Biochemistry L3 & L4
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
"What percentage of organisms is composed of water?"
"70-90%"
"What type of bond exists within a water molecule (intramolecular)?"
"Polar covalent bond"
"What type of bond exists between water molecules (intermolecular)?"
"Hydrogen bond"
"Define hydrophilic and hydrophobic."
"Hydrophilic: Molecules attracted to water
Hydrophobic: Molecules repelled by water"
“Why is water needed for its solvency?”
It is because the polarity and hydrogen bonding is highly needed for chemical processes to occur.
"What property allows water to transport nutrients in organisms?"
"Cohesion (H-bonding between water molecules) and adhesion (clinging to polar surfaces)."
"What is surface tension in water?"
"Water molecules at the surface cling tightly due to hydrogen bonding
"Why does water have high heat capacity?"
"Hydrogen bonds absorb heat without large temperature changes. The heat is absorbed and converted into energy to break the many bonds between water molecules, hence not being subjected to huge temperature changes.”
"How does sweating cool the body?"
"High heat of vaporization: Breaking H-bonds during evaporation dispels heat, reducing internal temperature of the body."
"Why does ice float?"
“ Water expands during freezing, the hydrogen bonds push away the water molecules during expansion, causing the water molecules to form a hexagonal lattice structure, which makes the ice less dense than water, allowing the ice to float on water.”
"What defines an acid?"
"Releases H⁺ ions when dissolved in water (pH < 7)."
"What defines a base?"
"Releases OH⁻ ions when dissolved in water. (pH > 7)."
"What is the pH range for human blood?"
"7.4 (slightly basic)." Anything below 6.8 or higher than 7.8 is considered dangerous (leads to metabolic acidosis.
"How do buffers maintain pH?"
"Resist changes by absorbing excess H⁺ or OH⁻ (e.g. Carbonic Acid Formation in the body.”
"What happens if blood pH drops below 6.8 or rises above 7.8?"
"Death can occur due to enzyme denaturation and metabolic failure."
"Why is carbon the backbone of life?" (Roles/Characteristics of Carbon)
“Carbon is able to form 4 bonds with its free 4 valence electrons. Carbon is also able to form non-polar or polar covalent bonds between molecules. Carbon is also able to bond to each other to form long chains or rings of carbon, which serves as the backbone of many organic molecules.”
"What are functional groups?"
“ Functional groups are a specific combination of atoms that always has the same chemical properties and react the same way. The way that Macromolecules or Organic Compounds react is largely reliant on its functional group.
"Name the 4 biological macromolecules."
"Carbohydrates, Proteins, Nucleic Acids and Lipids.”
"What is the general formula for carbohydrates?"
"(CH₂O)ₙ (1:2:1 ratio of C:H:O)."
"Compare healthy vs. unhealthy carbohydrate sources."
Healthy carbohydrate sources include whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, which provide essential nutrients and fiber. Unhealthy sources are refined grains and added sugars, which can lead to poor health outcomes.
"What are the 3 types of carbohydrates?"
"Monosaccharides , Disaccharides and Polysaccharides”
"Name 3 hexose monosaccharides."
"Glucose, Fructose, Galactose.”
"What is the role of glucose?"
"Primary energy source for processes in the body. Glucose is broken down into energy to produce ATP from Cellular Respiration. (broken down into ATP via respiration)."
"How are disaccharides formed?"
"Dehydration synthesis/Condensation Reaction: Glycosidic bond links 2 monosaccharides (loses H₂O)."
"Name 3 common disaccharides."
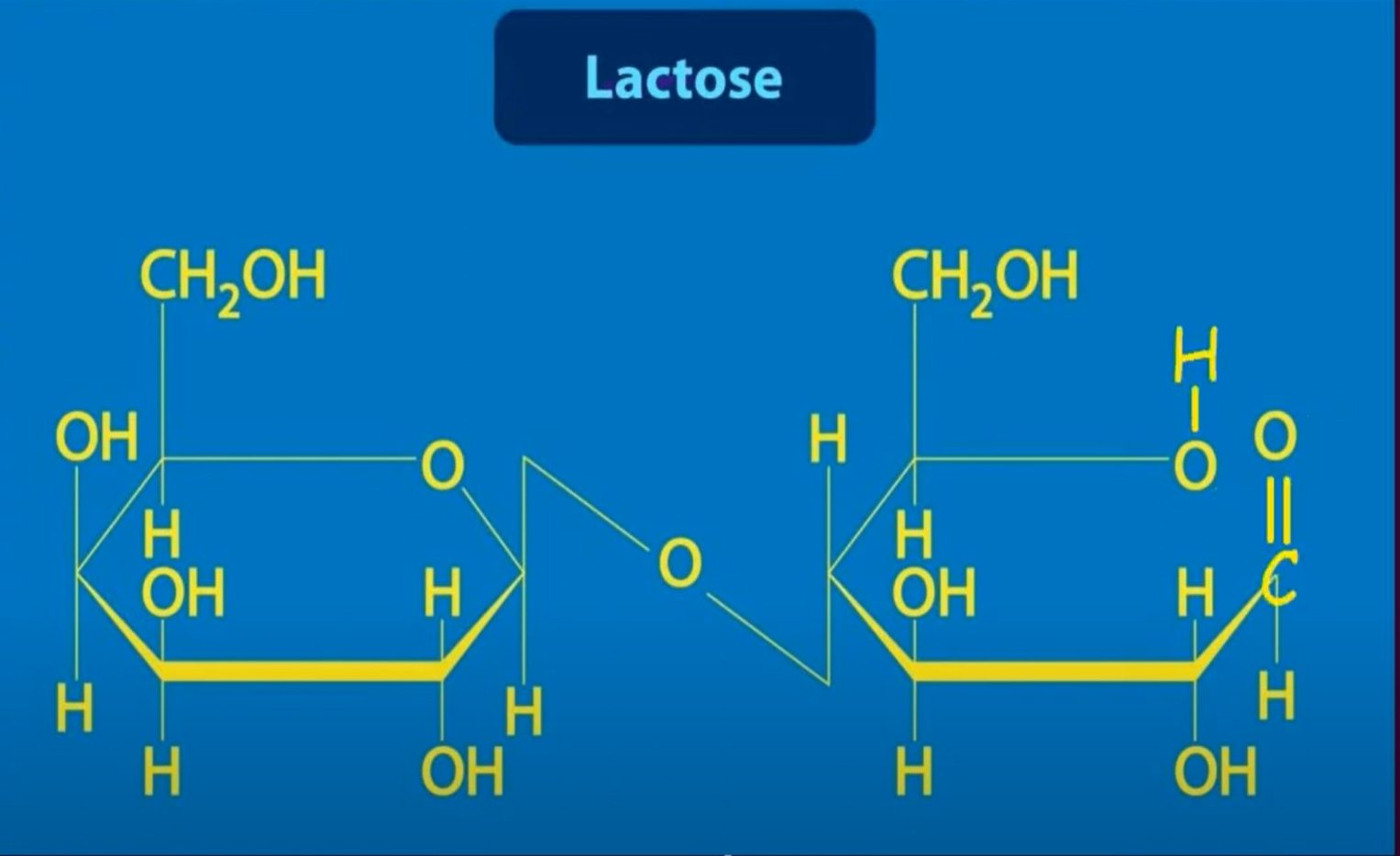
"Sucrose (glucose+fructose), Lactose(glucose+galactose), Maltose (glucose+glucose)
"Why must disaccharides be broken down?"
"Only monosaccharides can be used for energy (e.g. glucose), as larger sugars cannot be directly utilized.
"What polysaccharide do plants store?"
"Starch (α-glucose polymers)" and Cellulose (β-glucose polymers) are common polysaccharides in plants.
"What polysaccharide do animals store?"
"Glycogen (highly branched α-glucose)."
"How does cellulose differ from starch?"
“Cellulose is made out of β-glucose polymers while starch is made out of α-glucose polymers. Cellulose is also mainly used for structural properties like synthesis of the cell wall, while starch is used as food storage for a plant. Cellulose doesn’t have a coiled or branched structure like starch due to its alternating glucose molecule structure and the lack of the presence of 1-6 glucose molecules.”
"What is chitin?"
‘ made out of glucose monomers with modified form of cellulose with nitrogen component(amyl group) : found in insect exoskeletons/fungal cell walls."
"What defines a reducing sugar?"
A reducing sugar is a sugar that acts as a reducing agent, can be oxidized by oxidizing agents and has a free aldehyde or ketone group that can donate electrons to other molecules.
"Name two reducing disaccharides."
“ Maltose and Lactose (Sucrose is not a reducing sugar)”
"Why is sucrose non-reducing?"
"Its glycosidic bond locks the aldehyde/ketone groups
- more in depth:
Fructose / glucose in the sucrose molecule will not be able to open up into the linear form to provide a free ketone/aldehyde for reducing properties due to the acetal formation, preventing oxidation.
"What is the structural role of polysaccharides?"
"Cellulose (plant cell walls)”
"How do α and β glucose differ?"
"OH group position: α (down) β(up)”
"What is the primary energy storage in liver/muscles?"
"Glycogen which is broken down to glucose to produce ATP from cellular respiration."
"How do hydrogen bonds stabilize water’s properties?"
"Enable cohesion and adhesion between water molecules and other polar molecules.”
"What happens to carbon skeletons of monosaccharides?"
"Used to synthesize other molecules (e.g.
"Why are enzymes sensitive to pH?"
"pH changes alter enzyme shape/function (denaturation)."
"What is the role of the bicarbonate buffer system?"
"Maintains blood pH by converting excess H⁺ to H₂CO₃ (and vice versa)."
"How does water’s polarity enable solvency?"
"Partial charges attract and dissolve ions/polar molecules."
"What are oligosaccharides?"
"Short chains of 3-10 monosaccharides (e.g.
"Why is glycogen highly branched?"
"Increases solubility and allows rapid glucose release when needed." Glycogen is also highly branched as every glucose unit is connected by alpha-1,4-glycosidic bonds with branches formed by alpha-1,6-glycosidic bonds, every 10 subunits compared to amylopectin with it branching out every20 subunits, branching out way less often than glycogen enhancing its efficiency as an energy reserve.
"How do plants and animals differ in polysaccharide storage?"
"Plants: Starch (amylose/amylopectin). Animals: Glycogen (more branched)."
"What happens if the carbonic acid-bicarbonate equilibrium shifts?"
"Respiratory/metabolic acidosis/alkalosis (pH imbalance)."