Chapter 7- The Devlopment of T Lymphocytes
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Thymus
Where positive and negative selection occur, where t cells develop, primary lymphoid organ, only involved in the development, contains thymocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and thymic stroma, degrades after puberty and replaced with fat tissue
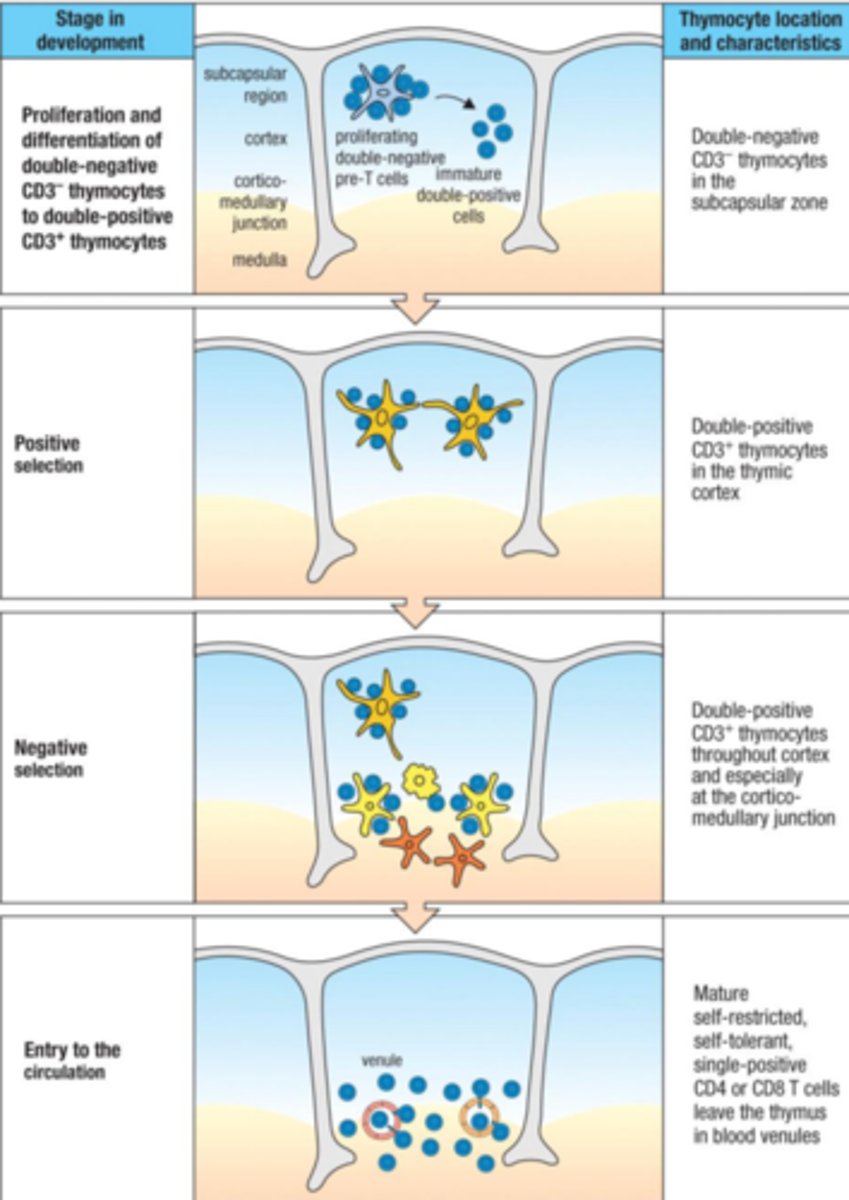
Cortex
Outer, close-packed cells consisting of ectodermal cells; contains thymocytes and macrophages
Medulla
inner, less dense and consists and endodermal cells; contains thymocytes, dendritic cells and macrophages
Thymic anlage
the combination of the ectodermal and endodermal cells early in early development that is later colonized by progenitor cells from the bone marrow, early thymus
Cortico-medullary junction
where T cells enter the thymus
Thymocytes
Immature T cells, and T cells in thymus, developing T cells when they are in the thymus, commit to the T-cell lineage before rearranging their T cell receptor genes
Macrophages
in dendritic cells, engulf dead thymocytes
Thymic stroma
epithelial cells, regulate development and repertoire development
Thymectomy
surgery to remove the thymus gland
IL-7
secreted by thymic stromal cells and helps develop T cells
Thymic stromal cells
Deals with IL-7
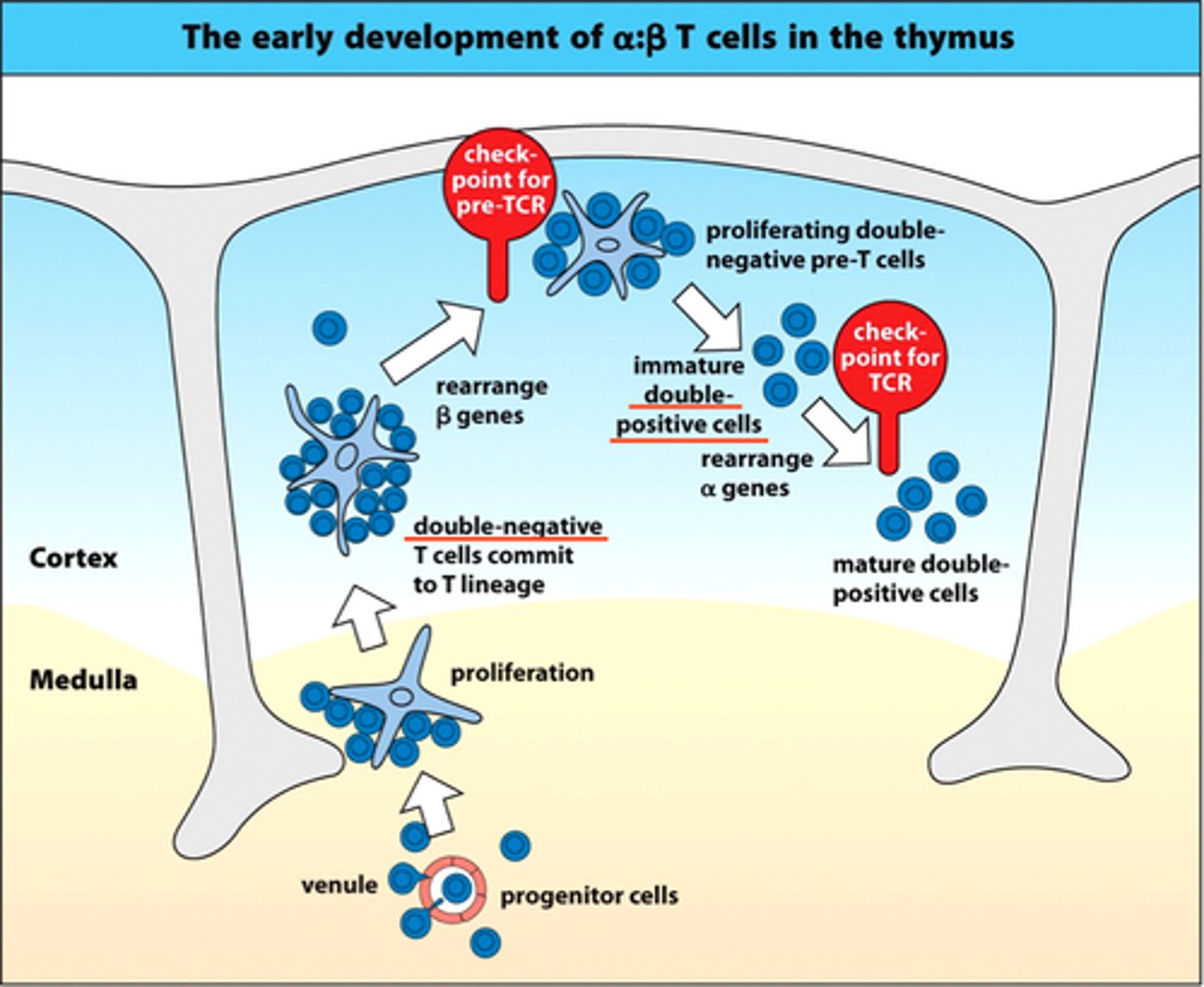
DN thymocyte
Have T cell characteristics but no CD4, CD8, CD3, and TCR, TCR gene rearrangement starts A race to become an alpha beta or gamma delta T cell, if successful in gene rearrangement, CD2
DP thymocyte
CD4 and CD8 are expressed if beta chain has rearranged, time when alpha, gamma, and delta are rearranging
alpha beta versus gamma delta lineage decision
Most T cells are alpha beta (90%)
When DN thymocyte starts gene rearrangement, all rearrange at once
If beta arranges first could still be cone a gamma delta T cell, initiate the pre-TCR and induces proliferation and expression of CD4 and CD8, then resumes rearrangement, has 4 chances to rearrange correctly, successful rearrangement leads to shut down of pre-TCR formation and RAG expression
Alpha chain rearrangement is more likely because of no D segments, when paired with beta chain RAG shutdowns
pre-TCR
pairs with pTa holds the Beta chain in place, forms a superdimer that signals via CD3 complex and the Lck kinase, can signal to itself to start rearrangement of alpha chain genes and stop pTa; also signals to cell to make CD4/CD8
pTalpha
Holds the beta chain in place, surrogate alpha chain, from committed T cell progenitor to second checkpoint
CD3
Signals pre-TCR to form a superdimer
unproductive versus productive rearrangement
unproductive: attempt to have a successful rearrangement
productive: having a successful rearrangement
T cell checkpoint
checkpoint one: pre- TCR formation and RAG shutdown
checkpoint two: TCR formation and RAG shutdown
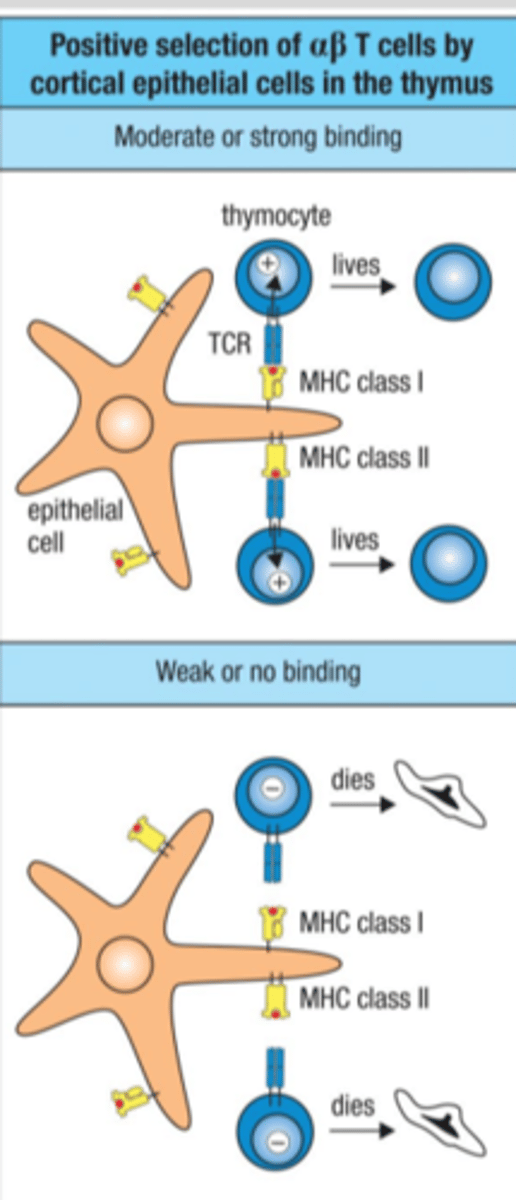
Positive selection
developing T cells that recognize self-MHC will be positively selected, sends signal to live, specific for thymus (find T cells that can bind)
Find TCRs that bind to MHC-self-peptide complex on thymic epithelial cells
affected by peptides produced by a thymus-specific proteasome
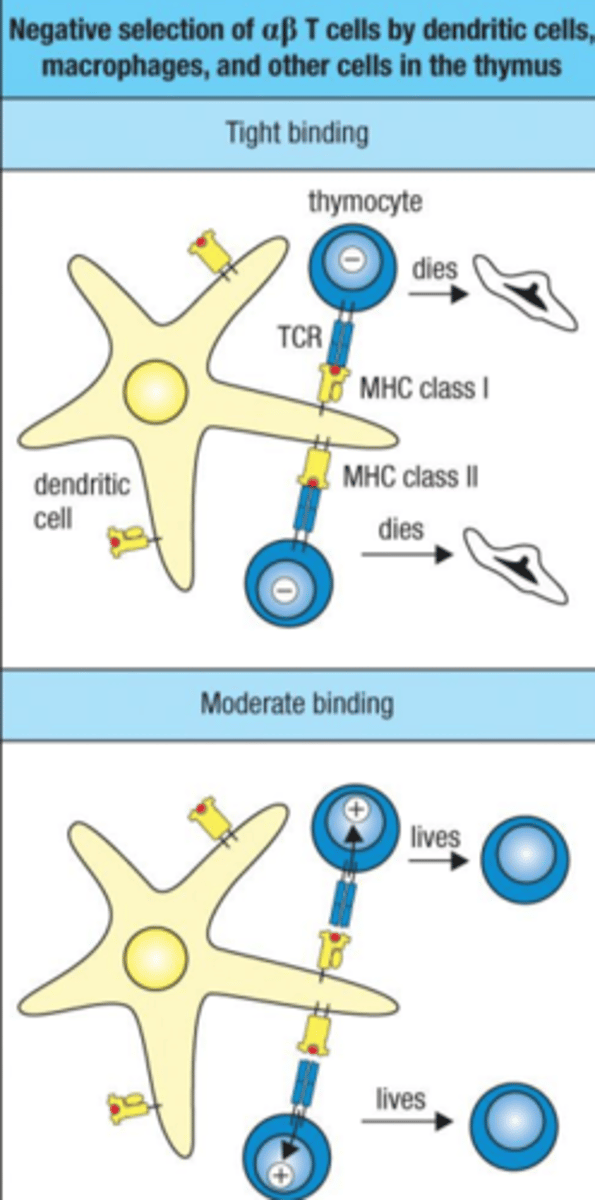
Negative selection
developing T cells that bind too tightly to self-MHC will be negatively selected (do not want them to be autoreactive)
Eliminate TCRs that bind very well to MHC-self-peptide on macrophages or dendritic cells
receptor editing
Process by which the T cell tries out different a-chains to find out if it can bind to self-MHC
Different the receptor editing in B cells which is the process by which you change binding so you do NOT bind to self-antigen
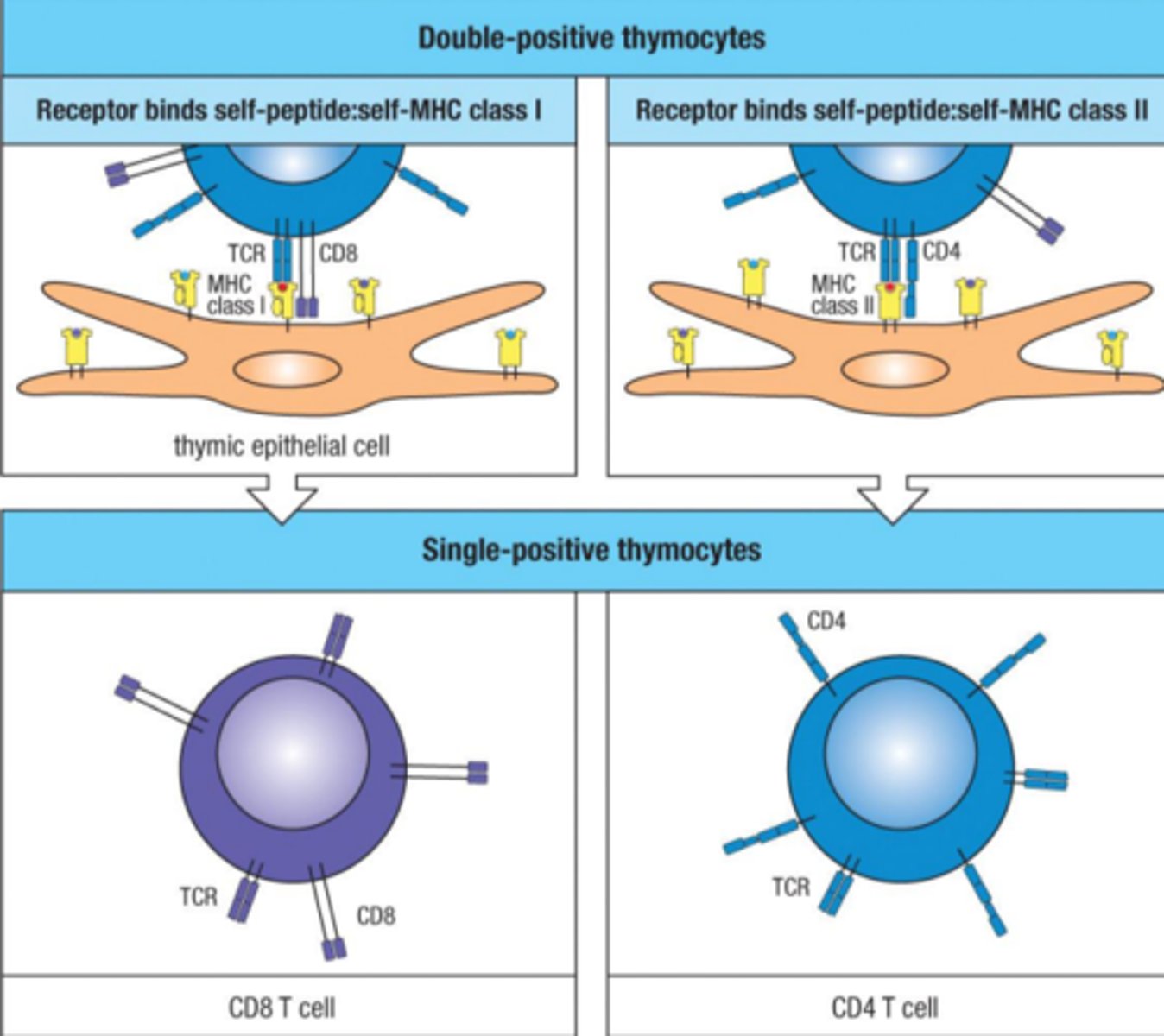
single positive thymocyte
when CD4 or CD8 is lost on a thymocyte
double-positive thymocyte has both CD8 and CD4
CD8- comes from a double-positive thymocyte, self-peptide to MHC class I
CD4- comes from double positive thymocyte, self-peptide to MHC class II
bare lymphocyte syndrome
mutations in the MHC complex or with the presentation of MHC molecules
APECED
Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy, when patients lack AIRE, the T cells are dying off at an increased amount, T cell binds to self antigen outside of thymus, results in activation or brief activation and death
AIRE
autoimmune regulator, transcription factor will force expression of non-thymic proteins in thymic epithelial cells in the medulla (insulin; normally made only by the Beta cells of the pancreas but we need to make sure T cells don't react to insulin)
Regulatory T cells
comprise a distinct lineage of CD4 T cells, subset of CD4 T cells that have cells that have specificity for self-antigen, form of tolerance in addition to the negative selection in the Thymus
suppress other CD4 T cells that react to self-antigens on the same host APC
Bone marrow transplant
HLA overlap will allow communication, graft versus host disease (GHD)- mature T cells from the donor attack the host
Organ rejection
Allograft rejection, recipient (host) immune system attacks the transplanted organ
Immunotherapy
Tumor therapy; select, enrich and amplify tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs)
TILs
tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, part of immunotherapy