AP Psychology - Unit 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:51 PM on 9/13/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
1
New cards
applied research
scientific study that aims to solve practical problems
2
New cards
basic research
pure science to increase knowledge
3
New cards
behaviorism
psychology should be an objective science that only studies, not mental processes (Ivan Pavlov, John B. Watson, and B.F. Skinner)
4
New cards
behavioral psychology
observable behavior and its explanation
5
New cards
biological psychology
studies links between biological and psychological processes
6
New cards
biopsychosocial approach
integrates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis
7
New cards
case study
one person is studied in depth to reveal universal principles
8
New cards
clinical psychology
studies, assesses, and treats people with psychological disorders
9
New cards
cognitive neuroscience
study of the brain activity linked with cognition
10
New cards
cognitive psychology
all mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
11
New cards
confounding variable
(other than independent variable) might produce an effect
12
New cards
control group
group that is not exposed to the treatment; comparison for evaluating the effects
13
New cards
correlation
the extent to which two factors may vary together; how well one factor predicts the other
14
New cards
correlation coefficient
index of relationship between two things (from -1 to 1)
15
New cards
counseling psychology
assists people with life problems and in achieving greater well-being
16
New cards
critical thinking
examines assumptions, discerns hidden values, evaluates evidence, and assesses conclusions (doesn’t blindly accept arguments)
17
New cards
cross-sectional study
analyze data from a population at a single point in time
18
New cards
dependent variable
what is observed or affected
19
New cards
developmental psychology
study of (physical, cognitive, and social) change throughout a life span
20
New cards
double-blind procedure
participants and staff are blind about whether the participants have received treatment or a placebo
21
New cards
educational psychology
how psychological processes affect and teaching and learning
22
New cards
empiricism
knowledge = (sensory) experience; science should rely on observation and experimentation; nurture
23
New cards
experiment
investigator manipulates the independent variable to observe the effect (dependent variable); aims to control other relevant factors (control variables)
24
New cards
experimental group
group that is exposed to the treatment (one version of the independent variable)
25
New cards
experimental psychology
study of behavior and thinking using the experimental method (Edward B. Titchener)
26
New cards
evolutionary psychology
roots of behavior and mental processes using principles of natural selection
27
New cards
functionalism
focused on how our mental and behavioral processes function (enabling us to adapt, survive, and flourish) (William James)
28
New cards
hindsight bias
thinking that you could have foreseen something after it happens
29
New cards
human factor psychology
the study of how people and machines interact (used to design of safe and easily used machines)
30
New cards
humanistic psychology
emphasizes the potential for personal growth by meeting one’s needs (Abraham Maslow, Carl Rogers)
31
New cards
hypothesis
a testable prediction
32
New cards
illusory correlation
perception of a relationship where there isn’t one
33
New cards
independent variable
what is changed; the effect is studied
34
New cards
industrial-organizational (I/O) psychology
applying psychological concepts and methods to workplaces
35
New cards
levels of analysis
differing views (biological, psychological, social-cultural) analyzing a phenomenon
36
New cards
longitudinal study
follows people over periods of time; continuous or repeated observations of the same variables
37
New cards
mean
the average of a distribution
38
New cards
median
the middle score in a distribution; half of the scores above, half below
39
New cards
mode
most frequently occurring in a distribution
40
New cards
naturalistic observation
observing behavior without trying to manipulate and control the situation
41
New cards
natural selection
trait variations contributing to survival are most likely to be passed on
42
New cards
nature-nurture issue
genes vs experience; what develops psychological traits
43
New cards
negatively skewed distribution
the tail on the left side of the distribution is longer; mean and median are less than the mode
44
New cards
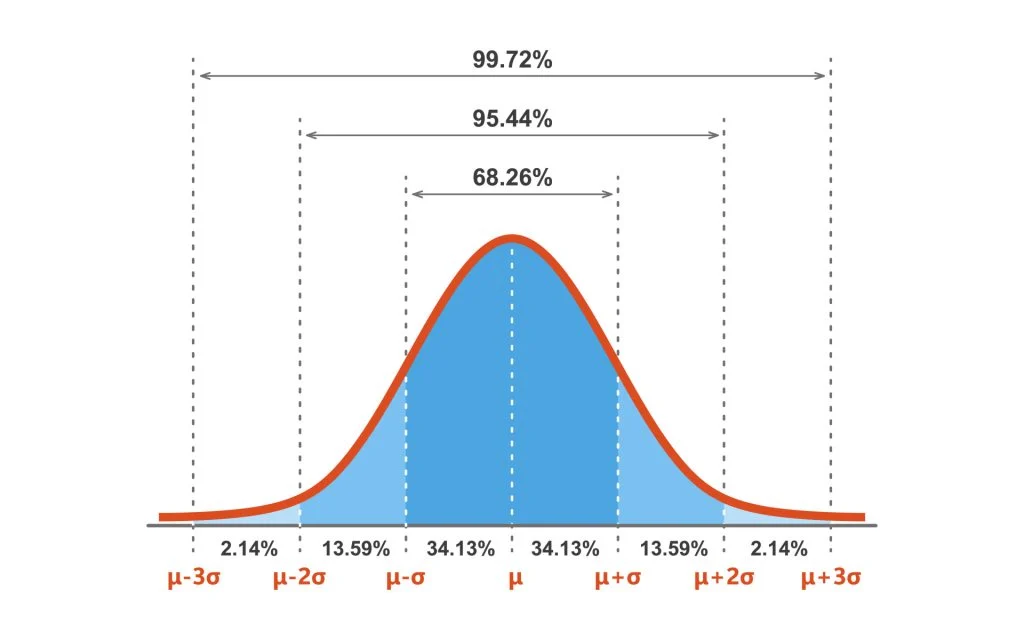
normal distribution (curve)
symmetrical curve; most scores are close to the average, few are extreme (2.14, 13.59, 34.13, 34.13, 13.59, 2.14)
45
New cards
operational definition
a statement of procedures (operations) used to define variables (ex: human intelligence = what an intelligence test measures)
46
New cards
personality psychology
individual’s characteristic pattern of thinking, feeling, and acting
47
New cards
placebo effect
experimental results caused by expectations alone
48
New cards
population
group studied, from which samples may be drawn
49
New cards
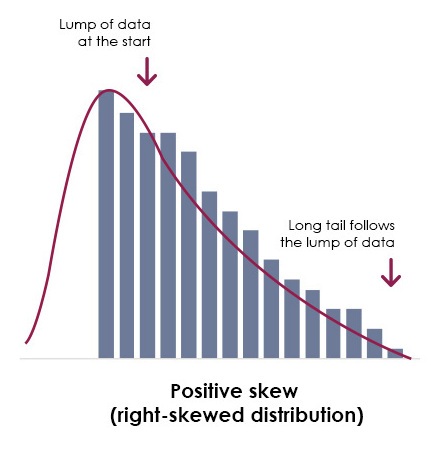
positively skewed distribution
the tail on the right side of the distribution is longer; mean and median are greater than the mode.
50
New cards
psychiatry
medicine dealing with psychological disorders
51
New cards
psychodynamic psychology
unconscious mind influencing behavior
52
New cards
psychology
science of behavior and mental processes
53
New cards
psychometrics
measurement of human abilities, attitudes, and traits
54
New cards
p-value
probability of not obtaining similar test results; how likely it is that there’s significant difference of data between groups
p>.05 = not statistically significant (more than 5% due to chance)
null hypothesis: there is no significant difference between specified populations
p>.05 = not statistically significant (more than 5% due to chance)
null hypothesis: there is no significant difference between specified populations
55
New cards
random assignment
assigning participants to experimental and control groups by chance
56
New cards
random sample
each member has an equal chance of getting in
57
New cards
range
difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
58
New cards
replication
repeating the essence of a research study to see if the findings extend to other people and circumstances
59
New cards
standard deviation
measure of how much scores vary around the mean score
60
New cards
scatterplot
graphed dots, representing the values of two variables; slope=direction of the relationship; amount of scatter = the strength of the correlation (little scatter=high correlation)
61
New cards
social-cultural psychology
how situations and cultures affect our behavior and thinking
62
New cards
social psychology
how we think about, influence, and relate to one another
63
New cards
statistical significance
measure of how likely it is that an obtained result did not occur by chance
64
New cards
structuralism
self-reflection to explore structural elements of the mind while people did mundane tasks (Edward B. Titchener, William Wundt)
65
New cards
SQ3R
study method: Survey the text, ask Questions, Read, Rehearse what you read, Review
66
New cards
survey
gets self-reported attitudes or behaviors of a particular group; questions a representative sample of the group
67
New cards
theory
explanation w/ set of principles; organizes observations and predicts events