L33 Linking adaptive and innate immune system
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary terms and concepts from the lecture notes on Immunology III: Inflammation, Phagocytosis & Complement and Linking innate and adaptive immunity.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Major immune cell communication methods
Soluble molecules (cytokines or chemokines) binding to receptors on a cell membrane; Cell surface-bound receptors binding to cell surface-bound ligand; Antigen (pathogen parts) being presented to cell surface-bound receptors
soluble chemical messengers binding to receptors
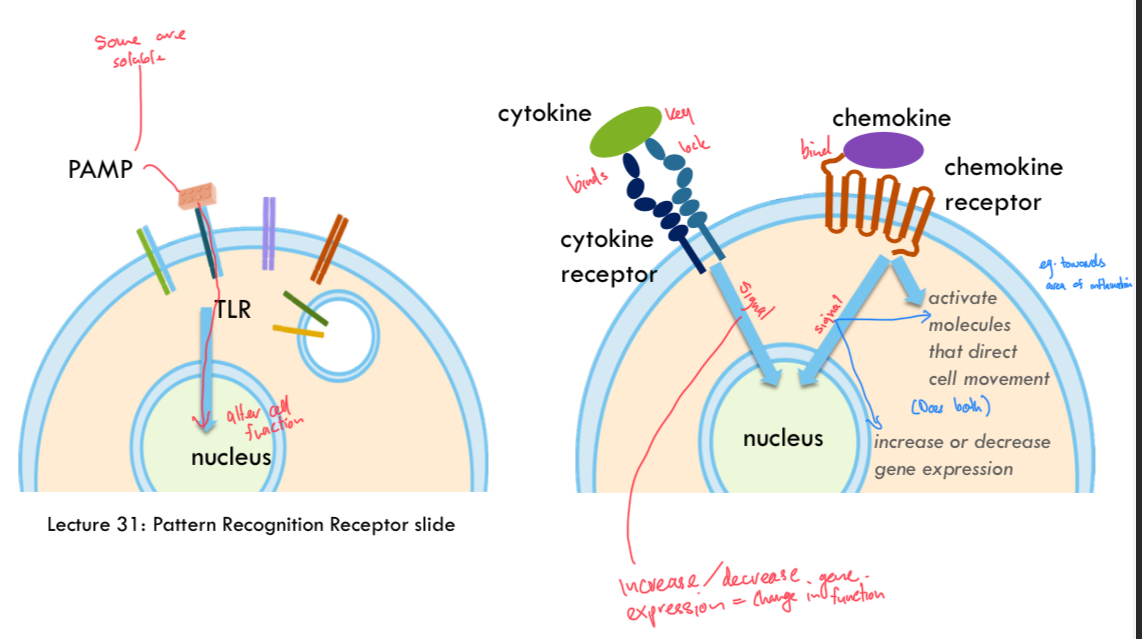
Cytokines
Molecules such as interleukins and interferons, bind to cytokine receptor and can alter gene expression of cell (altering function). Control growth and activity of immune cells.
Chemokines
Bind to chemokine receptor, activate molecules that direct cell movement (eg towards inflamation), and alter gene expression. Stimulate cell migration.
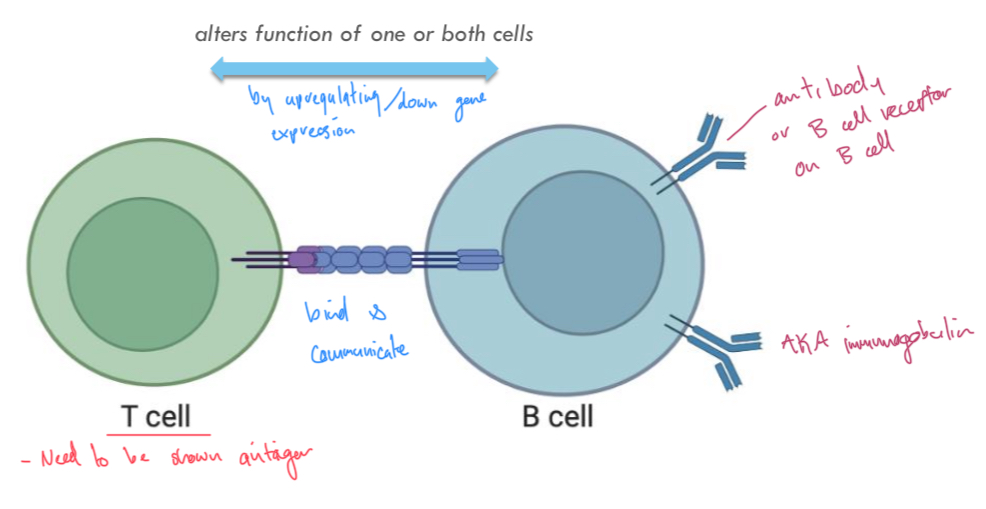
Cell surface-bound receptors binding to cell surface bound ligands
Eg helper T cells and B cells
Antigen being presented to a cell surface bound receptor
Eg activated dendritic cell and T cell.
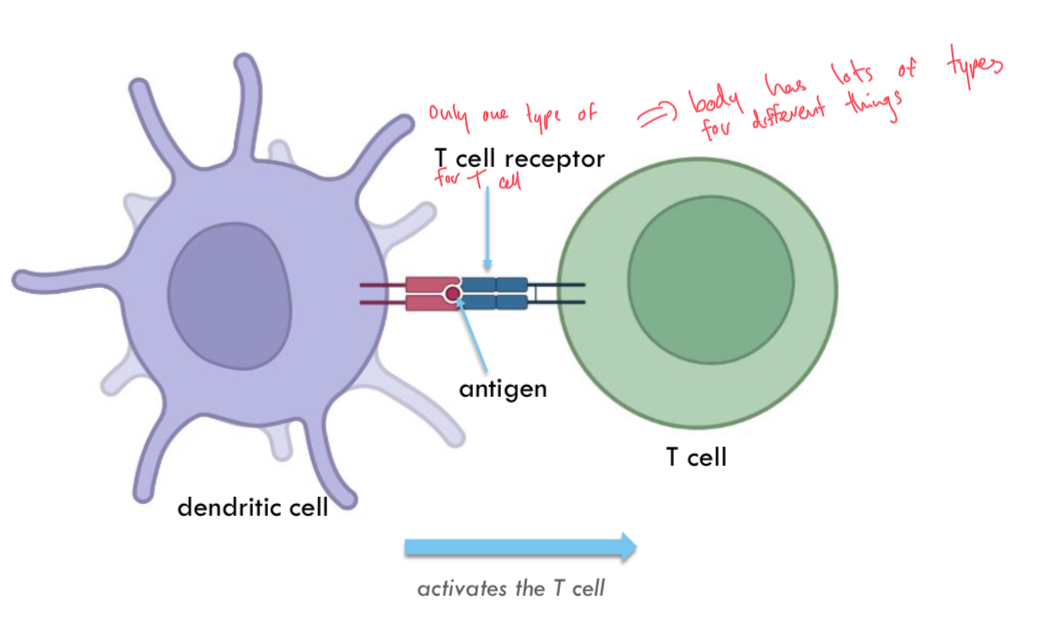
Antigen
Anything that has the potential to be recognised by the immune system. Can be foreign (from outside) or self-antigen (immune system usually tolereant of self-antigen).
Activated dendritic cells communicating with T cell
Make cytokines that bind to receptors on T cell membranes. Have cell surface-bound receptors that bind to T cell surface-bound ligand (or vise versa). Present antigen to cell surface-bound receptors on T cells= activation of T cell
MHC-I
Presents endogenous (intracellular) antigen to T cells, is expressed on all nucleated cells. Viral infections presented.
MHC-II
Presents exogenous (extracellular) antigen and is expressed only on antigen presenting cells eg. dendritic cells.
Helper T Cells
Helper T cells that have been activated by a dendritic cell can then “help” B cells by making cytokines that bind to receptors on B cell membranes= activation of B cell, and helps B cell make antibodies.
Linking innate and adaptive (B cells and complement)
Antibody binding to a pathogen can trigger the classical pathway. Complement fragments that are bound to antigen can also help activate B cells to make antibodies
Summary from standing on nail, to clearing pathogen
