Critical Care Exam 2
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What are the causes of elevated ICP?
increased brain volume (cerebral edema), increase in CSF, or an increase in blood volume.
How is Cerebral Perfusion Pressure (CPP) calculated?
MAP-ICP=CPP
What is the Glasgow Coma Scale?
A scale used to assess a patient's neuro function by assessing their eye opening, verbal response, motor response.
What GCS score is consistent with a coma?
3-8
As the nurse what should you do if your pt has a GCS of less than 5?
call the Indiana donor network (IDN) for possible organ donation.
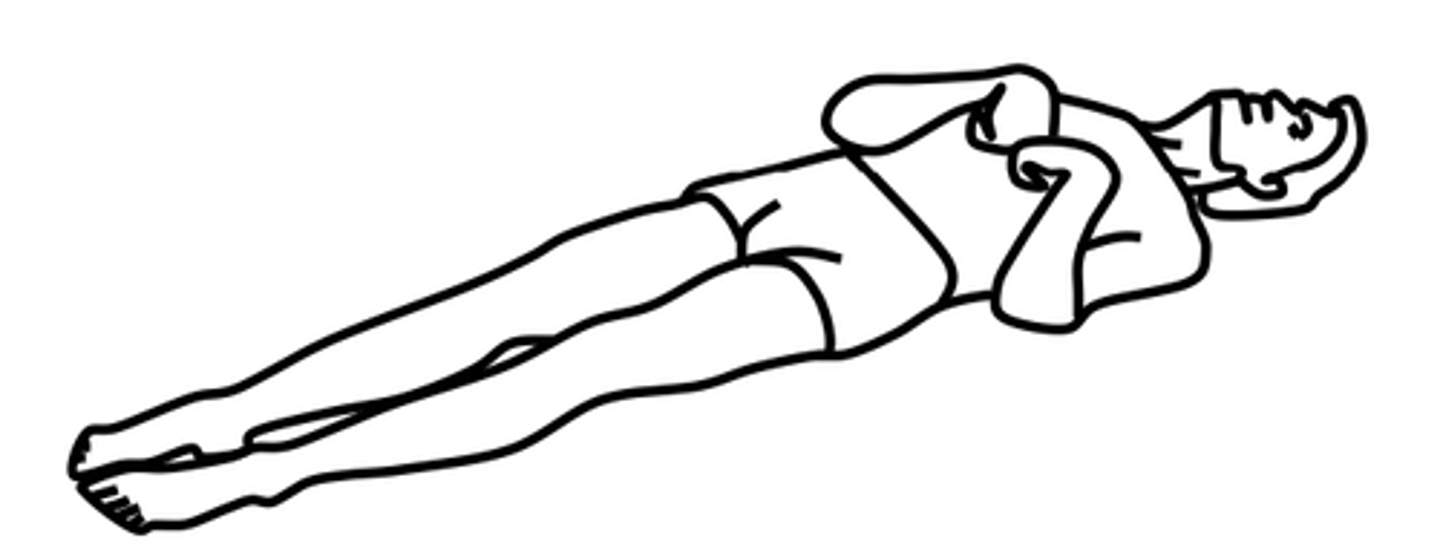
What is decorticate posturing?
Hands pulled to chest and hyper-extended. Internal rotation and adduction of the arms with flexion of the elbows, wrists & fingers.
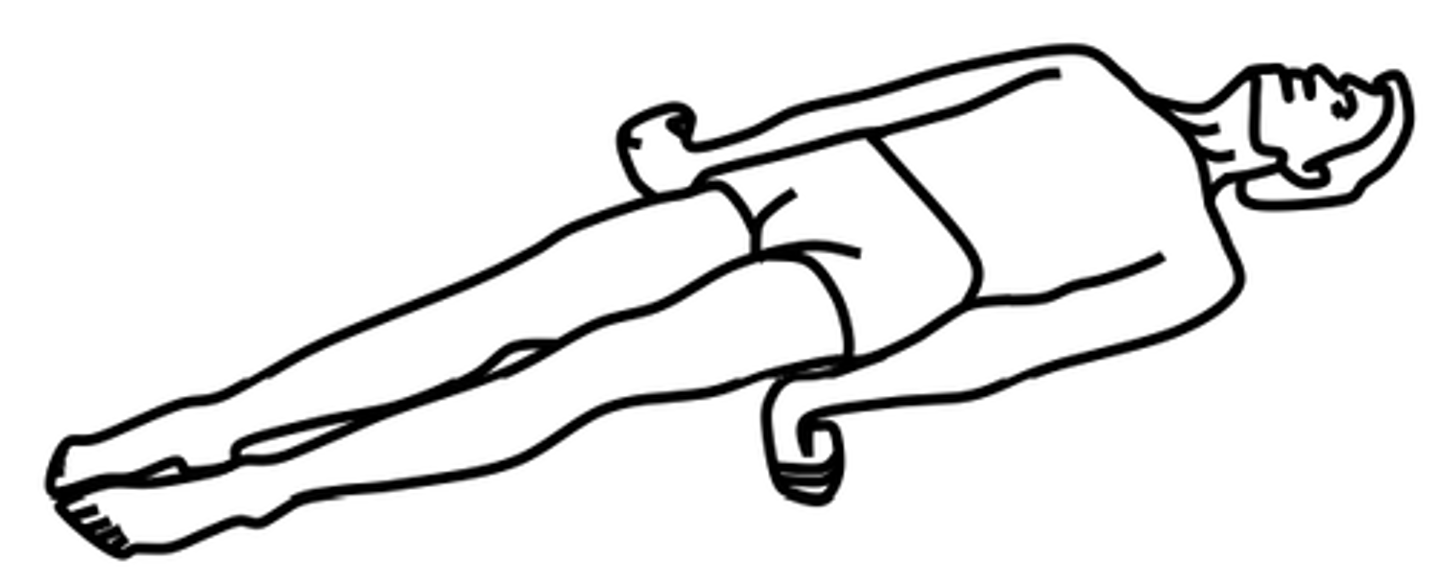
What is decerebrate posturing?
Abnormal body posture involves the arms and legs being extended straight out, the total is being pointed downward, and the head and neck being arched backwards.
What is the care of a client with an ICP monitoring device?
positioning: head of bed elevated to 30 degrees if appropriate. avoid trendelenburg's position.
moving: prevent flexion of the neck and hips. maintain neutral position of the head, prevent shivering.
stimulation: decrease environmental stimuli.
What is the normal value of ICP?
0-15 mmhg
What is considered an elevated ICP?
greater than 20 mmhg for 5 minutes or more
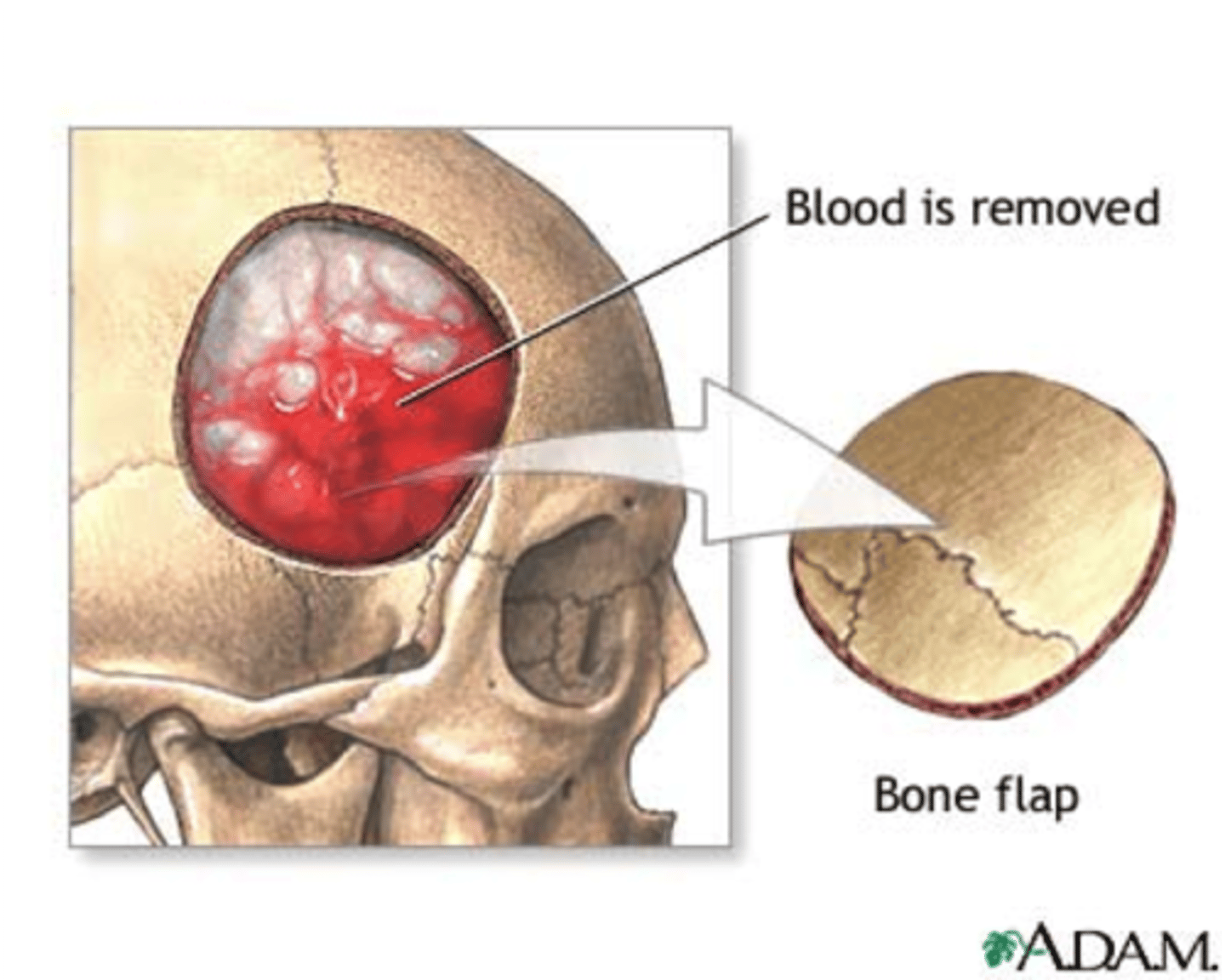
What is a craniotomy?
evacuate hematomas, remove bone fragments, remove foreign objects, by removing a portion of the skull to expose the brain
What is mannitol?
osmotic diuretic used to lower ICP. works by pulling water from the extracellular space into the vasculature. causes diuresis.
What are corticosteroids?
used to stabilize the cell membrane and reduce the leakiness in the blood-brain barrier. this decreases cerebral edema. clients must be tapered off of corticosteroids
What are anticonvulsants used for in ICP?
given prophylacticly to avoid seizures. examples of med: phenytoin, fosphenytoin, levetiracetam
Why are antipyretics and muscle relaxers given for ICP?
given to decrease temperature, decrease metabolism, decrease shivering.
examples of meds: acetaminophen, diazepam
Why are vasoconstrictors given for ICP?
given to maintain good cerebral perfusion pressure (above 70 is goal).
example of meds: norepinephrine, dopamine
What paralytic agents are given for ICP and what is the assessment for them?
cisatracurium. train of four assessment is done and 2 out of 4 twitches are goal.
What are the sedation agents given for ICP and what assessment is done for them?
propofol, lorazepam. BIS monitoring is done for these medications and goal is 40-60
What are the analgesics given for ICP and what assessments are done for them?
fentanyl, codeine. pain assessments are done for these medications using the FLACC scale. Respiratory assessments are also important.
What are the different types of ICP monitors?
Intraventricular catheter/ external ventricular drain (allows drainage), subarachnoid bolt (no drainage), epidural sensor (no drainage), Parenchymal Fiberoptic Catheter.
What is a subarachnoid bleed?
A brain bleed in the subarachnoid space caused by a traumatic injury, this increases the risk of vasospasm.
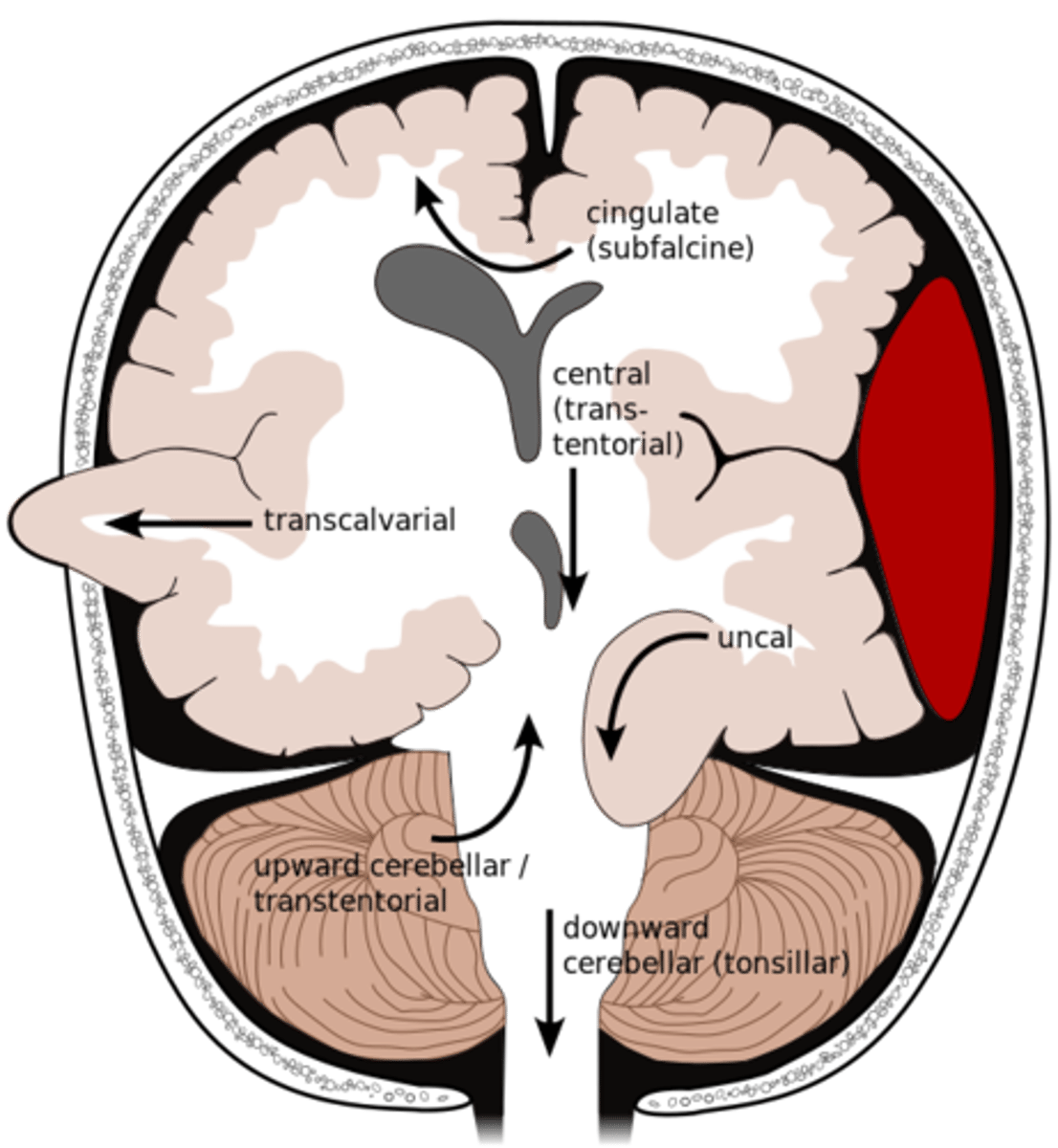
What is an uncal herniation?
most common.
unilateral lesions forces uncus of temporal lobe to displace and compress on the midbrain.
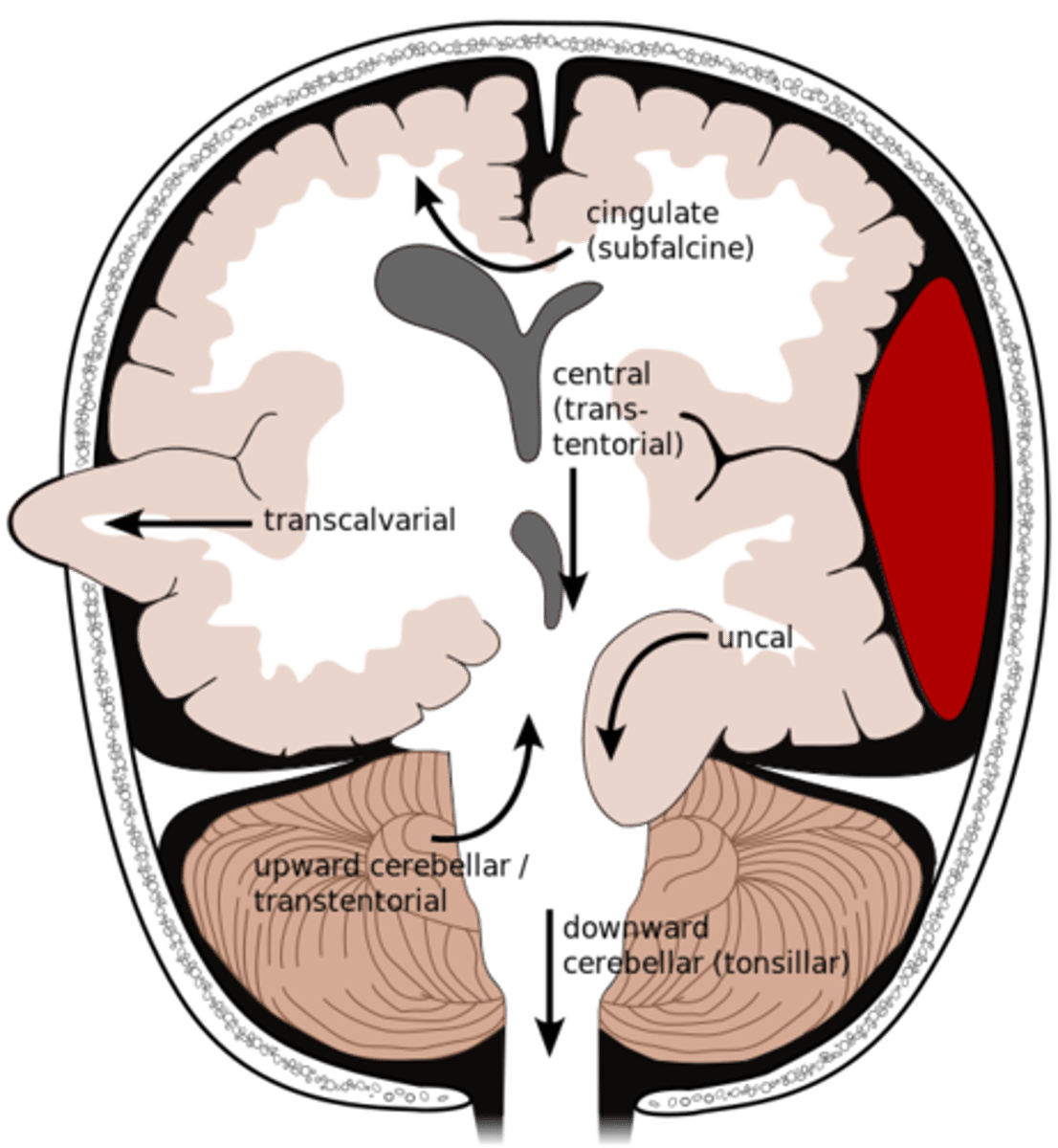
What is a central herniation?
Downward shift of cerebral hemisphere, compressing the brainstem
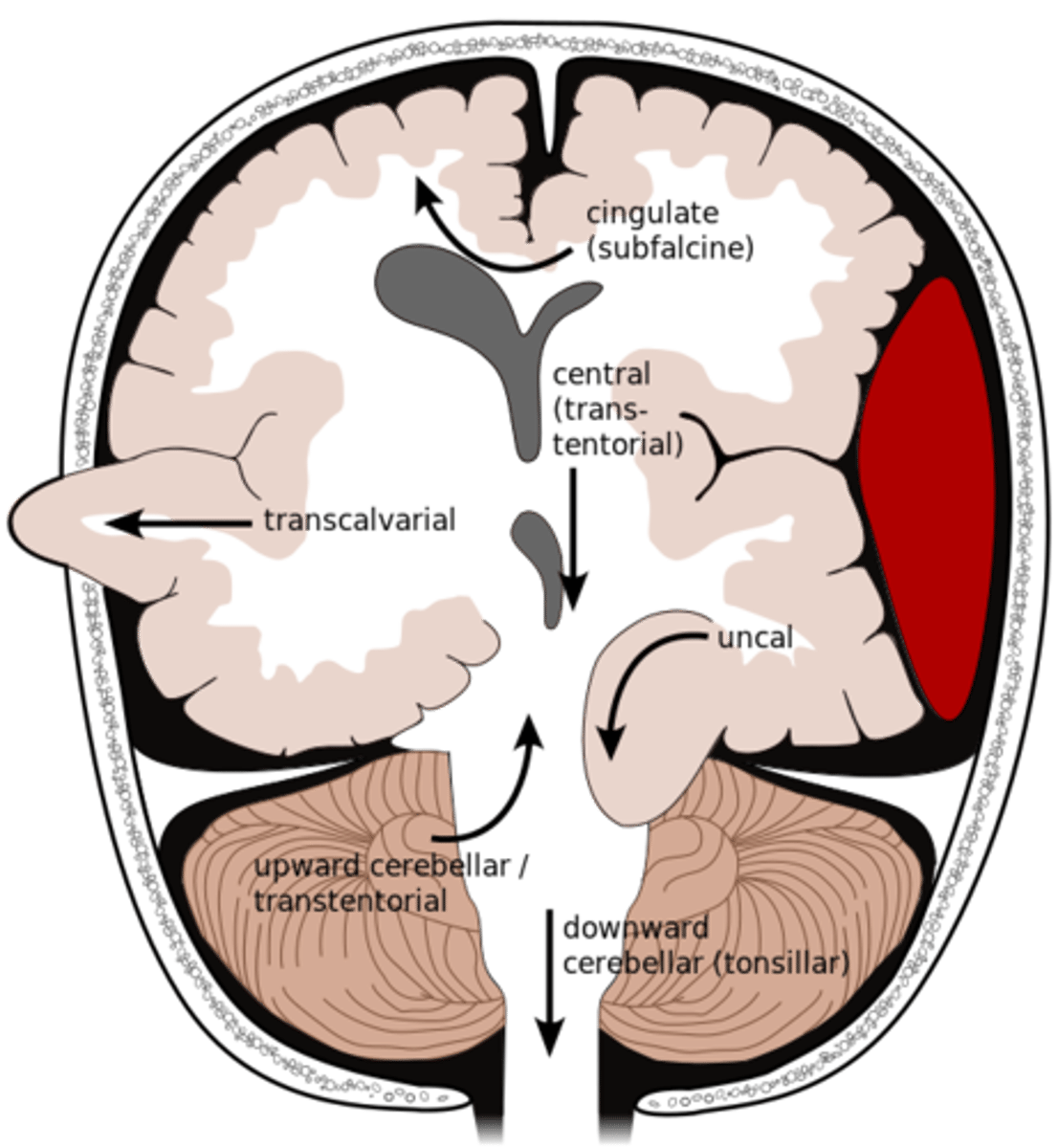
What is a cingulate herniation?
shift of brain tissue from one hemisphere to the other. Compress anterior cerebral artery.
Ischemic stroke may occur
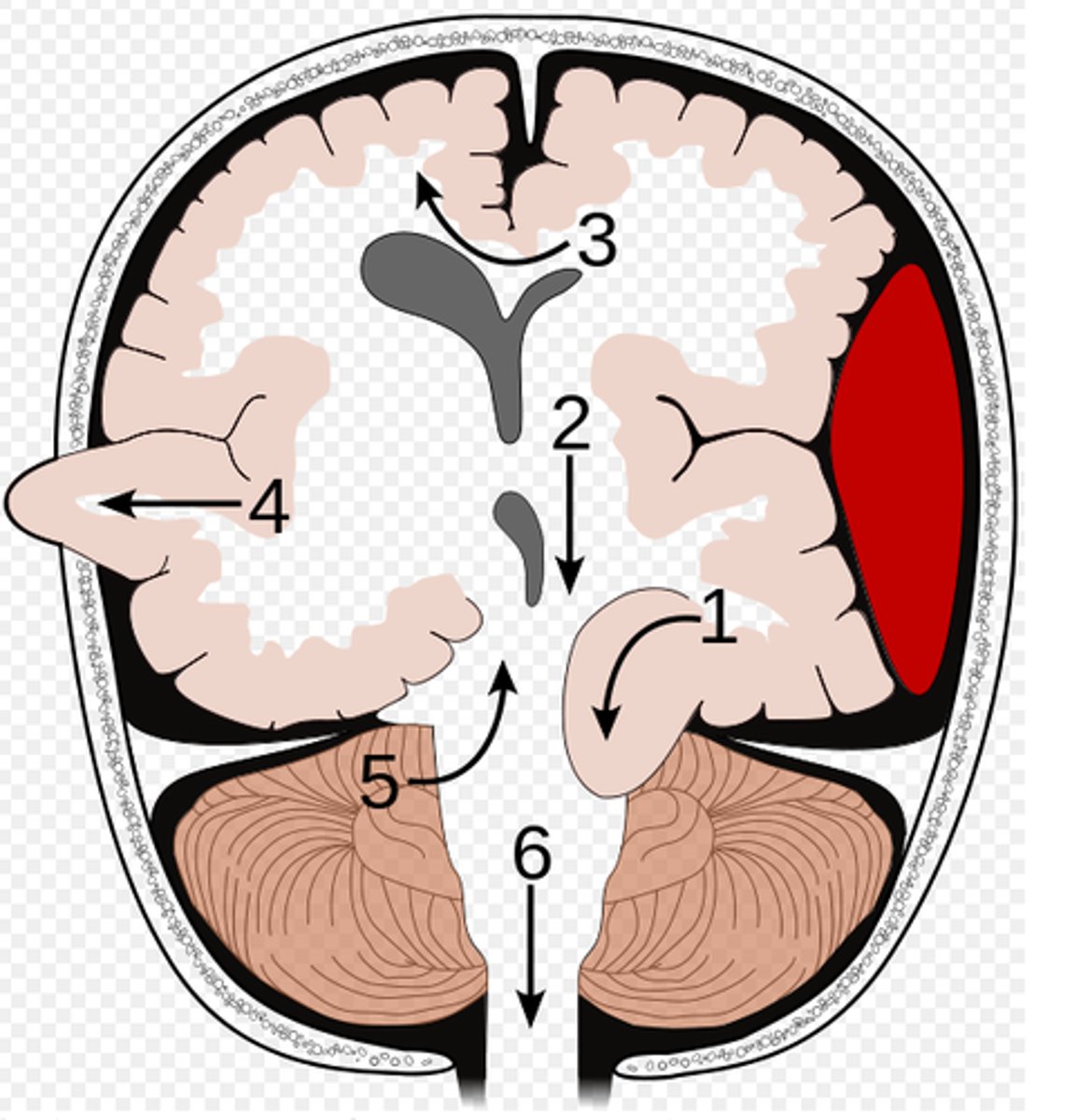
What is a transcalvarian herniation?
brain begins to herniate outside of the skull. the brain will squeeze out of fractures, burr holes, or surgical incisions.
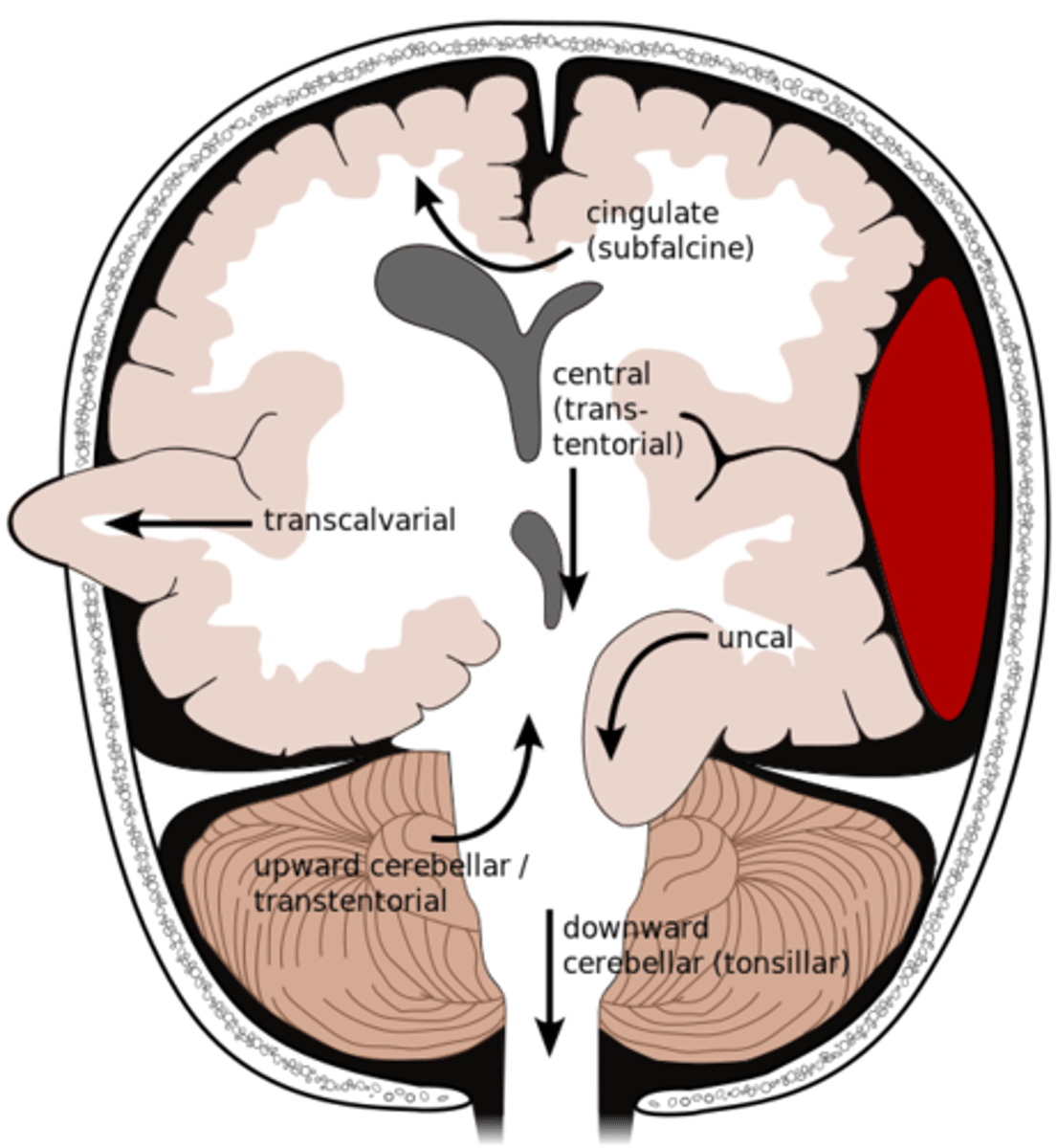
What is an upward herniation?
displacement of the cerebellum upward
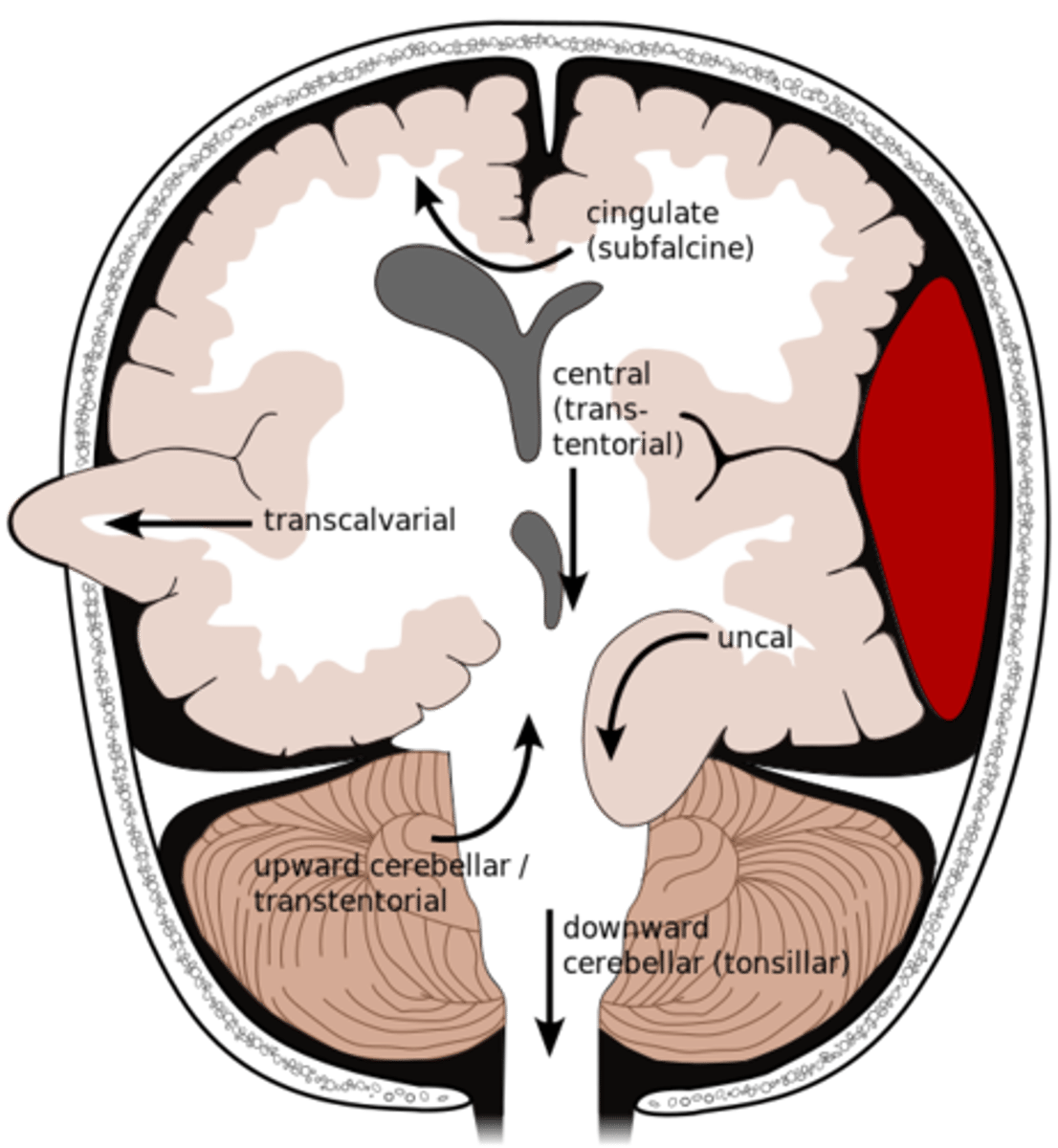
What is a cerebellar Tonsillar herniation?
displacement of cerebellar tonsils downward this compressing the pons/medulla
s/s: alterations in resp. and cardiac functions- rapidly progressing to cardiac arrest, Headache and neck stiffness, reduced muscle tone
What are dolls eyes and what does it tell us?
turn patient's head side to side while eyes are open, reflex is intact if eyes move opposite direction of head, reflex is if they do not move their eyes.
What are the most concerning signs and symptoms of a closed head injury?
abnormal respiratory patterns,
What is basilar skull fracture?
linear fracture at the base of the skull
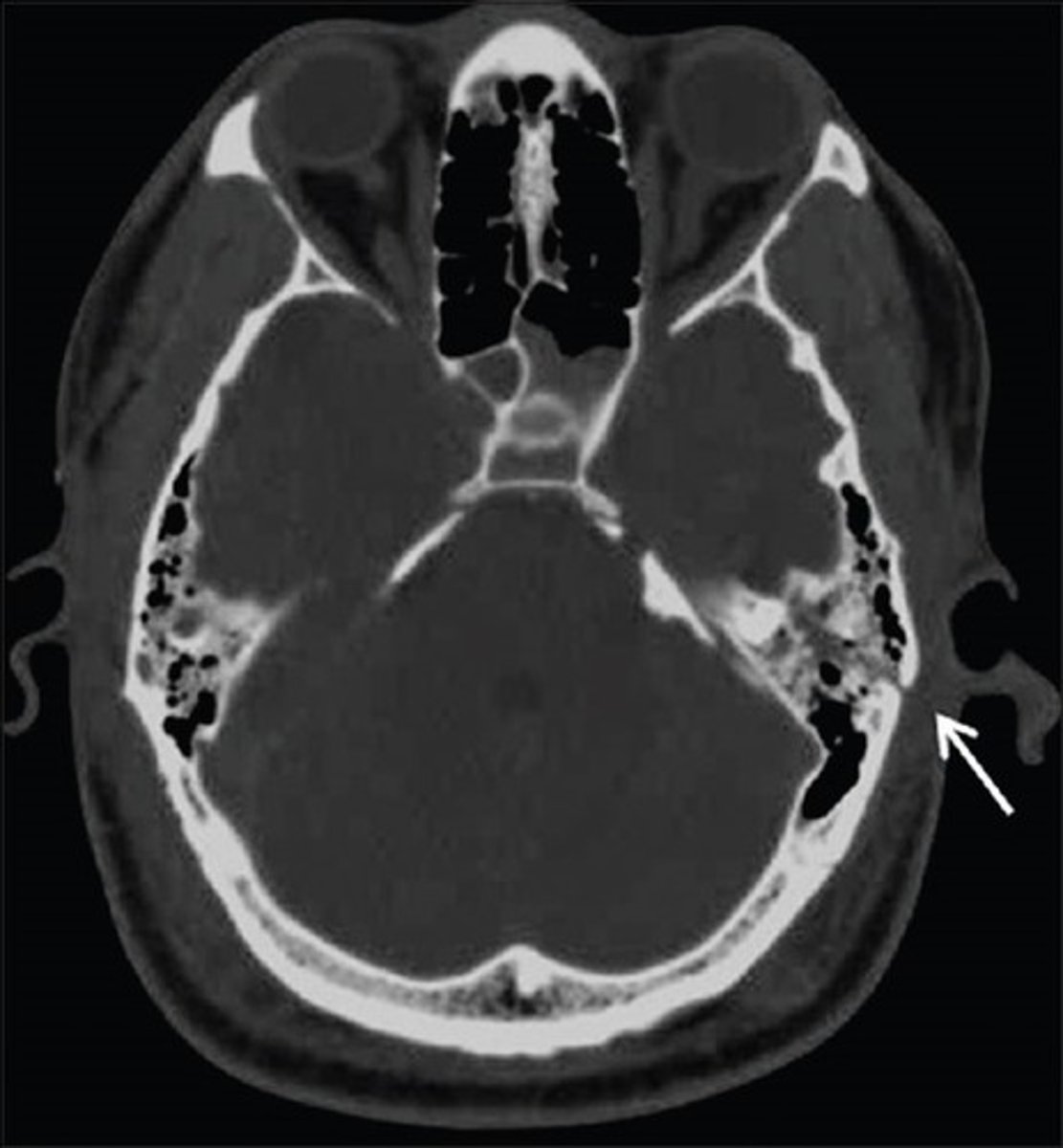
What are the signs and symptoms of a basilar skull fracture?
raccoon eyes (bruising around eyes), battles sign (bruising behind the ears), CSF leaking from the ears and/or nose.
What is the difference between an acute and a chronic subdural hematoma?
Acute: Within 48 hours and almost always seen with cortical or brainstem injury. Risk of death is high from injury to brain tissue and expanding hematoma. Surgical intervention probable.
Chronic: 2 weeks to several months after. Seen in the elderly, chronic alcohol abusers, and on anticoagulants/antiplatelets
From low velocity impact.
What is mannitol?
osmotic diuretic given for increased ICP. Pulls water from tissues to vessels. Monitor renal function, electrolytes, and serum osmo levels q6.
What should be monitored while giving mannitol?
hourly neuro assessments, ICP, CPP, serum osmolarity, electrolytes, ABGs, I/Os, VS.
What is the priority intervention for a severe TBI?
Reduce ICP, maintain airway, maintain CPP, prevent secondary brain injury, normothermia, surgical interventions, HOB 30
What interventions should you avoid with TBIs?
Trendelenburg, suctioning, pressure on abdomen, valsalva, straining, coughing, sneezing, monitor V/S, avoid narcotics, maintain nutrition.
What is an ischemic stroke?
strokes caused by blockage or interrupted blood supply to the brain by plaque or emboli. EX: Large Artery Atherosclerosis, Cardioembolic, Lacunar stroke, Crytogenic stroke.
What is a TIA?
signs and symptoms of a stroke are present due to decreased cerebral blood flow, but symptoms resolve within 24 hours. found with CT scan
What is a hemorrhagic stroke?
intracerebral: bleeding into the brain tissue
Ruptured cerebral aneurysm: dilation of a section of an artery that causes the vessel wall to weaken.
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM): miscommunication between the artery and the vein.
What is the NIHSS?
National Institute of Health Stroke Scale. used to assess the severity of a stroke.
What is the physical assessment of a stroke patient?
NIH, neuro checks, knowing where the stroke is in the brain will help with the assessment.
LEFT: language, math, and analytic thinking, Aphasia, agraphia, right weakness, slow caution behavior, quick to anger, visual changes.
RIGHT: visual and spatial awareness, overestimation of abilities, loss of depth perception, poor impulse control, left sides weakness, visual changes.
What diagnostic tests can be used for stroke?
CT without contrast, EKG, NIH, CBC, MRI, PT/INR, BMP, cardiac enzymes.
What is the treatment for ischemic stroke?
tPA can be given as treatment within 4.5 hrs of symptom onset. permissive HTN with tPA is SBP<185.
when tPA cannot be given permissive HTN is <220. need to maintain glycemic control, anticoagulants, NPO until swallow screen is complete.
What is the criteria for tPA to be given?
Able: less than 4.5 hrs from onset, older than 18, CT scan shows ischemia, measurable deficits.
Not able: more than 4.5 hrs from onset, rapidly moving, current hemorrhage or bleeding, recent head trauma, recent cns surgery, severe HTN
What is the treatment for a hemorrhagic stroke?
control HTN (MAP <130), reverse anticoagulants (Vit K, fresh frozen plasma), surgery (remove hematoma, external drain, decompressive hemicraniotomy, aneurysm coil or clip).
What are the possible complications of stroke?
hydrocephalus (increased ICP), Seizures can onset within 7 days, infection, intracerebral hemorrhage.
What are the different types of seizures?
focal: onset one side of brain, will experience aura.
focal motor: twitching, shaking, stiffening, or rubbing hands.
Focal non-motor: changes in senses, emotions, or thinking.
Alcohol withdrawal: brief, generalized, 30-50% become delerium tremors within 24 hr of last intake.. Can also be seen with barbituates or benzos
What is the assessment of a patient with seizures?
neuro (types of movements, aura, pupil changes, response to speech and touch, awareness of surroundings, LOC), respiratory, cardiovascular.
What should the nurse do when a patient is experiencing a seizure?
maintain airway and oxygenation, pad bedrails, turn pt to side.
What is the treatment for seizures?
lorazepam, levetiracetam, phenytoin
What is status epilepticus?
characteristics: More than 30 minutes or repeat for more than 30 minutes.
Causes: Tonic/clonic, Irregular epileptic drug use, ETOH withdrawal, drug withdrawal, head trauma
What are some causes of a spinal cord injury (SCI)?
MVC, falls, violence, sports, diving
What are the different types of SCI?
Complete: total loss of sensory and motor function
Partial: central (Incomplete loss of motor function), anterior (Loss of motor, pain, and temp), brown-sequard (Loss of motor, vibration, position, deep/light touch, pain, temp on opposite site)
What is the relationship of location of injury to functional loss?
more functionality is lost the higher the injury is on the spinal cord.
What is the medical management for spinal cord injuries?
corticosteroids: used for anti inflammatory and edema reducing effects, may interfere with healing.
muscle relaxers: used for clients with upper motor neuron injuries, helps control muscle spasticity.
vasoconstrictors: used to maintain perfusion to spinal cord (goal is to maintain map >85 for the first week post spinal cord injury)
What are the different system complications associated with spinal cord injury?
respiratory, neuro, hemodynamic, bowel, bladder, skin, psychosocial.
What is spinal shock?
complete loss of motor, sensory, and reflex. hypotension, usually occurs with injury above T6, can last weeks to months
What is neurogenic shock?
Disruption of ANS below level of injury
Loss of sympathetic input: vasodialation, hypotension, bradycardia, hypothermia
What is the treatment for neurogenic shock?
Pacemaker if symptomatic bradycardia
Resolves with sympathetic tone
What is autonomic dysreflexia?
a life-threatening emergency in spinal cord injury patients that causes a hypertensive emergency; it occurs AFTER spinal shock has resolved; the symptoms are severe headache, diaphoresis, nausea, nasal congestion, and bradycardia
What is the treatment for autonomic dysreflexia?
Controlled temp and relieve tight clothing, kinks in catheter, urine blockage, elevate HOB. meds: nitrates and nifedipine
What is a halo?
Static traction, headpiece with 4 pins into skull to give more mobility. Monitor neuro status or changes in movement
What is the management of a halo?
do not hold or pull, assess skin integrity.
Pin care: clean as prescribed, keep key close IOE, notify PCP if halo loosens or redness/swelling/drainage. Use foam to relieve pressure
What is the management of tongs?
Weights attaches as countertraction
Monitor neuro status, must hang freely, ropes remain in pulley, maintain body alignment, do not remove traction
What are the pharmacological and mechanical treatments for lethal arrhythmias?
Pharmacological: Epinephrine, amiodarone, vasopressin.
Mechanical: CPR, maintain airway, defibrillation
What are the components of cardiac output and how does the body compensate?
What are the dysrhythmia's effect on hemodynamics?
lowering CO because of the decreased filling time from increased heart rate
What are the mechanisms of neurogenic shock?
widespread vasodilation/ caused by spinal cord injuries, anesthesia complications / correct with fluids and pressors, cardiac parameters all low