Bonding
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
Size of ionic substances
All parts of ionic substances have different sizes
Any atom containing Nh4
HAS A COORDINATE BOND ALREADY
CO2 and SO4 are have double bonds
How many bonding pair and lone pairs do noble gases have
Bonding pairs-4
2-lone pairs
Electronegativity
Relative ability of an atom to attract the pair of electrons to a covalent bond
Why is a C-Cl bond polar
Chlorine has a higher electronegativity than carbon
Why is a CCl4 molecule non polar
Symmettrical value determined from its bond angle
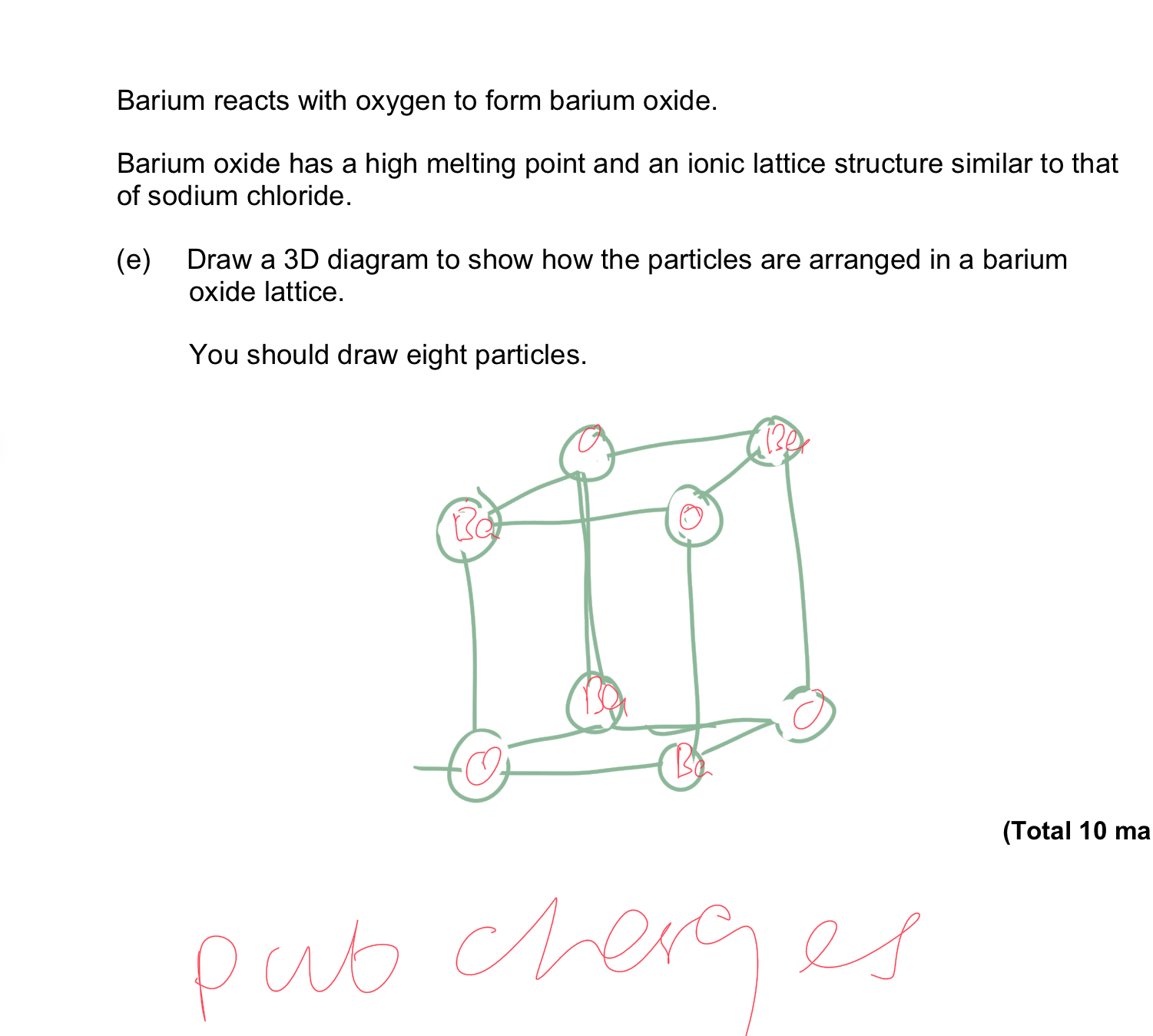
Draw a 3D diagram of barium oxide
Explain a 90 degree bond angle
All bond angels repel equally
Explain a 107 degree bond angle
Lone pair bond pair repulsion is greater than bond pair bond pair so bond angle reduced
Explain a 109.5 degree bond angle
Lone pair lone pair repel more than bond pair bond pair
So lp is far apart as possible
Which is more electronegative
O
N
O
Do inorganic ionic compounds always form giant structures
Yes
In what substances do covalent bonds break when it melts
Giant covalent structures
Silicon dioxide is an example of a giant covalent structure
What is the crystal structure of ionic substances
Simple molecular
Which molecule is the most polar?
Bromoethane
Dibromoethane
Tribromoethane
Tetrabromoethane
Tetrabromoethane
How does electronegativity change across a period
Increases across a period
CH4 -can it form a covalent bond
Can’t form a covalent bond
8 electrons around it no spaces available go to take lone pairs or give
Draw structural formula of it to determine this
Number of sticks multiplied by 2 is the number of electrons there are
Can BH3 form coordinate bond and how
Yes
No lone pairs
6 electrons only so can take 2
Can CH4 form coordinate bonds?
8e-
No space for e- to come
No lone pairs can come
Can’t form a coordinate bond
Can NH3 form a coordinate bond?
Yes
8 electrons
Can give 2 electrons as a lone pair
Can H2O form a coordinate bond
4e-
2 lone pairs of electrons
Can give electrons away
When can you not transfer lone electrons to something
When it already has a pair of lone electrons
What does the group number show about bonds
The group number is the number of valence electrons and how many bonds something can make
Which substance does not have any bond angles of 120
Graphite
Benzene
Cyclohexane
Boron trifluoride
Cyclohexane
Benzene does have 120
How do you know if an element can accept an electron pair in a dative coordinate bond
It only has 6 electrons in its outer shell
This could be as a compound or element so it has a space fr another 2
What reaction can a result in an overall change in shape around a carbon atom
oxidation of propanol with acidifies potassium dichromate
Polymerisation of tetrafluoethene
Reaction of bromoethane with an excess of concentrates ammonia
Reaction of methane with an excess of chlorine in ultraviolet radiation
Polymerisation of tetrafluoethene
Which substance has more electrons delocalisation
Graphite
Iodine
Graphite
1 delocalised electron per 3 carbon atoms bonded
What forces or bonds are broken when water is vaporised
Intermolecular forces are overcome
What is not responsible fro conducting electricity
Lone pair of electrons.
Which substance has no delocalised electrons
Methylbenzene
Polypropene
Polypropene doesnt’ have any delocalised electrons 3
Long chain of atoms
Which pair of reagents reacts to form a tetrahedral complex

How do you know if a compound will form a dative covalent bond
The main atom will need two more electrons as it will only have 6 electrons already
What factors affect metallic bonding
Number of valence electrons
Ionic charge
Atom size
How does the number of valence electrons affect the strength of a metallic bond
The more valence electrons there are then stronger the metallic bond
Which element has the lowest melting point
Sodium
Magnesium and potassium both have more electrons in the outer shell so stronger metallic bond high melting point
Sodium has less electrons in its shells so smaller atomic radius and greater attraction to electrons so harder to overcome needing more energy and a higher melting point
How are ionic compounds formed
Transfer of electrons from a metal to a non metal
Metal atoms …….electrons to become positive ions
Lose
Non metal atoms …… electrons to become negative
Gain
Positive Ions are called
Cations
Negative ions are called
Anions
Ionic bond
Electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely charged ions
What shape do ionic solids take
Ionic lattice structure
Lattice
Regular repeated three dimensional framework of atoms molecules or crystalline structure
What is the configuration of the ionic lattice of NaCl
6.6 configuration
Forms
What causes the crystalline nature of ionic compounds
Regular pattern of ions
Relationship between the size of the ions and the charge and strength of the ionic bond
Smaller the ions
Higher charge on ions
Stronger the ionic bond
Positive Ions are generally ….than the atoms from which they are formed
Smaller
Negative ions are generally …….than the parent atom
Larger
Why are positive ions smaller than the atoms they are made of
Metal atoms lose electrons from outer energy level so ion has an electron configuration with one less energy level occupied
Nuclear charge increases so electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus
Thus smaller atomic radius
Why are negative ions larger than the parent atom
Repulsion between electrons moves them further apart from each other
Nuclear charge decreases as there are more electrons with the same number of protons
Properties of ionic compounds
Lattice structure
Conduct as molten or aqueous
high melting and boiling point or solid at room temperature
Formula for surfate ion
SO4 ²-
Formula for nitrate ion
NO3^-
Formula of hydroxide ion
OH^-
Formula of carbonate ions
CO3²-
Formula of hydrogen carbonate ion
HCO3^-
Formula of ammonium ion
NH4^+
Covalent bond
One or more shared pair of electrons
Where are covalent bonds found
Molecular elements
Macromolecular elements
Molecular ions
In what do covalent bonds form
Non metals only
Boron trifluoride how does it form its covalent bonds-diagram

How does beryllium chloride from covalent bonds

How does methane form covalent bonds

How does ammonia form covalent bonds diagram

How does water form covalent bonds

How does sulfur hexafluoride

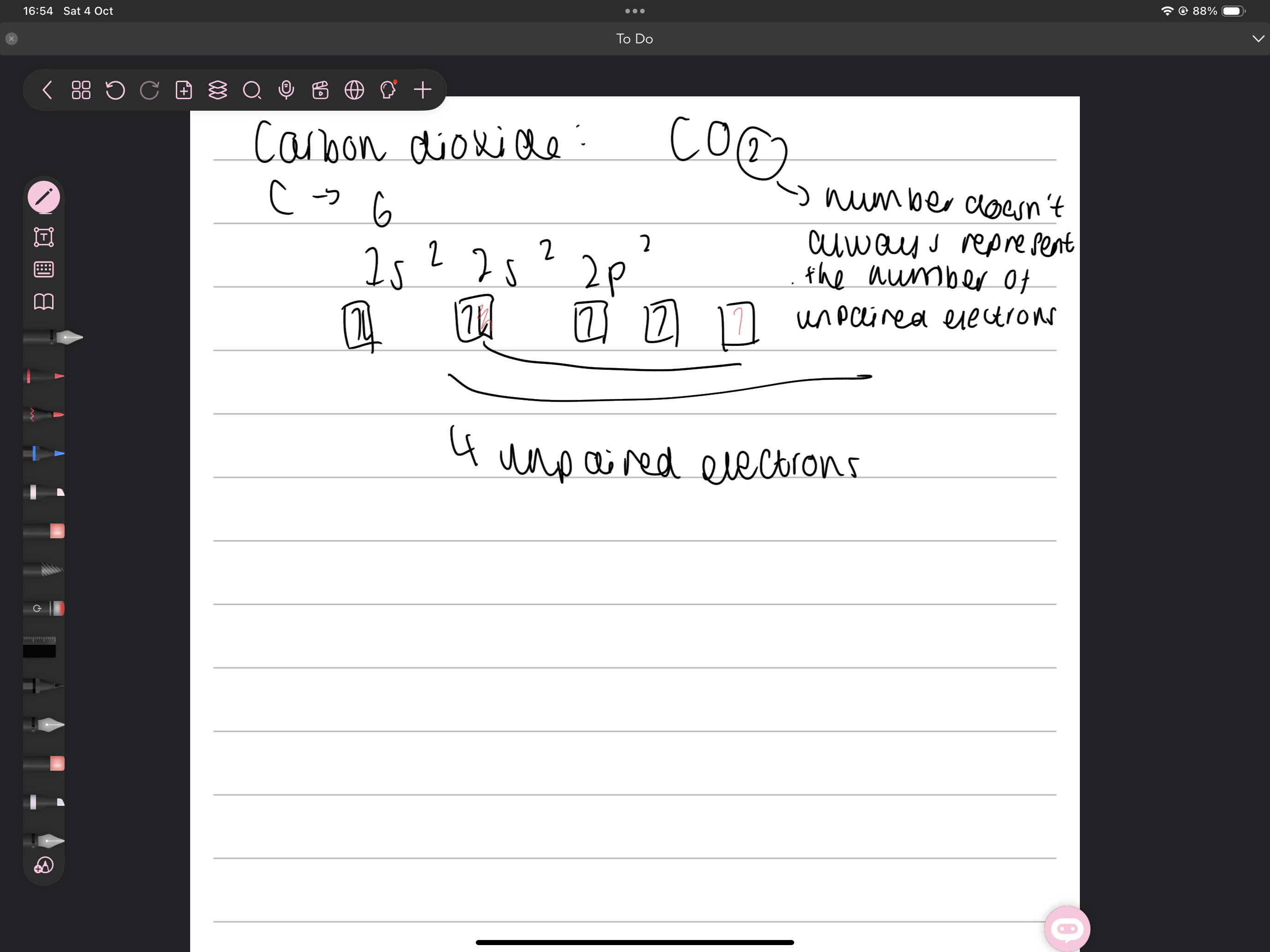
How does carbon dioxide form covalent bonds
Coordinate bond
Shared pair of electrons with both electrons supplied by one atom
Example of a coordinate bond
NH4^+
What colour are the fumes of ammonium chloride
White fumes
What does hydrochloride acid and ammonia solution react to give
Ammonium chloride
Formula for hydronium ion
H3O^+
What determines how many lone pair of electrons there are
The amount of empty orbital there are after having covalently bonded to something before
Arrangement of particles in a solid
Close together regular arrangement
Metallic structure of metals explain
Positive metal ions in a sea of delocalised electrons
Metallic bond
Electrostatic force of attraction between delocalised electrons and the positive metal ions in a lattice
Properties of metals
Conduct electricity
Conduct heat
Ductile and malleable
Hugh densities
High melting points s
Why can metals conduct electricity
Delocalised electrons move through the structure and carry charge
How can metals conduct heat
Delocalised electrons enable heat energy to be passed through the metal
Why are metals ductile and malleable
Layers can slide over each other without disrupting bonding
Why do metals have high densities
Positive ions are packed tightly together so density is high
Why does the melting point increase in some elements
Attraction between smaller positive ions and the negative delocalised electrons is greater
Name the two main types of covalent substances
Molecular -simple covalent
Macromolecular -giant covalent
How do you know if a substance is simple molecular
Exist as single molecules-can’t become anything else with themselves only
Name some simple molecular substances
Iodine
Ice
How does iodine form a crystalline structure
Large iodine molecules pack together into a regular arrangement
How does ice from a crystalline structure
Molecules of water arranged in a regular arrangement
Properties of molecular covalent crystals
low melting points
Brittle
Don’t conduct electricity
Why are molecular covalent crystals brittle
Don’t have strong bonds holding them together
Why can’t molecular covalent crystals conduct electricity
No charged particles to carry charge through the structure
What type of substances can form Macromolecular structures
Non metallic elements and compounds
Allotropes of carbon name
That u need to know
Graphite
Diamond
Properties of diamond
Hardest
High melting point
Doesn’t conduct heat or electricity
Why does diamond have a high melting point
Strong covalent bonds that require lots of energy to overcome
Why does diamond not conduct heat or electricity
No delocalised electrons that can move through the structure
Why is diamond hard
Each carbon is bonded to 4 others in a tetrahedral arrangement
Use of diamond
Cutting tools
Graphite properties
Conducts electricity
High melting point
Slippery
Why can graphite conduct electricity
One delocalised electron per carbon atom that can move through the structure and conduct electricity