Chapter 10 Cell Reproduction
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What occurs in Mitosis?
One cell produces two genetically identical daughter cells.
By mixing chromosomes from Two individual the _______ is increased.
Genetic diversity
What does the cells DNA make up?
Genome, which is in prokaryotes, one double stranded circular DNA molecules
What are the characteristics of Eukaryotic Genome?
Consists of several double stranded DNA molecules In the form of chromosomes
Example: Y chcormosme
What is the difference between somatic cells and Reproductive cells
Somatic:typically have 2 matched sets of chromosomes which make them diploid (2n)
Gametes (eggs and sperm cells) have half the number of chromosomes Haploid (1n)
Chromosomes that pair in reproduction of diploid cells are what?
Homologous
What are Heterologous pairs?
Genomes that have pairs that don’t match
Example: X and Y chromosomes
What are the phases in mitosis in order?
PMAT- Prophase, metaphase, Anaphase and telophase
What is the Histone DNA complex?
Short starches of DNA wrapped around a core of 8 histone proteins- string of breads
Contains a nucleosome
What are the characteristics of the 2 major cell cycle phases
Interphase- normal growth and preparation for cell Divison ( has 3 stages)
Mitotic phase- which he replicated DNA and the cytoplasm are split and the cell divides
What are the 3 stages of Interphase
G1:growth (first gap)
S phase:synthesis→ makes identical copies of the DNA are joined at cetromere. Centrosomes produce Millicent spindles to move chromosomes ( Duplicates the sister chromatids)
G2 phase:. Secondary growth
What occurs in Prophase in mitosis
Nuclear envelop breaks down
The chromosomes condense
Membranous organelles disperse toward edge of cell
Nucleolus disappears
Centrosomes begin migration to pole
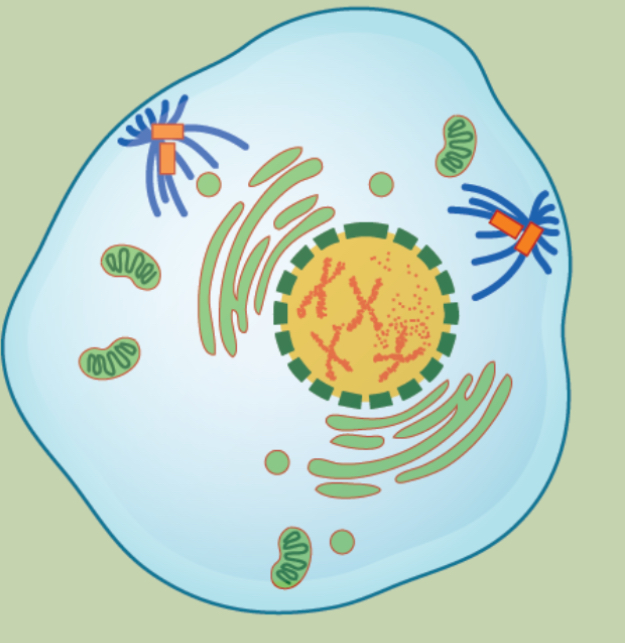
What occurs in metaphase in mitosis?
Mitosis spindle is fully developed and teh Centrosomes are at opposites poles of the cell
Chromosomes are lined up at the metaphase plate
Each sister chromatids is attached to a spindle fiber
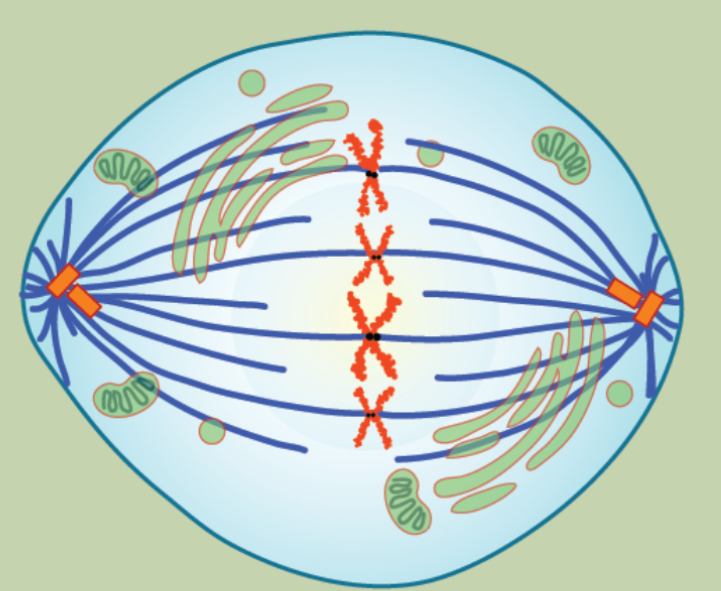
What occurs in Anaphase in mitosis?
Cohesion proteins degrade that allow chromatids to separate
Sister chromatids move in opposites directions toward Centrosomes
The cell elongates
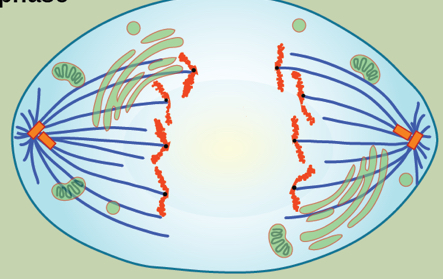
What occurs in Telophase in Mitosis?
Chromosomes reach opposite poles and begin to decondense
(Cell splits)
Spindles → tubulin that will form the cytoskeletal components for the daughter cell
Nuclear envelop from around the chromosomes
What is cytokinesis
Splitting of the cytoplasm→ physically separate into 2 daughter cells
( the cytoskeleton degrades into 2 cells)
Which stage of interphase does the cell spend teh most amount of time
G1 phase
What are the 3 checkpoints for the control of the Cell cycle?
G1 Checkpoint: Determines whether all conditions are favorable for cell divison ( check for damage and has to meet requirements, and will either stop the cycle or wait for conditions to get better)
G2 Checkpoint: Ensure all chomsomes have been replicates and that the replicated DNA is not damaged
The M Chechpoint: occurs at the end of metaphase→ spindle checkpoint, determines whether all sister chromatids are correctly attached to spindle microtubules
During which stage of mitosis do the spindle fibers disappear and chromosomes unravel
Telophase- chromosomes reach the poles and the cell begins to decondense and the spindle fibers break down
What are the two groups of intracellular molecules that regulate the cell
Positive Regulators: Promote movement to the next of the cell cycle
Negative Regulators: stop advancement of the cell cycle ( primarily at the G1 Checkpoint )
What does the term cancer mean?
Uncontrolled cell growth, begins with gene mutation that results in faulty protein that regulates cell reproduction
!. Tumors result in reproduction of mutated cells surpasses teh growth of normal cells