L5- Dislocation interactions + partial dislocations
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Cross slip
The movement of a dislocation from one glide plane to another
Line vector and Burgers vector must be common to both planes
Edge dislocation can’t cross slip only screw dislocation can.
For a mixed dislocation to cross slip it must straighten to a pure screw type.
Why can perfect dislocation dissociate into 2 so-called partial dislocations
an fcc dislocation is composed of two extra half planes
Why will partials repel each other?
They are of the same type + similar line sense
forms stacking fault + requires energy
Effect of stacking fault energy on hardening
cross-slip of partials = hardest with low stacking fault energy
as partials = most widely separated in this material
Stacking fault energy
Energy required to create a defect in the stacking sequence of atoms in a crystalline material
Lomer-Cottrell lock
produces a dislocation out of slip plane + is sessile→ i.e. stair rod dislocations
Peierls stress
The stress required to move a dislocation through a perfect crystal at 0k.
Eqn for Peierls stress
w = width of dislocation
b = burgers vector
G = shear modulus
ν = poissons ratio
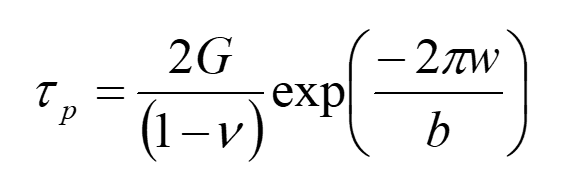
Consequence of Peierls stress
Dislocations with wide slip plane move more easily
OR smaller burgers vector