case study COMPLETE
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
Routine H&E (Progressive)
Haematoxylin (binds DNA/RNA) → Scott’s tap water (blueing) → Eosin (counterstain).
Mechanism: haematoxylin binds acidic structures, bluing converts to blue lake, eosin binds basic proteins.
Results: nuclei blue-black, cytoplasm pink, RBCs orange/red, fibrin deep pink.
Routine H&E (Regressive)
Haematoxylin → Scott’s tap water → 1% acid alcohol (differentiate) → Eosin.
Mechanism: overstain, remove excess with acid alcohol, reblue, counterstain.
Results: same as progressive (nuclei blue-black, cytoplasm pink).
PAS (Periodic Acid–Schiff)
Periodic acid → Schiff’s reagent → haematoxylin → Scott’s water.
Mechanism: oxidises carbohydrates to aldehydes, Schiff’s reacts → magenta.
Results: glycogen & carbs magenta, nuclei blue.
Alcian Blue (pH 2.5)
Acetic acid → Alcian blue → Nuclear fast red.
Mechanism: cationic dye binds anionic acidic mucins (electrostatic).
Results: acid mucins blue, nuclei red.
AB–PAS (Combined)
Acetic acid → Alcian blue → Periodic acid → Schiff’s reagent → Haematoxylin.
Mechanism: Alcian blue first (acid mucins), PAS second (neutral mucins).
Results: acid mucins blue, neutral mucins magenta, nuclei pale blue.
Ziehl–Neelsen (Acid-Fast)
Carbol fuchsin → Acid alcohol → Methylene blue.
Mechanism: carbol fuchsin penetrates waxy mycolic coat, acid alcohol decolorises non–acid-fast.
Results: acid-fast bacilli red, background blue.
Gram Stain
Crystal violet → Lugol’s iodine → Acetone → Safranin/Twort’s.
Mechanism: CV binds peptidoglycan, iodine forms complex, Gram+ retain stain, Gram– lose during decolorisation.
Results: Gram+ dark violet, Gram– pink/red, nuclei red/mauve, cytoplasm light green.
Grocott Methenamine Silver (GMS)
Chromic acid → silver bath → Gold chloride → Sodium thiosulphate → Light green.
Mechanism: oxidises fungal carbs → aldehydes → reduce silver → black.
Results: fungi black, background green.
Perl’s Prussian Blue (Iron)
HCl + potassium ferrocyanide → Nuclear fast red.
Mechanism: ferric iron forms ferric ferrocyanide (Prussian blue).
Results: haemosiderin dark blue, nuclei red.
Congo Red (Amyloid)
Congo red → Mayer’s haematoxylin.
Mechanism: binds β-pleated amyloid fibrils.
Results: amyloid red, apple-green birefringence under polarised light, nuclei blue.
Gordon & Sweet’s Reticulin
Potassium permanganate (oxidise)→ Oxalic acid (bleach)→ Ferric ammonium sulphate (sensitiser)→ Wilder’s solution (impregnate) → Formalin (reduces)→ Sodium thiosulphate (remove excess).
Mechanism: oxidation, sensitisation, silver impregnation → visible black reticulin.
Results: reticulin black, collagen brown.
Masson’s Trichrome
Bouin’s fixative → Weigert’s haematoxylin → brilliant crocein → phosphotungstic acid → Aniline blue → Acetic acid.
Mechanism: acid dyes separate muscle/collagen by charge/size.
Results: nuclei black, collagen blue/green, muscle red.
Gomori’s Aldehyde Fuchsin
Aldehyde fuchsin → 95% alcohol → Picric carmine–picric acid.
Mechanism: stains elastic fibres, beta cells & mucin purple; counterstain colours collagen/muscle.
Results: elastic fibres & mucin deep purple, collagen blue-green, muscle yellow.
steps to histopathology
Specimen reception
Fixation
Gross examination and cutting
Tissue processing
Embedding
Sectioning - microtomy
Staining
DCM
Microscopy
cytopathology checklist (cell)
Presentation
shape
cytopathology checklist (nucleus)
Size
Stain
Position
Chromatin
Granularity
Shape
Border
cytopathology checklist (cytoplasm)
Density
Colour
Texture
Differentiation
sputum
Mucus in airways in response to infection
bronchial washings
Normal saline washed over mucosa and suctioned back through bronchoscope into sterile container
bronchial brushings
Cytology brush rubbed against slide to dislodge cells
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)
Most distal parts of bronchial tree sampled using normal saline
Fine needle aspiration – transthoracic
Surpasses ribcage
Surpasses ribcage
Fine needle aspiration – transbronchial (TBNA)
Central/mediastinal structures (lymph nodes, tumours)
steps for immunohistochemistry
1. Section cutting
2. Antigen retrieval
3. Blocking
4. Primary antibody
5. Secondary antibody
6. Visualisation
Oestrogen receptor
malignant cells that have receptors for oestrogen, once bound is a cascade of events, divide and grow, driving force of cancer, key for engine
Progesterone receptor
only when staining pattern is paired up with ER
OR+, PR-: more aggressive clinical course than double pos
HMW cytokeratin
squamous epithelia; skin and esophagus
low MW cytokeratin
glandular epithelium
fundamentals to in situ hybridisation
1. Probe DNA > searches for needle
2. Needs a way to be visualised > fluorescent label in FISH attached to probe DNA
3. Denaturation
Breaking the hydrogen bonds (heat/chemical) between the double stranded probe and target DNA, so that it becomes single stranded
4. Hybridisation: labelled probe attaches to the complementary sequence of the target DNA
Probe forms new bonds with complementary sequence
5. Detection
6. Fluorescence microscope for fluorescent probe
steps to FISH
1. Sections cut at 4-5um on charged slides
2. Slides baked at 60 degrees
3. Dewaxing
4. Pre-treatment
a. Heat/pressure cooker
b. Enzyme treatment
c. (opens up molecular structure)
5. Dehydration in gradient alcohols
6. probe mix added to tissue
7. Denaturation
8. Place in hybrider (14-72 hours)
9. Washes
10. DAPI counterstain
11. View under fluorescence microscope
HER2 gene
Oncogene on chromosome 17
HER2 drug
Transtuzumab (herceptin) = anti-HER 2 antibody
EGFR
• Epidermal growth factor receptor
• Transmembrane receptor plays a role in intracelllular signalling pathways
• Mutations in EGFR gene affect the EGFR tyrosine kinase domain
ALK gene marker
Gene fusion (e.g., EML4–ALK) → constitutive activation
NSCLC, adenocarcinoma
cytoplasmic staining
ROS1 gene marker
Fusion with partners → continuous signalling
NSCLC
cytoplasmic/membranous staining
HER2 gene marker
Gene amplification → receptor overexpression
breast cancer
EGFR gene marker
Point mutations or overexpression → constant activation of downstream signalling
NSCLC
TTF-1
Positive in lung adenocarcinoma, some SCLC
nuclear staining.
Napsin A
Positive in lung adenocarcinoma
granular cytoplasmic staining.
CK7
Positive in lung, breast, and thyroid adenocarcinomas cytoplasmic staining.
CK20
Positive in colorectal and intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma
cytoplasmic staining.
CEA
Positive in adenocarcinomas (lung, colon, pancreas, breast)
cytoplasmic/membranous staining.
Ber-EP4
Positive in adenocarcinoma; negative in mesothelioma.
membranous staining;
EMA
Positive in epithelial tumours (adenocarcinoma, mesothelioma, SCC)
membranous or cytoplasmic staining.
Synaptophysin
Positive in SCLC
fine granular cytoplasmic staining.
CD56 (NCAM)
Positive inSCLC;
membranous staining.
Chromogranin A
Positive in SCLC;
coarse granular cytoplasmic staining.
PD-L1
Positive in NSCLC and other tumours eligible for immunotherapy;
membranous staining on tumour cells.
P40
Positive in squamous cell carcinoma;
strong nuclear staining.
CK5/6
Positive in squamous cell carcinoma and mesothelioma;
cytoplasmic staining.
P63
Positive in squamous cell carcinoma and basal cells of prostate;
nuclear staining.
p16
Positive in HPV-related squamous cell carcinoma (cervix, oropharynx);
nuclear and cytoplasmic staining.
P504S / AMACR
Positive in premalignant and malignant prostate lesions;
cytoplasmic staining (pink/red).
34βE12
Positive in benign prostate basal cells and SCC; negative in prostate carcinoma.
cytoplasmic/membranous staining;
CDX2
Positive in colorectal and intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma;
nuclear staining.
MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2
Positive in normal tissue nuclei;
loss of nuclear staining indicates MMR deficiency (Lynch/MSI-high).
HER2 (IHC)
Positive in breast and gastric carcinoma;
complete membranous staining (3+ IHC score).
Ber-EP4 & EMA (Combined)
Positive in adenocarcinoma;
Ber-EP4 membranous, EMA cytoplasmic.
TTF-1 & Napsin A (Combined)
Positive in lung adenocarcinoma;
TTF-1 nuclear, Napsin A cytoplasmic.
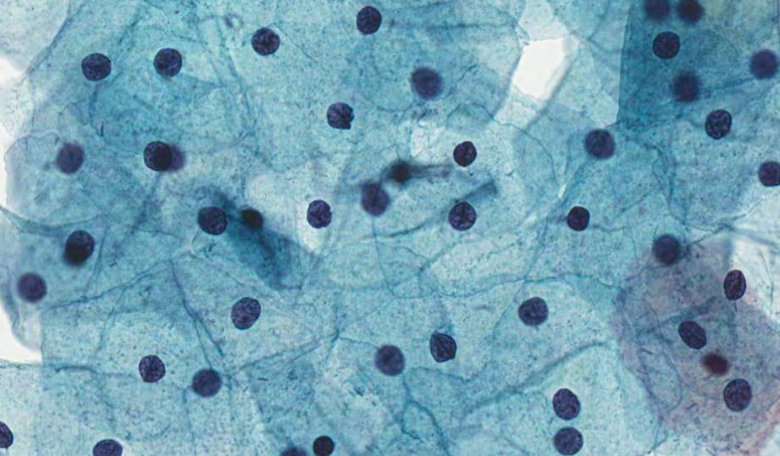
baseline cells
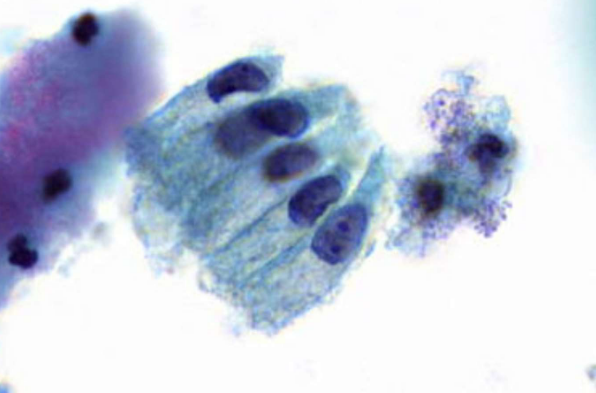
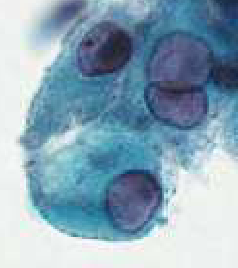
endocervical cells
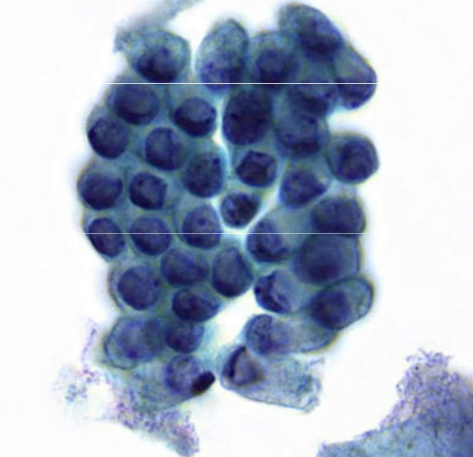
endocervical cells
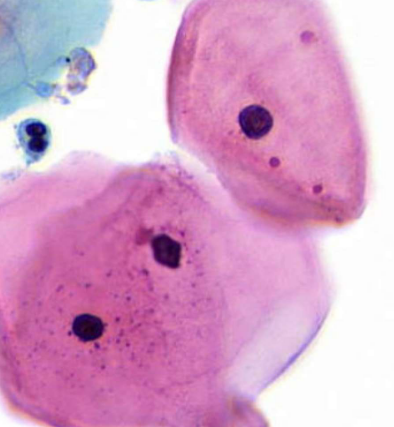
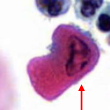
pyknosis
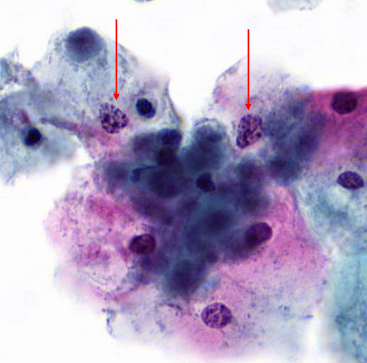
nuclear degenration - karyorrhexis
nuclear degenration - karyolysis
nuclear degenration - karyolysis
nuclear and cytoplasmic degenration
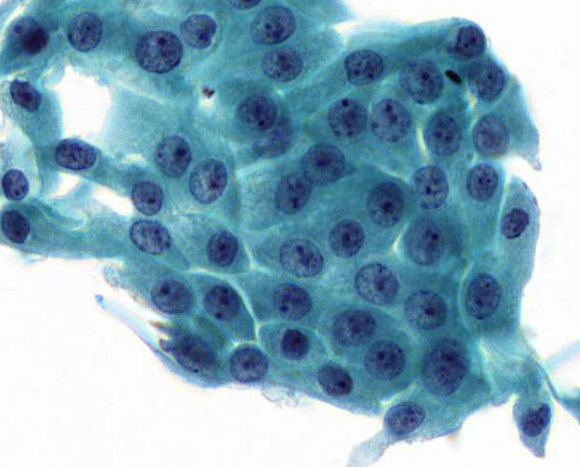
regenerative activity
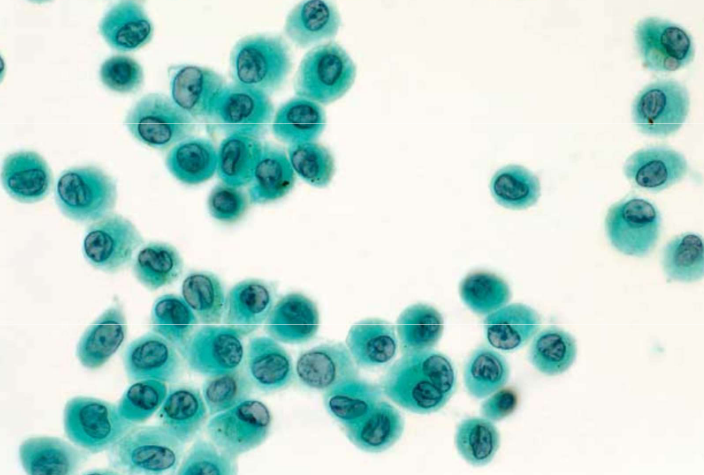
macrophages
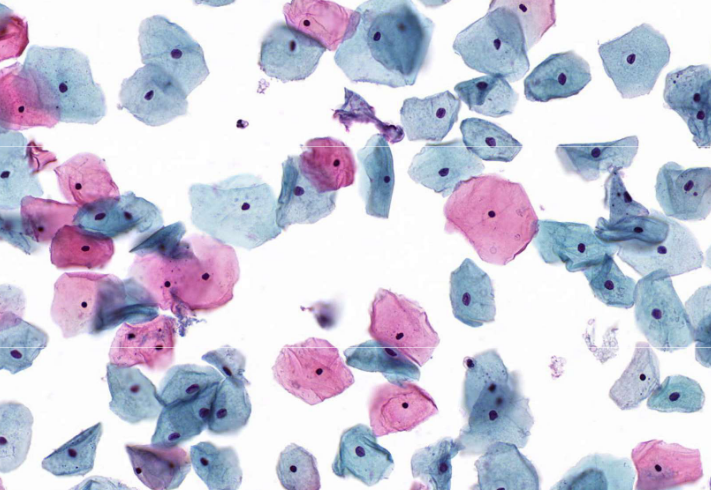
squamous cells
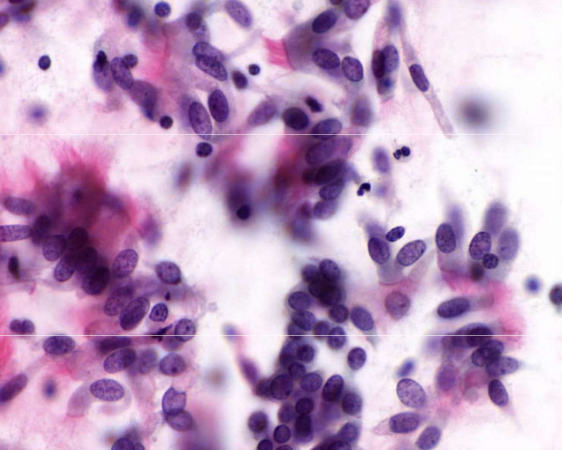
bronchial cells
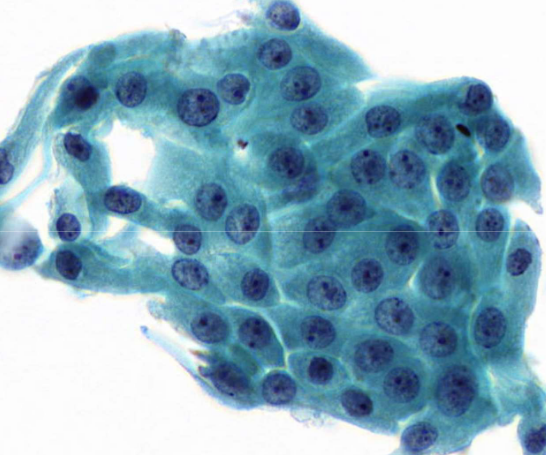
metaplastic cells
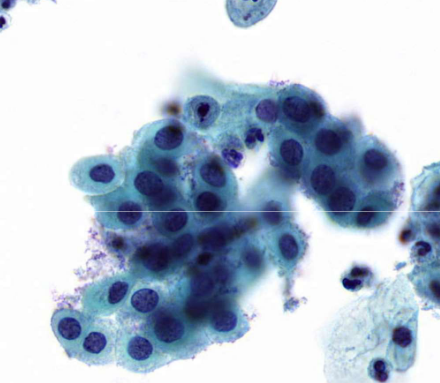
parabasal cells
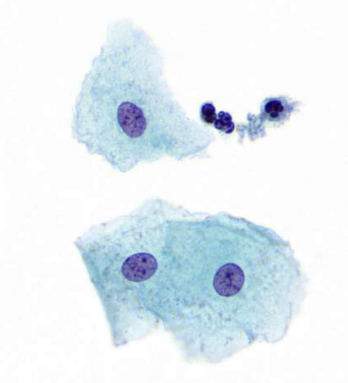
describe features
fine, evenly distributed chromatin, intermediate cells
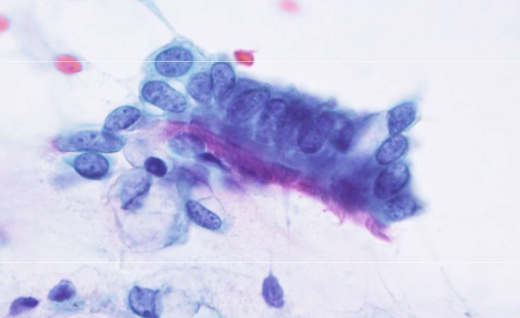
describe features
fine, evenly distributed chromatin bronchial cells
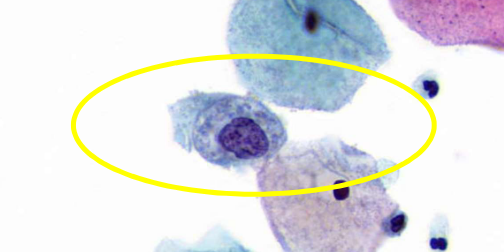
describe features
coarse, irregularly distributed chromatin
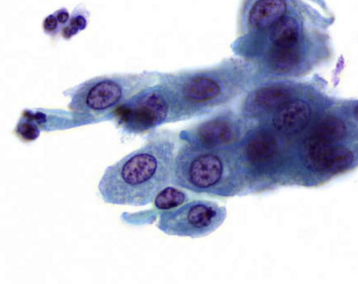
describe features
coarse, irregularly distributed chromatin
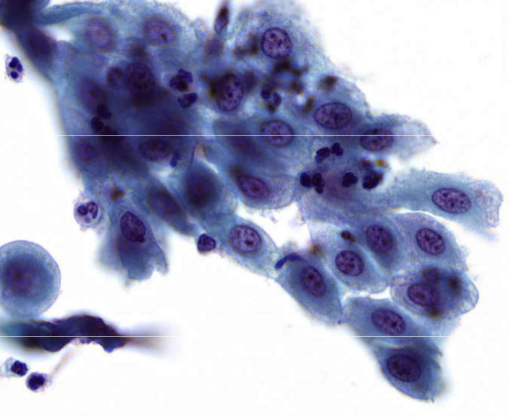
describe features
coarse, evenly distributed chromatin
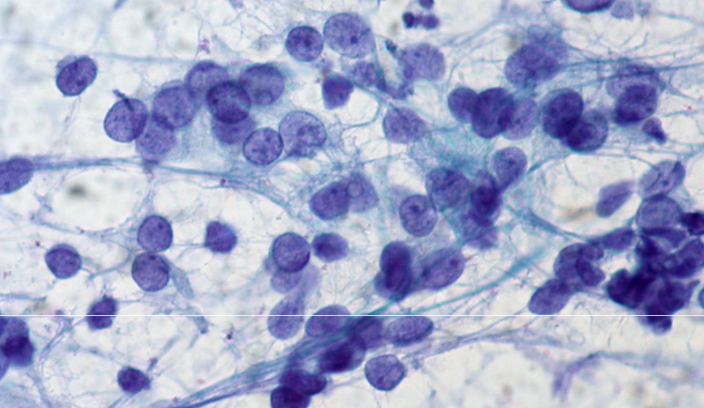
describe features
fine, evenly distributed chromatin
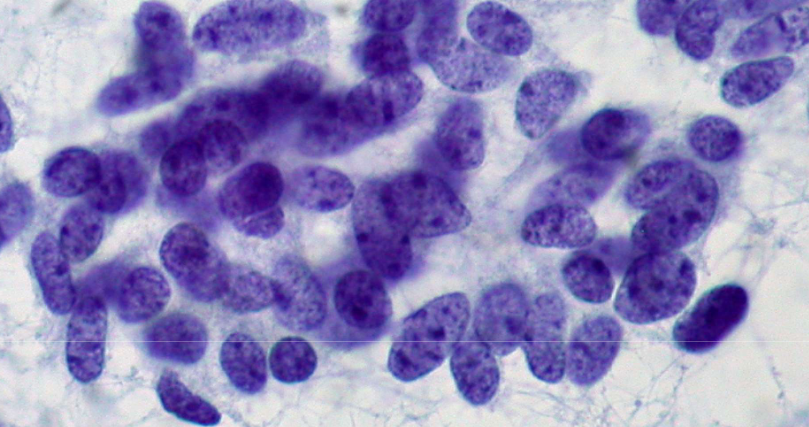
describe features
coarse, evenly distributed chromatin
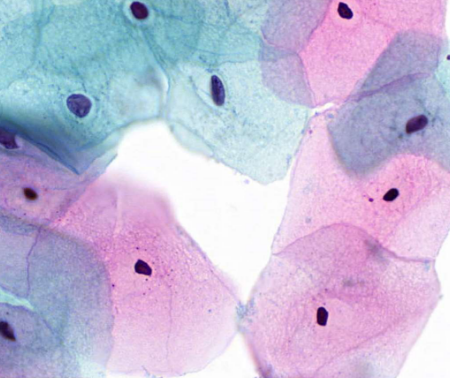
describe cytoplasm
non-vacuolated
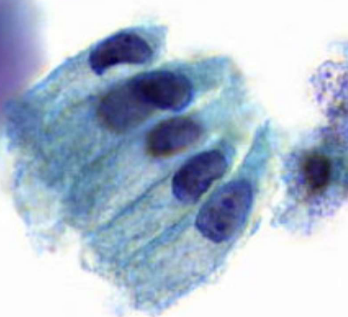
describe cytoplasm
finely vacuolated
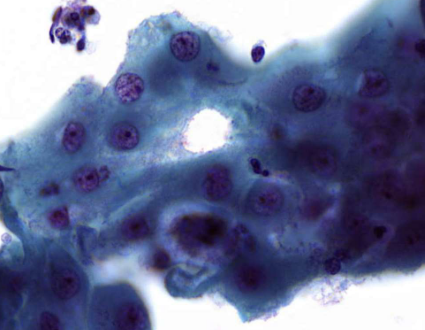
describe cytoplasm
dense
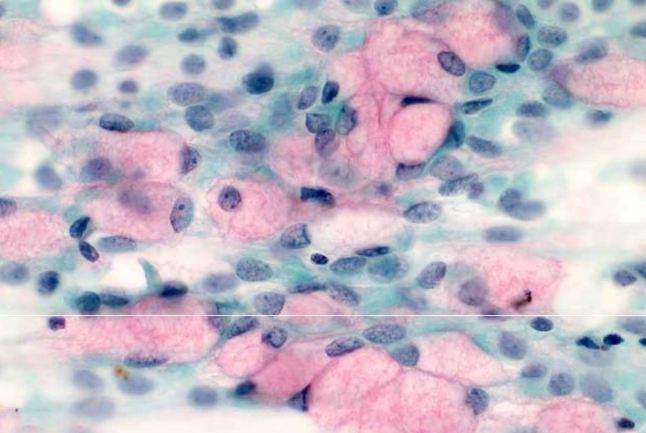
mucus producing cells - goblet cells
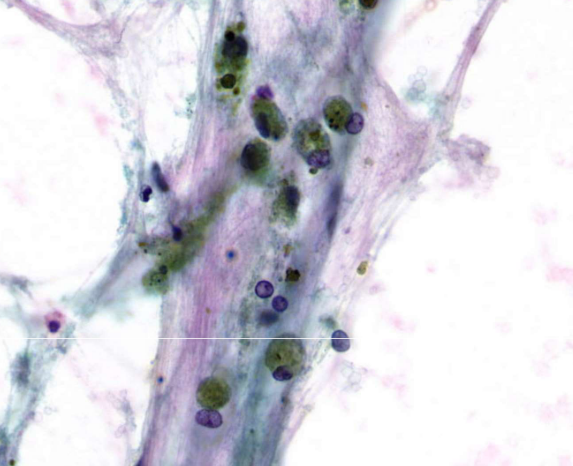
alveolar macrophages
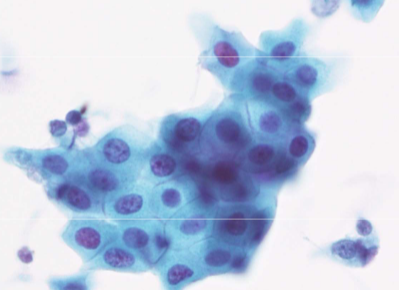
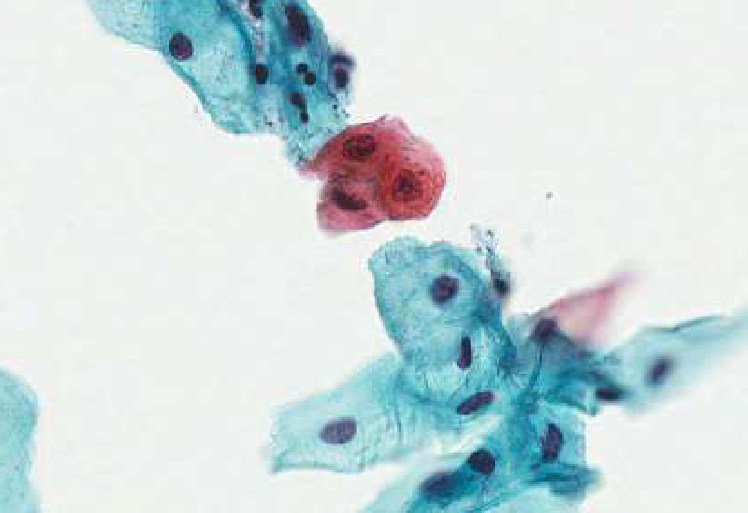
squamous metaplasia
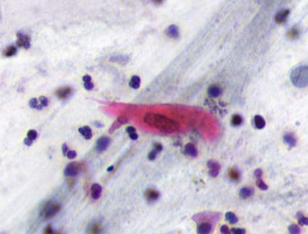
squamous cell carcinoma
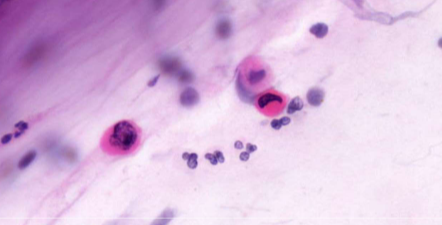
squamous cell carcinoma
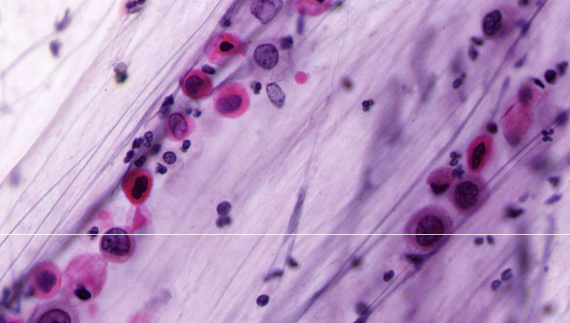
squamous cell carcinoma
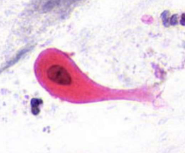
squamous cell carcinoma - tadpole cell
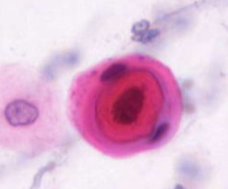
squamous cell carcinoma - pearl formation
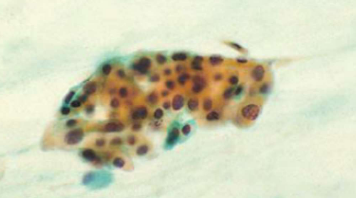
SCC differential - atypical squamous metaplasia
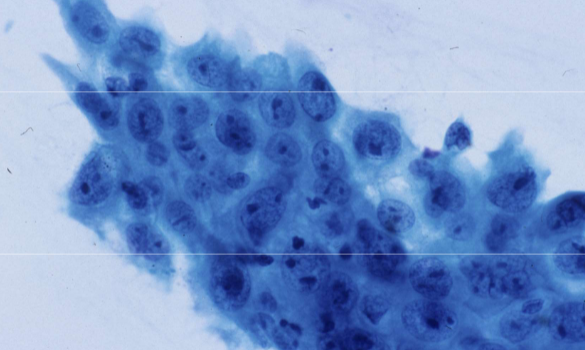
SCC differential - reactive changes
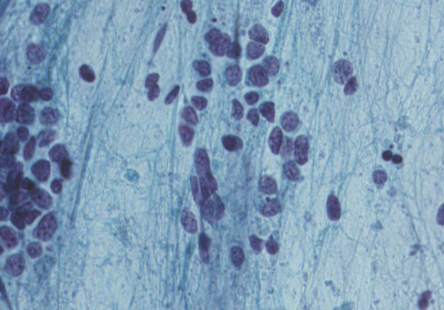
small cell carcinoma (SCLC)
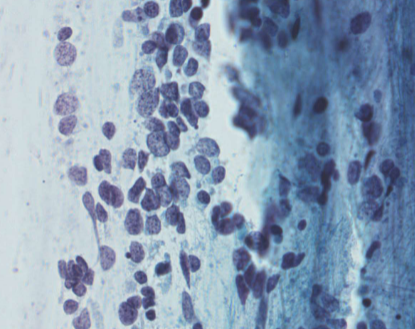
small cell carcinoma (SCLC)
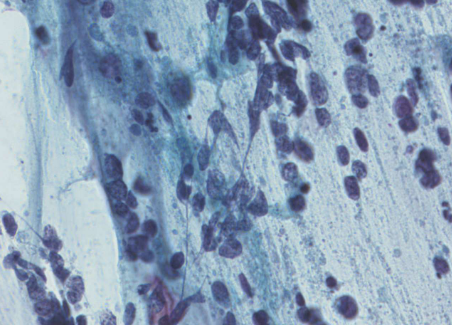
small cell carcinoma (SCLC)
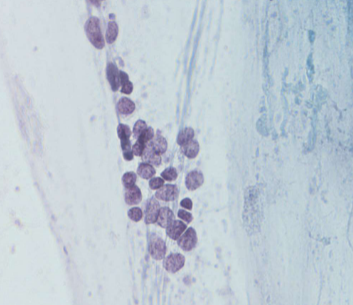
small cell carcinoma (SCLC)
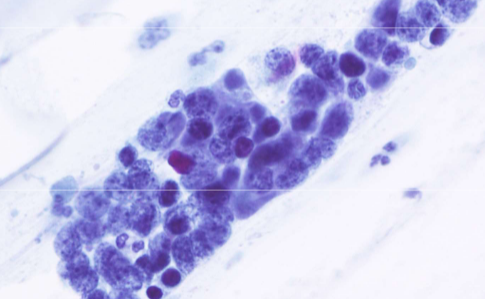
small cell carcinoma (SCLC)
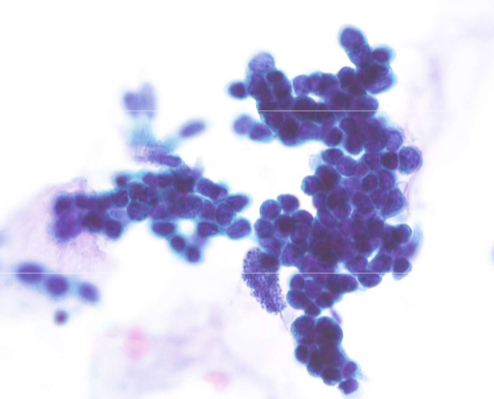
SCLC differential - reserve cell hyperplasia
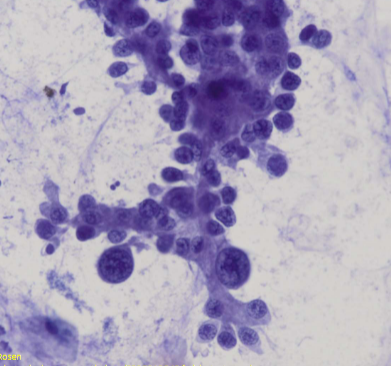
adenocarcinoma