Biology Exam 3
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
M
1. At what part of the cell cycle would you see a chromosome that looks like this?
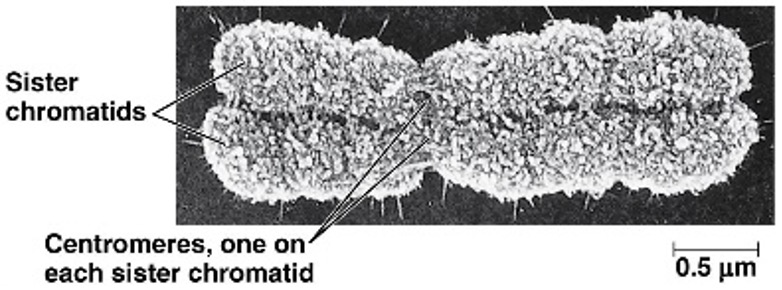
anaphase
The chromosome begins M phase looking as shown. When does it split?
a structure composed of several proteins that associate with the centromere region of a chromosome and that can bind to spindle microtubules
Which best describes the kinetochore?
two; one
From prophase through metaphase of mitosis, each chromosome has _____ DNA molecules, while from anaphase through telophase of mitosis, each chromosome has _____ DNA molecule(s).
look for a cell plate or a cleavage furrow
If you were given a slide and told that the cells on it were performing cytokinesis, how would you tell if you had plant cells or animal cells?
G2
Which comes immediately after S phase in the cell cycle?
cells with 4 copies of each chromosome and 0 copies of each chromosome
If a cell that had two copies of each chromosome, but problems with the spindle caused the sister chromatids to remain attached to each other and to only one spindle pole, what cells would result?
problem with expression of a cyclin
You are observing a line of rat cells and see that they repeatedly make mistakes in the cell cycle by going through the G2 checkpoint too early. This could be due to a
the degradation of cyclin
The decline of MPF activity at the end of mitosis is due to
G0
If a cell does not receive a go-ahead signal at G1 checkpoint during cell cycle, name the phase it enters as a nondividing state.
bacteria and animals both pinch in to separate the cytoplasm into two pieces.
Binary fission is more like animal cell division than plant cell division because
the two species have appreciably different genes
Privet shrubs and humans each have a diploid number of 46 chromosomes per cell. Why are the two species so dissimilar?
Both sets of chromosomes, which are present in somatic diploid cells, need to be examined
Why is it more practical to prepare karyotypes by viewing somatic diploid cells rather than haploid gametes?
meiosis increases genetic variation among offspring
Why does sexual reproduction (via meiosis) have an advantage over asexual reproduction (via mitosis)?
8
The mosquito Aedes aegypti has a karyotype of 2n = 6. Through independent assortment alone, how many chromosomal combinations can be made during meiosis?
a sperm
a human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is?
2x
If the DNA content of a diploid cell in the G1 phase of the cell cycle is x, then the DNA content of the same cell at metaphase of meiosis I will be
peas have an unusually long generation time
Which of the following is not a reason that peas were well suited for Mendel’s breeding experiments?
four gamete types: pY, py, PY, and Py
A pea plant is heterozygous at the independent loci for flower color (Pp) and seed color (Yy). What types of gametes can it produce?
dominance
A cross between homozygous purple-flowered and homozygous white-flowered pea plants results in offspring with purple flowers. This demonstrates
PpAa x PpAa
The following offspring were observed from many crossings of the same pea plants. What genotypes were the parents?
465 purple axial flowers 152 purple terminal flowers
140 white axial flowers 53 white terminal flowers
The alleles for purple, white, axial and terminal characters are P, p, A, a respectively
50%
In dragons, wings are a dominant trait, but some dragons are born wingless. If a wingless dragon is crossed with one that is heterozygous, how many of its offspring will be
Crossing two purple-flowered heterozygotes produced purple-flowered and white-flowered plants
Suppose that Mendel’s hypothesis that inheritance is “particulate” rather than due to blending were wrong. Which observation would he have not made?
TTAa
In peas, the allele for tall stems (T) is dominant to that for dwarf stems (t), and the allele for axial flowers (A) is dominant to that for terminal flowers (a). A plant of unknown genotype with tall stems and axial flowers is crossed with a plant with dwarf stems and terminal flowers. Among the offspring are 38 plants with tall stems and axial flowers, and 36 plants with tall stems and terminal flowers. What is the previously unknown genotype?
Xw+ or Xw
Morgan and his colleagues worked out a set of symbols to represent fly genotypes. Which of the following is representative?
This allele is passed to all male but no female offspring of a male with the allele
In some species of Drosophila, there are genes on the Y chromosome that are not on the X chromosome. Imagine that a new allele arises on the Y chromosome and reduces the size by half of individuals with the new allele. Which of the following statements is accurate with regard to this situation?
The phenotype of o-Y males is black/brown because the nonfunctional allele o does not convert eumelanin into phaeomelanin
In cats, an X-linked gene affects coat color. The O allele produces an enzyme that converts eumelanin, a black or brown pigment, into phaeomelanin, an orange pigment. The o allele is recessive to O and produces a defective enzyme, one that does not convert eumelanin into phaeomelanin. Which of the following statements is accurate?
linked genes
Genes which tend to be inherited together are called
franklin
Who conducted the X-ray diffraction studies that were key to the discovery of the structure of DNA?
telomerase
What enzyme compensates for replication-associated shortening of linear chromosomes?
Mouse dies after being injected with a mixture of heat-killed S and living R cells
Which of the following results from Griffith’s experiment is an example of transformation?
28%
Suppose a double-stranded DNA molecule was shown to have 22% guanine bases. What would be the expected percentage of adenine bases in that molecule?
L and O
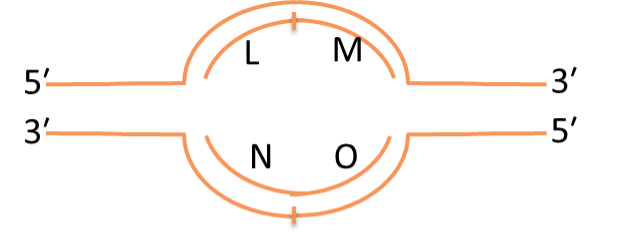
Consider the replication bubble diagrammed at the right. Which letters represent leading strands?
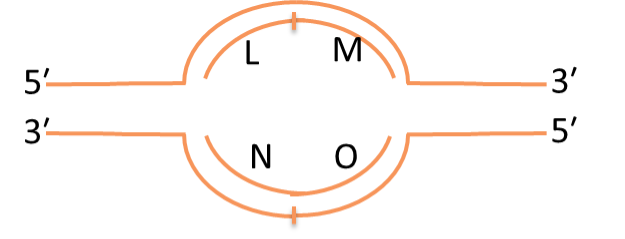
M and N
Consider the replication bubble diagrammed at the right. Which letters represent places where one could find Okazaki fragments?
all hybrid DNA
In Meselson and Stahl’s experiment proving semiconservative DNA replication, they started with bacteria grown in a heavy isotope of nitrogen and then switched them to a light isotope. They then observed the DNA density after one and two rounds of replication. What was the result after one round of replication?
both leading and lagging strands
Imagine a bacterial replication fork. Synthesis of which new strand(s) would be affected by mutations in the enzyme DNA polymerase III?
equal amounts of light and hybrid DNA
In Meselson and Stahl’s experiment proving semiconservative DNA replication, they started with bacteria grown in a heavy isotope of nitrogen and then switched them to a light isotope. They then observed the DNA density after one and two rounds of replication. What was the result after two rounds of replication?
DNA
Which of the following terms does not directly pertain to translation?
′-CGGTGCATAGT-3′
The template strand of a given gene includes the sequence 3′-GCCACGTATCA-5′. What is the sequence of the nontemplate strand?
Mouse fur color results from pigment formed by gene-encoded enzymes
Which of the following is the best example of gene expression?
1, 3, 2
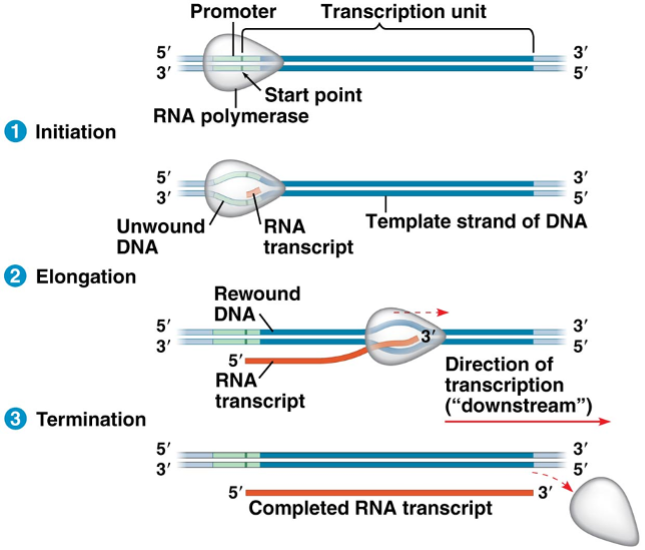
In the transcription process shown here, in which process order (1, 2, or 3) does the RNA polymerase bind to the promoter, in which is the RNA transcript released, and in which is the RNA transcript extended?
transfer RNA
Which of the following components does not form part of the transcription initiation complex at a eukaryotic promoter?
link a tRNA to its corresponding amino acid
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase is an enzyme whose function is to _____
-The 5′ end is capped.
-A poly-A tail is added to the 3′ end.
-Introns are removed.
-Exons are joined together
Which of the following is a modification made to eukaryotic mRNA before it is exported to the cytosol?
RNA polymerase requires a primer in bacteria; in eukaryotes, it does not
Which of the following statements comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription is not true?
5′-UUCACUGGUUCA
The nontemplate strand of a portion of a gene reads 5′-TTCACTGGTTCA. What is the sequence of the resulting transcript for this portion?
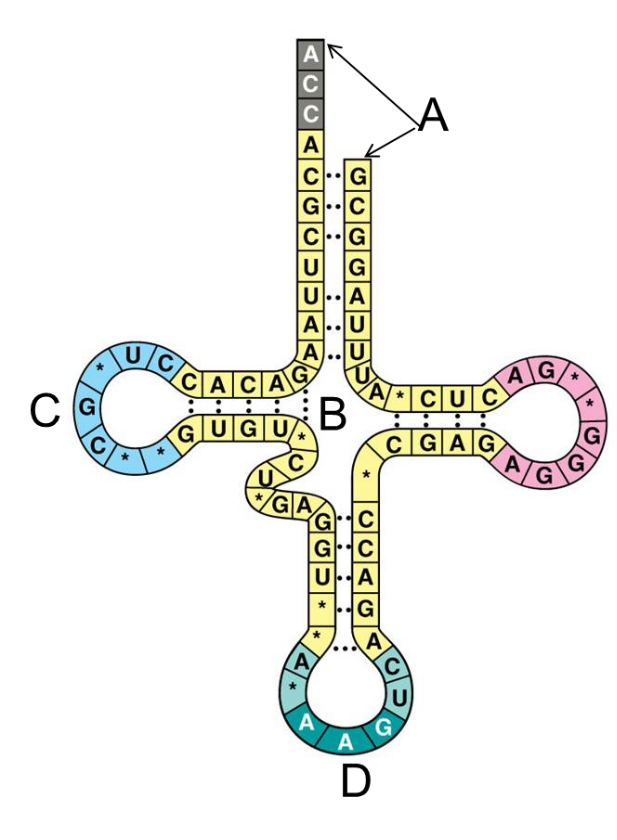
amino acid attachment site
Which of the following is incorrectly identified in this illustration of a tRNA?