electrochemistry
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
oxidation
loss of electrons
reduction
gain of electrons
oxidizing agent
species that is reduced
reducing agent
species that is oxidized
anode
the site of oxidation
cathode
the site of reduction
disproportionation reactions
a redox reaction in which the same species is both oxidized and reduced
oxidation states
Elements in their elemental form are in the zero oxidation state
Group 1 metals are +1 and Group 2 are +2 in compounds
Hydrogen is +1 except when bonded to a metal only (when it’s -1)
transition elements must be determined from anion’s charge (except Al = 3, Zn = 2, Cd = 2, Ag = 1)
the most electronegative elements get their typical oxidation state
The last element is assigned balance the charge of the compound/ion
electrochemical cells
the anode is always the site of oxidation
the cathode is always the side of reduction
electrons always flow from anode to cathode
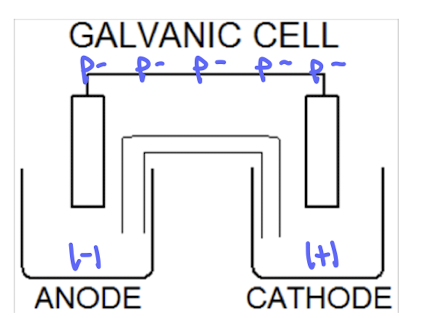
galvanic (voltaic) cells
spontaneous
produce electricity
anode (-) —> cathode (+)
Functions as batteries
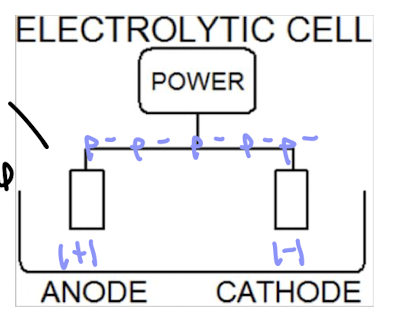
electrolytic cells
nonspontaneous
consume electricity
anode (+) to cathode (-)
produce elements