5 Peds Exam 1 (Lec 5): Prevention and Interception of Malocclusion
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
•Hypophosphatasia
•Down Syndrome patients with periodontal disease
•Chronic mercury poisoning ( acrodynia)
What are 3 conditions that can result in a generalized loss of primary teeth?
-Muscle forces from the lips, cheeks and tongue
-Occlusal forces
-Eruptive forces
What are the 3 forces that act on a tooth?
supra-erupt
when one tooth is prematurely missing, what action with the opposing tooth do?
drift/tip mesially
when one tooth is prematurely missing, what action will the tooth distal to the space do?
drift/tip distally
when one tooth is prematurely missing, what action with the tooth mesial to the space do?
drift/tip mesially
When a tooth has SEVERE distal caries, what action with the tooth distal to the space do?
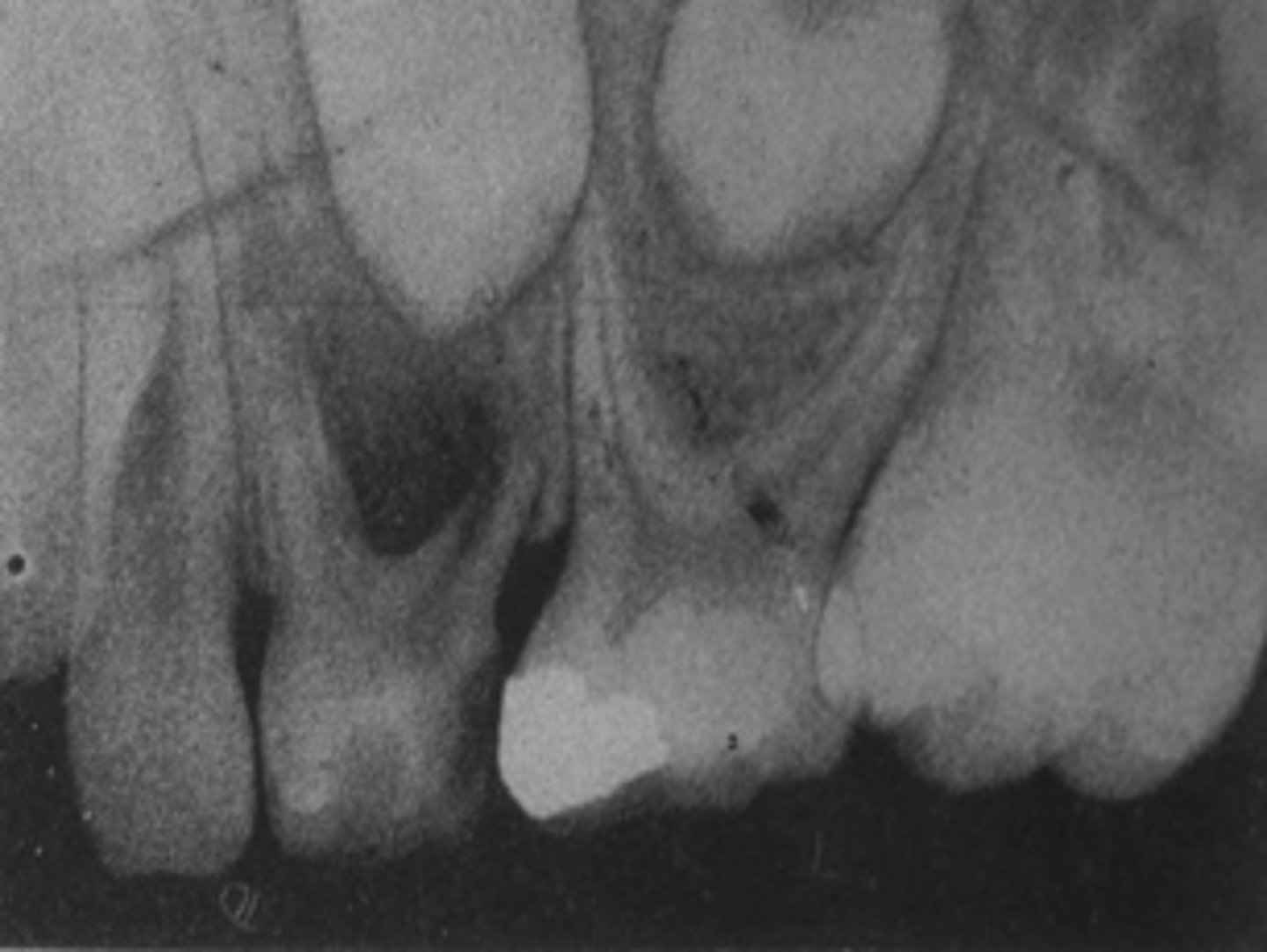
no space maintainer needed
When a primary molar tooth has to be extracted before 1st permanent molar erupts, what should you also recommend?
loss of space
When a patient experiences a premature loss of a primary anterior incisor, all of the following are concerns EXCEPT:
- loss of space
- delay of permanent incisor eruption
- speech
- esthetics
- tongue thrusting
D, L, N, T
When a patient experiences a premature loss of a primary anterior incisor, what letters will they experience difficulty pronouncing?
canines
premature loss of which primary anterior teeth will result in shifting and loss of space?
- central incisors
- lateral incisors
- canines
no space maintainer required
Indicate if a space maintainer is needed when there is early loss of the maxillary 1st primary molar:
-Before the eruption of the Maxillary 1st permanent molars
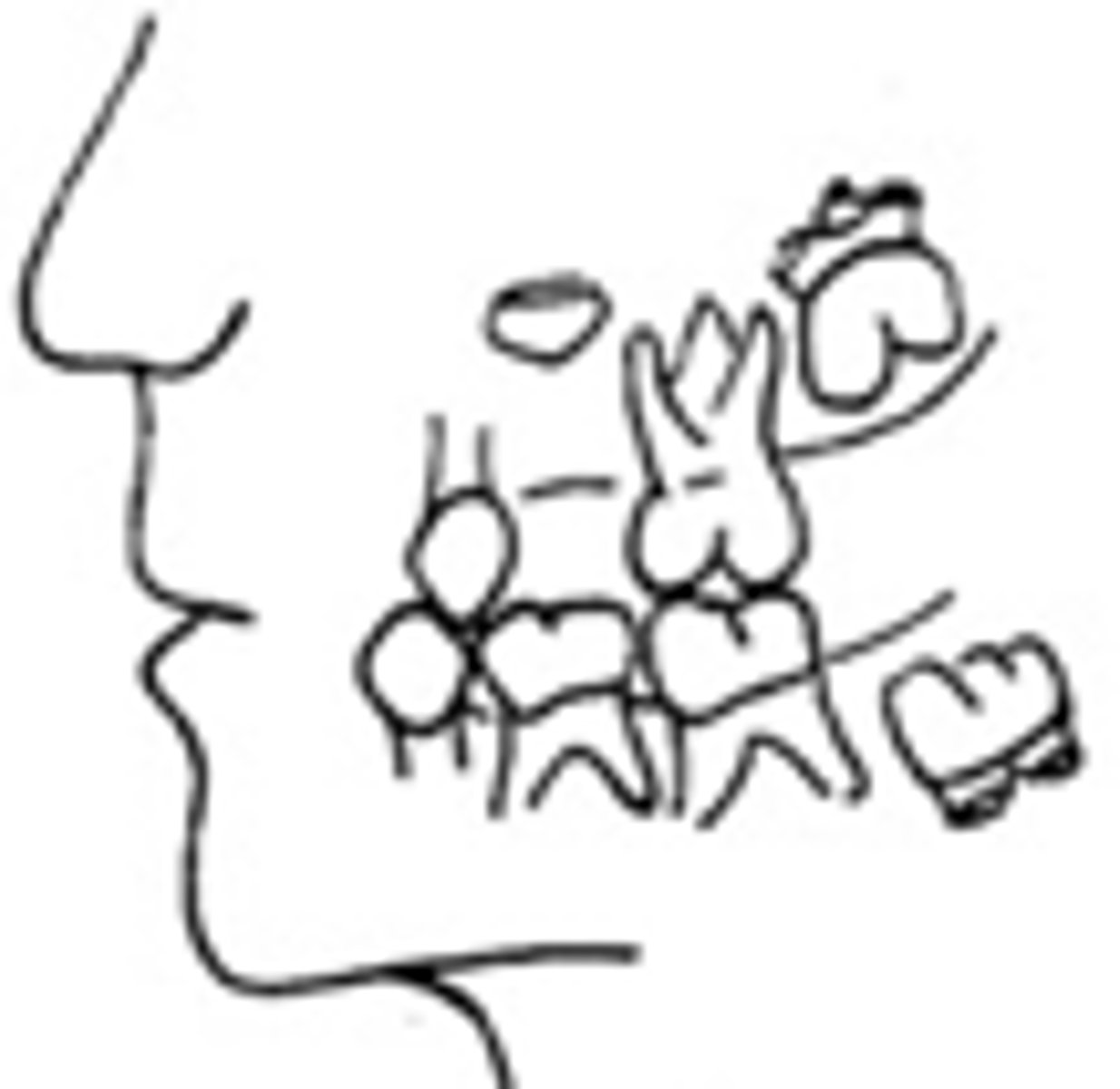
space maintainer required
Indicate if a space maintainer is needed when there is early loss of the maxillary 1st primary molar:
•During the eruption of the Maxillary 1st permanent molars
no space maintainer required
Indicate if a space maintainer is needed when there is early loss of the maxillary 1st primary molar:
•After the eruption of the maxillary 1st permanent molar, occluding opposite arch
no space maintainer required
Indicate if a space maintainer is needed when there is early loss of the maxillary 2nd primary molar:
•Before the eruption of the 1st maxillary permanent molar
space maintainer required
Indicate if a space maintainer is needed when there is early loss of the maxillary 2nd primary molar:
•During the eruption of the 1st maxillary permanent molar
space maintainer required
Indicate if a space maintainer is needed when there is early loss of the maxillary 2nd primary molar:
•After the Eruption of the 1st maxillary permanent molar, full occlusion
maxillary central incisors
what is the 1st most common permanent tooth that experiences early loss?
mandibular first permanent molar
what is the 2nd most common permanent tooth that experiences early loss?
maxillary first permanent molar
what is the 3rd most common permanent tooth that experiences early loss?
true
t/f: if a patient looses a permanent central incisor, you would be concerned about mesial shifting
false
t/f: if a patient looses a primary central incisor, you would be concerned about mesial shifting
1st and 2nd bicuspids
if the maxillary or mandibular 1st permanent molar is missing, which teeth would experience distal drifting and/or tipping
between cuspid and bicuspids
if the maxillary or mandibular 1st permanent molar is missing, where would you expect loss of interproximal contact?
the opposing 1st molar
if the maxillary or mandibular 1st permanent molar is missing, what tooth would experience supra-eruption?
space maintainer
The objective of these devices is to retain the original available space and allow proper eruption and position of all succedaneous teeth
•A passive treatment
•To intervene when there is an untimely tooth loss
•To prevent or reduce the severity of tooth migration arch space reduction malocclusion of permanent dentition (crowding, impaction, alignment problems)
false
t/f: space maintainers are active devices
true
t/f: space regainers are active devices
removable space maintainers
which type of space maintainer is functional?
- fixed space maintainers
- removable space maintainers
unilateral fixed space maintainer
what type of appliance is a Band and loop?
unilateral fixed space maintainer
what type of appliance is a Distal Shoe?
bilateral fixed space maintainer
what type of appliance is a Nance appliance?
bilateral fixed space maintainer
what type of appliance is a Lingual Holding Arch
bilateral fixed space maintainer
what type of appliance is a Fixed Anterior bridge
functional
All of the following are advantages of a Fixed space maintainer EXCEPT:
- minimal patient cooperation required
- can not be lost
- functional
- difficult to break
- less of a "food trap" than removable appliance
major food trap
All of the following are disadvantages of a Fixed space maintainer EXCEPT:
- major food trap
- decalcification of abutment teeth possible beneath bands
- longer chair time
- improper fabrication may make appliance active
- improper design may impinge upon erupting teeth
- possible loss of primary abutment tooth or teeth
- soft tissue injury
Distal Shoe
ID the appliance:
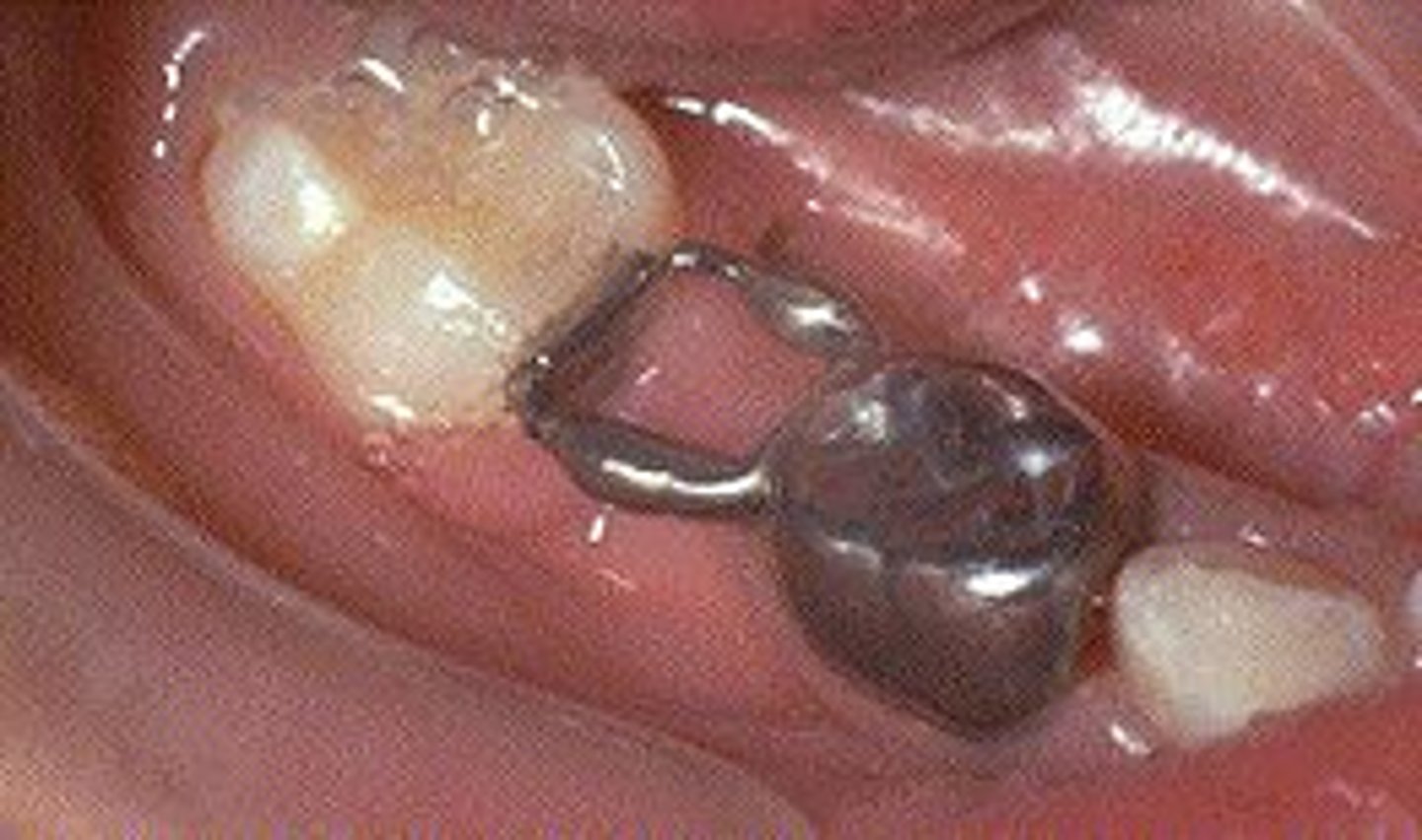
Distal Shoe
ID the appliance:
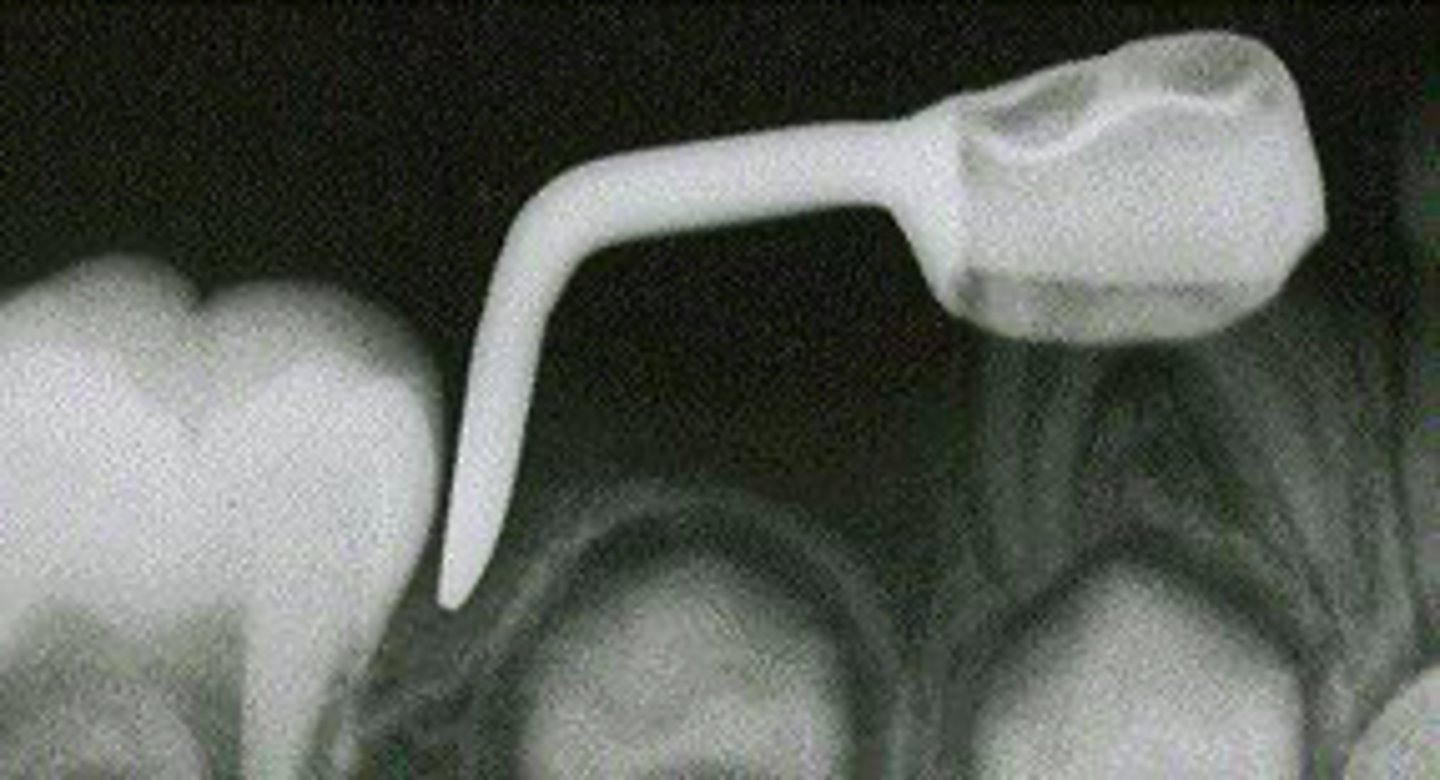
loss of 2nd primary molar before eruption of permanent molar
What is the ONLY time a distal shoe is indicated?
Distal Shoe
Your patient has a premature loss of the 2nd primary molar, but the permanent 1st molar has not erupted yet. What appliance would you recommend?
permanent 1st molar
if your patient has a premature loss of the 2nd primary molar, the presence of what tooth would contraindicate them from receiving a distal shoe space maintainer?
permanent lateral incisor
if your patient has a premature loss of the 1st or 2nd primary molar, the presence of what tooth would contraindicate them from receiving a band and loop space maintainer?
Band and Loop
ID the appliance:
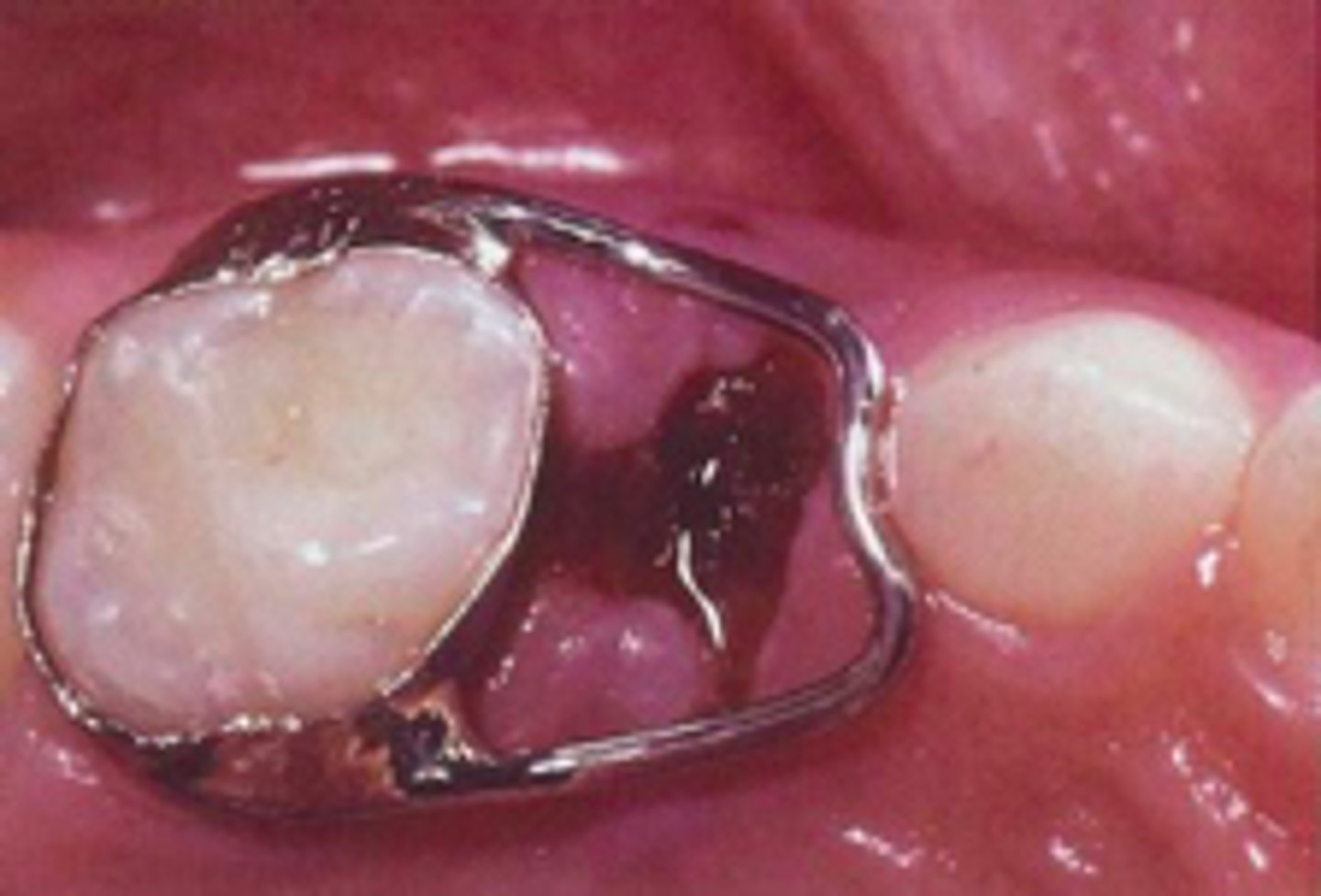
Band and Loop
Your patient has a premature loss of the 2nd primary molar, the permanent 1st molar has already erupted, but the permanent lateral incisors have not. What appliance would you recommend?
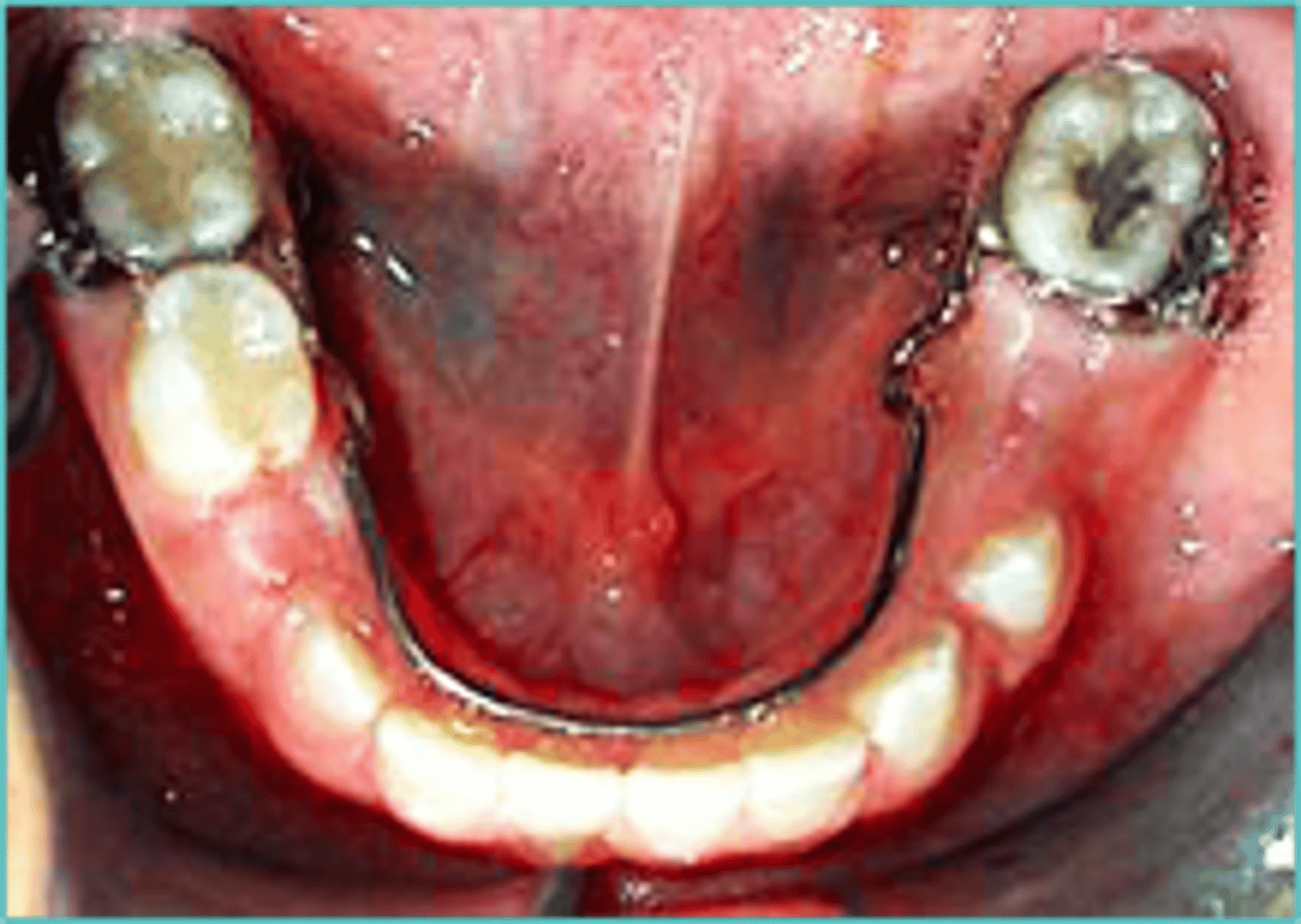
Lower Lingual Holding Arch (LLHA)
Your patient has a premature loss of the 2nd primary molar, the permanent 1st molar has already erupted and so have the permanent lateral incisors. What appliance would you recommend?
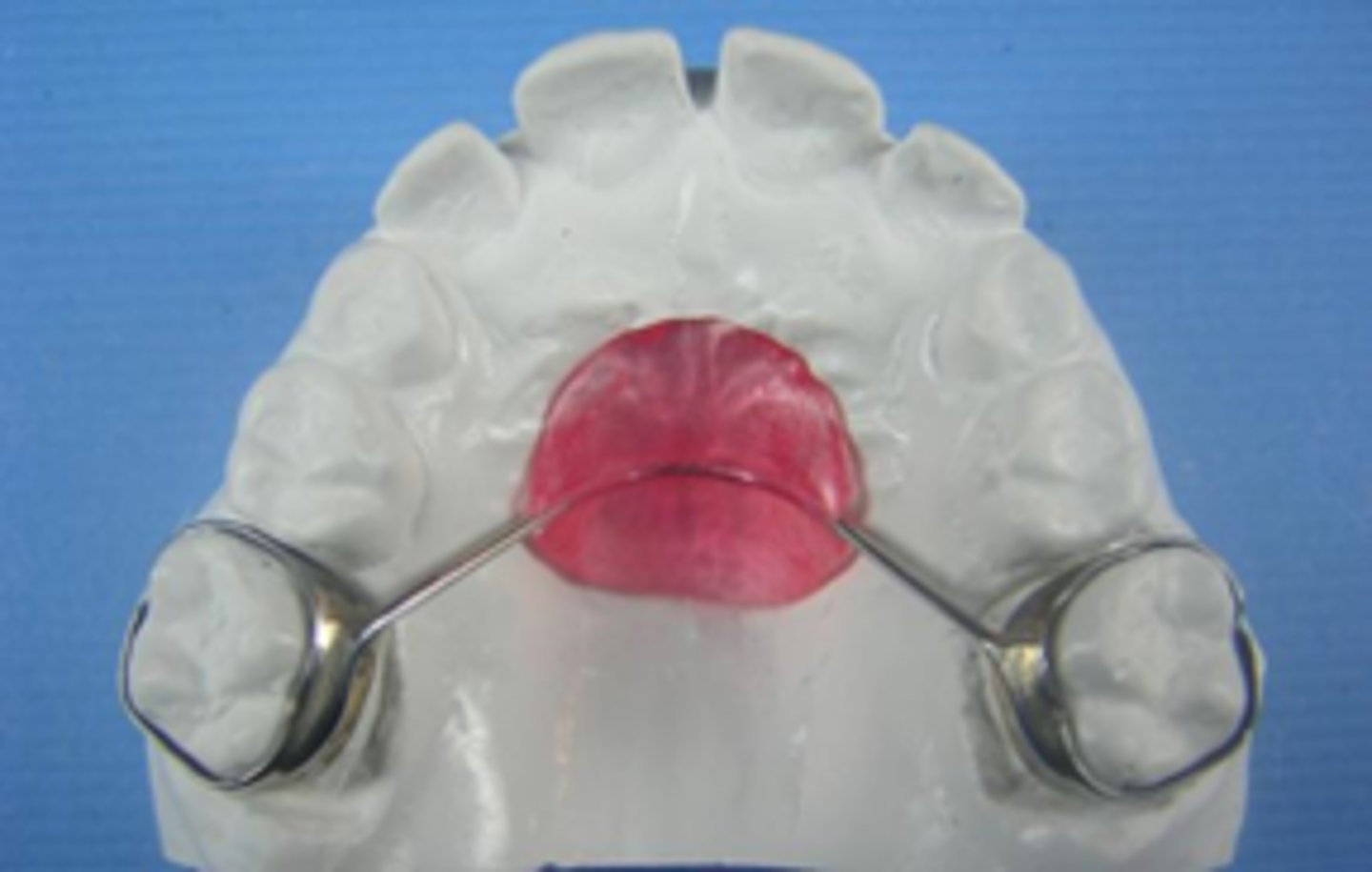
Nance appliance
ID the appliance:
Lower Lingual Holding Arch (LLHA)
ID the appliance:
Nance appliance
ID the appliance:
•Fixed Bilateral Space Maintainer
•Either primary/mixed dentition, as it does not interfere with eruption of permanent
maxillary incisors.
•Indicate for both unilateral 1st/2nd or both primary molars
•Bilateral primary molars MUST be erupted
- Placed on Maxilla arch only!
Lower Lingual Holding Arch (LLHA)
ID the appliance:
•Fixed Bilateral Space
•Premature loss of mandibular first/second primary molars after eruption of permanent lateral incisors
•Prevents loss of arch dimension, prevents mesial tipping of first permanent molar
- Placed on Mandibular arch only!
midline
If primary canine lost and no space maintainer placed, a ______ shift to affected side (and lingual shift of mand. incisors) will occur when permanent incisors erupt
Groper fixed anterior bridge
ID the appliance:
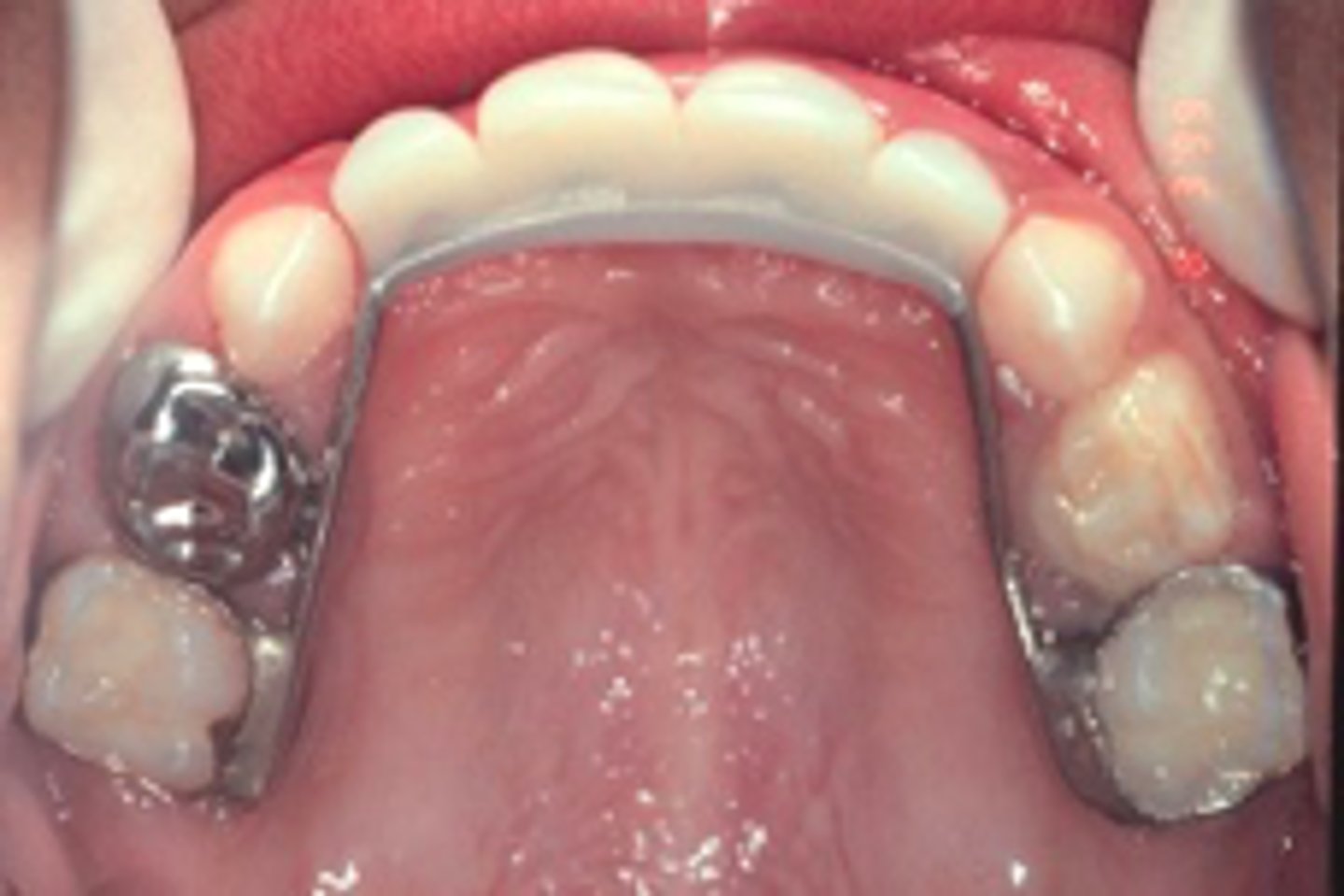
minimal patient cooperation required
All of the following are advantages of a Removable space maintainer EXCEPT:
- functional
- prevents supra-eruption of opposing teeth
- esthetic (anterior region)
- modified easily by grinding
- minimal patient cooperation required
decalcification of abutment teeth underneath bands
All of the following are disadvantages of a Removable space maintainer EXCEPT:
- requires maximum patient cooperation
- may be lost
- decalcification of abutment teeth underneath bands
- breakable
- "Food trap"; must be removed from mouth and cleaned regularly
- may lose stability
Posterior Adam's clasps
ID the appliance:
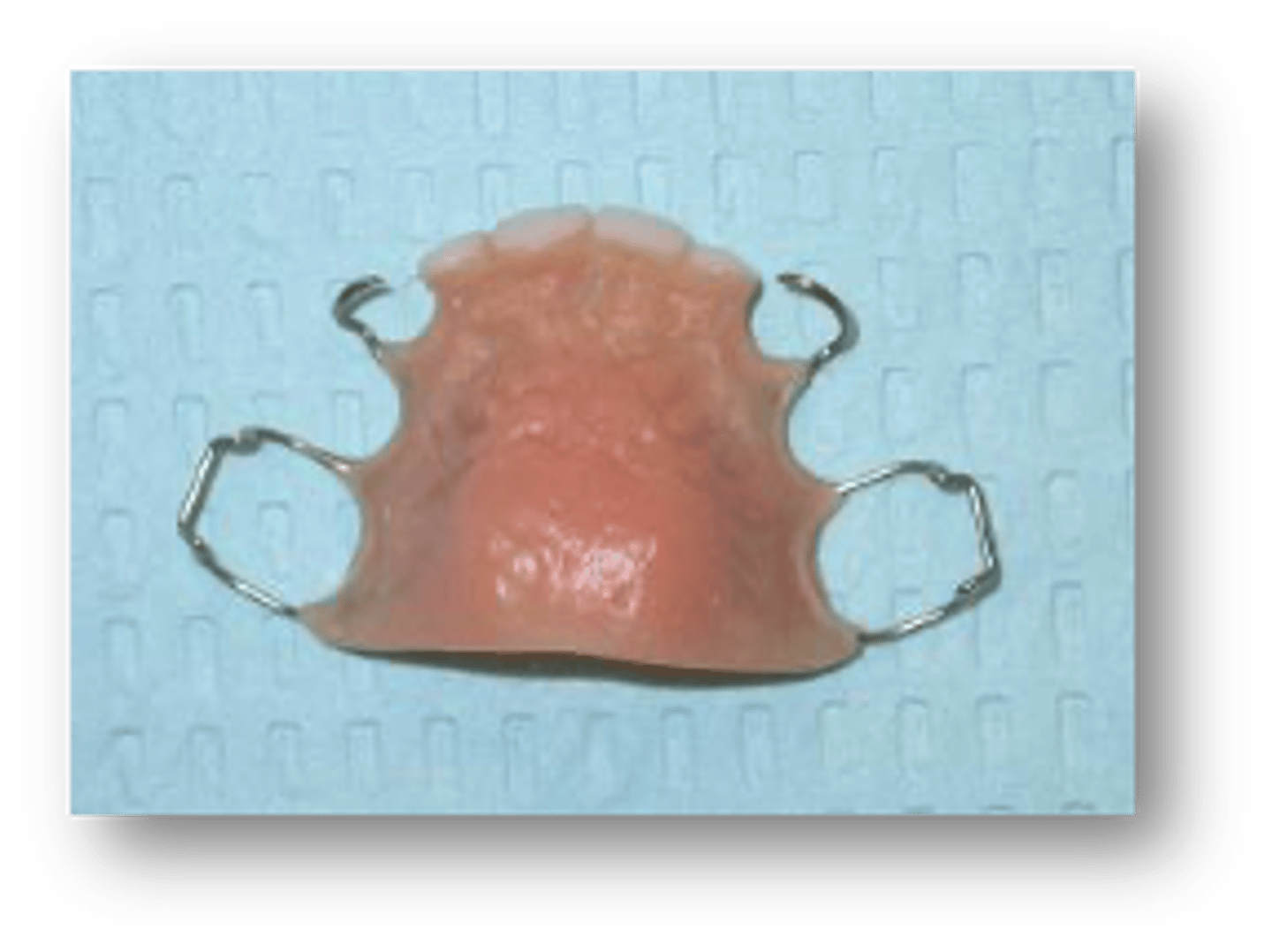
space regainer
The objective of these devices is:
•When space from the premature loss of a primary tooth has not been maintained
•Comprehensive evaluation to determine is space maintenance, space regaining or no treatment is indicated
• An appliance to regain lost space
•Prevent crowding and malocclusion
maxilla
which arch is it easier to regain space in, the maxilla or mandible?
Lip bumper
ID the appliance:
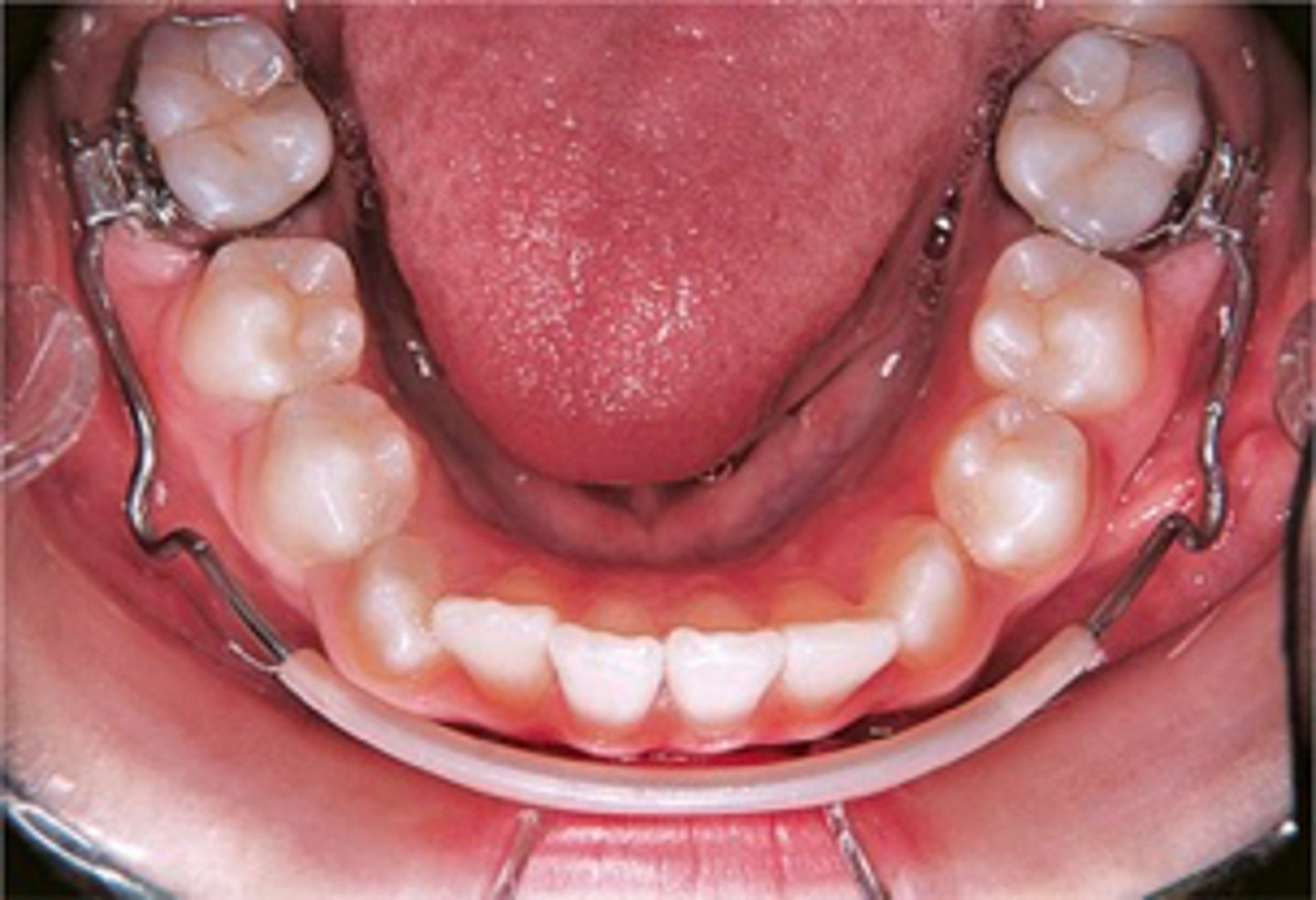
Lip bumper
ID the appliance:
- use of the mentalis muscle to push against the acrylic bar results in pushing back molar teeth
- can obtain about 2-3mm
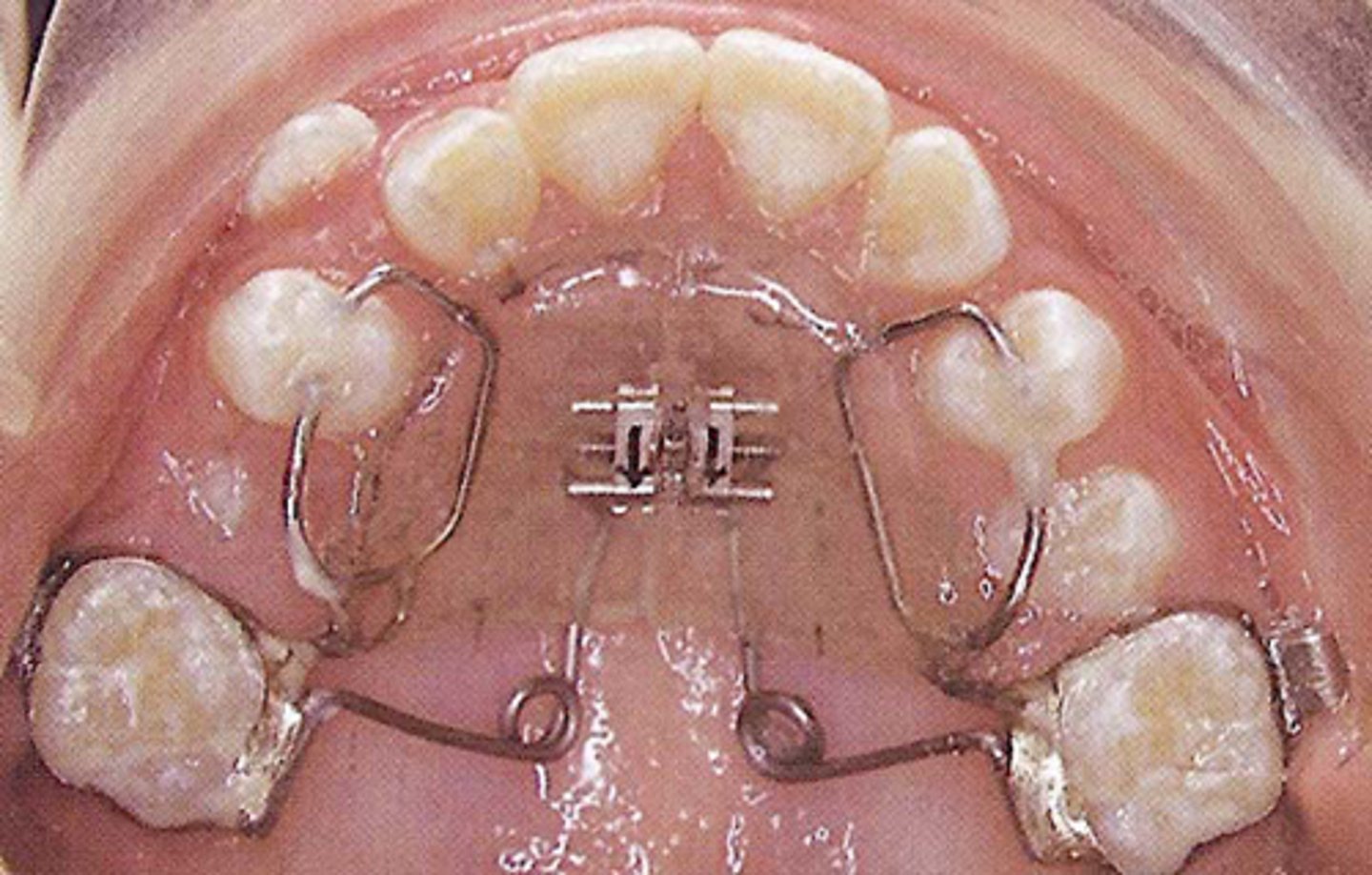
Pendulum appliance
ID the appliance:
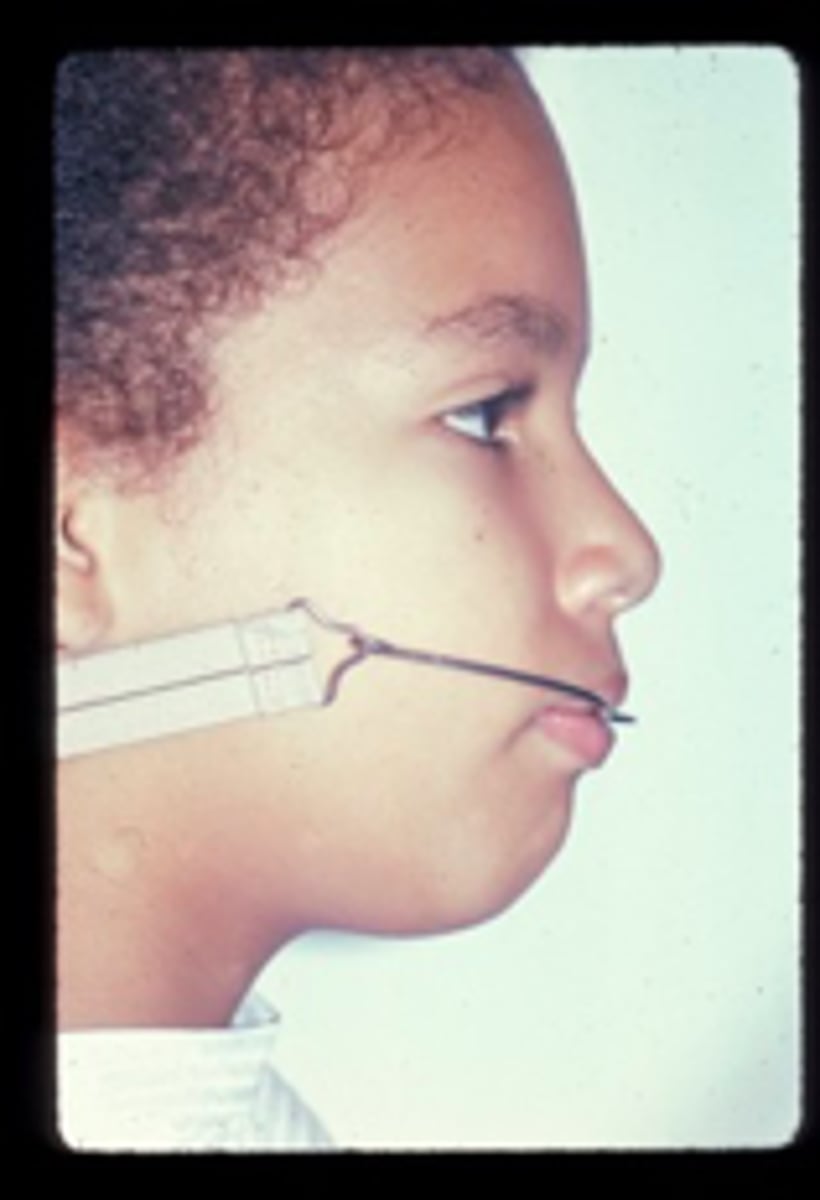
Head gear
ID the appliance:
myofunctional therapy
mechanical therapy
What are the treatment option for correcting tongue thrusting?
Increased overbite
All of the following are effects of thumb sucking habit, EXCEPT:
- Labial inclination of maxillary incisors
- Anterior and superior distortion of the maxillary anterior alveolar process
- Increased overjet
- Increased overbite
- Anterior open bite
- Lingual inclination of mandibular incisors
behaviorist therapy
mechanical therapy
What are the treatment option for correcting digit sucking?
tongue tamers
ID the appliance:
Bluegrass
ID the appliance:
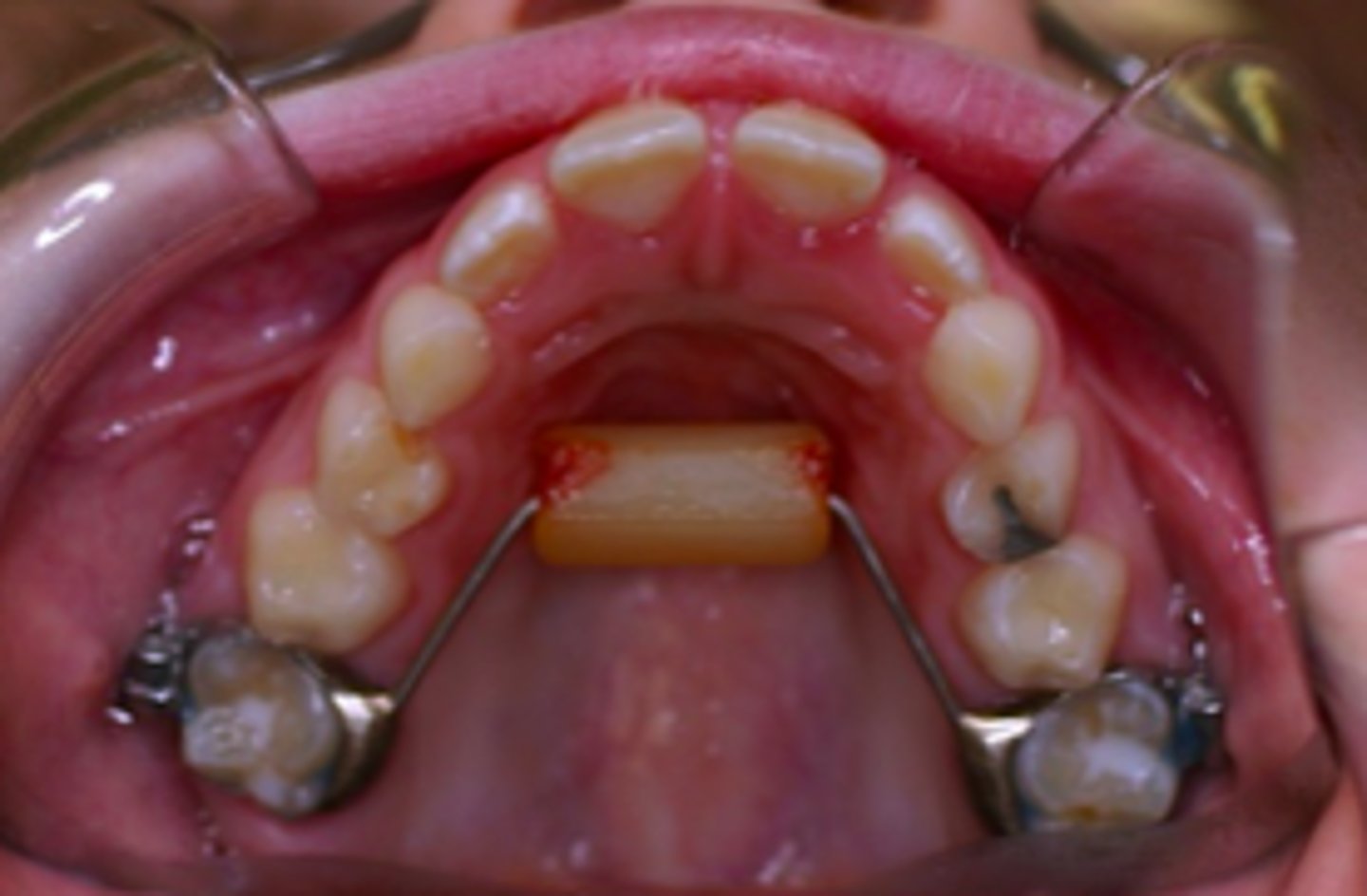
thumbsucking and tongue thrust
The Bluegrass device was designed to address what habit?
thumbsucking and tongue thrust
Tongue tamers were designed to address what habit?
Palatal crib
ID the appliance:
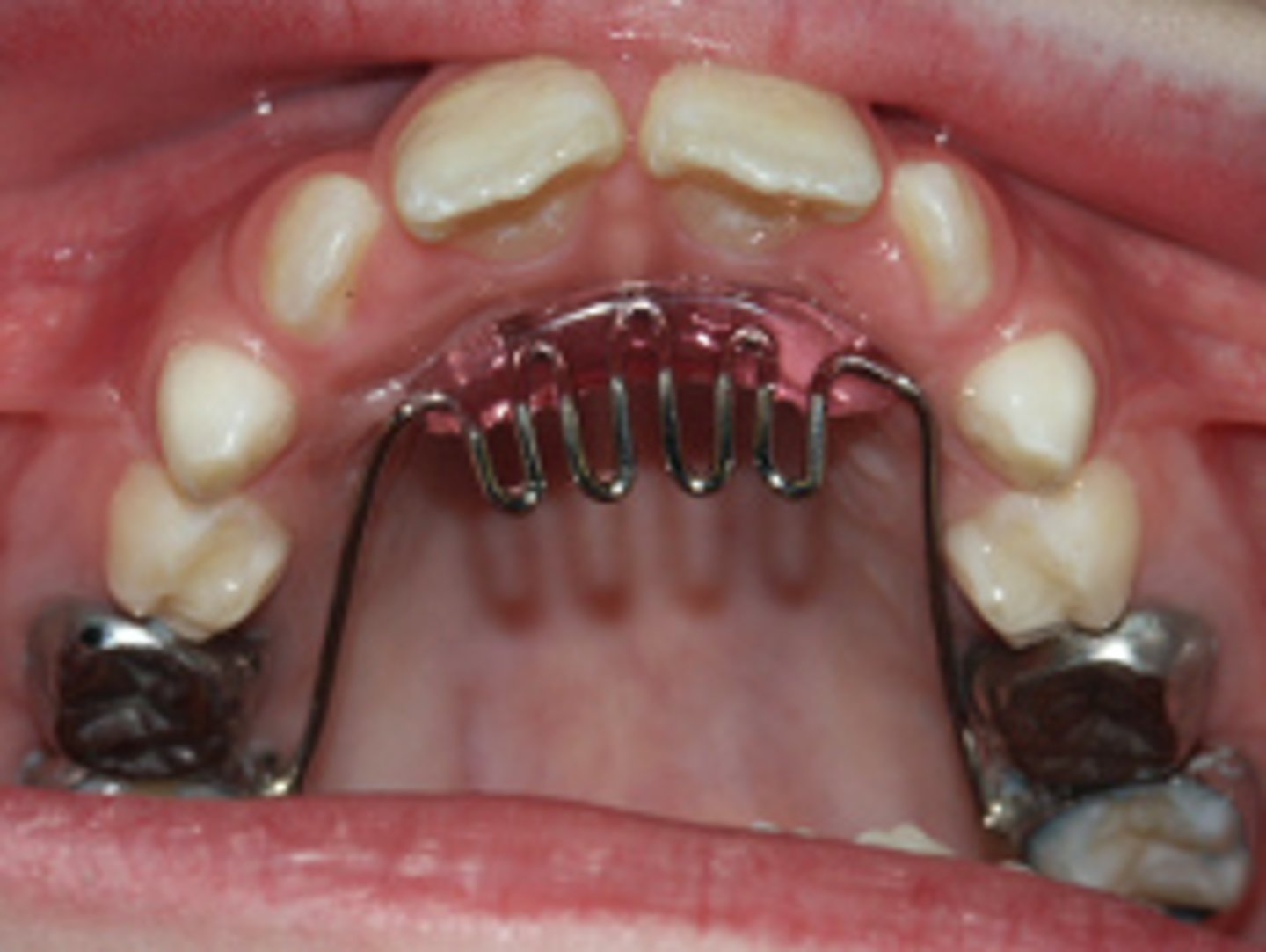
thumbsucking and tongue thrust
The Palatal crib device was designed to address what habit?
6-10 months
For patients that receive a habit correcting appliance, to prevent relapse, it is best for the appliance to remain in the patient for about ______
mouth breathing
Patients with chronic nasal obstruction are prone to ____
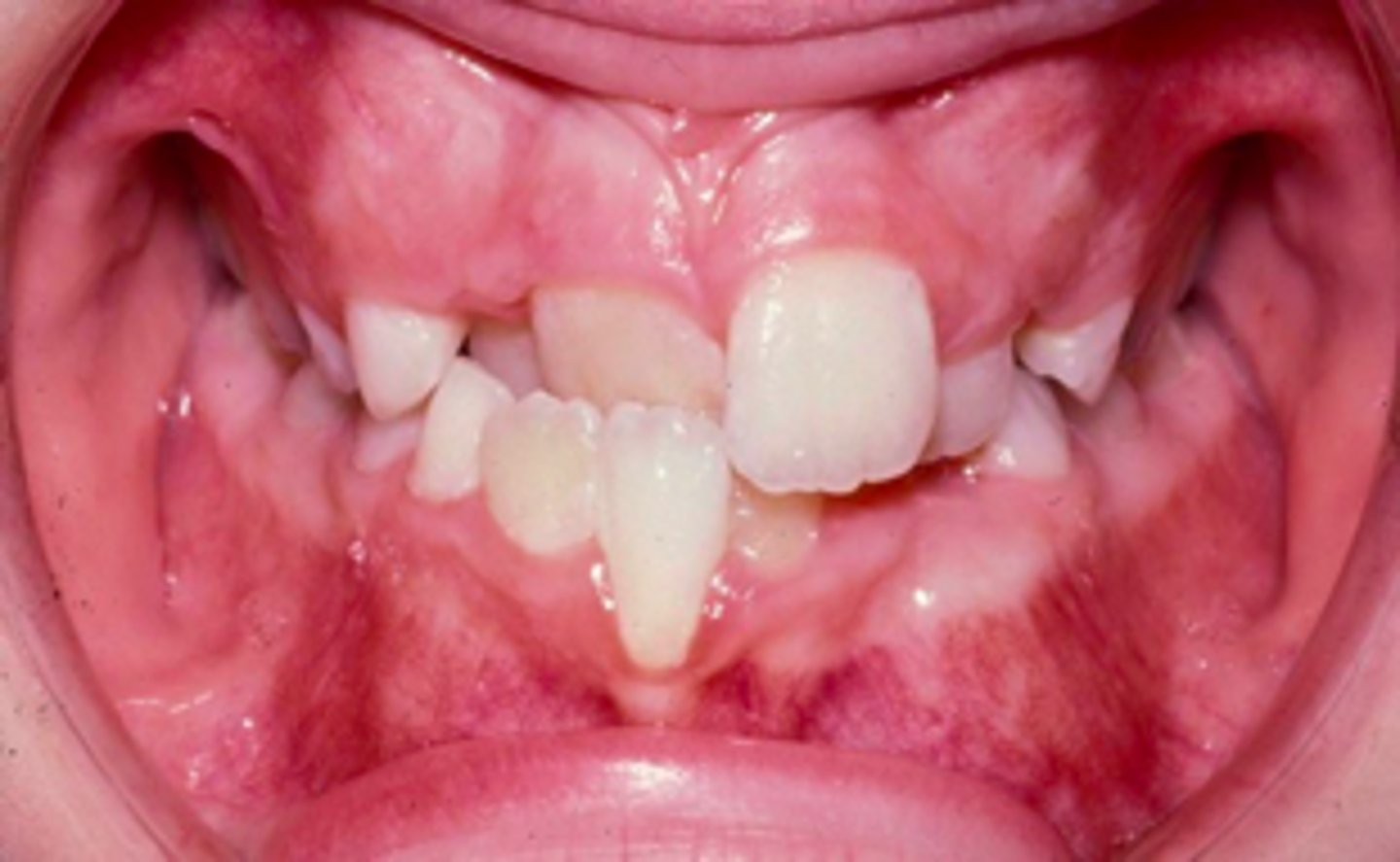
anterior crossbite
Abnormal labiolingual( bucco-lingual) relationship of teeth:
dental and skeletal
what are the two types of anterior crossbites?
Class I
Patients with a dental anterior cross bite are more likely to have what type of occlusion?
Class III
Patients with a skeletal anterior cross bite are more likely to have what type of occlusion?
anterior crossbite
ID the condition:
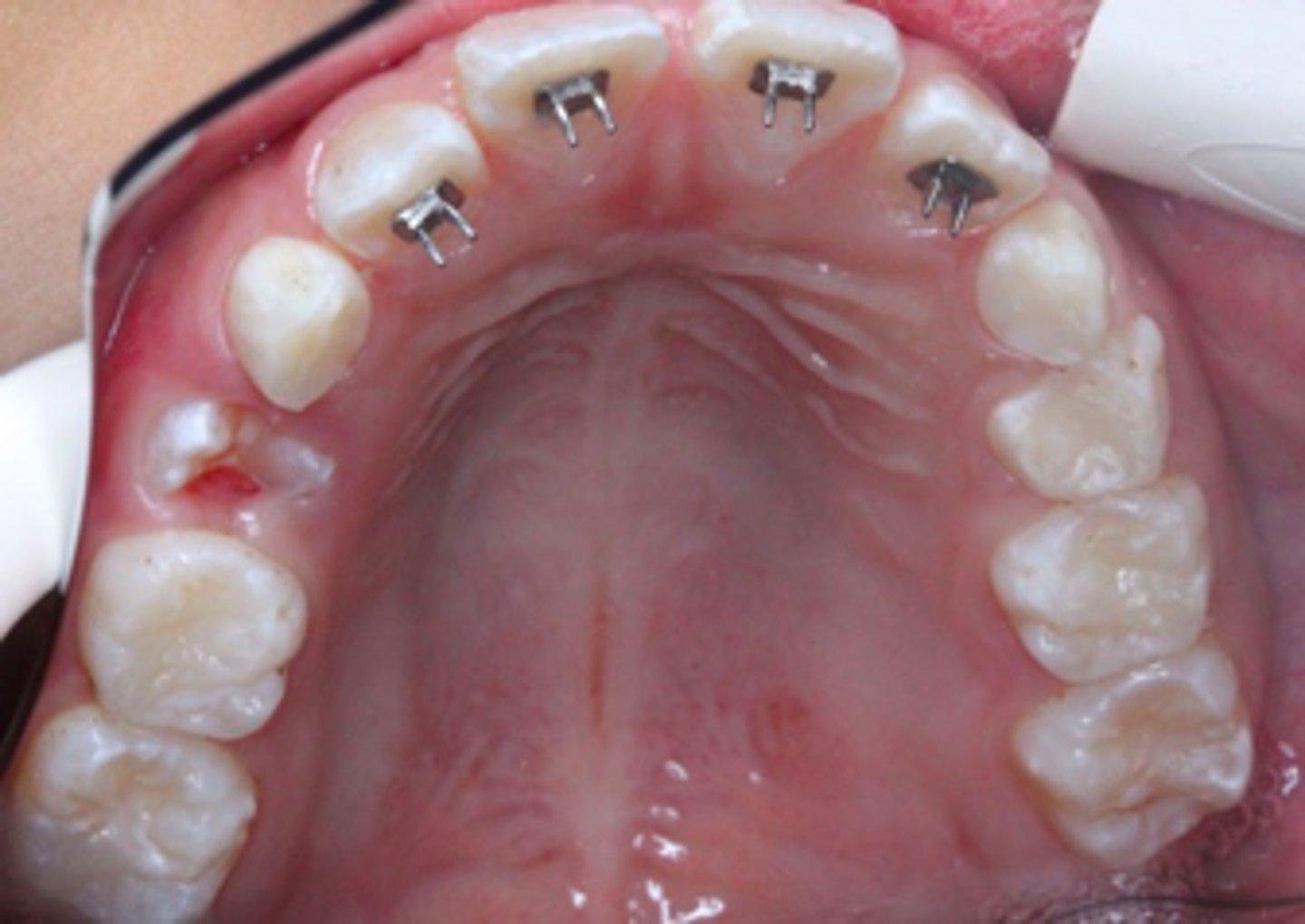
Quad-Helix
ID the appliance:
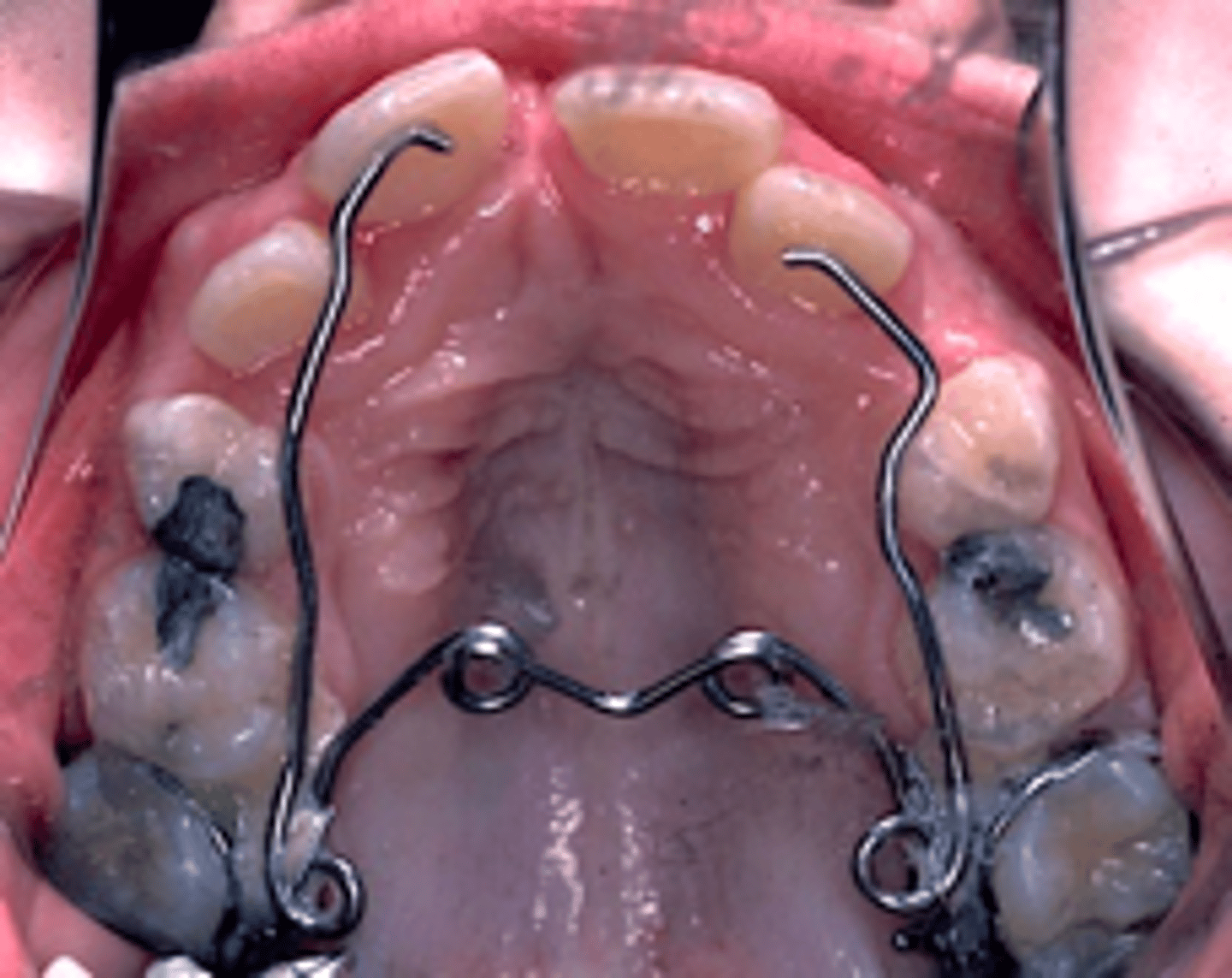
anterior crossbite
The Quad-Helix appliance is used to correct what?
Hawley with finger springs
ID the appliance:
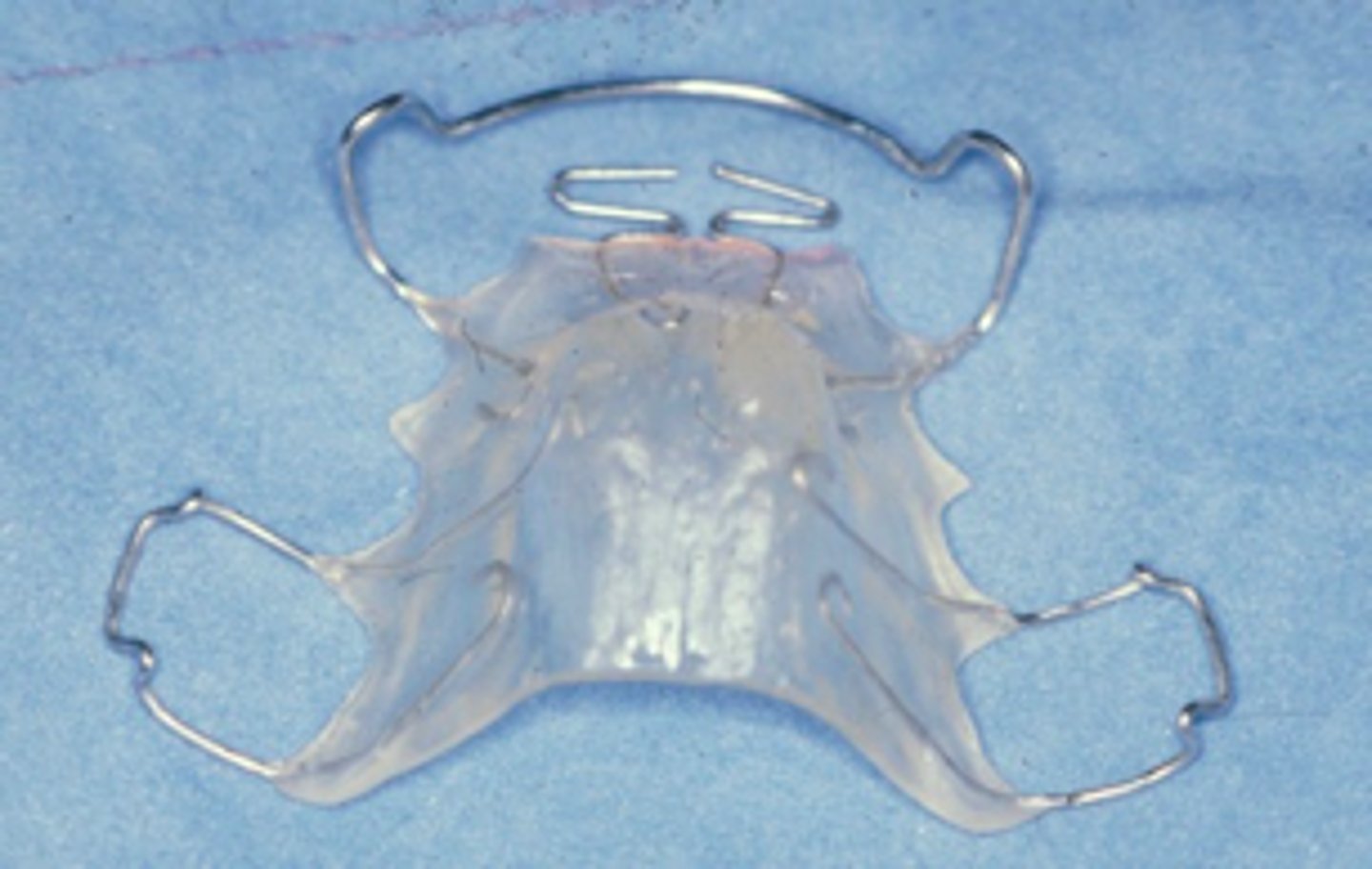
anterior crossbite
The Hawley with finger springs appliance is used to correct what?
Multi-loop or trapeze
ID the appliance:
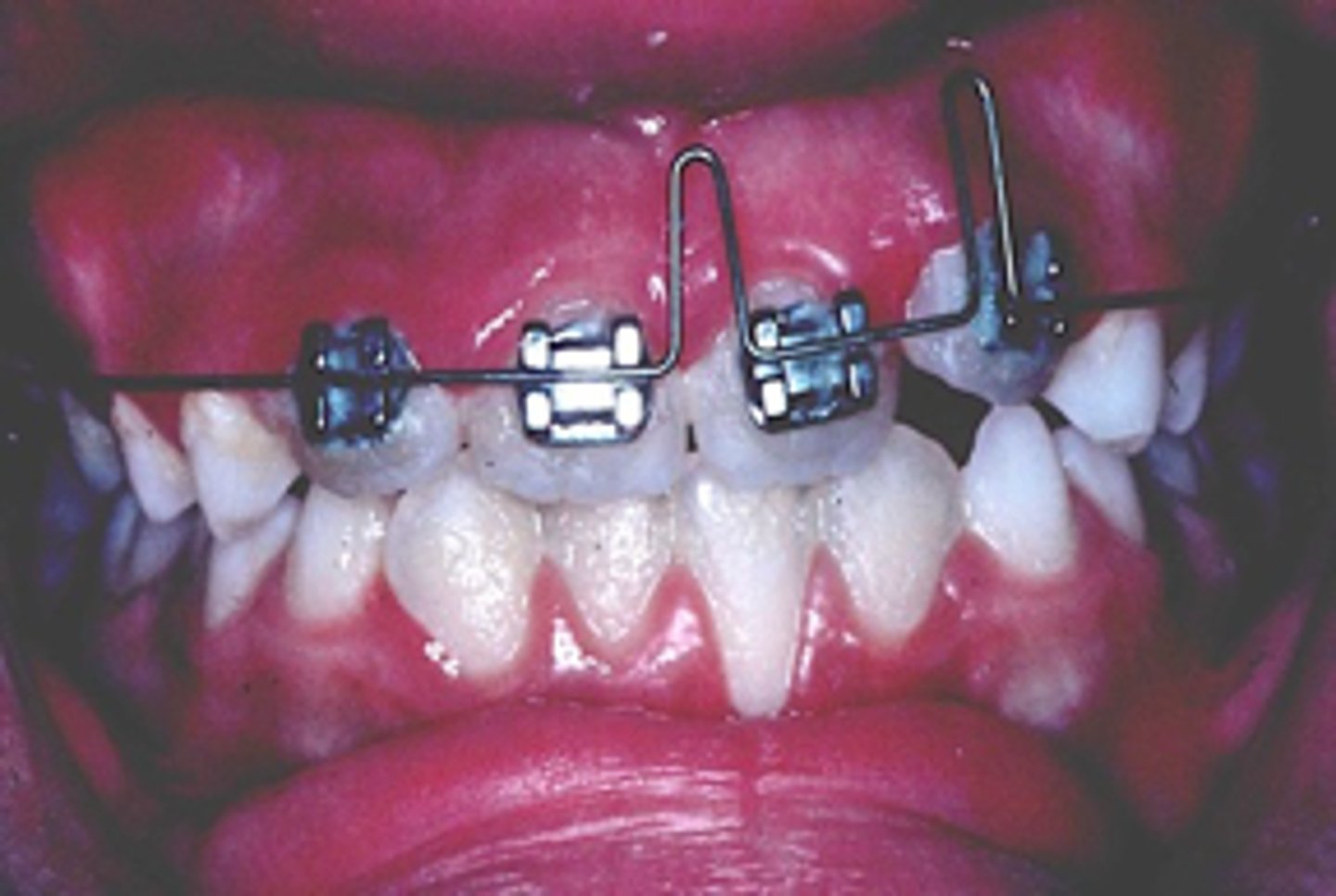
anterior crossbite
The Multi-loop or trapeze appliance is used to correct what?
Delta Loop
ID the appliance:
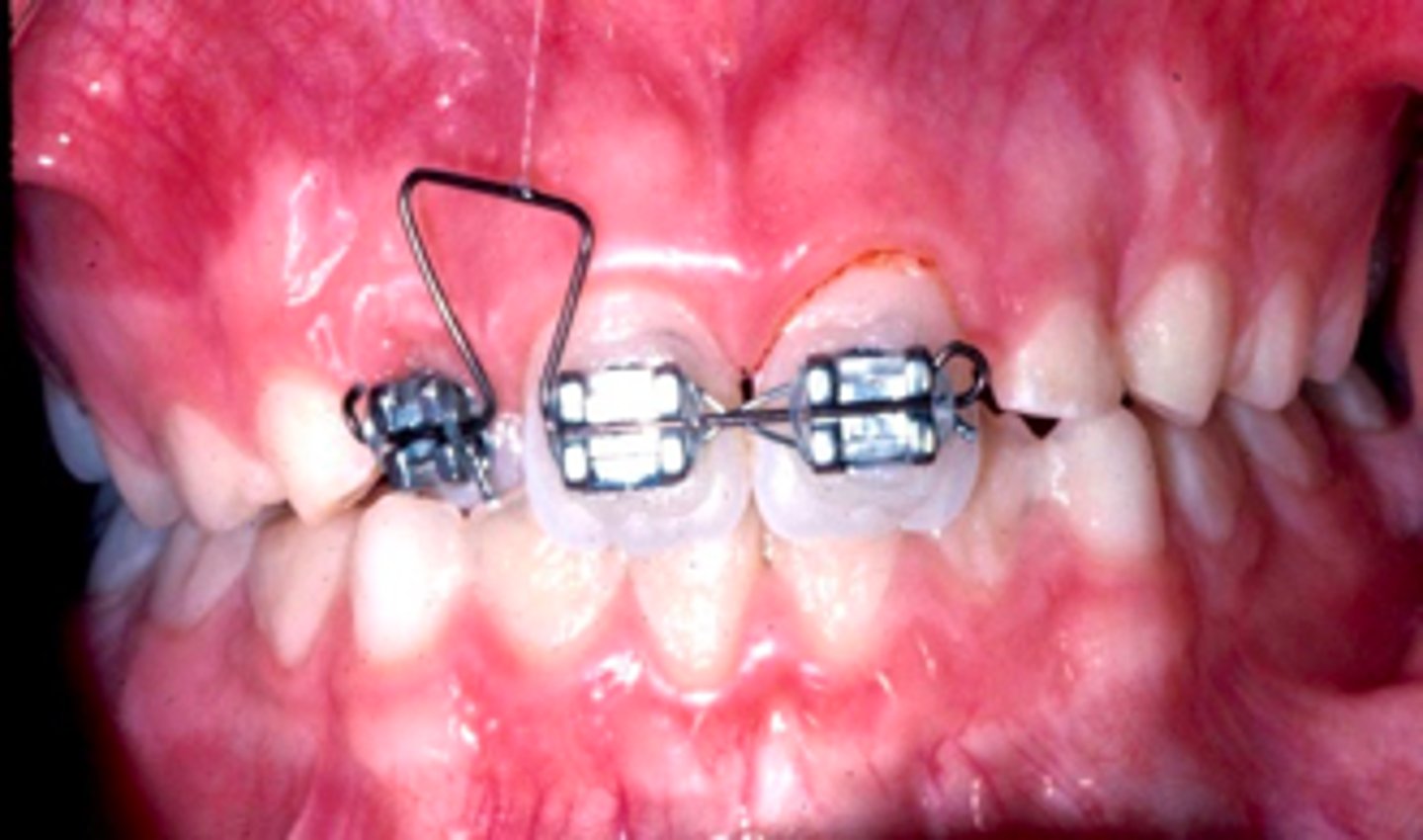
anterior crossbite
The Delta Loop appliance is used to correct what?
Facemask
ID the appliance:
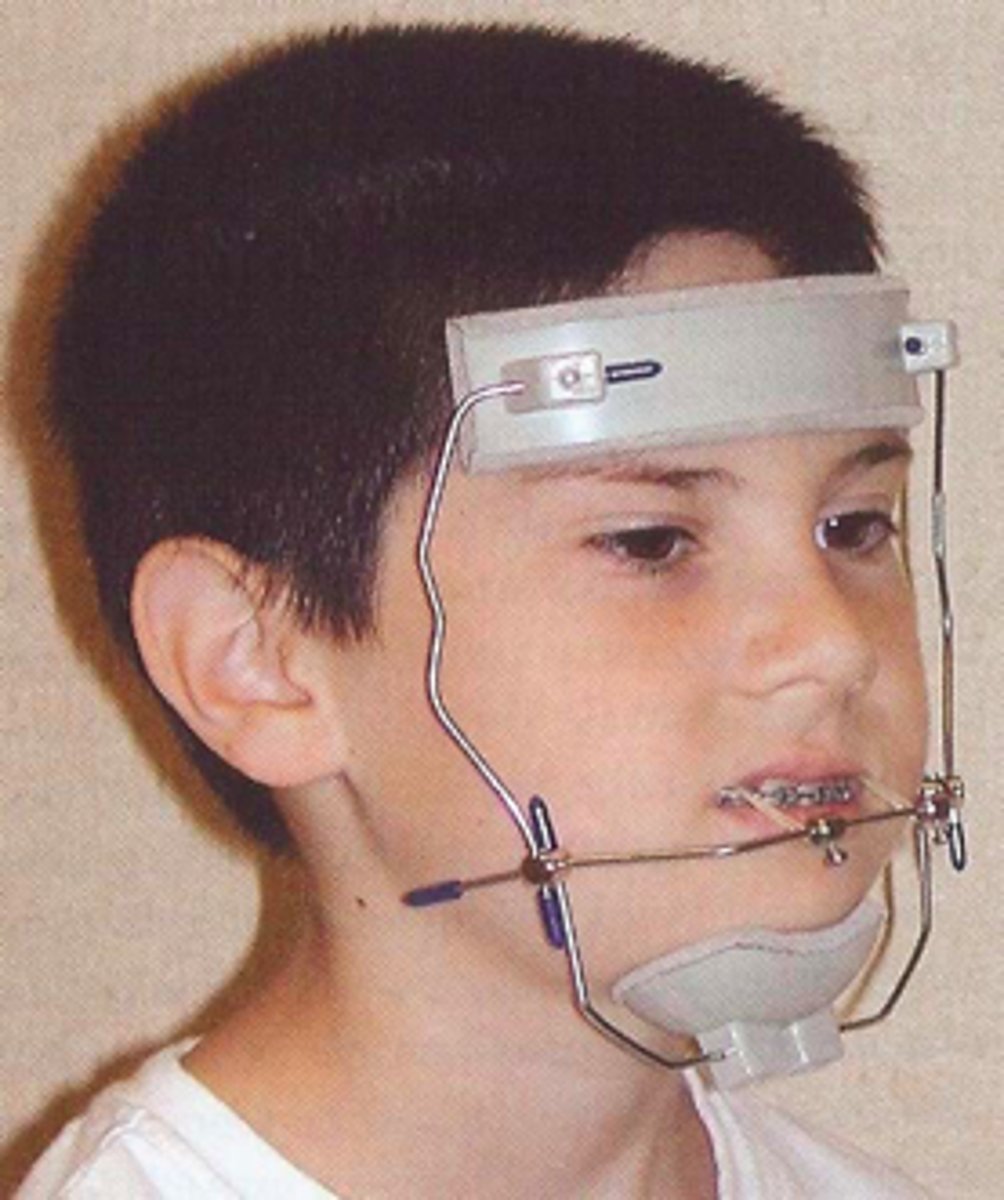
skeletal anterior crossbite
The Facemask appliance is used to correct what?
posterior crossbite
this type of cross-bite is NOT self correcting indicating the likelihood that a child would have a crossbite in the permanent dentition if he/she had one in the primary dentition
•Correction in the primary dentition appears to be stable and to have a positive influence on permanent tooth position
posterior crossbite
ID the condition:
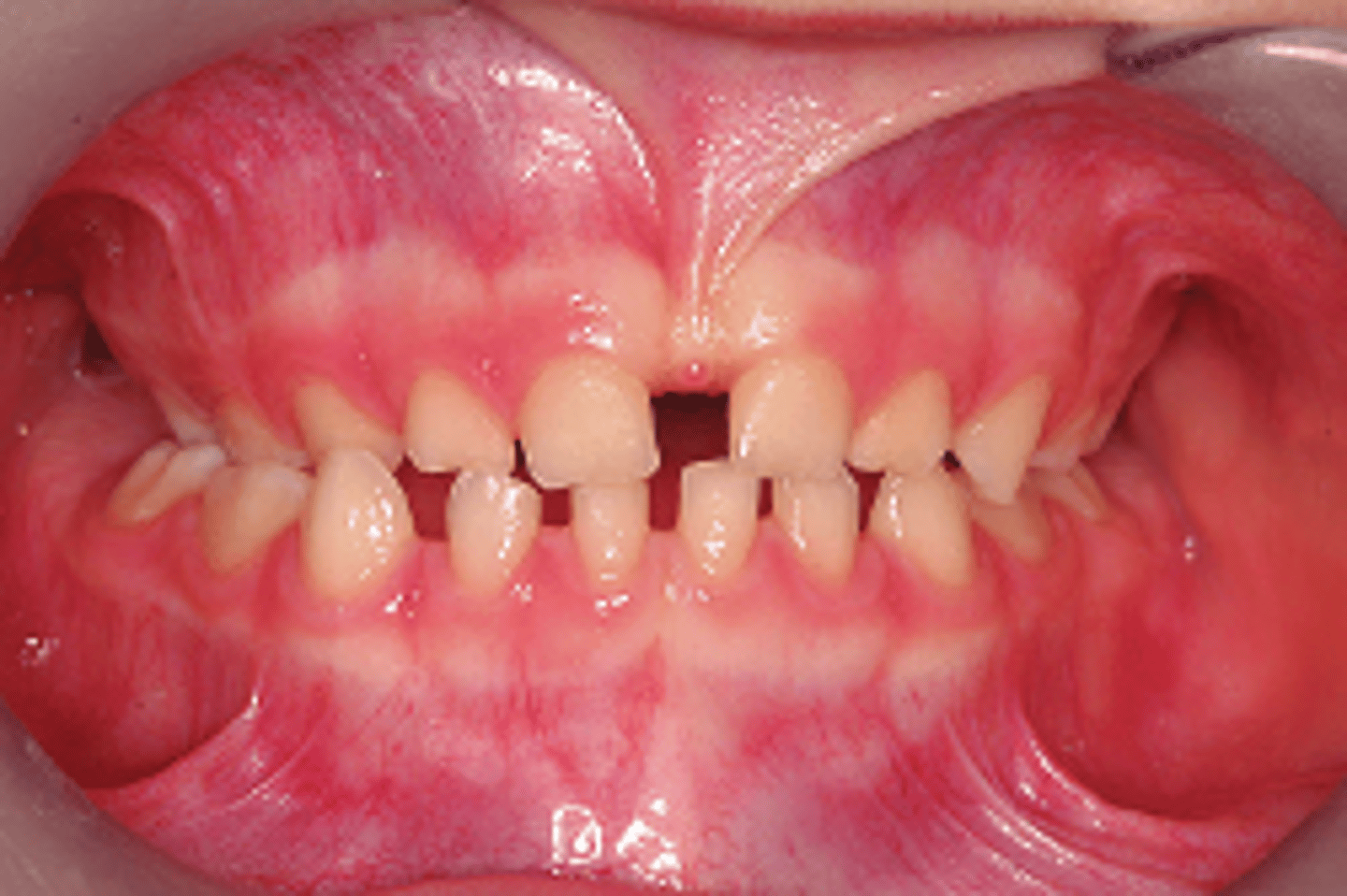
narrow maxilla
what is the etiology of the skeletal posterior crossbite?
interference of primary canine or single/multiple tooth malposition
what is the etiology of the dental posterior crossbite?
Orthopedic expansion (Rapid Maxillary Expansion appliances)
What is the treatment for posterior crossbite?
0.5-1mm / day
For patients with a posterior crossbite, Rapid Expansion appliances can achieve how much movement?
preschoolers
For patients with a posterior crossbite, Rapid Expansion appliances are contraindicated in what patient population?
Rapid Maxillary Expansion appliance
this appliance results in sutural space created that is initially filled with tissue fluids and hemorrhage, and a creation of a midline diastima:
1mm/ week
For patients with a posterior crossbite, Slow Expansion appliances can achieve how much movement?
Hyrax Appliance
ID the appliance:
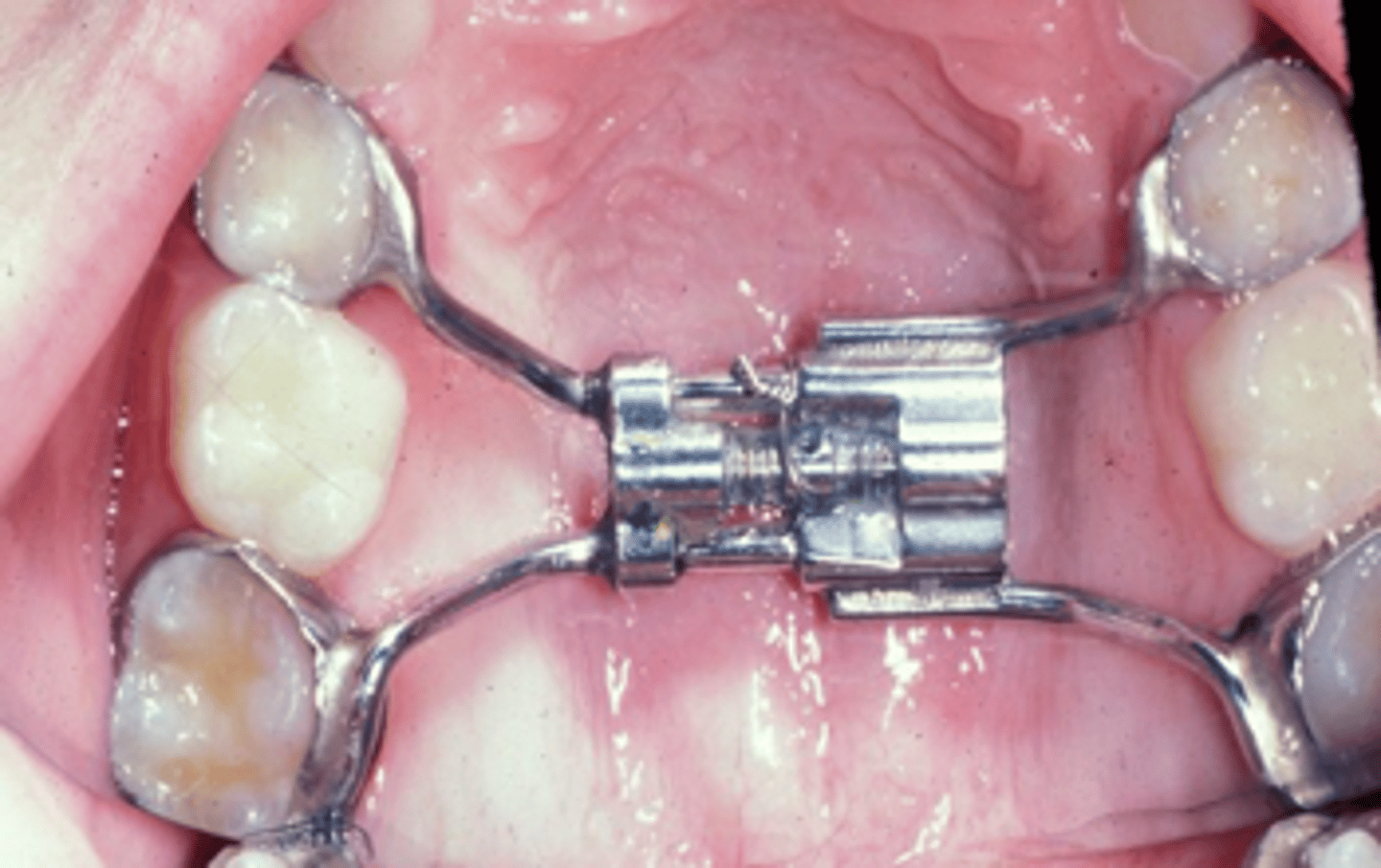
Hyrax Appliance
ID the appliance:
•Hygienic Rapid Expander
•Opens mid-palatal suture
•Generates heavy forces
•15-20lbs
•.25mm/turn
posterior crossbite
The Hyrax Appliance appliance is used to correct what?
W-arch
ID the appliance:
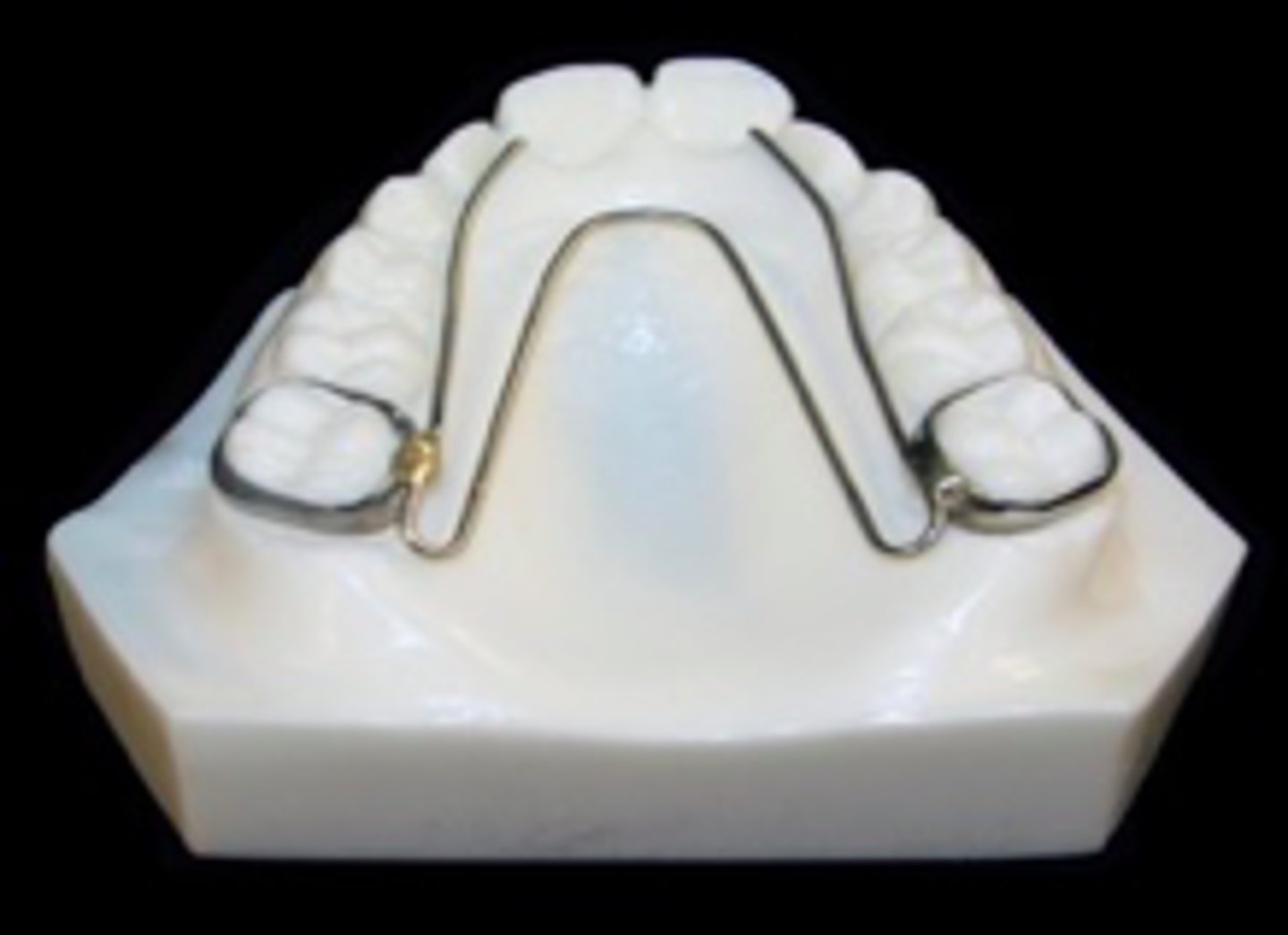
Haas-Type
ID the appliance:
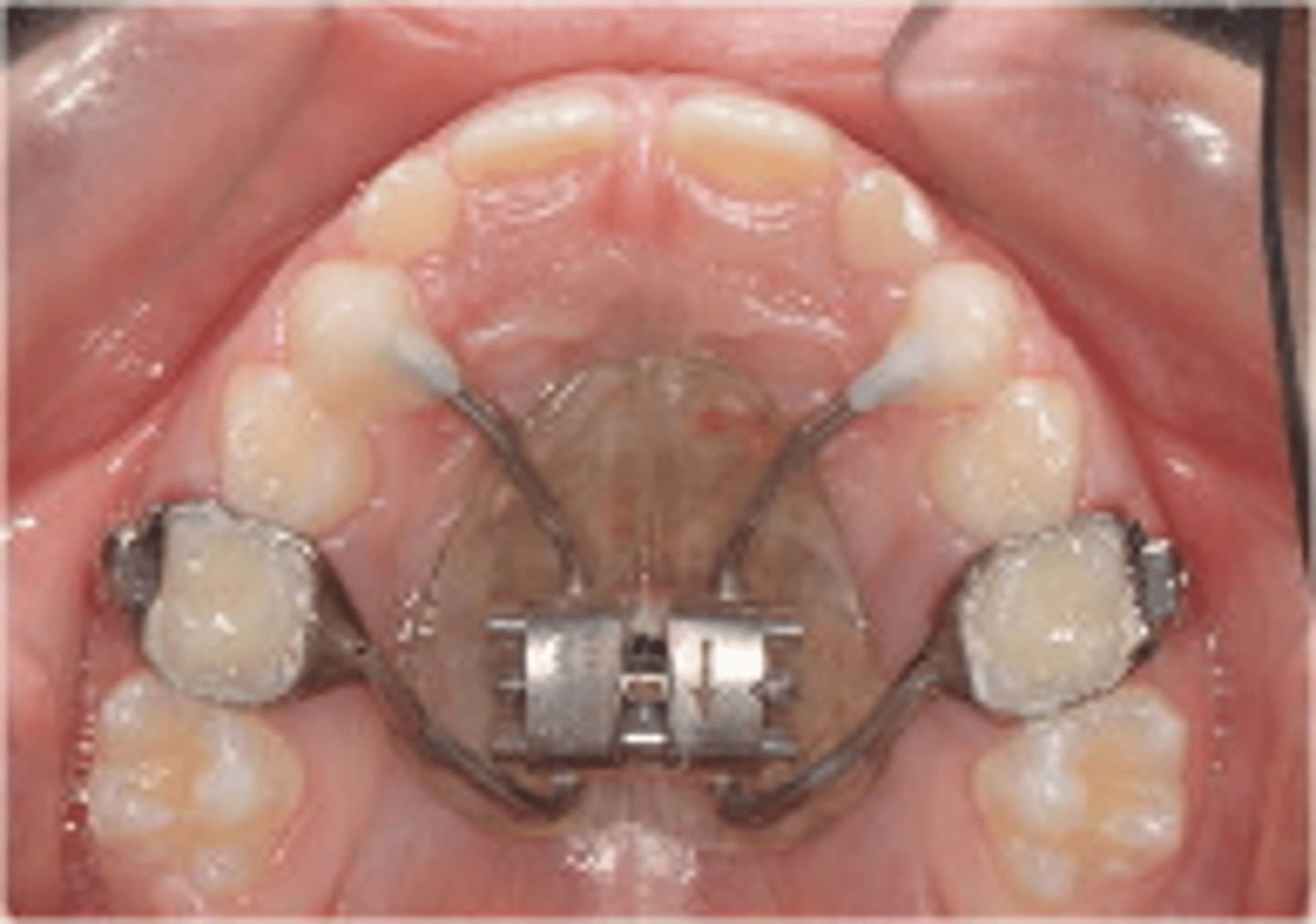
Hyrax Appliance
Haas-Type
Name two types of Rapid Maxillary expanders: