Anatomy midterm 😭
1/197
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
198 Terms
anatomy vs physiology
anatomy- study of the structure and shape of the body and its parts.
physiology- study of how the body and its parts work together
levels of structural organization
atoms:combined to form molecules
cells: smallest unit of all living things
tissue: consists of similar cells with common functions
organ level: composed of two or more tissue types to perform a specific function
organ system: group of organs that cooperate to accomplish a common purpose
organismal: all 11 body systems make up and organism
maintaining boundaries
skin separates insides from outsides
rib cage, diaphragm, intestin, blood vessels, skull
movement
locomotion: skeletal muscles
movement of substance: blood, hormones, O2, food/poop
Responsiveness/ Irritability
ability to sense change and react. How nervous systems react in the body
digestion
breakdown and absorption of nutrients
metabolism
relies on digestive and respiratory
chemical reactions within the body that produce energy
breaks down complex substances and puts together simpler ones
regulated by hormones (endocrine)
excretion
eliminating waste from metabolic reactions
urinary, digestive respiratory, integumentary (sweat)
reproduction
produces future generations (offspring)
ovaries and testes
fertilized egg= zygote
growth
increase cell size and number of cells
survival needs
Nutrients (carbs, proteins, fats, vitamins/minerals)
oxygen
water
body temperature
atmospheric pressure
homeostasis
the bodies ability to maintain relatively internal conditions although the outside world is changing
Homeostatic controls
receptors: responds to changes in the environment (stimuli), sends information to the control center along the afferent pathway
Control center: (brain) analyzes info and determines appropriate response (sends down effector pathway)
Effectors: carries out the response as directed by the control center (muscle or gland)
negative feedback mechanism
works like human thermostat
most common
regulates heart rate and blood pressure to make sure that are at a normal rate
positive feedback mechanisms
rare in human body
reaction occurs at a fast rate
increases the original stimulus to push variable further
blood clotting and giving birth
superior/ inferior
above/below
anterior/posterior
towards front/ towards back
ventral/ dorsal
front of animals/ back of animals
cranial/ caudal
towards head/ towards tail
proximal/ distal
closer to point of attachment/ further from point of attachment
specific to appendages
medial/ lateral
closer to midline/ further from midline
superficial/ deep
close to body’s surface/ further from body’s surface
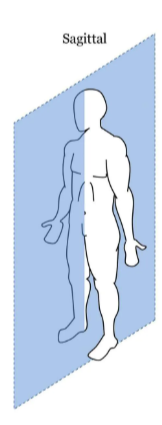
sagittal plane
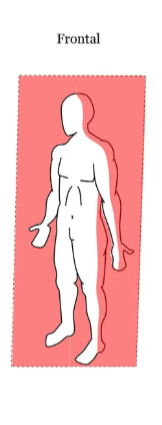
coronal (frontal) plane
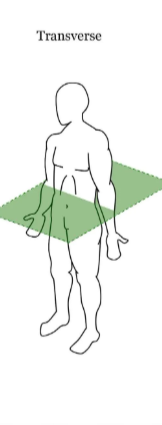
transverse plane
section vs. plane
plane=equal cut of body into sections
sections= unequally cut section of body
oral
mouth
orbital
bony eye socket
buccal
cheek
cervical
neck
acromial
top of shoulders
thoracic
chest
axillary
armpit
mammary
breast
brachial
upper arms
antebrachial
forearm
antecubital
front of elbow
carpals
wrists
abdominal
in between diaphragm and hips
inguinal
where thigh meets trunk
femoral
thigh
pubic
pubic bone region
patella
knee
tarsal
ankle
pedal
foot
digital
fingers/ toes
otic
ear
nasal
nose
palmar
palm of hand
crural
shin
coxal
hip
pectoral
upper chest
sternal
sternum
mental
chin
frontal
forehead
umbilical
belly button
cephalic
the whole head
deltoid
curve of shoulder
scapular
shoulder blades
olecranal
back of elbow
lumbar
lower back
gluteal
butt
popliteal
back of knee
sural
calf
calcaneal
heal
plantar
bottom of foot
cubital
elbow
dorsum
whole back
manus
whole hand
fibular
lateral part of lower leg
ipsilateral
same side of body
contralateral
opposite side of body
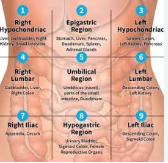
abdominal regions
simple squamous function
filtration
diffusion
simple cuboidal and simple columnar function
absorption
secretion
pseudostratified columnar function
propulsion
stratified squamous function
protection
transitional function
stretching
four types of tissues
epithelial
muscle
connective
nervous
simple cuboidal
single layer of cube like cells
small glands and their ducts
kidney tubules, covers the ovaries, salivary glands
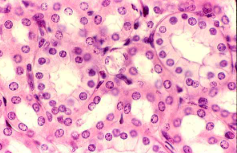
apical layer
top of tissue
basal layer
bottom of tissue
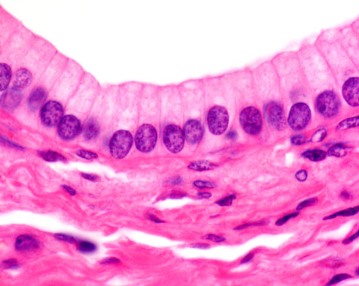
simple columnar
single layer of tall cells
often includes mucus producing goblet cells
lines most of digestive tract, gallbladder, uterus, and uterine tubes
small bronchi and bronchioles
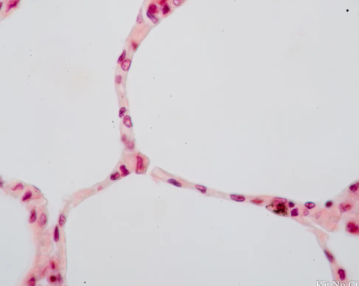
simple squamous
single layer of flat cells
usually forms membranes
lines body cavities
lines lungs and circulatory organs and ventral body cavities
forms serous membranes
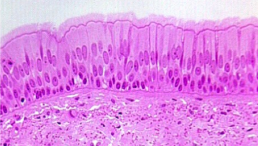
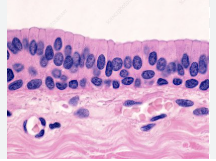
pseudostratified columnar
single layer but some cells are shorter than others
often looks like a double layer of cells
ciliated in much of respiratory tracts
nonciliated lines male reproductive tracts
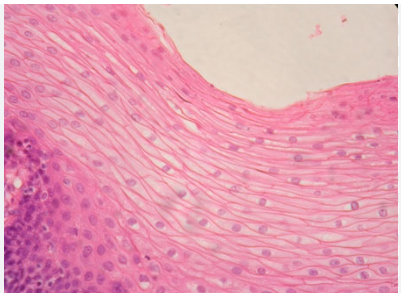
stratified squamous
basal surface has cubed shaped cells
cells of apical surface are flattened
found as a protective covering where friction is common
skin/ mouth/ esophagus
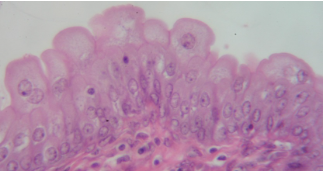
stratified cuboidal
two layers of cube cells
found in ducts of large glands and ovarian follicles
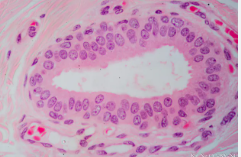
stratified columnar
surface cells are columnar, cells underneath vary in size and shape
rare in body
male urethra/ parotid gland
transitional epithelium
shape of cell depends upon amount of stretching
lines organs of the urinary system (bladder)
endocrine glands
ductless since secretion diffuse into blood vessels
all secretions are hormones
exocrine glands
secretion empty through duct to the epithelial surface
sweat / oil glands
main functions of connective tissue
transportation
protection
insulation
storage of energy reserve
variations in blood supply
some well vascularized (blood vessels)
some poor blood supply (tendons) or avascular (cartilage)
extracellular matrix (ECM)
non-living portion of tissue
majority of tissue volume
determines specialized functions
Ground substance (ECM)
clear, colorless, viscous
fills space between cells and slows movement of pathogens
can be solid, gelatinous, or liquid
Fibers (ECM)
made by cells
three types: collagen fibers (internal fibers & strongest), elastic fibers, reticular fibers
loose vs dense CT
Loose: more ground substance, less fibers (Adipose tissue)
Dense: more fibers, less ground substance (Tendons)
fibroblasts
inmiture fiber cells
macrophages
cell eaters (phagocytic) consumes anything foreign
adipocytes
fat cells