B2- Organisation
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
1
New cards
What are cells
the basic building blocks that make up all living organisms.
2
New cards
What is the order of how cells become organ systems
Cells > Tissues > Organs > Organ Systems
3
New cards
Is a leaf a tissue?
No its an organ
4
New cards
Name 3 tissues
* Muscular tissue
* Glandular tissue
* Epithelial tissue
* Glandular tissue
* Epithelial tissue
5
New cards
Name 3 organs (tissues that work together to perform a function)
* Stomach
* Pancreas
* Liver
* Pancreas
* Liver
6
New cards
What is an organ system
A group of organs working together to perform a particular function e.g. the digestive system breaks down and absorbs food it contains:
1. Glands e.g. pancreas and salivary glands which produce digestive juices
2. The stomach and small intestine , which digest food.
3. The liver, which produces bile.
4. The small intestine, which absorbs soluble food molecules
5. The large intestine, which absorbs water from undigested food leaving faeces
1. Glands e.g. pancreas and salivary glands which produce digestive juices
2. The stomach and small intestine , which digest food.
3. The liver, which produces bile.
4. The small intestine, which absorbs soluble food molecules
5. The large intestine, which absorbs water from undigested food leaving faeces
7
New cards
What are Enzymes
Enzymes are catalysts produced by living things
8
New cards
What is a catalyst
A substance which increases the speed of a reaction without being changed or used up in a reaction
9
New cards
How do enzymes connect to substrate
On the enzymes active site as they have to fit to the substrate perfectly
10
New cards
How does the active site change slightly to make the connection to the substrate tighter
It changes shape so the substrate can bind to it which is called an induced fit
11
New cards
What changes the rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction
The temperature and PH of conditions
12
New cards
What happens to an enzyme if it gets too hot
Its active site starts to deform causing it to denature
13
New cards
How can you investigate the effect of PH on Enzyme Activity
The effect of pH on amylase through iodine placed in spotting tiles
Solutions filled test tubes of
Tube A- starch solution (2cm cubed)
Tube B- amylase solution (2cm cubed)
Tube C- pH 5 buffer solution (2cm Cubed) (used to control pH
then leave all solutions in a water bath set at 30 degrees Celsius for 10 minutes to make sure they are the correct temperature.
Then mix all the solutions together into one test tube and place straight back into the 30 degree water bath and start the stop watch
then after 30s us a pipette to transfer a drop of solution into the spotting tiles with iodine in it
If the solution turns blue black it means it still contains starch
then every 30s we keep testing the iodine until it stays iodine which indicates to us that starch is no longer present in the solution meanng the amylase has broken down the starch. (Reaction completed)
Repeat the experiment two or 3 more times with different pH buffers to find whichever is the most efficient. (Reacts in the least amount of time)
Solutions filled test tubes of
Tube A- starch solution (2cm cubed)
Tube B- amylase solution (2cm cubed)
Tube C- pH 5 buffer solution (2cm Cubed) (used to control pH
then leave all solutions in a water bath set at 30 degrees Celsius for 10 minutes to make sure they are the correct temperature.
Then mix all the solutions together into one test tube and place straight back into the 30 degree water bath and start the stop watch
then after 30s us a pipette to transfer a drop of solution into the spotting tiles with iodine in it
If the solution turns blue black it means it still contains starch
then every 30s we keep testing the iodine until it stays iodine which indicates to us that starch is no longer present in the solution meanng the amylase has broken down the starch. (Reaction completed)
Repeat the experiment two or 3 more times with different pH buffers to find whichever is the most efficient. (Reacts in the least amount of time)
14
New cards
What is an issue with this experiment
Difficult to tell when reaction has finished can be solved by getting other peoples opinion.
15
New cards
What is amylase
A carbohydrase which breaks down starch into maltose and other sugars
* It is produced in the salivary glands, the pancreas and the small intestine
* It is produced in the salivary glands, the pancreas and the small intestine
16
New cards
What is protease
It converts proteins into amino acids
* It is produced in the stomach, pancreas and small intestine
* It is produced in the stomach, pancreas and small intestine
17
New cards
What is Lipase
Converts Lipids into Glycerol and fatty acids
* Produced in the pancreas and small intestine
* Produced in the pancreas and small intestine
18
New cards
What is and Bile and where is it produced
Bile neutralises the stomach acid in order to allow enzymes in the small intestine to work properly as bile is alkaline and the enzymes there work best in alkaline.
Additionally it emulsifies fats which means to break them down into smaller droplets increasing their surface area allowing them to be digested faster.
Produced in the liver stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine
Additionally it emulsifies fats which means to break them down into smaller droplets increasing their surface area allowing them to be digested faster.
Produced in the liver stored in the gallbladder and released into the small intestine
19
New cards
What are the purposes of enzymes around the body
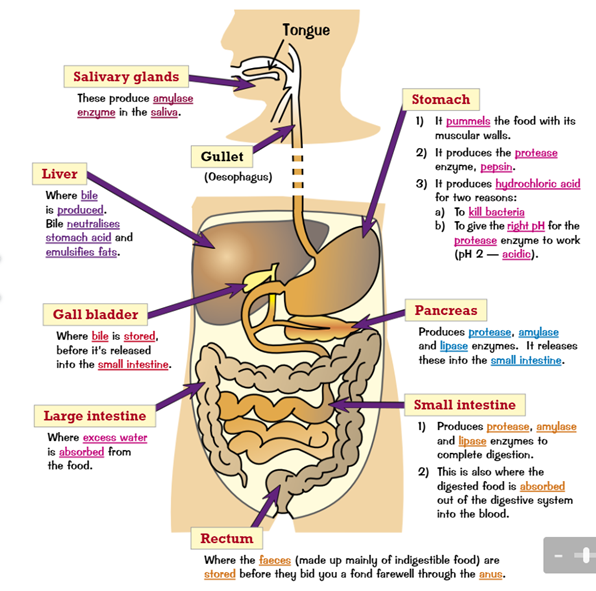
20
New cards
What is the Benedict’s test for and what are the colour indicators
Sugar which when benedict’s is added the solution is then placed in a 75 degree Celsius water bath and left for 5 minutes
When first added it will turn blue then to green, yellow and at most brick red depending on the amount of sugar.
When first added it will turn blue then to green, yellow and at most brick red depending on the amount of sugar.
21
New cards
What is Iodine test for and what are the colour indicators
Starch if present colour will change blue black
If not brown orange
If not brown orange
22
New cards
What is Biuret A and Biuret B
Proteins. Prepare a sample of food and transfer 2cm cubed to a test tube add 2 cm cubed of biuret solution. If protein present solution will change from blue to purple
23
New cards
What is the Sudan III test for
Lipids
24
New cards
What are stents and the pros and cons
Stents are inserted into the coronary arteries to keep the arteries clear preventing fat blocking the artery and preventing blood from flowing through.
\
Stents Positives
Long term keep the arteries open and lower risk of a heart attack
quick recovery from surgery
Negatives
Surgical procedure which is risky
cauld cause blood clots thrombosis
heart attack
infection
\
Stents Positives
Long term keep the arteries open and lower risk of a heart attack
quick recovery from surgery
Negatives
Surgical procedure which is risky
cauld cause blood clots thrombosis
heart attack
infection
25
New cards
Statins
Statins are a drug taken to reduce the production of bad cholesterol (LDL) in the bloodstream which slows down the production of fatty deposits in the arteries
Positives
\-No surgical procedure required
\-Reduces chances of strokes, heart attacks and CHD
\-Increases amount of ‘good’ cholesterol produced (HDL)
\
Negatives
\-Long term drug which can be forgotten to be taken
\-Can cause side affects like headaches or serious ones like kidney failure, liver damage or memory loss
\-effect of statins take time to kick it
Positives
\-No surgical procedure required
\-Reduces chances of strokes, heart attacks and CHD
\-Increases amount of ‘good’ cholesterol produced (HDL)
\
Negatives
\-Long term drug which can be forgotten to be taken
\-Can cause side affects like headaches or serious ones like kidney failure, liver damage or memory loss
\-effect of statins take time to kick it
26
New cards
What can be made artificially
Hearts, Blood and valves
27
New cards
Advantages of artificial heart
Less likely to be rejected than donor but tehy don’t work as well as natural ones and can lead to bleeding and infection. Patient also has to go thinners which causes more bleeding in accidents
28
New cards
Advantages of artificial valves
Replace old or stiffened valves with mechanical or biologoical ones but it is major surgery
29
New cards
Advantages of artificial blood
Can be used even when someone has lost 2 thirds of their blood in order to support their body until they are able to produce new red blood cells
30
New cards
What is cancer
Uncontrolled growth and division of cells caused by the formation of a tumour
31
New cards
What are the two types of tumours
Benign- Stays in one place and grows until there is no more room and is not cancerous so not usually dangerous
Malignant- Tumour grows an spreads to neighbouring healthy tissue. Cells break off and spread out through the bloodstream causing the formation of of secondary tumours around the body on healthy tissue
Malignant- Tumour grows an spreads to neighbouring healthy tissue. Cells break off and spread out through the bloodstream causing the formation of of secondary tumours around the body on healthy tissue
32
New cards
What are the risk factors which increase possibility of cancer due to lifestyle?
Smoking- linked to lung cancer as well as bowel, mouth, stomach and cervical cancer
Obesity- Linked to many different cancers including bowel, liver and kidney
UV exposure- Skin cancer sunny climate or sun beds
Viral infection- Infection with hepatitis B and C can increase risk of liver cancer this can depend on lifestyle e.g. sharing needles or having unprotected sex
Obesity- Linked to many different cancers including bowel, liver and kidney
UV exposure- Skin cancer sunny climate or sun beds
Viral infection- Infection with hepatitis B and C can increase risk of liver cancer this can depend on lifestyle e.g. sharing needles or having unprotected sex
33
New cards
Risk factors linking to Genetics
Faulty genes
Mutations in BRCA genes have been linked to an increase likelihood of breast and ovarian cancer
Mutations in BRCA genes have been linked to an increase likelihood of breast and ovarian cancer
34
New cards
What are 3 organs in a plant
* Stems
* Roots
* Leaves
* Roots
* Leaves
35
New cards
What tissues are the leaf made up of as an organ
Waxy cuticle- stops leaf from drying out
Upper Epidermis- transparent to allow light through to meso
Palisade mesophyll- contains tons of chloroplast Air space
Spongy mesophyll tissue- air space to allow carbon dioxide to diffuse from the stomata to the palisade cell. Oxygen also does the opposite
Epidermis tissue Stomata- Control amount of water leaves leaf Guard cell
Upper Epidermis- transparent to allow light through to meso
Palisade mesophyll- contains tons of chloroplast Air space
Spongy mesophyll tissue- air space to allow carbon dioxide to diffuse from the stomata to the palisade cell. Oxygen also does the opposite
Epidermis tissue Stomata- Control amount of water leaves leaf Guard cell
36
New cards
What is the purpose of the xylem
transports water from the roots to the stem and leaves and some of it is used in photosynthesis it also transports dissolved mineral ions such as magnesium which is used to make chlorophyll
37
New cards
What is the purpose of the phloem
Transports dissolved sugars from the leaves to the rest of the plant sugars are used in respiration also stored as starch
This movement of sugars through the phloem is called translocation
This movement of sugars through the phloem is called translocation
38
New cards
What is meristem tissue
Growing in tips roots and shoots they contain stem cells
39
New cards
How are the xylem and phloem adapted for their purpose
Phloem- pores in the end walls to allow cell sap through goes in both directions
Xylem- made up of dead cells joined end to end strengthened by lignin (no end walls
Xylem- made up of dead cells joined end to end strengthened by lignin (no end walls
40
New cards
What is transpiration
The evaporation of water out of the leaf cell water vapour diffuses through the air spaces of the spongy mesophyll and out through the stomata. The water lost is then replaced by water coming up through the xylem which is drawn from the roots. Transports magnesium which is important for the plant.
Cools the leaf down in hot weather
Cools the leaf down in hot weather
41
New cards
What increases the rate of transpiration
* Increase in temperature,
* dry conditions,
* windy conditions (removes water vapour)
* increase in light intensity (increases rate of photosynthesis)
* dry conditions,
* windy conditions (removes water vapour)
* increase in light intensity (increases rate of photosynthesis)
42
New cards
Stomata
Have two guard cells which swell when light intensity is high to allow carbon dioxide to diffuse into the leaf when in hot conditions the stomata close to reduce water loss but it means photosynthesis can’t take place.