Lecture 9: Pharmacodynamics
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Pharmacokinetics Vs. Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetics
- study of ADME
- what the body does to drug
Pharmacodynamics
- study of the biochemical/physiological effect of a drug and their mechanisms of action at organ system/subcellular/macro cellular levels
- the drug action on the body
For PK assumptions to be valid, a ______________________ must exist between the plasma concentration and effect (PD)
different realtionship
The effects of a drug may be....(2)
- directly related
- indirectly related to its plasma concentration
(ex effects of B-blockers result in direct interaction with receptors, effects of warfarin are indirect)
Examples of reversible drug effects
β –blockers and warfarin
- when the drug is removed, the effects disappear
Examples of irreversible drug effects
anticancer drugs and antibiotics
- when the drug is removed, effects will not disappear
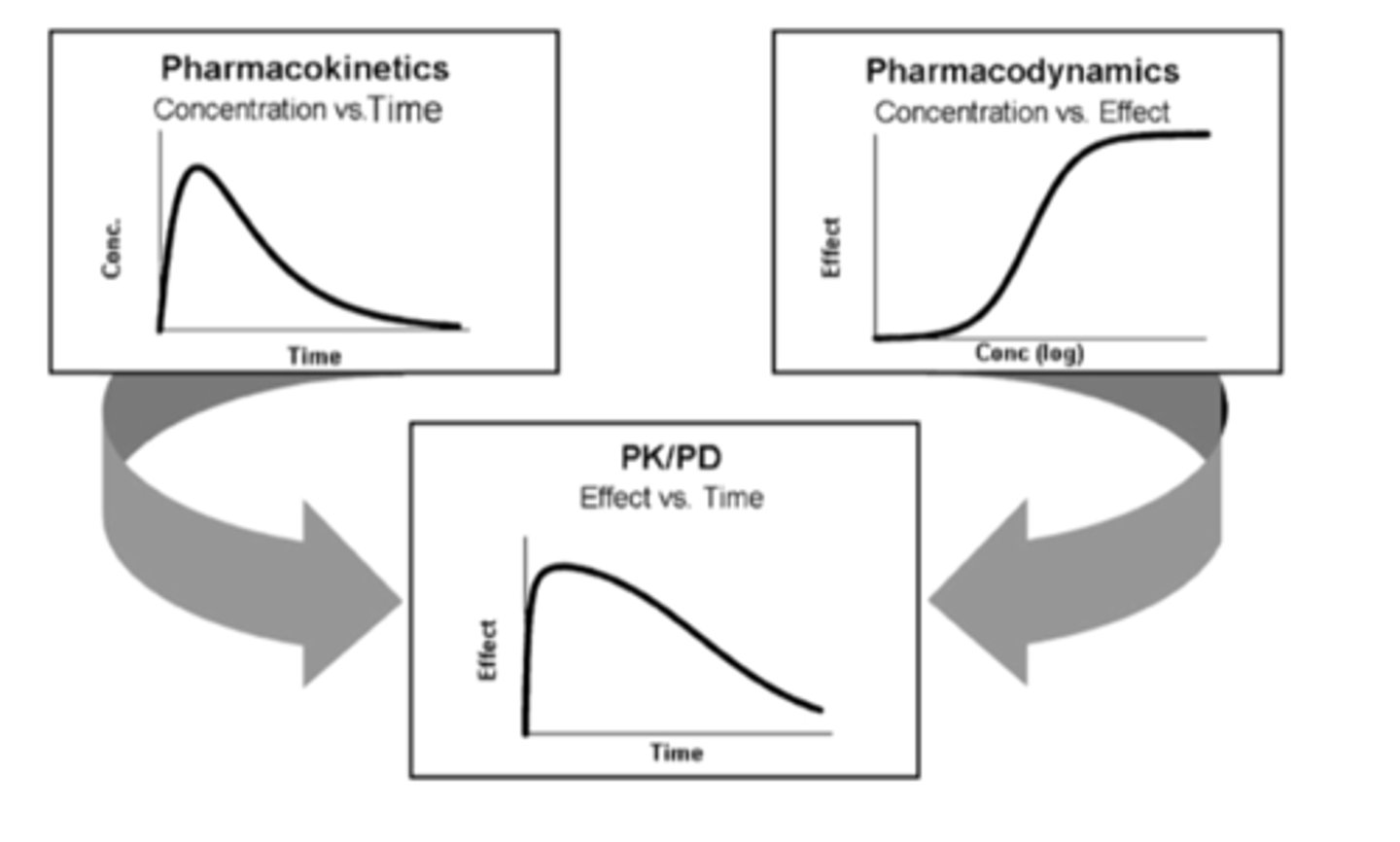
Pharmacokinetic vs pharmacodynamics models (graphs)
PK: concentration depends on time
PD: effect depends on conc.
PK/PD: effect depends on time
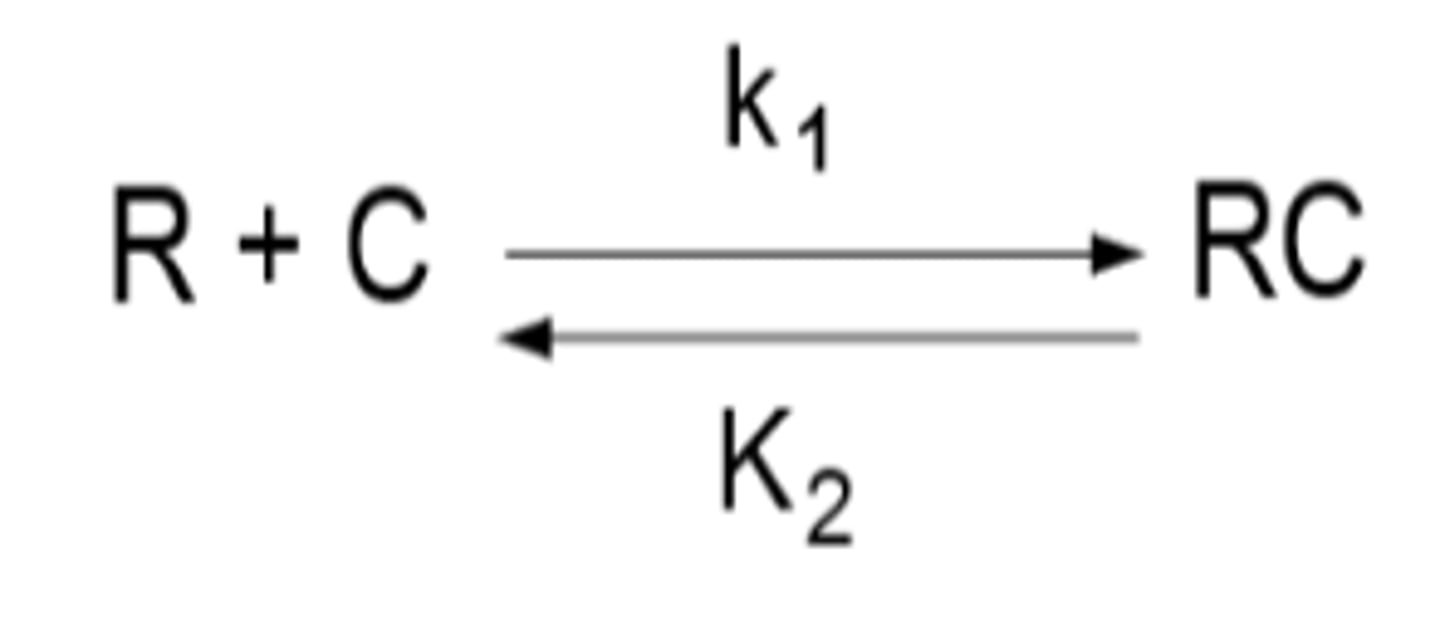
Drug-Receptor Interaction
R + C <------> RC
-------> (K1)
(K2)<-------
R- the concentrations of unoccupied receptors
C- the concentrations of drug
RC- the concentrations of the drug-receptor complex
- K1 and K2 are the association and dissociation rate constants
The produced effect (E) is directly related to what?
the concentration of RC (drug-receptor complex)
Because the number of receptors is limited, what occurs when the drug occupies all the receptors?
a further increase in drug concentration would not increase the effect
The possible maximum effect (Emax) is produced due to...
is produced due to the interaction of all the receptors with the drug
The equation that connects E, Emax, and C
E = Emax x C/Kd + C
Kd- equilibrium dissociation constant (binding affinity)
- the basis for one of the most widely used PD models, called the Emax model
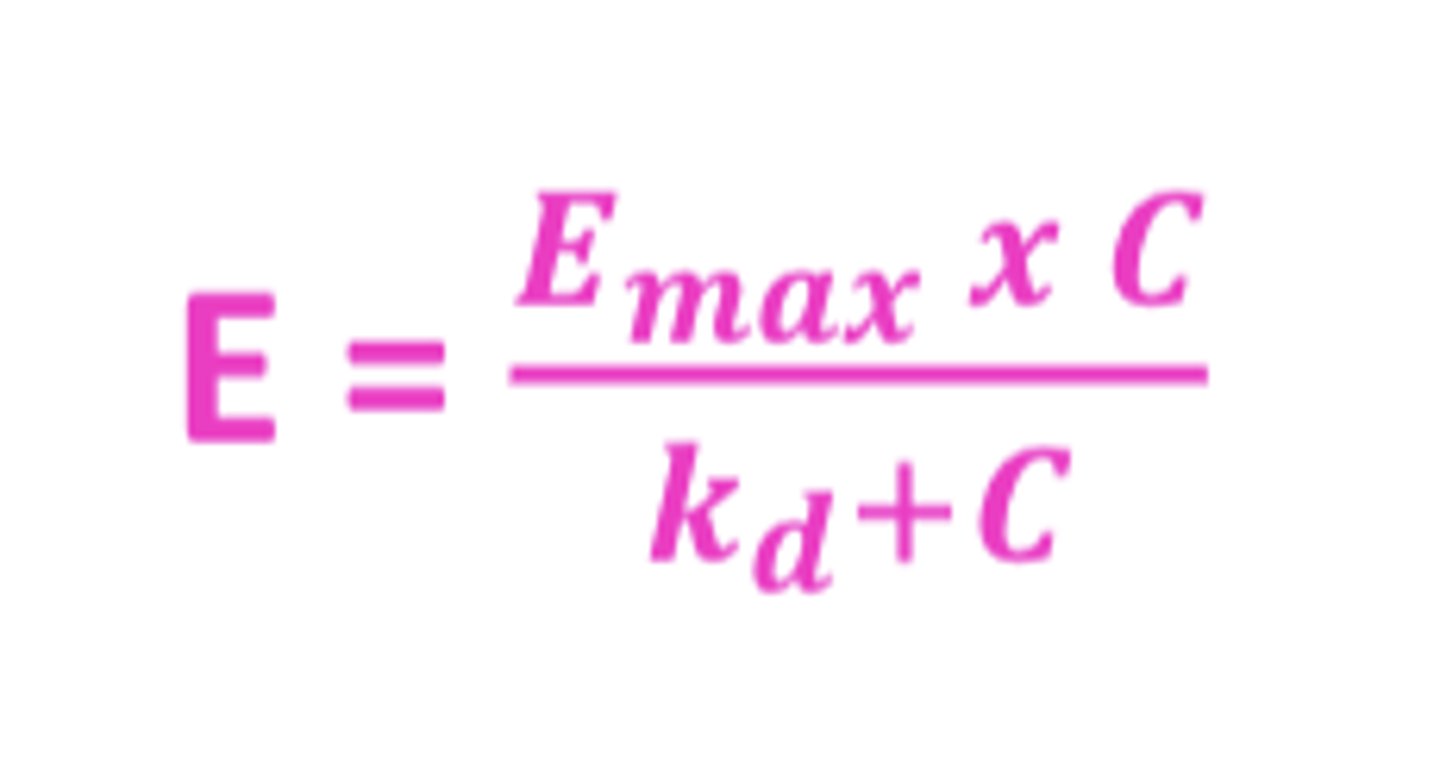
Kd
equilibrium dissociation constant (binding affinity)
Kd = k2/k1
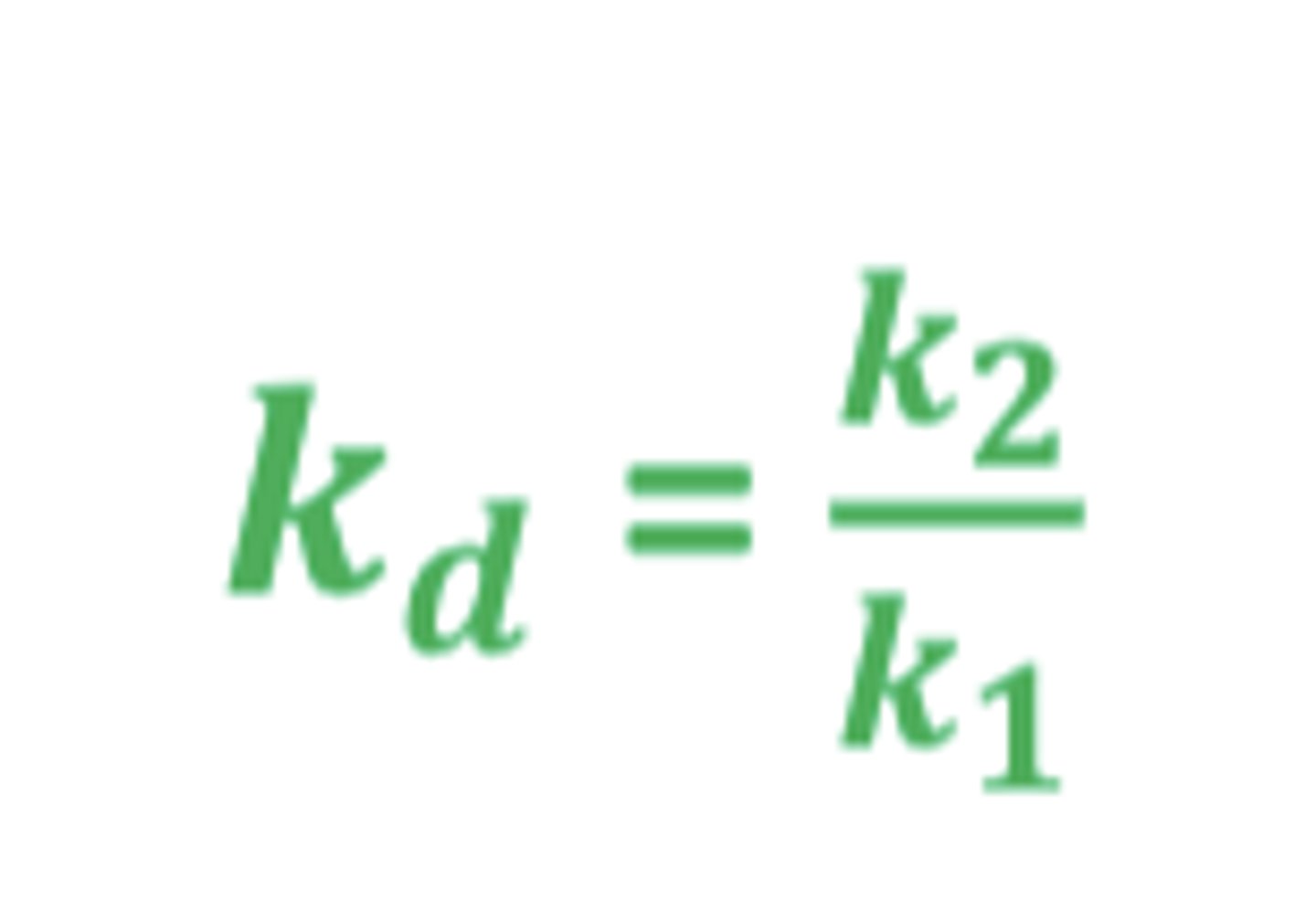
Kd is inversely related to what?
to the affinity of the drug-receptor complex
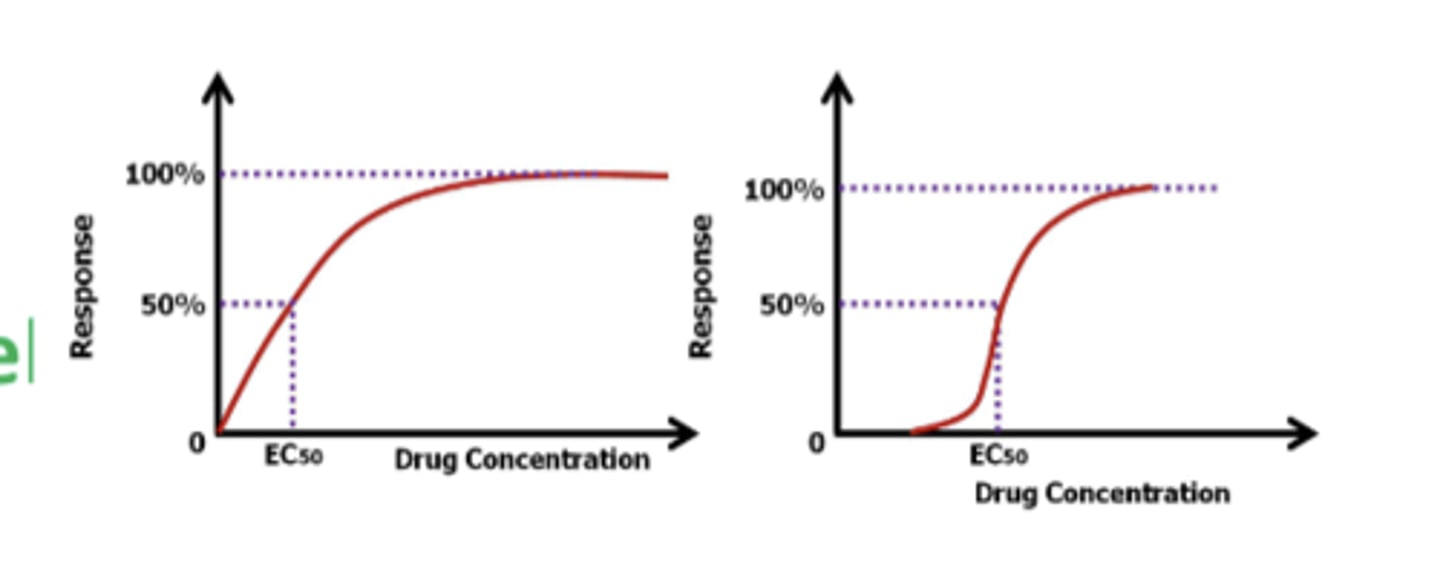
Emax Model
- based on the equation developed for drug-receptor interaction with minor modification
- Kd is replaced with EC50
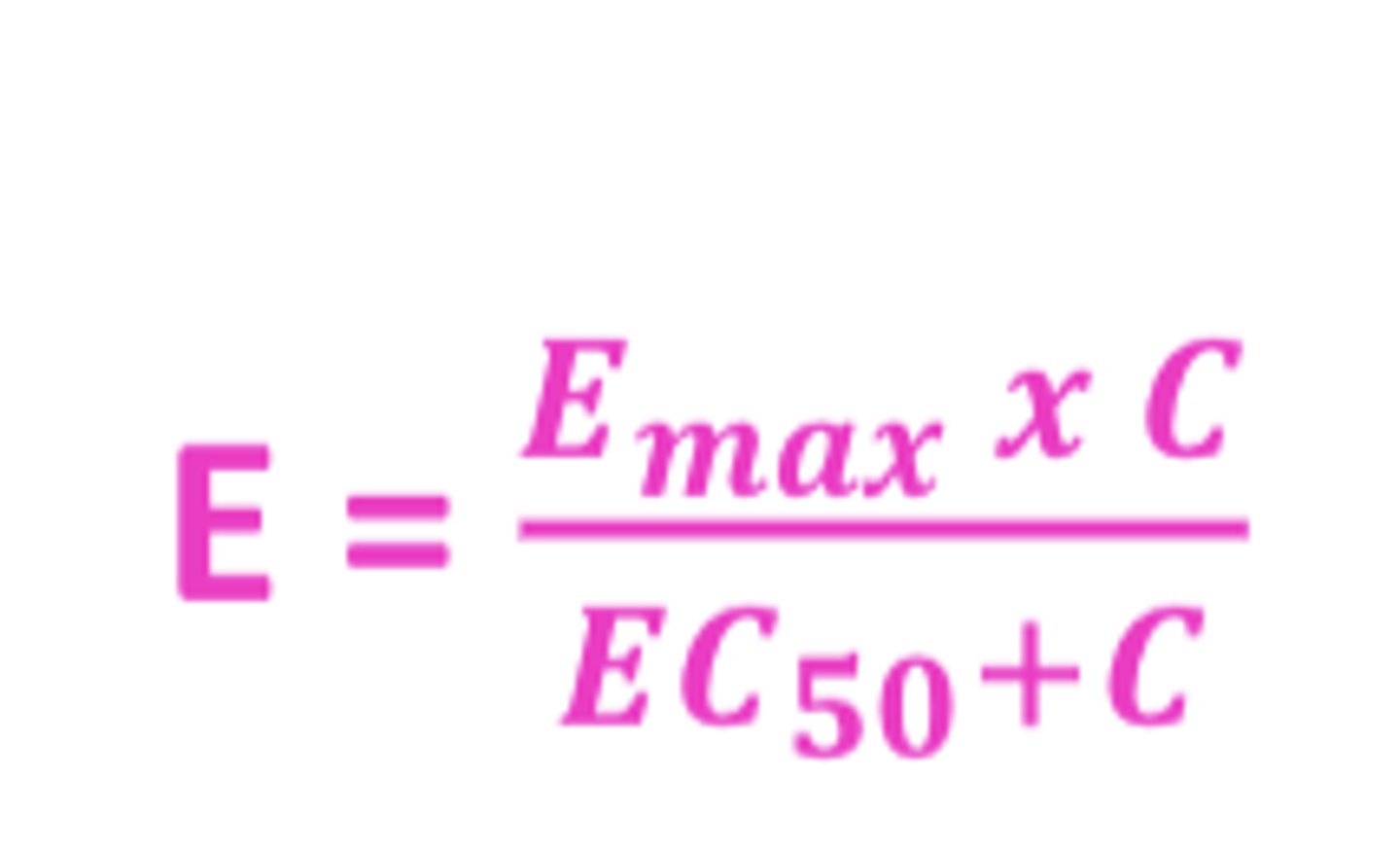
EC50
the concentration the produces half of the maximum effect
EC50 is inversely related to what?
the affinity of the drug-receptor complex
When the drug-receptor affinity declines, EC50 ______________, thus requires __________ concentrations to produce the same effect
- increases
- higher concentrations
The relation between E (expressed as a percentage of the maximum effect) and C is....
nonlinear
Drug receptor theory and Emax model
- most receptors are unoccupied at very low concentration
- increase in C would almost linearly increase RC
- when all receptors are occupied, at higher concentration, increase in C would have no effect
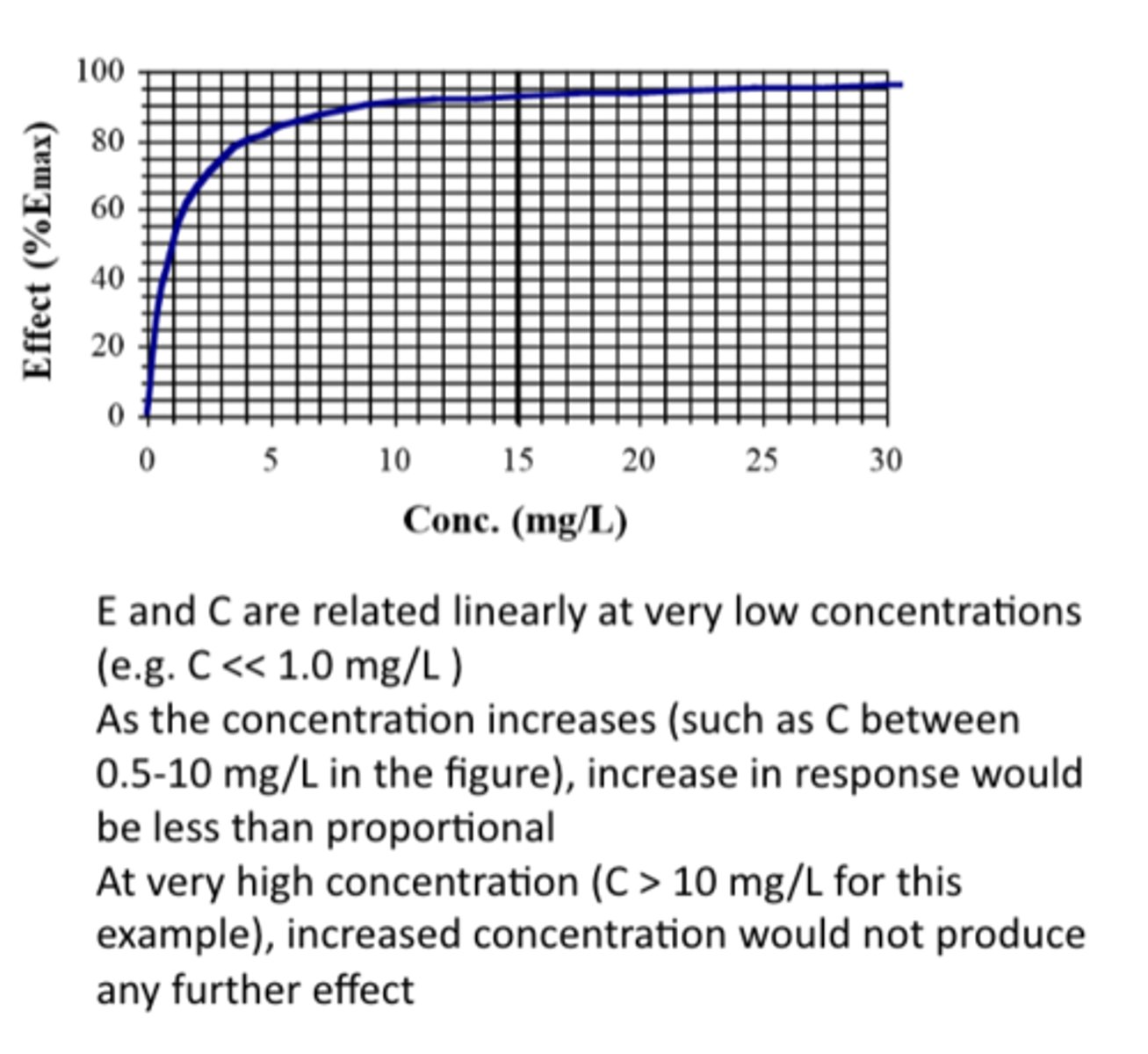
E and C are related linearly at...
very low concentrations (e.g. C << 1.0 mg/L )
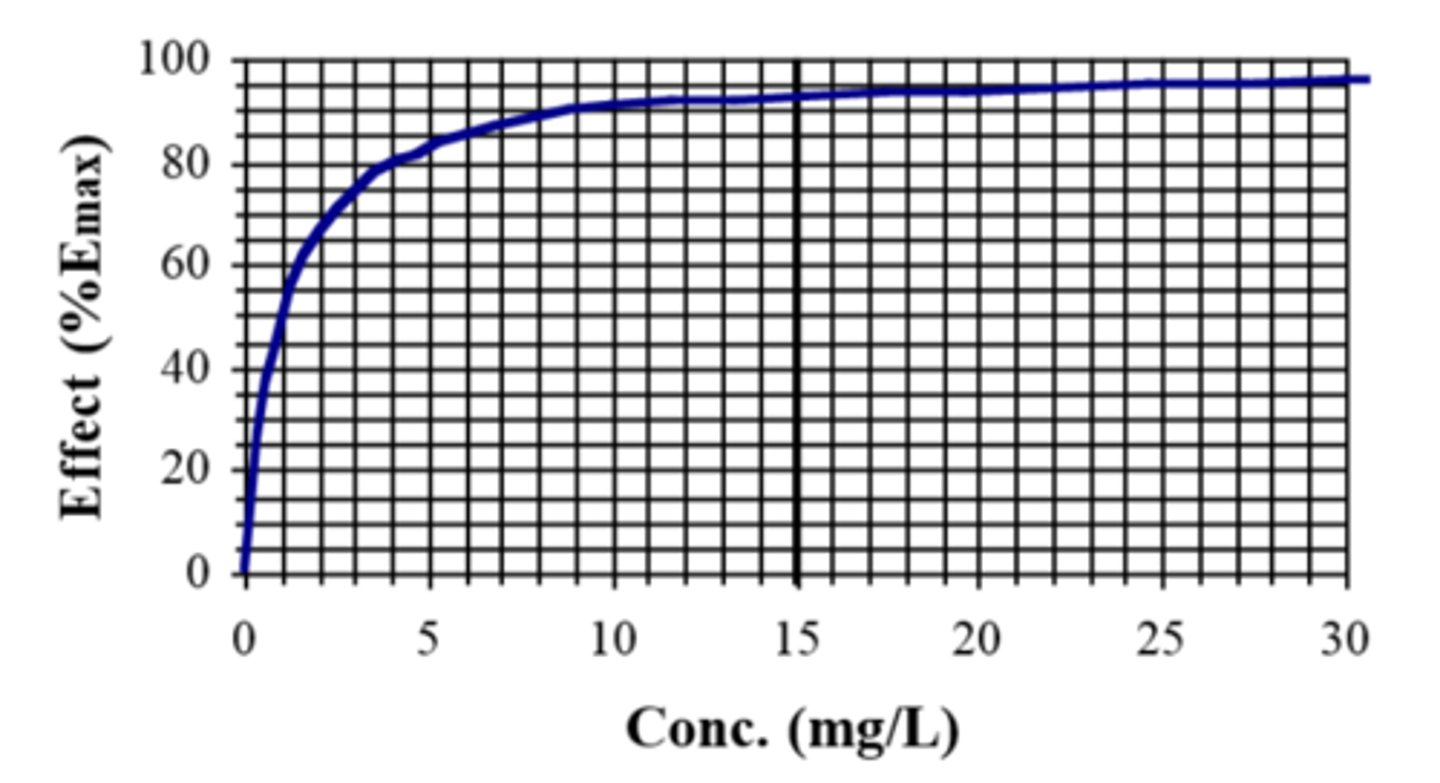
As the concentration increases (such as C between 0.5-10 mg/L in the figure), increase in response would be.....
less than proportional
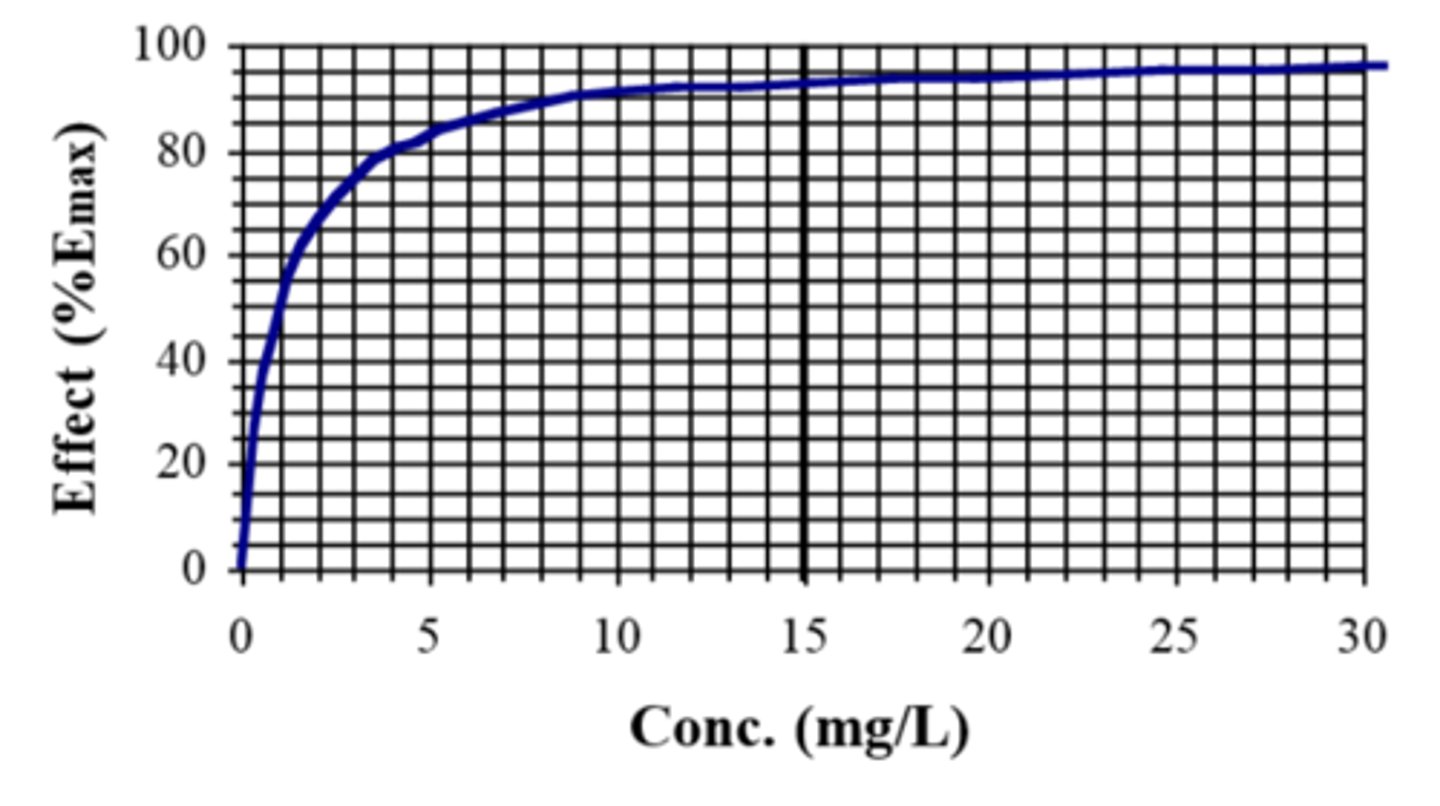
At very high concentration (C > 10 mg/L for this example), an increased concentration would...
not produce any further effect
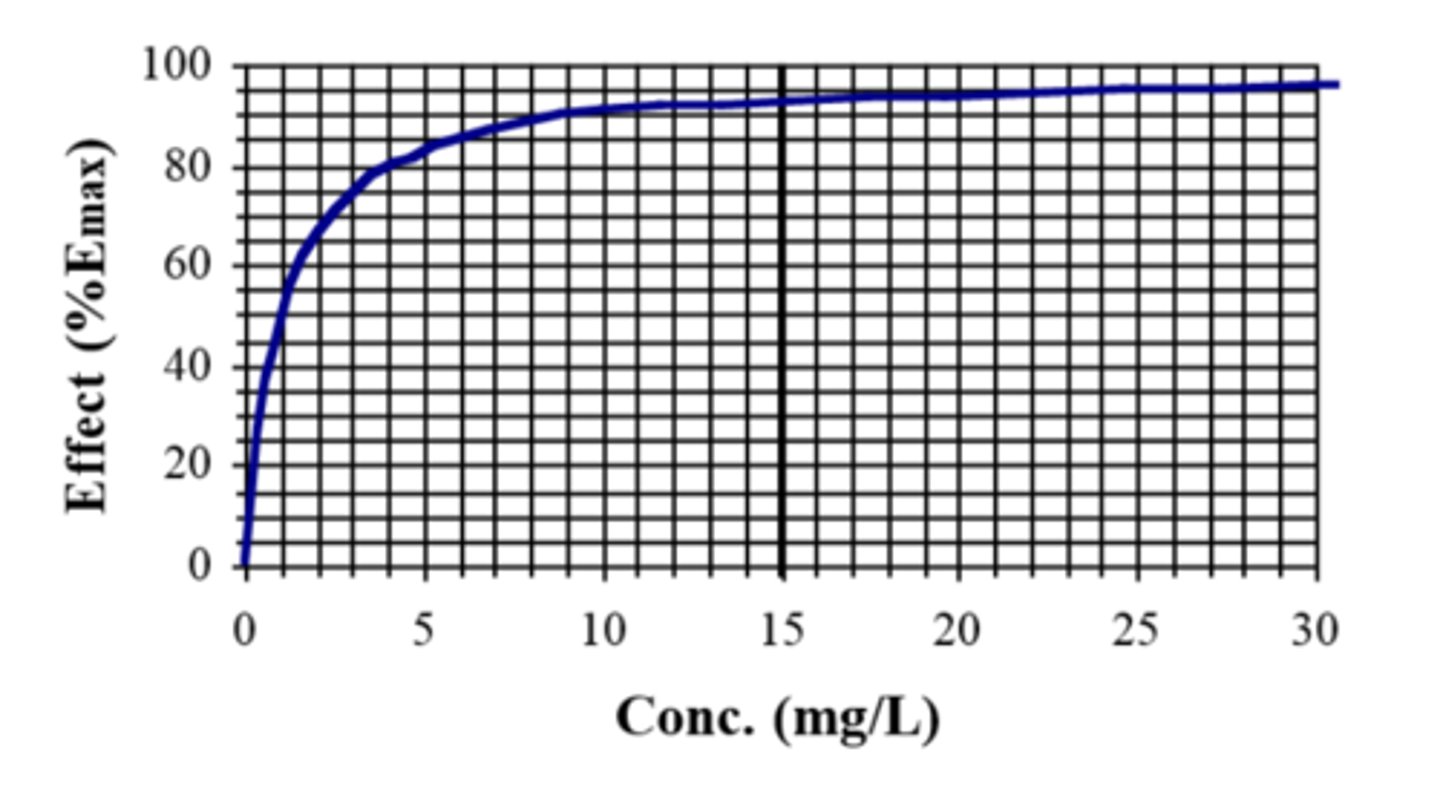
What can you determine Emax from?
the plateau and read EC50 from the concentration that produces half of the effect
- in figure, EC50 is 1 mg/L
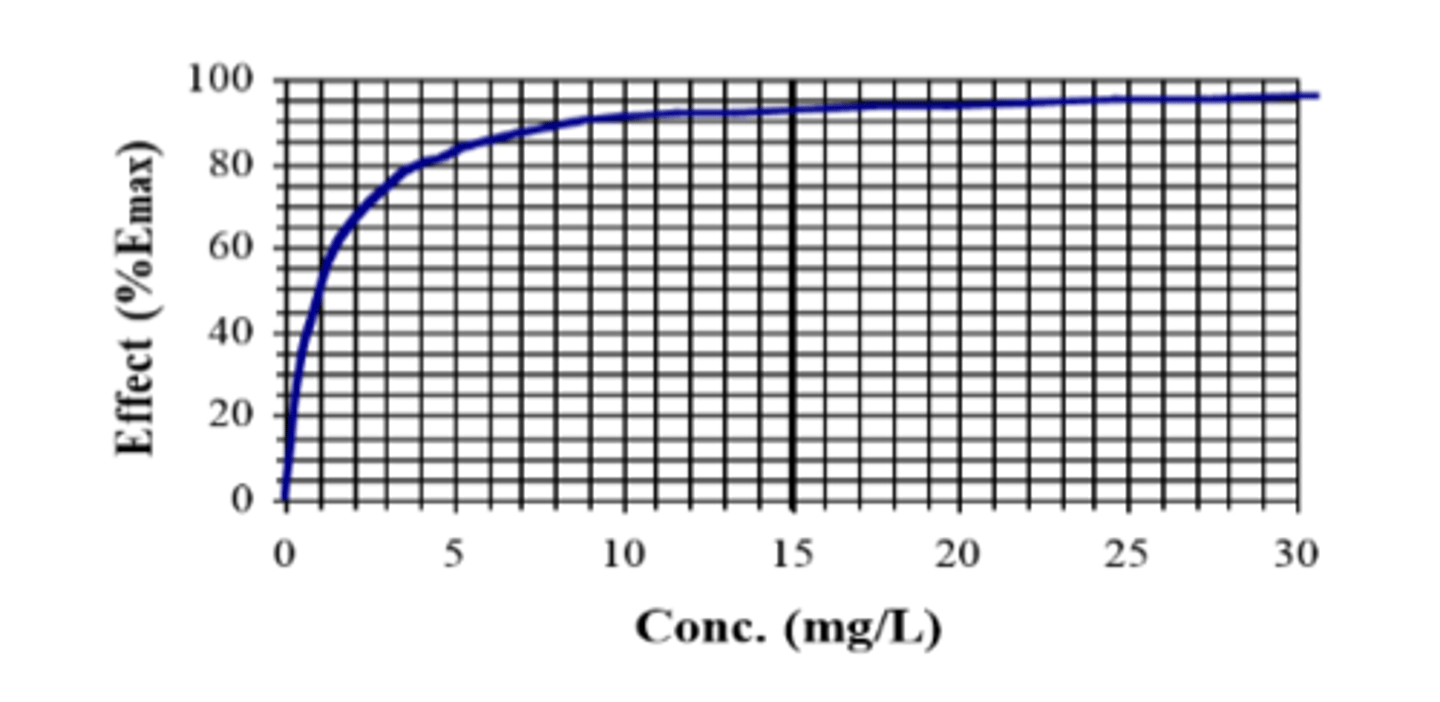
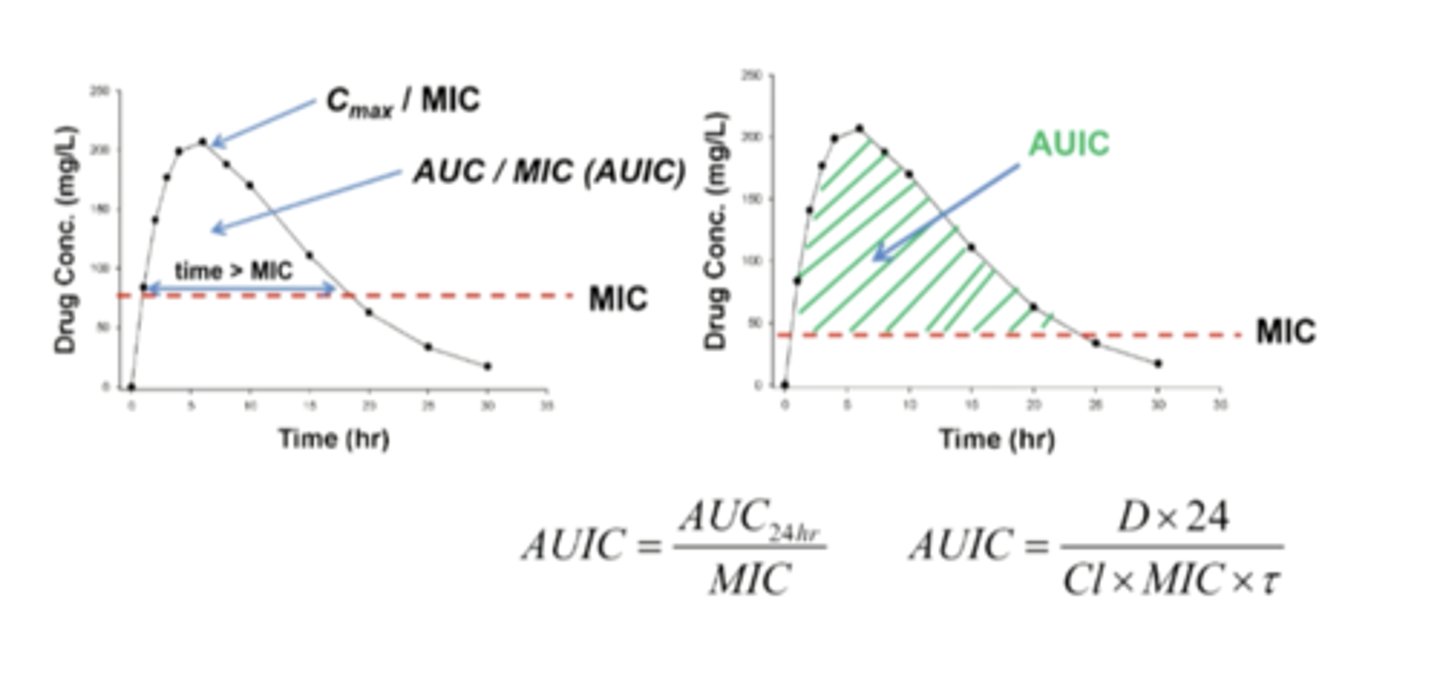
The PK-PD of antibiotics
the relationship of drug concentration in plasma or tissues to the effects on the infectious bacteria
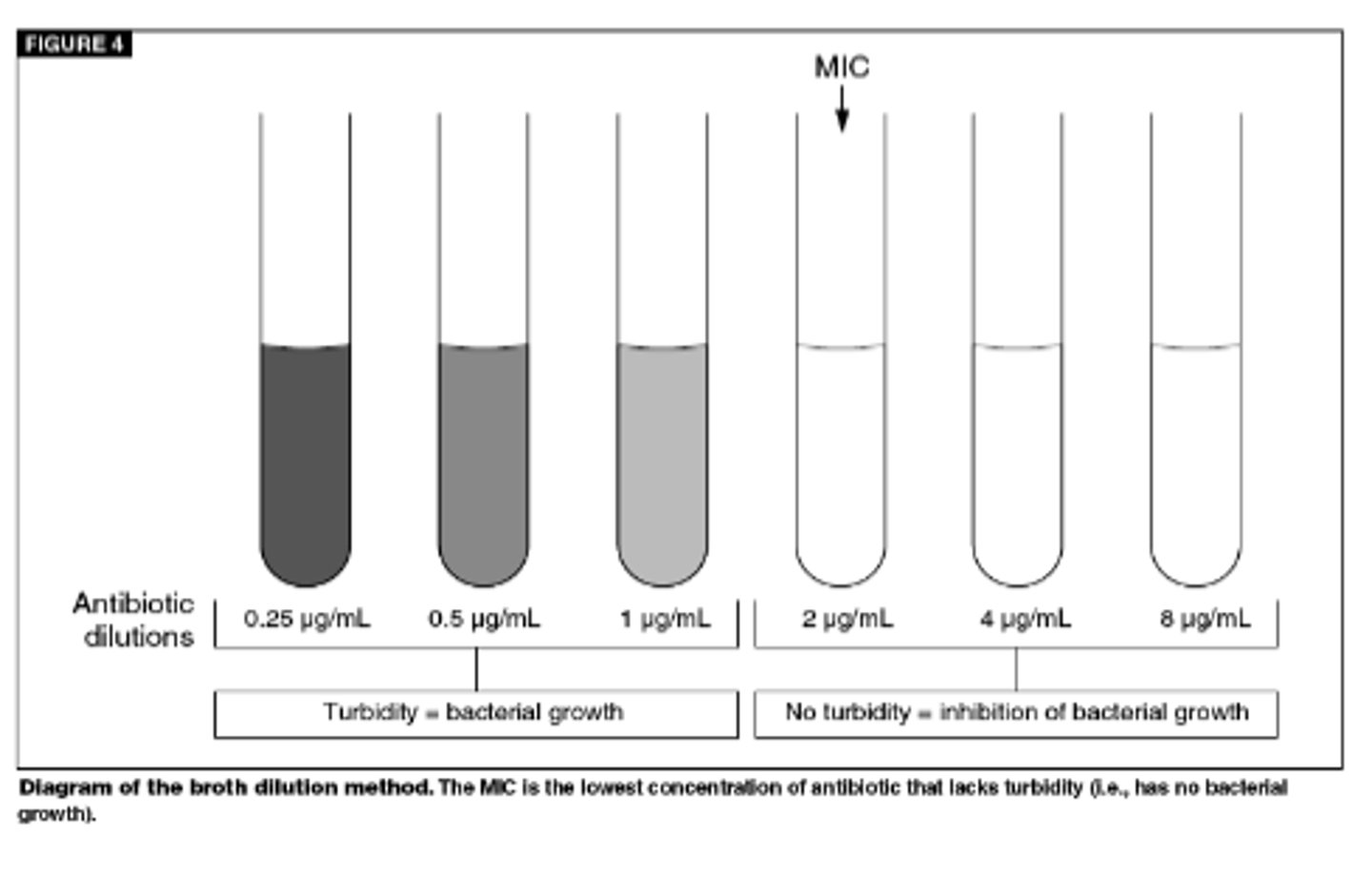
MIC (minimum inhibitory conc.)
minimum plasma drug concentration needed to inhibit bacterial growth
- MIC is a PD parameter of anti-infectives
PK-PD Indices of antibiotics (graph)
AUC is a PK parameter
AUIC is a PD parameter
AUIC formula
AUIC = Dose x 24/Cl x MIC x 𝜏
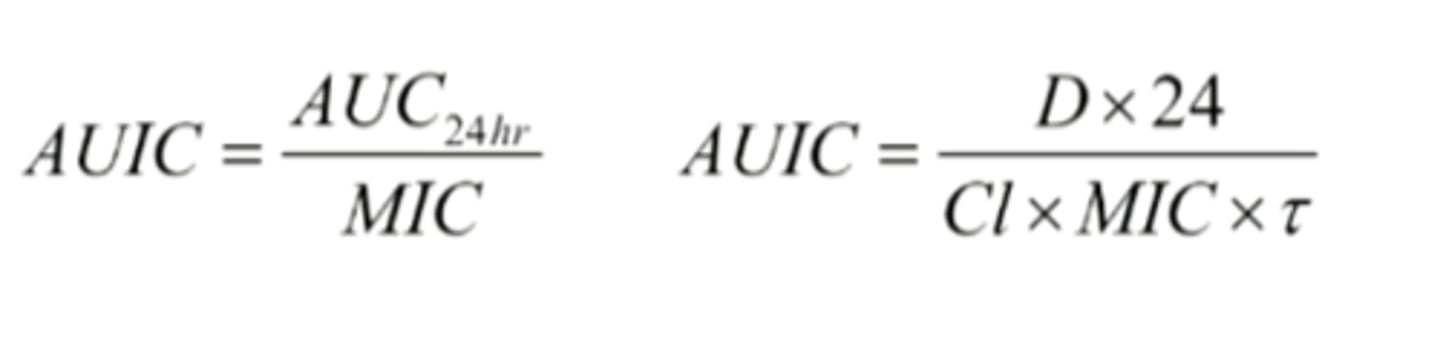
T/F: In the Exmodel, the decline in drug effect can be explained by the fall in plasma concentration
FALSE
cannot be explained
When the drug concentrations are at maximum, the plasma concentrations...
decline to one half after one half-life
The effects may not decline much if the concentrations are...
greater than EC50
Even after one plasma half-life, most the receptors remain.....
occupied because drug concentration is still higher than available receptors
When the effect is between 20% and 80% of Emax, what happens to the effect?
the effect declines over time
When the effect is lower than 20% (C < 0.25 x EC50'), what happens to the effect?
effect declines based on the fall in concentration
T/F: Halving of drug concentration would halve the E when plasma concentration is <0.25 x EC50
TRUE
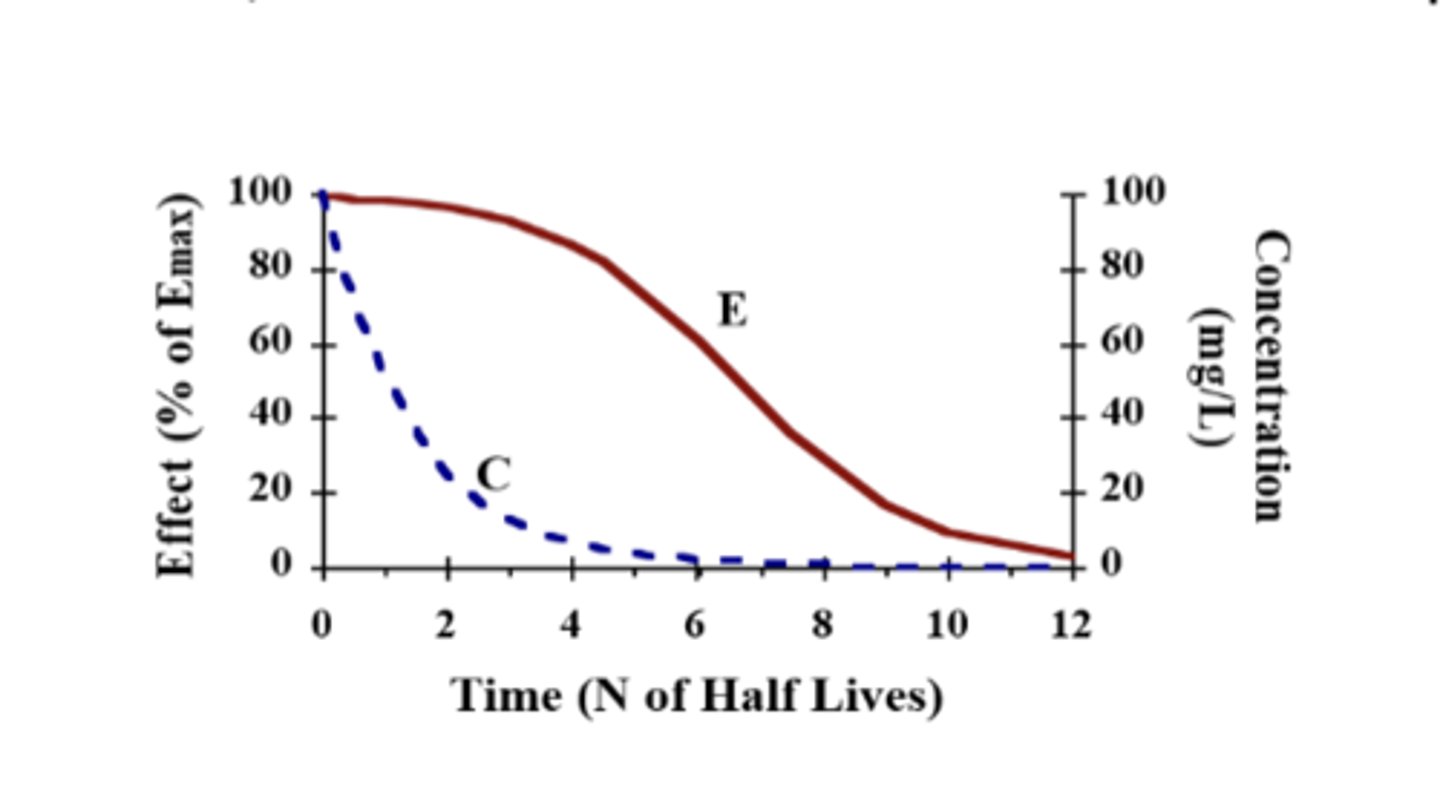
When the effect is less than 20%, what happens to the effect?
the effect half-life is the same as plasma half-life
Why are unlike PD parameters not used that much in clinical practice?
because of lack of PD data in the literature
Recent package inserts of some newer drug contain both ______ and ________ parameters such as the __________ and _________ values
- PK and PD
- Emax and EC50
Where can you find PD parameters?
in some reference book such as PDR
PD parameters can also be used to propose....
individualized dosing