AP Human Geography Unit 4
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Boundary
invisible line that marks the extent of a state's territory
Centripetal Force
An attitude that tends to unify people and enhance support for a state
Centrifugal Force
a force that divides people and countries
Cold War
A conflict that was between the US and the Soviet Union. The nations never directly confronted each other on the battlefield but deadly threats went on for years.
Colonies
a group of people who leave their native country to form in a new land a settlement subject to, or connected with, the parent nation.
European Union
An international organization of European countries formed after World War II to reduce trade barriers and increase cooperation among its members
Geopolitics
An interest in or taking of land for its strategic location or products
Government
the system or form by which a community or other political unit is governed
Imperialism
A policy in which a strong nation seeks to dominate other countries politically, socially, and economically.
Nationalism
A strong feeling of pride in and devotion to one's country
Nation-State
A country who's population share a common identity.
Sovereignty
Ability of a state to govern its territory free from control of its internal affairs by other states.

Stateless Nation
A nationality that is not represented by a state.
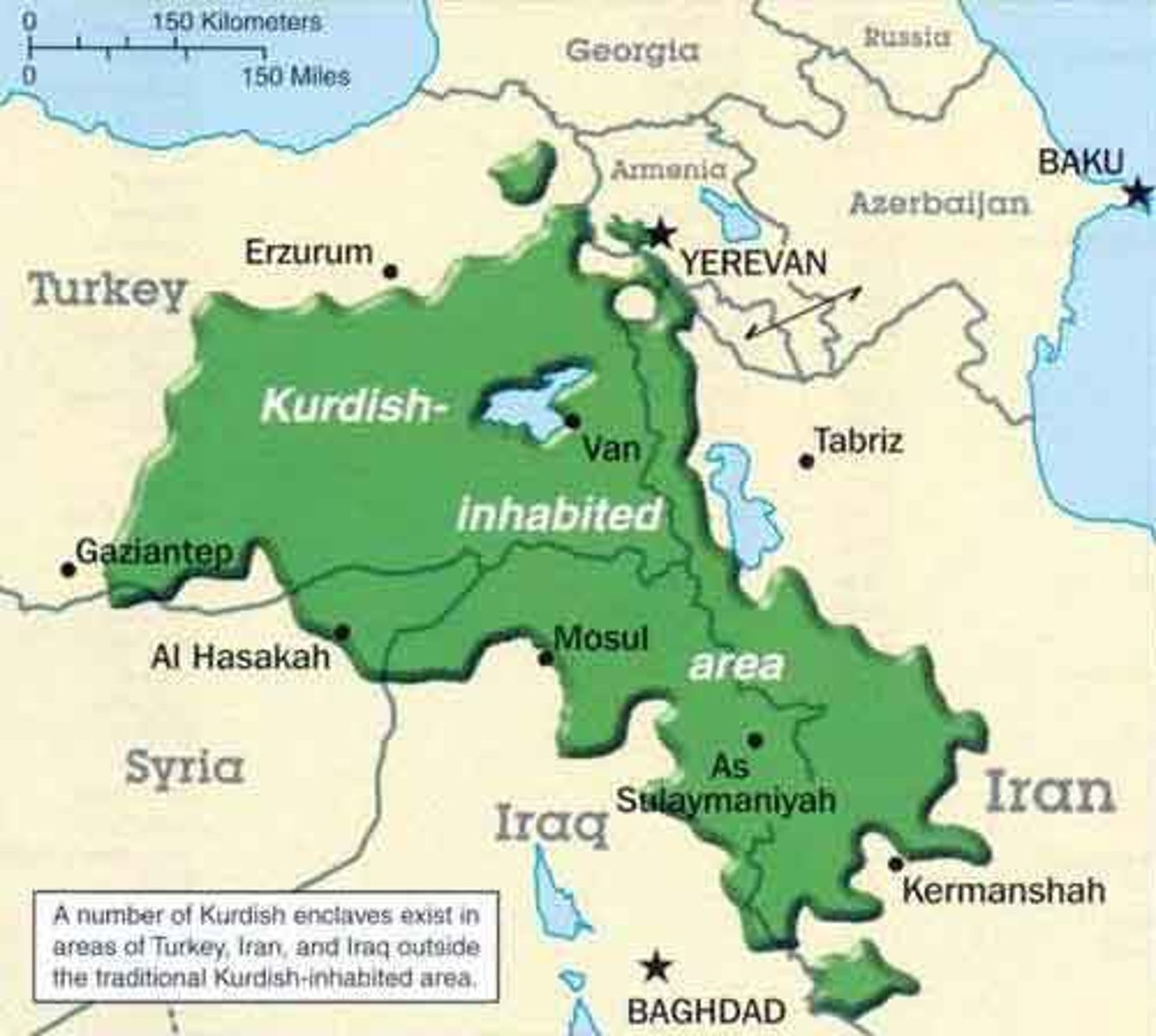
State
A politically organized territory that is administered by a sovereign government and is recognized by the international community.
Territoriality
In political geography, a country's or more local community's sense of property and attachment toward its territory, as expressed by its determination to keep it inviolable and strongly defended.
Autonomous region
an area of a country that has a degree of autonomy, or has freedom from an external authority
Balance of power
a political situation in which no one nation is powerful enough to pose a threat to others
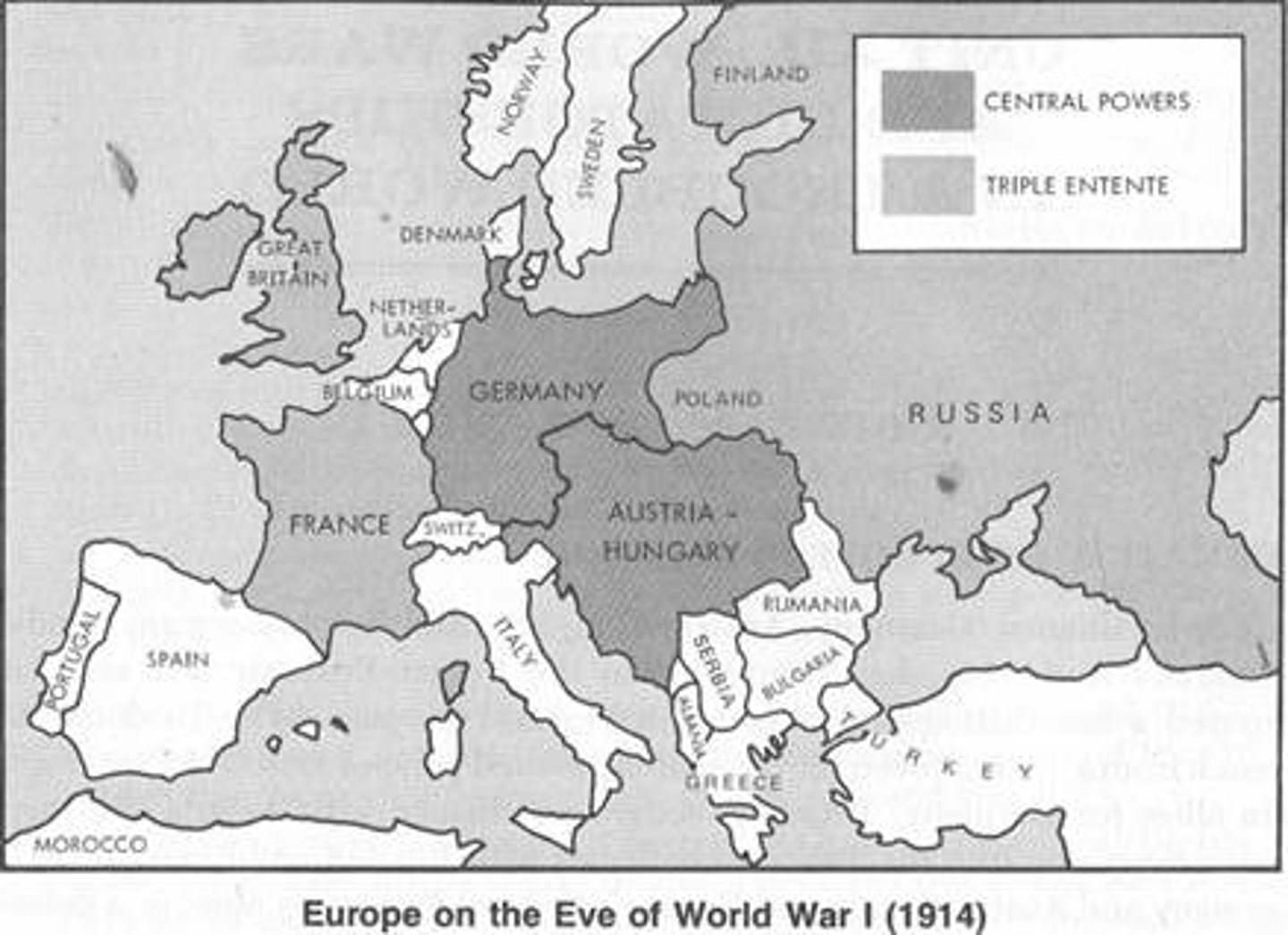
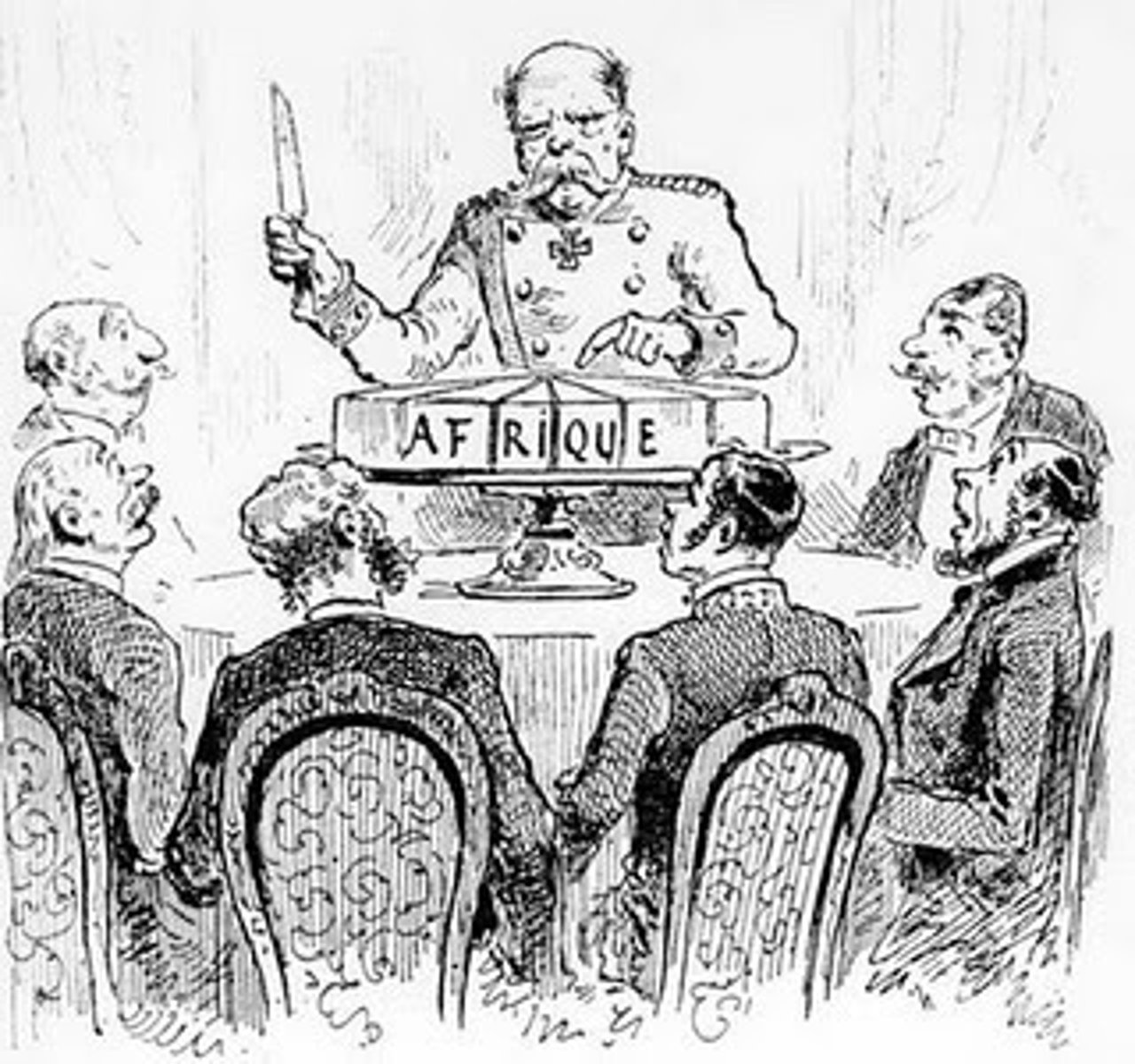
Berlin Conference
Conference that German chancellor Otto von Bismarck called to set rules for the partition of Africa. It led to the creation of the Congo Free State under King Leopold II of Belgium.

Capital city
The city where the central government of a country is.
city-state
A sovereign state comprising a city and its immediate hinterland.
colonialism
the policy or practice of acquiring full or partial political control over another country, occupying it with settlers, and exploiting it economically.
Devolution
The process whereby regions within a state demand and gain political strength and growing autonomy at the expense of the central government.
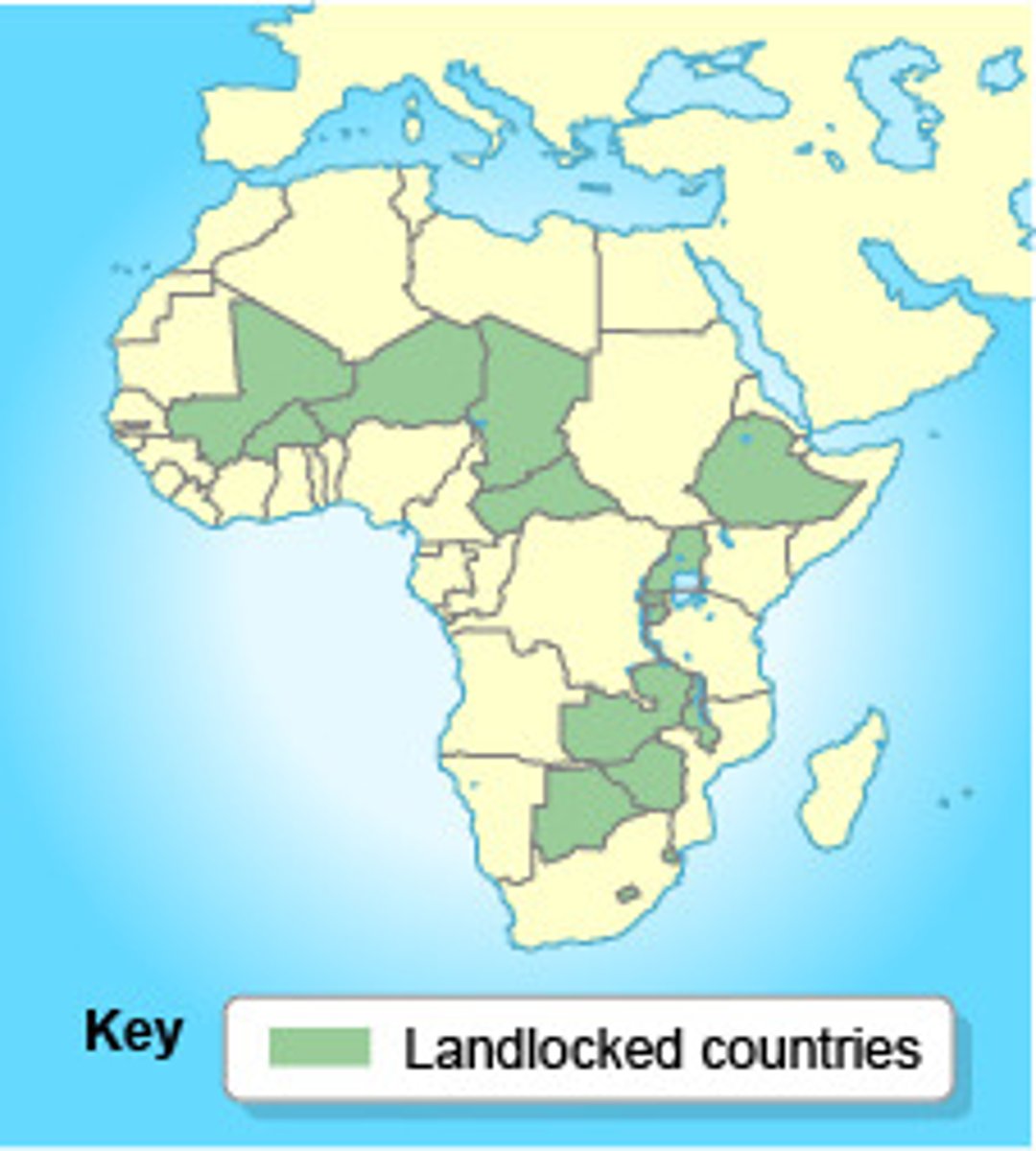
Landlocked State
A state that does not have a direct outlet to the sea.
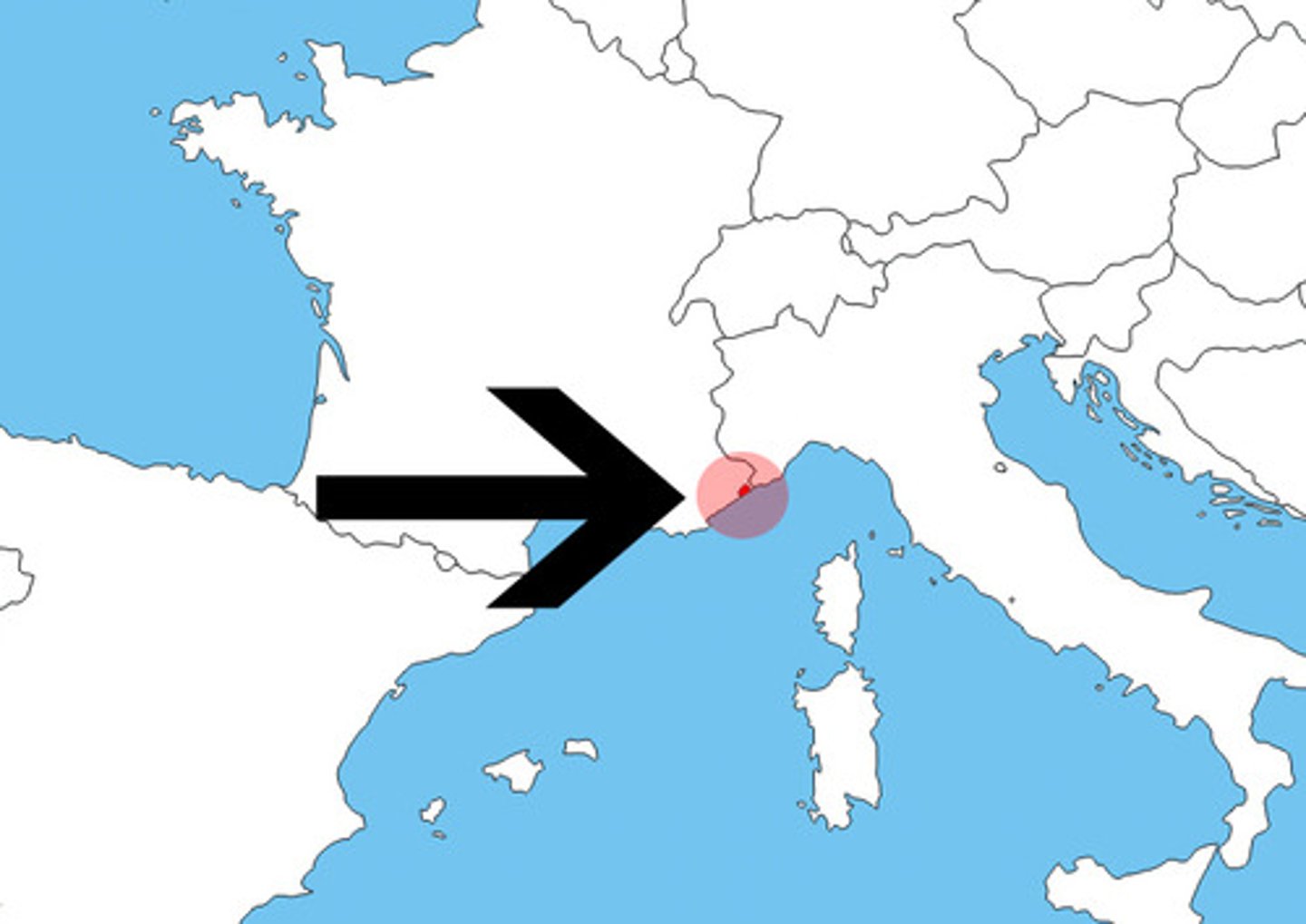
microstate
A state or territory that is small in both size and population.
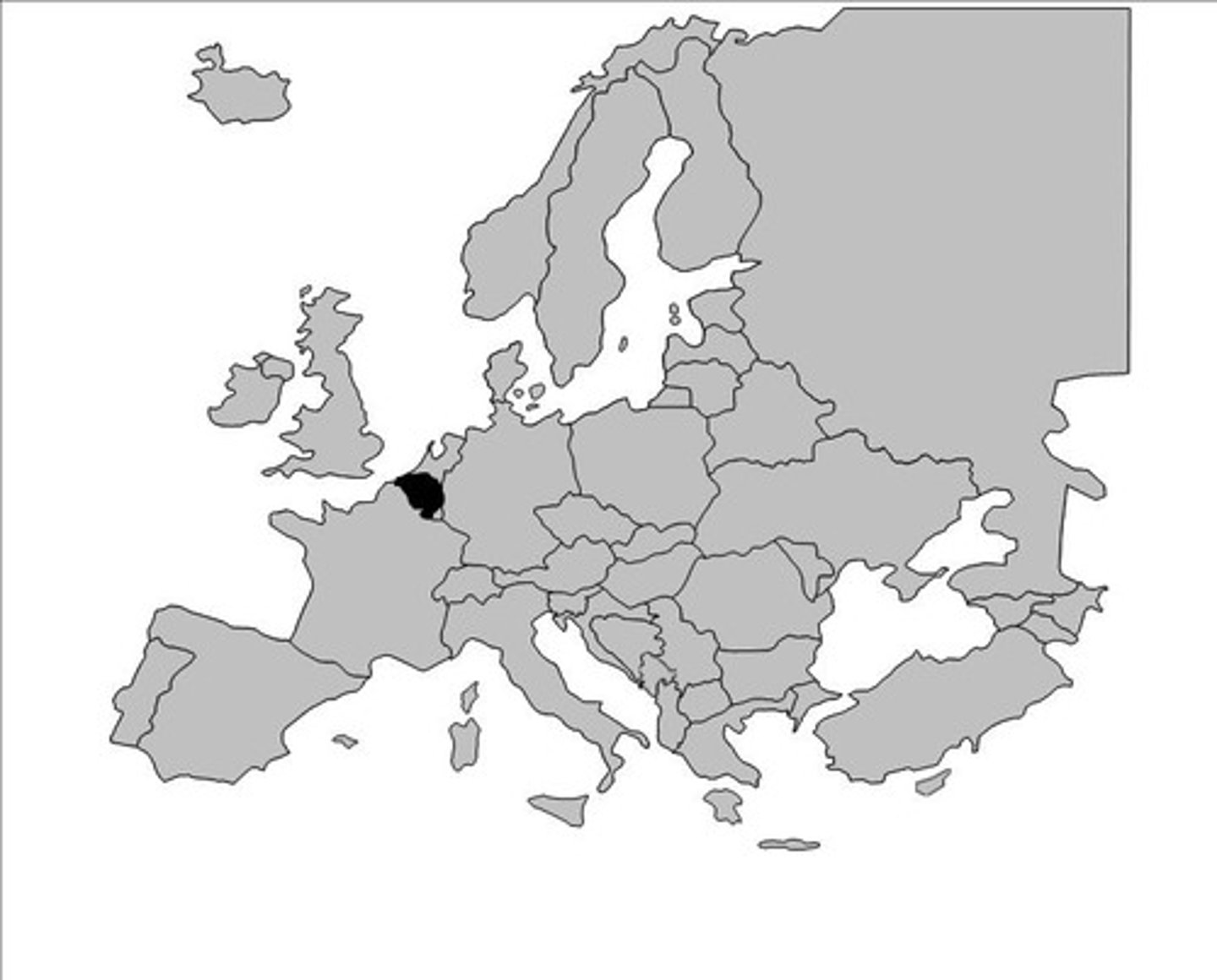
multinational state
State that contains two or more ethnic groups with traditions of self-determination that agree to coexist peacefully by recognizing each other as distinct nationalities.
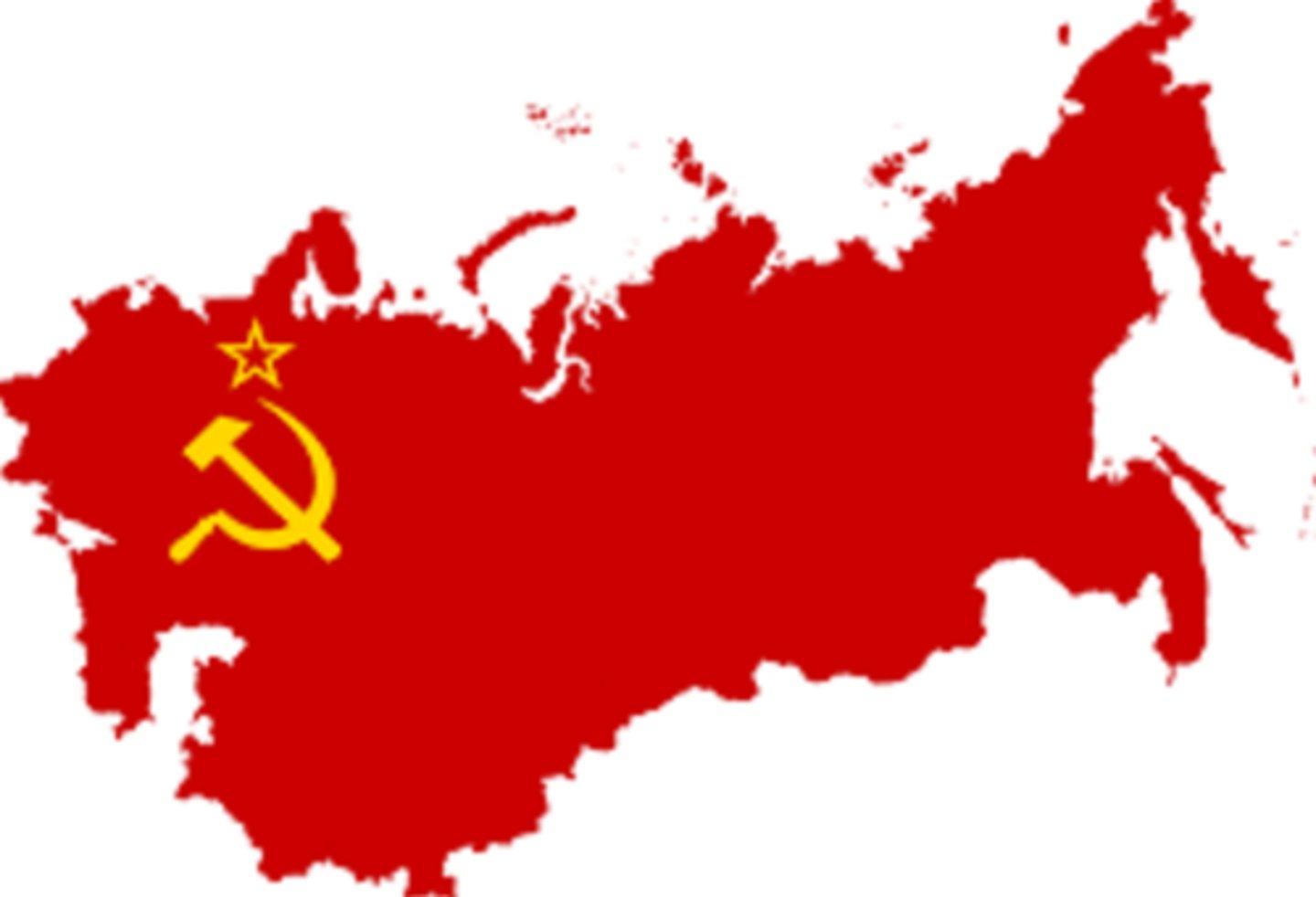
Soviet Union
A Communist nation, consisting of Russia and 14 other states, that existed from 1922 to 1991.
United Nations
An international organization formed after WWII to promote international peace, security, and cooperation.

NATO
North Atlantic Treaty Organization; an alliance made to defend one another if they were attacked by any other country; US, England, France, Canada, Western European countries

ethnicity
A social division based on national origin, religion, language, and often race.

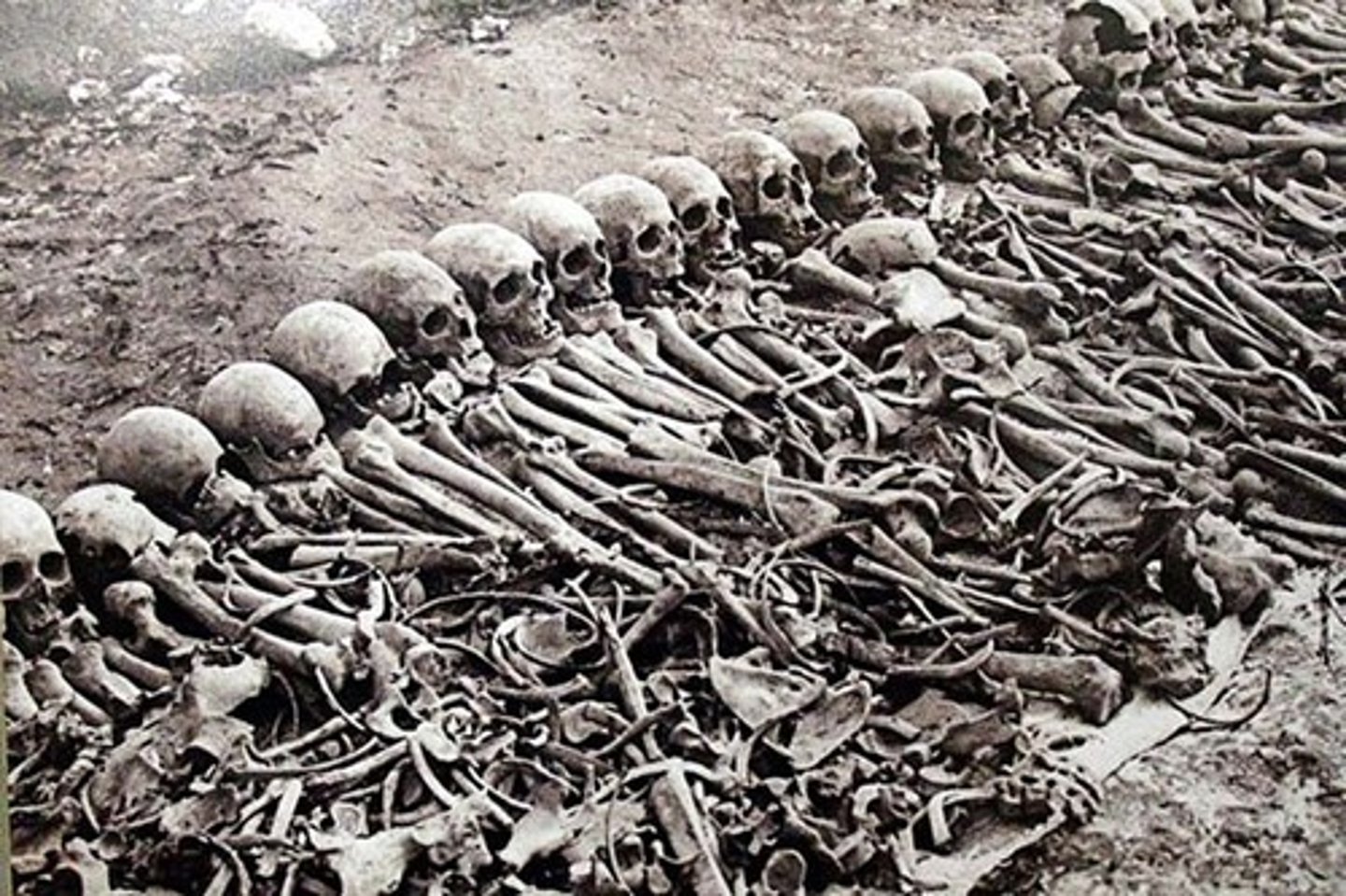
genocide
Deliberate extermination of a racial or cultural group

Nationalism
pride in one's country

nationality
Identity with a group of people that share legal attachment and personal allegiance to a particular place as a result of being born there.

nation-state
a sovereign state whose citizens or subjects are relatively homogeneous in factors such as language or common descent.
race
A group of human beings distinguished by physical traits, blood types, genetic code patterns or genetically inherited characteristics.

Self-determination
the right of people to choose their own form of government

Federal State
allocates strong power to units of local government within the country
Unitary State
places most power in the hands of central/national government officials
Annexation
The adding of a region to the territory of an existing political unit.
China and Taiwan
-Officially recognized as part of the Republic of China
-Taiwan not recognized as part of the United Nations
multinational state
a state with more than one nation inside its borders
semi-autonomous region
an area which can govern itself in certain areas, but does not have complete power to govern
Imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.
Colonialism
acquiring full or partial political control over another country, occupying it with settlers, and exploiting it economically.
Early Colonialism
The first wave of European colonialism was led by Spain and Portugal, and then by France and Britain; established empires in the Americas
Later Colonialism
led by Great Britain, France, the Netherlands Belgium, Italy and Germany focused on controlling Africa and Asia. Began with the Berlin Conference in 1884-1885.
Berlin Conference of 1884
Africa divided unequally among European nations. The rights of Africans were disregarded.
Self-determination
The ability of a government to determine their own course of their own free will
Decolonization
the action of changing from colonial to independent status; having sovereignty over a territory
Genocide
the deliberate killing of a large group of people, especially those of a particular ethnic group, religion, or nation.
Cold War
A conflict that was between the US and the Soviet Union. The nations never directly confronted each other on the battlefield but deadly threats went on for years; Began in 1945 after WWII and ended with breakup of Soviet Union in 1991
sattelite state
a country that is economically and politically dominated or dependent on another country
Territoriality
A country's or more local community's sense of property and attachment toward its territory, as expressed by its determination to keep it strongly defended.
Religious Conflicts
Violence between members of different religious groups; Ex: Sunni & Shia Muslims divided on question of who should succeed Muhammad
Economic Conflicts
A type of conflict over territory that is important for trade routes or resource production (Ex: South Asian nations claiming sovereignty in the South China Sea)
Neocolonialism
Also called economic imperialism, this is the domination of newly independent countries by foreign business interests that causes colonial-style economies to continue.
Modern Globalization
After WWII, trade barriers were lowered with the creation of the UN leading to a new era of globalization
choke point
Strategic, narrow waterway between two larger bodies of water that leads to congestion and potential important economic benefits
Strait of Hormuz
a strategically important strait linking the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman; Arguably the world's most important choke point
Physical geographic boundaries
natural barriers between areas such as oceans, deserts, and mountains
cultural boundaries
borders based on culture traits, like language and religion
antecedent boundary
a boundary line established before the area in question is well populated or developed a cultural landscape
subsequent boundary
a boundary line that is established after the area in question has been settled and that considers the cultural characteristics of the bounded area
ethnographic
relating to cultural phenomena
superimposed boundary
a boundary line placed over and ignoring an existing cultural pattern
landlocked states
A state that does not have a direct outlet to the sea.
relic boundary
A boundary no longer observed but that still affects the present-day area (e.g. border between West and East Germany in Berlin)
geometric boundary
Political boundaries that are defined and delimited by straight lines.
consequent boundary
A type of subsequent boundary that is drawn to accommodate existing linguistic, cultural, or religious boundaries
open boundary
a boundary where crossing is unguarded and with little to no political intervention
Militarized Boundary
A boundary that is heavily guarded and discourages crossing and movement.
territorial dispute
Any dispute over land ownership
Irredentism
a policy of cultural extension and potential political expansion by a country aimed at a group of its nationals living in a neighboring country
Boundary Disputes
Conflicts over the location, size, and extent of borders between nations. There is conflict over where exactly the border is between the U.S. and Mexico, especially along the Rio Grande because the river has changed course and moved, and it is the traditional border.
Exclave
a part of a country that is separated from the rest of the country and surrounded by foreign territory.
Enclaves
Any small and relatively homogenous group or region surrounded by another larger and different group or region
Shatterbelt
A region caught between powerful forces whose boundaries are continually redefined.
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
a code of maritime law approved by the United Nations in 1982 that authorizes, among other provisions, territorial waters extending 12 nautical miles from shore and 200-nautical-mile-wide exclusive economic zones
Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ)
coastal states can explore, extract minerals, and manage up to 200 nautical miles
electoral geography
the study of how the spatial configuration of electoral districts and voting patterns reflect and influence social and political affairs
voting districts
Wide variety of small polling areas, such as election districts, precincts, or wards, that State and local governments create for the purpose of administering elections
electorate
the citizens eligible to vote
Reapportionment
the process of reassigning representation based on population, after every census
Redistricting
The redrawing of congressional and other legislative district lines following the census, to accommodate population shifts
Gerrymandering
Process of redrawing legislative boundaries for the purpose of benefiting the party in power.
Ethnic Separatism
The advocacy of a state of cultural, ethnic, tribal, religious, racial, governmental or gender separation from the larger group.
Terrorism
the use of violence by groups against civilians to achieve a political goal
subnationalism
Identification with small ethnic and regional groups within a nation.
Balkanization
Process by which a state breaks down through conflicts among its ethnicities
Globalization
Actions or processes that involve the entire world and result in making something worldwide in scope.
Supranationalism
a venture involving 3 or more national states political economic or cultural cooperation to promote shared objectives
European Union
An international organization of European countries formed after World War II to reduce trade barriers and increase cooperation among its members.
OPEC
An international oil cartel originally formed in 1960. Represents the majority of all oil produced in the world. Attempts to limit production to raise prices. It's long name is the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries.
WTO (World Trade Organization)
the only international body dealing with the rules of trade between nations
Transnational Corporation
conducts research, operates factories, and sells products in many countries
Ethnonationalism
the tendency for an ethnic group to see itself as a distinct nation with a right to autonomy or independence. A fundamental centrifugal force.