Chemistry 1.3 Water
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What are four harmful substances found in ‘natural’ water supplies?
Microorganisms, ions, dissolved gases, and pollutants
Why are microorganisms in ‘natural’ water supplies treated? How are they treated?
Many of the bacteria and microorganisms cause disease, so they must be treated - most commonly chlorine is used to kill the microorganisms.
How do ions end up in ‘natural’ water supplies?
Water dissolves ions from rocks and other materials as it flows within rivers to reach lakes. Although a small amount of dissolved ions is important, too much is dangerous for your health.
What are the dissolved gases in ‘natural’ water supplies?
Oxygen and carbon dioxide, a byproduct of respiration from the microorganisms living in the water - essential for photosynthesis in aquatic plants. Other gases from the atmosphere can dissolve into natural water.
Which dangerous pollutants can dissolve into ‘natural’ water supplies?
Pesticides, herbicides, and chemical fertilisers - in high concentrations, these can affect health.
How do you maintain a sustainable water supply?
Reduce water consumption, reduce environmental impacts of abstracting water, distribute and treat water efficiently.
Give examples of how we can reduce water consumption
Take short showers instead of baths Turn off taps when they’re not being used Install a short flush button on toilets Use leftover bath water for things like watering the plants Eat less meat Put on full washing machine loads Use dishwashers instead of washing by hand Buy less cotton clothes - it takes 10,000 litres to make a single pair of cotton jeans!
Give examples of water abstraction
Desalination of seawater Building dams and reservoirs Collecting from surface sources such as rivers, lakes, and streams Collecting rainwater Accessing underground sources
What are the 3 main steps for treatment of water?
Sedimentation, Filtration, Chlorination
What is sedimentation?
Water is added to a large tank. This stops it from flowing, allowing large insoluble particles to sink to the bottom of the tank.
What is filtration?
Water is flowed through beds of sand and gravel of different sizes, which removes small insoluble particles.
What is chlorination?
Chlorine gas is bubbled through the water to kill the bacteria and other microorganisms.
What is water fluoridation?
The process where fluoride is added to water.
What are the advantages of fluoridation?
Strengthens the enamel of teeth which prevents tooth decay and cavities Protects teeth by demineralisation
What are the disadvantages of water fluoridation?
It is a form of mass medication as people do not have a say in how much fluoride is in their water If children are exposed to too much fluoride they can develop fluorosis People can make a choice themselves about fluoride by using a toothpaste that contains it Links have been made between fluoride and thyroid problems, neurological disorders, and some cancers - although evidence is not concrete
What is desalination and what are the two main methods?
Desalination is the removal of salt from seawater. Distillation and reverse osmosis
What are the advantages of desalination?
Useful water to supply to countries with low rainfall and lots of coastlines Water produced is of a higher quality than the required standards of potable water Using water from the ocean can help protect habitats for animals in natural sources such as rivers or lakes
What are the disadvantages of desalination?
Requires a lot more energy than typical water treatment processes More expensive so harder for poorer countries to afford Increases GHG emissions as more fuel is required in desalination Desalination plants are often far from where the water is needed, so lots of piping must be installed Building of desalination plants is an expensive and high-energy process
What is the process of distillation?
The seawater is heated, causing pure water to evaporate The water vapour is collected and cooled, causing it to condense back into a liquid, giving distilled water The leftover salt may be used for various purposes
What is a miscible liquid and how is it distilled?
A miscible liquid is where one liquid completely dissolves into another liquid solution. You must heat liquids to various temperatures to individually evaporate and condense them.
What is solubility?
A substance (called the solute) is described as soluble if it will dissolve in another substance, known as a solvent.
How is solubility measured?
In terms of the maximum mass of solute (in grams) that will dissolve in a given volume of solvent.
What is the method of determining solubility?
Gradually add the solute to a known volume of solvent so it dissolves Add solute until no more solute dissolves Filter the undissolved solute and discard it Heat the leftover solution to evaporate the solvent, leaving the solute that had dissolved Weigh the remaining solute and calculate the mass of solute that was dissolved
What is a solubility curve?
A solubility curve shows the variation of how solubility changes with temperature - generally, solubility increases as temperature increases.
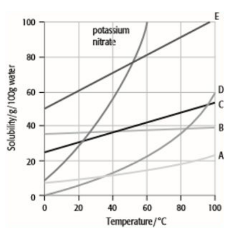
What causes hardness in water?
Hardness in water is caused by dissolved calcium and, to a lesser extent, magnesium.
What do hard water and soap form?
They form scum, as it is difficult to form a lather with hard water.
What do soft water and soap form?
They readily form a lather.
What is temporary hardness in water?
Caused by dissolved calcium hydrogencarbonate The hardness can be removed by boiling the water and thermal decomposition occurs
What is permanent hardness in water?
Caused by dissolved calcium sulphate This hardness cannot be removed by boiling the water
What are the processes to soften water?
There are three: Distillation Adding sodium carbonate Using an ion exchange column
What are the advantages of using distillation to soften water?
Removes both temporary and permanent hardness.
What are the disadvantages of using distillation to soften water?
High energy process and therefore high cost.
What are the advantages of using sodium carbonate to soften water?
Cheap and easy. Removes both temporary and permanent hardness.
What are the disadvantages of using sodium carbonate to soften water?
The calcium carbonate (limescale) builds up and can block pipes.
What are the advantages of using an ion exchange column to soften water?
Removes both temporary and permanent hardness.
What are the disadvantages of using an ion exchange column?
The column is expensive. The column becomes saturated and less efficient.
How does using distillation to soften water work?
The hard water is heated so the water evaporates. The water then condenses and is collected, leaving behind the ions that made it hard.
How does an ion exchange column work?
A column is packed with resin which contains sodium ions. As hard water flows through the column, Mg2+ and Ca2+ are exchanged for Na+ ions, removing the magnesium and calcium ions, leaving the water soft.
How does adding sodium carbonate make water soft?
The carbonate ions in Na2CO3 react with the calcium ions in the water to form solid calcium carbonate.
What are the advantages of hard water?
Contains calcium and magnesium, which are good for bones and teeth. The minerals can provide a better taste for some people. Hard water can reduce the risk of certain heart diseases./