bio exam 2
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
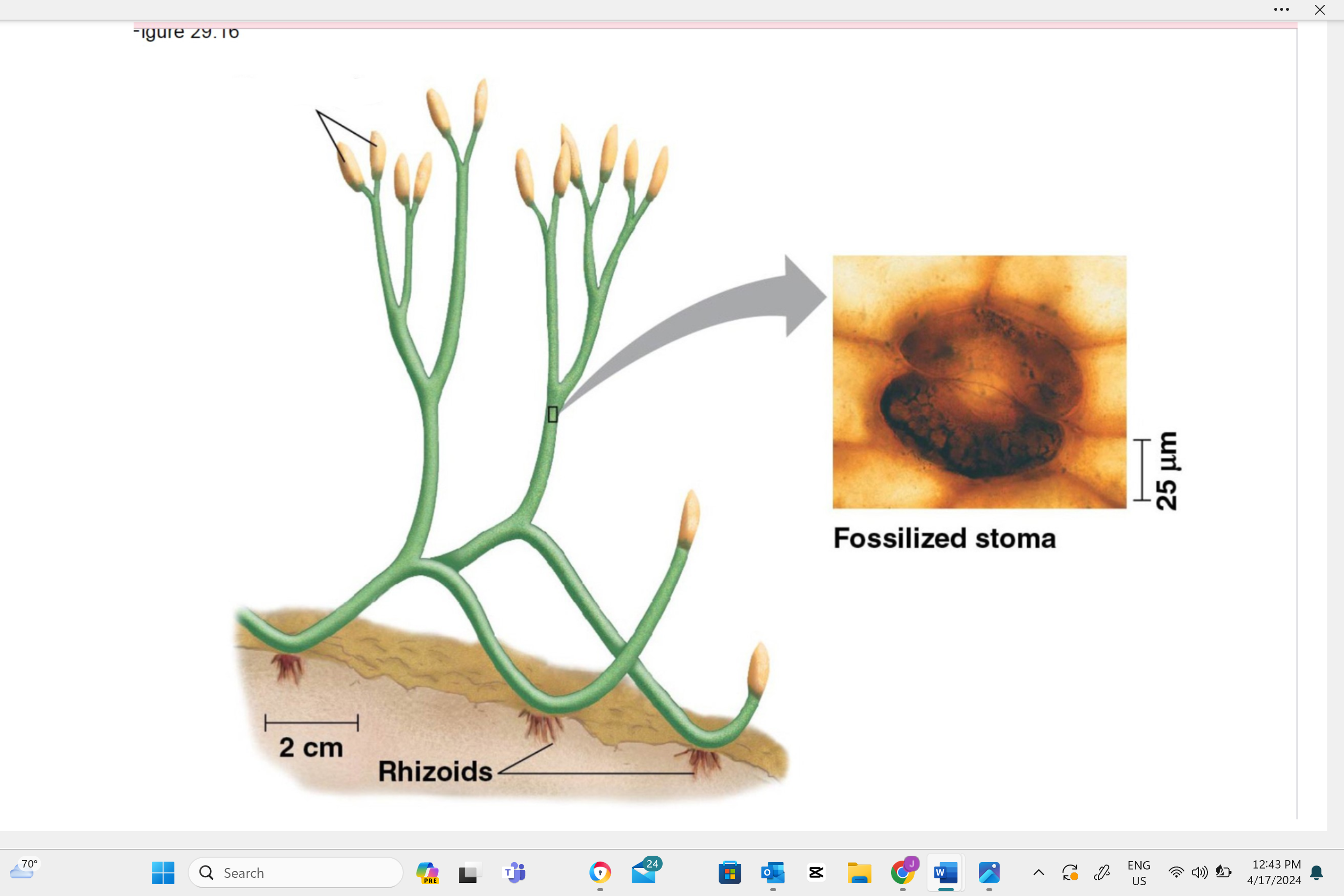
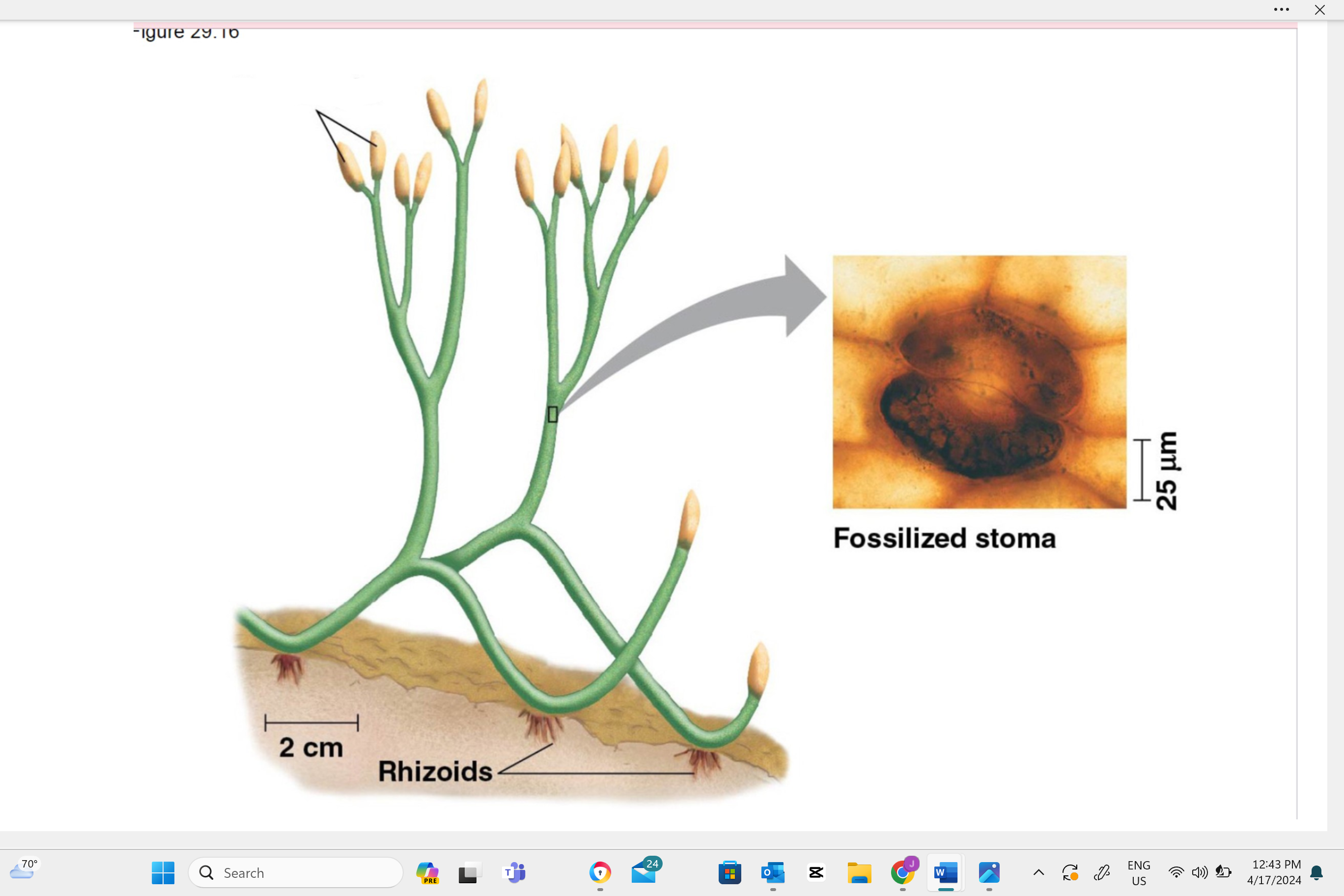
write the name of this structure
plant sporangia
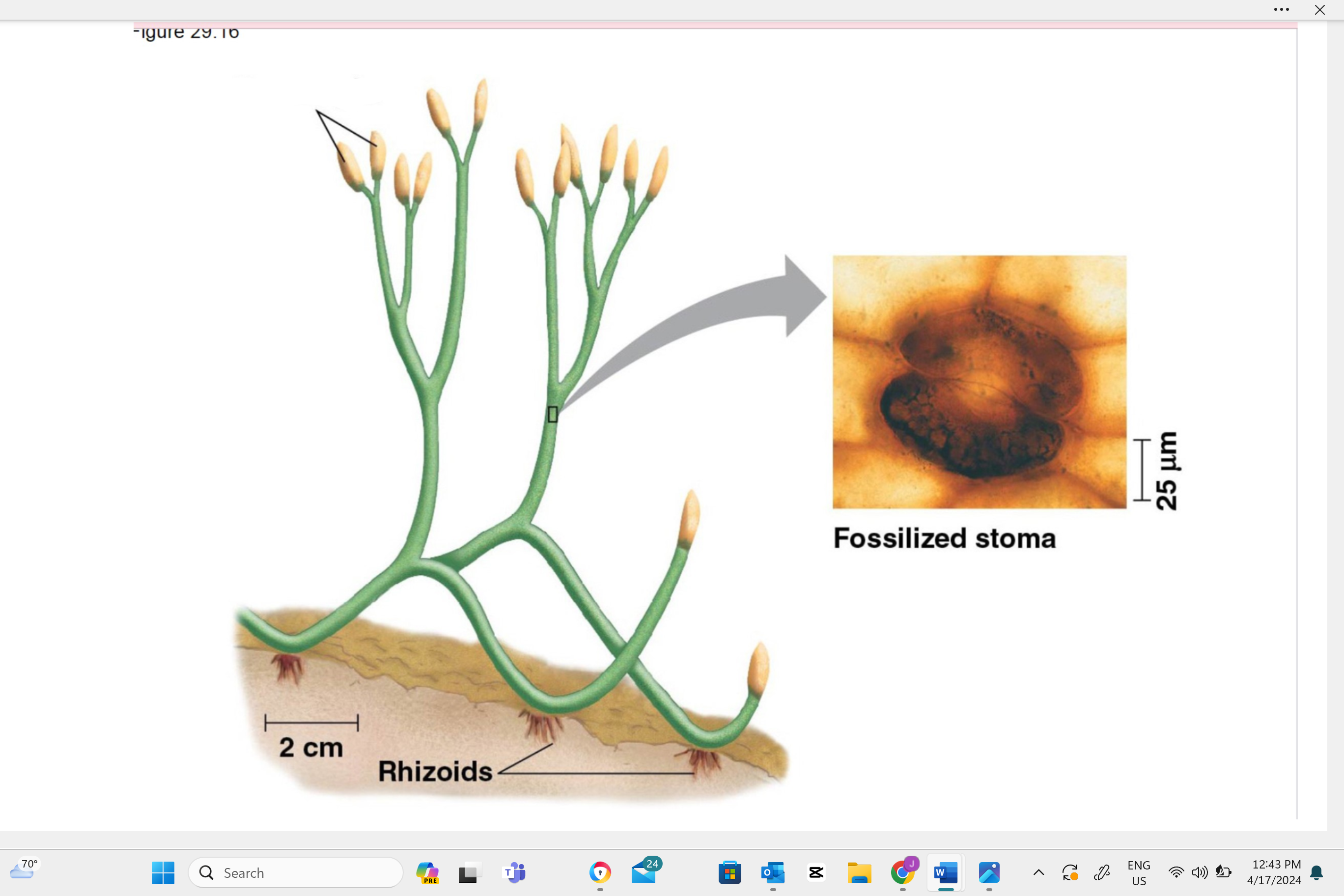
Describe one or more features of you can observe to distinguish the identity of this structure.
The sporangia is identified by its appearance as a small, round or elongated capsule. This structure can often be found on a stalk or at the end of a leaf (especially in ferns) and contains spores. Look for a tiny, capsule-like shape on the plant to identify the sporangium.
Name the type of cell division that occurs in this structure to make reproductive cells.
Meiosis. During meiosis, the cells in the sporangium divide to produce haploid spores, which have half the number of chromosomes compared to the original cell. These spores can grow into new plants.
Identify the type of reproductive cell produced in this structure.
Spores. Spores are haploid cells that can grow into new plants without the need for fertilization.
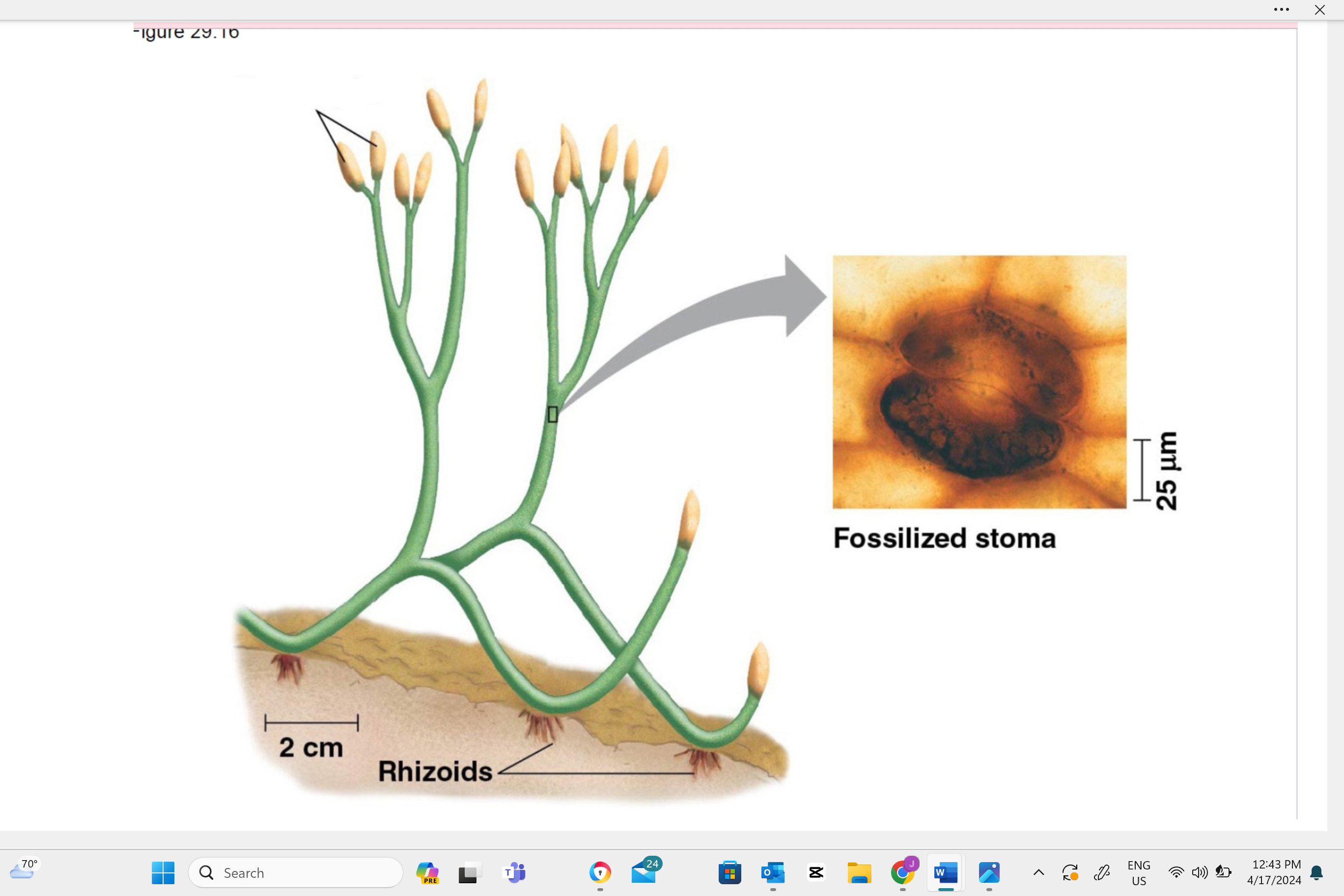
Identify this structure as haploid, diploid, or dikaryotic.
Diploid because they contain two sets of chromosomes. The cells in sporangia undergo meiosis to produce haploid spores, which have only one set of chromosomes. Therefore, while the sporangium itself is diploid, the spores it produces are haploid.
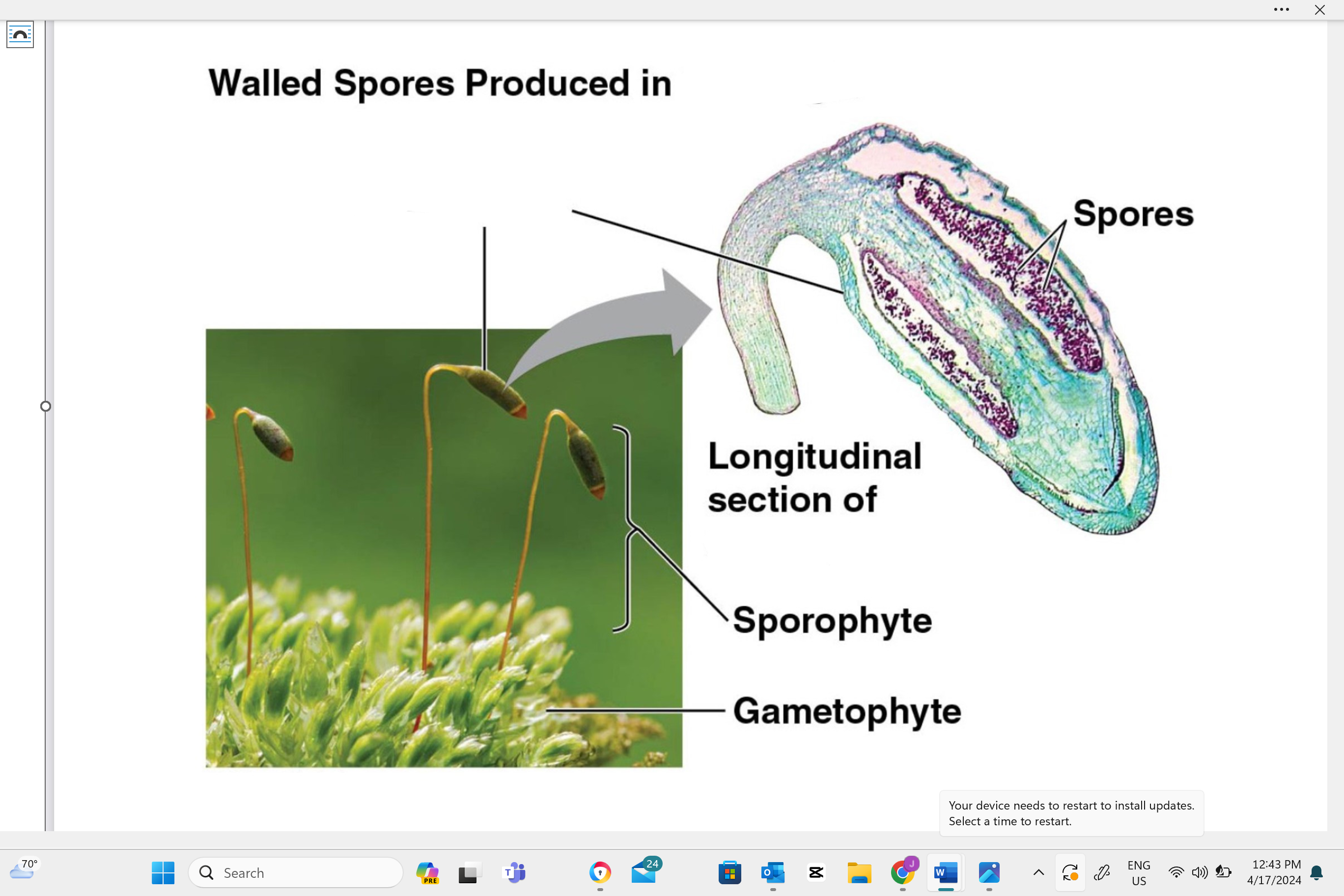

Write the name of this structure.
Gametangia

Describe one or more features of you can observe to distinguish the identity of this structure.
Female gametangia (archegonia) may look like tiny, upright stalks with a bulbous end, while male gametangia (antheridia) may appear as small, round, or oval structures on the surface of the gametophyte. (picture comparing both is not from textbook, it’s just for context)
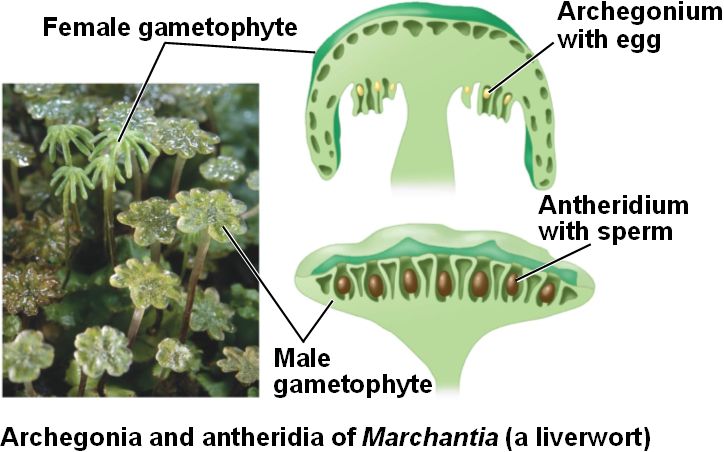

Name the type of cell division that occurs in this structure to make reproductive cells.
In gametangia, meiosis occurs to produce haploid gametes (sperm and eggs) for sexual reproduction.

Identify the type of reproductive cell produced in this structure.
The type of reproductive cells that occur in the gametangia are gametes, specifically sperm cells in male gametangia (antheridia) and egg cells in female gametangia (archegonia).

Identify this structure as haploid, diploid, or dikaryotic.
Gametangia are haploid structures in plants and fungi. This means they contain a single set of chromosomes. Gametangia produce haploid gametes (sperm and eggs) for sexual reproduction.
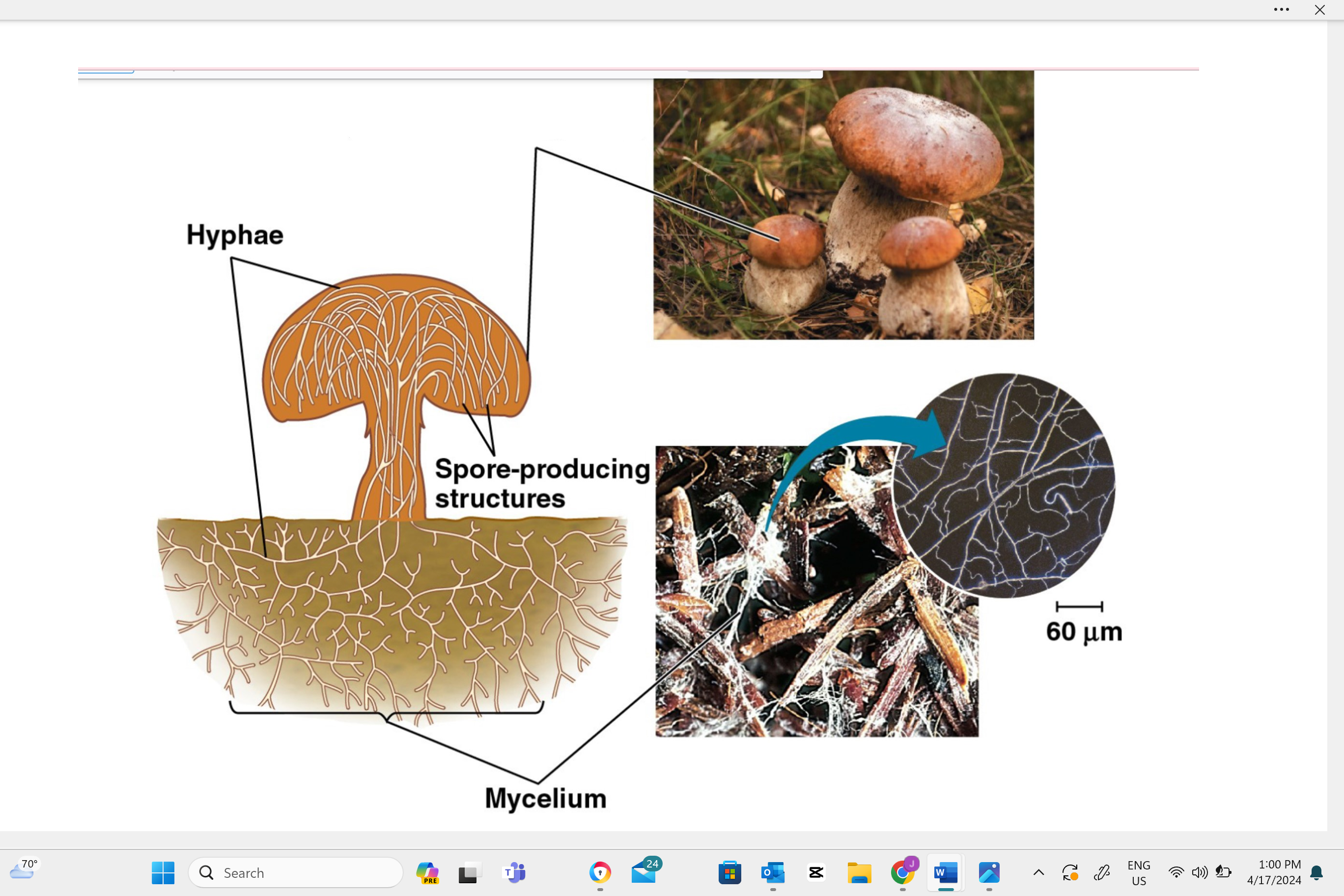
Write the name of this structure.
sporocarps (fungal fruiting bodies)
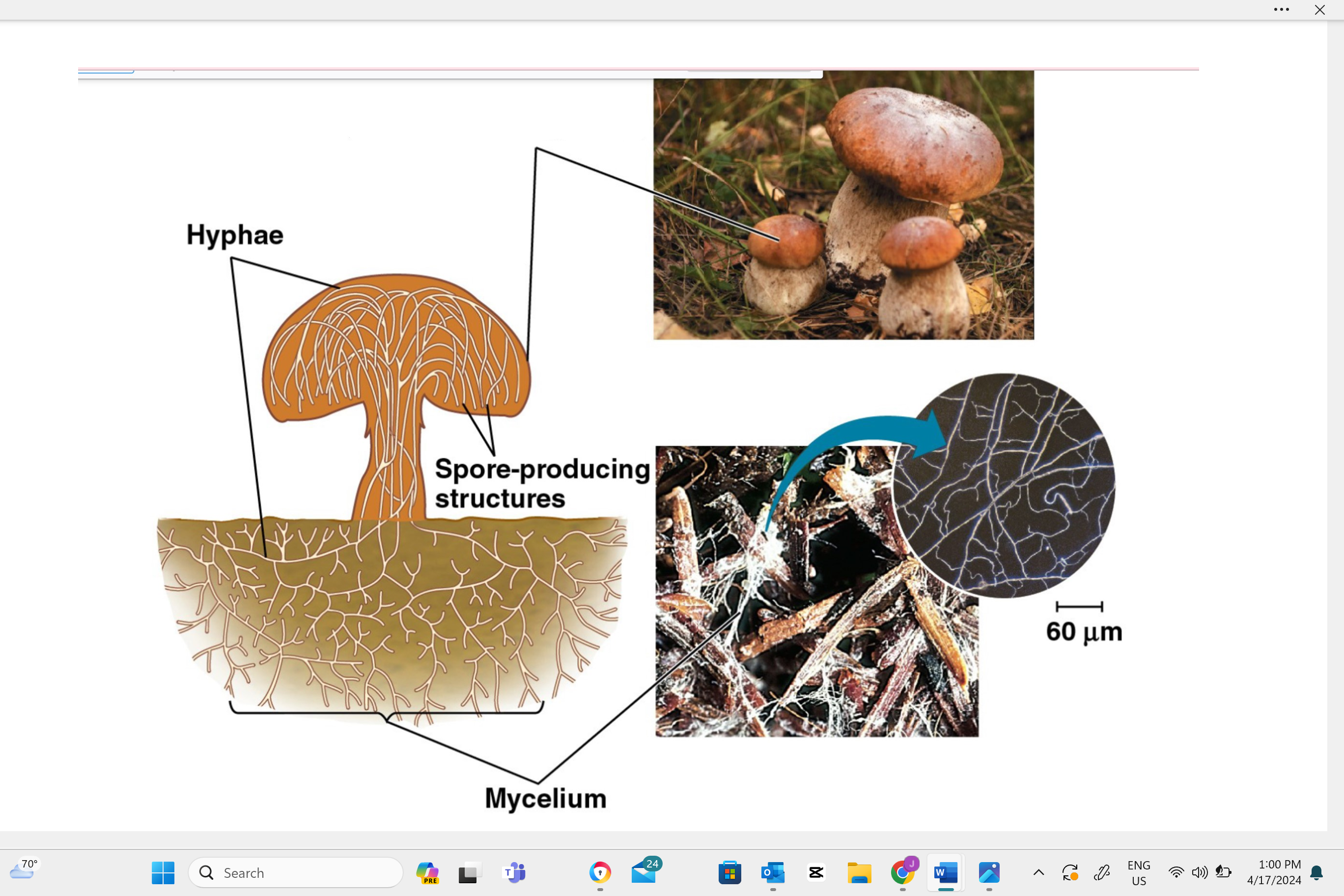
Describe one or more features of you can observe to distinguish the identity of this structure.
Sporocarps can take various forms such as umbrella-like mushrooms, round puffballs, cup-shaped fungi, or even coral-like branching structures.
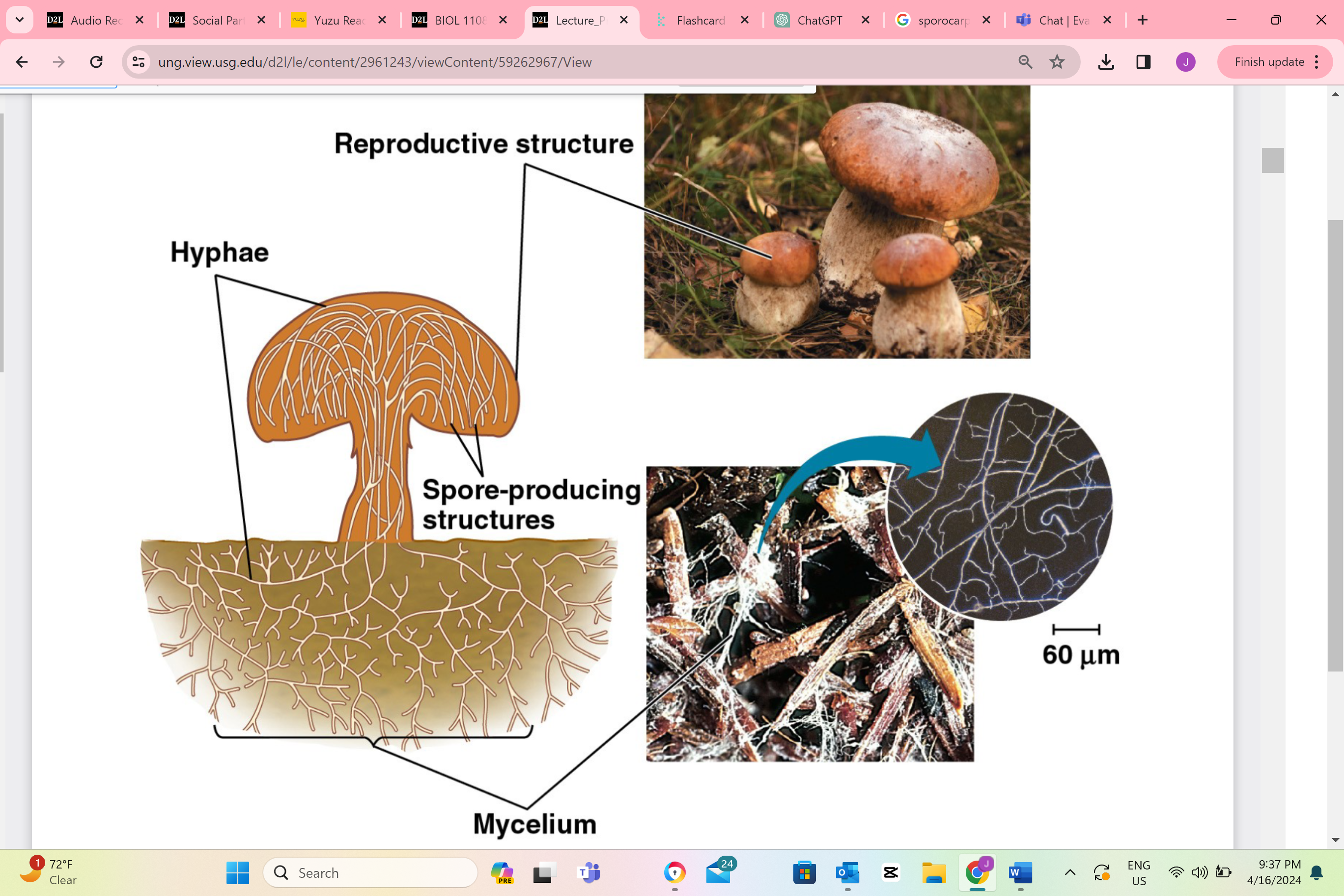
Name the type of cell division that occurs in this structure to make reproductive cells.
In a sporocarp, the type of cell division that occurs is called meiosis. This is a special kind of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes by half, creating spores. These spores can then grow into new fungi.
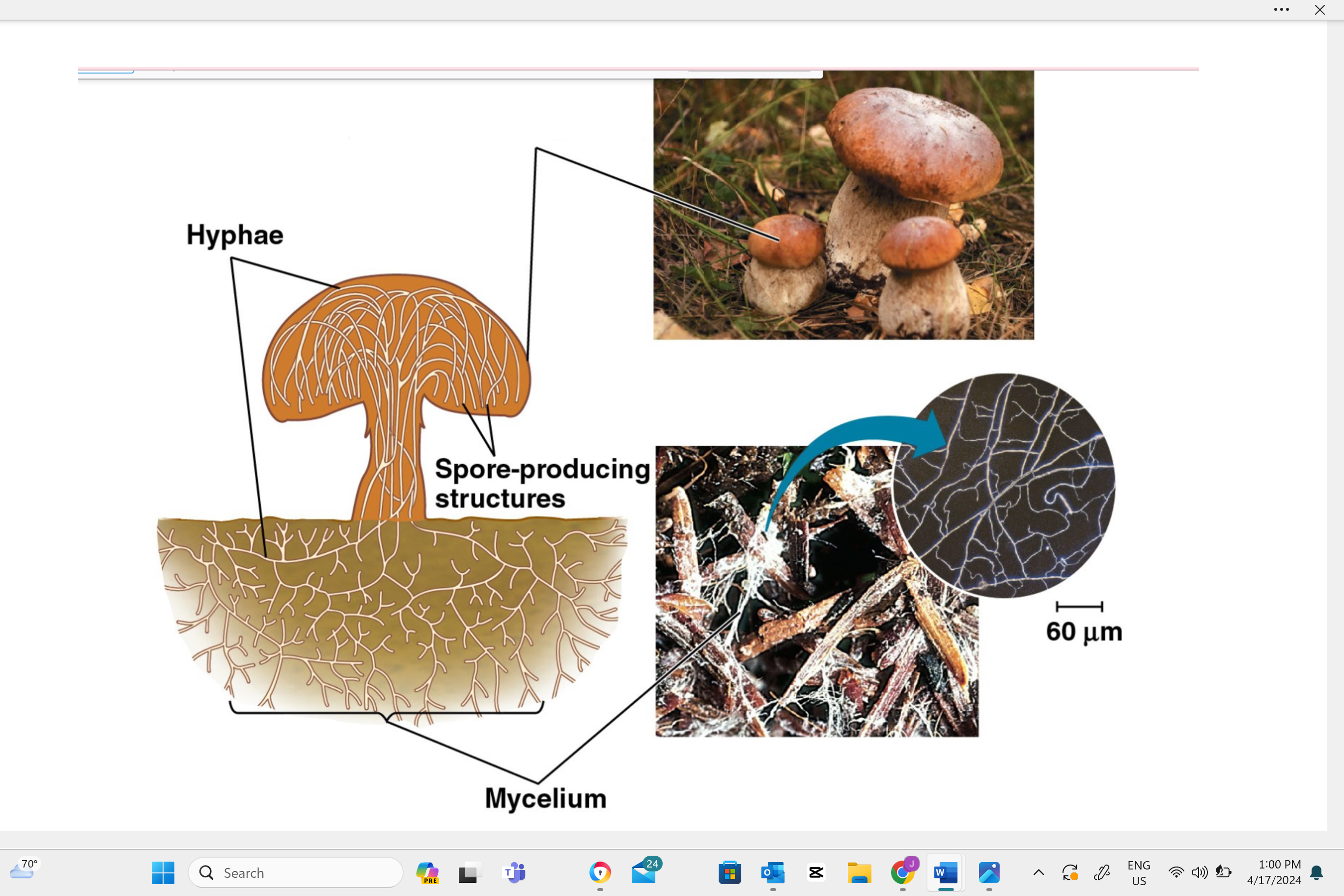
Identify the type of reproductive cell produced in this structure.
In a sporocarp, the type of reproductive cell produced is called a spore.
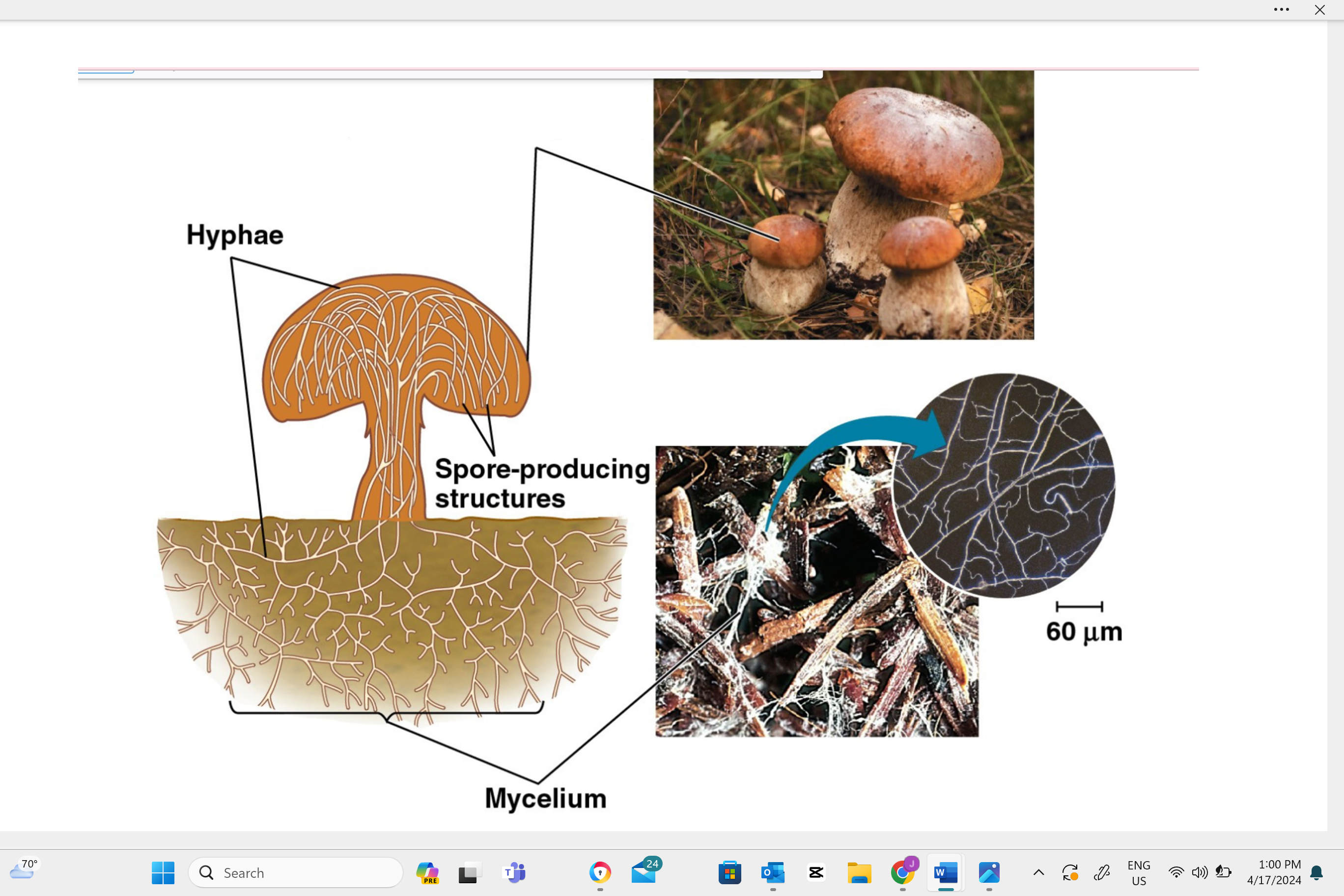
Identify this structure as haploid, diploid, or dikaryotic.
Sporocarps in fungi are typically dikaryotic, which means they contain two separate, genetically distinct nuclei in each cell.
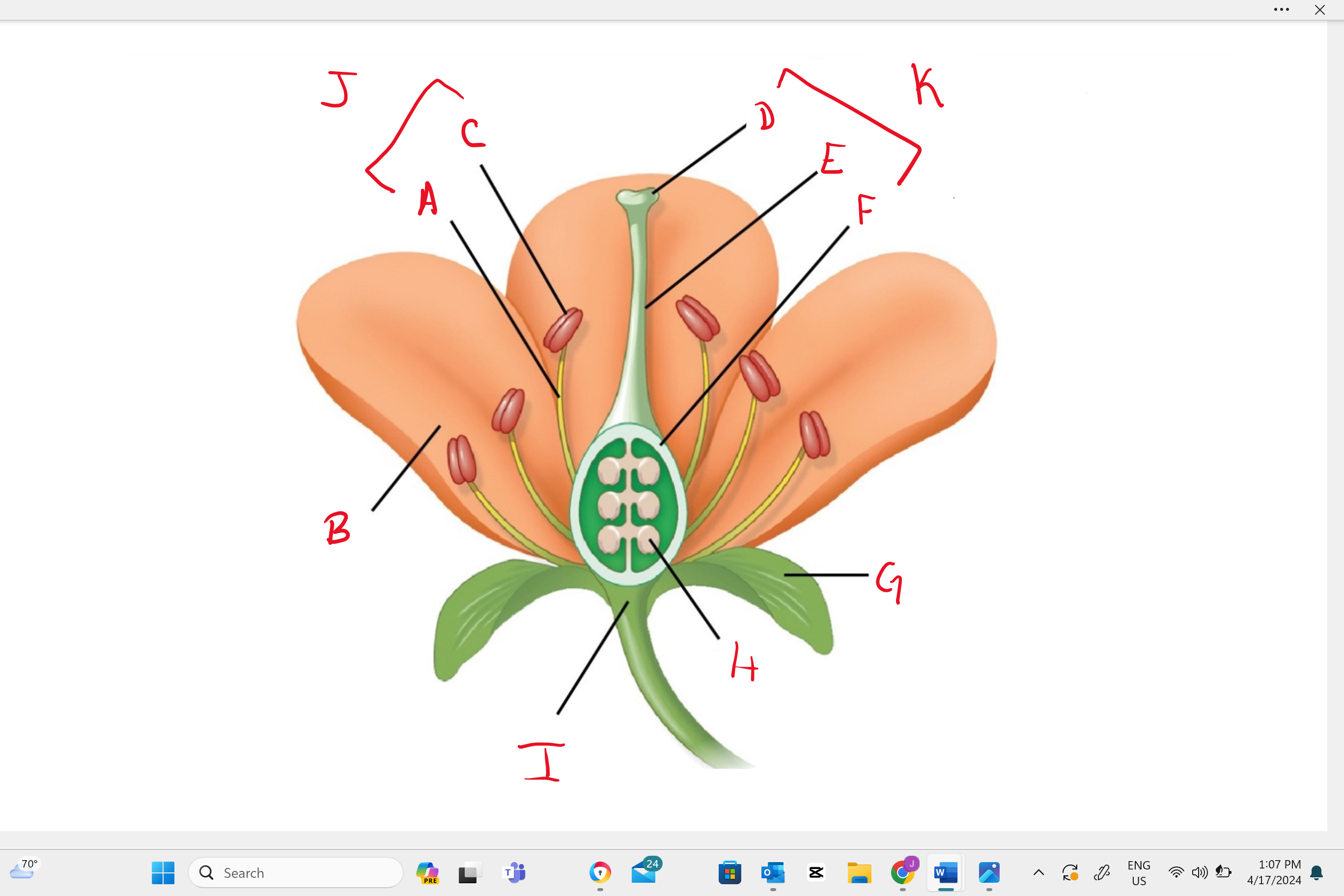
Identify structure “B”
petal
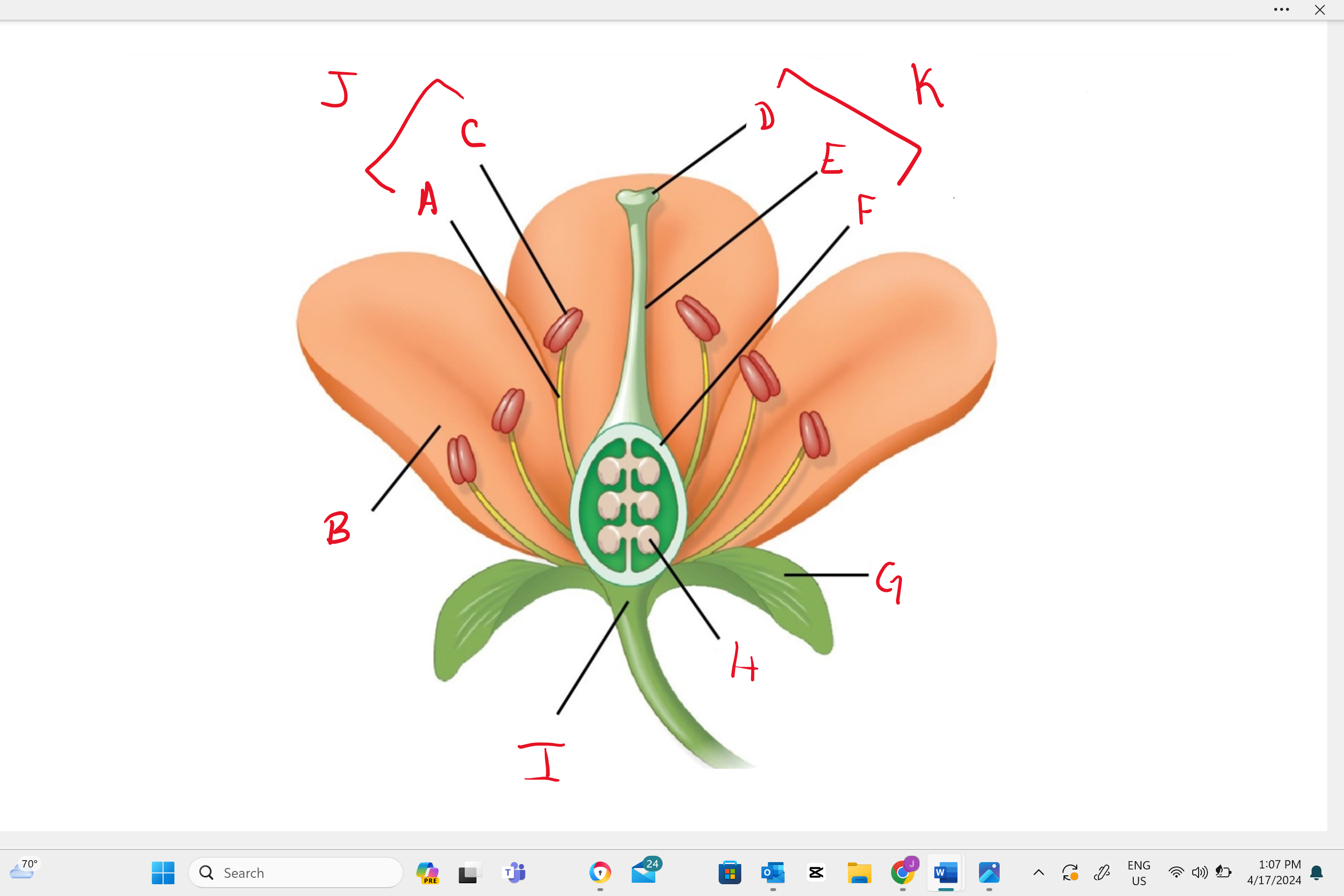
Identify structure “a”
filament
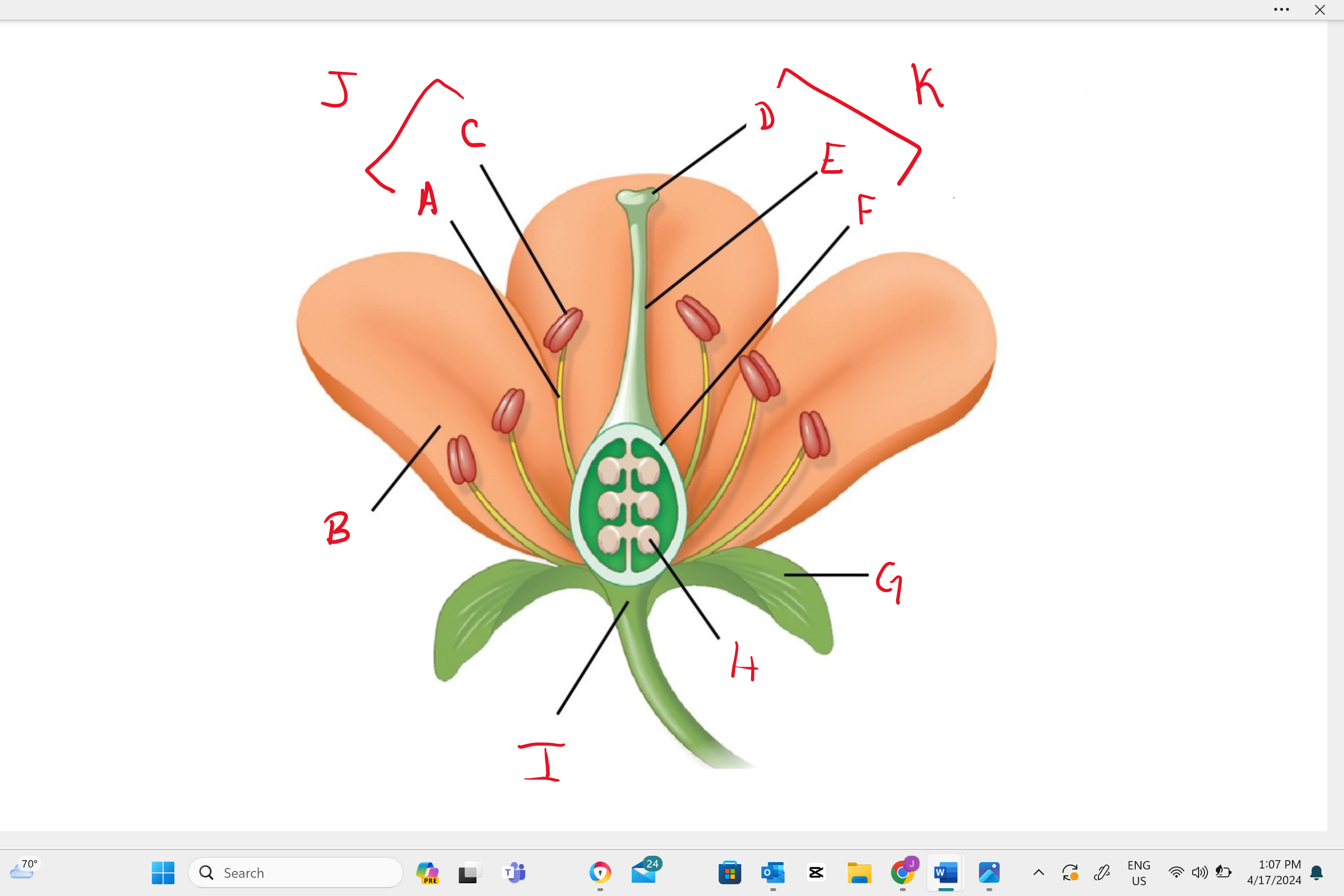
Identify structure “c”
anther
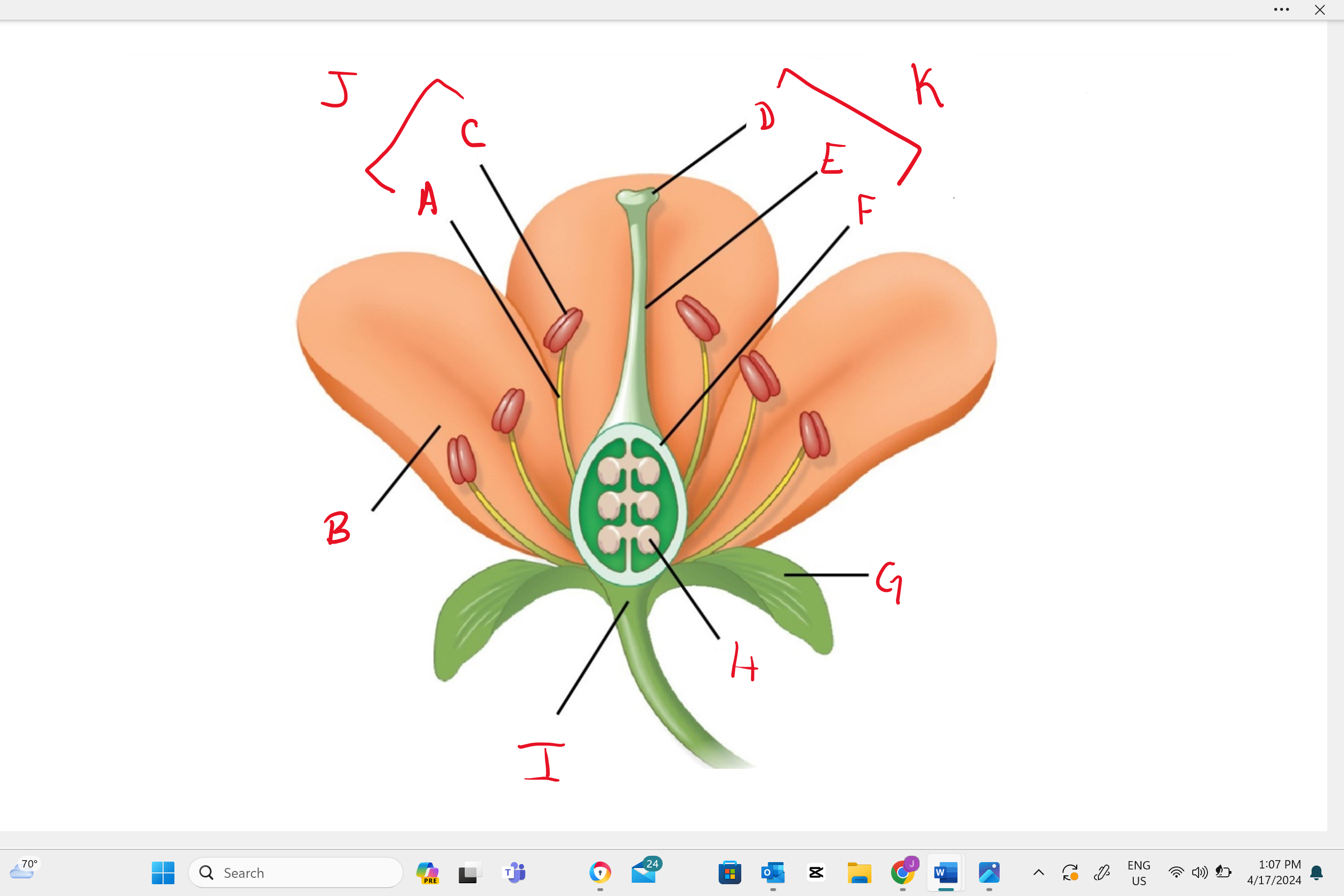
Identify structure “d”
stigma
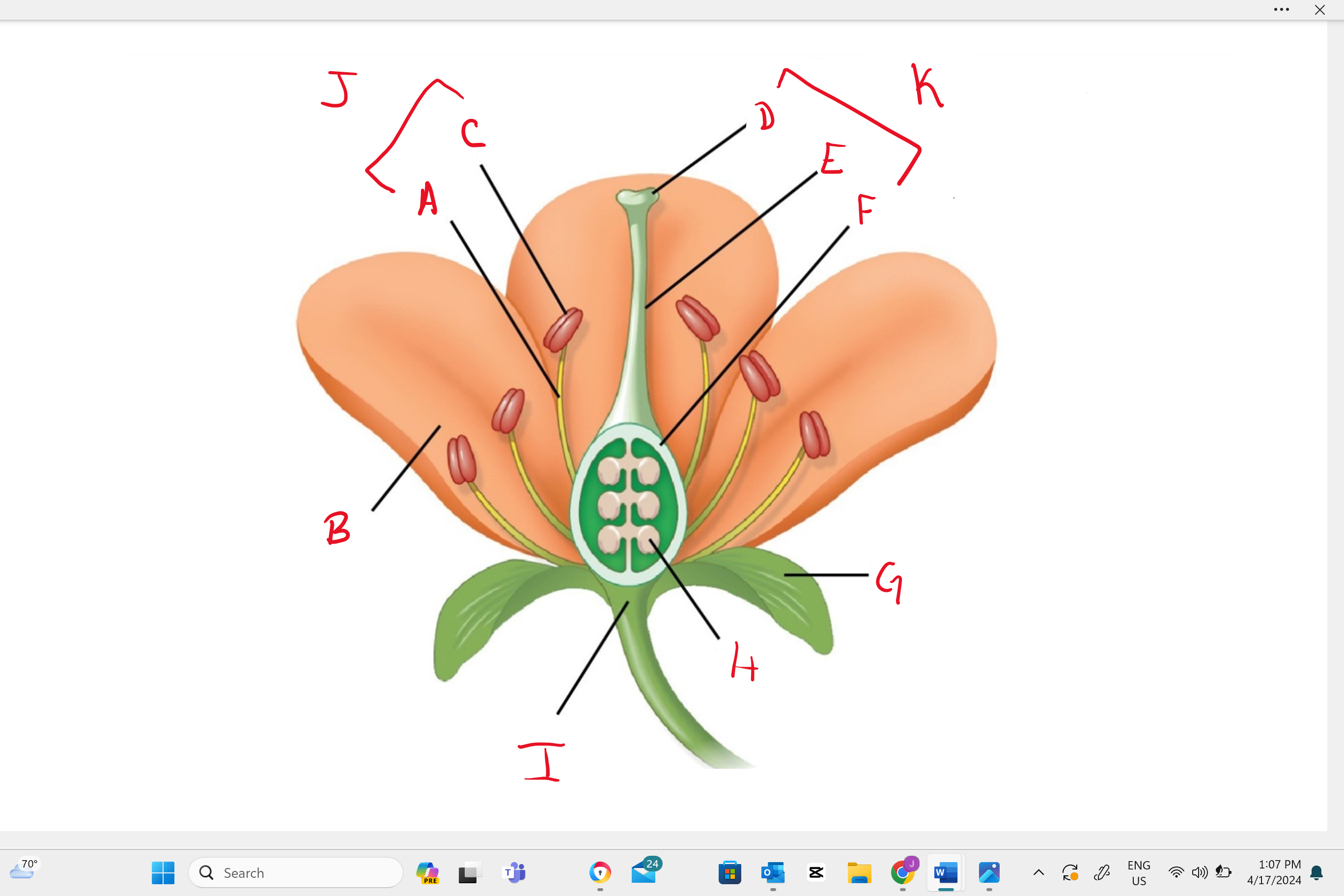
Identify structure “e”
style
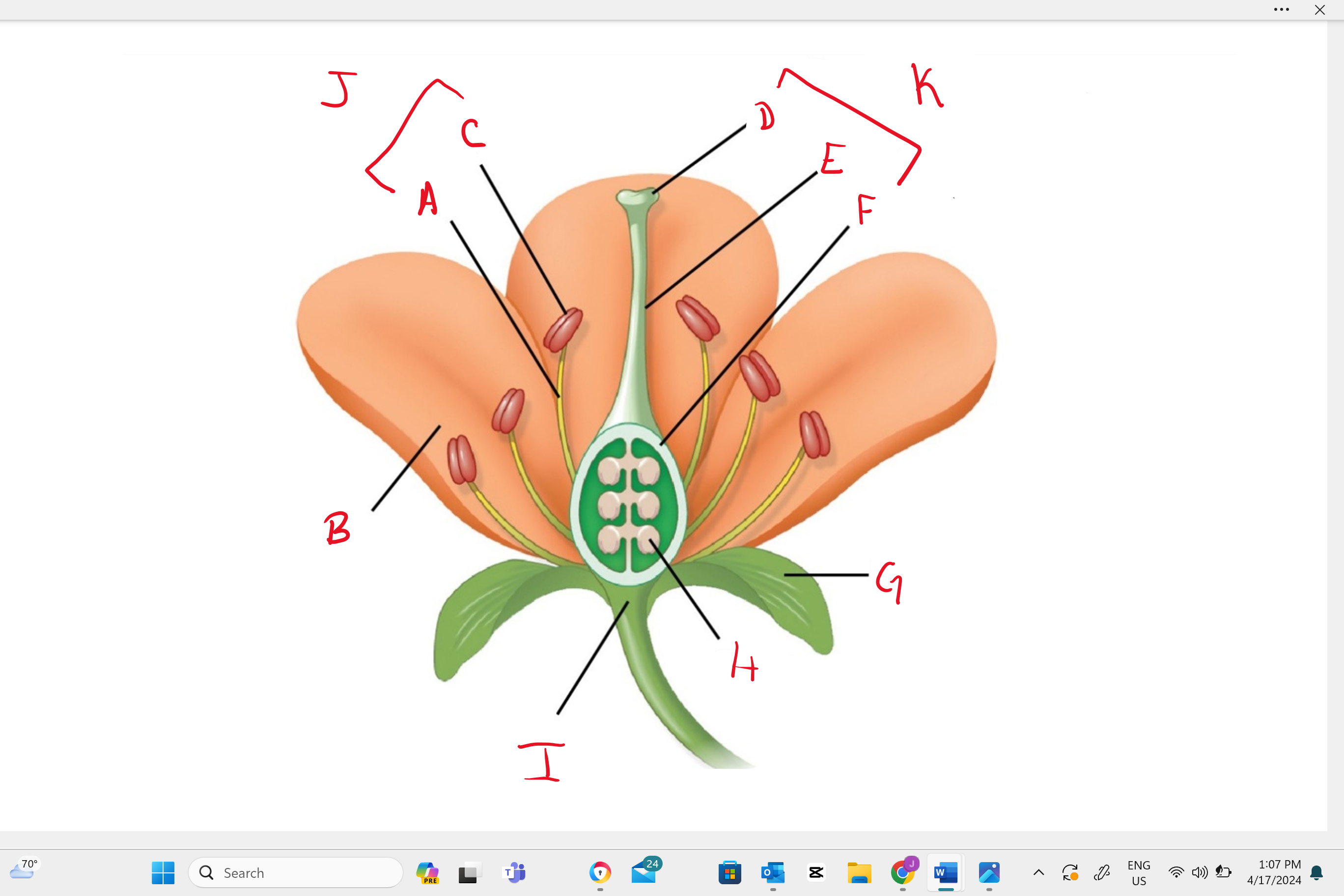
Identify structure “f”
ovary
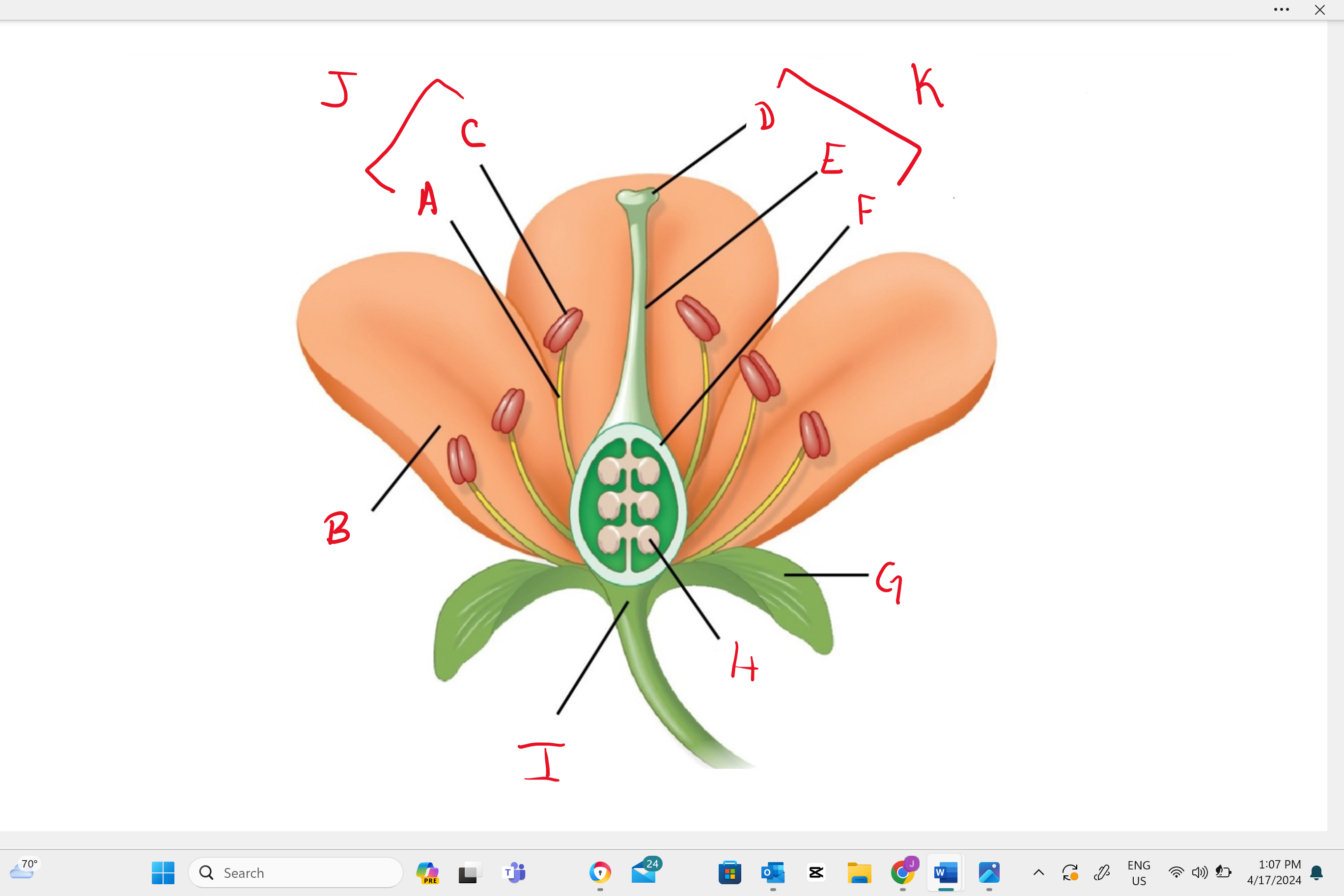
Identify structure “g”
sepal
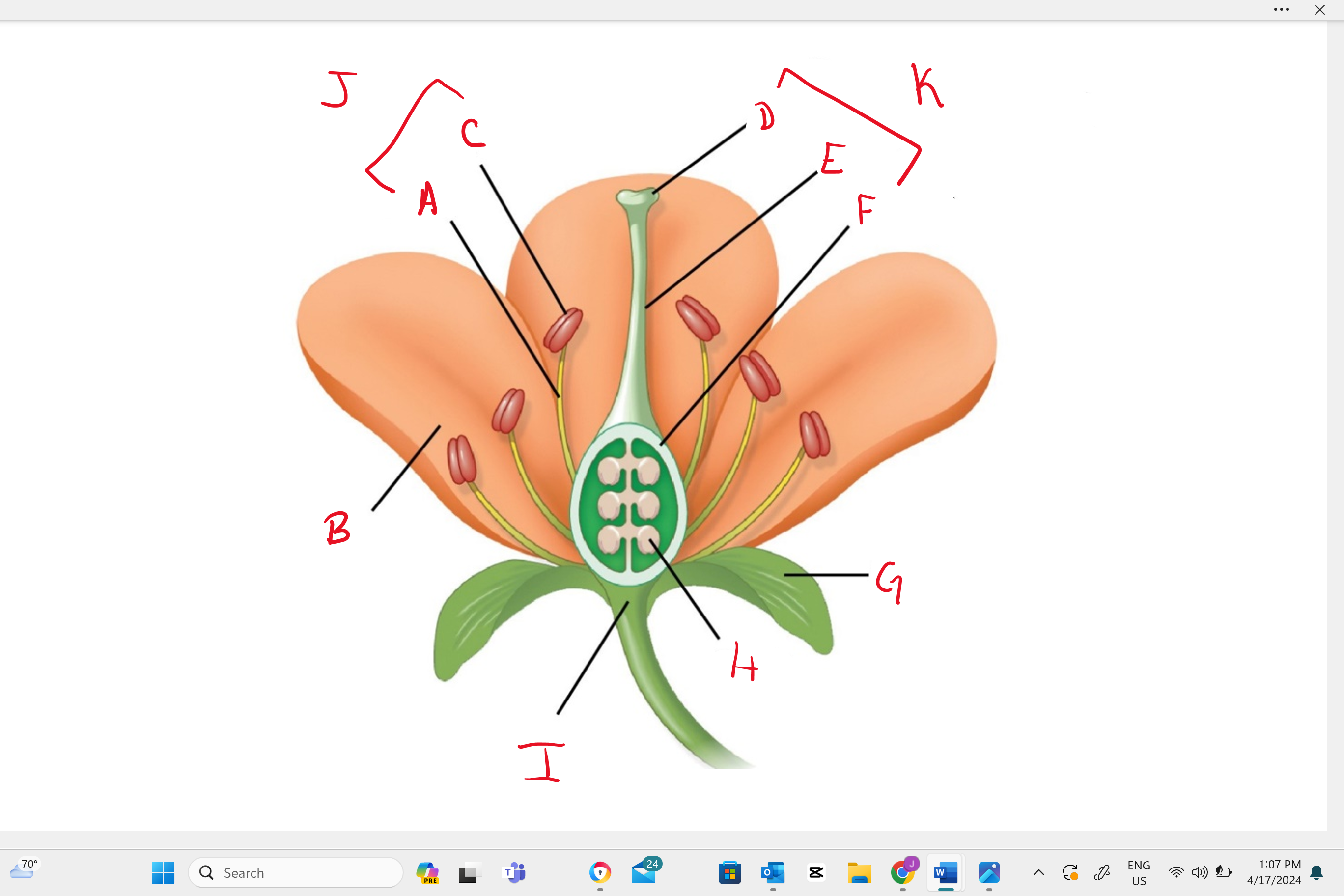
Identify structure “h”
ovule
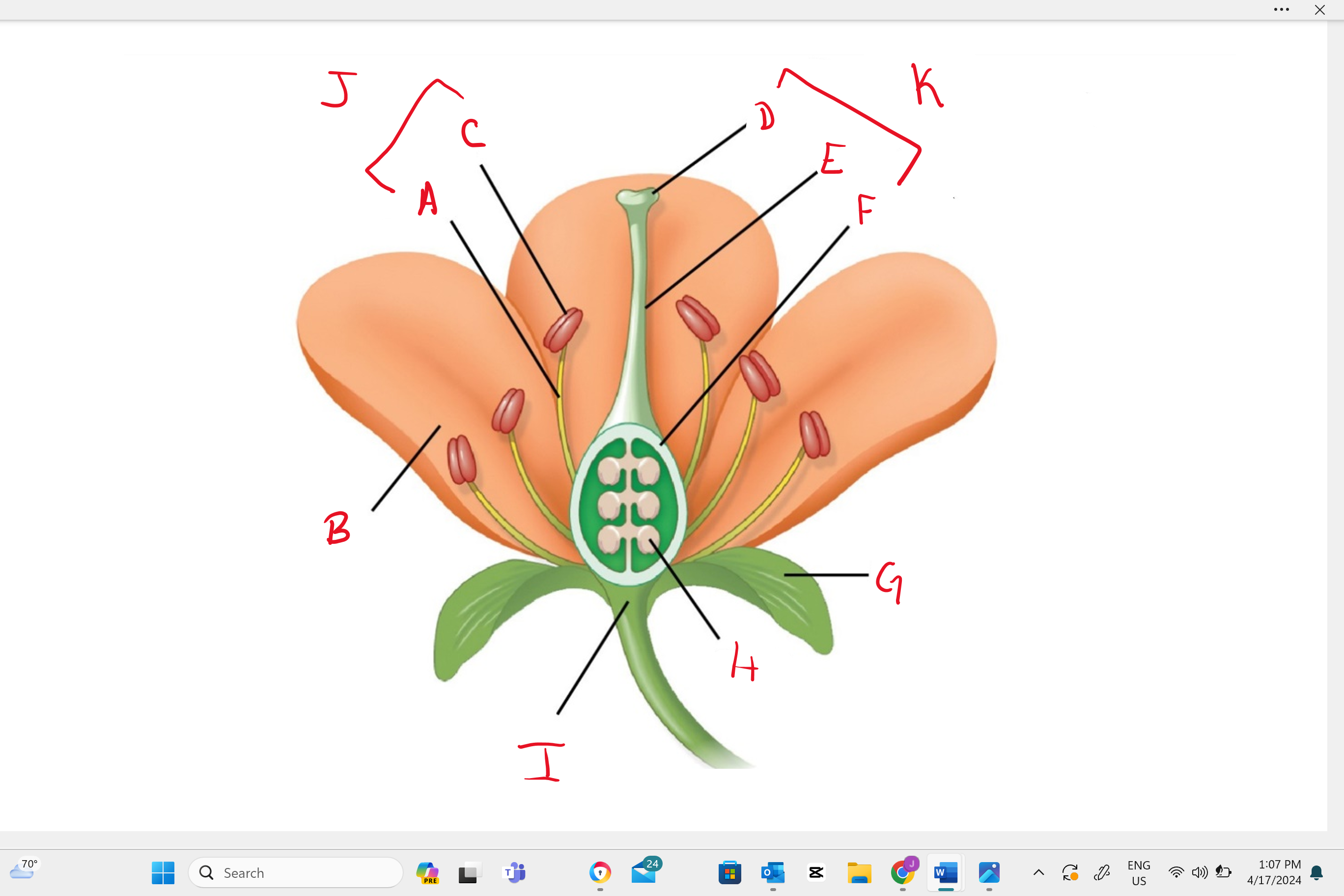
Identify structure “i”
receptacle
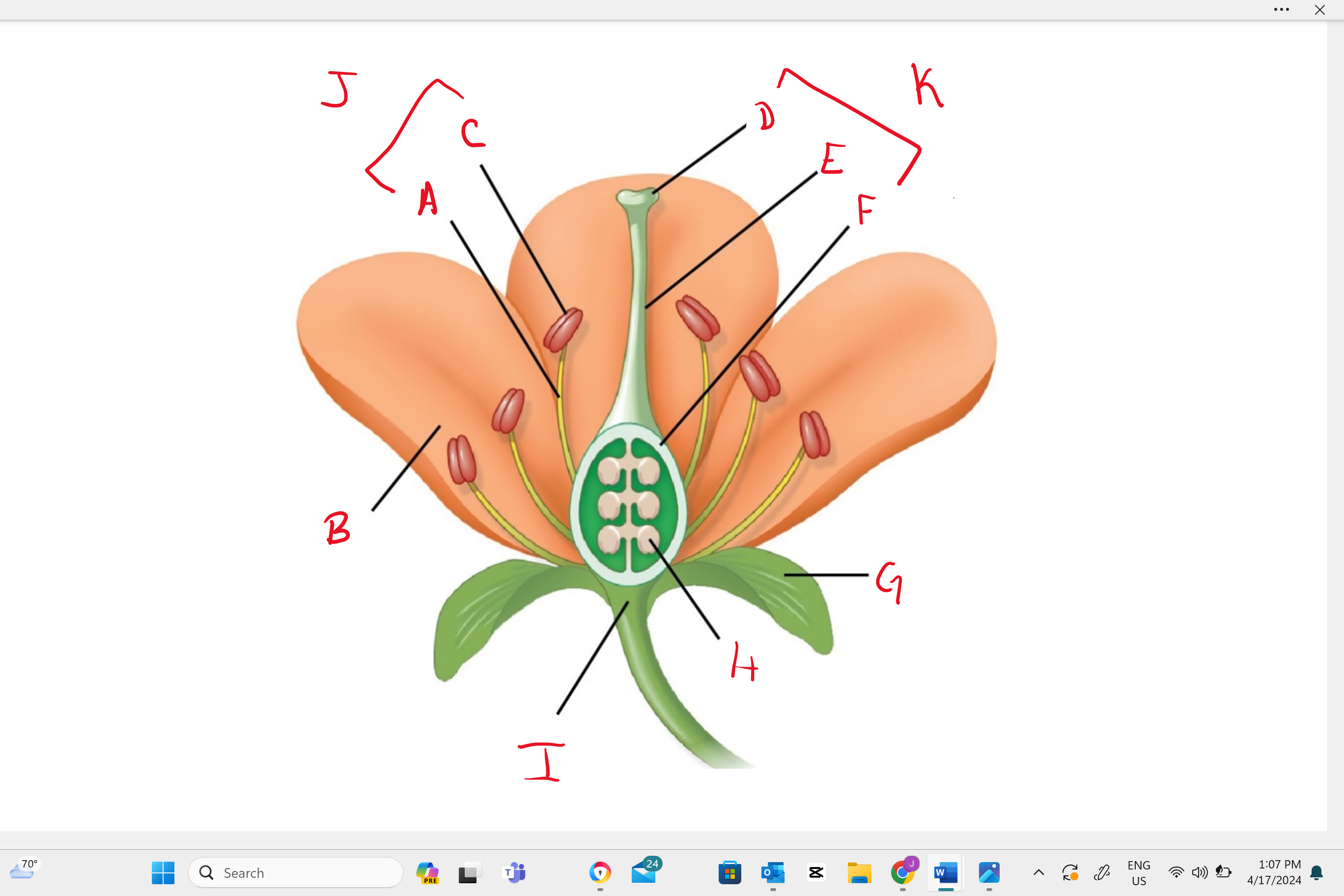
Identify structure “j”
stamen
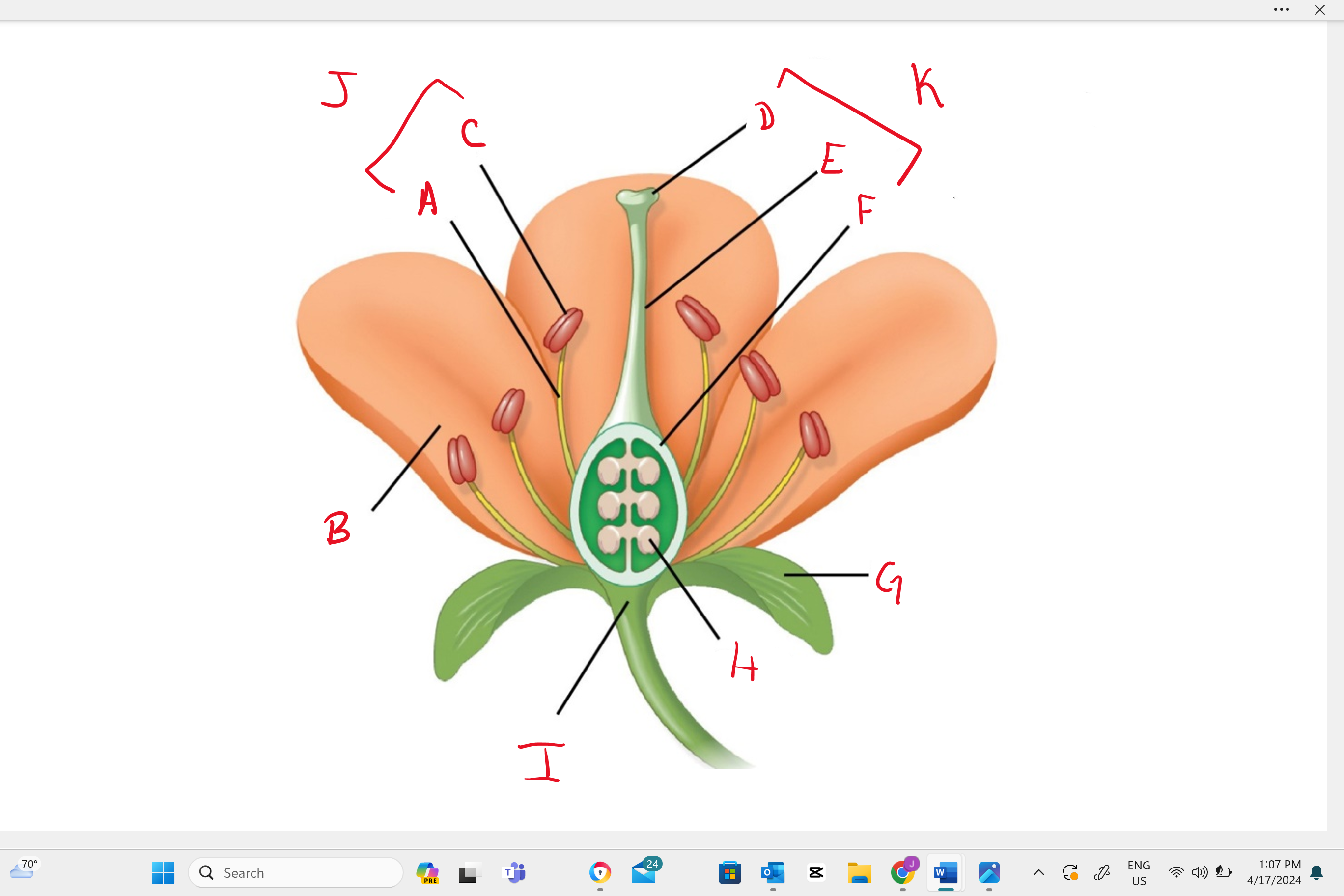
Identify structure “k”
single carpel (simple pistil)
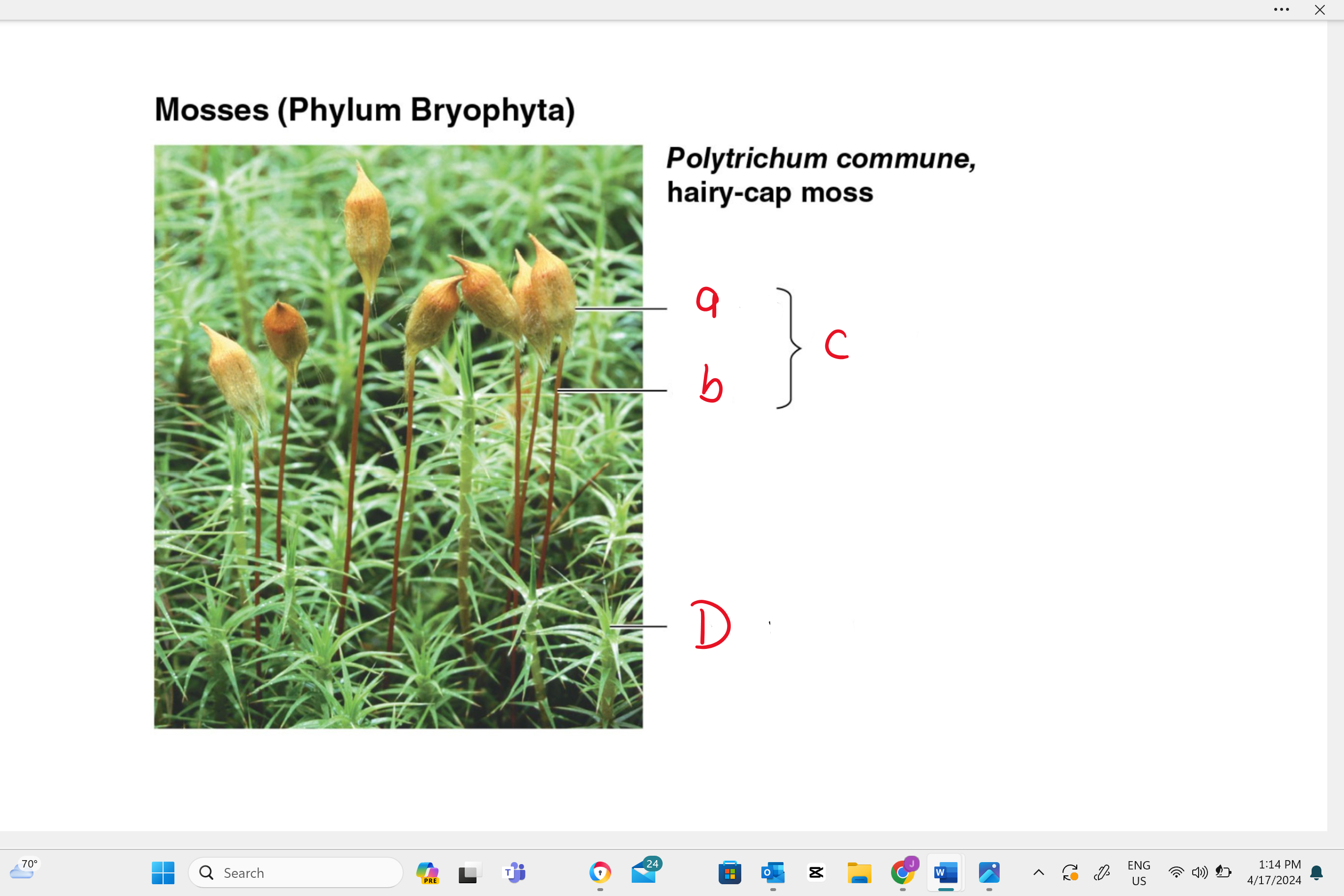
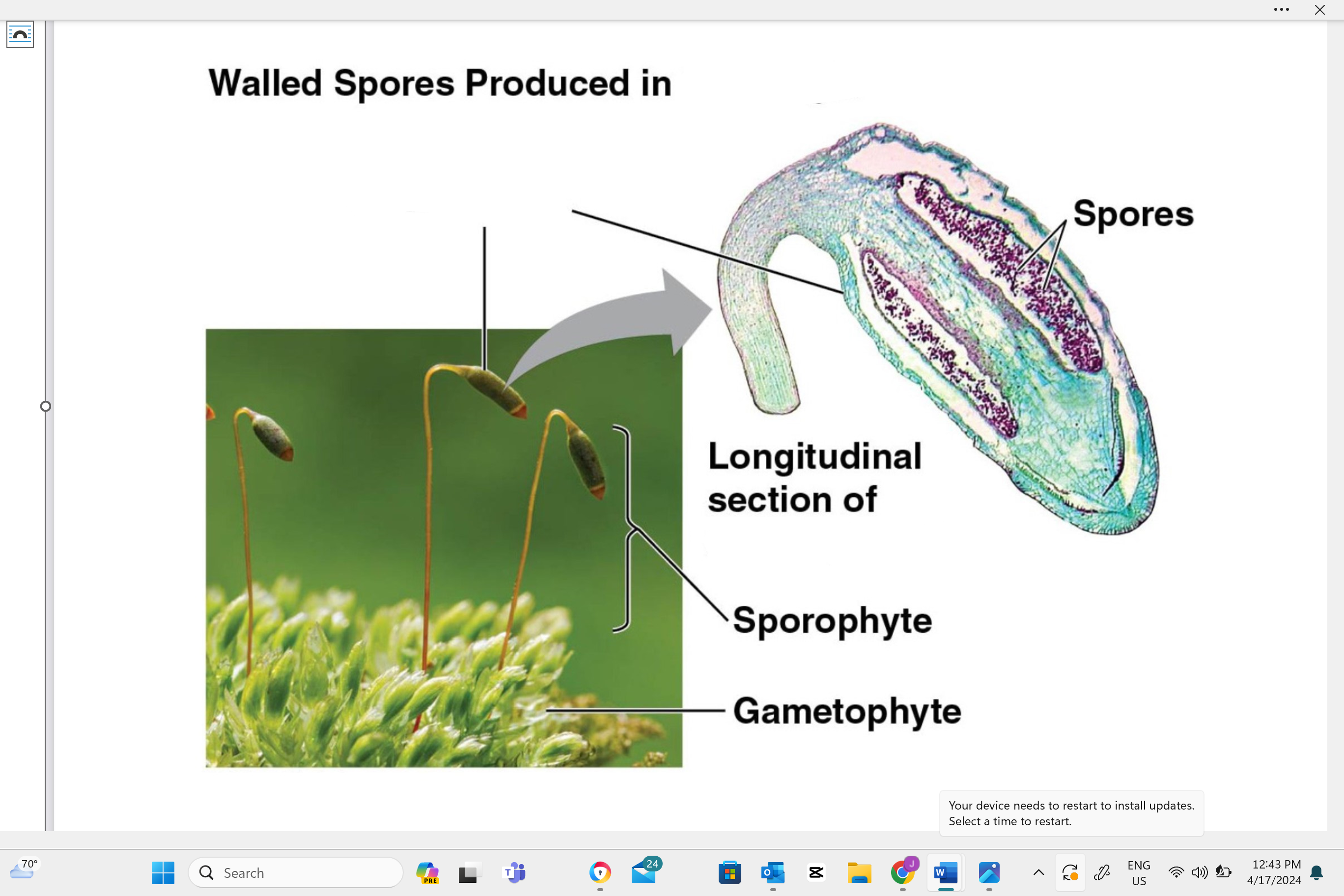
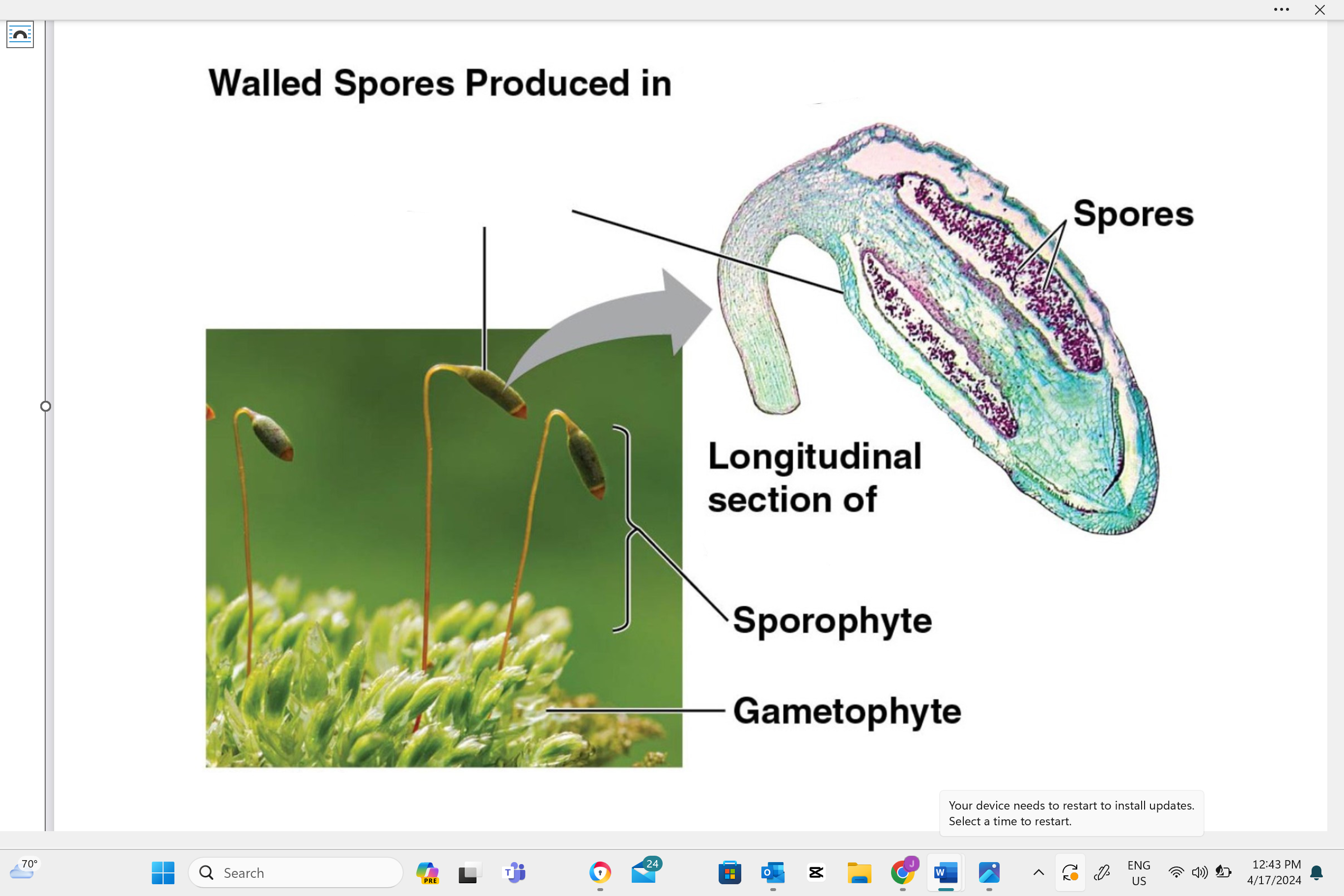
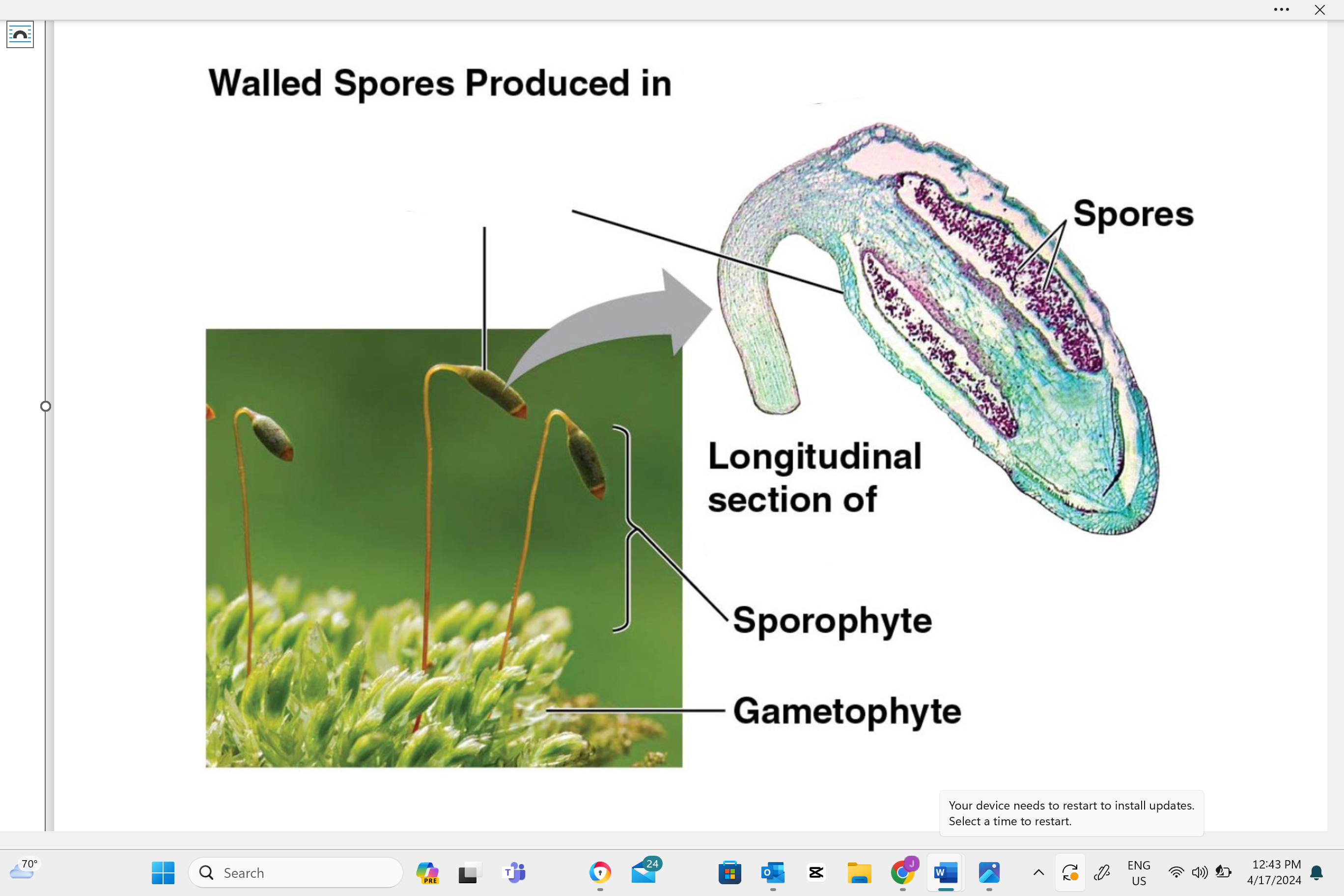
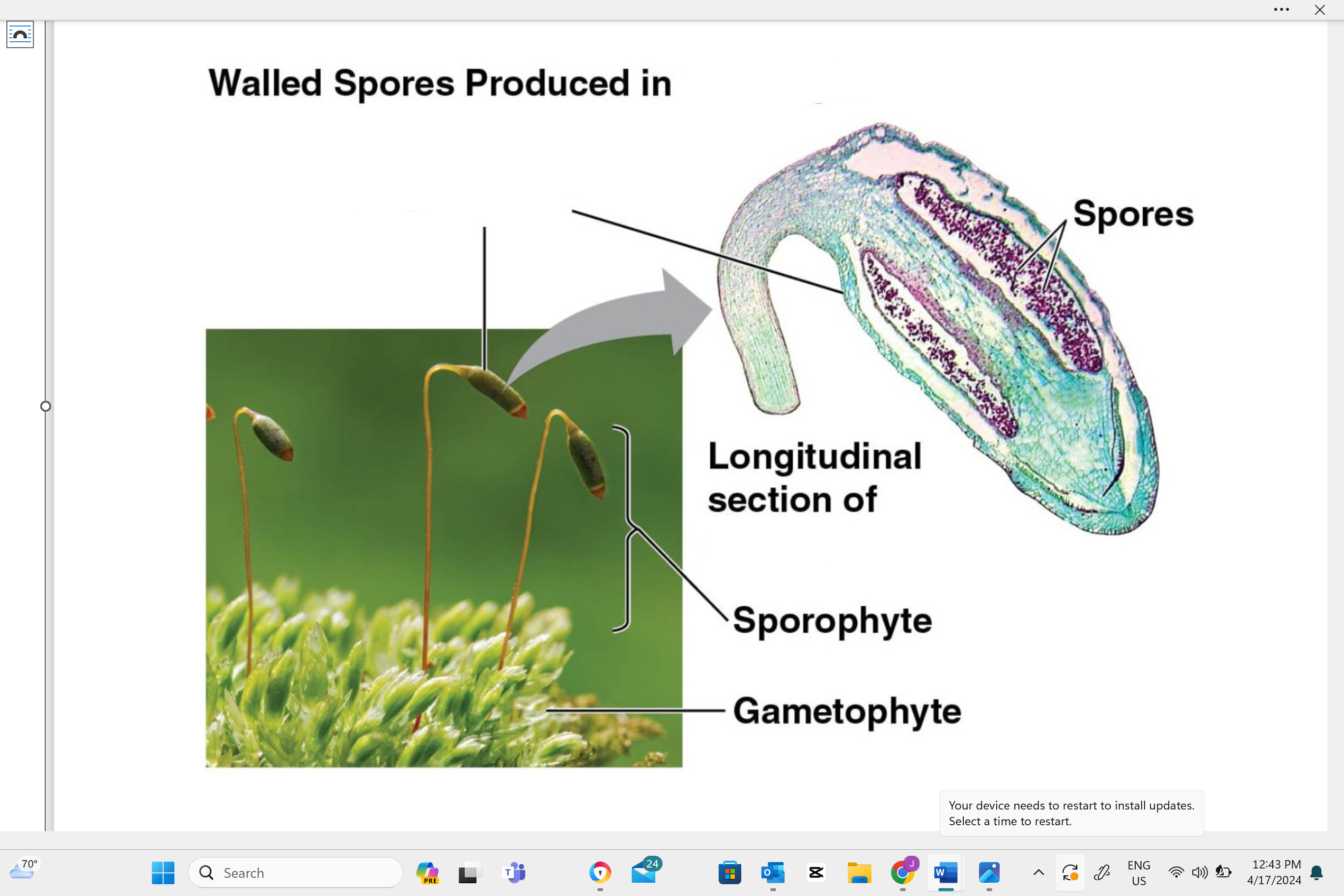
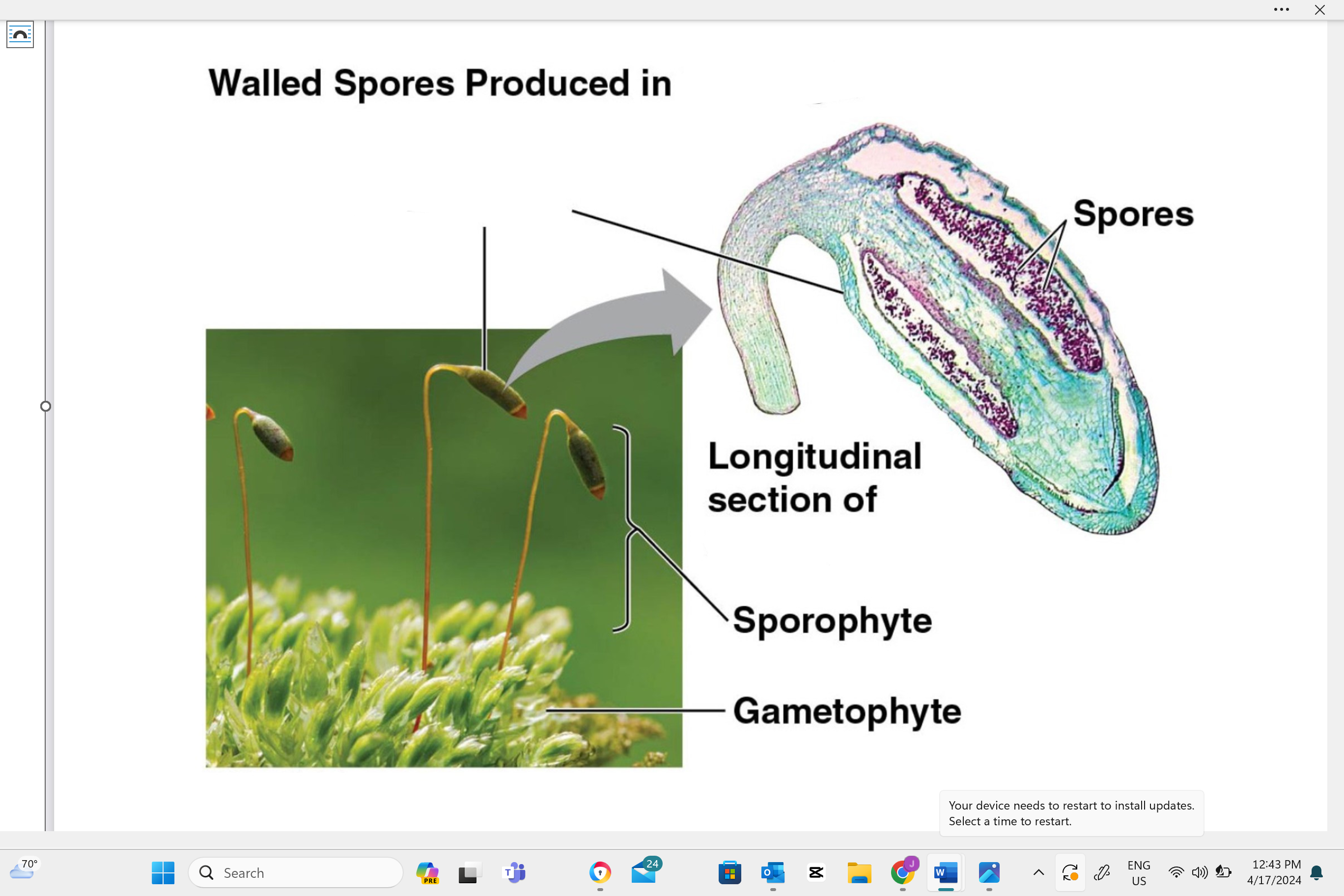
identify structure “A”
capsule
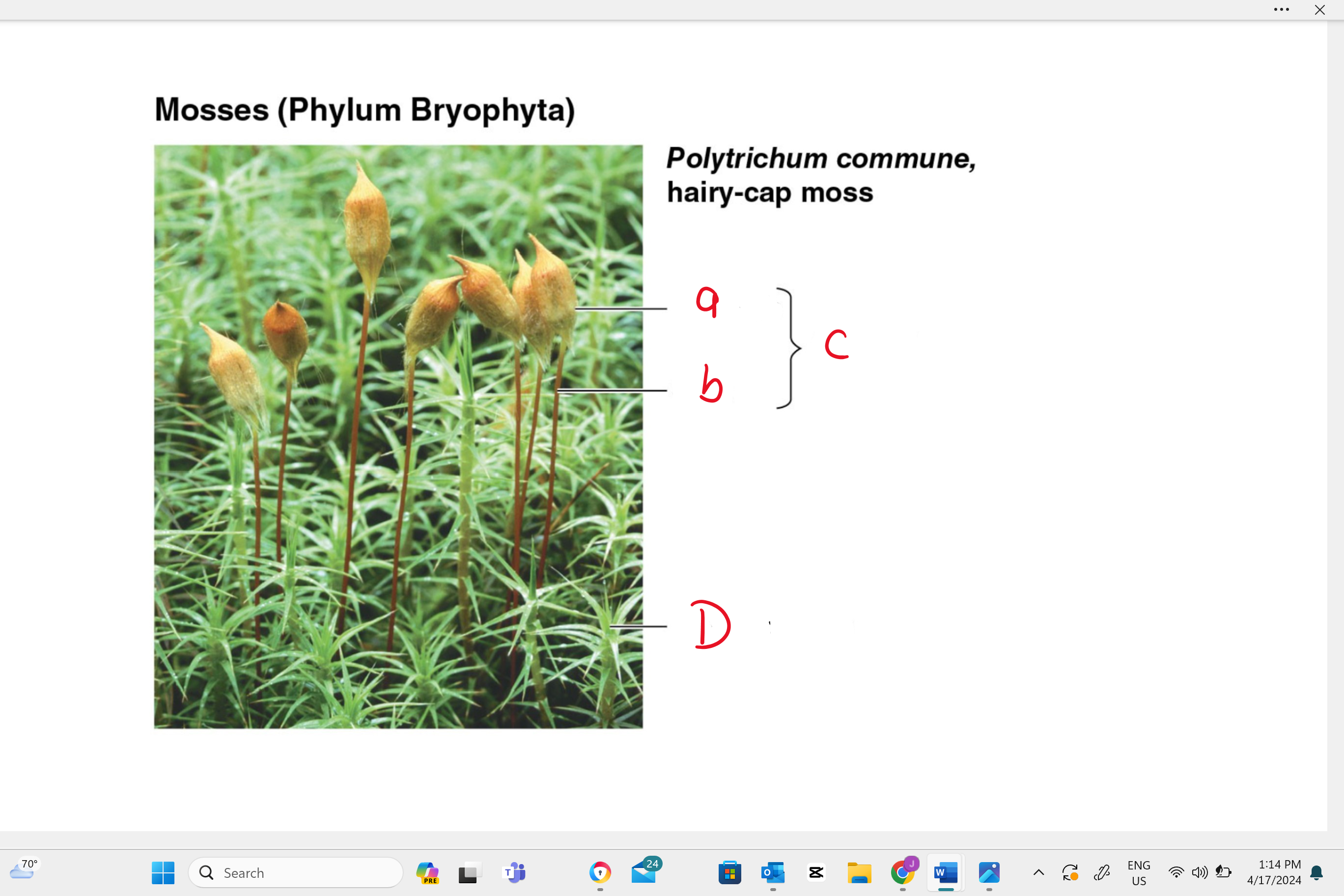
identify structure “b”
seta
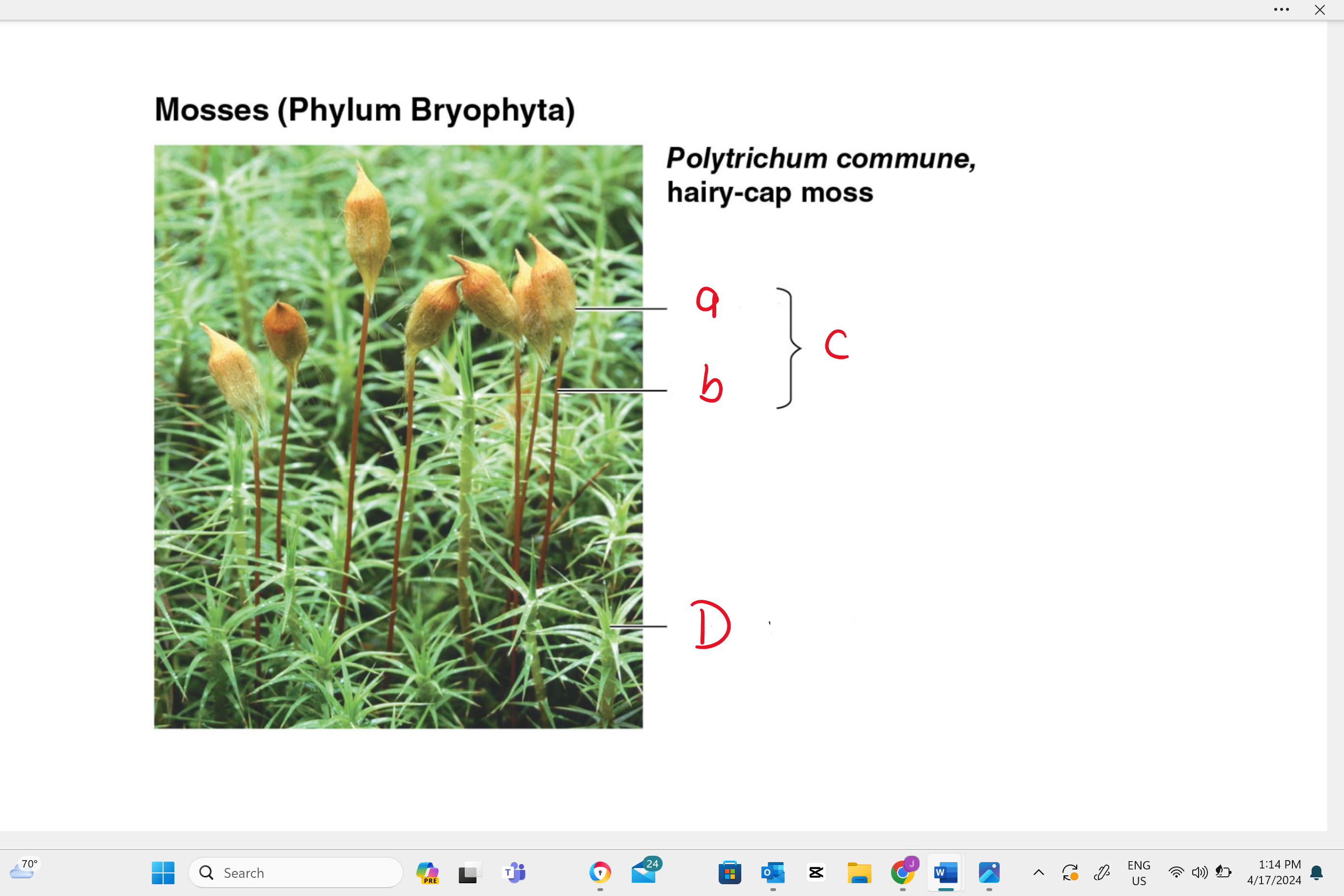
identify structure “c”
sporophyte
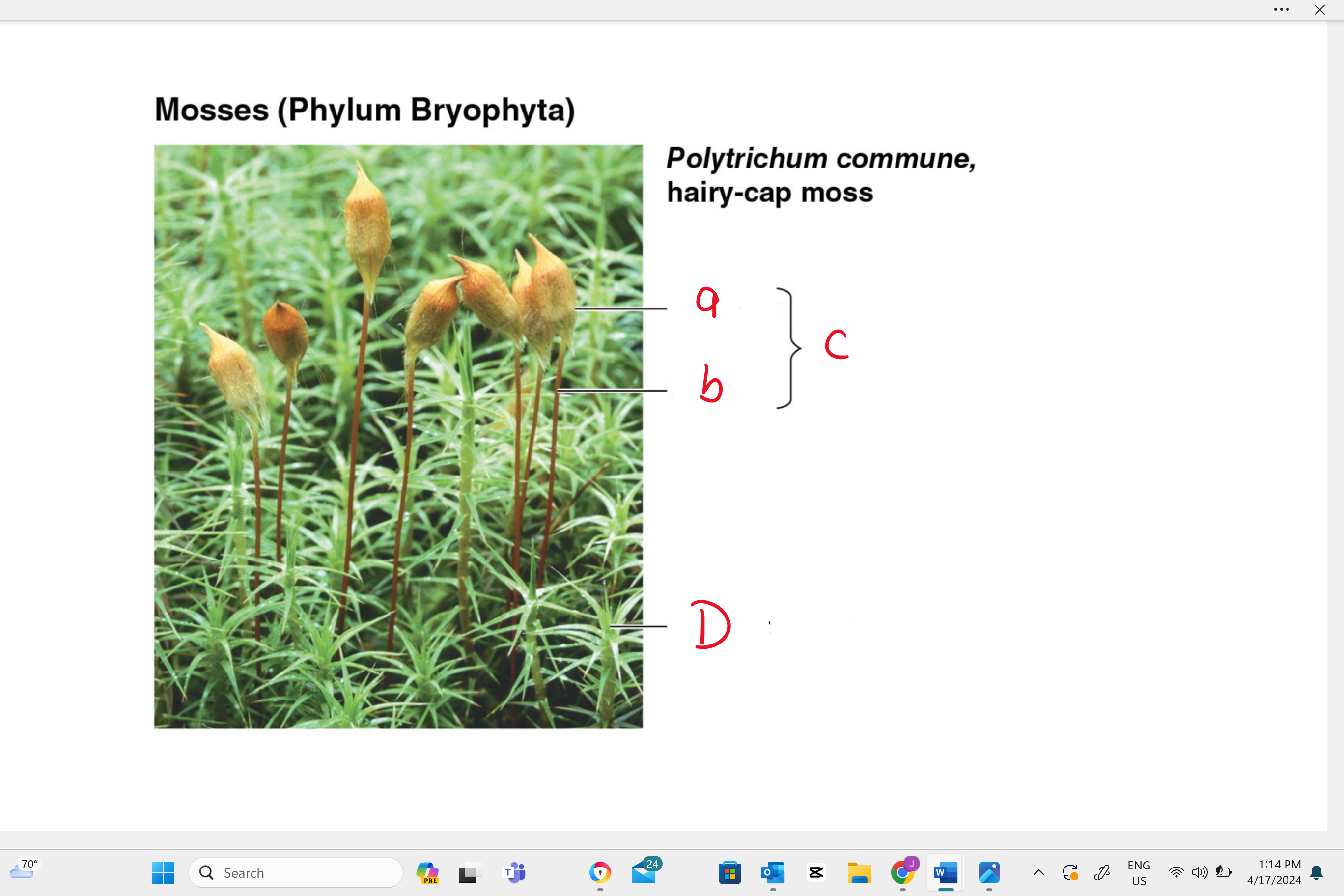
identify structure “D”
gametophyte