Ch: 26 carbonyls and carboxylic acids
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
what functional groups do aldehydes and ketones contain
C=O
where is the carbonyl functional group found in a carbon chain
at the end of a carbon chain
how is the aldehyde group written
CHO
what is the simplest aldehyde
HCHO
how is the ketone group written as in its structural formula
CO
what is the simplest ketone
propanone
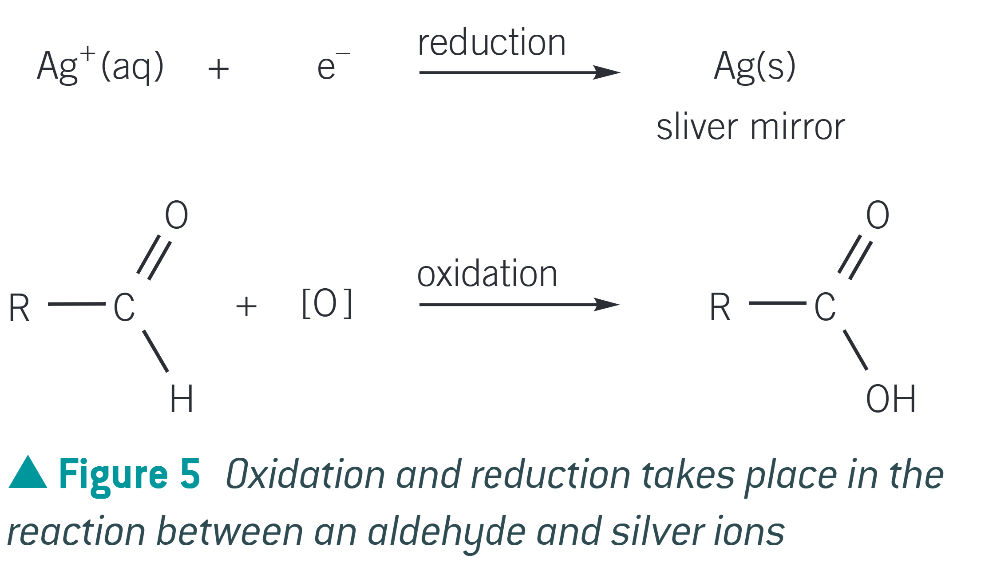
aldehydes can be oxidised to…
carboxylic acids
how can aldehydes be oxidised
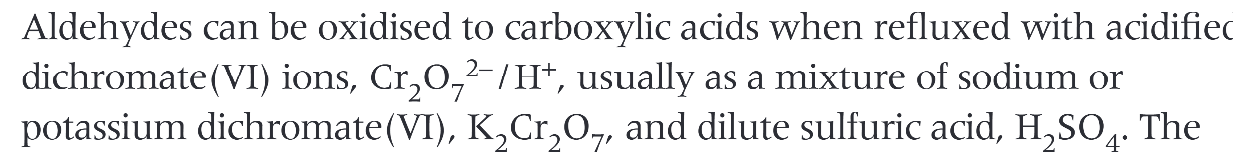
oxidation of butanal
how do you distinguish between aldehydes and ketones
ketones dont undergo oxidation reactions
what happens to dichromate solution for aldehydes
changes colour from orange to green
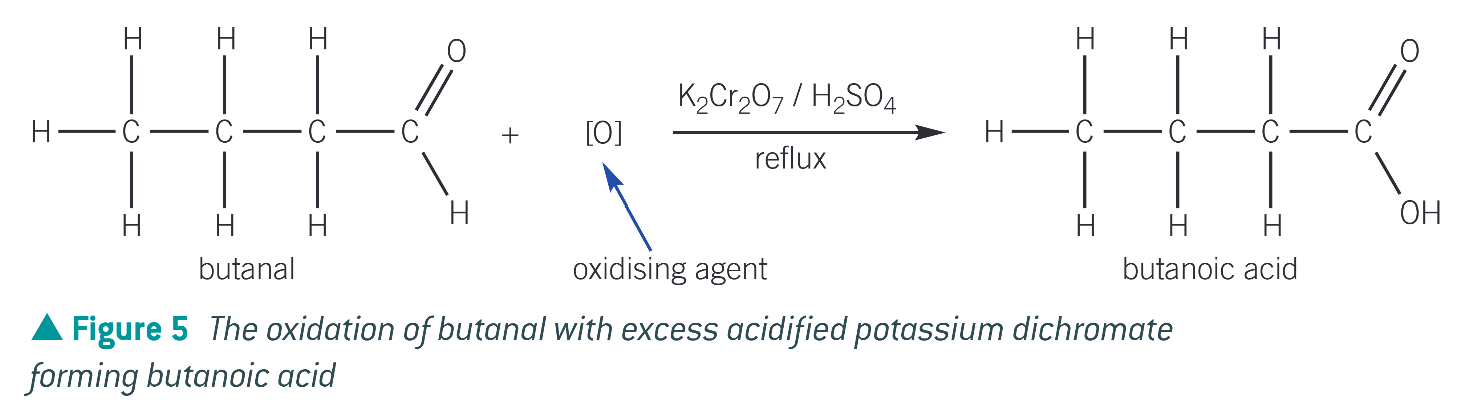
what is used to detect carbonyl functional groups in aldehydes and ketones?
a solution of 2,4 - dinitrophenylhydrazine ( brady’s reagent )
what happens with 2,4 - DNP in the presence of a carbonyl group?
a yellow/ orange precipitate called 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone is produced
how do u use 2,4 - DNP safely
normally dissolved in methanol and sulfuric acid as a pale orange solution called Brady’s reagent
why is solid 2,4-DNP dangerous
it can be dangerous because friction or a sudden blow can cause it to explode
structure of 2,4 - dinitrophenylhydrazine
Testing for the carbonyl group in aldehydes and ketones ( method )
add 5cm depth of DNP, this is in excess
use a dropping pipette, add 3 drops of the unknown compound
if no crystals form, add a few drops of sulfuric acid
a yellow / orange precipitate indicates presence of required substance
test tube containing precipitate can then be put to one side and analysed later to identify the aldehyde or ketone
Distinguishing between aldehydes and ketones
once compound has been identified as containing a carbonyl group, a fresh sample can be classified using tollen’s reagent
what is tollen’s reagent
a solution of silver nitrate in aqueous ammonia
what happens when using a tollen’s reagent
in the presence of an aldehyde group, a silver mirror is produced
why should tollen’s reagent be made up immediately before carrying out the test
it has a short shelf - life
method with using tollen’s reagent
add 3cm depth of aqueous silver nitrate in test tube
add aqueous sodium hydroxide to the silver nitrate until the brown precipitate of silver oxide is formed
add dilute ammonia until the brown precipitate just dissolves to form a clear colourless solution. this is the reagent
pour 2cm depth of the unknown solution into a clean test tube
add an equal volume of freshly prepared tollen’s reagent
leave the test tube to stand in a beaker of warm water at about 50 degrees for about 10-15 mins and then observe whether any silver mirror is formed
equation for aldehyde and tollen’s reagent
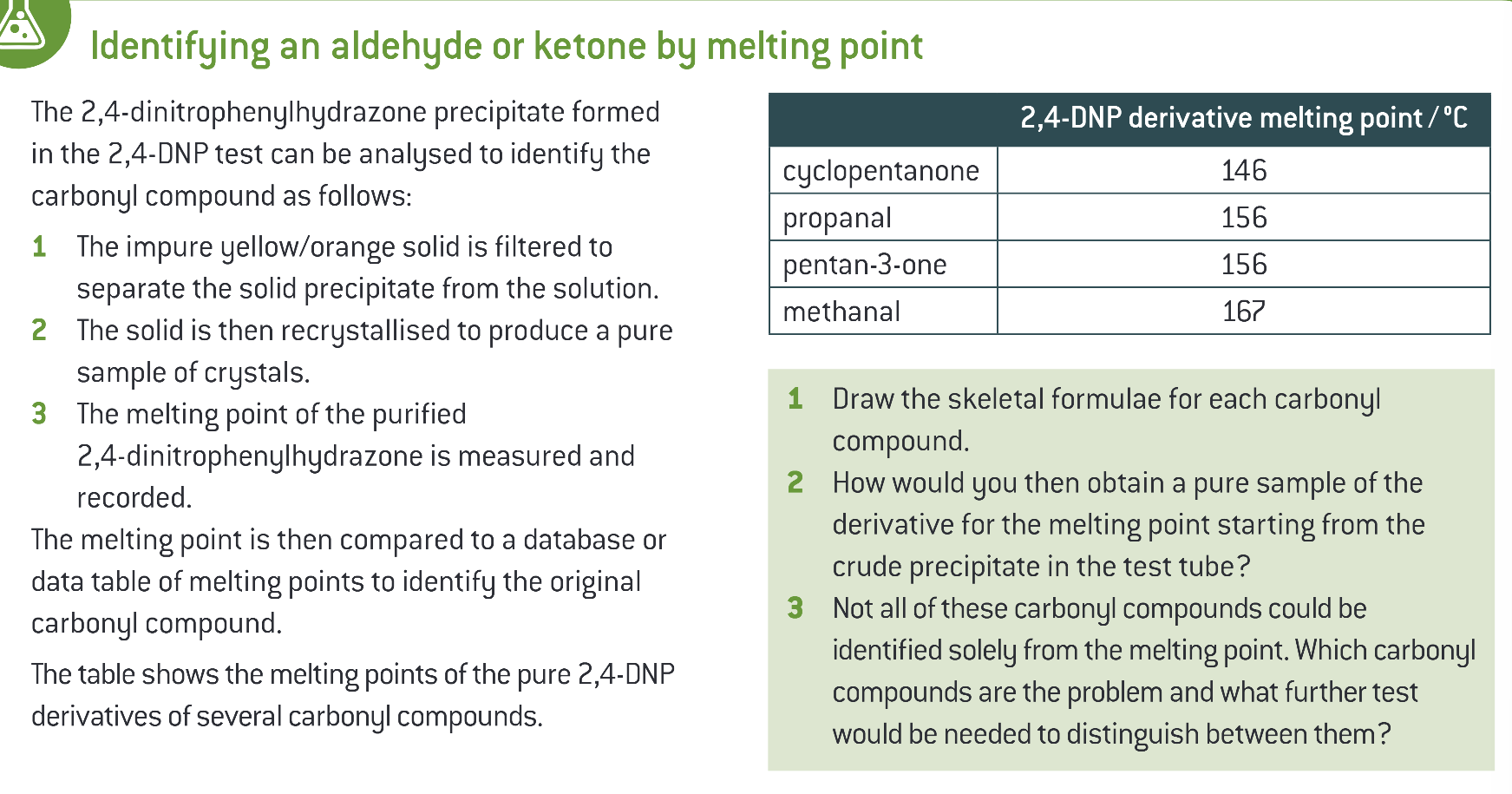
how do you identify an aldehyde or ketone by mp
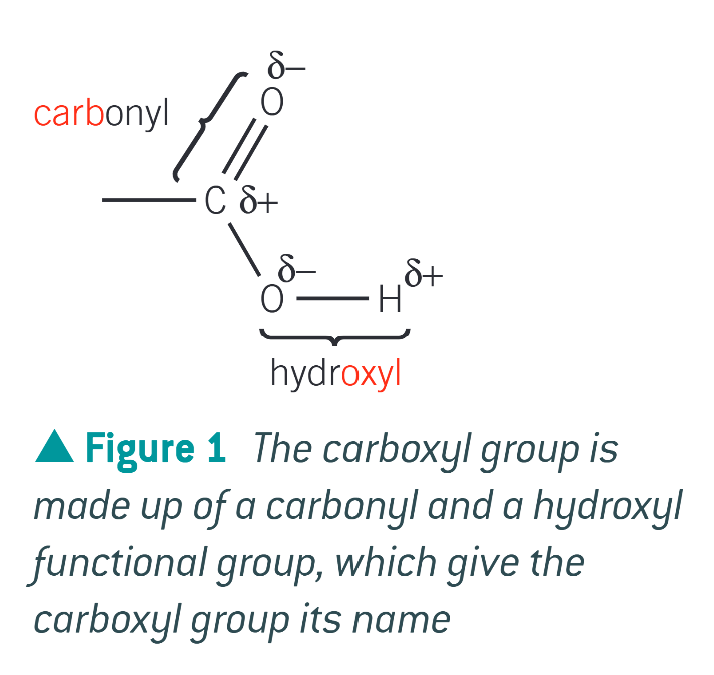
what is a carboxylic acid
an organic acid which contains the carboxyl functional group
what does a carboxyl group contain
a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group
where can you find carboxylic acids
medicines, fruit juices, vinegar, rhubarb leaves


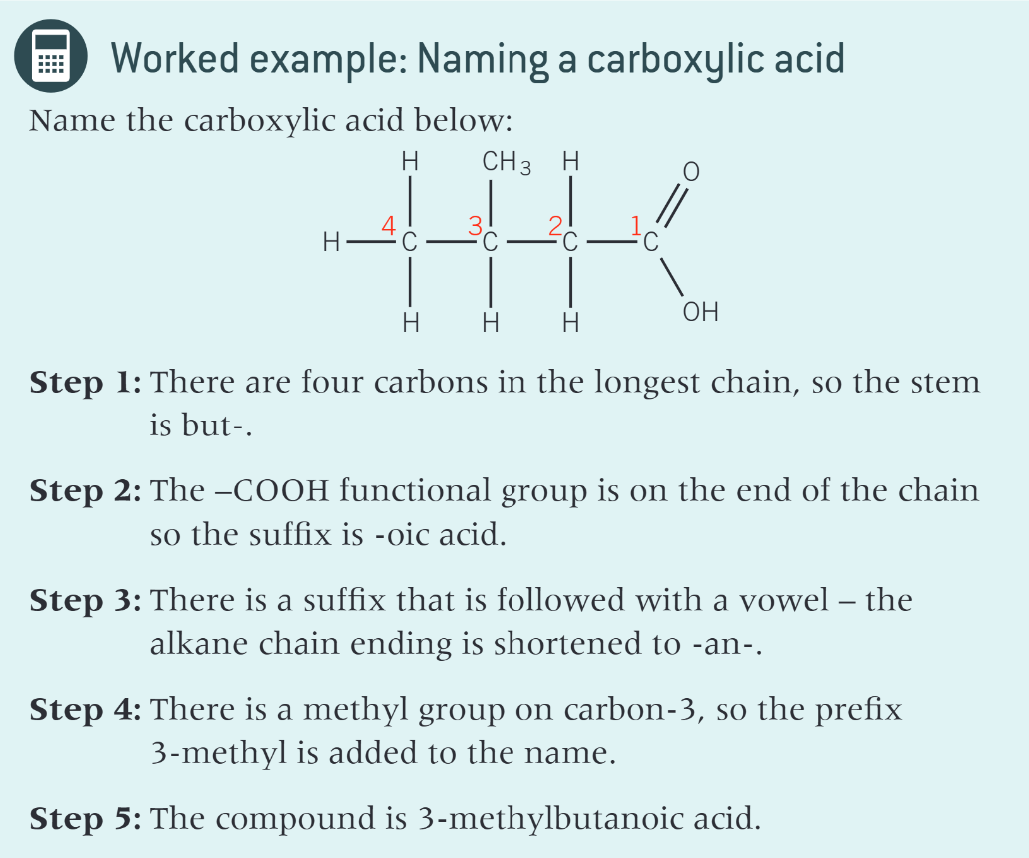
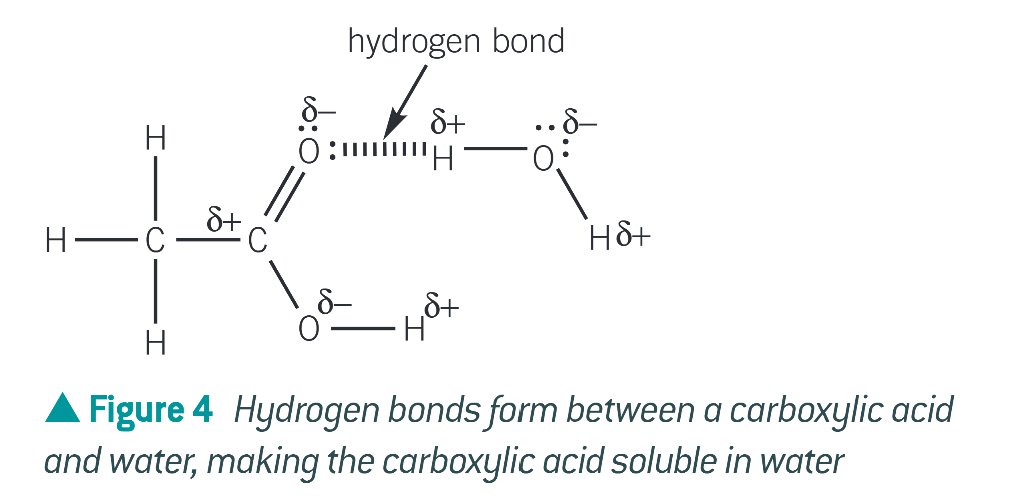
what allows carboxylic acids to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
the C=O bonds in carboxylic acids are polar
carboxylic acids with up to 4 carbon atoms are?
soluble in water
what happens as the number of carbon atoms increases in a carboxylic acid
the solubility decreases as the non - polar carbon chain has a greater effect on the overall polarity of the molecule
diagram of a carboxylic acid forming a hydrogen bond with water
what are the qualities of dicarboxylic acids
they have 2 polar carboxyl groups to form hydrogen bonds, solids at room temperature and dissolve readily in water
carboxylic acids are classified as what type of acid?
weak acid
what is the simplest carboxylic acid
HCOOH
when dissolved in water, carboxylic acids?
partially dissociate
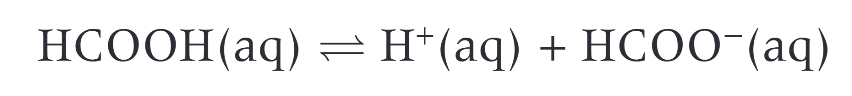
carboxylic acids take place in?
redox reactions with metals, neutralisation reactions with bases( alkalis, metal oxides, and carbonates )
what do carboxylic acids form in acid reactions
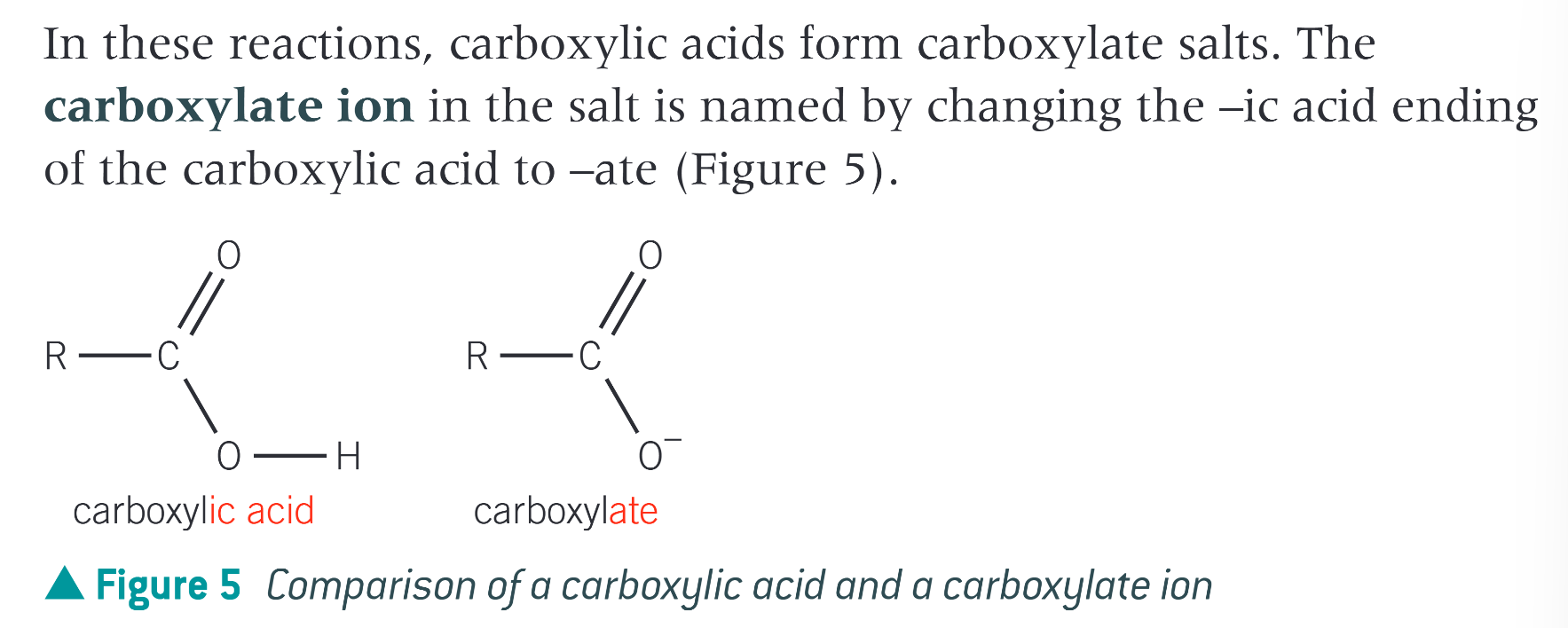
aqueous solutions of carboxylic acids react with metals in a redox reaction to form?
hydrogen gas and the carboxylate salt
what would you observe in a redox reaction of carboxylic acids with metals
metal dissapearing and effervescence as hydrogen gas is evolved
reaction of propanoic acid with magnesium
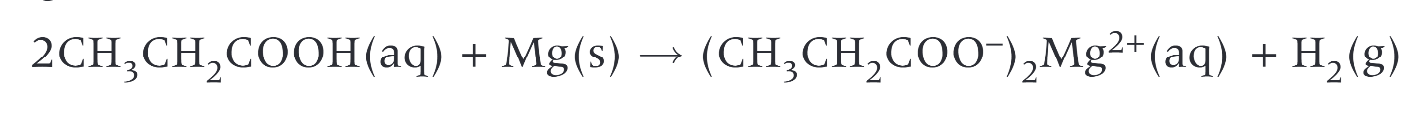
carboxylic acids react with metal oxides to form…
a salt and water
reaction of aqueous ethanoic acid with calcium oxide to form calcium ethanoate and water
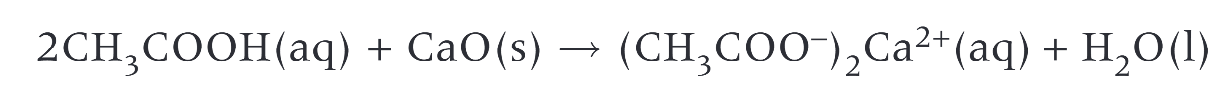
carboxylic acids react with alkalis to form?
salt and water
why would you not see any reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alkali
the 2 solutions may react together to form an aqueous solution of the salt
equation of ethanoic acid reacting with sodium hydroxide to form?
sodium ethanoate and water
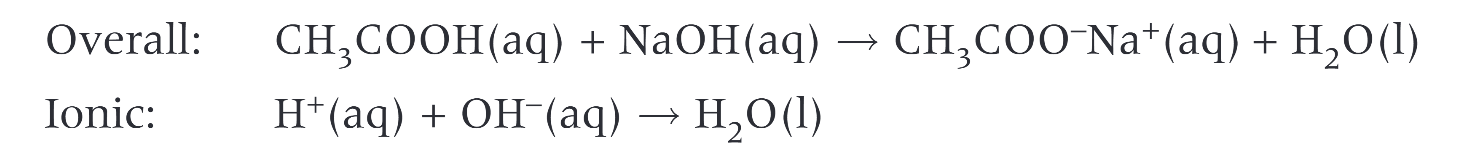
when a carbonate is added to a carboxylic acid what happens
carbon dioxide gas is evolved
what would happen if a carboxylic acid is in excess when added with carbonate
a solid carbonate would disappear
reaction between ethanoic acid with aqueous sodium carbonate

why is the neutralisation reaction of carboxylic acids with carbonates useful

when writing the formula of the salt, you can…

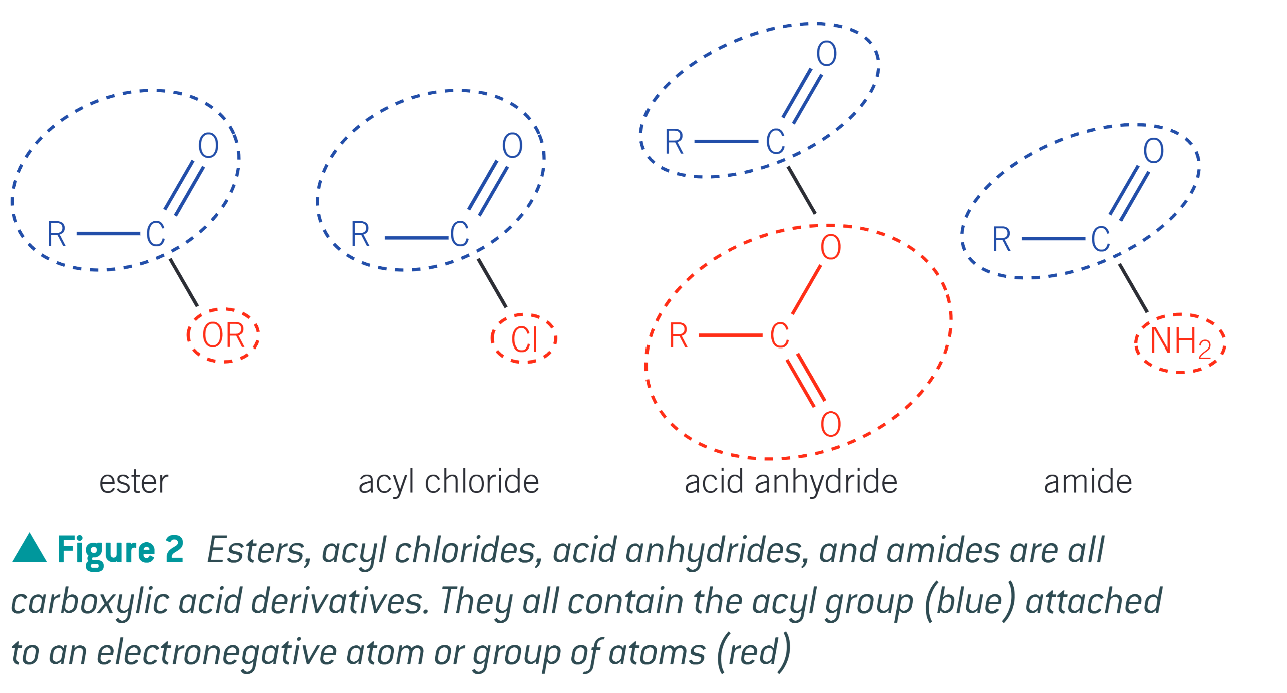
what is a derivative of a carboxylic acid
a compound that can be hydrolysed to form the parent carboxylic acid
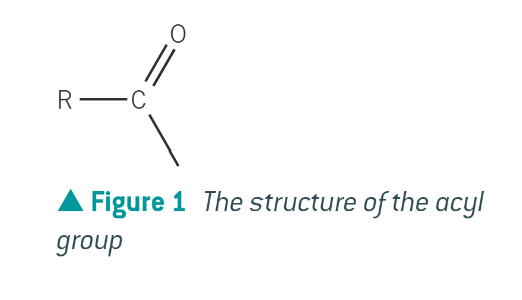
carboxylic acid derivatives have a common sequence of atoms in their structure, known as…
an acyl group
structure of acyl group
the 4 carboxylic acid derivatives