Chapter 4: Histology - Part 1
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Tissues
a group of structurally and functionally related cells, surrounded by the extracellular matrix
Extracellular matrix
liquid component (water, nutrients, ions, macromolecules) and protein fibers (collagen, elastic, and reticular fibers)
Integral proteins
link neighboring cell’s plasma membranes
Cell junction
ways neighboring cells bind to one another (tight junction, desmosomes, gap junction)
Tight junction
hold cells closely together, integral proteins of adjacent cell’s plasma membranes are locked together, forming a seal around apical perimeter of cell
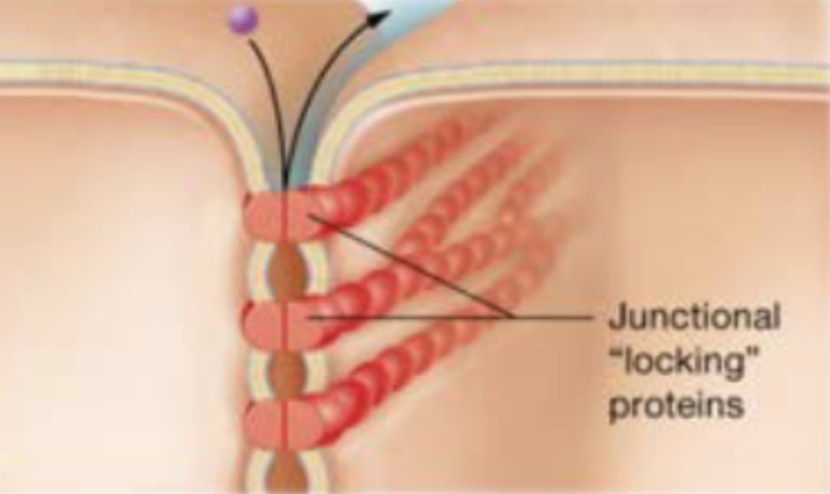
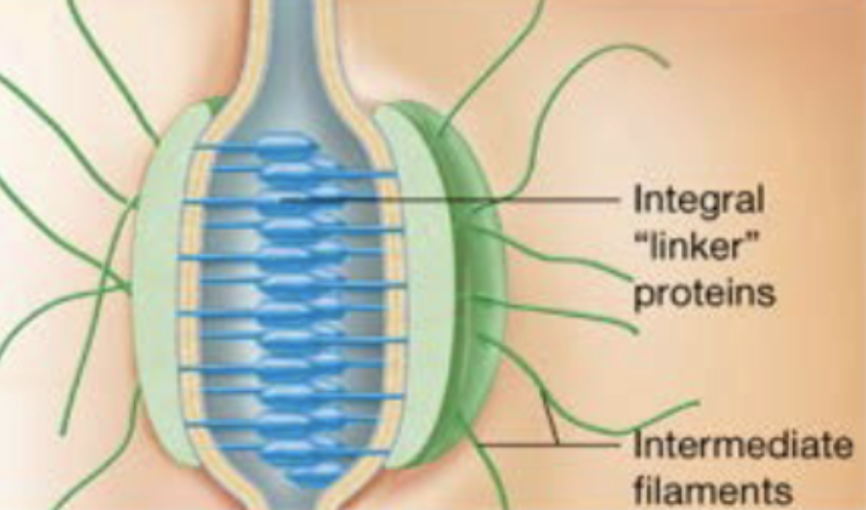
Desmosomes
strongly hold cells together but allow materials in extracellular fluid to pass through space between cells (tissues subjected to great mechanical stress-epithelia of skin)
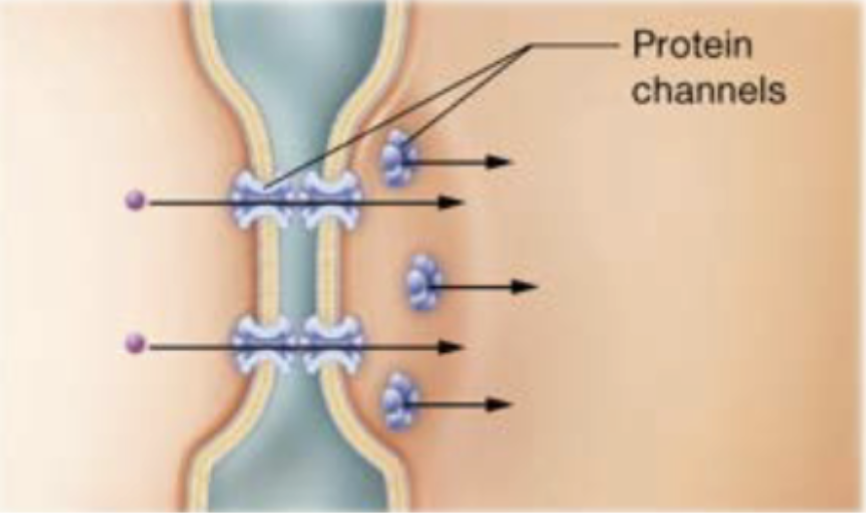
Gap junctions
channels between adjacent cells that allow small substances to move from one cell to another (cells that communicate with electrical signals-cardiac muscle cells)
Pemphigus vulgaris
autoimmune disease that attacks desmosomes
Types of tissues
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous tissues
Epithelial tissues (epithelia)
cover and line all body surfaces (outside wall of organs, inner lining of hallow organs, walls of body cavities, skin) and cavities, constantly injured cell type
Classifying epithelia
depends on number of cell layers and cell shape
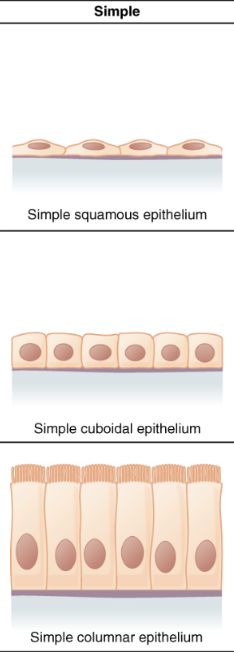
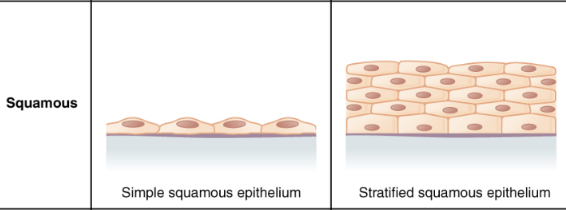
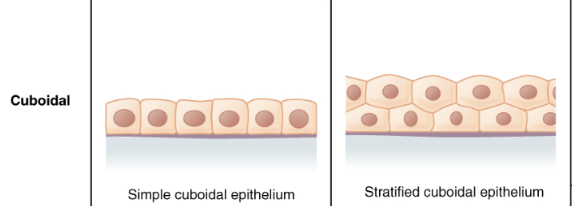
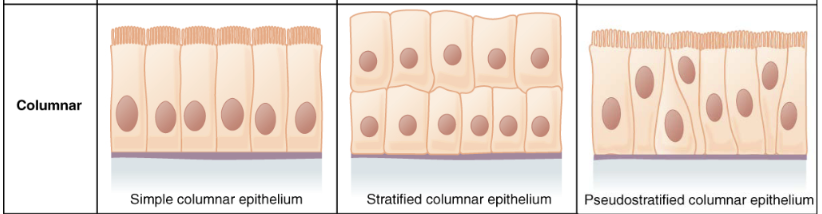
Simple epithelium
1 layer of cells
Stratified epithelium
multiple layers of cells
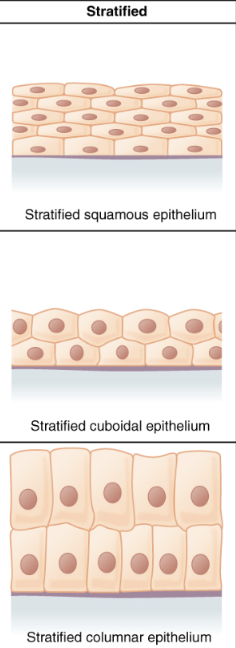
Squamous epithelium
flattened, irregularly shaped cells
Cuboidal epithelium
cube-shaped cells
Columnar epithelium
column-shaped cells
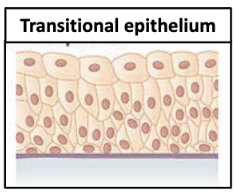
Transitional epithelium
Apical cells dome-shaped when relaxed and flattened when stretched
Functions of epithelium
protection (skin), secretion (glands), absorption (small intestines), sensory (taste buds), filtration (glomerulous)
Characteristics of epithelia
attached to a basement membrane, composed of closely packed cells held together by intercellular junctions, avascular (no blood vessels), innervated (contains neurons), high rate of regeneration
Basement membrane
an acellular structure produced by both epithelial and underlying connective tissue cells
Basal surface
the side of epithelial cells that touches the basement membrane
Apical surface
the side of epithelial cells that doesn’t touch the basement membrane