Cheat Sheet 8: Molecular Genetics
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
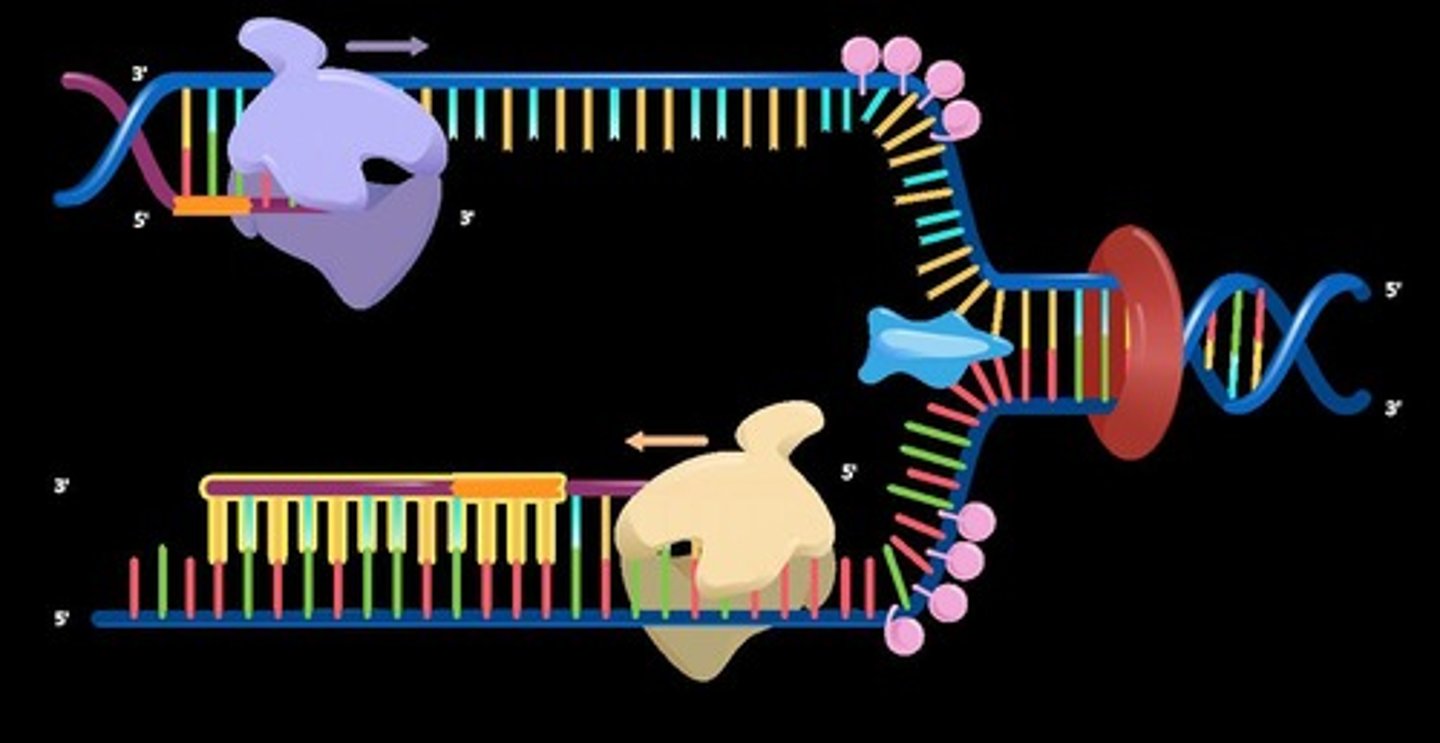
DNA Replication
Copying genetic information in cells.
Leading Strand
Synthesized continuously during DNA replication.
Lagging Strand
Synthesized discontinuously with Okazaki fragments.
Okazaki Fragments
Short nucleotide stretches formed on lagging strand.
DNA Polymerase III
Enzyme synthesizing new DNA in 5' to 3' direction.
Helicase
Unzips DNA double helix into single strands.
RNA Primer
Initial RNA segment for DNA synthesis initiation.
Primase
Enzyme creating RNA primer for DNA replication.
Ligase
Seals gaps between Okazaki fragments.
Topoisomerase
Relieves stress from unwinding DNA strands.
Telomere
DNA segment protecting chromosome ends from degradation.
Telomerase
Enzyme adding telomeres to chromosome ends.
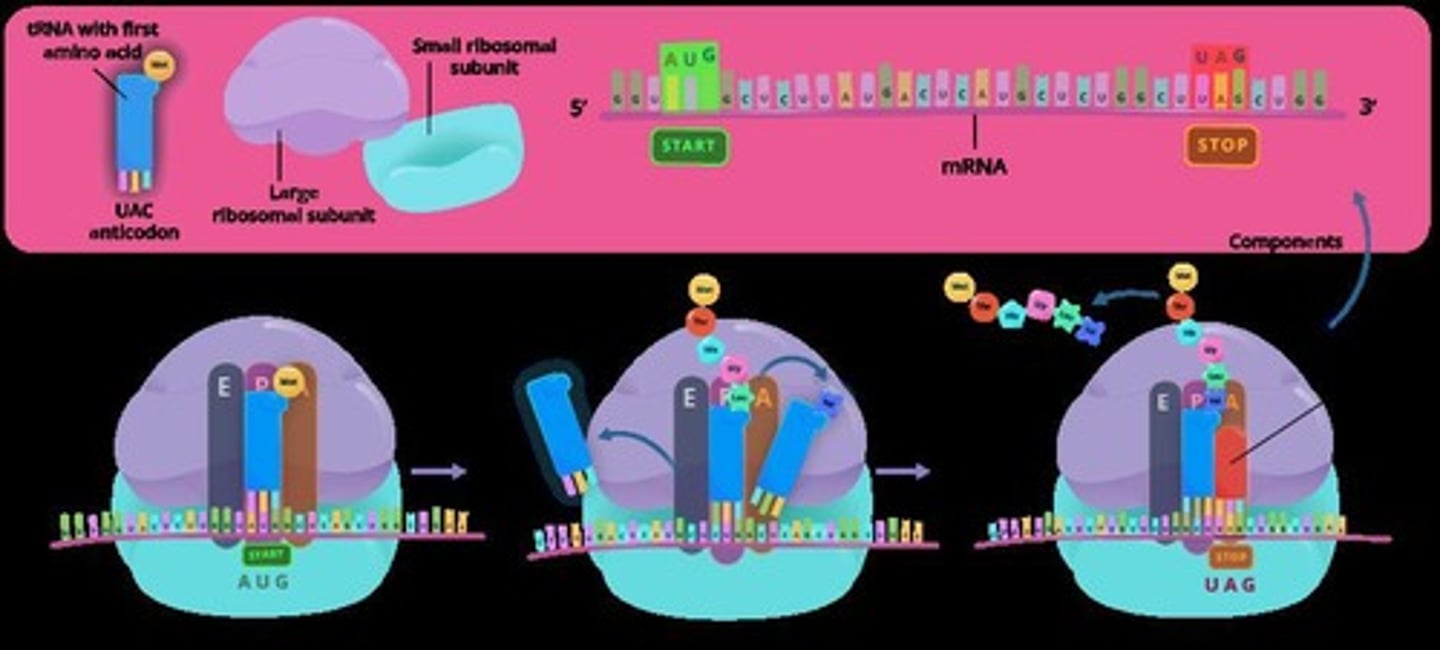
mRNA
Messenger RNA for protein synthesis.
tRNA
Transfers amino acids to mRNA codons.
rRNA
Forms part of ribosomes for protein synthesis.
Transcription
Synthesizing RNA from a DNA template.
RNA Splicing
Removing introns and reconnecting exons in mRNA.
Exons
Protein-coding regions of the genome.
Introns
Non-coding regions in pre-mRNA.
Translation
Synthesis of proteins from mRNA sequence.
Point Mutation
Single nucleotide change causing substitution, insertion, or deletion.
Frameshift Mutation
Shifts reading frame of RNA transcript.
Silent Mutation
Codon change does not alter amino acid.
Missense Mutation
New codon encodes a different amino acid.
Nonsense Mutation
Codon change results in a premature stop codon.
Wild Type
mRNA sequence without any mutation.
Plasmids
Small, circular DNA molecules in bacteria.
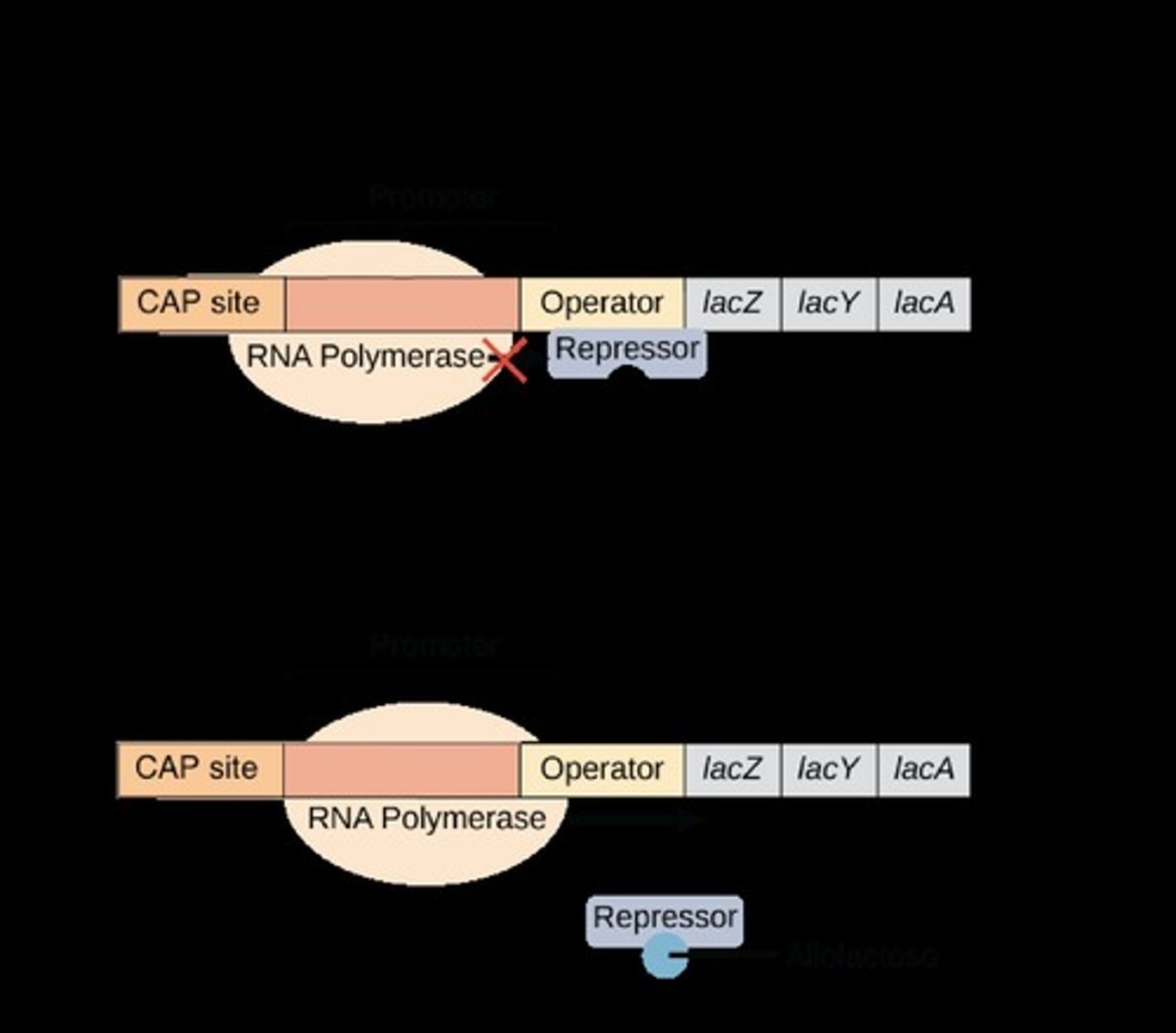
Lac Operon
Operon for lactose processing in prokaryotes.
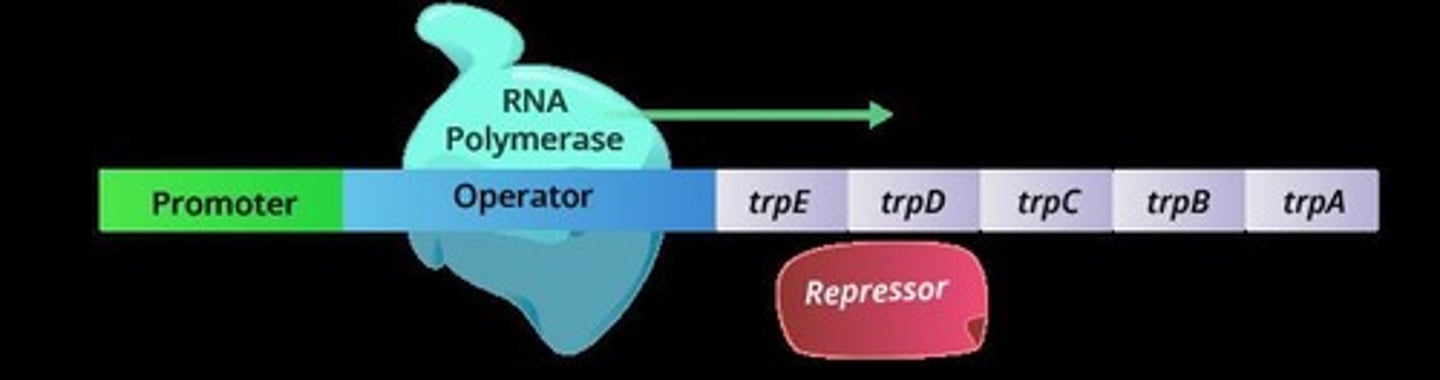
Trp Operon
Operon for tryptophan synthesis in prokaryotes.
Operons
Gene clusters controlling transcription in prokaryotes.
Conjugation
DNA transfer via cell-to-cell contact in bacteria. Pilus (bridge) between bacteria is formed
Transformation
Uptake of free DNA from surroundings by a competent bacterium.
Transduction
DNA transfer via bacteriophage infection. EX: Virus that infects bacteria.
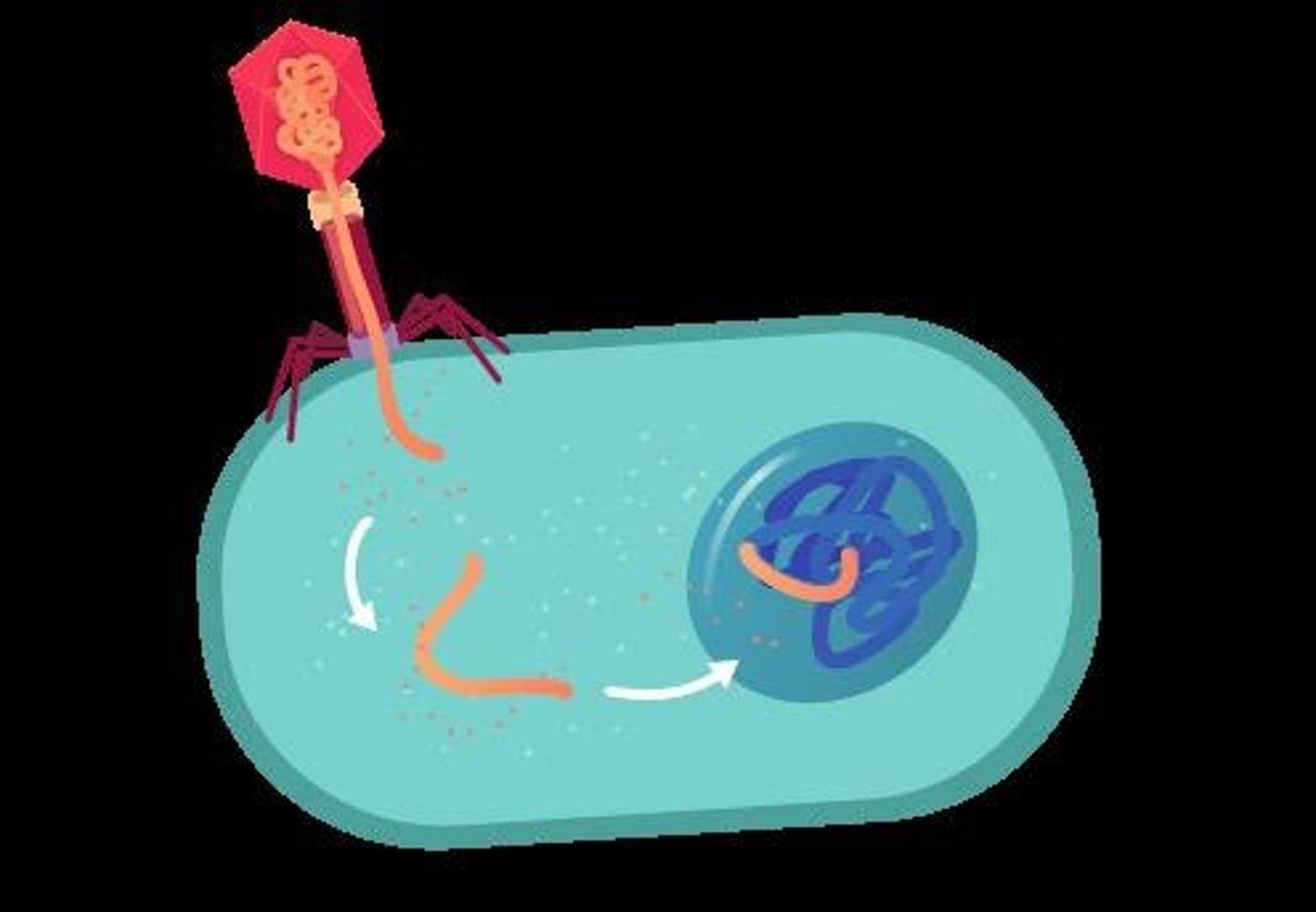
Genome
Complete genetic information of an organism.
Transcriptome
All RNA molecules produced by a cell.
Proteome
Complete set of expressed proteins in an organism.
Post-transcriptional processing
Adding 5' cap to 5' end and poly-A tail to 3' end of mRNA for stability
Initiation
1st step in transcription: RNA polymerase attaches to promoter region and unzips DNA into 2 strands
Elongation
2nd step in transcription: RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA nucleotides using one DNA strand as template
Termination
3rd step in transcription: RNA polymerase reaches a special sequence, detaches from DNA, and disassembles from complex