kin 232 - g2 tissue response to different types of loading
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:05 PM on 9/8/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
cancellous bone
spongy/trabecular part of the bone
2
New cards
cortical bone
the compact dense part that makes the outside shell
3
New cards
composite
bones are an example of a ___________ tissue as it has different materials
4
New cards
higher, lower
the cortical part of the bone is expected to have the ________ young modulus and can withstand _______ strain
5
New cards
lower, higher
the trabecular part of the bone is expected to have a ____ young modulus and can withstand ______ strain
6
New cards
anisotropic material
any material that has a different material properties depending on the direction of the applied load
7
New cards
isotropic material
a material that has the same material properties regardless of loading direction
8
New cards
true
a longitudinal force has the greatest young modulus and ultimate stress
t or f
t or f
9
New cards
false
a transverse force has the greatest young modulus and ultimate stress
10
New cards
compression force
this force involves pushing down onto the tissue
11
New cards
tension force
this force involves pulling two ends of a bone
12
New cards
true
the ultimate strength of a bone depends on the loading type
t or f
t or f
13
New cards
neutral axis
the point where tension and compression is 0
14
New cards
bending forcew
this type of loading causes tension at the top and compression at the bottom
15
New cards
true
in bending, the part being stretched is the area with the most concern
t or f
t or f
16
New cards
tension
what loading type causes this bone failure
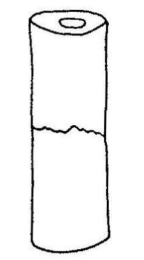
17
New cards
compression
what loading type causes this bone failure
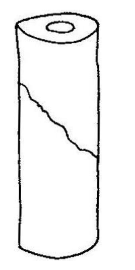
18
New cards
torsion
what loading type causes this bone failure
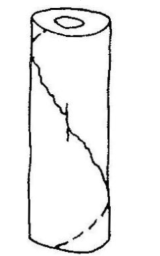
19
New cards
bending
what loading type causes this bone failure
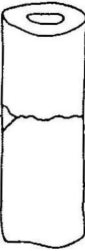
20
New cards
combined loading
what loading type causes this bone failure
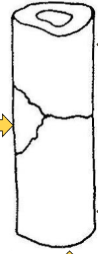
21
New cards
true
during bending, a bone would fail first at the point where there is tension
t or f
t or f
22
New cards
stress risers
small concentrated areas (holes, notches, etc) of stress thats causes CSA to be very small
23
New cards
increase
a decrease in CSA causes the stress to
24
New cards
finite model
breaks bones into elements to be analyzed and see the distribution of stress through the material
25
New cards
false
changes in material does not cause a stress riser
t or f
t or f
26
New cards
true
cement can be used to help ease the transition of metal to bone
t or f
t or f