biochem unit 4
1/393
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
394 Terms
what are the mechanisms of catalysis
covalent catalysis
acid base catalysis
low barrier hydrogen bonds
metal ion catalysis
biochemical nucleophile serine
-OH → found in serine proteases (chymotrypsin, trypsin)
cysteine as a biochemical nucleophile
-SH → found in cysteine proteases (cascades, papain)
lysine as a biochemical nucleophile
-NH2 → important in schiff base formation (aldose)
histidine as a biochemical nucleophile
(imidazole group) → can act as a nucleophile and base
water as a biochemical nucleophile
acts as a nucleophile in hydrolysis reactions
in covalent catalysis the enzyme forms a temporary covalent bond with the substrate creating a
reactive intermediate that facilitates the reaction
chymotrypsin
a protease that uses both covalent and acid/base catalysis
covalent catalysis increases the rate of biochemical reactions by
stabilizing high energy intermediates via covalent bonds
chymotrypsin cleaves the carboxyl side of large hydrophobic aromatic amino acids such as
phe, met, tyr and trp
acid-base catalysis
a proton is transferred to catalyze reactions
specific acid base catalysis involves
H+ or OH- that diffuses into the catalytic center
in specific acid base catalysis the rate of the reaction on depends on
the pH of the solution, not the concentration of the buffer
in acid base catalysis the rate of the reactions determined by the concentration of
H+ for acid catalysis and OH for base catalysis
“general” acid base catalysis
acids and bases other weak acids and bases
the rate depends on ph and concentration of buffer
all bronstead acids are h+ donors and bases are h+ acceptors and contribute to the rate
examples of enzymes that employ general acid-base catalysis
serine and aspartic acid proteases
in the active site of serine proteases, the serine residue is usually paired with a _____ to promote nucleophilic attack on the peptide bond
proton withdrawing group (histidine residue)
aspartyl proteases activate a ____ to serve as the nucleophile rather than using a functional group on the enzyme itself
water molecule
lower barrier hydrogen bonds
special type of hydrogen bond where the proton is more equally shared between the donor and the acceptor rather than being strongly associated with one
usually strong and play a critical role in enzyme catalysis by stabilizing transition states
the typical hydrogen bond strength is
10-30kj/mol
as distance between hetero atoms becomes smaller…..
H bonds become stronger
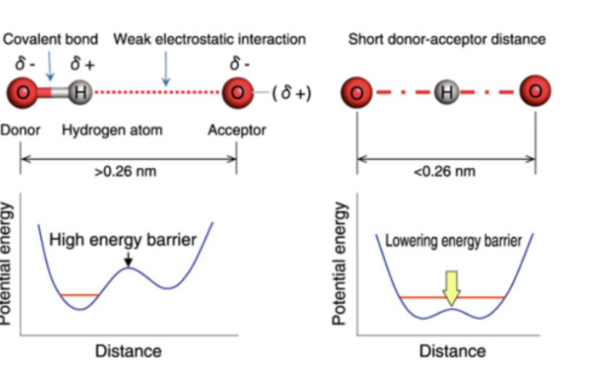
name the type of hydrogen bonds on left and right
left = ordinary
right = low barrier hydrogen bond
describe the differences
Left: the hydrogen atom is between the two donor atoms - LBHB
Right: the H atom is covalently bound - ordinary
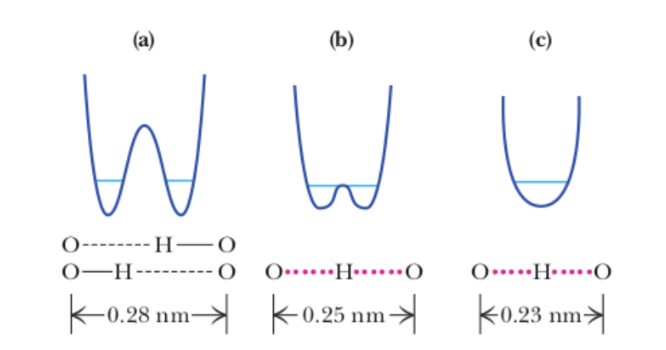
label the types of hydrogen bonds
A= weak
B/C= low barrier
As the distance between the hydrogen bonds gets shorter,,,
the highest bond energy is observed
the steps for low barrier hydrogen bonds
S binds to E via hydrogen bonding
2. hydrogen bond strengthens/shortened and transition state stabilizes
transition state collapses through cleavage or bond formation
LBHB reverts to normal hydrogen bond
common residues for hydrogen bonding
Asp, Glu, His and Tyr
_____ in an enzymes cofactors interact with the substrate stabilizing the transition state and orienting the substrate for reaction
metal ions
mechanistic steps for metal ion catalysis
water activates, substrate binds, transition state is stabilized, leaving group leaves
three ways enzymes are regulated
presence of allosteric regulators or inhibitors
genetic regulation
compartmentation
the adenylyl cyclase reaction
converts ATP to cyclic AMP, a second messenger involved in signal transduction.
driven forward by hydrolysis of pyrophosphate by the enzyme inorganic pyrophosphatase
cAMP
intracellular agent of extracellular hormones
second messanger
hormone binding stimulates GaBy protein binding to GTP triggering its subunit
binding of Ga(GTP) to ______ activates cAMP production
adenylyl cyclase
hormone binding to its receptor leads via _____ activation to cAMP synthesis
G-protein
cyclic AMP- dependent protein kinase is composed of
catalytic and regulatory subunits
Cyclic AMP-depdent protein kinase is a ______ in mammalian cells
170-LD R2C2 tetramer
in cyclic AMP the two regulatory subunits bind ___ equivalents of cAMP each; and then cAMP binding releases the R subunits from the Catalytic subunits
two
in cAMP dependent protein kinase the catalytic subunits are enzymatically active as ___
monomeric forms
genetic regulation of enzyme levels
transcriptional control, gene expression can be upregulated or down regulated in response to needs
example of genetic regulation of enzyme levels
lac operon in prokaryotes
presence of lactose upregulates the expression of lacZ, lacY, lacA
absence of lactose down regulates gene expression
enzyme regulation by compartmentation
enzymes and regulatory molecules are in separate compartments so that opposing pathways are either close together or far apart to increase efficiency
enzymes may also be attached to
cytoskeleton or a membrane
definition of metabolism
the sum of all chemical reactions in living organisms
the two types of metabolism
catabolism and anabolism
catabolism
breaking down molecules to produce cellular energy
anabolism
building biomolecules using cellular energy
glycolysis is catabolic or anabolic
catabolic
glycogenesis catabolic or anabolic
anabolic
phototrophs metabolic pathways
use CO2 or organic matter and light to produce cellular energy
heterotrophs or chemotrophs
use CO2 or organic matter and REDOX active molecules to produce cellular energy
autotrophs vs heterotrophs
autotrophs - use CO2
heterotrophs - use organic carbon
the three stages of catabolism
large biomolecules are broken down into building blocks and then degraded into common product and then simple end products
what are the common degradation products of catabolism
pyruvate and acetyl coa
what comes before the citric acid cycle
acetyl coa
what comes before acetyl coA
pyruvate, fatty acids other than amino acids
what comes after glucose but before pyruvate for polysaccharides
glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate (glycolysis)
end products in catabolism
h2o co2 and ammonia, atp
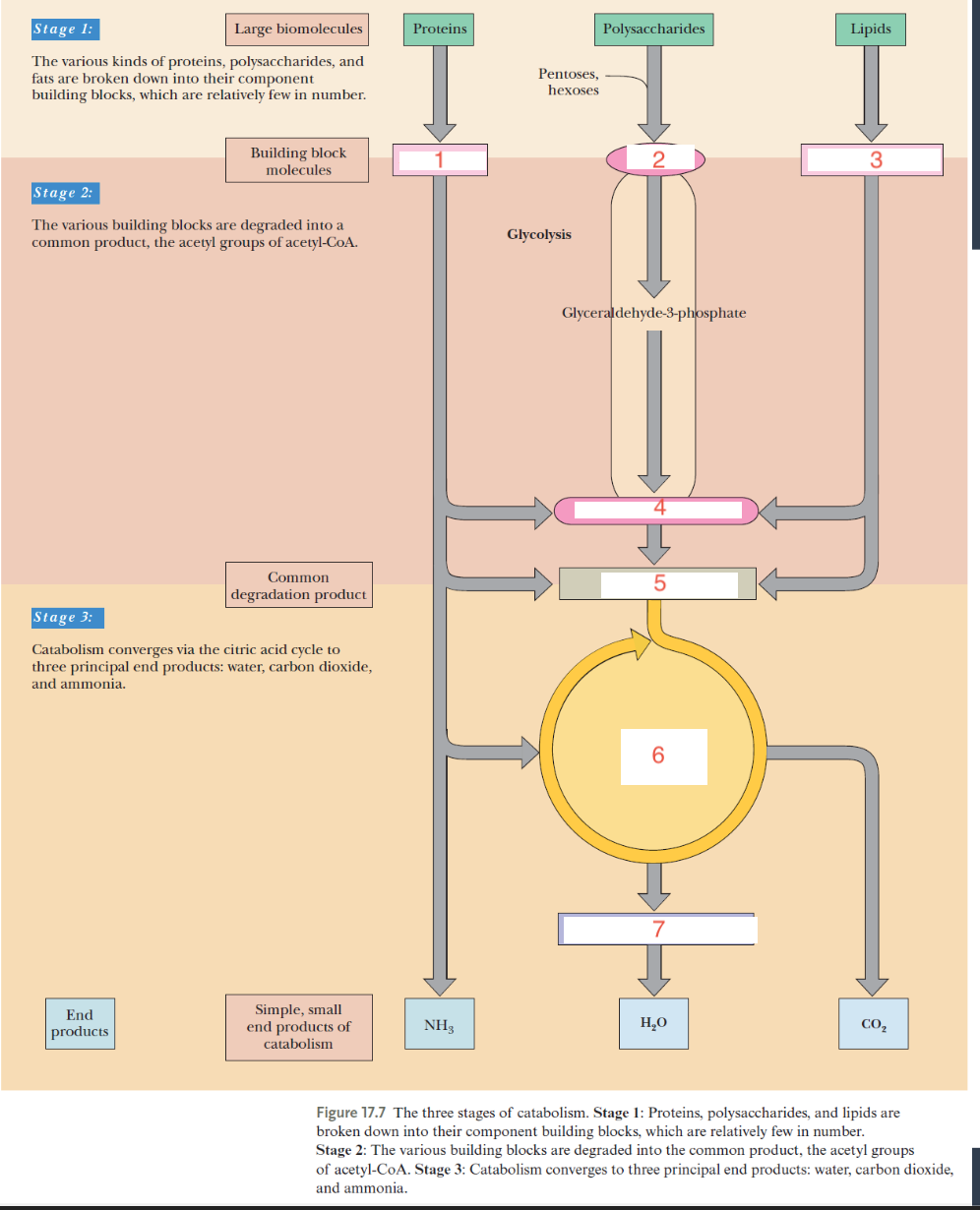
1- amino acids
2- gluose
3-glycerol, fatty acids
4-pyruvate
5-acetyl-coa
6- citric acid cycle
7- oxidative phosphorylation
parallel pathways of catabolism and anabolism must differ in at least _______ so that they can be regulated independently
one metabolic step
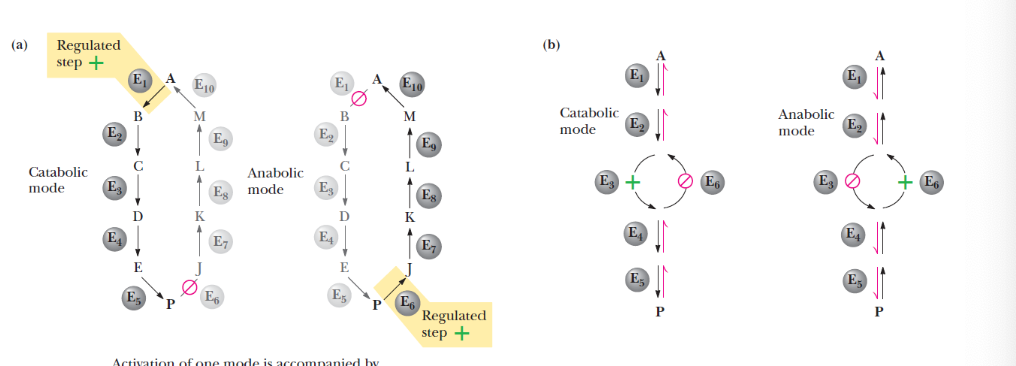
describe this image
in A parallel sequences proceed by independent routes
in B only one reaction has two different enzymes
ATP is considered _____ of the cell
the energy currency
NADH and FADH2 are considered
electron carriers involved in redox reactions
what drives energonic reactions
reaction coupling of ATP
ATP is formed via ____ in photorophic cells
photosynthesis
energy requiring cellular activities are powered by
ATP hydrolysis that liberates ADP and Pi
NADH and FADH2 transfer electrons to the
electron transport chain
_____ collects electrons released in catabolism
NAD+
ATP is formed by _____ in heterotrophic cells
catabolism
hydrogen and electrons released in catabolism are transferred as hydride ions to the _______ nucleotide
pyridine
in catabolism NAD forms NADH+ H+ IN ______ REACTIONS
dehydrogenase
in catabolism NADH passes ____ to other acceptors
H+
the final acceptor of electrons is
O2 and becomes reduced to h2o
the ultimate oxidizing agent
O2
atp hydrolysis is formed by
biosynthesis
osmotic work
cell motility/muscle contraction
_____ is oxidative, _____ is reductive
catabolism, anabolism
____ can be viewed as the carrier of electrons from catabolic reactions to anabolic
NADPH
NADPH can be described also as
reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
biosynthesis usually relies on
reducing equivalents from NADPH
proteins, carbohydrates and lipids are good sources of chemical energy because
their carbon is reduced
the oxidative reactions of catabolism release reducing equivalents from carbohydrates, lipids and proteins often in the form of
hydride ions
chains of -ch2- groups are the most ____ form of reduced carbon
energy rich source of chemical energy.
______ is the final product of catabolism and the most oxidized form of carbon
carbon dioxide
____ is an example of catabolism
glycolysis
the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation take place in
the mitochondria
glycolysis occurs in
the cytosol
glycolysis turns one glucose molecule into
2 pyruvate during cellular respiration.
vitamins defintion
organic micronutrients which are required in small daily amounts
the two major classes of vitamins
water soluble and fat soluble
most vitamins are essential nutrients bc
humans can’t synthesize the basic form
we obtain vitamins in food after digestion and absorption most have to be _____ in our bodies
chemically modified/activated
diseases with vitamins
too little or too much can cause
the active form of many water soluble vitamins are also known as
coenzymes
most of the b complex vitamins are
coenzymes
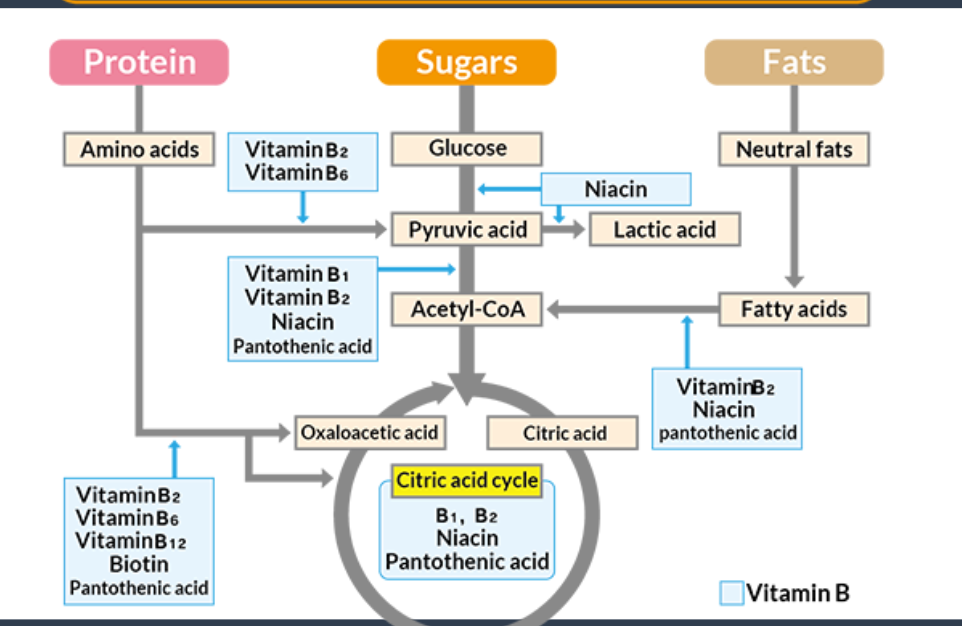
this graph depicts what
the relationship between energy production and the vitamin B complex
vitamin B1
thiamin
the active coenzyme for thiamin is
thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
thiamin pyrophosphate is formed by
the addition of 2 phosphate groups by the enzyme thiamine pyrophosphate transferase
thiamine pyrophosphate contains two ring systems:
a pyrimidine and a thiazole
thiamin functions
TPP is a coenzyme for enzymes that preform decarboxylation and transketolation
transketolation is
the transfer of two carbon units