cvp 1: anatomy of the pulmonary and cardiovascular systems
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
pulmonary/respiratory system anatomy includes
bony thorax, muscles of ventilation,upper and lower airways, pulmonary circulation
pulmonary/respiratory system anatomy functions
gas exchange, fluid exchange, maintains a low volume blood reservoir, filtration and metabolism
thorax houses
2 lungs and heart (mediastinum)
Bony thorax covers and protects the
major organs of the cardiopulmonary system (heart and lungs)
Boundarie of thorax
front: sternum, cartilage, ribs
lateral: ribs
back: 12 vertebrae
what are the sections of the sternum
manubrium, body, xiphoid process
Manubrium (top of sternum) - articulates with
clavicles and 1st and 2nd ribs
jugular or suprasternal notch at the superior border of the manubrium has what behind it
trachea
body of the sternum articulates with what
ribs 3-7
what is the xiphisternal joint
point where sternal body and xiphoid process fuse
Angle of Louis/Sternal angle between manubrium and body significance
place to find 2nd ribs laterally (costal cartilage), T4 and T5 posteriorly, bifurcationof trachea into L and R mainstem bronchi
where is the 1st rib
under the clavicle
different kind of ribs
true ribs
false ribs
free ribs
what are true ribs and which rib numbers are they
ribs that attach to the sternum directly via their costal cartilages
ribs 1-7
what are false ribs and which rib numbers are they
Attach to cartilage of the rib above, not to the sternum directly, via their costal cartilage
ribs 8-10
What are floating ribs? Which rib numbers are they?
ribs that end freely
ribs 11-12
what does the costal groove house?
intercostal nerve and vessels
Pulmonary ventilation
Air moved in and out of the lungs - 'breathing'
how does inspiration occur
The diaphragm moves down, the external intercostal muscles contract, and the chest cavity expands, which allows air to move into the lungs.
muscles change volume of thorax - more negative compared to the atmosphere (intrathoracic pressure)
Bucket and pump handle mechanisms increase intrathoracic volume
muscles of inspiration
-Primary muscles of inspiration: diaphragm, EXTERNAL intercostals
-Accessory muscles of inspiration: sternocleidomastoid, scalenes, levator costarum, serratus, trapezius, and pectorals
when are the accessory muscles for inspiration:
used when a more rapid or deeper inhalation is required or in disease
inspiration is what kind of process
ACTIVE
describe the diaphragm
a dome sheet of muscle separating the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity
innervated by the phrenic nerve
right dome: 5th rib
left dome: 6th rib
openings in the diaphragm allow IVC, esophagus, aorta..
describe the external intercostals
11 on each side of the sternum
oblique, forward, and downward fibers allow the ribcage to elevate and cause lateral and anterior expansion
actions of the accessory muscles of inspiration

expiration is what kind of process at rest
PASSIVE
Recoil of lungs and relaxation of ext. intercostals and diaphragm
when does active expiration occur? what muscles are at play?
cough, huff
rectus and transverse abdominis, int and ext obliques; increase abd pressure and Interosseous portion depress ribs
pleura types
visceral and parietal
describe the pleura
visceral: Covers outer surface of the lung, attached to lung tissue
parietal: Covers inner surface of the chest wall, diaphragm,mediastinum
what is the pleural space/pleural cavity? what does it do?
Potential space between the two pleurae
pleurae are in intimate contact with each other - thin serous fluid
Constant negative pressure within this space maintains lung inflation
what is the lung made of?
parenchyma--substance of lung, porous, and spongy filled with alveoli
how is the lung shaped?
apex, base, three borders, and surfaces
3 borders: ant, post, inf
3 surfaces: costal, medial, diaphragmatic
what is the hilus
point at which nerves, vessels (pulmonary artery and vein), primary bronchi enter the lung parenchyma at 5-7th thoracic vertebrae
difference between right and left lobes of the lung
Right: upper, middle (CANNOT FEEL IN THE BACK), lower lobes
Left: upper (lingula - where middle would be) and lower
what is the horizontal fissure?
separates the superior and middle lobes of the right lung
from the level of the right fourth costal cartilage horizontally to a junction with the oblique fissure at approximately the midaxillary line at the 4th rib
ONLY ON RIGHT LOBE
what is the oblique fissure
the line that divides each lung roughly in half
extends from the level of 4th thoracic vertebra posteriorly to the diaphragm anteriorly and inferiorly. 6th ribanteriorly to 5th rib in axilla
where is the middle lobe of the (right) lung
Ribs 4 - 6 in the front
where is the lingula of the left lobe
Xiphoid process ~ rib 6
What is the cardiac notch?
indentation in the left lung where the heart lies
where is the lower lobe of the lung
From 1 inch below the spine of the scapula to T10
what is the upper respiratory tract
nose, pharynx, larynx
what is the lower respiratory tract
trachea
mainstem bronchi
segmental bronchi respiratory/terminal bronchioles
alveolar ducts
alveolar sacs
Respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveolar sacs are
gas exchange airways
trachea, primary bronchus, bronchus, bronchi and terminal bronchioles are
conducting airways: conduct, warm, humidify, filter
peripheral nervous system types
Autonomic nervous system: (Parasympathetic (PSNS) and sympathetic(SNS))
peripheral nervous system innervates
bronchial and vascular smooth muscles, glands
PSNS Vagus nerve functions
bronchial constriction, pulmonary arterialsmooth muscle dilation and increased glandular secretions
SNS nerve functions
bronchial relaxation, pulmonary arterial smooth muscleconstriction, decreased glandular secretions (bronchodilators)
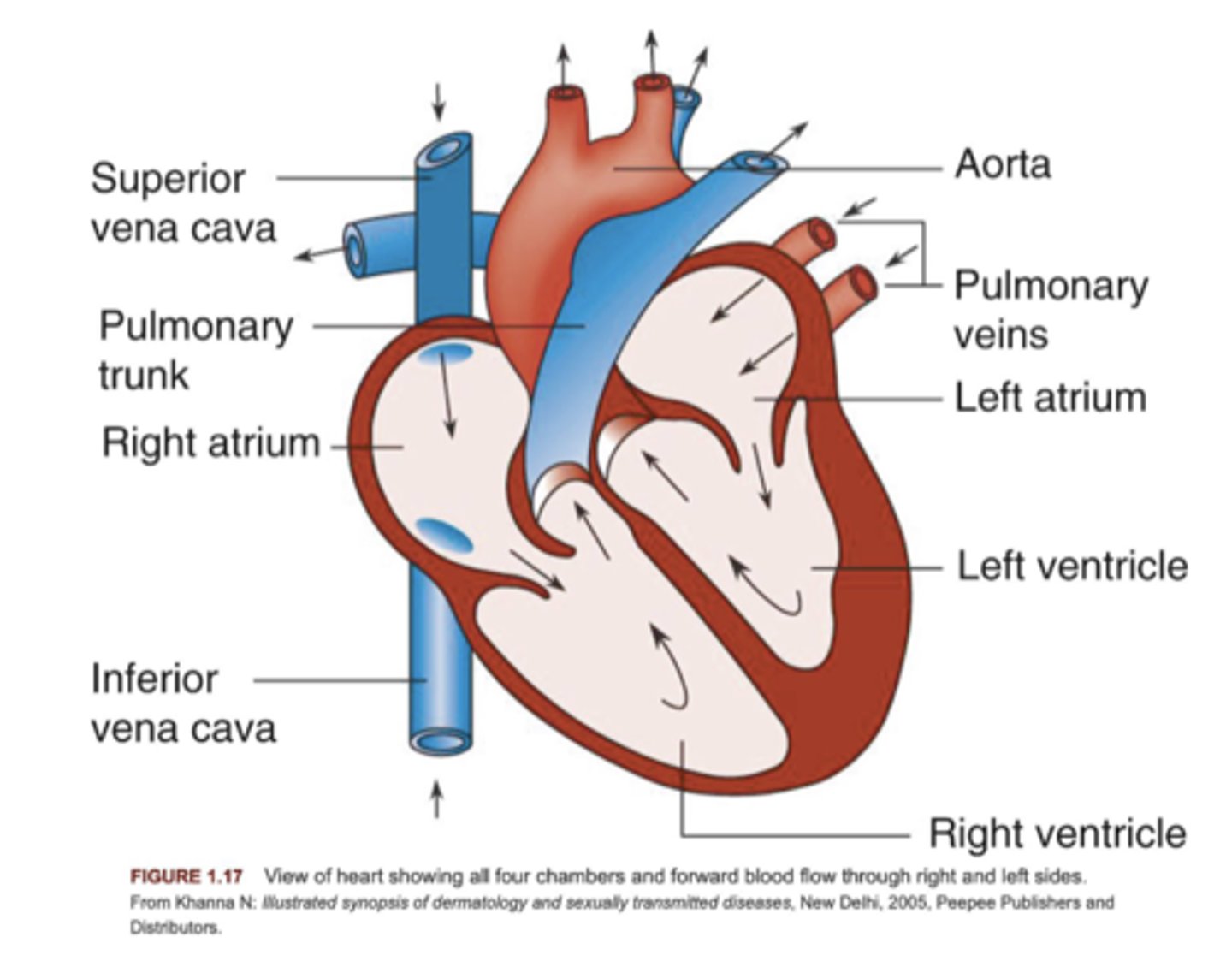
circulation of the heart
RA-> Tricupsid Valve-> RV -> Pulmonic Valve-> Lungs-> Back into pulmonary veins-> LA-> Mitral Valve (bicupsid)-> LV-> Aorta-> Body
Pulmonary arteries function
carry oxygen-poor blood from the right side of your heart to your lungs
pulmonary veins function
blood vessels that transfer freshly oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atria of the heart
Cardiovascular System Anatomy
what is the mediastinum
structure separating the right and left thoracic cavities/pleura
contains all thoracic viscera except lungs
Contains the heart, great vessels of the heart, esophagus, trachea, phrenic nerve, thymus.
what is a mediastinal shift
Shift of thoracic structures to one side of the body
what is a tension pneumothorax
air stuck in the pleural space
describe the heart
Pumps blood thru the entirevascular system
Lies obliquely in the mediastinum
key ways to find the heart
Base: superior portion - made up of two atria - level of 2nd intercostal space
Apex: tip of left ventricle, 5th intercostal - midclavicular line
heart tissue layers
endocardium-innermost layer
myocardium-middle layer
epicardium-outermost layer
what does the myocardium do?
Performs pumping action of the heart
what does the pericardium do?
Protects and anchors the heart
Prevents overfilling of the heart with blood
Allows for the heart to work in a relatively friction-free environment
what does the endocardium do?
lines the inside of the heart
what is pericarditis?
inflammation of the pericardium
what is endocarditis?
inflammation of the inner lining of the heart
what is serous pericardium?
thinner, more delicate membrane, double layer (parietal layer fused to fibrous pericardium and visceral layer called epicardium)
heart pressures
Central venous pressure: 0-8 mmHg - normal diastolic pressure to enable filling
Right ventricle: diastolic pressure: 0-8 mmHg, systolic: 15-30 mmHg
Left atria: diastolic pressure: 4-12 mmHg
Left ventricle: diastolic: 4-12 mmHg, systolic: 80-120 mmHg
heart valves
atrioventricular valves and semilunar valves
chambers of the heart
right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle
atrioventricular valves include
tricuspid and bicuspid (mitral)
semilunar valves include
pulmonary valve and aortic valve
right-sided valves
tricuspid and pulmonic
Left sided valves:
mitral and aortic
AV valves function
prevent backflow of blood into the atria during ventricular contraction or systole
semilunar valves function
prevent backflow of blood from the aorta and pulmonary artery into the ventricles during diastole
diastolic pressure
occurs when the ventricles are relaxed; the lowest pressure against the walls of an artery (lower number)
systole
contraction phase of the heartbeat/ contracting of the ventricle
conduction system of the heart
SA node, AV node, Bundle of His, Purkinje fibers
the autonomic nervous system influences...
the rate of impulse generation, and strength of contraction
parasympathetic relationship to HR
vagus nerves realeases acetylcholine and decreases HR on SA and AV nodes (NO MUSCLE CONTRACTILITY)
sympathetic relationship to HR
cardiac plexus releases norepinephrine, increase HR and muscle contractility, Beta receptors
the SA node is the...
junction of the SVC and right atrium
the SA to AV node is
internodal tracts
describe the aorta
largest artery in the body and carries oxygenated blood at high pressure
receives ejected blood from the left ventricle
3 parts: ascending aorta, aortic arch, descending aorta
describe the ascending aorta
originates at the base of the left ventricle
contains the opening to coronary arteries
describe the aortic arch
originates at level of R 2nd costal cartilage
courses upward backward and leftward
ends at level of L 2nd costal cartilage
what comes off the aorta
brachiocephalic trunk
left common artery
left subclavian
right and left coronary arteries
coronary arteries
receives blood during diastole
the right coronary artery supplies
-right atrium right ventricle
-posterior and inferior surface of the left ventricles
-the SA and AV nodes (80% of population)
right coronary artery divides
posterior descending artery
supplies posterior walls of both ventricles and L inf ventricles(sometimes L or co-dominant)
left coronary artery supplies
Left atrium left ventricle
SA node in 40% of people
The anterior septum
left coronary artery divides
left anterior descending branch
70% of L ventricle
left cricumflex artery
diagonal branch
cardiac veins drain
into common sinus which empties into RA
thebesian veins drain
directly into the myocardium and into all four chambers
describe pulmonary veins
transport oxygenated blood to the left atrium of the heart
2 veins from each lung: superior and inferior
originate in capillary beds
drains into the left atrium
describe the pulmonary arteries
carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs
originate at pulmonary trunk from base of RA
runs anterior to Left of ascending aorta
becomes right and left at the level of T5
describe arteries and arterioles
composed of elasic and fibrous connective tissue
aorta and pulmonary artery is more elastic and has more strethc with heart pumping
smooth muscles receives autonomic stimulation from alpha receptors (smaller arteries and arterioles)
describe endothelium functions
functions: filtration, permeability, vasomotor, clotting, and inflammation
Atherosclerosis is initiated through
endothelial dysfunction
evidenced by endothelial cells that are extensively permeable to fat cells and white blood cells.
describe venules and veins
thinner walls. larger diameter, less elastic tissue
valves create unidirectional flow
blood transferred back to the heart through the muscle pump and by negative pressure during inspiration
venules and veins functions
to act as conduit vessels, transporting blood back to the heart from the body's organs and tissues (i.e., the venous return); and
to act as capacitance vessels, accommodating large volumes of blood
Very distensible - expand easily