SAP Exam
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/157
Last updated 5:01 PM on 1/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
1
New cards
Oral stage
**Age:** Birth - 1½
**Erogenous Zone:** mouth
**Major Development:**Weaning off breast milk or bottle
**Adult Fixation:** drinking, eating, smoking, nail biting
**Erogenous Zone:** mouth
**Major Development:**Weaning off breast milk or bottle
**Adult Fixation:** drinking, eating, smoking, nail biting
2
New cards
Anal stage
**Age:**1½ - 3
**Erogenous Zone:** anus
**Major Development:**Toilet training, bowel and bladder control
**Adult Fixation:** Orderliness or messiness
**Erogenous Zone:** anus
**Major Development:**Toilet training, bowel and bladder control
**Adult Fixation:** Orderliness or messiness
3
New cards
Phalllic
**Age:**3-6
**Erogenous Zone:**genitals
**Major Development:**Resolving Oedipus Complex
**Adult Fixation:**Sexual dysfunction
**Erogenous Zone:**genitals
**Major Development:**Resolving Oedipus Complex
**Adult Fixation:**Sexual dysfunction
4
New cards
Latency Stage
**Age:**6-Puberty
**Erogenous Zone:**repressed sexuality
**Major Development:**Developing social + intellectual skills, and defense mechanisms
**Adult Fixation:**none
**Erogenous Zone:**repressed sexuality
**Major Development:**Developing social + intellectual skills, and defense mechanisms
**Adult Fixation:**none
5
New cards
Genital stage
**Age:**Puberty Onward
**Erogenous Zone:**Genitals
**Major Development:**sexual reawakening/maturity, source of sexual pleasure becomes someone outside the family
**Adult Fixation:**If other stages completed successfully, individual should now be well-balanced
**Erogenous Zone:**Genitals
**Major Development:**sexual reawakening/maturity, source of sexual pleasure becomes someone outside the family
**Adult Fixation:**If other stages completed successfully, individual should now be well-balanced
6
New cards
__Conscious Mind__
Information that we are aware of, performs thinking when we take in new information.
7
New cards
__Unconscious Mind__
Information in our mind that we are unaware of, holds our thoughts, feelings + memories.
8
New cards
__**Behaviourism**__
John Watson (1878-1958)
* In order to be scientific, psychology should only study what can be observed.
* Since the mind itself cannot be observed, behaviour was the only available source of data.
* Studies how individuals react to the environment.
* Believe that psychologists can predict/control/modify human behaviour by identifying the factors that motivate it in the first place.
* In order to be scientific, psychology should only study what can be observed.
* Since the mind itself cannot be observed, behaviour was the only available source of data.
* Studies how individuals react to the environment.
* Believe that psychologists can predict/control/modify human behaviour by identifying the factors that motivate it in the first place.
9
New cards
__**Classical Conditioning**__
__**Ivan Pavlov (1849-1936)**__
* Once neutral stimulus comes to produce a particular response after pairings with a conditioned stimulus
* Learning to transfer a natural response from one stimulus to another
* Involuntary reflexive behaviour
* Once neutral stimulus comes to produce a particular response after pairings with a conditioned stimulus
* Learning to transfer a natural response from one stimulus to another
* Involuntary reflexive behaviour
10
New cards
__Conditioning__
Acquiring patterns of behaviour in the presence of an environmental stimulus
11
New cards
__Unconditioned Stimulus__
A stimulus that naturally triggers a response
12
New cards
__Unconditioned Response__
Natural, automatic, unlearned response to an unconditioned stimulus
13
New cards
__Conditioned Stimulus__
An originally neutral stimulus that triggers a conditioned response after being paired with an unconditioned stimulus
14
New cards
__Conditioned Response__
The learned response to a previously neutral stimulus
15
New cards
__**Operant Conditioning**__
__**B.F. Skinner - (1904-1990)**__
* **Uses rewards and punishment to achieve desired behaviour**
* Voluntary behavioural outcomes
* If you find the motive of behaviour you have the power to control/change behaviour.
* Use of rewards and punishment can influence behaviour
* Rewards can be more effective compared to punishments because rewards indicate what behaviour is desired, whereas punishments only indicate what not to do
* **Uses rewards and punishment to achieve desired behaviour**
* Voluntary behavioural outcomes
* If you find the motive of behaviour you have the power to control/change behaviour.
* Use of rewards and punishment can influence behaviour
* Rewards can be more effective compared to punishments because rewards indicate what behaviour is desired, whereas punishments only indicate what not to do
16
New cards
__Positive reinforcement__
event/situation that increases likelihood certain behaviour will recur
17
New cards
__Negative reinforcement__
event/situation that decreases likelihood certain behaviour will recur
18
New cards
__Humanistic Psychology__
Carl Rogers + Abraham Maslow
* Argued that humans are not helplessly controlled by unconscious or environmental forces
* We have free will, goals, aspirations and other positive motives which should be studied
* Argued that humans are not helplessly controlled by unconscious or environmental forces
* We have free will, goals, aspirations and other positive motives which should be studied
19
New cards
__Carl Jung:__
__Personal Unconscious__
__Personal Unconscious__
unique to the individual
20
New cards
__Collective Unconscious__
memories of ancestors
21
New cards
personality divided into 4 psychological functions
__sensation, intuition, thinking, feeling__
22
New cards
__Introvert__
* Use psychological power to look inward, emotionally self-serving
* Don’t need many close personal relationships to give them reassurance and confidence
* Don’t need many close personal relationships to give them reassurance and confidence
23
New cards
__Extrovert__
* Use psychological power to look outward
* Outgoing and more comfortable in large groups of friends
* Outgoing and more comfortable in large groups of friends
24
New cards
__Trust vs Mistrust__
\- Infant-18 months
* Favourable outcome: faith in environment + future events
* Unfavourable outcome: suspicion, fear of future events
* Favourable outcome: faith in environment + future events
* Unfavourable outcome: suspicion, fear of future events
25
New cards
__Autonomy vs shame doubt__
\- 18 months-3 years
* Favourable outcome: sense of self control + adequacy
* Unfavourable outcome: feelings of shame and self-doubt
* Favourable outcome: sense of self control + adequacy
* Unfavourable outcome: feelings of shame and self-doubt
26
New cards
Initiative vs Guilt
- 3-5 years
* Favourable outcome: ability to initiate one's own activities
* Unfavourable outcome: sense of guilt and inadequacy to be one's own
* Favourable outcome: ability to initiate one's own activities
* Unfavourable outcome: sense of guilt and inadequacy to be one's own
27
New cards
__Industry vs Inferiority__
\- 5-13 years
* Favourable outcome: ability to learn how things work, understand + organize
* Unfavourable outcome: sense of inferiority at understanding + organizing
* Favourable outcome: ability to learn how things work, understand + organize
* Unfavourable outcome: sense of inferiority at understanding + organizing
28
New cards
__Identity vs Role confusion__
\- 13-21 years
* Favourable outcome: seeing oneself as a unique + integrated individual
* Unfavourable outcome: confusion of who + what one really is
* Favourable outcome: seeing oneself as a unique + integrated individual
* Unfavourable outcome: confusion of who + what one really is
29
New cards
__Intimacy vs Isolation__
\- 21-39 years
* Favourable outcome: ability to make commitments to others to love
* Unfavourable outcome: inability to form affectionate relationships
* Favourable outcome: ability to make commitments to others to love
* Unfavourable outcome: inability to form affectionate relationships
30
New cards
__Generativity vs Stagnation__
\- 40-65 years
* Favourable outcome: concern for family + society in general
* Unfavourable outcome: concern for one's own self well being + prosperity
* Favourable outcome: concern for family + society in general
* Unfavourable outcome: concern for one's own self well being + prosperity
31
New cards
__Integrity vs Despair__
- 65+
* Favourable outcome: a sense of integrity + fulfillment, willingness to face death
* Unfavourable outcome: dissatisfaction with life, despair over prospect of death
* Favourable outcome: a sense of integrity + fulfillment, willingness to face death
* Unfavourable outcome: dissatisfaction with life, despair over prospect of death
32
New cards
__**Neurosis**__
Mental distress that, unlike psychosis, does not prevent rational thought or daily functioning. It is an over exaggerated defense mechanism to fear or anxiety.
\
\
33
New cards
Phobia
* anxiety about a specific object, activity, or situation, ex. spiders, enclosed spaces
* Can cause psychological reactions like increased heart rate, sweaty palms, fear
* Can cause psychological reactions like increased heart rate, sweaty palms, fear
34
New cards
ADD/ADHD
* Developmental disorder characterized by inattention, impulsiveness, and overactivity
* Key cognitive/thinking skills slower to develop in children with ADHD
* Key cognitive/thinking skills slower to develop in children with ADHD
35
New cards
Agoraphobia
* Anxiety disorder, fear and avoid places/situations that might cause you to panic and make you feel trapped, helpless or embarrassed
36
New cards
OCD
* Uncontrollable, recurrent obsessions/compulsions, feels the urge to repeat over and over.
* Phases of obsessive thoughts, anxiety, compulsive behaviour and temporary relief
* Intrusive thoughts, excessive worries, rule driven, fear of unknown/losing control
* Phases of obsessive thoughts, anxiety, compulsive behaviour and temporary relief
* Intrusive thoughts, excessive worries, rule driven, fear of unknown/losing control
37
New cards
Anorexia Nervosa
* Self-starvation/malnourishment, excessive exercise, obsessive weight loss,
* Fear of gaining weight, distorted body perception,
* Amenorrhea (loss of menstruation)
* Fear of gaining weight, distorted body perception,
* Amenorrhea (loss of menstruation)
38
New cards
__Bulimia Nervosa:__
* Cycles of starvation, devouring food, and purging, frequent binge episodes
* Purges can occur through laxatives, forced vomiting, or excessive exercise
* Typically a form of poor mental/emotional coping
* Purges can occur through laxatives, forced vomiting, or excessive exercise
* Typically a form of poor mental/emotional coping
39
New cards
__Binge eating disorder:__
* Frequent impulsive/uncontrollable eating at least once a week over long time
* Binges include fast eating, absence of hunger, feeling uncomfortably full after
* Feelings of no control + guilt during/after binges
* Binges include fast eating, absence of hunger, feeling uncomfortably full after
* Feelings of no control + guilt during/after binges
40
New cards
__**Psychosis**__
Mental state involving the loss of contact with reality, causing the deterioration of normal social functioning.
* Includes delusions + hallucinations
* Includes delusions + hallucinations
41
New cards
Schizophrenia
A mental disorder where one interprets reality differently, such as having hallucinations and delusions which impacts their daily functioning
42
New cards
Bi-Polar Disorder
* Brain disorder, unusual shifts in mood/energy/activity levels, ability to carry out day-to-day tasks.
* Extreme- HIGHS and lows
\
* Extreme- HIGHS and lows
\
43
New cards
Manic Depression
* A long period of feeling "high," or an overly happy or outgoing mood
* Extremely irritable mood, agitation, feeling "jumpy" or "wired."
* Extremely irritable mood, agitation, feeling "jumpy" or "wired."
44
New cards
Clinical Depression
* No one cause, biochemical imbalance in the brain, can be from life distressing events
* Negative or pessimistic view of life, long period of feeling worried or empty
* Loss of interest in activities once enjoyed
* Negative or pessimistic view of life, long period of feeling worried or empty
* Loss of interest in activities once enjoyed
45
New cards
Dementia
* Deterioration of the brain
* Affects all brain functioning: thought processes, judgment, reasoning, memory, communication, and behaviour
\
* Affects all brain functioning: thought processes, judgment, reasoning, memory, communication, and behaviour
\
46
New cards
Alzetheimers
* Type of dementia
* Changes in memory, communication, judgment, personality, overall cognitive functioning
* Changes in memory, communication, judgment, personality, overall cognitive functioning
47
New cards
__**Defense Mechanisms**__
* Behaviour patterns we use to protect ourselves, positive or negative solutions to problem
* Can be self aware of using defense mechanisms to maintain a healthy mental state
* Many don’t realize they’re relying on defense mechanisms, can lose touch with reality
* Can be self aware of using defense mechanisms to maintain a healthy mental state
* Many don’t realize they’re relying on defense mechanisms, can lose touch with reality
48
New cards
\
Repression
Repression
* blocking of unacceptable impulses from consciousness, removes traumatic experiences from conscious memory
49
New cards
Rationalization
* Cognitive reframing of perceptions to protect ego in the face of changing realities
* Ex. promotion one wished for and didn’t get becomes: “a dead end job for brown nosers”
* Ex. promotion one wished for and didn’t get becomes: “a dead end job for brown nosers”
50
New cards
Displacement
* Redirecting thoughts/feelings/impulses from an object that causes anxiety to a safer, more acceptable one, replacing a threatening object with a less threatening one
* Ex. being angry at your boss and kicking the dog
* Ex. being angry at your boss and kicking the dog
51
New cards
Denial
* Refusal to accept reality and to act as if a painful event, thought or feeling did not exist
52
New cards
Reaction Formation
* Converting wishes/impulses that are perceived to be dangerous into their opposites
* Finding reasons why others shouldn’t do something that we’ve done
* ex. a woman who is furious at her child + wishes harm becomes overly protective
* Finding reasons why others shouldn’t do something that we’ve done
* ex. a woman who is furious at her child + wishes harm becomes overly protective
53
New cards
Projection
* The attribution of ones undesired impulses onto another
* E.g., an angry spouse accuses their partner of hostility “It’s not my fault, you started it”
* E.g., an angry spouse accuses their partner of hostility “It’s not my fault, you started it”
54
New cards
Regression
* Is the reversion to an earlier stage of development in the face of an unacceptable impulse
* Ex. overwhelmed child becomes clingy, begin sucking their thumb or wetting their bed
* Ex. overwhelmed child becomes clingy, begin sucking their thumb or wetting their bed
55
New cards
Fantasy/Daydreaming
* The channeling of unacceptable or unattainable desires into imagination
* Protects self-esteem by imagining success in areas where expectations are not being met
* Protects self-esteem by imagining success in areas where expectations are not being met
56
New cards
Sublimation
* The channeling of unacceptable impulses into more acceptable outlets
* E.g., expressing anger in a hockey fight rather than street fight
* E.g., expressing anger in a hockey fight rather than street fight
57
New cards
Compensation
* Psychologically balancing perceived weaknesses by emphasizing strength in other arenas
* The “I'm not a fighter, I'm a lover” philosophy
* The “I'm not a fighter, I'm a lover” philosophy
58
New cards
Compartmentalization
* Separating parts of the self from awareness + behaving one set has separate sets of values
\
\
59
New cards
Undoing
* Is the attempt to take back behaviour or thoughts that are unacceptable
* Ex. excessively praising someone after having insulted them
* Ex. excessively praising someone after having insulted them
60
New cards
Functionalism - William James (1842-1910)
* **Argued that consciousness cannot be broken down into elements.**
* Ongoing conscious experience and the functions of mental processes.
* **Aims to find meaning and purpose in what we experience**
* **Mental state is more a matter of what it does, not what it is made of.**
* Focused on how things worked together
* Examined how the mind functions in different environments
* Used objective techniques to explore memories and emotions
* Ongoing conscious experience and the functions of mental processes.
* **Aims to find meaning and purpose in what we experience**
* **Mental state is more a matter of what it does, not what it is made of.**
* Focused on how things worked together
* Examined how the mind functions in different environments
* Used objective techniques to explore memories and emotions
61
New cards
Structuralism - Wilhelm Wundt (1832-1920)
* Uncovers the structure of consciousness by breaking down mental processes into most basic components
* Examined the capabilities of different parts of the mind
* Used introspection to study feelings and sensations
* Examined the capabilities of different parts of the mind
* Used introspection to study feelings and sensations
62
New cards
__Alfred Adler__
* Believed power was the key to understanding personality, people motivated by power
* people were aware of their goals and values that guided them
* Maladjusted people choose to pursue goals that are useless to themselves and society
* Maladjusted lack self-esteem, would pursue better goals if they gained self-esteem
* Believed birth order was important to shape personality
\
* people were aware of their goals and values that guided them
* Maladjusted people choose to pursue goals that are useless to themselves and society
* Maladjusted lack self-esteem, would pursue better goals if they gained self-esteem
* Believed birth order was important to shape personality
\
63
New cards
Inferiority complex
* low self-esteem, is a feeling of intense insecurity, inferiority or of not measuring up
* People feel inferior at some point + compensate by seeking sense of power
* People feel inferior at some point + compensate by seeking sense of power
64
New cards
__Types of Power:__
Fear/Intimidation
Fear/Intimidation
– having the ability to scare or threaten people
65
New cards
__Types of Power:__
Authority
Authority
– having privileges and dominance
66
New cards
__Types of Power:__
Superiority
Superiority
– being better than others
67
New cards
__Types of Power:__
Demands
Demands
– ability to express needs
68
New cards
__Types of Power:__
Independence
Independence
– no needing to rely on others
69
New cards
__Types of Power:__
Money
Money
– having mobility in society
70
New cards
__Types of Power:__
Control
Control
– having power in a situation
71
New cards
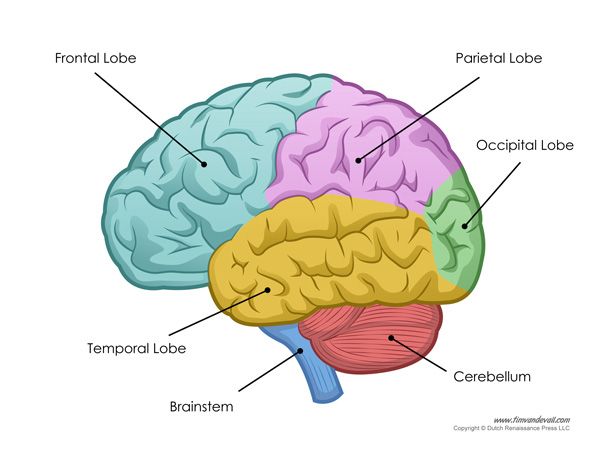
Parts and Lobes of the Brain- Neuroscience
72
New cards
__**Frontal Lobe**__
Conscious thought, behaviour, emotion, planning, personality, organising, problem solving. Most uniquely human of all the brain structures. Front of brain.
73
New cards
__**Parietal Lobe**__
Integrations of sensory information from primary sensory areas --perceptions, arithmetic, spelling, manipulations of objects. Middle top of brain.
74
New cards
__**Temporal Lobe**__
Senses of smell & sound, as well as processing of complex stimuli like faces & scenes, memory, understanding language. Temple region.
75
New cards
__**Occipital Lobe**__
Sense of sight. Extreme back of brain.
76
New cards
__Cerebrum__
Carries out higher thought processes involved with language, learning, memory, & voluntary body movements.
77
New cards
__Cerebellum__
Responsible for balance & coordination.
78
New cards
__Brainstem__
Relays signals between the brain & spinal cord.
79
New cards
__Pons__
Relays signals between cerebrum and cerebellum. Helps control breathing rate.
80
New cards
__Medulla Oblongata__
Relays signals between the brain & the spinal cord, controls blood pressure, heart rate, & breathing rate.
81
New cards
__Amygdala__
the integrative center for emotions, emotional behavior, and motivation.
82
New cards
__hippocampus__
complex brain structure embedded deep into temporal lobe. It has a major role in learning and memory
83
New cards
__hypothalamus__
acts as your body's smart control coordinating center.
\-main function is keep your body in a stable state called homeostasis.
\-main function is keep your body in a stable state called homeostasis.
84
New cards
Right brain
Creative + Intuitive hemisphere of the brain, controls the left side of the body
* creative, innovative, imaginative, holistic, arts and music.
* creative, innovative, imaginative, holistic, arts and music.
85
New cards
Left brain
Logical + Analytical hemisphere of the brain, controls the right side of the body
* analytic, thought, logic, rational, language, science and math
* analytic, thought, logic, rational, language, science and math
86
New cards
Perception
The process that allows us to select, organize & interpret sensory signals in the brain.
87
New cards
Id
-Born with it, allows us as newborns to get our basic needs met
* It is the instinctual part of the mind. Our pleasure principle. Food, sleep, and sex
* Doesn't care about reality or the needs of anyone else, only its own satisfaction
* When the id wants something, nothing else is important
* It is the instinctual part of the mind. Our pleasure principle. Food, sleep, and sex
* Doesn't care about reality or the needs of anyone else, only its own satisfaction
* When the id wants something, nothing else is important
88
New cards
Ego
* Develops within next three years of life as child interacts more and more with the world
* Reality principle, understands that other people have needs and desires and that sometimes being impulsive or selfish can hurt us in the long run.
* Strongest personality so that it can satisfy the needs of the id, not upset the superego, and still take into consideration the reality of every situation.
* Mediator between the Id and Superego.
* Reality principle, understands that other people have needs and desires and that sometimes being impulsive or selfish can hurt us in the long run.
* Strongest personality so that it can satisfy the needs of the id, not upset the superego, and still take into consideration the reality of every situation.
* Mediator between the Id and Superego.
89
New cards
The Superego
* Develops by age 5
* Moral part of us, our conscience as it dictates our belief of right and wrong
* Develops due to the moral and ethical restraints placed on us by our caregivers
* Moral part of us, our conscience as it dictates our belief of right and wrong
* Develops due to the moral and ethical restraints placed on us by our caregivers
90
New cards
**Cultural Relativism(Franz Boas)**
\-Cannot compare 2 cultures because each culture has its own internal rules that must be accepted
\-People see other cultures through the lens of their own culture
\-a response to cultural evolutionism (the theory that all cultures evolve from “savage” to “barbarian” to “civilized”) --which assumed an ethnocentric view that 19th century European culture was superior to all others
\-People see other cultures through the lens of their own culture
\-a response to cultural evolutionism (the theory that all cultures evolve from “savage” to “barbarian” to “civilized”) --which assumed an ethnocentric view that 19th century European culture was superior to all others
91
New cards
Ethnocentrism
believing that one’s own culture is superior to all other
92
New cards
**Functional Theory (Bronisław Malinowski)**
* Believed that social institutions (school, peers, religion) work together to provide a stable environment
* The idea that every belief, action, or relationship in a culture functions to meet the needs of individuals
* Functionalists would say that the medical element of culture (doctors) exist to help people
* The idea that every belief, action, or relationship in a culture functions to meet the needs of individuals
* Functionalists would say that the medical element of culture (doctors) exist to help people
93
New cards
**Cultural Materialism (Marvin Harris)**
* Materials or conditions within the environment (climate, food, geography, supply) influence how a __culture develops__, creating the ideas and ideology of a culture
* Society develops on a trial & error basis
* Society develops on a trial & error basis
94
New cards
**Culture is** __**learned**__
**-It is not biological; we do not inherit it. Much of learning culture is unconscious.**
**-We learn culture from families, peers, institutions, and media.**
**-We learn culture from families, peers, institutions, and media.**
95
New cards
**Culture is** __**shared**__
**-Because we share culture with other members of our group, we are able to act in socially appropriate ways as well as predict how others will act. Despite the shared nature of culture, that doesn’t mean that culture is homogenous (the same).**
96
New cards
**Culture is based on** __**symbols**__
**-A symbol is something that stands for something else. Symbols vary cross-culturally and are arbitrary. They only have meaning when people in a culture agree on their use.**
**- (Ex. Language, money and art)**
**- (Ex. Language, money and art)**
97
New cards
**Culture is** __**integrated**__
**-All aspects of a culture are interrelated to one another and to truly understand a culture, one must learn about all of its parts, not only a few.**
98
New cards
**Culture is** __**dynamic**__
**-This simply means that cultures interact and change. Because most cultures are in contact with other cultures, they exchange ideas and symbols**
99
New cards
__Primatology__
* The study of the anatomy and behaviours of living primates, investigating what makes humans similar and different.
* Observe primates both in their natural habitats and in laboratory’s to study physical and complex social behaviours and relationships
* Observe primates both in their natural habitats and in laboratory’s to study physical and complex social behaviours and relationships
100
New cards
__Primatologists:__
Dian Fossey
Dian Fossey
* Analyzed mountain gorilla behavior and lifestyle in Rwanda, Africa
* Observed that gorillas have a highly structured social system and hierarchy
* Studies were funded by The Leakey Family
* Died in Rwanda (was found murdered in cabin)
* Observed that gorillas have a highly structured social system and hierarchy
* Studies were funded by The Leakey Family
* Died in Rwanda (was found murdered in cabin)