gene expression and neurones
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
define mutation
a change in the DNA base sequence
What are the 6 types of mutations?
substitution, inversion, translocation (these 3 don’t cause a frame shift but may change the AA produced) deletion, addition, duplication
what’s a mutagenic agent and how do they work?
increase the rate of a mutation which results in a different AA sequence by either:
acting as a base
altering bases
changing the DNA structure
What are stem cells? what are the 4 types?
Unspecialised cells that have the ability to become any other type of cell
totipotent (embryonic cells and can become ANY cell,) pluripotent, multipotent, unipotent
what are induced pluripotent cells
adult cells reprogrammed using transcription factors to make pluripotent cells.
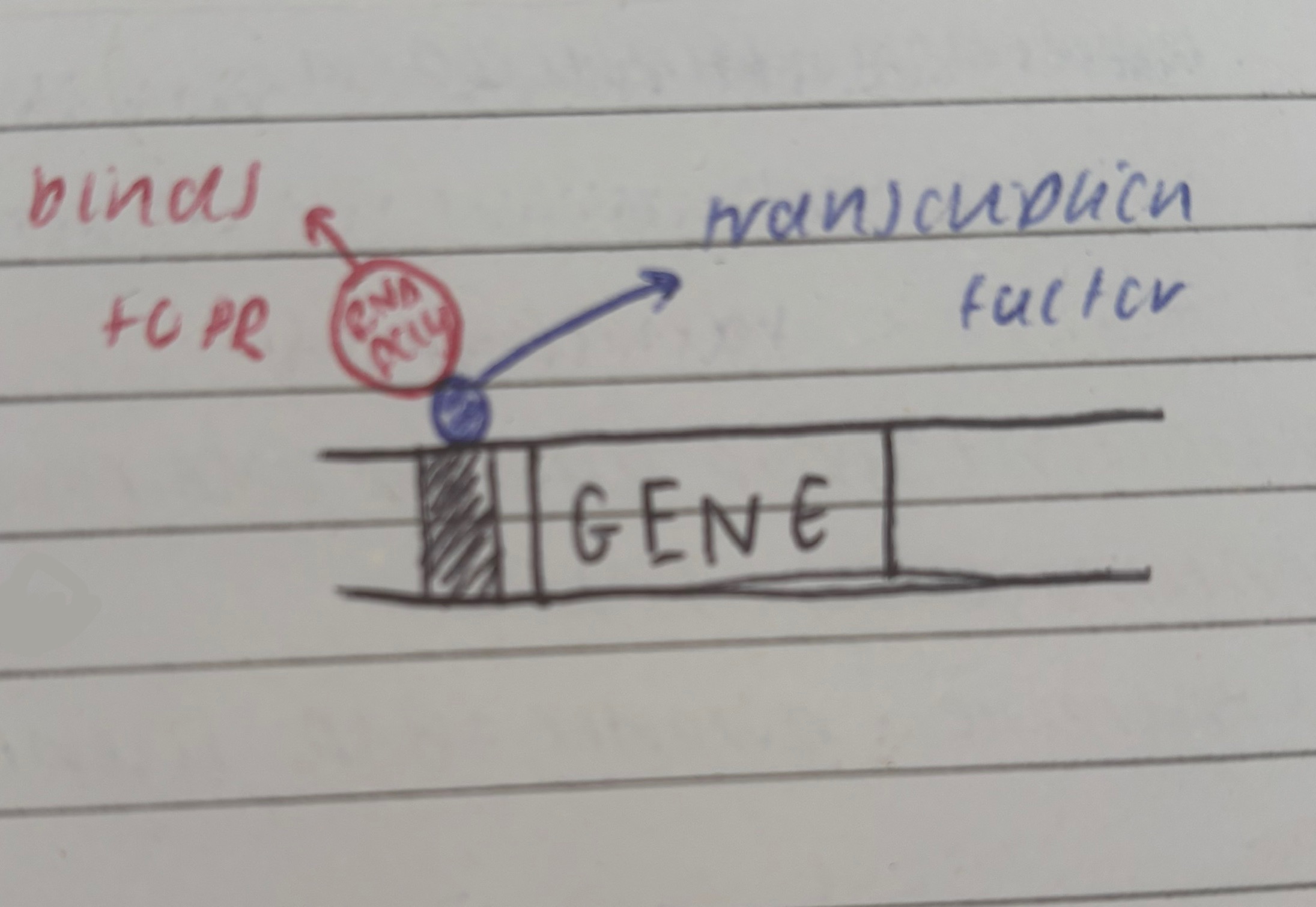
what are transcription factors
molecules that bind to DNA (in the promoter region) that initiate transcription by allowing RNA polymerase to bind to them
what’s epigenetics?
how environmental influences alter genetic inheritance. involves heritable changes in gene function WITHOUT changing the DNA BASE SEQ.
how does acetlyation affect gene expression/ transcription
acetyl groups added to histones. histones forced apart which makes it easier for RNA polymerase to bind an activate transcription
remove acetyl groups = decreased transcription
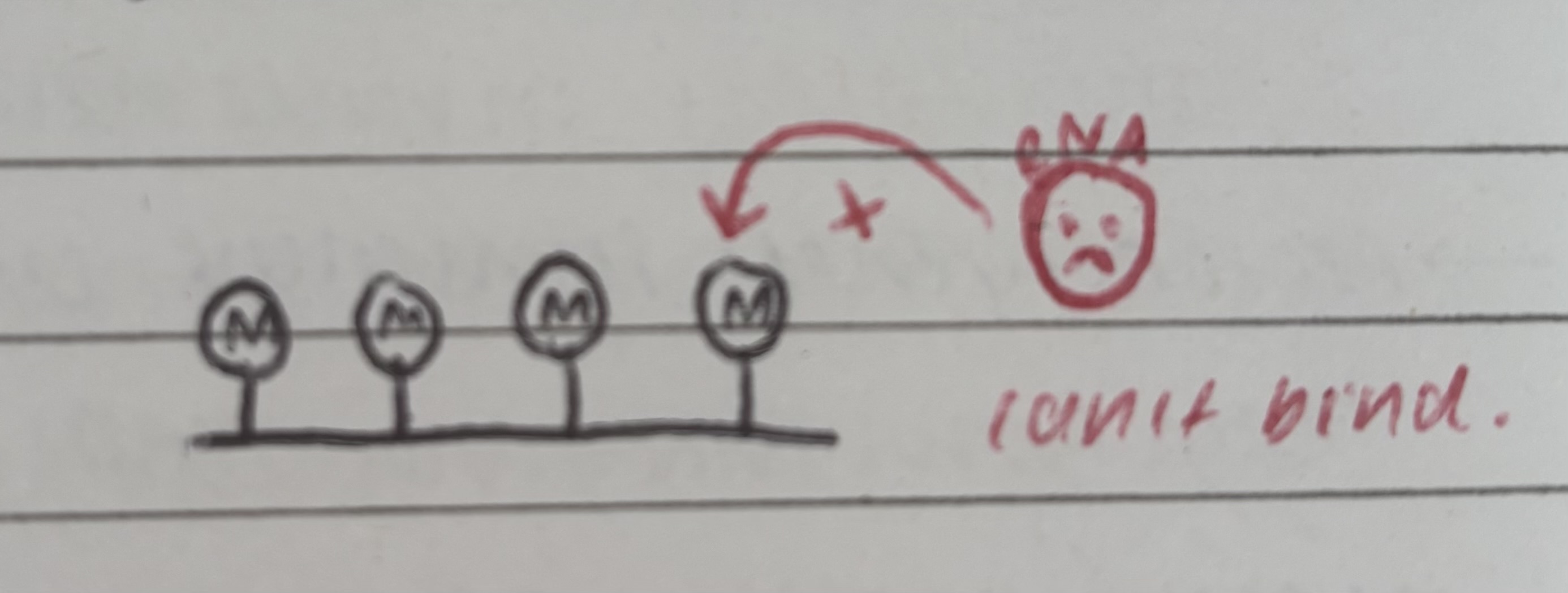
how does methylation affect gene expression/transcription.
methyl groups attach to cytosine bases. silences genes because T.F and RNA polymerase can’t bind/move along DNA strand and activate transcription
what does siRNA do?
stands for short interfering RNA. silences genes by destroying target/preventing transcription
(ds)RNA hydrolysed into smaller (ss) siRNA which binds to complementary mRNA (becoming dsRNA) and forms a group of proteins called RISC which breaks down mRNA so that they can’t be translated to form functional proteins
what do the 3 types of neurone do
sensory: carries impulse from receptors to CNS
relay: relays impulse from sensory neurone to motor neurone
motor: carries impulse to effector organ
what is resting potential and how is it maintained?
-70mv
outside membrane is more +ve than inside. this difference in charge = membrane is polarised.
Na+ pumped out but can’t diffuse back in which creates electrochemical gradient due to more +ve ions outside
k+ pumped in but some diffuses back out which keeps outside membrane more +ve
Describe the process of an action potential?
begins at resting potential. stimulus excites neoprene so Na+ diffuses in. at threshold of -55mv more Na+ channels open and more Na+ diffuses in (depolarisation)
at p.d 30mv. Na+ channels close and k+ channels open. K+ diffuses in and down gradient. (repolarisation)
K+ channels slow to close, too many K+ diffuse out so p.d now more negative than resting potential (hyper polarisation)
channels rest Na+ pump returns membrane back to resting potential
what does the refractory period do?
ion channels recover and can’t open which acts as a time delay between action potentials
what three things affect the speed of an impulse?
myelination
axon diameter
temperature
describe the process of synaptic transmission
presentation neoprene contains NT in vesicles
a.p causes NF to be released from vesicles into synaptic cleft
NT diffuses across to post synaptic membrane and bind to specific receptors. triggers a.p and causes muscle contraction
NT removed from cleft, broken down or reuptaken
what does excitatory and inhibitory mean?
excitatory: depolarises posty synaptic membrane so an action potential is more likely to fire
inhibitory: hyperpolarises post synaptic membrane which prevents action potential from firing
what happens at a neuromuscular junction?
NT acetylcholine (ACh) binds to cholinergic receptors called nicotine cholinergic receptors.
post synaptic membrane has lots of folds that form clefts which store an enzyme that breaks down ACh called AChE
ACh is always excitatory = a.p will always trigger muscle response
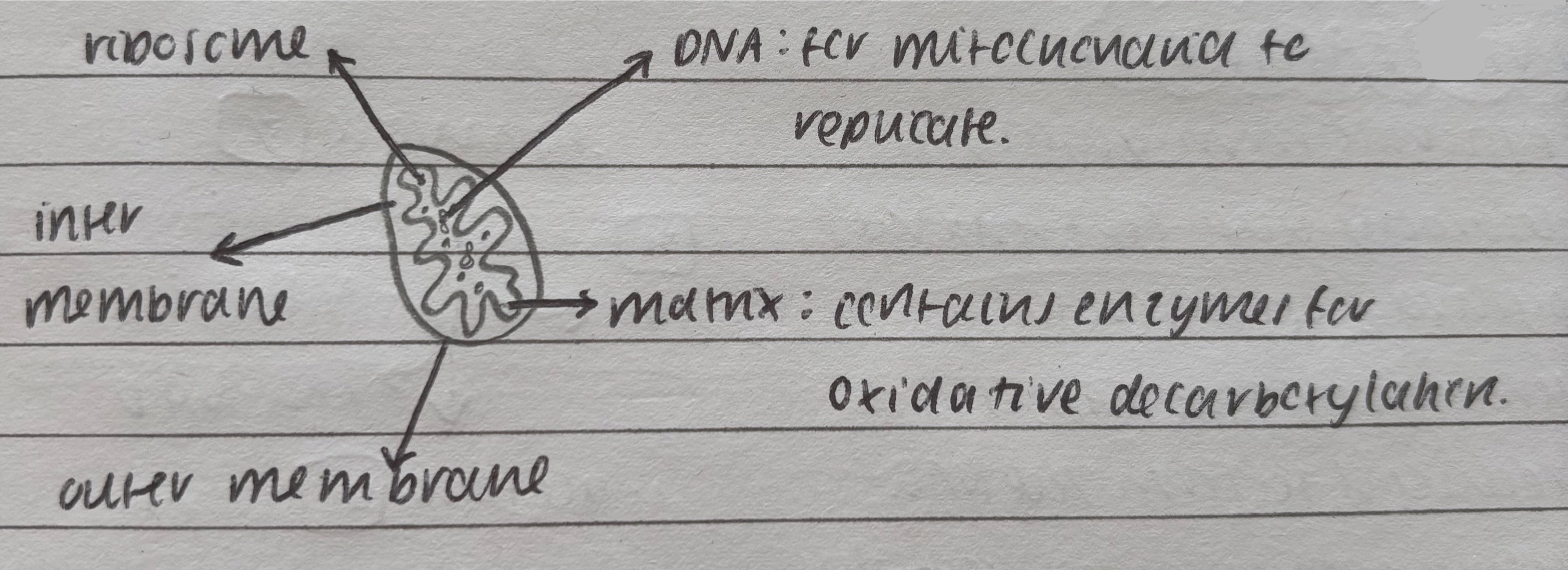
describe the structure of the mitochondria?
matrix contains enzymes for oxidative phosphorylation
inner, inter and outer membrane
ribosomes
DNA for mitochondria to replicate
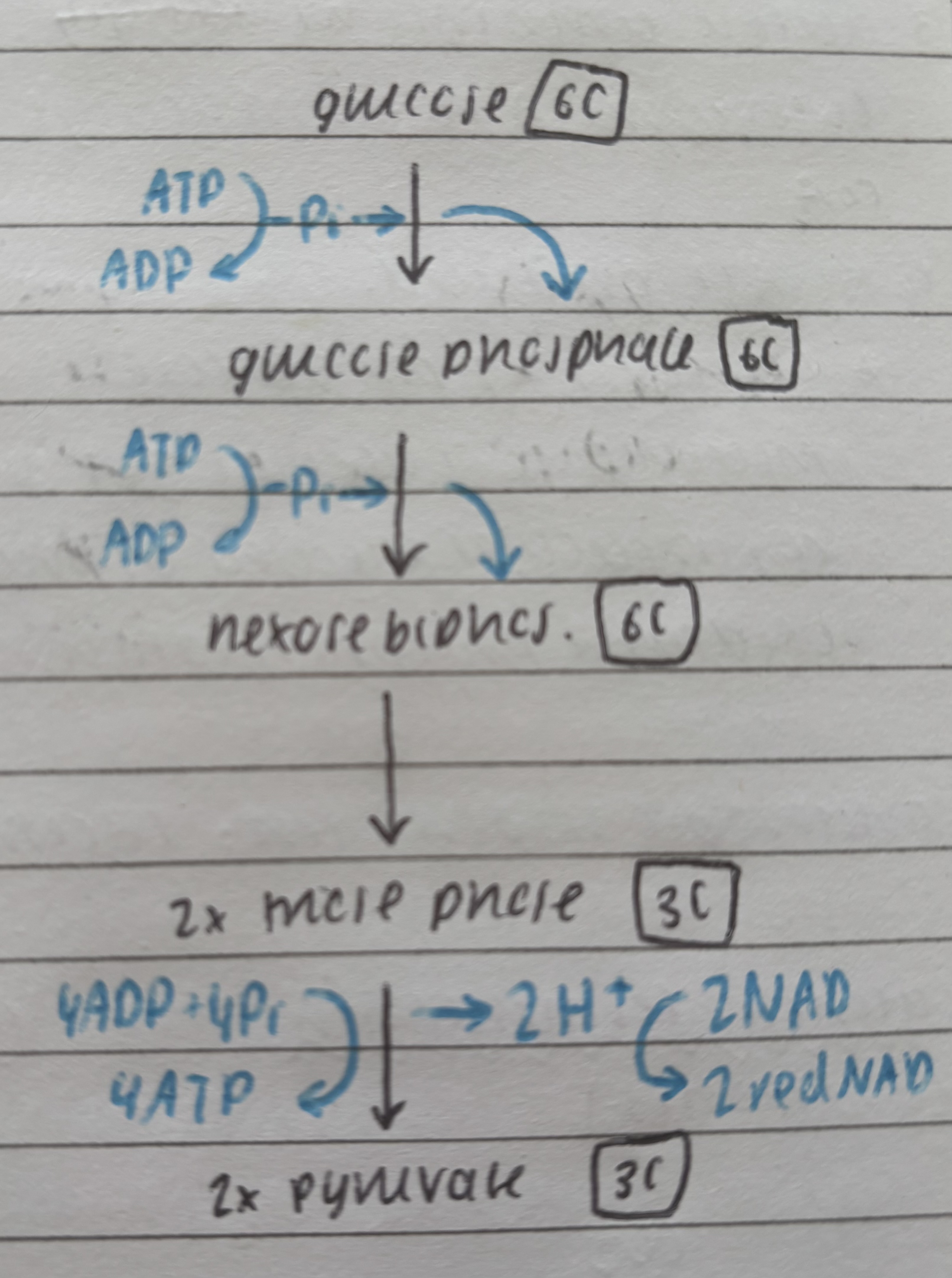
describe the process of glycolysis
glucose phosphorylated to form glucose phosphate (and 1ADP)
ATP used to add another phosphate and form expose biphophate (and 1ADP)
heckles bi. split into 2 molecules of triose phosphate
tri.phos. oxidised so loses H+ which forms 2 red NAD
2 pyruvate formed
describe the process of the link reaction?
private decarboxylated (Co2 removed)
pyruvate oxidised to form acetate and NAD is reduced to form red. NAD
acetate combined with coenzyme A to form Acetyl CoA
occurs twice per glucose molecule