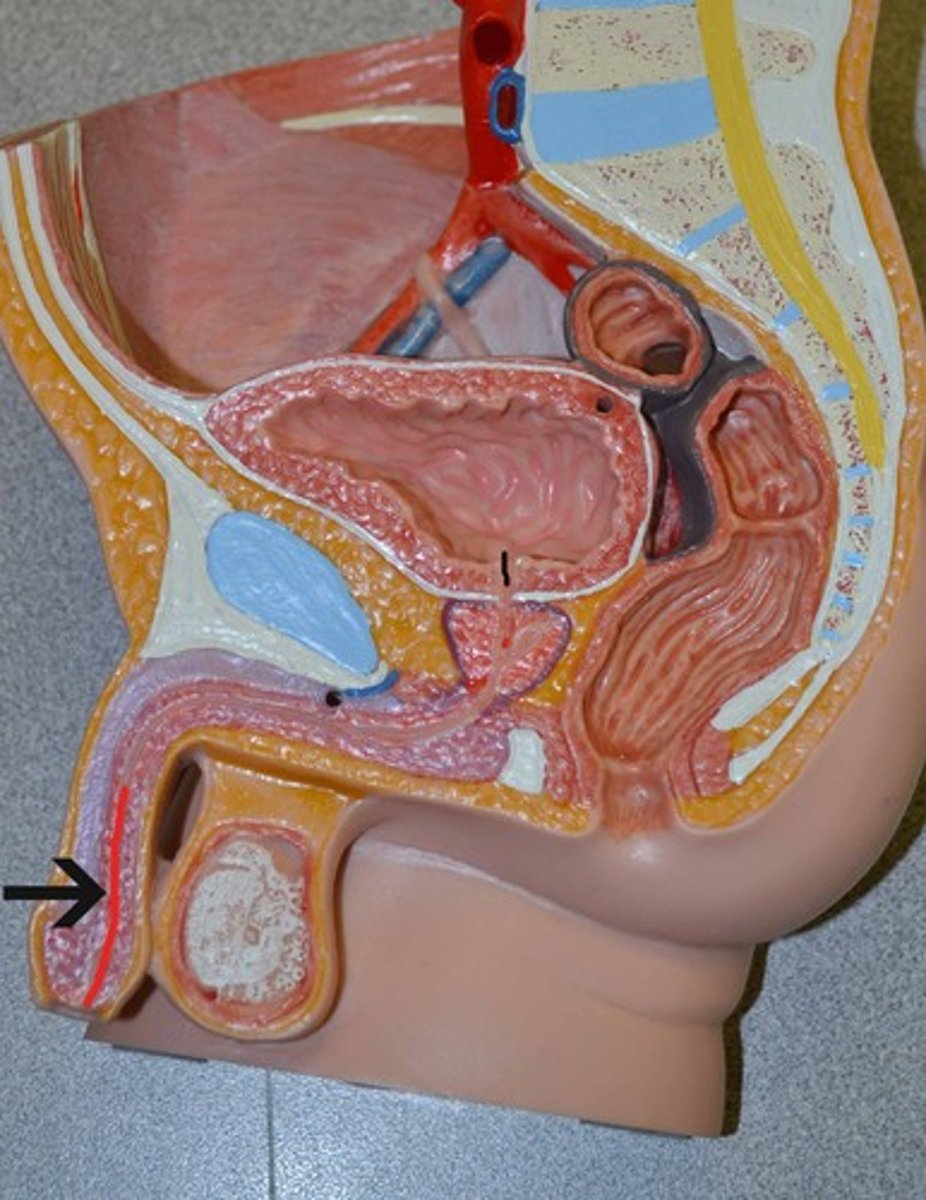
Urethra
allows urine to pass out of the body
Afferent arteriole of nephron
B
Deliver blood to the nephron
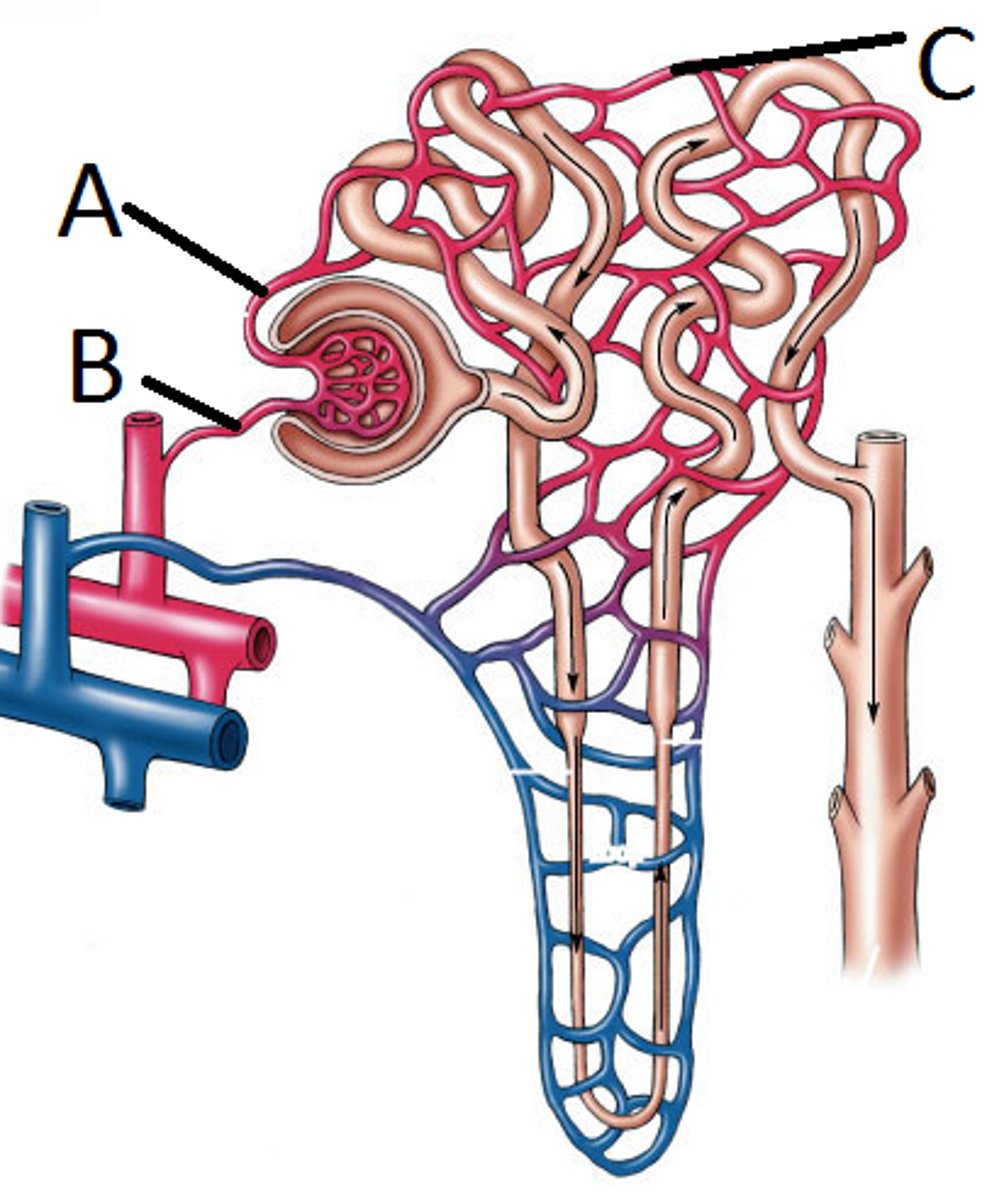
Efferent arteriole of nephron
A
Collects blood form the glomerulus and continues along to form capillary network around other portions of the nephron
Smaller in diameter = increased hydrostatic pressure within the glomerulus
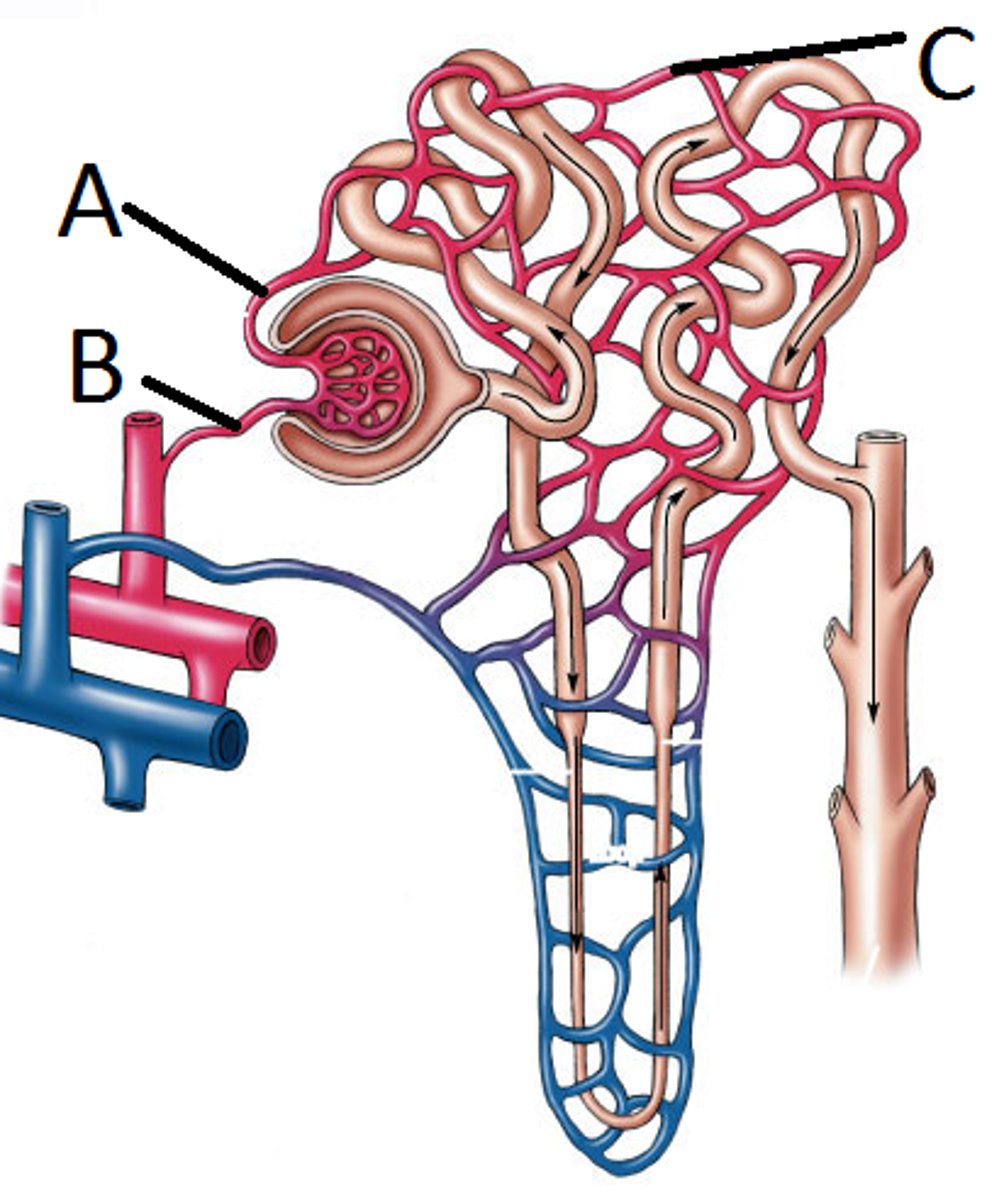
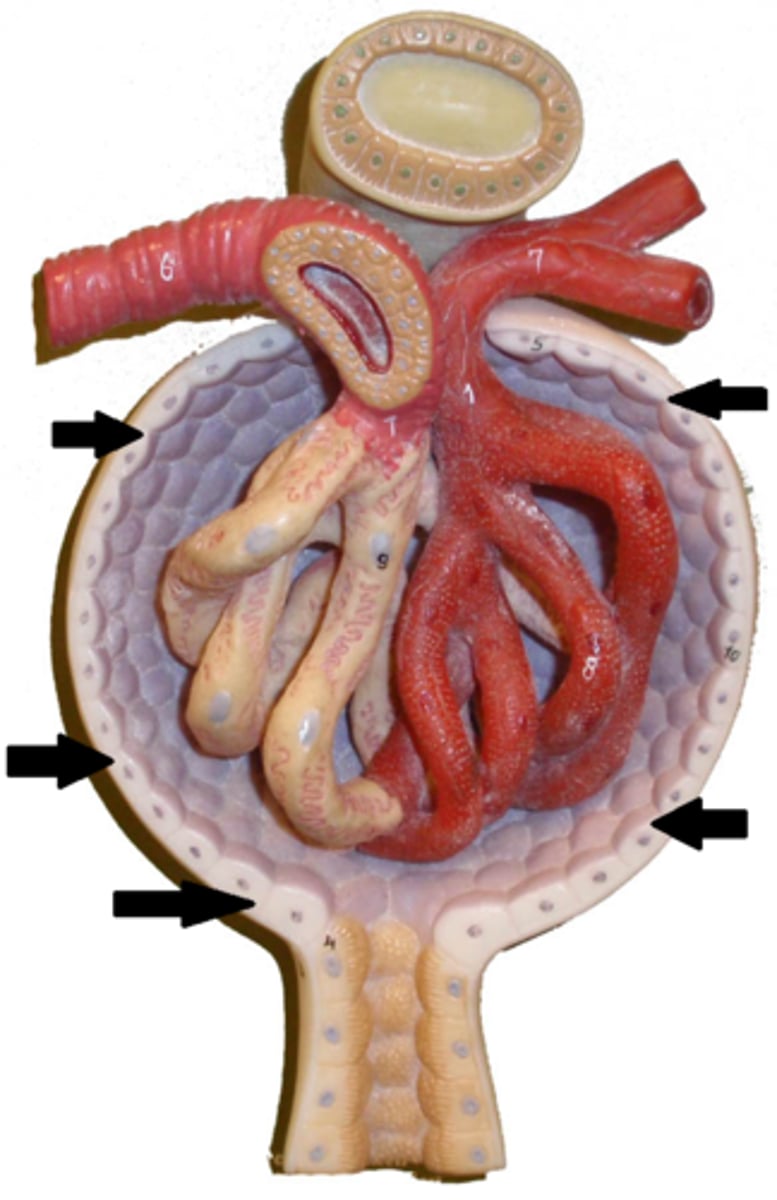
Glomerulus of nephron
cluster of tiny blood vessels in the nephron that filters blood
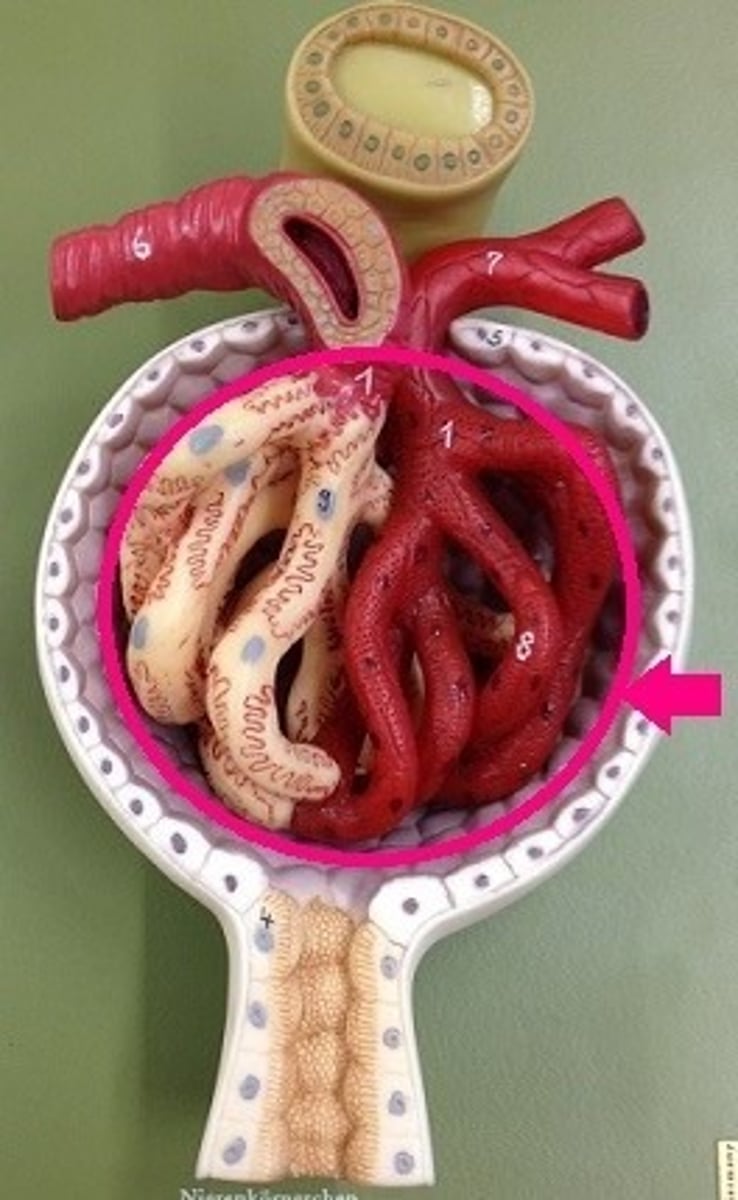
Bowman's capsule of nephron
participates in the filtration of blood from the glomerular capillaries
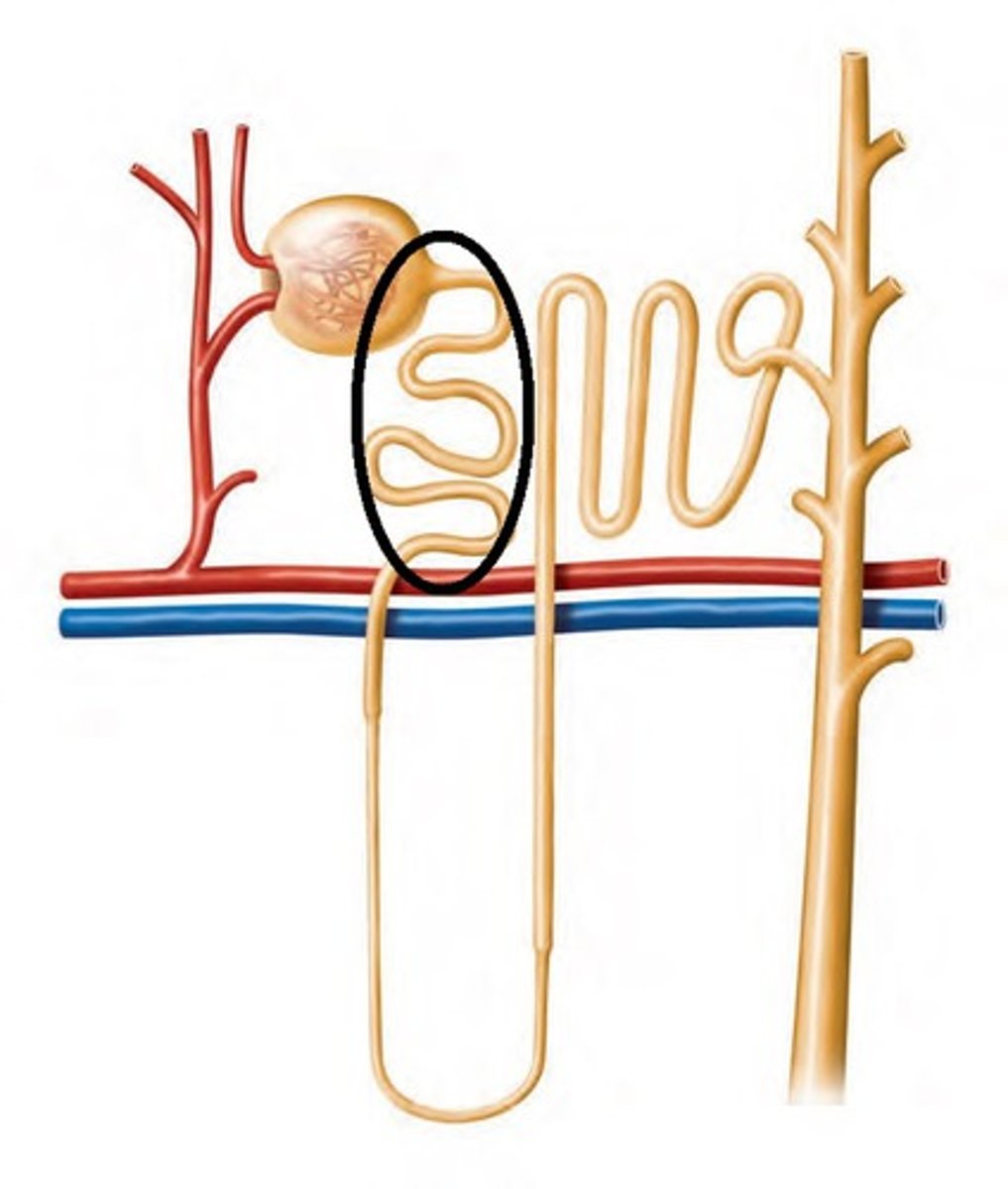
Proximal convoluted tubule of nephron
reabsorbs water and salts from filtrate
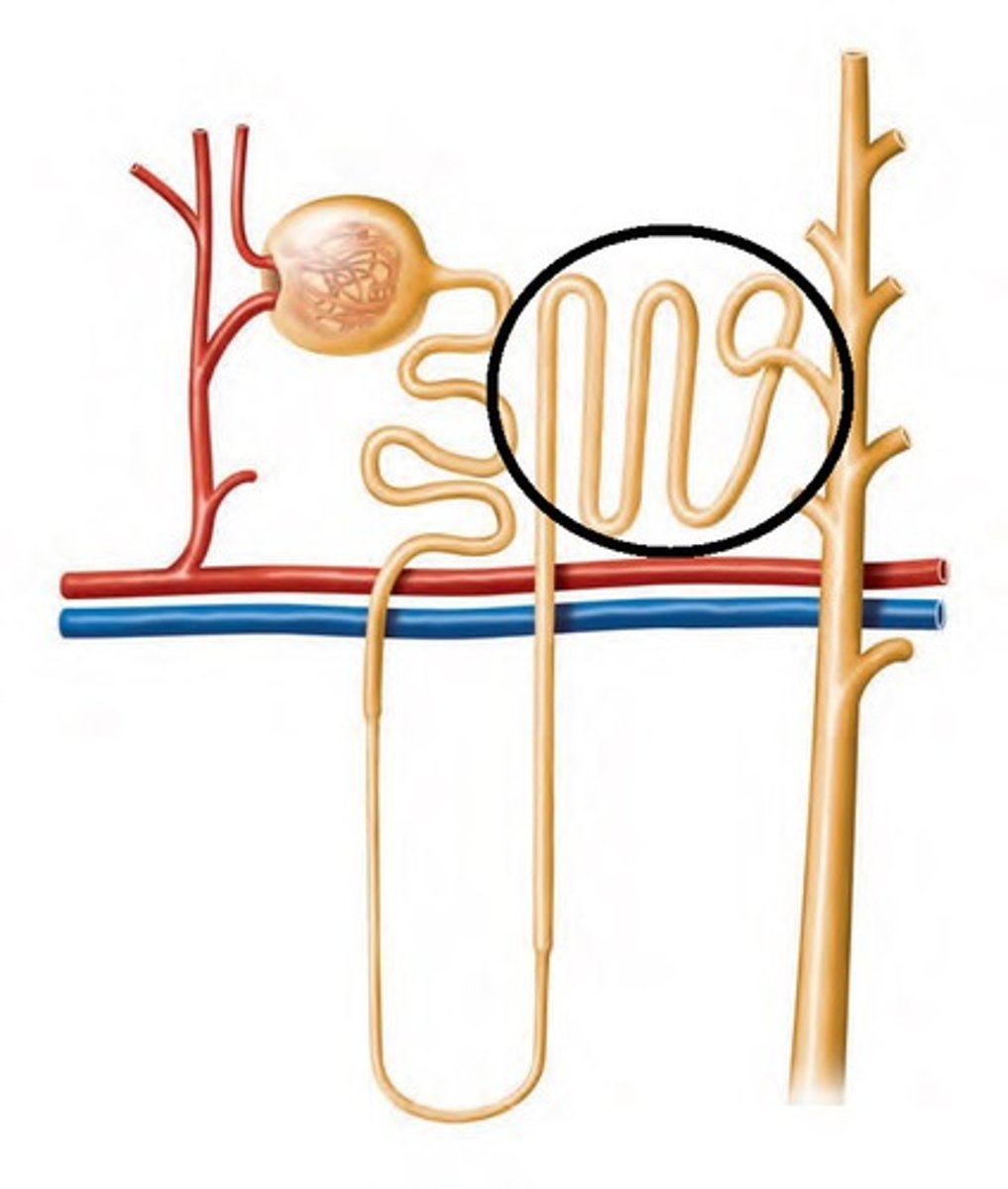
Distal convoluted tubule of nephron
plays a critical role in a variety of homeostatic processes, including sodium chloride reabsorption, potassium secretion, and calcium and magnesium handling
Nephron loop ascending limb
impermeable to water and contains carrier proteins to actively pump sodium and chloride ions from the tubular fluid
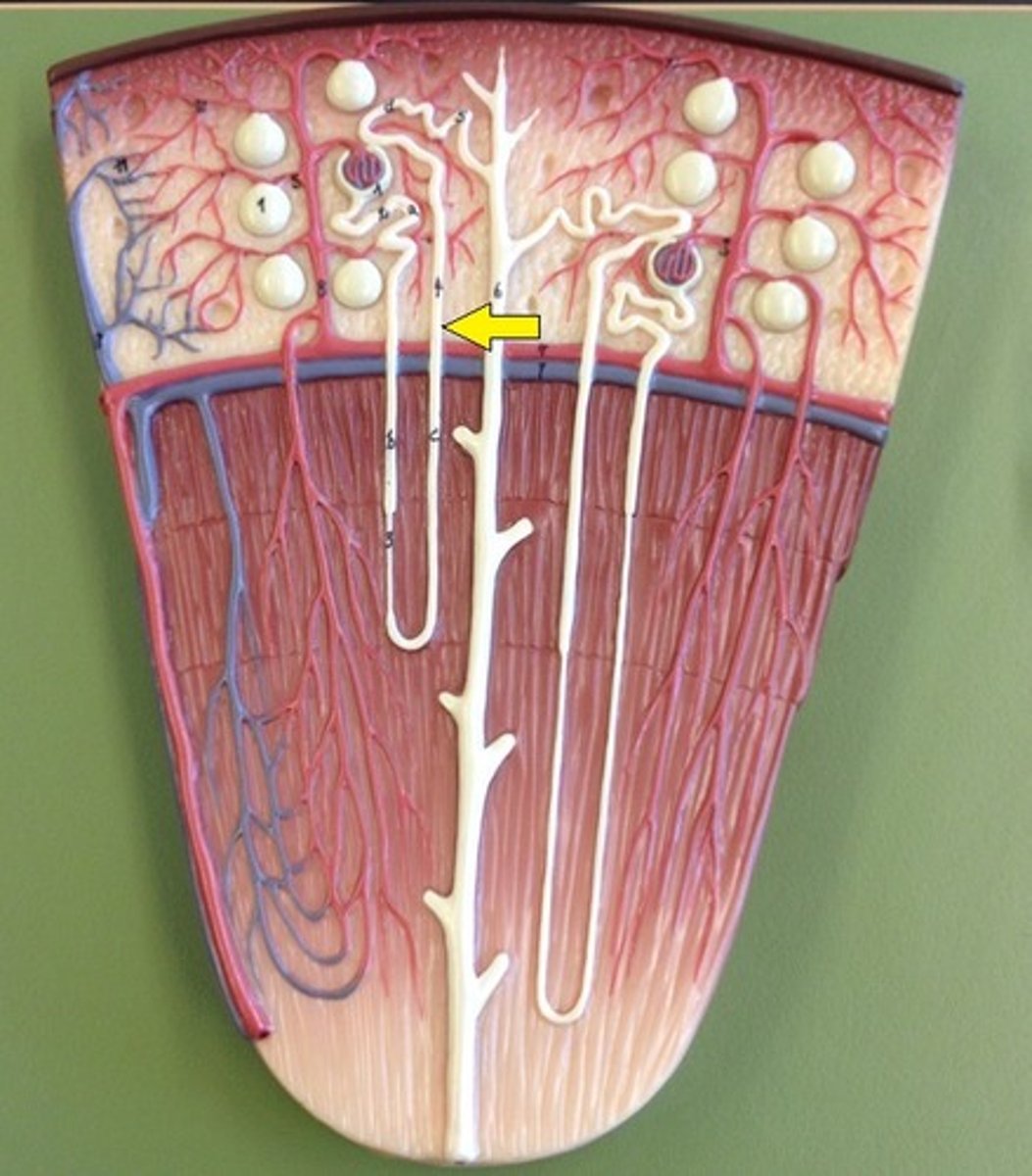
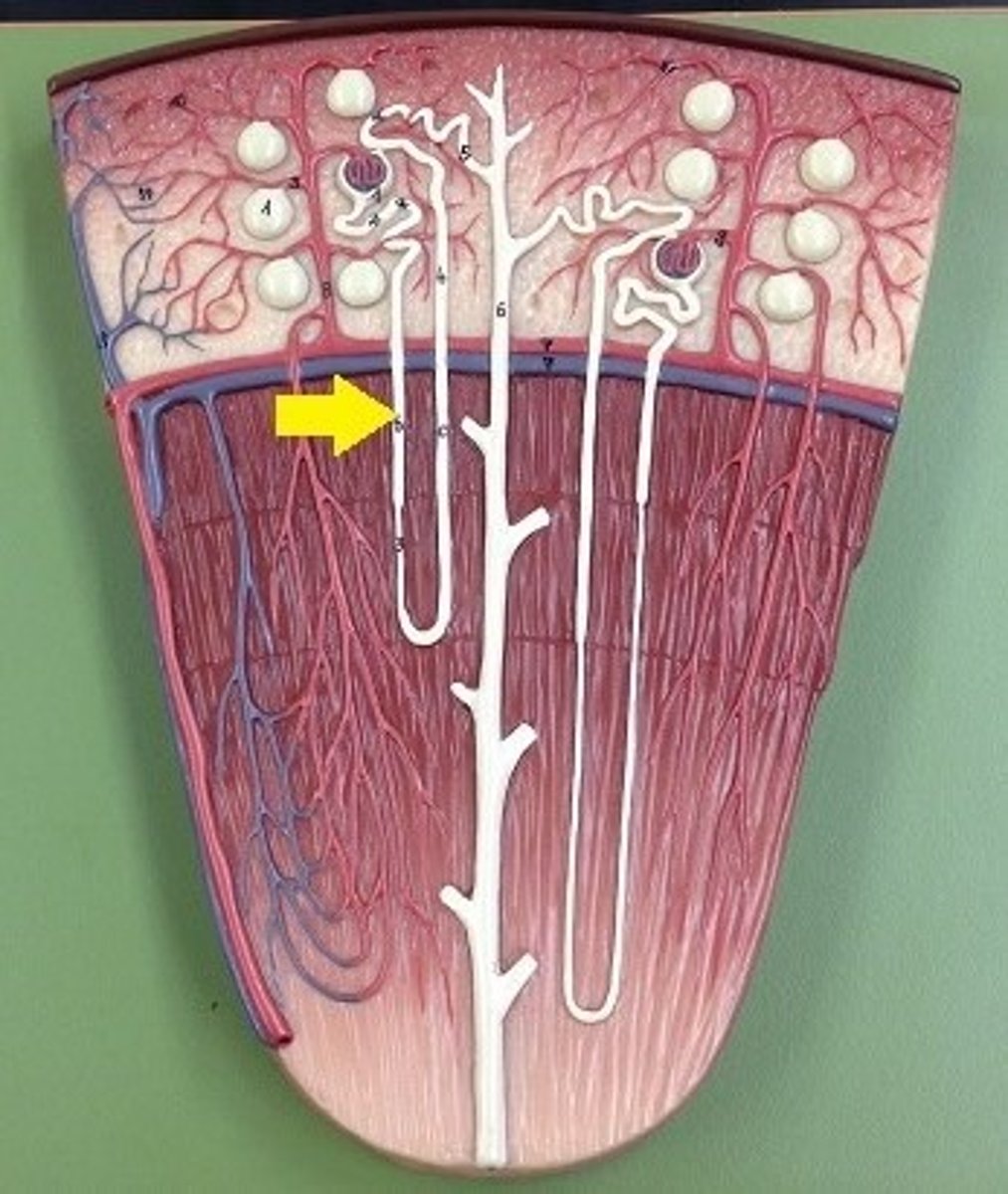
Nephron loop descending limb
permeable only to water
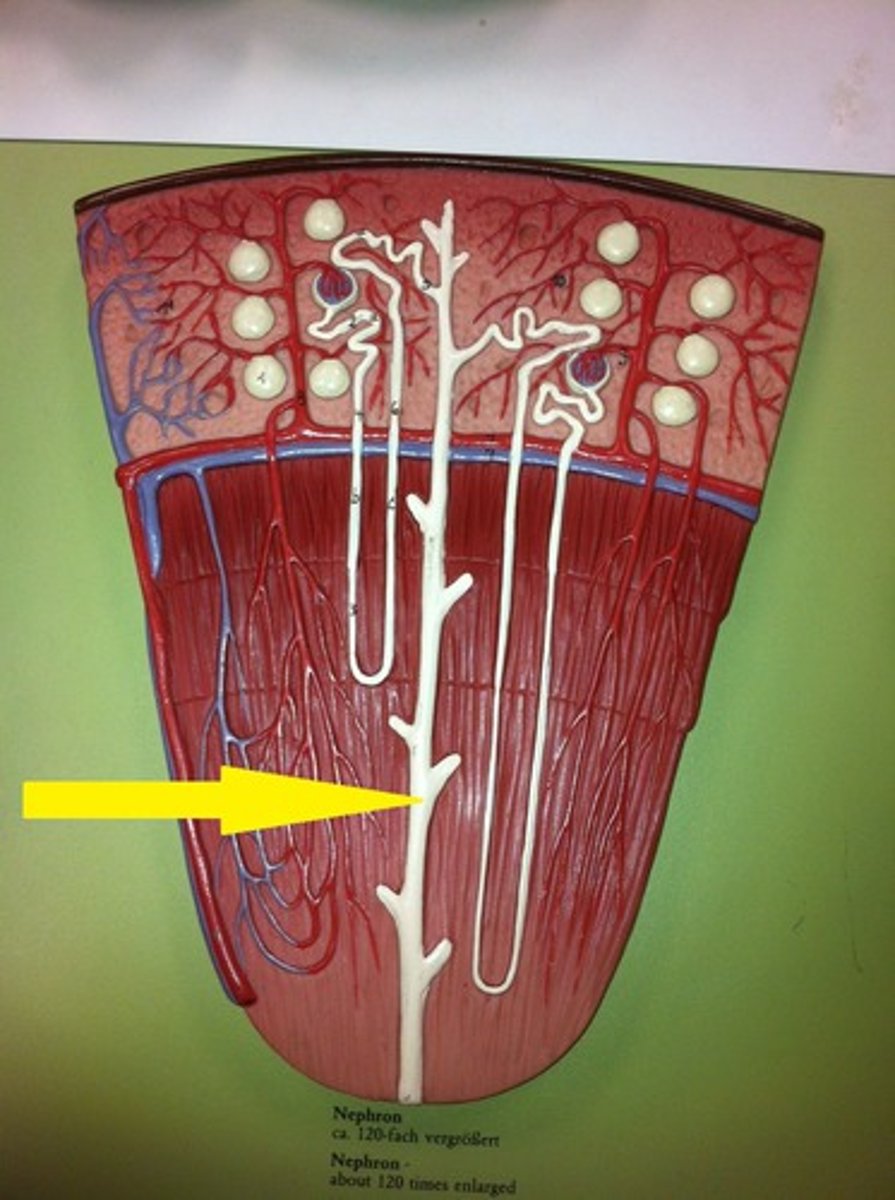
Collecting duct of nephron
The last part that collects urine from the nephrons
Filtration at glomerulus components
Endothelium of glomerular capillary
Basement membrane
Filtration slits
Process of filtration in the glomerulus
the process where blood is filtered within the kidney's glomerulus, forcing small molecules like water and waste products from the blood into the Bowman's capsule, while larger molecules like proteins and blood cells remain in the bloodstream due to a specialized filtration barrier made up of the capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and podocytes
Type of cells lining the lumen of the bladder and its importance
urothelial cells which are classified as a transitional epithelium
they can change shape depending on the bladder's fullness
pH of normal urine
4.5-8
Specific gravity of normal urine
1.0-1.03
Volume of normal urine
1200 ml/day
Glucose, protein, blood levels of normal urine
negative (0)
Glycosuria
urine contains high level of glucose
Proteinuria
urine contains high level of protein
Hematuria
urine contains blood