Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
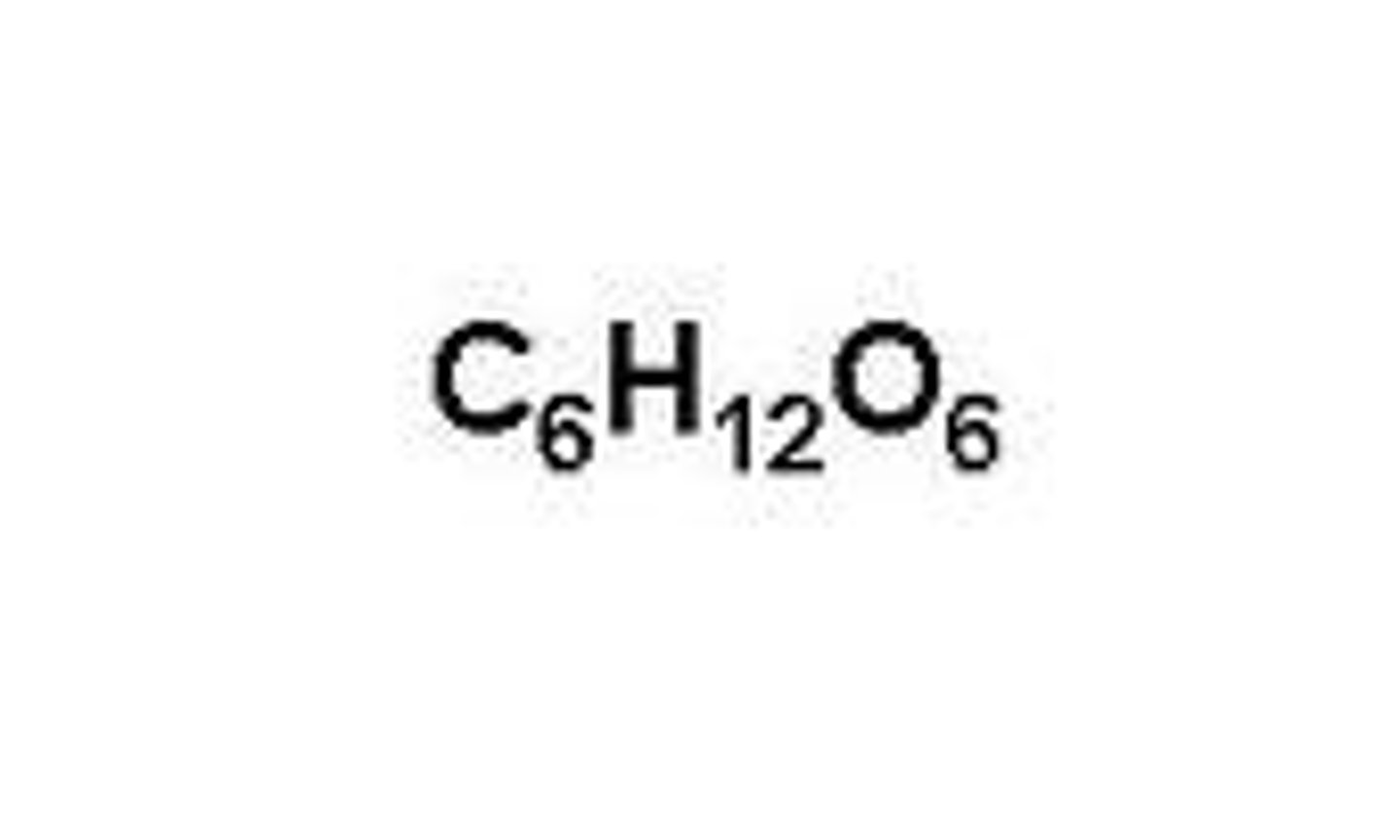
Chemical formula for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H20 --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
ADP is reusable. True or False
True
Photosynthesis definition
plants use light energy to convert H2O and CO2 into glucose and oxygen
Consumer (heterotroph) examples
Animals, fungi, protozoans, most bacteria
Producers (autotroph) examples
plants, algae, photosynthetic bacteria

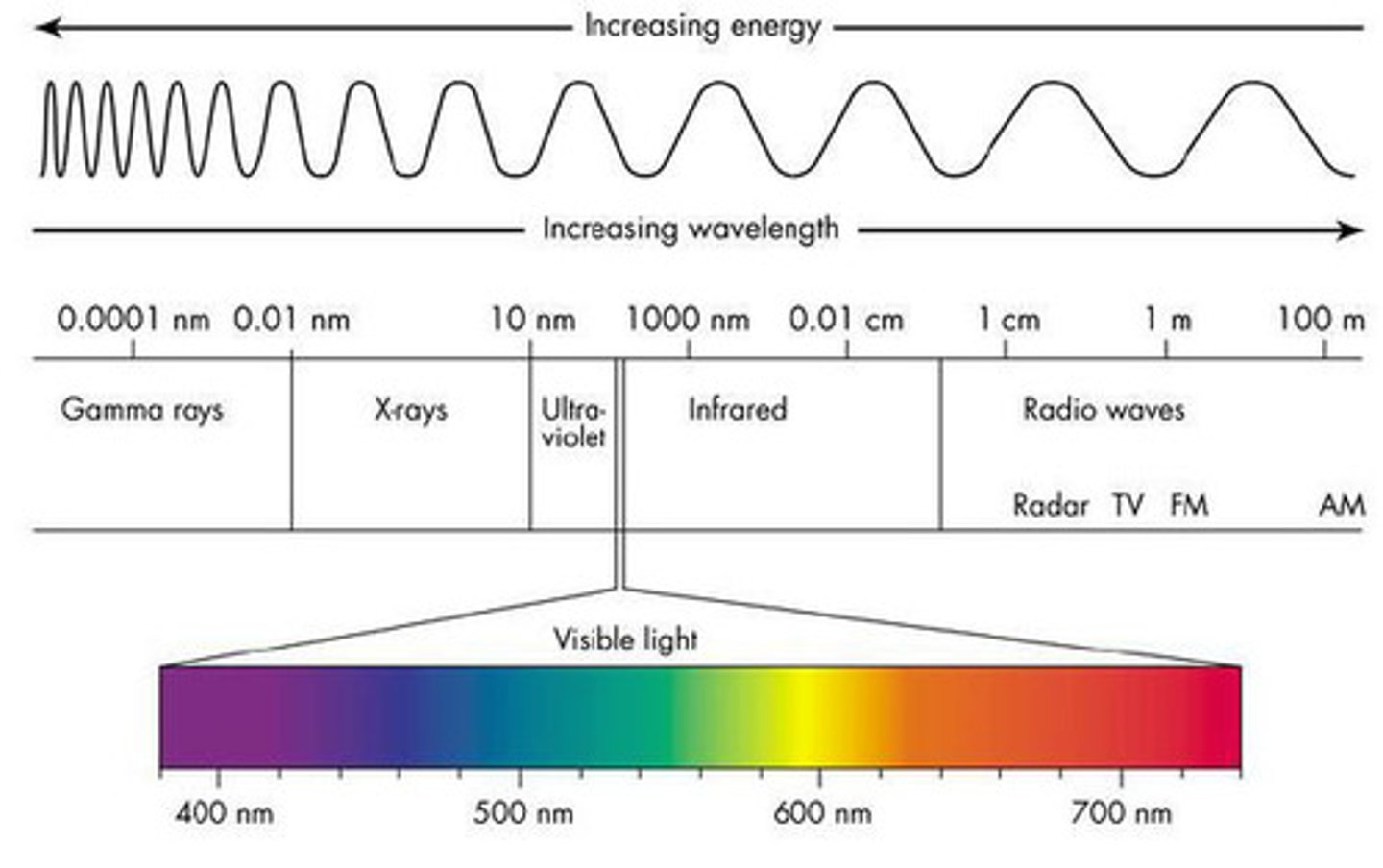
Visible spectrum of light from
violet to red
Pigment
compound that absorbs light
Photosynthetic organisms capture energy from sunlight with
pigments (chlorophyll)
Chlorophyll
a pigment that absorbs mostly blue and red light and reflects green and yellow light

Accessory pigments
Absorb green and blue light, reflects red, orange and yellow light

Biochemical pathway
A series of chemical reactions occurring in the cell. The product of one reaction is reactant in next reaction
Light dependent reactions occur across the
thylakoid membrane
Light dependent reaction makes things needed for the _______ _____ , such as ____ and ____
Calvin Cycle, ATP, NADH
Input of light dependent reaction
light, H2O
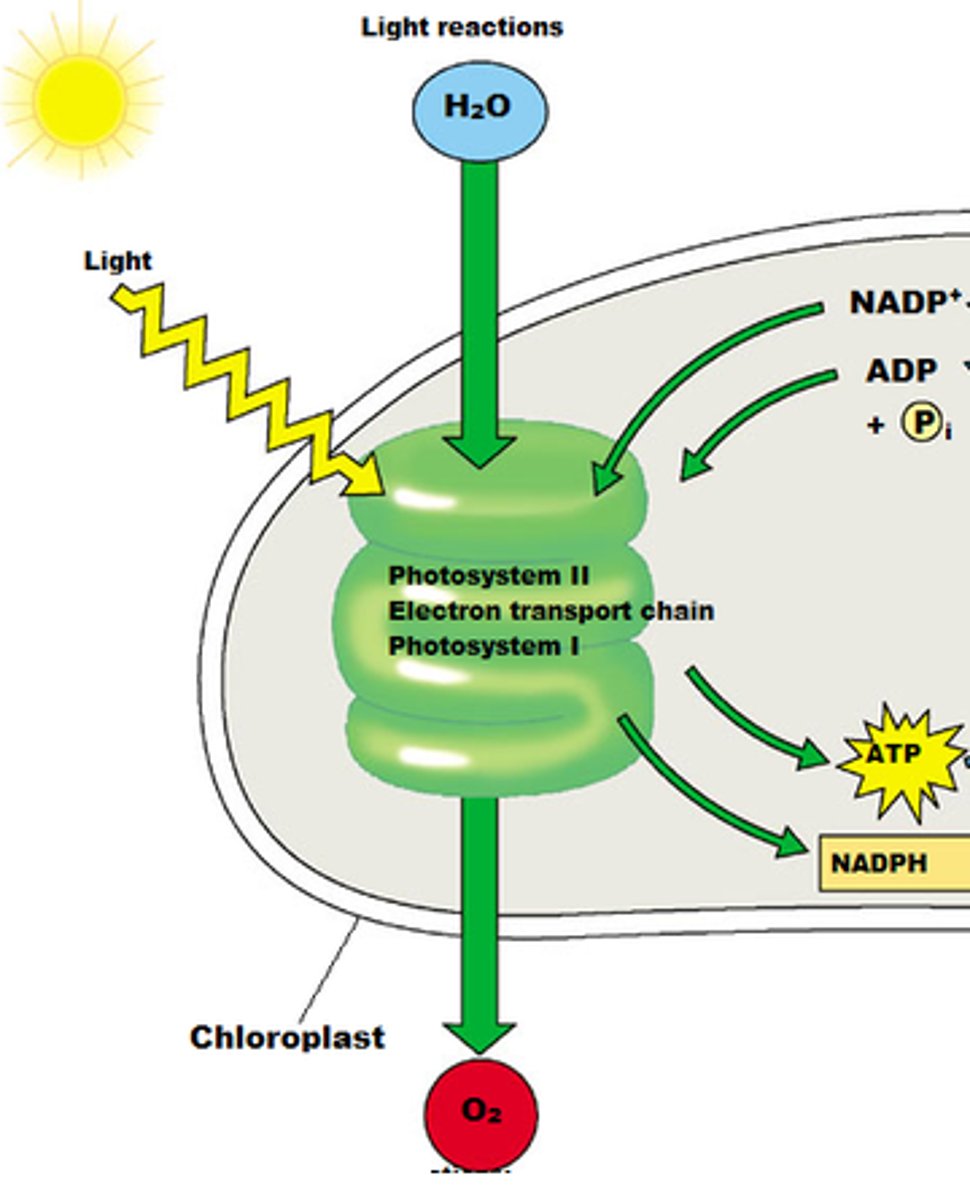
Byproduct of light dependent reaction
O2
light independent reactions occur in the
stroma
Light independent reaction uses _____ to make ____
CO2, glucose
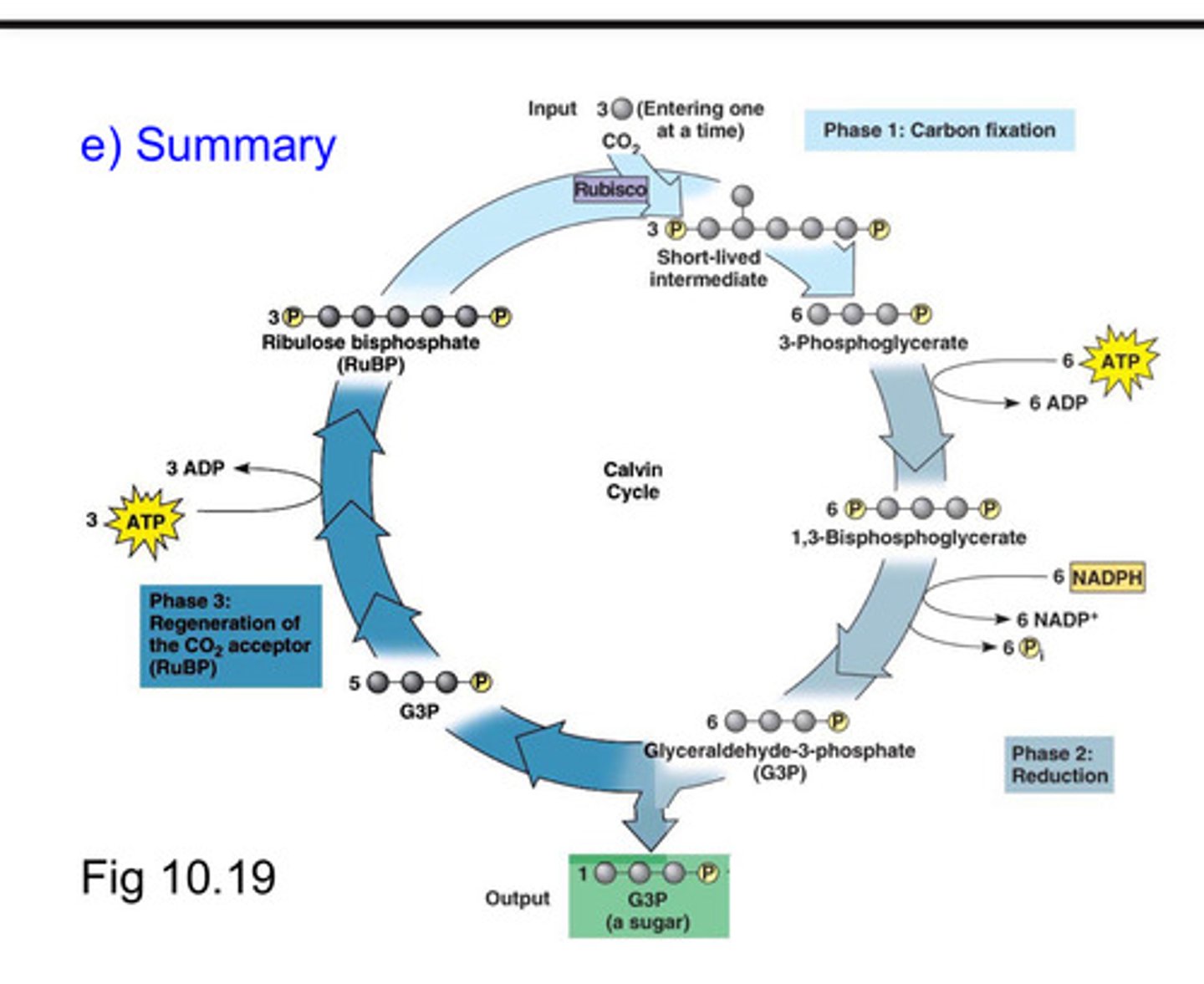
First step of Calvin cycle
carbon fixation
Chlorophyll is stored in
the thylakoid membrane
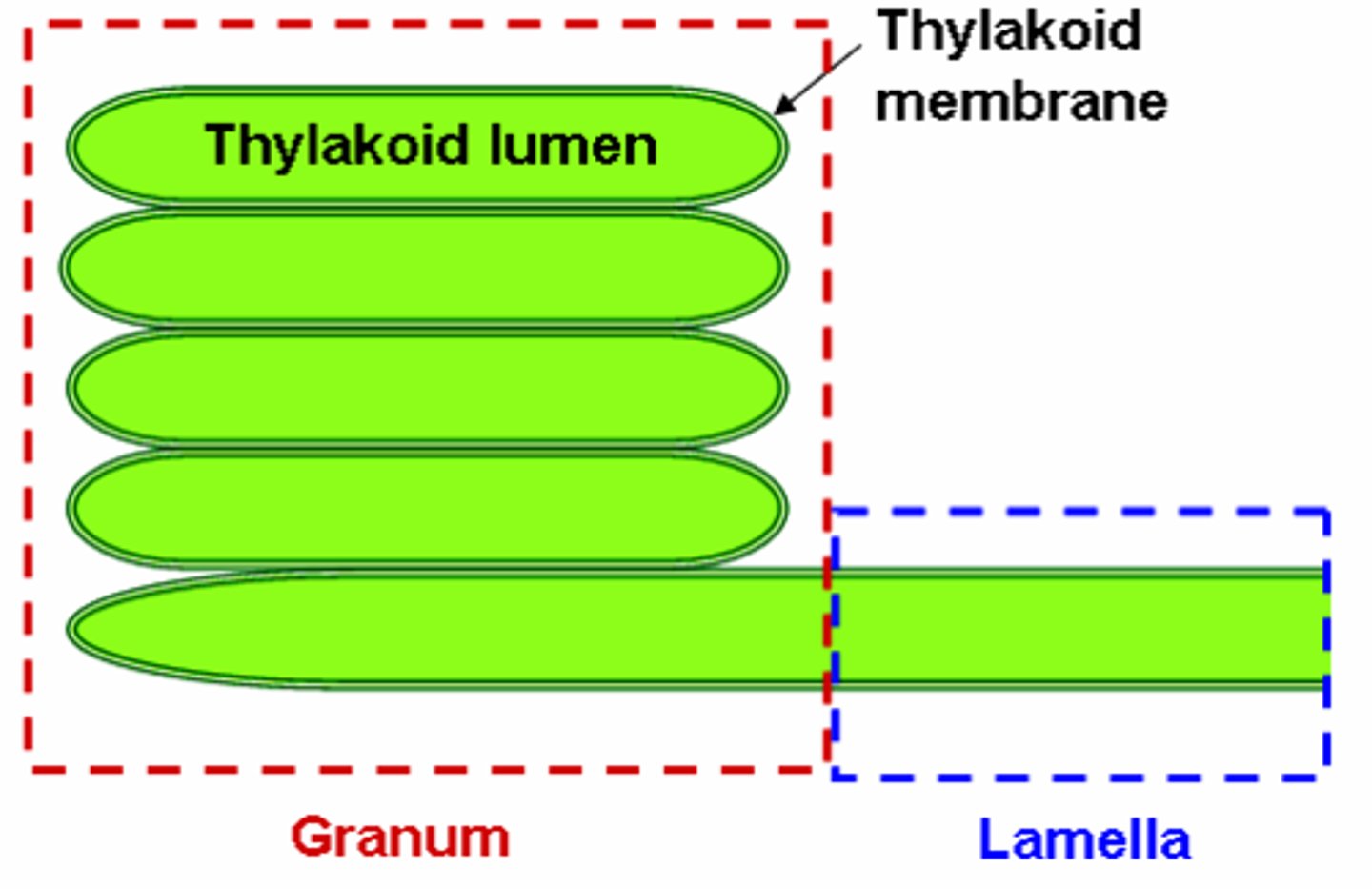
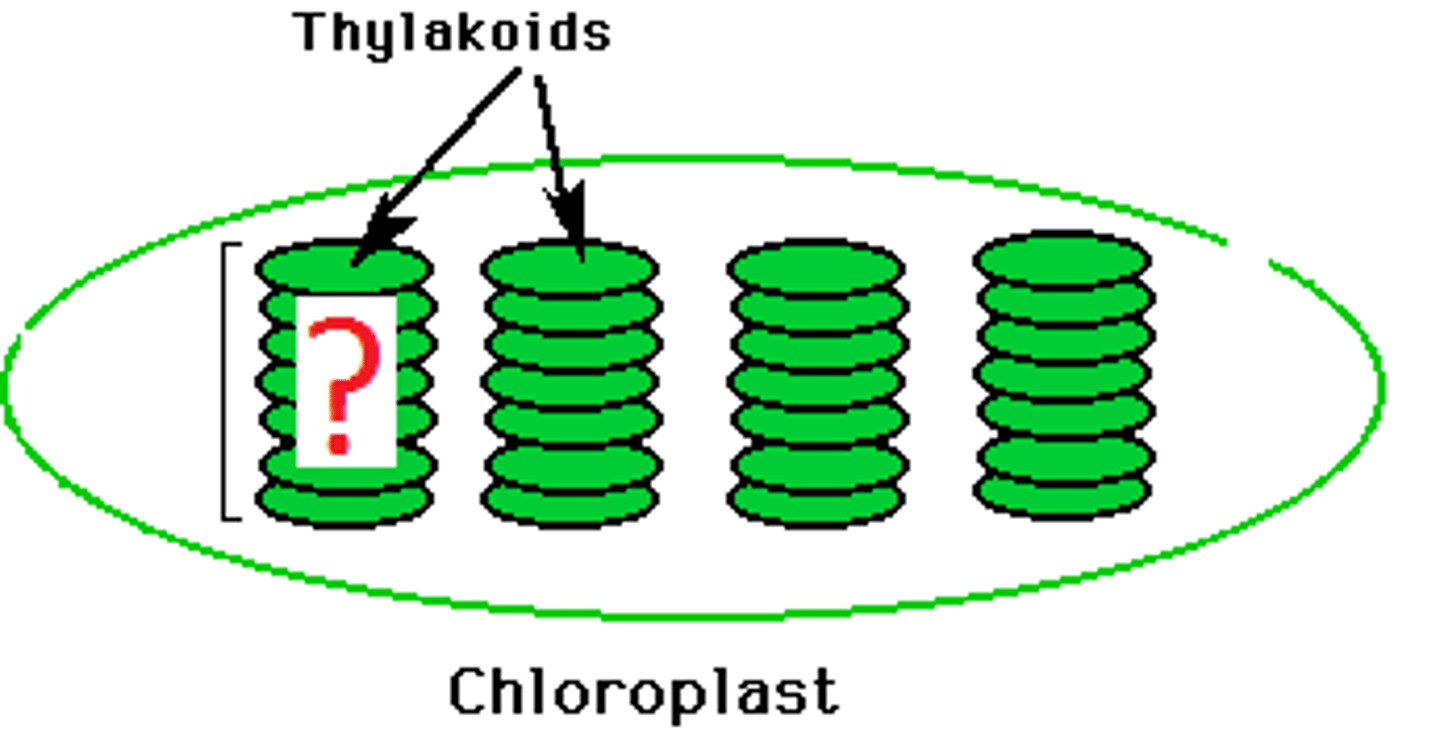
Granum
stack of thylakoids
Stroma
Fluid that fills chloroplast
Two names for light dependent reaction
electron transport chain, light rxn
Two names for light independent reaction
calvin cycle, dark rxn
Purpose of light dependent rxn
Capture energy from the sun and store energy in "energy-carrying molecules" (ATP and NADPH)
Light dependent reaction summary
- Water molecules are split into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Oxygen is released as a waste product.
- ATP and NADPH are charged up by the sun.
Light independent reaction purpose
use ATP and NADPH, the "energy-carrying molecules" from the light rxn to make glucose
Calvin cycle summary
- Series of enzyme-assisted chemical reactions powered by ATP and NADPH that produce three-carbon (3-C) sugars from CO2 and the H+ from water.
- The cycle happens twice and then these 3-C sugars combine to make glucose = C6H12O6
Consumers synonym
heterotroph

Producers synonym
autotroph

Cellular respiration chemical equation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O (+ ATP but is not considered product)
Goal of cellular respiration
convert chemical energy in glucose to chemical energy stored in ATP
Energy is released in the form of ATP during cellular respiration but isn't considered a ______
product
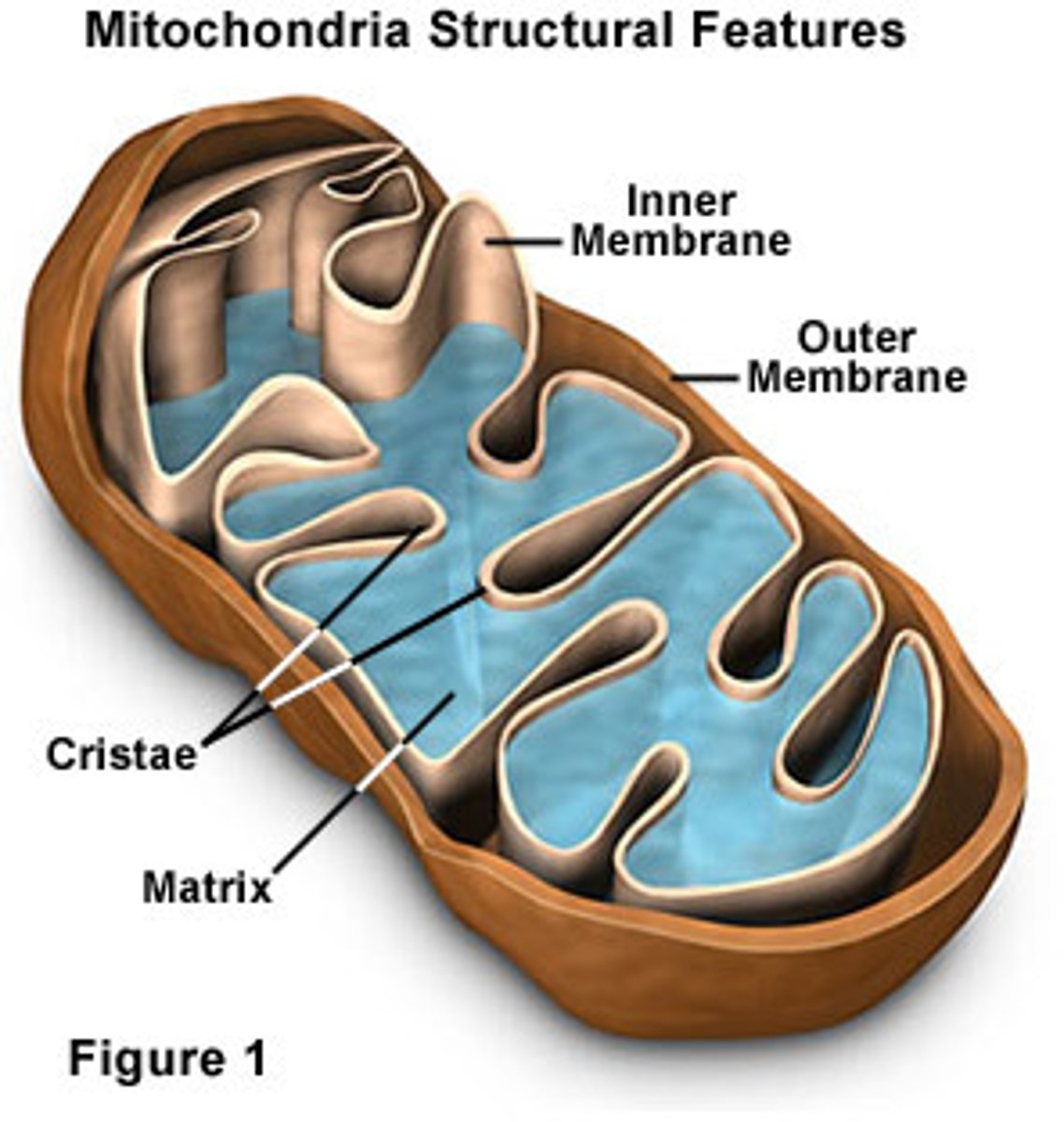
Matrix
fluid-like substance that fills the space inside the inner membrane
Glycolysis is located in the
cytoplasm
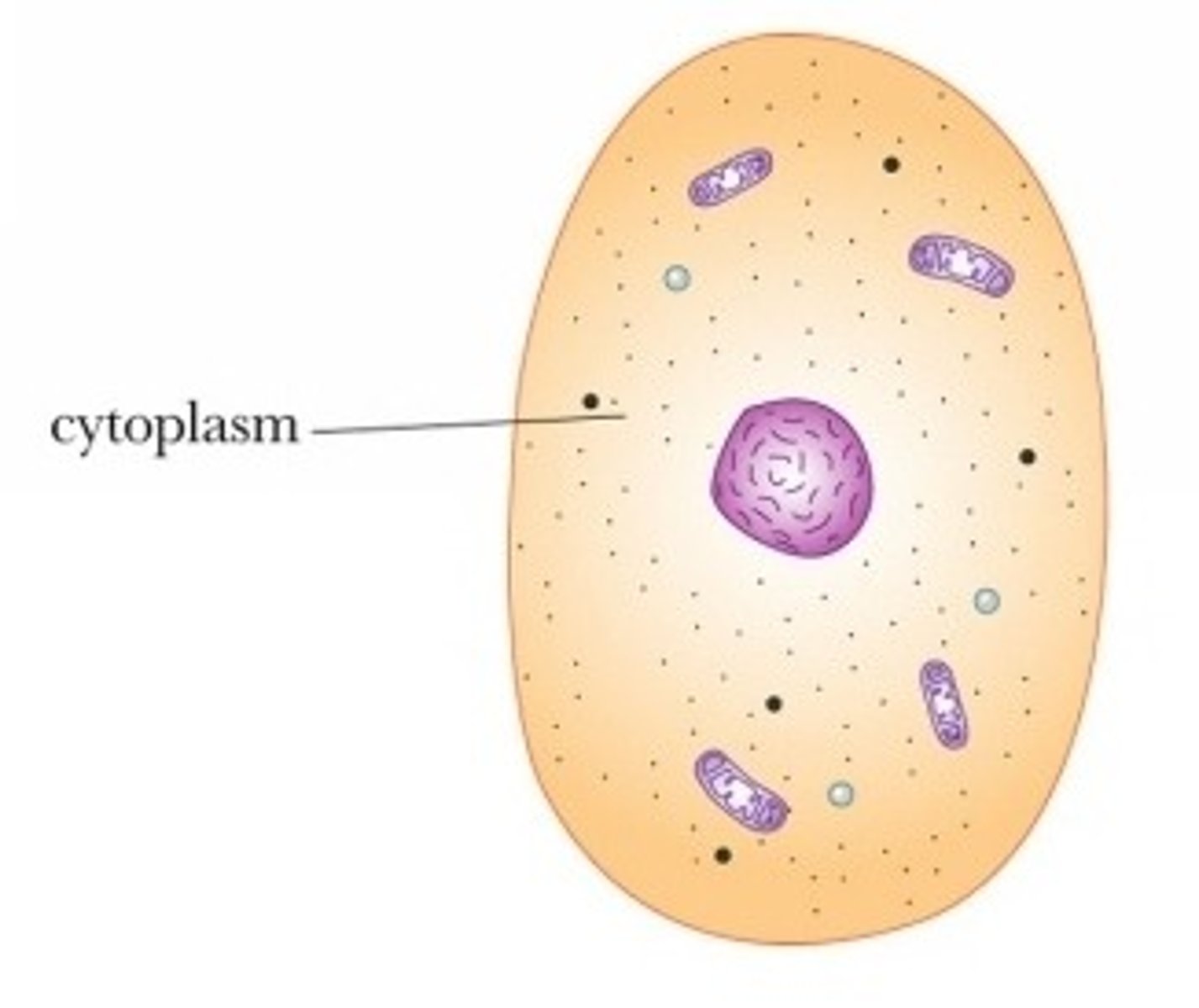
All living things can do this step: ____
DOES NOT require ___ nor _____
glycolysis, O2, mitochondria
Purpose of glycolysis
to breakdown glucose into 2 smaller molecules called pyruvate
Glycolysis produces
2 ATP
After glycolysis, if ___ and ____ are present, the cell will go through ____ respiration
O2, mitochondria, aerobic
After glycolysis, If oxygen is NOT present, then the cell will go through _______ respiration, most commonly ________
anaerobic, fermentation
2 steps to aerobic respiration
1. Citric acid/krebs cycle
2. Electron transport chain
Citric Acid /Krebs Cycle occurs where
mitochondrial matrix
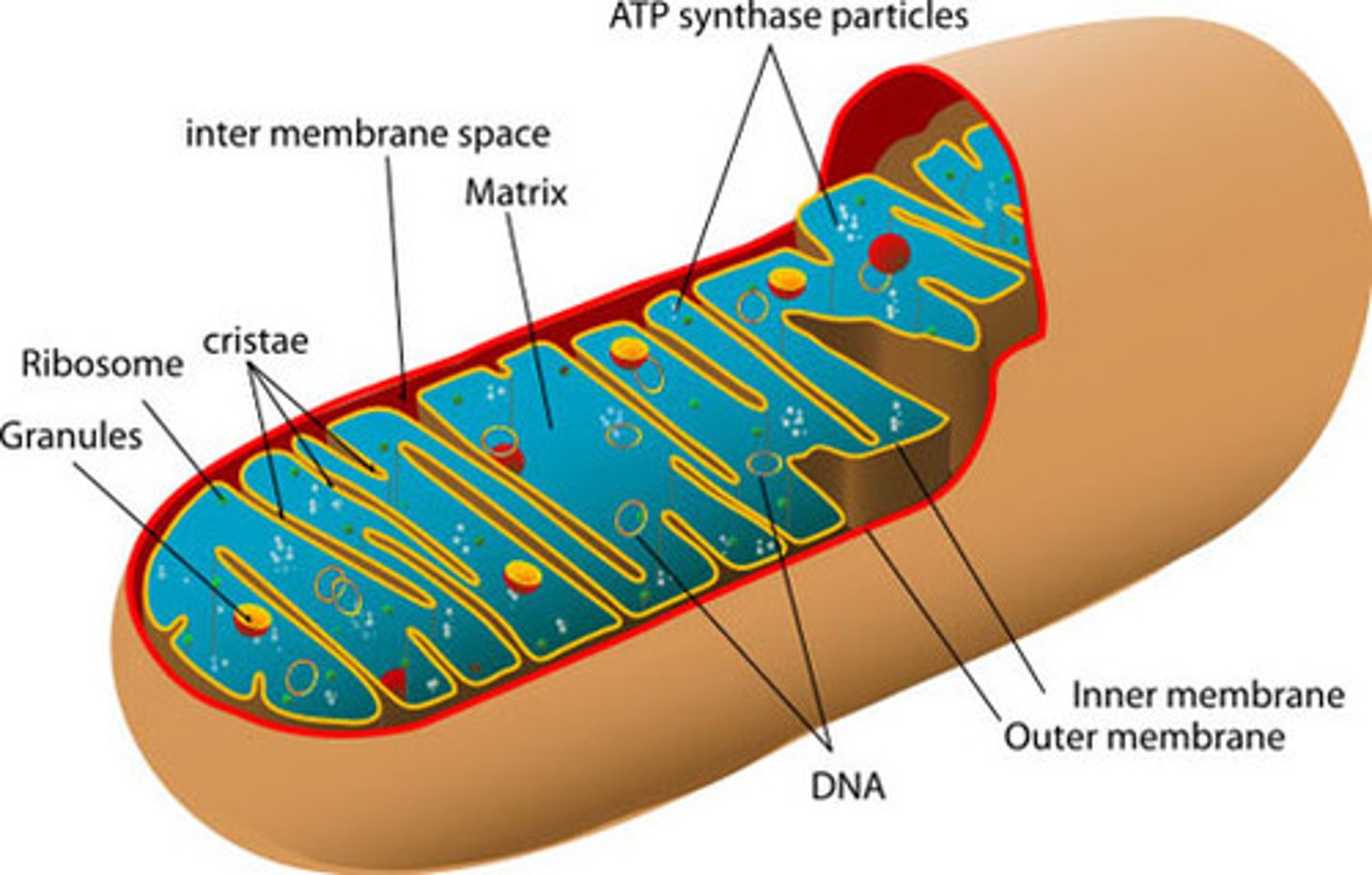
Krebs Cycle Process
2 pyruvate molecules from glycolysis are broken down to make 2 ATP molecules
Even though the Krebs cycle does not directly consume ______, it is still considered an ______ process
oxygen, aerobic
Net yield of ATP from Krebs Cycle
2 ATP
Krebs cycle byproduct (waste)
CO2
Aerobic respiration only occurs in
eukaryotic/mitochondrial cells
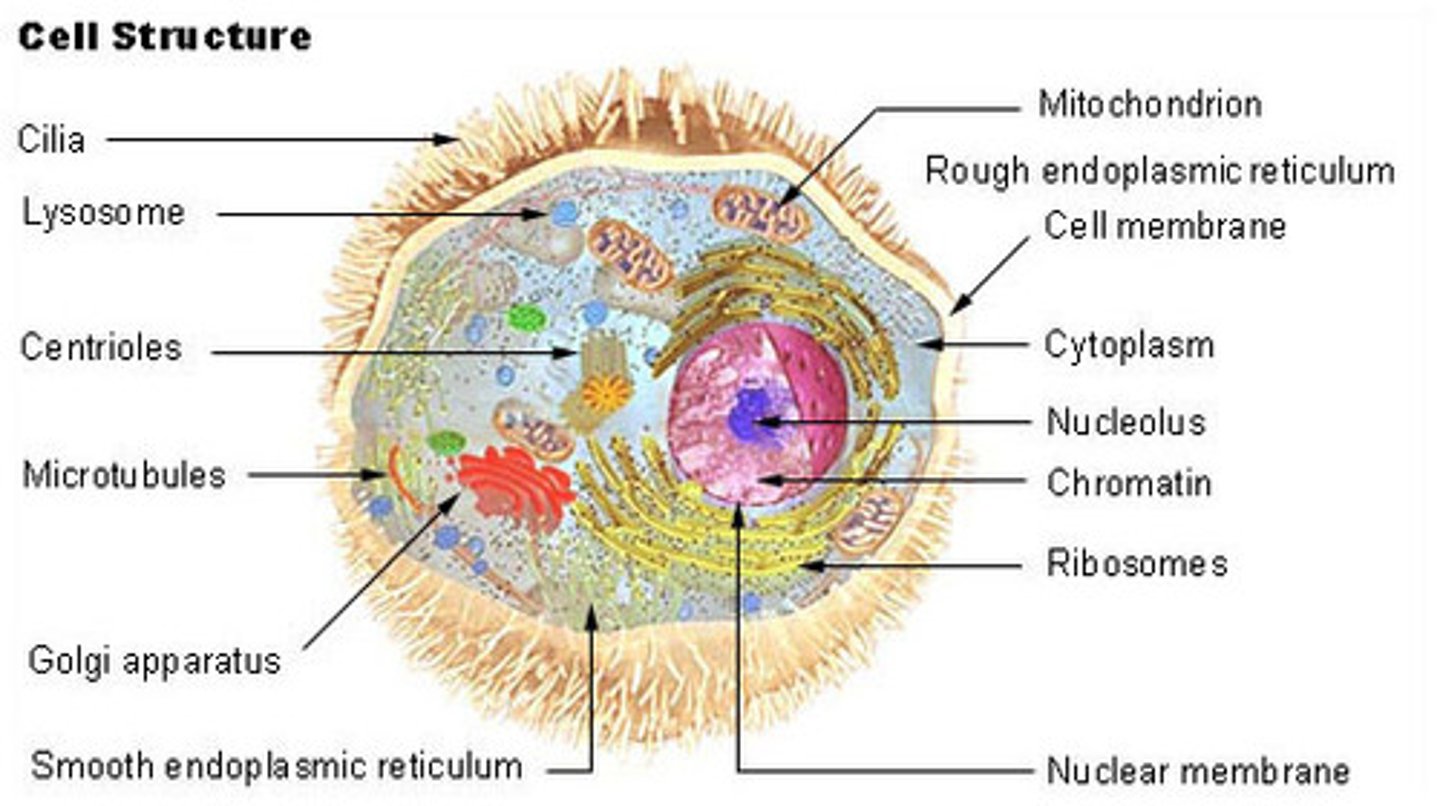
Electron transport chain location
Inner Membrane of mitochondria
Electron transport chain
A series of reactions that uses hydrogen ions and oxygen to synthesize ATP
Electron transport chain byproduct (waste)
H2O
Two types of fermentation
Lactic Acid Fermentation and Alcohol fermentation
Lactic acid fermentation occurs in
bacteria and some animal cells (muscles)
In lactic acid fermentation
pyruvate molecules from glycolysis are converted to lactic acid
In lactic acid AND alcohol fermentation no
additional ATP is produced but molecules that are needed for glycolysis are synthesized at this step (nad+)
Alcohol fermentation occurs in
yeast

In alcohol fermentation, _____ from _____ is broken down into
pyruvate, glycolysis alcohol and CO2
Glycolysis does not require
oxygen (O2) or mitochondria
Krebs cycle (1st step of aerobic respiration) requires
mitochondria
Electron transport chain (2nd step of aerobic respiration) requires
o2 and mitochondria
Glycolysis does not require o2, meaning it is
anaerobic
Aerobic respiration yields ____ ATP
36-38
Anaerobic respiration yields
2-4 ATP
Electron transport train products (atp + waste)
Makes up to 34 ATP + water as waste
Process is very fast, thousands of ATP molecules can be made in milliseconds. What process?
glycolysis
Pyruvate is a ___ _________ compound
3 carbon
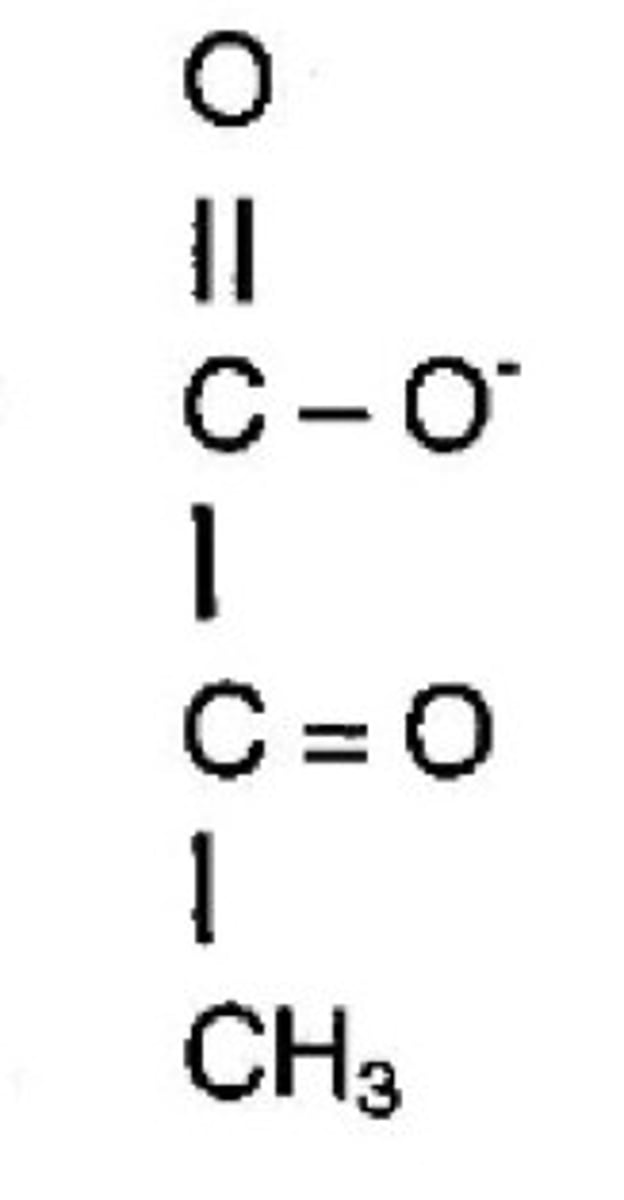
In the Krebs Cycle, _______ is broken down into _____
pyruvate acid, CO2
Cellular respiration
the process that releases energy from food in the presence of oxygen
The electron transport chain in cellular respiration uses the electrons form Krebs Cycle to move
H+ ions across the inner mitochondrial membrane
Substance needed to begin glycolysis
ATP
Inputs and outputs of light-independent rxn
Inputs: light, H2O
Outputs: O2
(makes atp and nadh for calvin cycle)
Inputs and outputs of calvin cycle, dark rxn
Inputs: CO2
Outputs: C6H12O6 , glucose
Glycolysis splits glucose into two __-carbon sugars
three
Inputs and outputs of glycolysis
Input: C6H12O6 (glucose)
Output: 2 net ATP, 2 pyruvate
Inputs and outputs of Krebs Cycle
Input: 2 pyruvate
Output: CO2, 2 ATP
Inputs and outputs of electron transport chain
Inputs: H+ ions, oxygen
Outputs: 34 ATP and water (H2O)