Chemical bonding (noble gas, e-, polarity)
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Describe the electronic configurations of the noble gases.
Fully filled valence shell
Helium has _____ configuration
duplet
All noble gases except helium has _____ configuration.
Octet
Duplet and octet configurations are _____.
Stable and unreactive
What type of electronic configurations do atoms want to achieve?
Noble gas electronic configurations
How can atoms achieve noble gas electronic configurations?
Atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons.
Define electronegativity
A measure of its ability to attract the electrons in a covalent bond to itself.
When does electronegativity increase or decrease?
Electronegativity increases across the period and decreases down the group.
When the atomic radius is smaller, what happens to the electronegativity?
The smaller the atomic radius, the more tightly held the valence electrons are to the nucleus, the greater the electronegativity.
Distance between the nucleus and negative electrons are very close to → stronger attractive forces → higher electronegative value
Why does electronegativity decrease down the group?
Down the group, the no. of electron shell increases → larger atomic radius → distance between nucleus and valence shell larger → weaker electrostatic forces of attraction → lower value of electronegativity
Most electronegative elements?
Fluorine, oxygen, nitrogen
Covalent electronegative difference
0 - 1.5
Non-polar electronegative diff
0-0.5
Polar electronegative diff
0.6-1.5
Ionic electronegative diff
>1.6
Polarisation
In a covalent bond between 2 different atoms, one atom will have a greater electronegativity than the other.
The more electronegative atom acquires a partial negative charge while the less electronegative atom acquires a partial positive charge.
This unequal sharing of electrons is polarisation.
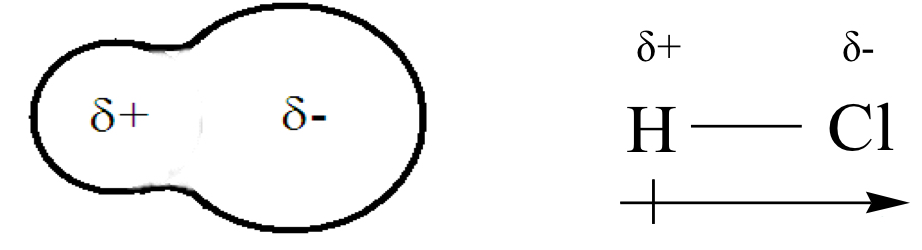
What does the arrow represent?
Dipole moment
Shows the movement of electron cloud towards a more electronegative atom.
Factors determining polarity of molecules
Molecules of elements
Molecules of compounds
Molecules of elements - non polar?
Made up of atoms of the sane element which have the same electronegativity. There is equal distribution of electron cloud in these molecules.
Molecules of compounds
Made up of atoms of different elements, the overall dipole of a molecule depends on its shape. (enrichment) No net resultant dipole → non-polar
A molecule is polar and thus has a net dipole moment if ____
its covalent bonds are polar
its shape does not allow complete cancel out of the individual dipoles
Do elements with stable noble gas configuration have electronegativity?
No, they have zero electronegativity as they have fully filled valence shell