Assisted Reproductive Techniques_ Gyn US
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
what is infertility?
common disease that impacts 1 in 8 couples.
when is an infertility diagnosis made?
for couples where the woman is less than 35 and there is a failure to conceive after 1 year of unprotected intercourse
for couples where the woman is OVER 35 and there is failure to conceive after 6 months of attempts
what are things that contribute to rising infertility?
increasing sexually transmitted disease
delay of childbearing
increasing damage from endometriosis
what is included in reasons for increasing sexually transmitted disease?
Earlier onset sexual activity
Multiple partners
More women having cervical procedures due to cervical dysplasia or cancer
what does increasing sexually transmitted disease result in?
Results in higher incidence of PID
what is included in reasons for delay of childbearing?
women putting career first
couples choosing to delay for many years
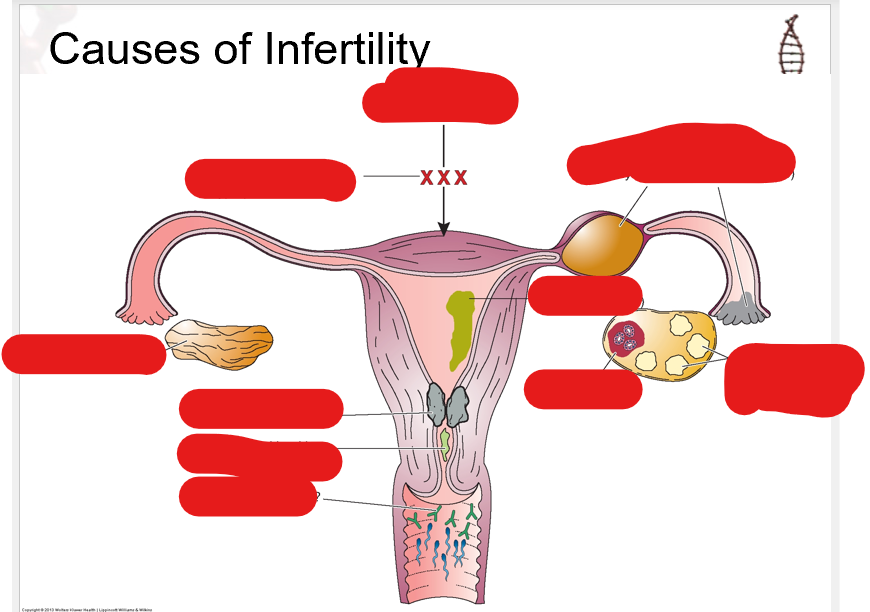
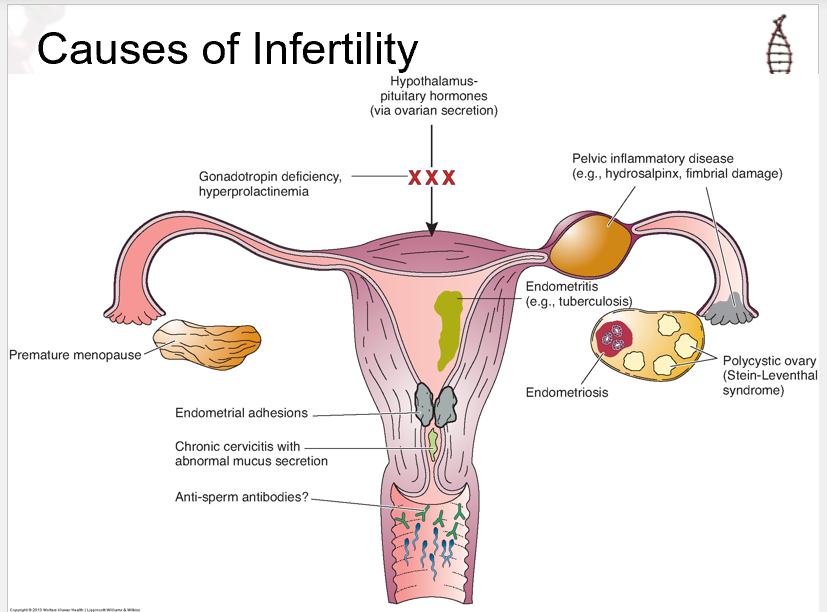
know this image
how does sonography help?
in treatment and diagnosis of infertility
how can sonography be used to aid in diagnosis?
transvaginal US
structural anomalies and pathologies of uterus, tubes and ovaries
Saline Infused Sonohysterography
evaluate infertility in males
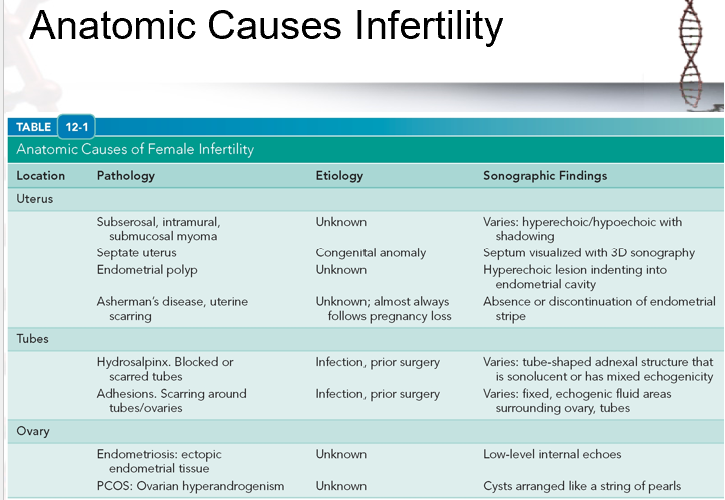
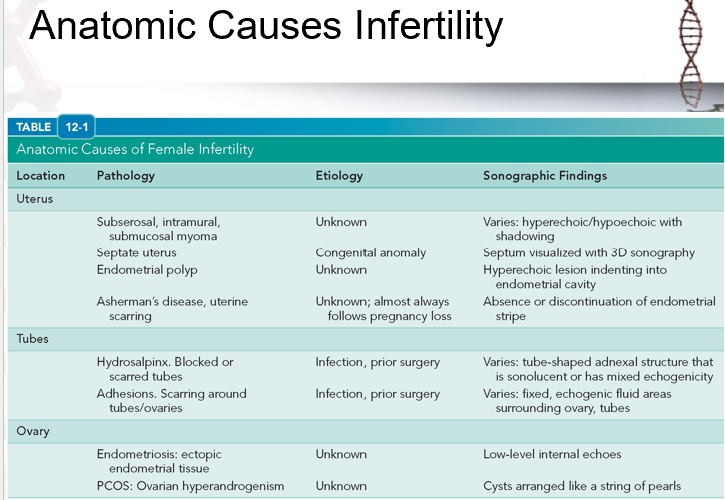
evaluate this image
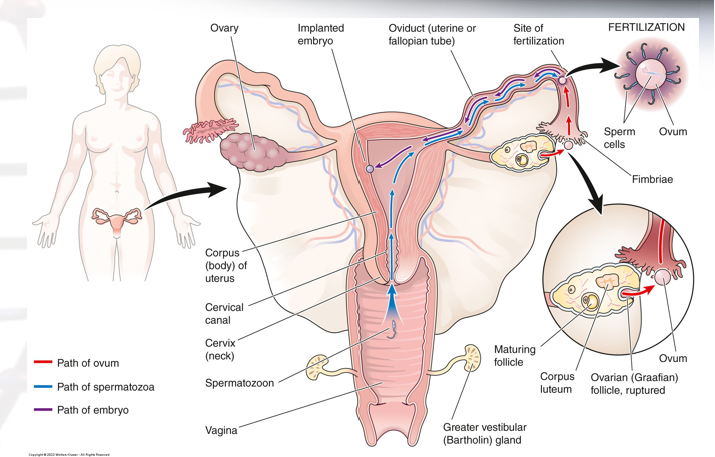
what does uterine assessment evaluate?
congenital anomalies
expected appearance of endometrium during stage of uterine cycle
uterine fibroids
3D uterine evaluation is rapidly growing as a technique to detect…
endometrial and myometrial abnormalities
what uterine congenital anomaly is most commonly associated with infertility?
septate uterus
what uterine congenital anomaly is associated with premature labor?
bicornuate uterus
what uterine congenital anomaly is associated with 2nd trimester pregnancy loss?
unicornuate uterus
where is the focus when assessing ovaries?
ovarian reserve and antral follicles
define ovarian reserve:
estimation of a woman’s remaining follicles
define antral follicle count:
the number of follicles measuring 2-10 mm early in the ovarian cycle (chocolate chip cookie count!)
what does antral follicle count do?
helps assess a woman’s potential for success for fertility treatments
varies according to woman’s age
antral follicle count is obtained via…
US using sweeping technique by sonographer
what is antral follicle count compared to?
AMH levels?
helps in diagnosis of decreased ovarian reserve (DOR)
how does sonography assist in evaluating ovarian dysfunction?
evaluating amenorrhea and oligomenorrhea
detecting PCOS appearance which indicates anovulation
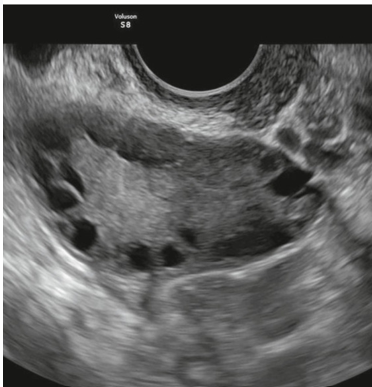
what endometrial measurement indicates poor implantation rate?
less than 6 mm
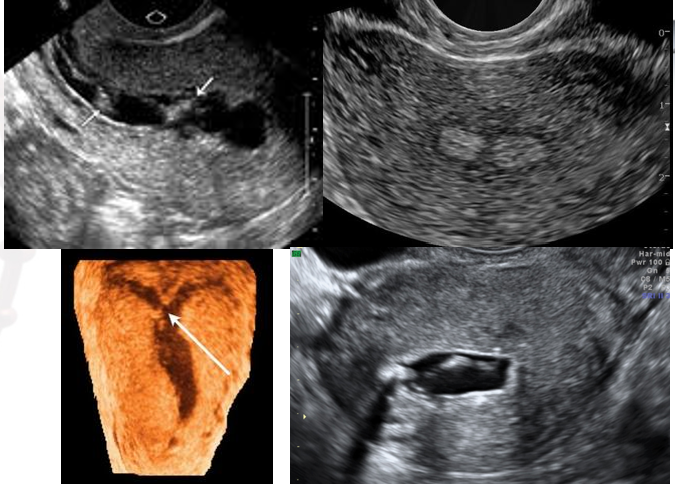
what is shown?
Asherman Syndrome/ Intrauterine Synechiae
what is shown?
endometrial polyp
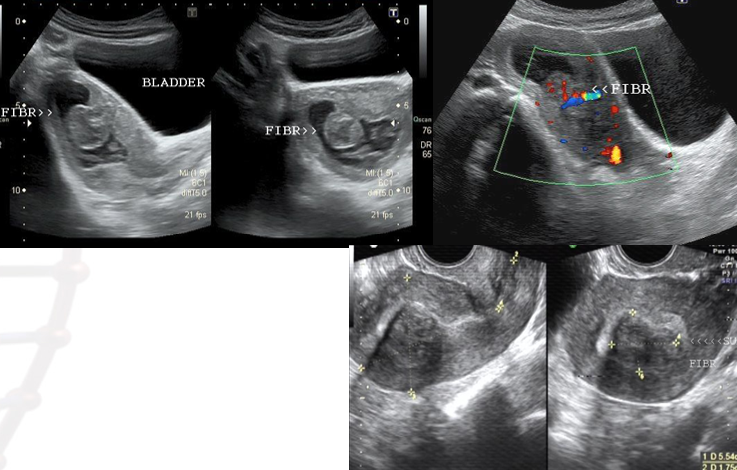
what is shown?
submucosal leiomyoma
what plays a vital role in evaluating the myometrium?
3D Endovaginal sonography (EVS)
can avoid radiation exposure of HSG if using 3D ultrasound
what structural anomalies are found in the myometrium?
Fibroids
Distort Uterine Cavity
Impair blood supply to placenta
Congenital Anomalies
Adenomyosis
Cause infertility by interfering with implantation
treatment of adenomyosis will…
render woman infertile
what is the source of infertility in approx. 14% of couples
occlusion of fallopian tubes
what is the source of about 25-35% of infertility?
damage to fallopian tubes
what can cause damage to fallopian tubes?
endometriosis
tubal infections (PID)
previous ectopic pregnancy
previous tubal surgery
congenital strictures
one case of PID…
greatly increases risk of infertility
gold standard for assessing Fallopian Tubes?
laparoscopy
what is the imaging method of choice for fallopian tubes?
hysterosalpingogram (fluoroscopy)
what does SIS do?
saline infused sonohysterography (SIS)
avoids radiation exposure and helps visualize the tubes
what does visualization of fluid in cul de sac following an SIS mean?
demonstrates patency of at least one tube
what helps improve visualization of fluid flowing out of tube?
Color Doppler
what is a baseline sonogram?
done as part of initial workup
evaluates structures and do antral follicle count
when must a baseline sonogram be done?
preferred to do in first few days of cycle/ EARLY FOLLICULAR phase (around day 3)
we do baseline US on period/ late period because there is nothing going on hormone wise
MUST be done prior to any sort of medication treatment
what is in vitro fertilization?
fertilization of harvested oocyte by selected sperm in a petri dish
“test tube baby”
what are ART methods?
controlled stimulation of ovaries
intrauterine insemination
oocyte harvest from stimulated follicles
intracystoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
what is oocyte harvest from stimulated follicles?
IVF with embryo transfer
what is intracystoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)?
sperm is injected into oocyte
what does a baseline sonogram evaluate for?
uterine anomalies (fibroids, endometrial abnormalities, and congenital anomalies)
ovarian masses
PCOS
baseline antral follicle count
measure ovarian follicle
what are Clomid and Letrozole?
common fertility medications that stimulate secretion of FSH and LH from pituitary gland
what do hCG injections do?
helps induce/ force ovulation
what are progesterone suppositories?
support implantation and early pregnancy by improving receptivity of endometrium
what is the first step of fertility treatment usually?
ovulation induction with fertility medication like letrozole (aka femara)
what does ovulation induction result in?
a single dominant follicle
the ovulation induction technique is used on what women?
women who are anovulatory
draw serial blood samples to monitory hormone levels
do serial EV sonograms to monitor development of follicle
what is Controlled Ovarian Hyperstimulation (COH)?
used for couples with unexplained infertility
deliberately induce formation of multiple follicles for oocyte harvest or IUI
what is IUI?
want 3-4 follicles to develop and ovulate to improve chances of sperm finding one to fertilize
increase likelihood of multiple pregnancy
what is used in IUI?
use either clomid or gonadotropins
what is oocyte harvest?
use injectable gonadotropins
once follicles reach 16-20 mm diameter, use US guidance to aspirate oocytes from follicles
what does oocyte harvest have increased risk of? what is there no increased risk of?
Increased risk of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
No increased risk of high order multiples because not all eggs are fertilized/implanted.
for patients on clomid/ letrozole, may…..
may only do a single EV exam 5 days after last dose of medication to document follicle response
follicle should grow 1-2 mm/ day and should reach about 20 mm diameter at ovulation
for patients on injections…
closer monitoring is needed
medication dosage adjusted based on follicular response seen sonographically
ASRM recommends performing sonogram after 4-5 days of treatment and then every 1-3 days following depending on follicular response.
Important to monitor for OHSS & to time hCG injection
how do you measure ovarian follicles?
inner to inner
get average diameter by measuring length, width, and height. add them together and divide by 3.
when monitoring ovarian follicles, what follicles should be measured and reported?
measure and report mean diameters of each follicle greater than 10 mm
when should hCG injections be timed/ done?
when largest follicle has mean diameter of about 17 mm and other follicles are at least 15 mm
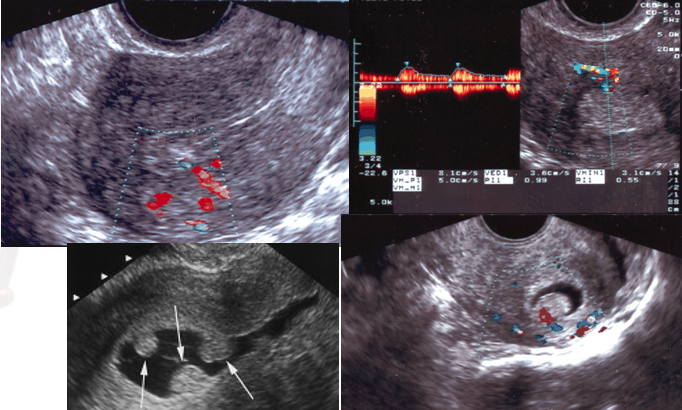
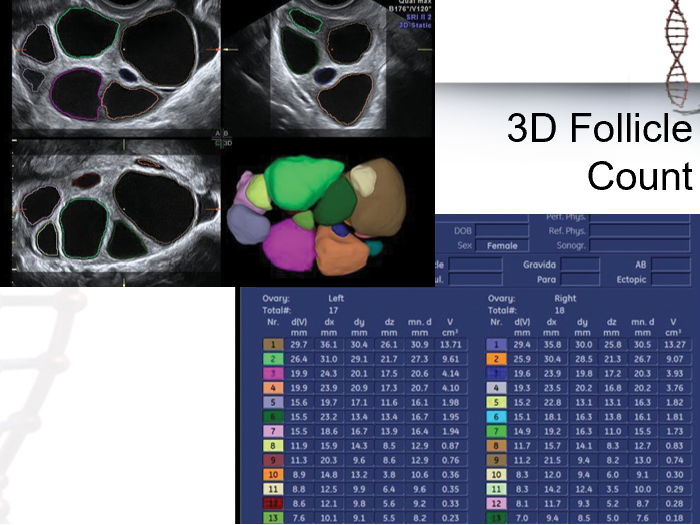
what does 3D US aid in with the monitoring of ovarian follicles?
automated measurement and counting of follicles
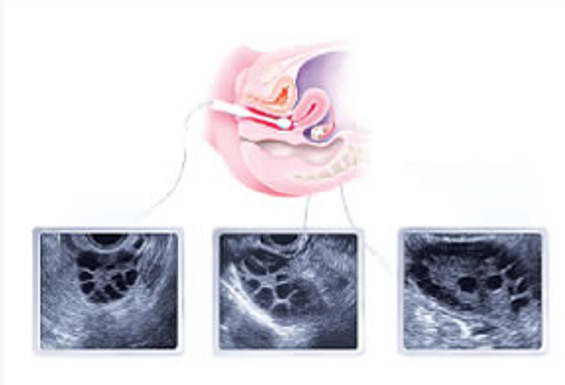
what is visualized?
controlled ovarian stimulation
understand 3D follicle count image:
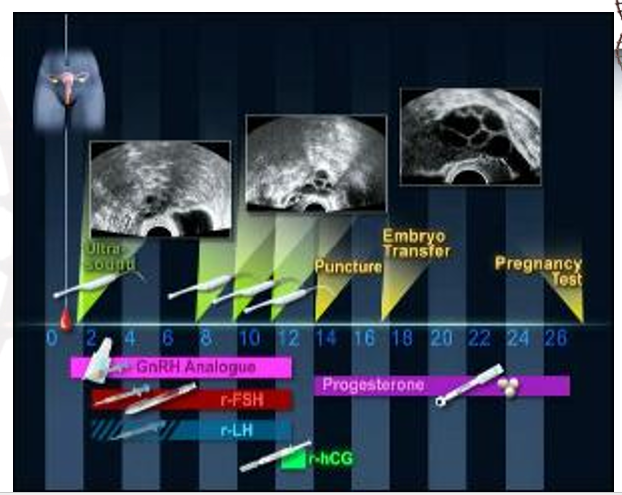
what occurs during the periovulatory period?
At mid-cycle, document follicle size and endometrial thickness and appearance.
When follicles reach desired size, hCG is injected to trigger ovulation for patients undergoing IUI or timed intercourse or to mature follicles for aspiration.
Ultrasound guidance is utilized for oocyte harvest.
what is ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome?
OHSS
serious complication
symptoms of Ovarian Hyperstimulation?
mild abdominal discomfort
hemodynamic shift resulting in massive ascites and pleural effusions
acute renal failure manifested as oliguria
in severe cases, what can occur in ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome?
ovaries will be very large (over 10 cm in diameter) and are at increased risk of torsion or rupture.
rupture and hemorrhage can be fatal
what should be done if OHSS is mild?
if severe?
if no pregnancy?
If mild, continue treatments and monitor
If severe, discontinue treatments, withhold hCG injection, monitor closely.
If no pregnancy, symptoms will resolve on their own.
Most often accompanies pregnancy, resulting in hospitalization & paracentesis with severe symptoms.
what is shown?
controlled ovarian stimulation
oocyte harvest is done under…
EV sonographic guidance using sterile technique
what occurs during embryo transfer?
After IVF or ICSI, zygote is incubated for 3-5 days before implantation.
Goal is successful singleton pregnancy
Done with sonographic guidance.
transabdominal approach with a full bladder.
some countries ban…
why?
anything more than one embryo transferred at a time
increases cost for patients if they dont have have a successful first time
reduces multiple pregnancy outcomes
in USA, typically how many embryos are implanted?
can be 1-5 embryos depending on patient’s age and history predicting likelihood of success.
TYPICALLY implant 1-2, rarely more than 3
how do we monitor success of implantation?
Regardless of technique, pregnancy test and/or sonogram are performed 1-3 weeks following ovulation, insemination, or oocyte harvest. (About 1-2 weeks after embryo transfer)
Of course, will monitor pregnancy throughout gestation as with any “high risk” pregnancy
when should you look for heartbeat in monitoring success of implantation?
6.5 weeks after LMP or 4 weeks after fertilization
what is multi-fetal reduction?
In cases of development of 3 or more embryos, couples may be counseled to abort all but 2 embryos.
Saline injected into gestational sac of embryos who are smaller or who are easier to access.
Done with sonographic guidance.