neuroanatomy final
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Who systematically numbered the cytoarchitecture areas of the mammalian neocortex?
Korbinian Brodmann
who deduced the idea that information flows in one direction, from dendrites and soma to axons and their synapses?
Cajal
what sequence of events describes the ionic basis of an action potential?
an influx of sodium followed by an efflux of potassium
identify the structural-functional pair that is correctly matched
prefrontal cortex - executive function
what visual function is mediated by the rod circuits?
motion detection
what visual function is enhanced by retinal disparity?
depth perception
what anatomical feature mediates orientation preferences of simple cells in area 17?
columnar organization of neuronal response properties
what technique is best for revealing en passant terminals?
anterograde labeling
which structure is responsible for recycling retinal photopigments?
pigment epithelium
where are simple cells located in the visual system?
layer iv of brodmann area 17
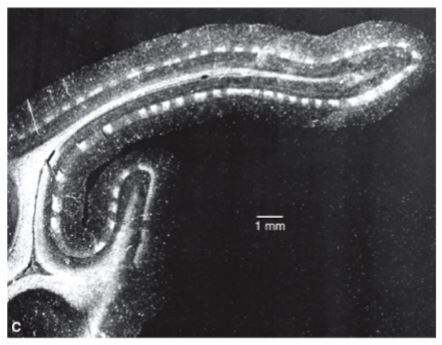
what is illustrated in this photomicrograph?
ocular dominance columns in striate cortex
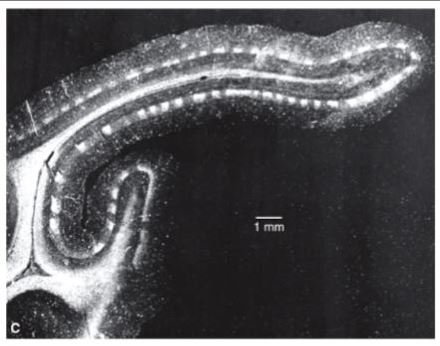
how was this photomicrograph acquired?
by injecting radioactive amino acid into one eye
where do most thalamocortical neurons terminate?
cortical layer iv
which neurons uses GABA as a neurotransmitter?
cortical chandelier cells
where do corticocortical feedforward projections terminate?
cortical layer iv
what function is related to the small neuron size in the parvocellular layers of the LGN?
visual acuity
how do large diameter axons differ from small diameter axons?
large axons have lower cytoplasmic resistance
what happens at most synapses between a photoreceptor and an off-bipolar cell?
glutamate release causes depolarization
which cns subdivision contains the neocortex?
telencephalon
who characterized the ionic basis of action potentials?
hodgkin and huxley
what prevents an action potential from reversing its direction midway thorugh the axon?
an efflux of potassium ions on its trailing edge
inactivation of sodium channels on its trailing edge
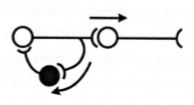
identify this type of neural processing
recurrent inhibition
what neurotransmitter is used in the output of cortical neurons?
glutamate
voltage-gated sodium channels exist in what states?
resting, open, and inactivated
which is NOT a property of a “Driver” synapse in the thalamus?
innervates the reticular nucleus
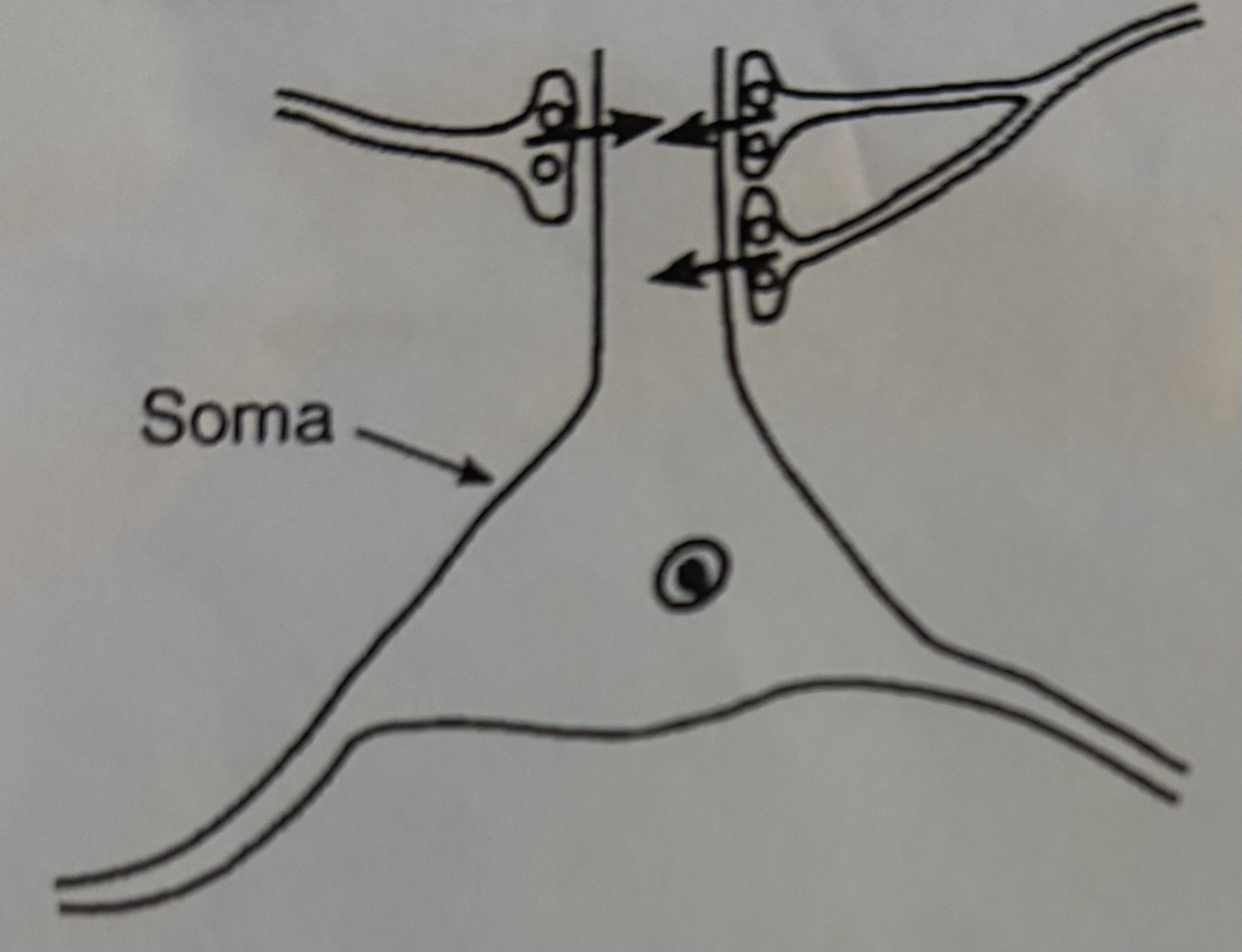
identify this type of synaptic configuration
synaptic convergence
who developed the process for staining myelin?
weigert
what layer of neocortex receives input from the thalamus?
layer four
which is not a property of the reticulospinal tract?
reticulospinal fibers descend bilaterally in the crus cerebri
which is NOT a feature which contributes to perceptual binding?
electrodes traversing the cortex vertically encounter neurons with different orientation preferences
the rubrospinal and tectospinal tracts augment which pathway?
corticospinal
which cranial nerve is affected in Bell’s palsy?
facial
descending projections from the brainstem release what two neurotransmitters to activate enkephalin interneurons?
serotonin and norepinephrine
which nerve tract modulates muscle tone?
reticulospinal tract
what method can be used analyze coordinated activity among interconnected neurons?
cross-correlation analysis
which is essential for CONSENSUAL pupillary light reflex?
midline-crossing fibers from the pretectal olivary nuclei
what neurotransmitter do all motor nuclei in the brainstem use?
acetylcholine
during the development of the brainstem:
alar plates differentiate into sensory nuclei and basal plates differentiate into motor nuclei
lesions to which area would cause deficits in declarative memory?
medial temporal lobe
identify two characteristics of the parasympathetic nervous system
cholinergic preganglionic neurons, discrete innervation
what area does the dentate gyrus project to in the trisynaptic circuit?
CA3
which limbic circuit helps regulate motivational behavior?
amygdalofugal efferents to the ventral striatum
the limbic system receives which neurotransmitter from which areas?
raphe nucleus / serotonin
which happens during Long Term Potentiation (LTP)?
repeated CA3 stimulation (tentanus) evokes a stronger response in CA1
inputs to basolateral nuclei of the amygdala come from where?
thalamus
which cns structure is activated by an increase in blood pressure?
caudal solitarius
the mammalian hippocampus uses which neurotransmitter and cell type for its output
glutamate via pyramidal layer
which limbic circuit helps regulate physiological responses?
central efferents via stria terminalis to the hypothalamus
what structure receives inputs from baroreceptors in the aortic arch?
nucleus of the solitary tract
what structure innervates the striated muscles of the pharynx and larynx?
nucleus ambiguus
what structure coordinates the lateral and medial recti during horizontal eye movements?
nucleus abducens
select the nucleus correctly paired with its efferent pathway
basal pontine nucleus - middle cerebellar peduncle
what brain region encodes sound localization?
superior olive
what structure is most likely to be damaged by excessive exposure to loud sounds?
cochlear hair cells
in the cochlea, what structure directly contact the stereocilia of the outer hair cells?
tectorial membrane
which physiological measure can indicate the prognosis of a comatose patient?
brainstem auditory evoked potentials
what structure in innervated by the ventral tegmental area?
nucleus accumbens
according to delong, what pathway disinhibits the thalamic nuclei that project to motor cortex?
direct striatopallidal pathway
what brain region projects to the ventral anterior thalamus?
substantia nigra pars reticulata
which neurotransmitter is used by striatal projections to the external globus pallidus?
GABA
which brain region DOES NOT project directly to the cerebellar cortex?
red nucleus
according to delong’s model, what functional change in the basal ganglia is likely to be associated with Huntington’s chorea?
increased activity in the direct pathway
which cortical area is active during mental rehearsal of complex finger movements?
supplementary motor cortex
which projection system use GABA as a neurotransmitter?
striatopallidal neurons
what does prolonged stimulation of the limb region in MI cortex evoke?
hand movements to a specific target
which structure DOES NOT receive direct projections from motor cortex?
globus pallidus
traumatic damage to which of the following structures could produce dysrhythmia?
cerebellar cortex
of the following structures, which one plays a major role in motor planning?
lateral cerebellar cortex
which mammalian neural structure seems most likely to represent an example of phylogenetic conversion from its ancestral condition?
neocortex
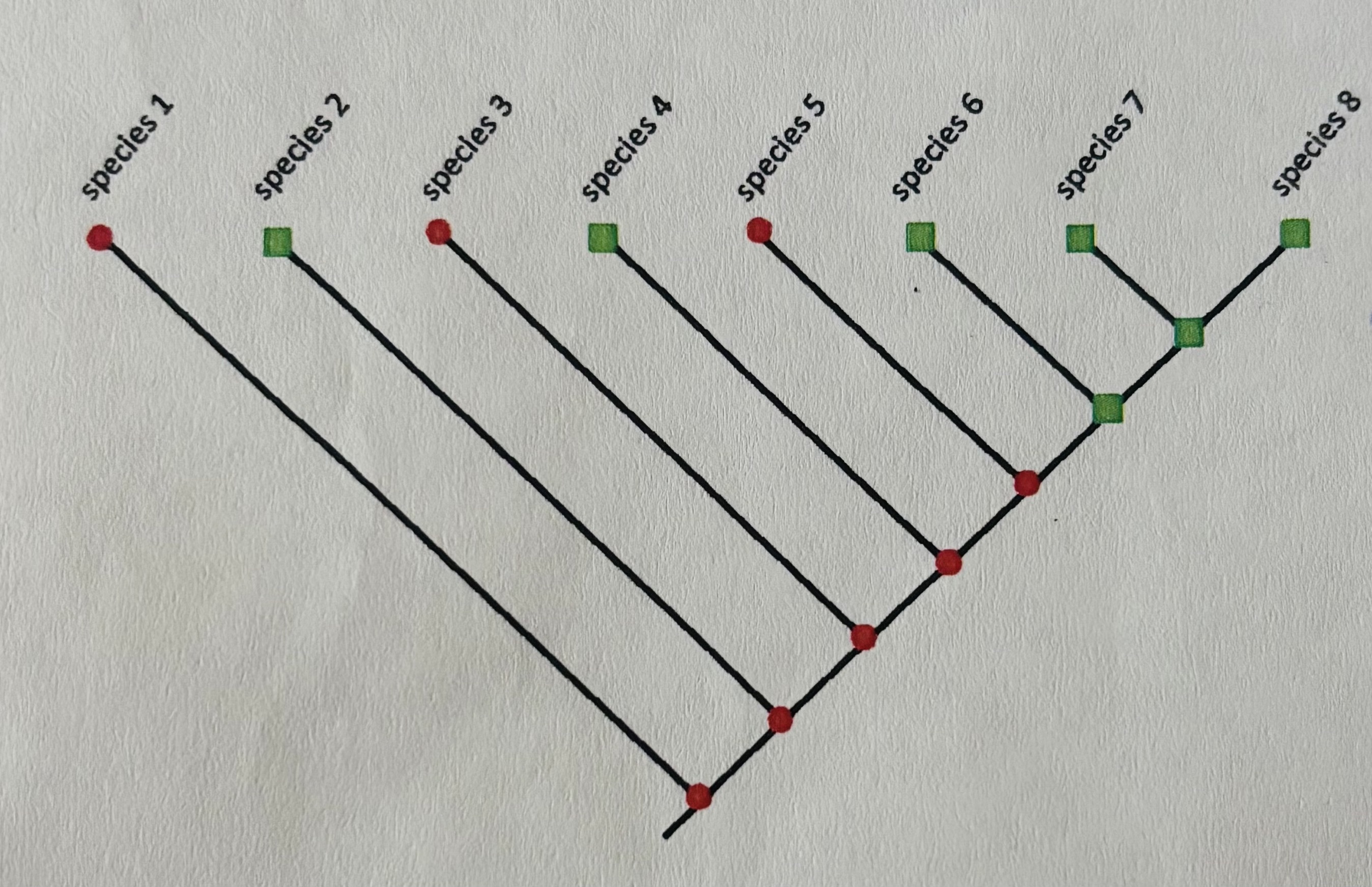
which species display shared primitive characters?
1 and 3
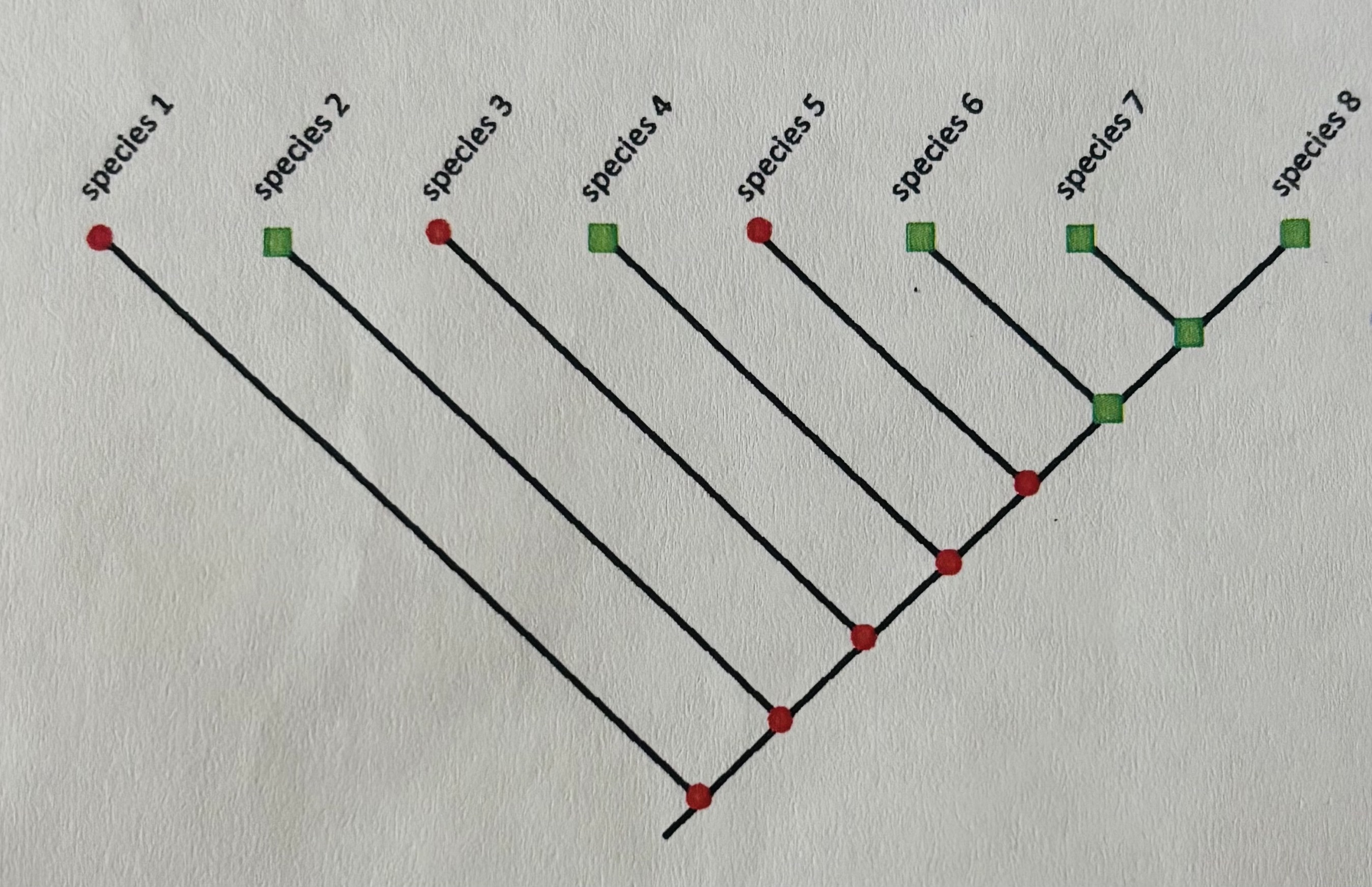
which species display shared derived character?
6 and 8
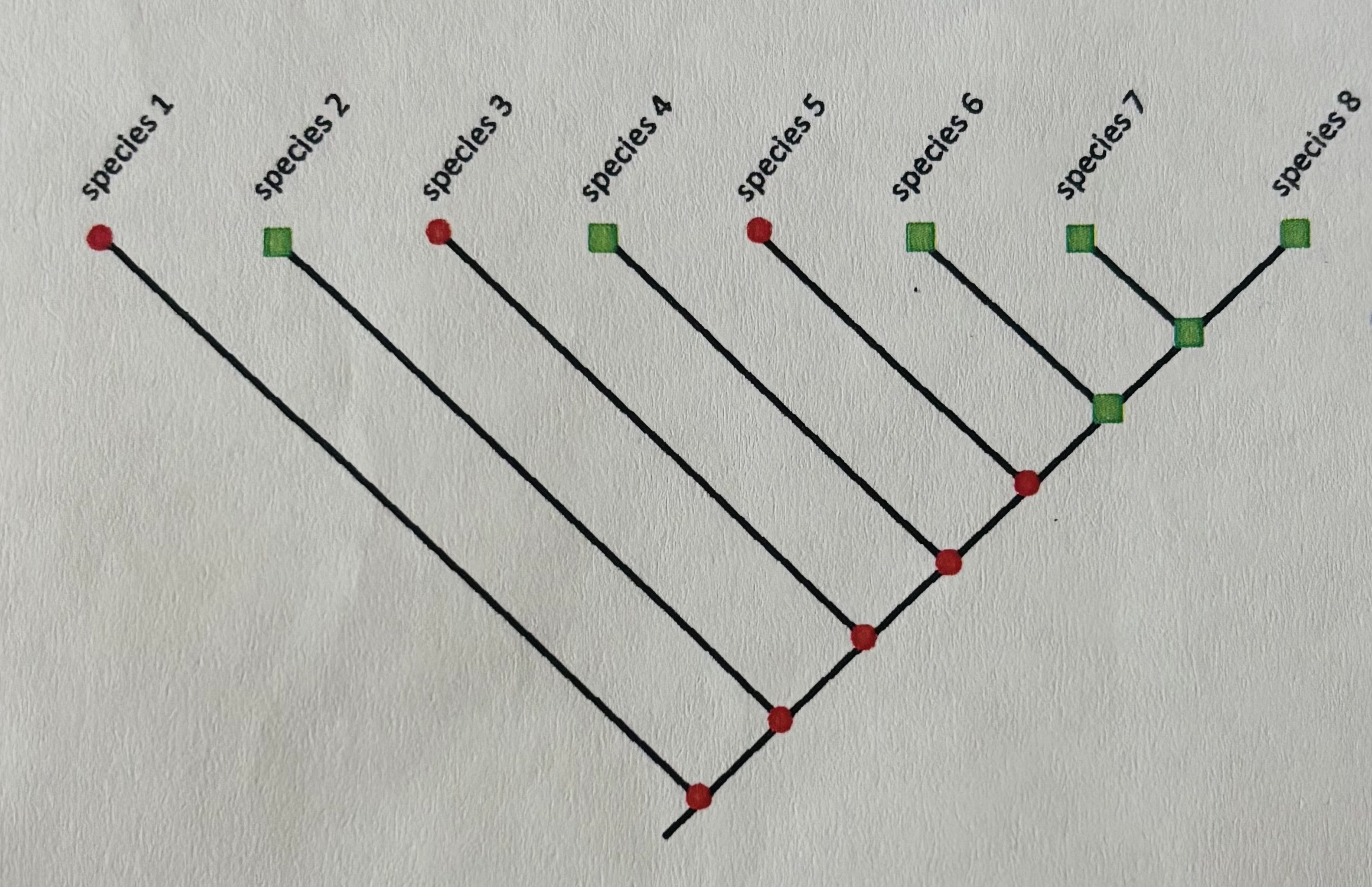
which species display homoplasous characters?
2 and 4
what is a criticism of the neuromeric model of brain development?
the forebrain doesn’t have well defined segments
evolution of the nervous system is:
none of the above
how many times has gyrencephaly arisen over the course of vertebrate evolution?
4
primate brains are associated with which special features?
all of the above
what is the relationship between brain size and body size?
allometric
why did nervous systems evolve?
all of the above