Dopamine & Dopaminergic Drugs
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Most important sites of dopamine in the brain
substantia nigra
ventral tegmental area
ventral hypothalamus
Dopamine containing cells in the substantia nigra project where (& pathway name)
substantia nigra → striatum
(nigrostriatal pathway)
nigrostriatal pathway function
Movement regulation
Dopamine containing cells in the ventral tegmental area project where (& pathway name)
ventral tegmental area → nucleus accumbens, frontal cortex and amygdala (mesolimbocortical pathway)
mesolimbocortical pathway function
Reward regulation
Dopamine containing cells in the ventral hypothalamus project where (& pathway name)
ventral hypothalamus → median eminence and pituitary gland (tuberohypophyseal system)
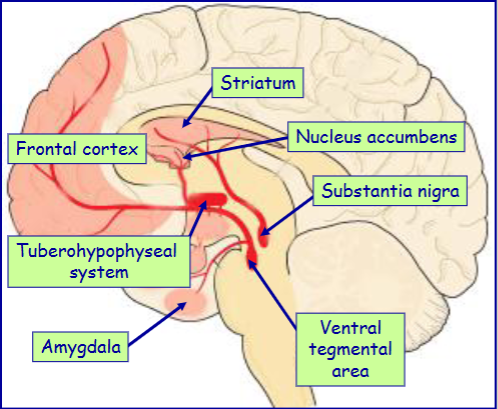
How do the nigrostriatal & mesolimbocortical pathways link up in drugs when treating Parkinson’s
People receiving dopamine to treat Parkinson’s can develop addictions associated with overstimulation of the mesolimbocortical pathway
Tyrosine is taken into the neuron via …….
carrier mediated transport
Tyrosine is converted to dopamine in 2 steps catalysed by what
tyrosine hydroxylase & DOPA decarboxylase
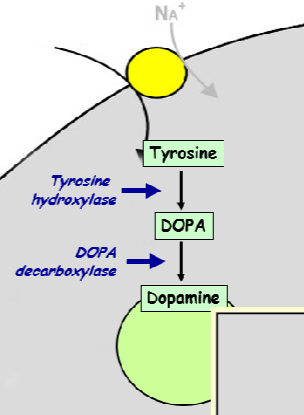
Dopamine is actively/passively packaged into vesicles by _____
Dopamine is actively packaged into vesicles by an amine transporter
Release of dopamine is released via what mechanism
via classical Ca2+-mediated exocytosis
How is dopamine action terminated
Termination is via uptake by a dopamine transporter
How is dopamine degraded
Degradation is via monoamine oxidase, aldehyde dehydrogenase and catechol-o-methyltransferase
Dopamine exerts its effects via 2 types of receptors - name them
D1-type receptors
D2-type receptors
What are the subtypes of D1 & D2 type receptors
D1 type receptor subtypes:
D1
D5
D2 type receptor subtypes:
D2
D3
D4
D1-type dopamine receptors act via what G-protein to cause what effect
Gs (stimulates adenylate cyclase → ↑cAMP)
D2-type dopamine receptors act via what G-protein to cause what effect
Gi (inhibits adenylate cyclase → ↓cAMP)
Gq (activates PLC → ↑ IP3/DAG)
Activation of the D1 type of dopamine receptor mainly causes excitation/inhibition of the pre/post-synaptic neuron
Activation of the D1 type of dopamine receptor mainly causes excitation of the post-synaptic neuron
D2-type receptors location
Widespread in the brain
Located both presynaptically and postsynaptically
Effect of D2-type receptors
Mostly inhibitory effects on presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons. (For example, D2 receptors can be presynaptic inhibitory receptors and/or presynaptic inhibitory autoreceptors supressing release of dopamine from dopaminergic neurons.)
Stimulates/Inhibits hormone release
Dopamine uses 3 pathways of dopaminergic neurons. Name them & their functions
Nigrostriatal pathway → Motor control
Mesolimbocortical pathway → Mediating effects of rewarding stimuli
Tuberohypophyseal pathway → Neuroendocrine function
Dopamine mediates the ‘_____’ impact of natural rewards (e.g. food/sex)
hedonic
What part of mesolimbocortical is the most detrimental to affect
nucleus accumbens
In the tuberohypophyseal pathway, what hormone does dopamine inhibit & what hormone does it promote
Dopamine inhibits prolactin and stimulates growth hormone secretion
Loss of which dopaminergic neurons is associated with Parkinson’s disease
dopaminergic nigrostriatal neurons
First-line therapy for Parkinson’s disease
dopamine replacement: L-DOPA (the DA precursor!)
What type of drugs cause schizophrenia-like symptoms
Drugs which release dopamine (e.g. amphetamine)
Which dopaminergic pathway is affected in Schizophrenia & in what way is it affected
Hyperactivity of mesolimbocortical DAergic pathway
What type of drug is used as treatment for Schizophrenia
dopamine antagonists (esp. D2 receptor)
What is the link between drug addiction & dopamine
Many drugs of abuse (e.g. amphetamine and cocaine which release and block DA reuptake respectively) hijack the DA reward system to mediate their rewarding effects
What type of disease is Parkinson’s
A progressive neurodegenerative disorder
Parkinson’s symptoms
- Tremor at rest
- Muscle rigidity
- Bradykinesia
Parkinson’s affects what % of the population over 65
1%
Parkinson’s is associated with the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons of what pathway
nigrostriatal pathway
Parkinson’s is associated with the formation of what
formation of Lewy bodies (misfolded proteins containing alpha-synuclein)
What is the specific cause of the motor symptoms associated with Parkinson’s
loss of dopamine from the striatum
Symptoms manifest after what % of the nigral dopamine neurons have degenerated & what % of striatal dopamine has been lost
Only after 60% have degenerated & 80% of striatal dopamine has been lost
(our brain can compensate for quite a while so by the time symptoms appear, lots of degeneration has already happened)
Function of treatment for Parkinson’s
All current drug therapy simply provides relief from Parkinsonian symptoms
They do not provide a cure for the disease, nor do they slow the unrelenting degeneration of the nigrostriatal neurons
The symptoms of PD (Parkinson’s) are mainly treated using drugs that enhance dopaminergic transmission by a variety of methods. Name some of these methods
- Drugs that replace dopamine (L-DOPA)
- Drugs that inhibit dopamine metabolism (COMT inhibitors, MAO inhibitors)
- Drugs that mimic dopamine action (dopamine receptor agonists)
- Drugs that release dopamine
Parkinson’s is also treated using drugs that block what receptors
block muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
(cf. acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter)
Most effective treatment for Parkinson’s disease is what specific drug which is a what?
L-DOPA (levodopa) which is a dopamine precursor
L-DOPA (levodopa) is usually given when what, why?
It is usually given with a DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor that is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier (e.g. carbidopa, benserazide) so that conversion to dopamine only occurs in the brain (thus reducing peripheral side effects)
What % of patients respond positively to levodopa with what % restored to virtually normal motor function
About 80% of patients respond positively to levodopa with ~20% restored to virtually normal motor function
Why does the effectiveness of L-DOPA wear off as the disease progresses
intact dopamine neurons are at least partially required for its effectiveness
main side effects of levodopa treatment
Dyskinesias - Abnormal involuntary movements affecting the face and limbs
On-off effects - Rapid fluctuations in clinical state where the symptoms reappear suddenly and can last for minutes to hours
Dyskinesias usually occurs within how long since starting treatment
Manifests in the majority of patients within 2 years of starting levodopa therapy
How is Dyskinesias dealt with
Can be reduced by lowering the levodopa dose but this causes symptoms to reappear
Other than levodopa (DA precursor), what 4 other types of drugs can be sued
Inhibition of dopamine metabolism
Dopamine receptor agonists
Muscarinic cholinergic antagonists
NMDA receptor antagonists
Give 2 drugs that would cause the Inhibition of dopamine metabolism
MAO-B inhibitors e.g. selegiline
COMT inhibitors e.g. entacapone
Give an example of a non-selective, slight selective & selective Dopamine receptor agonists
Non-selective dopamine receptor agonists (e.g. apomorphine)
Slightly selective D2 receptor agonists (e.g. bromocriptine, pergolide, cabergoline)
Selective D2 receptor agonists (e.g. pramipexole, ropinirole)
Give 2 examples of Muscarinic cholinergic antagonists & the reason why they work
Since the cholinergic interneurons in the striatum oppose the effects of dopamine, blocking their actions (e.g. trihexyphenidyl and benztropine) partly overcomes the loss of dopamine
Give an example of an NMDA receptor antagonists
Non-competitive antagonist of the NMDA receptor (e.g. amantadine)
Schizophrenia is a disabling brain disease that affects what % of the population
1%
When does Schizophrenia normally manifest in men/women
Men: late teens / early 20s
Women: late 20s / early 30s
True/False Schizophrenia is a neurodevelopmental disorder
True - It is thought to be a ‘neurodevelopmental’ disorder in which certain brain structures (esp. the cerebral cortex) do not develop properly
Schizophrenia is relapsing & remitting or Chronic & progressive
Both - Schizophrenia can be relapsing & remitting or Chronic & progressive
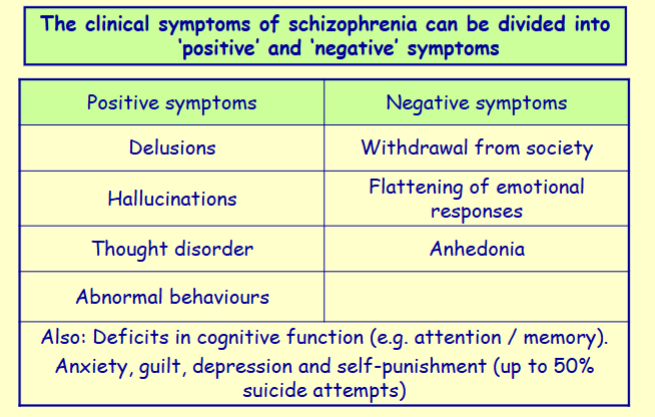
Clues to the neurochemical nature of schizophrenia came from analysing what
the effects of known anti-schizophrenic drugs
Name 4 Neurotransmitter systems that have been implicated in schizophrenia
-Dopaminergic system
- Glutamatergic system
- Serotonergic system
- Noradrenergic system
dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia
overactivity in the dopaminergic system leads to the disease
dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia is based on two main observations. What are they?
1) All anti-schizophrenic drugs act as antagonists at dopamine receptors and clinical potency correlates with D2 receptor affinity
2) Amphetamine (which releases dopamine from neurons) causes schizophrenic-like symptoms in users
All antipsychotic drugs act as agonists/antagonists at what dopamine receptor
All antipsychotic drugs act as antagonists at dopamine D2 receptors
In addition to the dopaminergic system, antipsychotic drugs may also affect other what 4 other neurotransmitter systems
Noradrenergic, histaminergic, cholinergic, serotonergic
(mostly contribute to the side effects of antipsychotics)
Activity of antipsychotic drugs at what receptor provides clinical benefit / reduced side effects
activity at 5-HT receptors (serotonin)
They can act as antagonists at 5-HT2A and as agonists at 5-HT1A receptors
Explain the difference between the acute & chronic mechanisms of action of anti-schizophrenic drugs
Acute: antagonists at dopamine D2 receptors → block the effects of dopamine released from the mesolimbic pathway (reduced positive symptoms). Initial spike in DAergic neuron activity.
Chronic: Long term decrease in DAergic neuron activity.
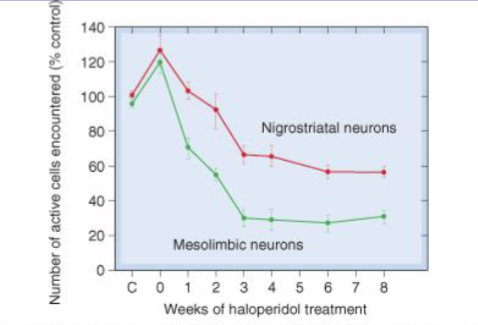
Antipsychotic effects require ~__% block of D2 receptors
80%
Anti-schizophrenic drugs are also known as what 3 names
antipsychotic drugs
neuroleptic drugs
major tranquillisers
How many anti-schizophrenic drugs are currently in clinical use
40
Antipsychotic drugs limitations
Only effective in ~70% of patients (The remaining ~30% are ‘treatment-resistant')
They can only control the positive symptoms of schizophrenia - don’t control the negative symptoms
Name the 4 Classical ‘typical’ antipsychotics
- Chlorpromazine
- Haloperidol
- Thioradazine
- Flupenthixol
Name the 5 Recently-developed ‘atypical’ antipsychotics
- Sulpiride
- Clozapine
- Risperidone
- Sertindole
- Quetiapine
In what ways are the atypical’ antipsychotics better than the classical ones
atypical have:
Lower incidence of side effects
Higher efficacy in treatment resistant patients
Higher efficacy against negative symptoms
Better selectivity for the dopamine D2 receptor
Blocking of what 2 pathways causes side effects in anti-schizophrenic drugs? What are the side effects?
Blocking effects of the nigrostriatal pathway:
→ Acute (first few weeks of treatment) dystonia (Parkinsonian-like syndrome with involuntary movements)
→ Tardive dyskinesia (Severe disabling involuntary movements affecting the face and limbs after months or years of treatment (tardive))
Blocking the tuberohypophyseal pathway:
→ Increase in plasma prolactin concentration → breast swelling, pain & lactation (gynecomastia) in men & women
Which of the side effects are & are not reversible on stopping treatment (dystonia & dyskinesia)
Acute dystonia → Reversible on stopping treatment
Tardive dyskinesia → Often gets worse on stopping treatment
How do neuroleptics cause the side effect: Sedation (what does this lead to?)
due to H1 block
(Often causing daytime drowsiness and difficulty in concentrating)
How do neuroleptics cause the side effect: Anticholinergic effects (what does this lead to?)
due to muscarinic block
(Dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision, urinary retention etc
How do neuroleptics cause the side effect: Postural hypotension
due to a-adrenoceptor block
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome due to neuroleptics side effects leads to?
Muscle rigidity, fever, autonomic instability, delerium
What are some Miscellaneous reactions that can be side effects of anti-schizophrenic drugs
Jaundice, urticaria (hives), leucopenia/agranulocytosis (reduction in white blood cells), antipsychotic malignant syndrome