2 - Corruption and its global impact
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is the definition of corruption?
Distortion in decision-making process that creates opportunities for some and costs for others
What are the levels of corruption
Petty corruption: small payments to low-levbel bureaucrats in order to get small favours in return
Grand corruption: related to higher level beaurcrats or politicians. It involved large amounts of money and the favours are respectively bigger e.g. Michelle Mone scandal
What are the variants of corruption?
Bottom u: Low-level officials collect bribes which they share with their superiors
top down: high-level officials collect bribes and share with low- level employees
What are the categories of corruption and their description
Bribery
act of dishonestly persuading someone to act in ones favour by a payment or other induscement. Inducements can take the form of gifts, loans, fees, rewards or other advantages. Use of bribes can lead to collusion and/or extortian
Embezzlement
To steal, misdirect or misappropriate funds or assets placed in one’s trust or under ones control. From a legal point of view, embezzlement need not necessarily be oor involve corruption
Facilitation payment
a small payment, also called a ‘seed’ or ‘grease’ payment made to secure or expedite the performance of a routineor necessary action to which the payer has legal or other entitlement
Frauf
the act of intentionally and dishonestly deceiving someone in order to gain an unfair or illegal advantage
Collusion
arrangement between 2 or more parties designed to achieve an improper purposes, including influencing improperly the actions of another party
Extortion
the act of impairing or harming or threatening to impair or harm, directly or indirectly, any party or the property of the party to influence improperly the actions of a party
Patronage,clientelism and nepotism
Patronage at its core means the support given by a patron, in gov, it refers to the practice of appointing people directly
What are the causes of corruption? (Part 1)
1. Size and structure of governments
gov expenditure: 2 perspectives
large gov leads to more corrupt politicians → increases the rents from illegal behaviour
Large gov is more effective in fighting corruption → it has a bigger budget for law enforcement
Risk of reverse causality: countries with high levels might not be effective in generating financial resources
2. Salaries of civil service
Negative correlation - higher wages correspond with less corruption due to its costs of dishonest behaviour → if a bureaucrat accepts bribes and get detected, he will lose his job
The evidence is weak
Reverse causality?
some countries might pay low salaries to their employees because there is commonon notion that the bureaucrats make enough money off corruption (anyway involved in corruption
3. Democracy and the political system
political moderinsation is usually accompanied by an increase in corruption → underdeveloped institutions
Democracy reduces corruption but only if the institution are evolved and fully functional - level of naturalisation
Inverted U pattern between corruption and the durability of new democracies
4. Quality of institutions
Negative correlation btw level of corruption and proxies for quality of institutions:
institutional quality measured by a rule of law index and an index of government effectiveness - standardised of whole world to make it easier to do
Institutional quality measured by the risk of expropriation
Institutional quality measured by an index of regulation of market entry, inc: required procedures, costs and time to start a new business
5. Economic Freedom/ openness of the economy
Negative correlation btw level of corruption and indexes of economic freedom:
The more competition, the harder it is to high corrupt payments → competitors might uncover the corrupt activities - when they can see others bids - creates another layer of checks and balances
What are the causes of corruption? (Part 2)
6. Press freedom and judiciary
Negative correlation
a high quality and uncensored press sheds light on misuse of power and makes it more difficult to engage in it undetected
Risk of reverse causality: it might be that it is not a free press that lowers corruption levels, but a corrupt gov that lowers the freedom of press.
7. Cultural determinants
Trust → negative relationship. Trust facilities and encourages cooperation between all members of society, reducing corruption
Religion → positive correlation between the % of population belonging to ‘hierarchical’ religions and corruption
8. Percentage of women in labour force
negative correlation → countries with a high share of women in the labour force suffer less from opportunistic behaviour at public expenses
Women engages in less corruption than men
Female representation in Gov corresponds to lower levels of corruption
Corruption is higher in societies where women are less able to participate in the social life
9. Colonial heritage
depends on the country of heritage
10. Endowment of natural resources
2 perspectives:
Abundance on natural resources should have a positive effect on development → it encourages trade and investment
Resource - curse: In the presence of resource abundance Gov become less efficient → citizens and officials compete for rents and invest less in other forms of capital - when a country discovers rich supplies of NR, strong institutions are necessary to prevent the rise of corruption
What is the Rational Choice theory?
models human behaviour as the result of individual, self-interested preferences
What are the 3 rational choice explanations for corruption?
Cooperation game (prisoners dilemma)
Individuals have incentives to pursue self-interest rather than work with others towards the collective good → docial dilemma
Regardless of optimal outcome for everyone
Collective action (prevailing norms
Corruption might widespread because of the existence of pro-corruption social norms
In this type of contect corruption is the expected form of behaviour → no sanctioning ag/ corruption
If corruption is a normative issue tehre are a few benefits of acting athically in a predominantly corrupt environment - cultural movement
Principal-agent model:
A way of organising cooperative behaviour which requires delegation of responsibility for tasks both to and within institutions and organisation
Relationship btw:
The principal - top level gov
the agent - an official who take sthe bribes from the private individuals interested in a gov produced good
Is corruption “grease in the wheel” or “sand in the wheel”?
“Grease in the wheel”
some economists claim that corruption has economic advantages
Corruption is an opportunity to allocate resources to individuals with the highest WTO - therefore most productive
Can help to increase efficiency in bureacratic process
Avoid over regulation
“sand in the wheel”
corruption cannot speed up complex bureaucratic processes → but an official can help to delay them
evidence of negative impacts of corruption prevail on the economic literature
What are the consequences of corruption?
1. Corruption reduces GDP
strong negative corrleation btw corruption and GDP
Reverse cauality? Does corruption reduce GDP or does a low GDP generate corruption?
High corruption deters investment and creates inefficiet levels of production
Low GDP restricts the abilities of a country to control corruption → more corruption
2. Corruption increases inequality
positive corelation between corruption and inequality
bribes are paid to the officials in power with the possibility of giving something in return
Corruption often occurs in sectors where the gov offers goods to all social classes
3. Corruption reduced total investment and capital flow
it increases transaction costs for investor
Grand corruption is preferred to petty corruption - by investor
4. Corruption reduces Foreign Direct Investment
Corruption reduces the likeligood of FDI taking place
Effect is more damaging for developed countries
Corrupt countries have a higher level of politicak and economic instability. Corrupt officials are decision-makers
5. Corruption reduces foreign trade
generates competitive disadvantages
What are the different measures of corruption?
Global corruption Barometer → transparency international
measures ordinary household interaction with corruption in basic services delivery
Bribe Payers Index → Transparency International
measures the corruption angegament of the private sector
How often do firms headquarterred in that country engage in bribery in this country - survey
Countries are scored on scale 0-10
10: companies from that country never bribe
0: companies frm that country always bribe
Corruption Perception Index (CPI) → transparency international
measures the degree to which politicians are believed to accept bribes
ranks countries by their perceives levels of public sector corruption as determined by expert assessment and opinion surveys
CPI ranks 180 countries on a scale from 100 to 0. Support for the CPI is centred on the acknowledgement that while it is not a perfect tool it is one of the best available
What are the global implications of corruption?
Corruption is an international phenomenon in scope and consequences
global amount of bribes paid ~ $1 trillion USD/year
Global cost of corruption ~ $2.6 trillion USD/year
UN announces global cost of corruption at least 5 % of world GDP in 2018
Combting corruption calls for broad-based international collaboration
What is the effect of globalisation on corruption
2 theories
globalisation has increased the opportunities for corruption and made corruption practices more difficult to detect
Globalisaton has led to a decrease in corruption → countries must comply with international anti-corruption regulations
Evidence suggests a non-linear relationship btw globalisation and corruption
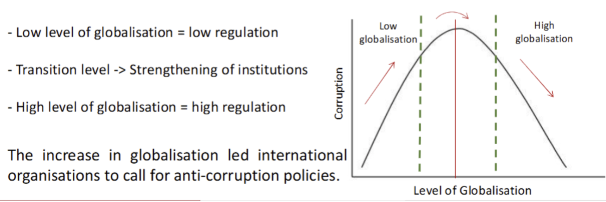
what was the OECD anti-bribery convention (1997)?
Objective: create a level of playing field to imrpove the international business environment
first and only international anticorruption instrument focused on the supply side of bribery
First anti-corruption initiative with global reach
43 member states
Weaknesses:
Enforcement: Most policies are recommendation → OECD members are not forced to implement standards
What was the UN convention against corruption UNCAC (2003)?
UN convention Against Corruption UNCAC(2003)
Objective: Facilitate the fight against corruption by strengthening policies and by promoting international cooperation. It requires signatory parties to prohibit their officials and enterprises from receiving bribes
first global treaty against corruption with broad international consensus
186 member states
Weaknesses
- no definition of corruption
No follow up system to ensure the implementation of recommendations
Fails to criminalise certain acts: bribery of a foreign public official, trading in influence abuse of public functions or illicit enrichment
What are the limits of international anti-corruption institutions
There is little evidence of a decrease inthe incidence of corruption in, and by nationals of, the participating countries
Why have international anti-corruption institutions been inefficient in reducing corruption?
How can we achieve a more robust implementation of international anti-corruption
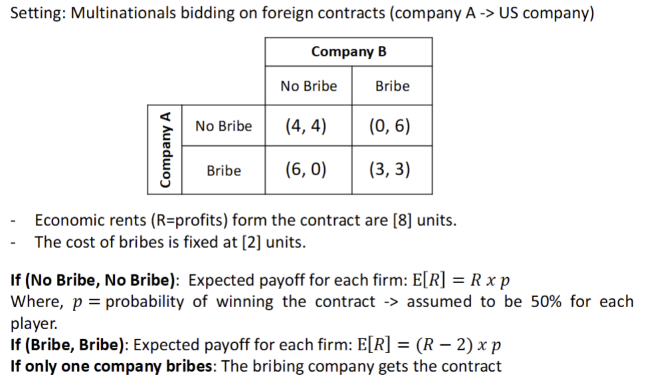
Case study: OECD Anti-bribery convention → a game theoretic approach
What is the game theory approach to international corruption?
A game ceased to be a prisoner’s dilemma following the passage of the US Foreign Corrupt Practices Act
during 1970s - number of corruption scandals worldwide → only in the US did congress pass legislation
1977- US congress approved the fCPA → it makes it illegal for US firms to pay bribes to foreign Gov officials
US fims complaints: The FCPA placed them at a competitive disavnatge relative to international firms based in other countries
US Department of Commerce estimates that during 1994-1996 US firms lost about $11 billion in contracts due to bribes
The FCPA changed the payoffs of the game for US companies
whats the dominant strategy in the game theory approacj D
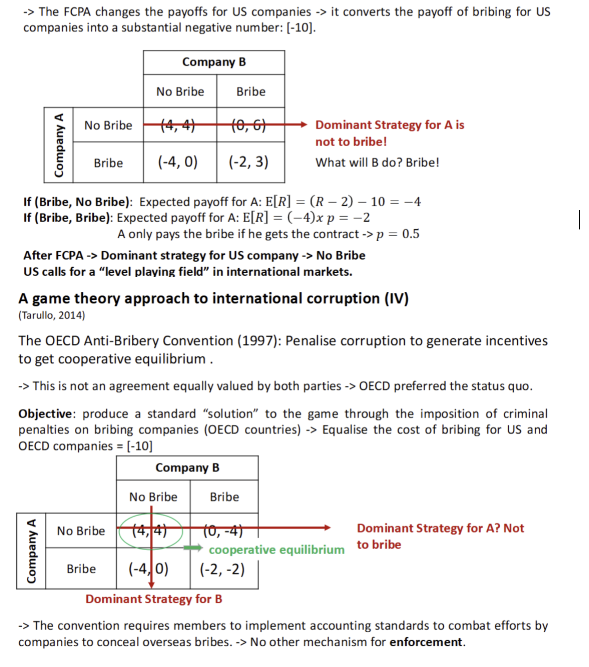
Why have the conevntion been inefficient in reducing global corruption?
Only one prosecution initiated by a country other than the US for bribery of a foreign official → canada
There was a lack of will or capacity of OECD members to meet their obligations
No cost, no enforcement
Having looked at enforcement, is an inefficient outcome surprising
The convention did not represent a credible threat for OECD members → no change in expected payoffs
With the US committed for cooperation due to internal regulation (and politics) → bribery remine dthe dominant maximising strategy for foreign companies
International anti-bribery policy should focus on achieving an effective change in expected payoffs → enforcement
there are 22 countries showing little or no enforcement
countries that fail to investigate and prosecute foreign bribery include Japan, Russia, Spain, South Korea and the Netherlands
Is it feasible to end corruption?
there are no quick fixes or simple solutions for corruption
reforms that open up and liberalise the economy
reforms that eliminate unnecessary regulation
Political reforms that give more power to citizens and voters
Reducing corruption takes real resources. thus cust must also be considered in the development of anticorruption strategies and the selection of particular tactics
IMF, World bank, etc. can lend valuable support for anticorruption efforts in a variety of ways. these agencies can provide advice, technocal assistance and financial support for institutional and policy reforms
International institutions also have a role to play. they can encourage and support the internal reforms