L2, Ch 5: Introduction to Clinical Education
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Importance of Clinicals
allows the student to integrate the knowledge gained from didactic courses into clinical practice while caring for patients
Education as a medical imaging professional will include three areas of learning:
Cognitive - behaviors requiring various levels of thought: knowledge, understanding, reason, and judgment
Affective - behaviors guided by feelings and emotions that are influenced by an individual’s interests, attitudes, values, and beliefs
Psychomotor - behaviors involving physical actions, neuromuscular manipulations, and coordination
Requires prior learning in the classroom and laboratory
Permits one-on-one, direct patient contact
Learning is a
continuum
As your education proceeds, it will necessarily shift from didactic instruction to more clinical education, in a variety of clinical settings
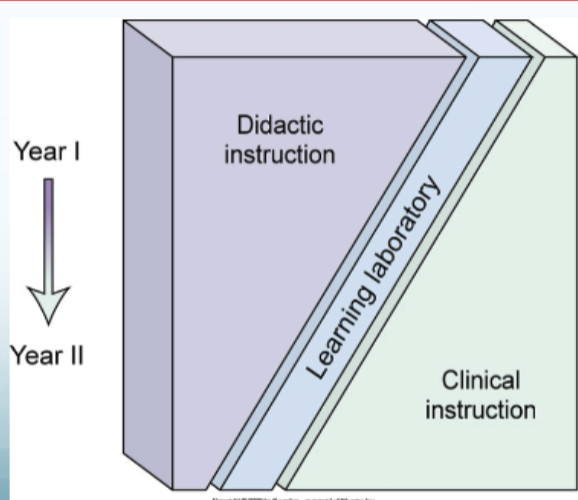
Learning Process
Based on performance objectives
Learning observed and measured by way of competencies
Learning outcomes → treat these goals as a staircase trying to reach the top
Competencies
ARRT has established a minimum number of clinical competencies in various exam categories
Clinical competence must be performed independently consistently, and effectively
Student supervision can be direct and indirect.
Eligibility for the ARRT credentialing examination requires all clinical skills and competencies completed and documented by program officials
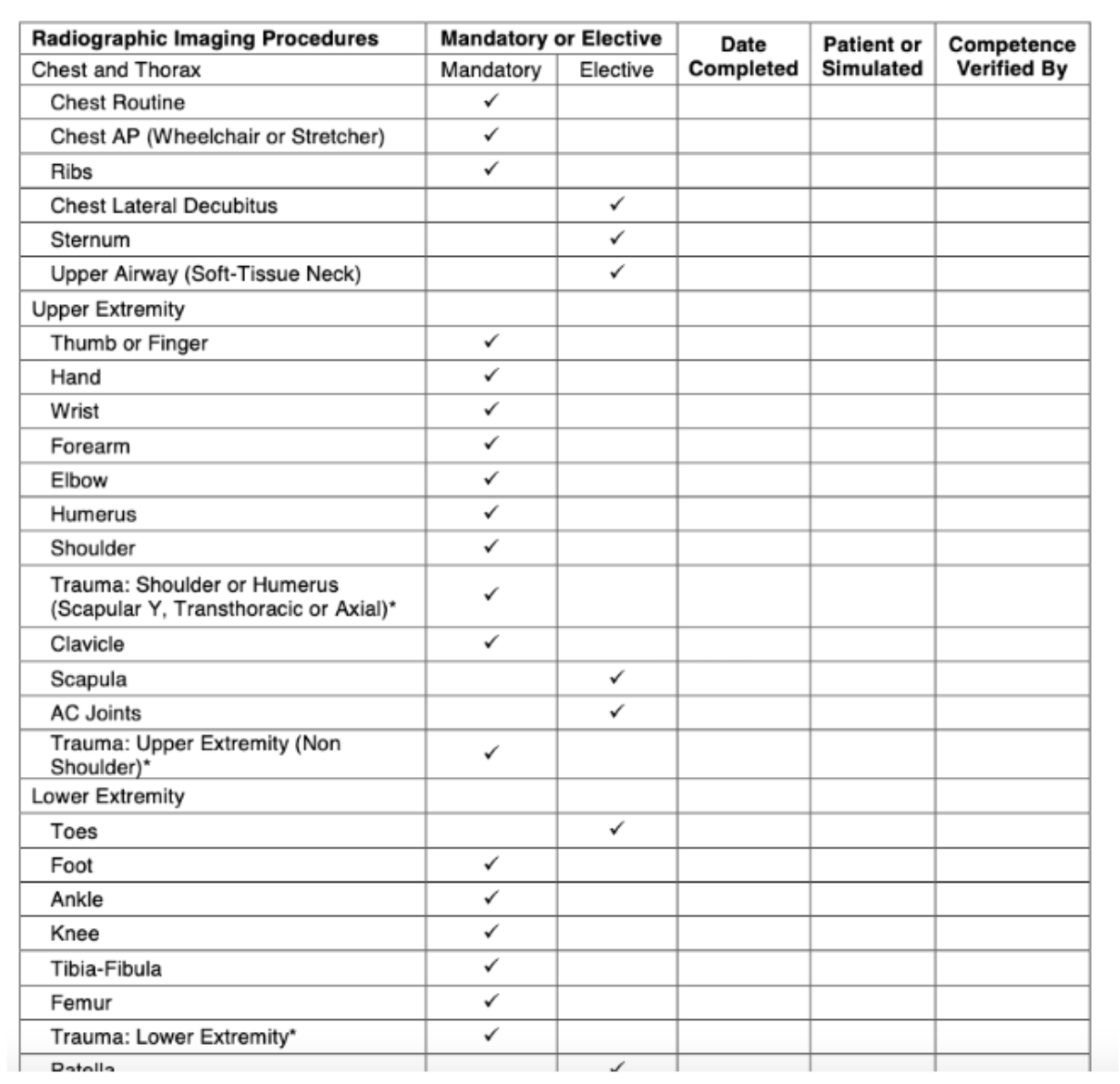
Competencies Requirements
Ten mandatory general patient care activities
37 mandatory imaging procedures
15 elective imaging procedures selected from a list of 34 procedures
One of the 15 elective imaging procedures must be selected from the head section; and
Two of the 15 elective imaging procedures must be selected from the fluoroscopy studies section, one of which must be either upper GI or contrast enema
Stages of clinicals
observation
assistance
performance
Direct Supervision
qualified radiographer
review the request for examination in relation to the student’s achievement
evaluate the condition of the patient in relation to the student’s knowledge
be physically present during the conduct of the procedure
review and approve the procedure and/or image
Indirect Supervision
qualified radiographer
reviews, evaluates, and approves the procedure as for direct supervision
immediately available to assist students regardless of the level of student achievement
“Immediately available” is interpreted as the physical presence of a qualified radiographer adjacent to the room or the location where a radiographic procedure is being performed
Major Clinical Education Policies
Supervision
Performance of actual examinations
Simulations
Assessments
Radiation protection
Practices
Disciplinary Procedures
Professional ethics
Practice standards
HIPAA
Professional appearance and behavior
Attendance and tardiness
Pregnancy
Getting Comps or Signed off
Students who want to get an exam signed off must perform the following steps. Note: If one of these steps does not happen, you cannot get signed off and will need to try again
Ask to be signed off prior to getting the patient.
Once you get the okay from a technologist or CI, there can be no assistance from the technologist
If the technologist intervene at any time of the procedure you have failed and will need to try again
Getting signed off involves naming anatomy, setting the technical factors. etc.
Student Course Development
The curriculum is not designed to make the student fail, rather to make the student succeed in delivering optimum patient care.
JCERT Standards
Competency based
Designed in three phases
Allows for the translation of theory into practice in a real-world setting
Do’s and Dont’s in Clinical Setting
Do arrive early or on time
Do not arrive late. Arriving late shows a lack of RESPECT the department, the CI, and yourself.
Do not argue with the tech or get into department politics.
Do not compare what you were taught to what the technologists teaches you. Remember, you have to learn both
When you have time to lean, you have time to clean.
TeamSTEPPS to Patient Safety
an evidence-based teamwork system
TeamSTEPPS approach uses highly effective teams, necessary to the best patient outcomes.
Consists of five (5) key principles
Team structure
Communication
Leadership
Situation monitoring
Mutual support
TeamSTEPPS to Patient Safety Videos
Root cause of medical errors
poor communication
Joint Commission #2 the effectiveness of communication among
caregivers to Implement a standardized approach to handoff including
an opportunity to ask and respond to questions
Patient-Centered Care
treating patients as partners, involving them in planning their health care and encouraging them to take responsibility for their own health
SBAR
A strategy to improve communication when “handing off” a patient from one health care worker to another Consist of four (4) elements
Situation
Background
Assessment
Recommendation
SBAR is a structured communication process that provides for accurate sharing of patient information between health care workers when patient handoff occurs
SBAR Video
Transfer of learning
The principle of transfer of learning is exemplified in the clinical education component, with the student recalling prior knowledge learned and using this knowledge in performing diagnostic or therapeutic procedures to develop both the skills and the confidence to work with a wide variety of patients
competency
the observable, successful achievement of the performance objectives
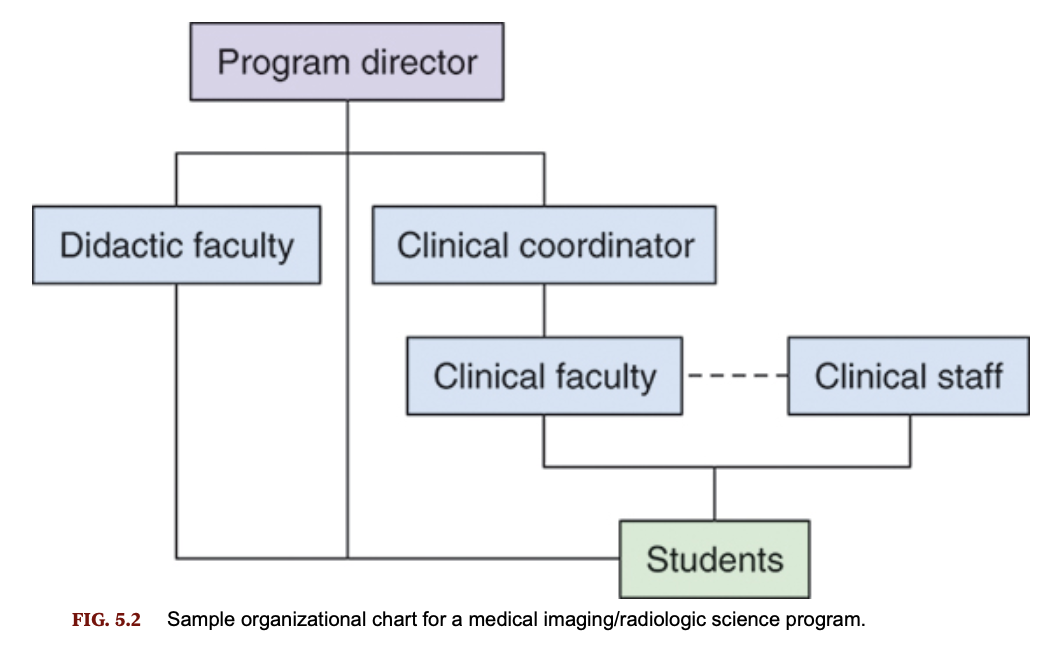
Organizational chart for radiologic science program
The program director works full time in organizing, administering, and assessing the radiography program. This person is responsible for the didactic and clinical effectiveness of the program.
The clinical coordinator works closely with the program director in ensuring program effectiveness through a regular schedule of coordination, instruction, and evaluation.
The clinical instructor works directly with the student in the clinical setting
Members of the clinical staff are employees of the healthcare institution and provide student supervision and guidance
Interprofessional education (IPE)
one approach to teaching students and healthcare workers how to interact and work with each other in the clinical setting. IPE allows for healthcare and social care workers or students, from two or more professions, to engage in learning with, from, and about each other. This interprofessional learning environment cultivates professional collaborative practice to support patient-centered healthcare
DMI Application Window
July 10 - August 15
DMI Application is submitted
online only
DMI Application: Volunteer Hour Verification
40 hours of patient and radiographer observation in general radiographic procedures in acute hospital (not rehabilitation, not urgent care, not film library, not ambulatory care/clinic etc)
40 hours in general radiography (skeletal, chest XR, fluoroscopy, surgery) or
30 hours in general radiography and 10 hours in another modality (MRI, CT, US, Mammo, DEXA, IR)
Don’t list only chest XR’s lol
DMI Application: Professional Questions
If more than 2 incorrect/poorly answered questions, application disqualified
College level writing
Wikipedia is not a reputable source
DMI Application: Academic Requirements
Prerequisite Courses GPA: 2.5
Overall GPA: 2.0
Grades lower than “C” and “Pass/No Pass” are not acceptable in prerequisite courses
Prerequisites
General college chemistry + lab
English
Human anatomy + lab
Human physiology + lab
Intermediate Algebra
Introductory physics + lab
If prereq done at different college, need Dean of department sign off course equivalency
Academic history more than 2 incomplete grades, withdrawals, or repetition in last 7 years of prerequisite courses due to failures, academic probation, etc may be cause for application disqualification
DMI Application: Drug Screen
no marijuana
DMI Application: Felonies or Misdemeanors
federal level background check
If applicant has felony or misdemeanor conviction, ARRT must determine eligibility for the Registry examination before applicant has completed the program
DMI Application: cohort
Fall or Spring