Biochem Unit 2
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
Thermodynamics of Transport for Charged Species
Where C is the concentration,
Z is the on the ion being transported
F is the Faraday constant (96.5 kJ/volt-mol) and psi is the electrical potential of the solution
Delta psi is the voltage difference across the membrane
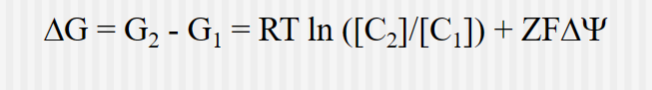
Passive Diffusion
For uncharged molecules, passive diffusion is an entropic process. If C2 is less than C1 , then delta G is negative, and the process occurs
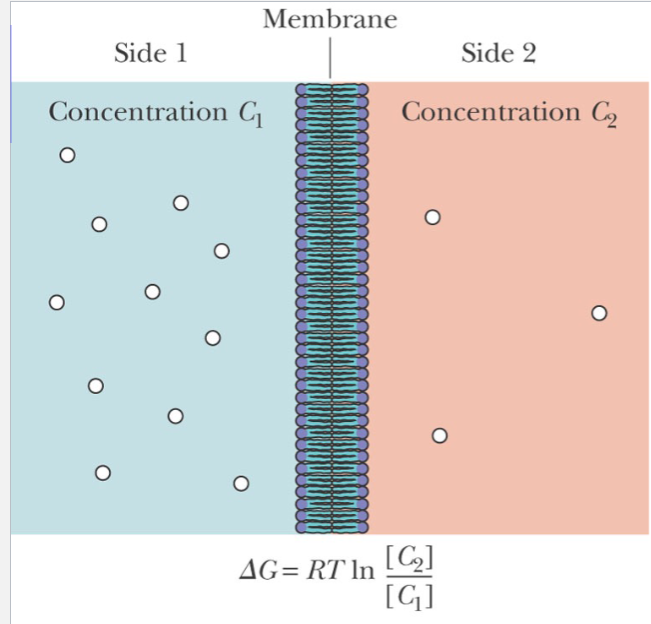
facilitated diffusion
Transported species moves down electrochemical gradient
Usually faster than passive processes
Membrane protein or other “carrier” involved
Passive vs facilitated diffusion
For passive diffusion, the rate is proportional to concentration of diffusing species
For facilitated diffusion, the rate of transport is saturable
Example of Facilitated Diffusion
Glucose transporter in erythrocytes
cytochalasin B
a inhibitor from a fungus, that binds competitively to the glucose transporter and inhibits it
Active Transport
Energy of ATP hydrolysis used to do work of transport
Na +, K+ -ATPase
Pumps Na + out of cells, K+ into cells (2K+/3Na +)
Ion gradients important in nerve transmission, and in “cotransport” of other species
Two subunits
Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation and two protein conformations (conformations change after binding to ATP) involved
Specific inhibitor—cardiac glycosides
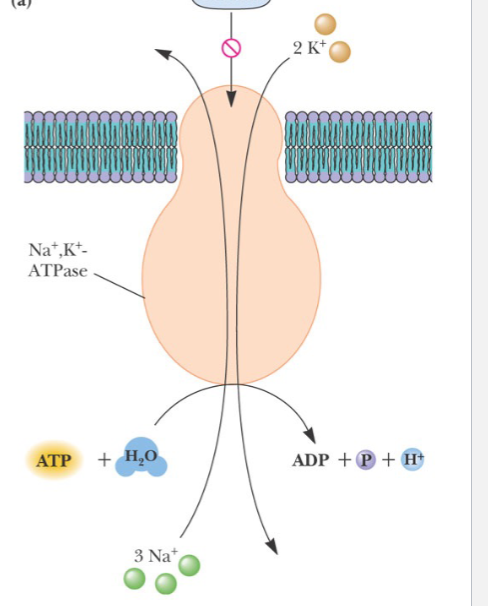
This process is
charge neutral due to H+ and 2K+ coming in
Ca 2+ -ATPase
Ca 2+ is a cellular “second messenger” in virtually all cells
Normally Ca 2+ is kept low by pumping it into cellular vesicles called the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Pumping is by an ATP-driven, Ca 2+ -ATPase
Important in lowering concentration of Ca 2+ released after muscle contraction
Some protein homology to Na +, K+ -ATPase, both in structure and in mechanism
H+ -ATPases
Gastric H +, K+ -ATPase
K+ , Cl - symport makes it an HCl pump
Vacuoles and Osteoclast
Mitochondrial and Chloroplast ATPases
Role of these pumps is to use proton gradient to drive synthesis of ATP rather than ATP hydrolysis to drive pumping of protons
Osteoclast Proton pump
The osteoclast pumps out protons right by the bone, solubilizing it, for providing Ca+2 elsewhere in the body
Ion Gradient Driven Active Transport/Secondary Active Transport
cotransport ions go down their electrochemical gradient and other molecules (glucose or amino acids) goes up their electrochemical gradient
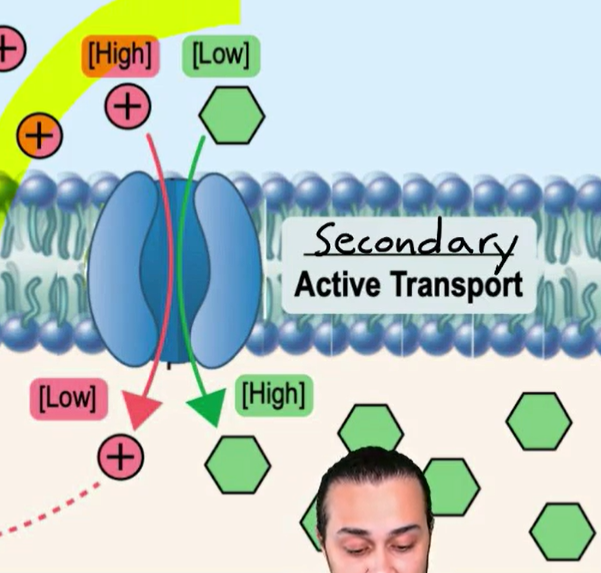
Symport
Substance transported in same direction of ion
Antiport
Substance transported in opposite direction of ion
Light Driven Transport
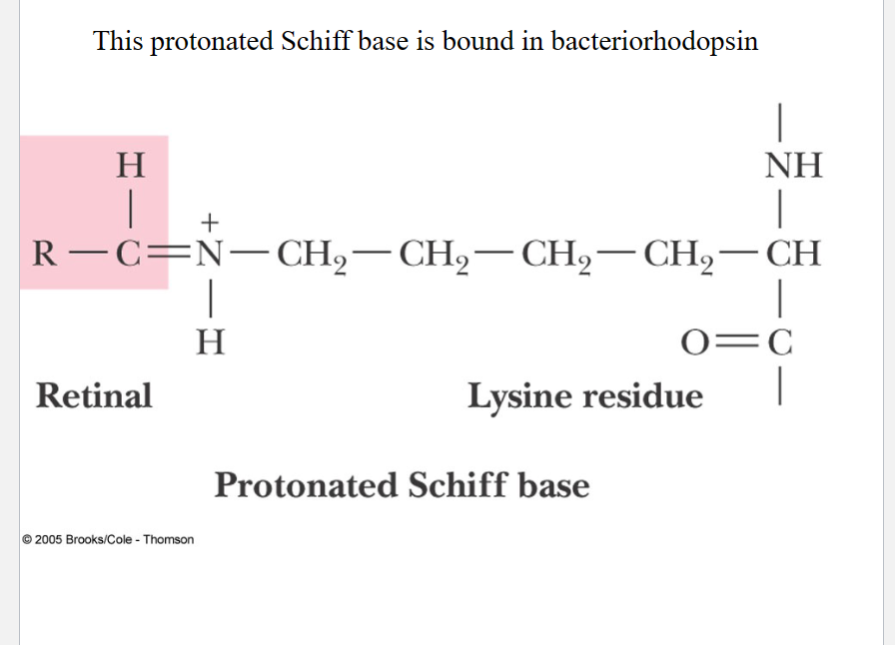
Bacteriorhodopsin
a major membrane protein of Halobacterium halobium, forming purple patches in membrane
Retinal bound as Schiff base to lysine residue of bacteriorhodopsin
Light absorption promotes trans to cis isomerization
of the retinal
Conformational changes during isomerization results in pumping protons out of cell
Porins
Pore forming proteins
Relatively non-specific
Outer membranes of bacteria and mitochondria
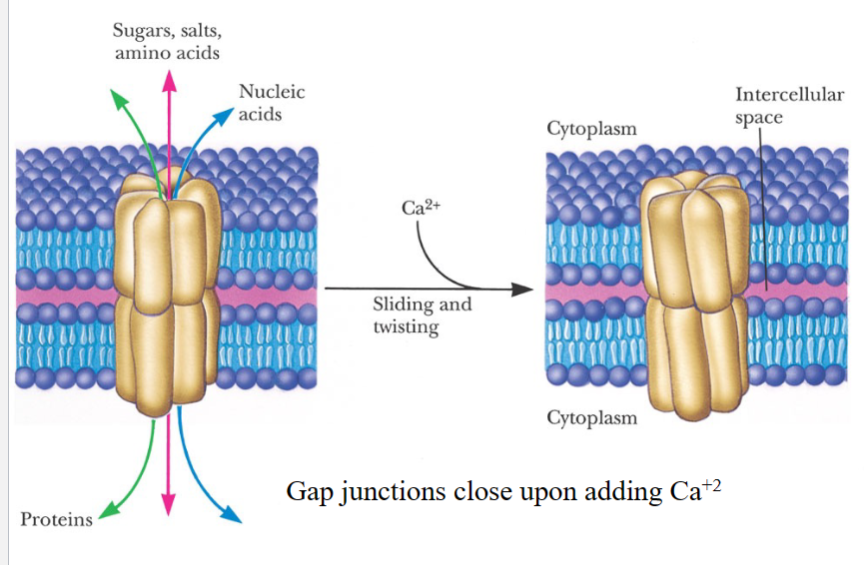
Gap Junctions
Forms connections between cells
(the one shown in this picture is a homohexamer)
Ionophores
Mobile carrier
Cyclic peptide, valinomycin, is an example
Channel forming peptides
Gramicidin as an example
cyclic ionophore, valinomycin
specific for K+1
prefix m
x 10^-3
prefix µ
x 10^-6
prefix n
x 10^-9
monomer of nucleic acids
nucleotides
Nucleotides composition
Heterocyclic Base
Pentose
Phosphate
pyrimidine ring
Note the numbering system is different for the two types of ring structures
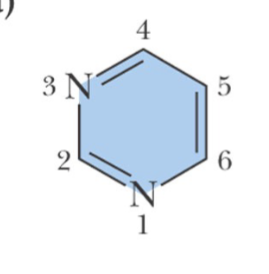
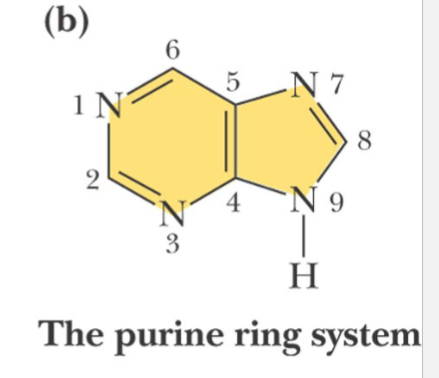
purine ring
Note the numbering system is different for the two types of ring structures
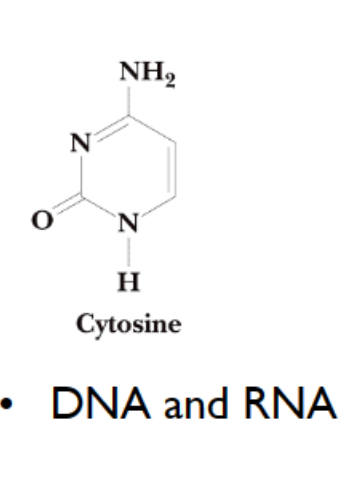
cytosine
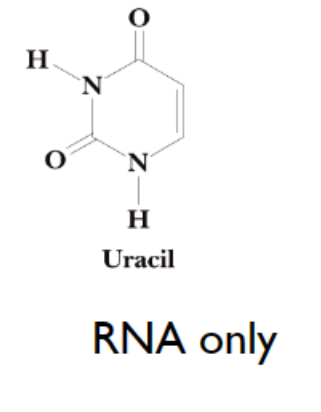
uracil
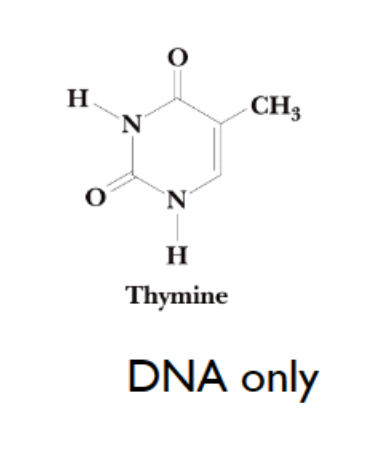
thymine
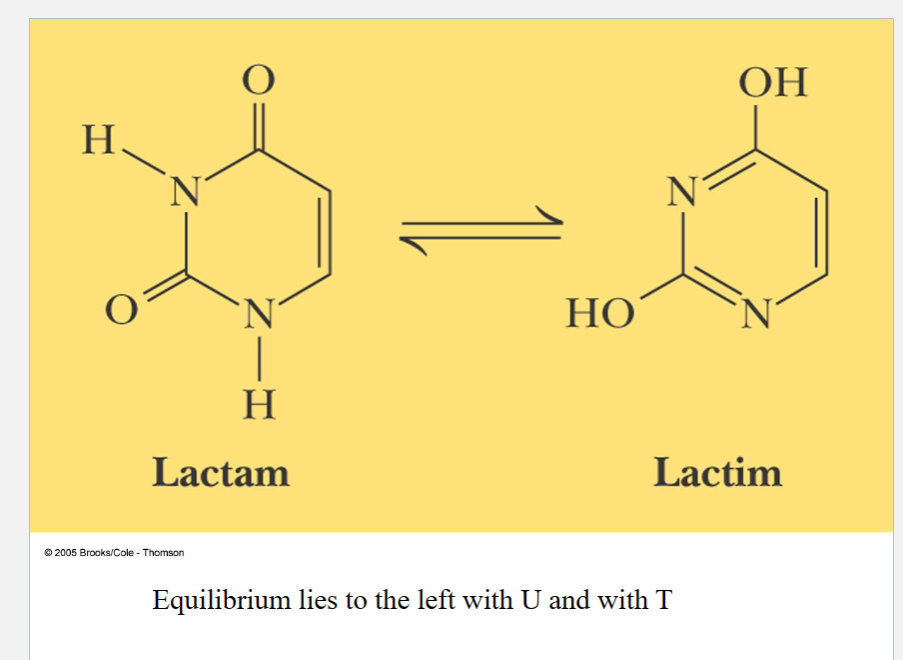
carbonyl is more stable
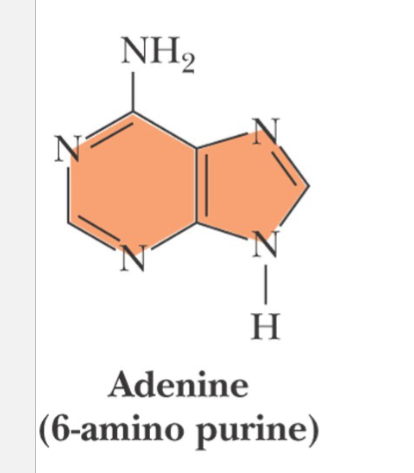
adenine
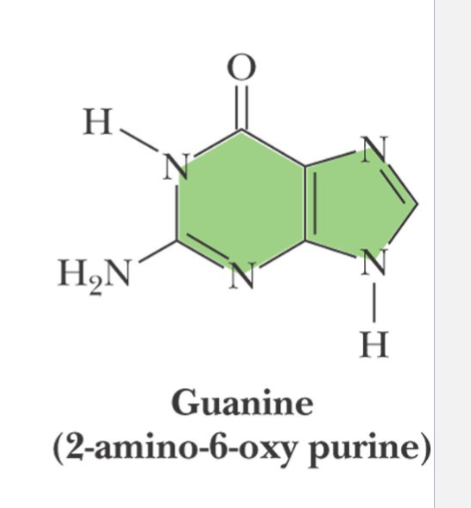
guanine
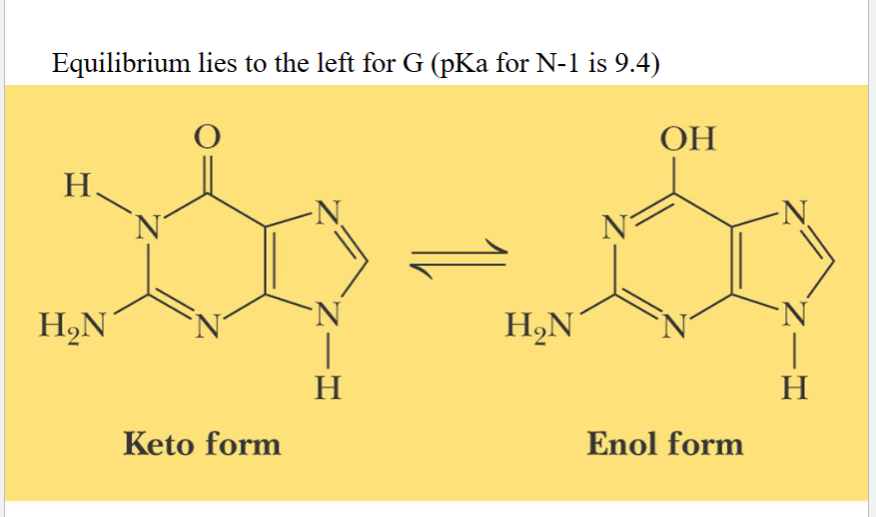
carbonyl is more stable
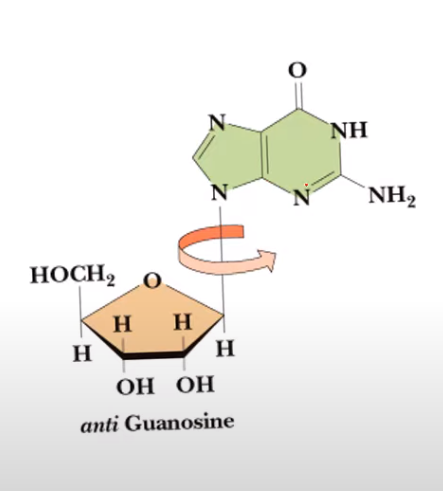
syn conformation
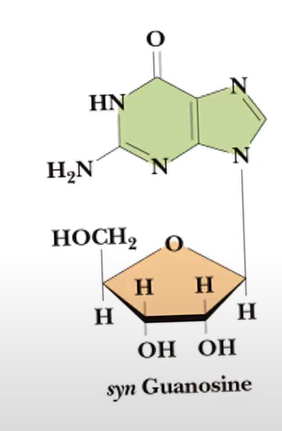
anti conformation
useful property in measuring quantities of nucleic acid in a sample
Both pyrimidines and purines have strong absorbance in the UV spectrum around 260 nm
Nucleosides
beta glycosidic linkage at N-1 of pyrimidine
and N-9 of purine
Nucleoside Nomenclature for pyrimidine
add -idine to the root name
Nucleoside Nomenclature for purine
add -osine to the root name
expect hypoxanthine
Nucleosides of deoxyribose are deoxyribonucleosides and are prefixed by
deoxy
expect for thymidine (only found in DNA anyway)
Nucleotides nomenclature
Add –ylic acid to base stem
Nucleotides
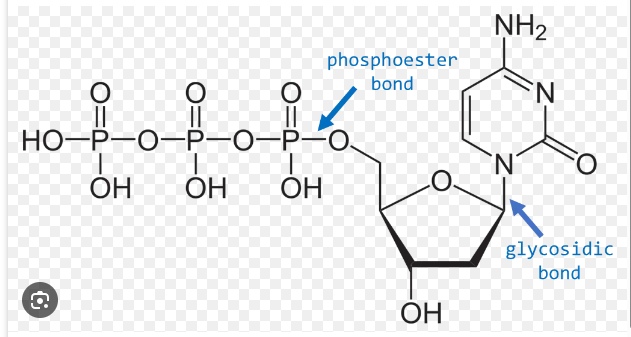
• Nucleotides are phosphate esters of nucleosides
• Named as “nucleoside-X’-phosphate” where X’ is the ribose position to which the phosphate is attached
• Example: adenosine-5’-monophosphate
Triphosphates are
energy intermediates
– ATP major energy currency
– GTP involved in driving protein synthesis
What kind of chemical bond links nucleotides together?
phosphodiester
How to read DNA
READ IT 5’ to 3’
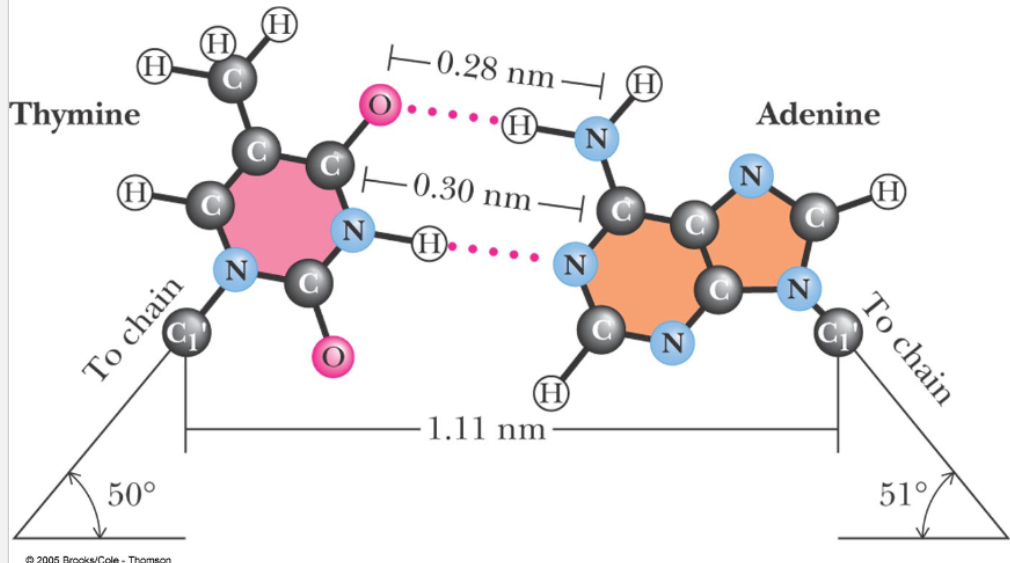
How many H-bonds are there per base pair?
2
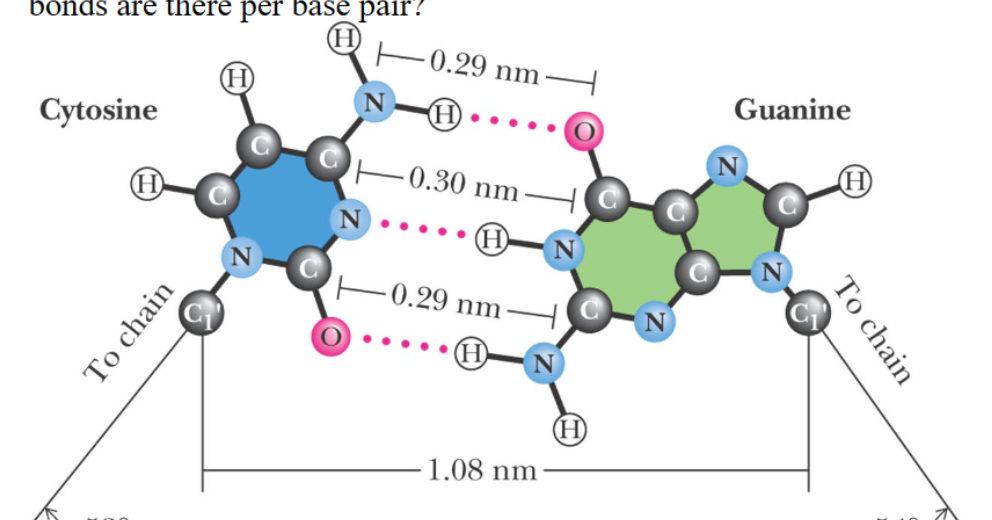
How many H- bonds are there per base pair?
3
Nature of DNA Helix
• Antiparallel strands
• Ribose phosphate chain on outside
• Bases stacked in middle like steps in a spiral staircase
• Complementary strands provide possible mechanism for replication
Messenger RNA
“Transcription” product of DNA
Carries sequence information for proteins
Prokaryote mRNA may code for multiple proteins
Eukaryote mRNA codes for single protein, but code (“exon”) might be separated by non-coding sequence (“introns”)
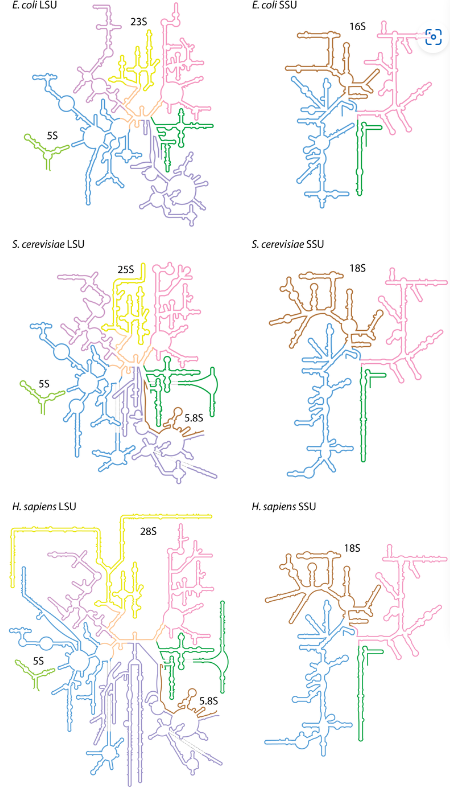
Ribosomal RNA
“Scaffold” for proteins involved in protein synthesis
RNA has catalytic activity as the “peptidyl transferase” which forms the peptide bond
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes have slightly different ribosomal structures
Ribosomal RNA contains some modified nucleosides
Transfer RNA
Small molecules—73-94 residues
Covalently carries an amino acid for protein synthesis
One or more t-RNA’s for each amino acid
“Anti-codon” in t-RNA recognizes the nucleotide “code word” in m-RNA
3’-Terminal sequence always CCA
Amino acid attached to 2’ or 3’ of 3’-terminal A
Many modified bases
Small Nuclear RNA’s
Found in eukaryotic cells, principally in the nucleus
Similar in size to t-RNA
Complexed with proteins in small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles or snRNPs
Involved in processing eukaryotic transcripts into m-RNA
RNA hydrolysis
RNA can be hydrolyzed by base because of the 2’-OH group. Mixture of 2’ and 3’ nucleotides produced
DNA hydrolysis
DNA can be hydrolyzed by an acid, by only the glycosidic bonds of the purines are broken (apurinic acid)
Exonucleases
hydrolyze terminal nucleotides
Endonucleases
hydrolyze in middle of chain. Some have specificity as to the base at which hydrolysis occurs
a type nucleases
cleaves the 3’ phosphate bond
Produces 5’-phosphate products
b type nucleases
cleaves the 5’ phosphate bond
Restriction Endonucleases
Enzymes of bacteria that hydrolyze “foreign” DNA
Name based on “restricted growth” of bacterial viruses
Enzymes specific for a short sequence of nucleotides (4-8 bases in length)
Methylation of the same sequence protects “self” DNA from hydrolysis
Specificity of Restriction Endonucleases
4-base sequence occurs randomly every 4^4
bases, or every 256 bases
6-base sequence occurs randomly every 4^6
bases, or every 4096 bases
8-base sequence occurs randomly every 4^8
bases, or every 65,536 bases
palindromes
Many target sequences, called “restriction
sites”
Cleavage of palindromic sites leave single stranded “sticky ends”, either 5’ or 3’
Restriction Mapping
Samples of DNA cut with a particular restriction enzyme yield a set of characteristic polynucleotides, separable electrophoresis according to size.
Each enzyme produces its own characteristic set of sized fragments
Fragments can be reassembled as in a jigsaw puzzle to produce a “restriction map”
Electrophoresis of DNA molecules
separates them according to size, the largest being retarded in their migration through the gel pores while the smallest move relatively unhindered
B-form of DNA
- Right-handed
~10 bp per turn
most common (no space for water in the middle)
-anti conformation
A-DNA
- -Right-handed
~11 bp per turn
-evenly spaced (and room for water)
-anti conformation
Z-DNA
-Left-handed
-CG base pair
-12 bp per turn (less space for water)
syn conformation
how many hydrogen bonds in AT base pairs?
2
how many hydrogen bonds in CG base pairs?
3
glycosidic bond
bond between sugar and nitrogenous base
Methylation of C
promotes B DNA to Z DNA switch
Increase of CG content and increase of ionic strength equals
increase in DNA stability
Reannealing of DNA
• Reannealing is the term given to the
renaturation—the reformation of the helix
• Temperature must be lowered slowly for proper
nucleation to occur
• Renaturation is a second order process, so the rate depends on concentration of complementary base
sequences
Chromatin
The nucleoprotein complex of DNA found within the eukaryotic cell nucleus
histones
pairs of histones (chromatin is wrapped around histones) aggregate to form octameric nucleosomes
Transfer RNA Structure
• Secondary structure shows a “cloverleaf”
pattern. All tRNA’s are similar.
• All end in CCA- 3’ , with amino acid attached at
the 3’-OH
• Lots of unusual modified bases.
• Tertiary structure is L-shaped
– Lots of “noncanonical H-bonding.
Ribosomal RNA Structure
A great deal of intra-strand sequence complementarity
Enzymes are intrinsically different from ordinary chemical catalysts
1) Higher reaction rate reactions must proceed on the time scale of living systems
2) Milder reaction conditions reactions must take place in an aqueous environment
3) Greater specificity many biological metabolites appear similar in structure
4) Capacity for regulation ability to sense moment to moment metabolic needs
Rate Enhancment
kcat /knon
t 1/2 (half life)
(ln 2)/kobs
Lock-and-Key Models
Molecules, like enzymes and substrates, need to fit together like a lock and key for things to work correctly
Induced Fit Theory
So, the key idea here is that the protein only reacts with the right substrate by changing its shape in a specific way
substrate
The biological molecule that gets chemically transformed by an enzyme
active site
the unique three-dimensional pocket where the substrate binds and where chemistry takes place
cofactor
If an enzyme makes use of any non-proteinogenic compound to facilitate catalysis (vitamins)
inhibitor
Any molecule that interferes with enzymatic catalysis by slowing any step of the chemical transformation
Ligase
1) forming C-O bonds
2) forming C-S bonds
3) forming C-N bonds
4) forming C-C bonds
usually powered by ATP hydrolysis
Oxidoreductases
These enzymes conduct oxidation-reduction reactions on biomolecules using a variety of oxidizing/reducing agents
Transferases
These enzymes catalyze the transfer of many functional groups including phosphoryl, methyl, acyl, glycosyl, etc
Hydrolase
These enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of various chemical bonds within biomolecules
Specific Example: BamHI restriction endonuclease Phosphodiester bond hydrolysis
Lyases
These enzymes cleave chemical bonds, often via addition across a double bond
Isomerase
These enzymes catalyze the interconversion of structural isomers
prosthetic group
an organic molecule thats is a helper and is tightly bound, or covalently attached to the enzyme
Holoenzyme
enzyme plus prosthetic group
Apoenzyme
enzyme lacking it’s prosthetic group
keq (rate constant)
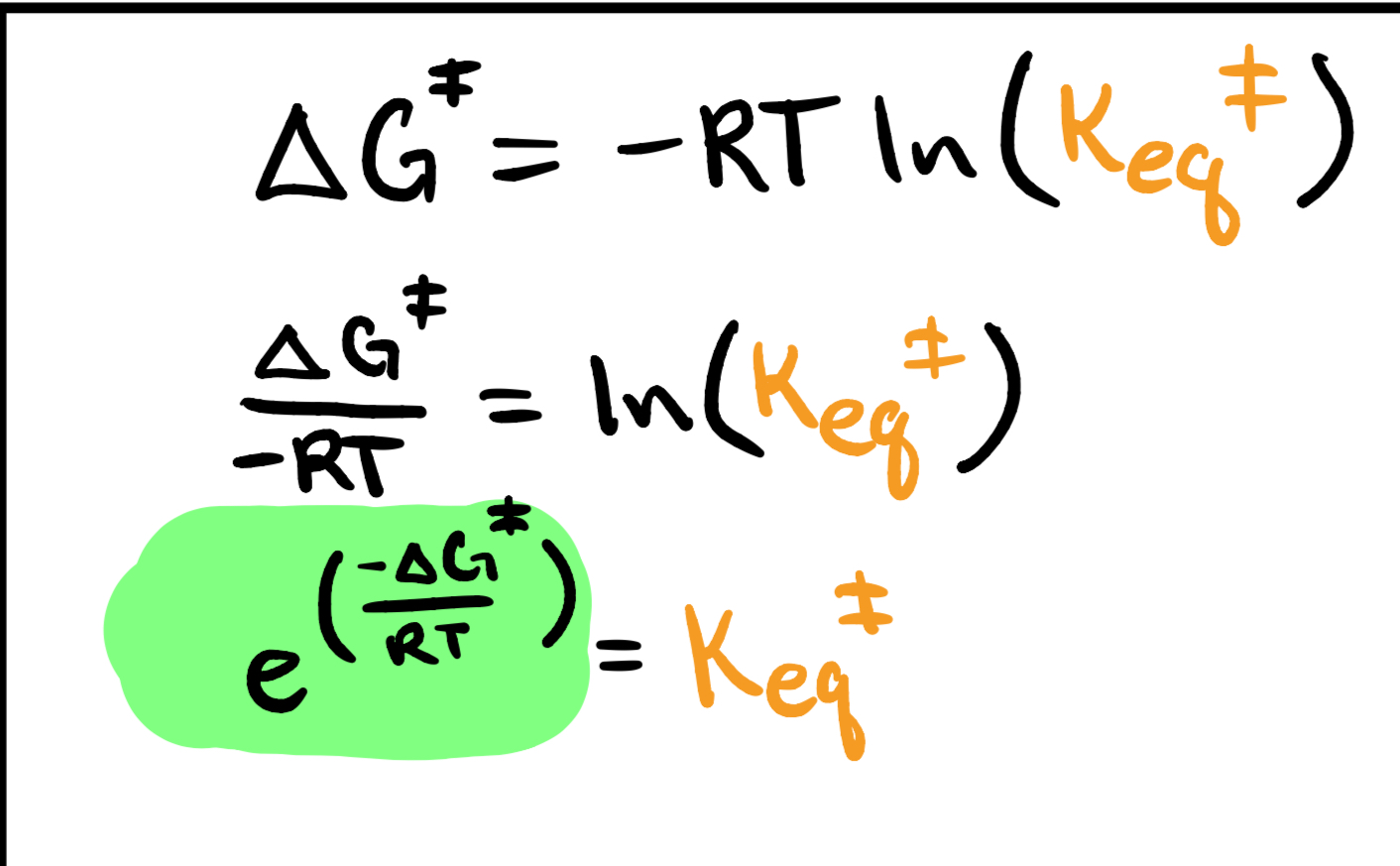
kdec
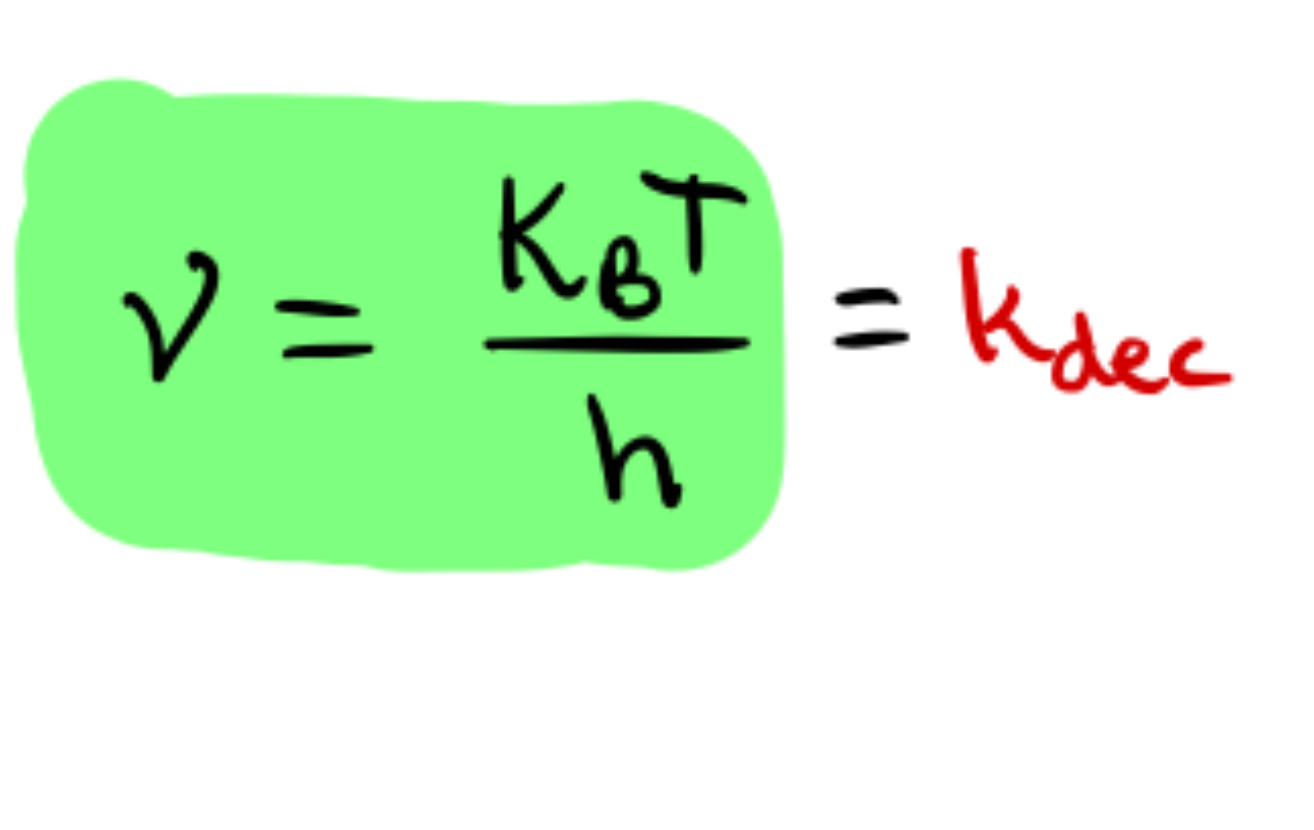
k obs
Keq * Kdec
Kcat and knon
are types of kobs
enzymes and kinetics
They speed up the rate of reactions, without affecting the thermodynamics of the reaction
They are able to do this by lowering the Activation Energy