CVA: CIRCULATION
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Is the lymphatic system pumped by the heart?
No
What else does fluid mvmt also regulate?
Temp and pressure
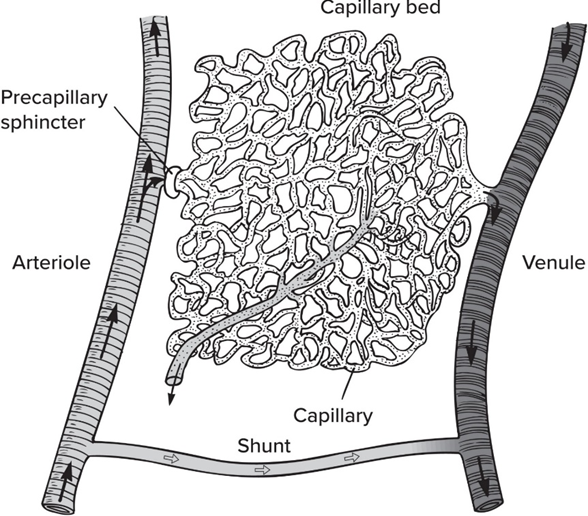
Arteries
Carries blood AWAY from heart
MOST carry O2-rich blood
Elasticity > veins
Start off big then thins out
Arterioles
v small arteries
Viens
Carries blood towards heart
MOSTLY carries O2-poor blood
1-way valves control flow
Start off small then thickens as you approach the heart
Venules
v small veins
Capillaries
tiny ass vessels b/w arteries and veins; sites of exchange
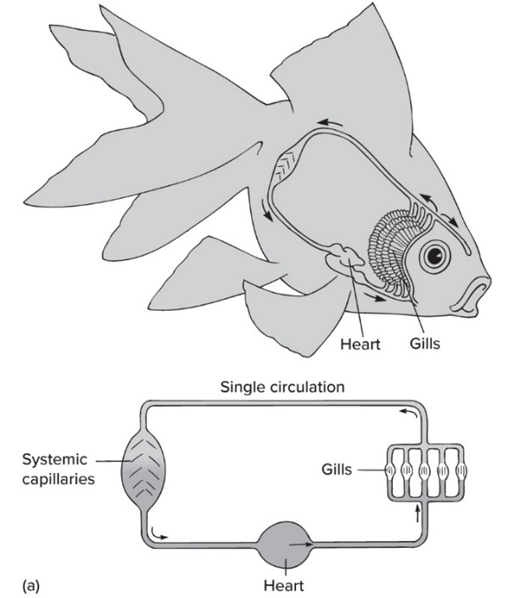
1x Circuit
Once through heart per circuit (most fishes)
(Heart→gills→systemic→Heart)
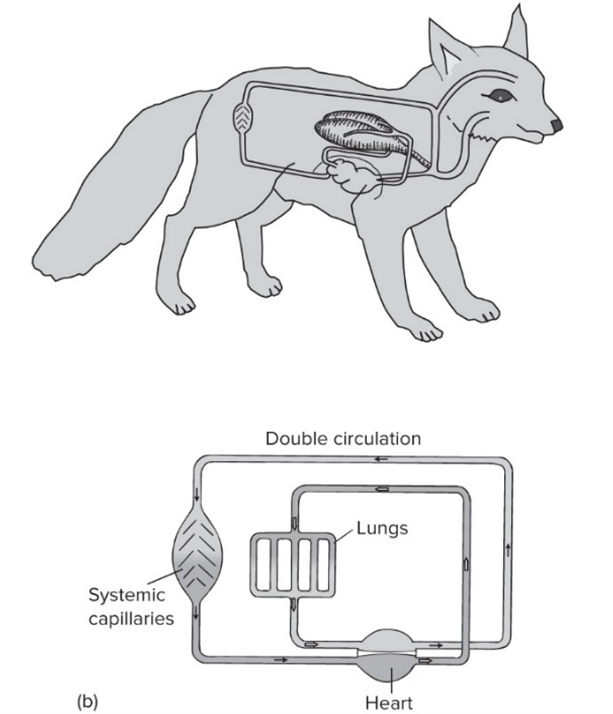
2x Circuit
twice through heart per circuit (amniotes)
Includes pulmonary circuit to oxygenate blood before systemic circuit
Lungfishes, amphibians, and some reptiles have
intermedite-type systems
Aortic arches
paired arteries immediately after heart (and ventral aorta)
Aortic arches are numbered I to IV based on embryo with 6 arches, but Arch I is almost always
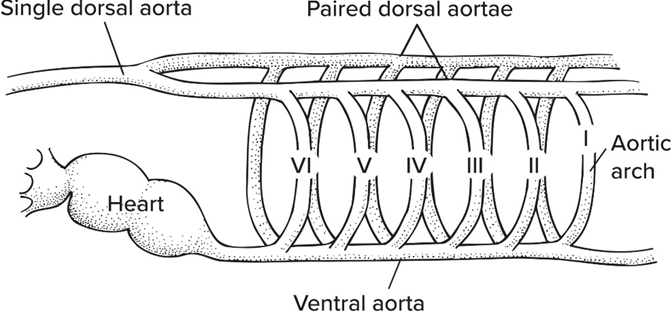
lost
Afferent branchial arteries
enter gills
Efferent branchial arteries
exit gills
W/in sharks, the 1st arch is reduced to
spiracle
Arch II supplies
internal carotid (to brain)
Arch II-VI supplies
the rest of the body
Arch I and II are lost in
amphibians
Salamanders
Arches III-V carry external gills
Arch VI forms pulmonary artery (to lungs) (except in neotenic taxa like Necturus)
III and IV: form common carotid artery (to head)
Frogs
III-VI form gills in larvae; gills lost along with all of V
III: head
IV: body
VI: pulmonary circuit
Arches tend to become asymmetric in
amniotes
Vertebrate hearts probably originated as contractile blood vessel as in
lacelets
What’s the valve(s) between the Atrium and Ventricle?
Atrioventricular valve(s)
The 4 seried chambers of the heart:
Sinus venosus → Atrium → Bulbus cordis (embryo) or conus arteriosus or bulbus arterious (adults)
What do valves create?
1 way flow; permit aspiration filling of chambers
Hagfish hearts are
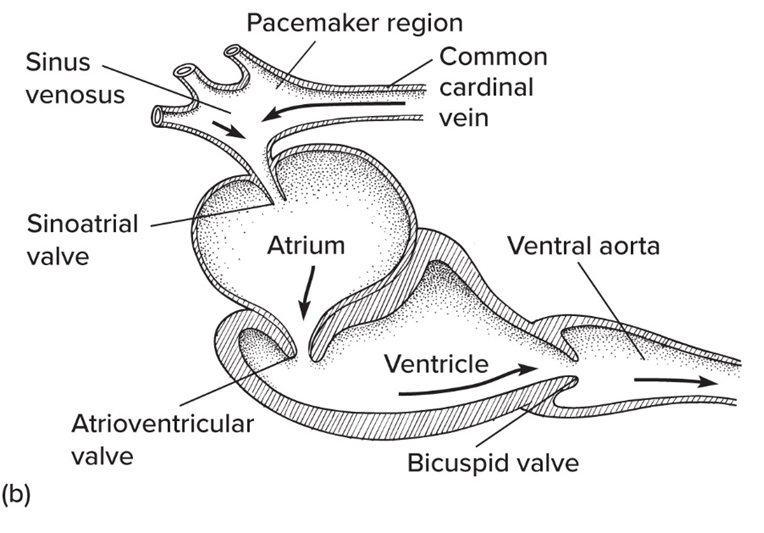
3 chambers (no bulbus/ conus arteriousus) and are not controlled by nerovous impulse
Lampreys hearts are
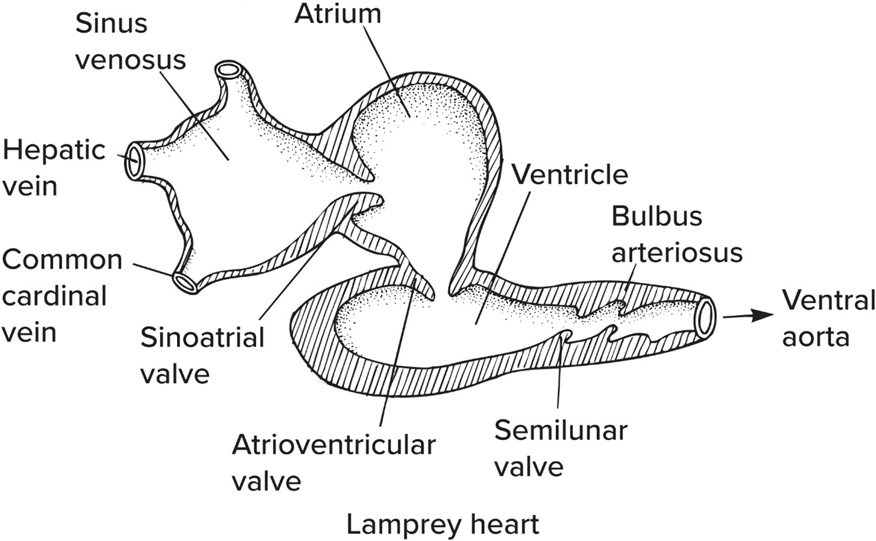
innervated with a basic 4 chamber plan that includes the bulbus arteiousus
Chondrichthyes' hearts are
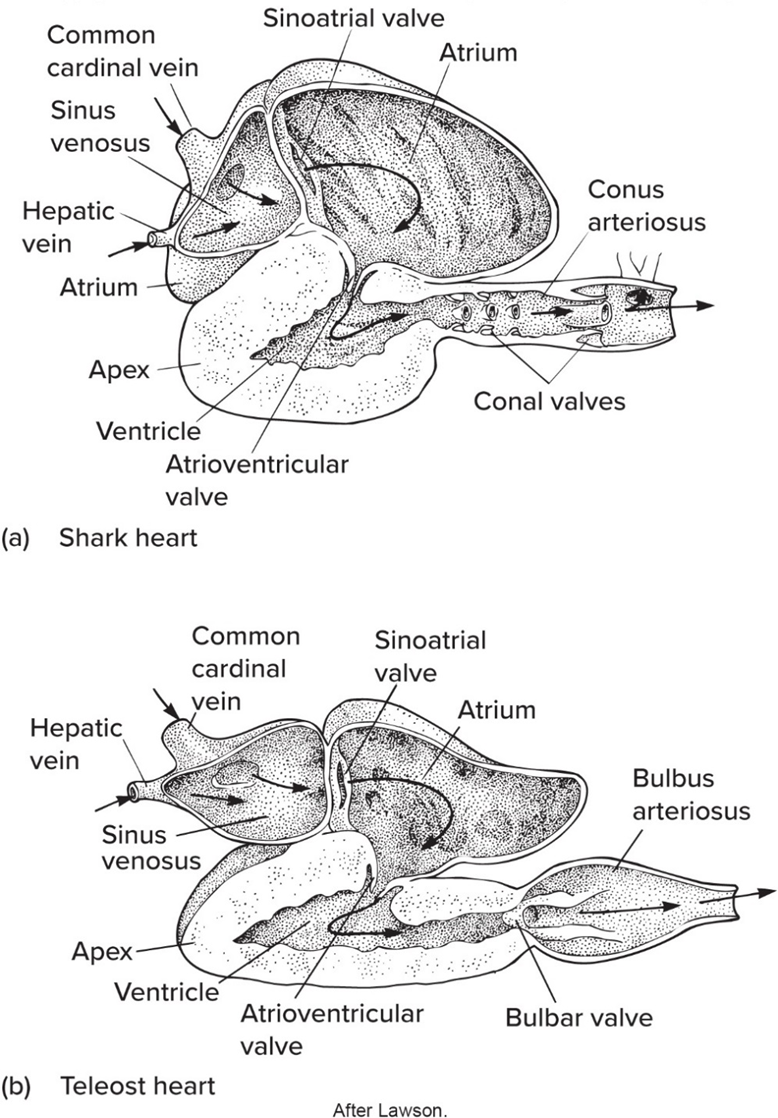
4 chamber plan incl. conus arteriosus (muscular)
Osteichthyes hearts are
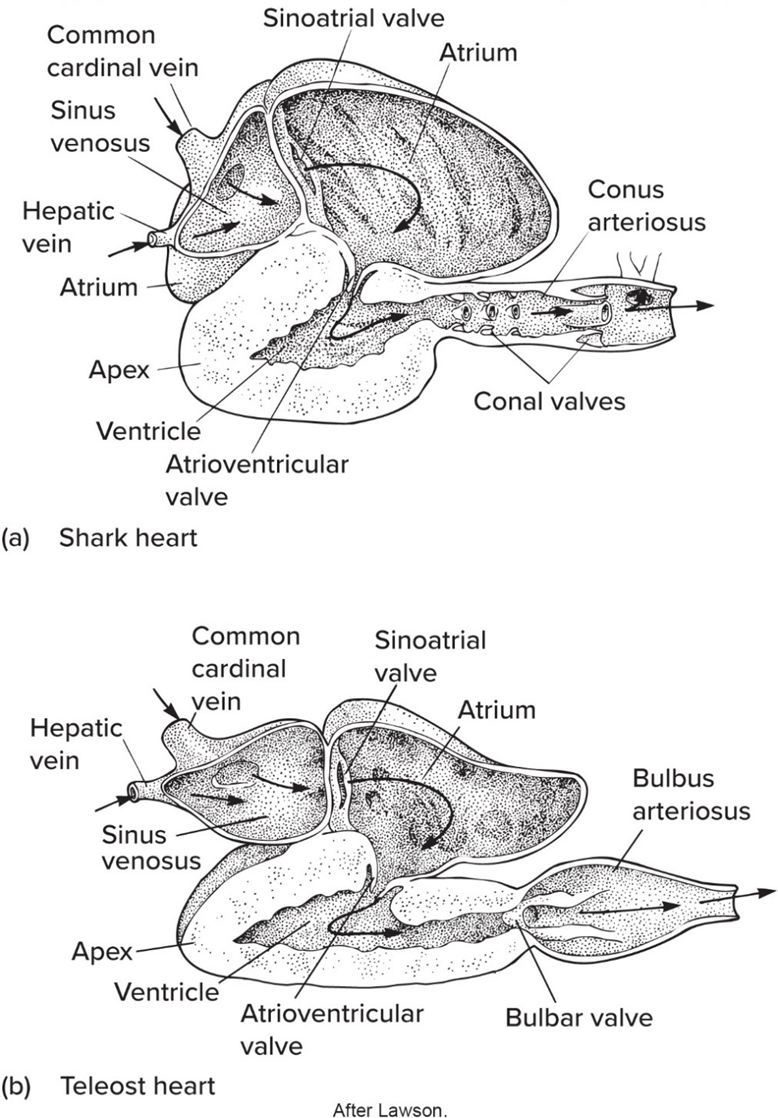
4 chamber plan + bulbus arteriosus (nonmuscular)
Lungfish hearts have
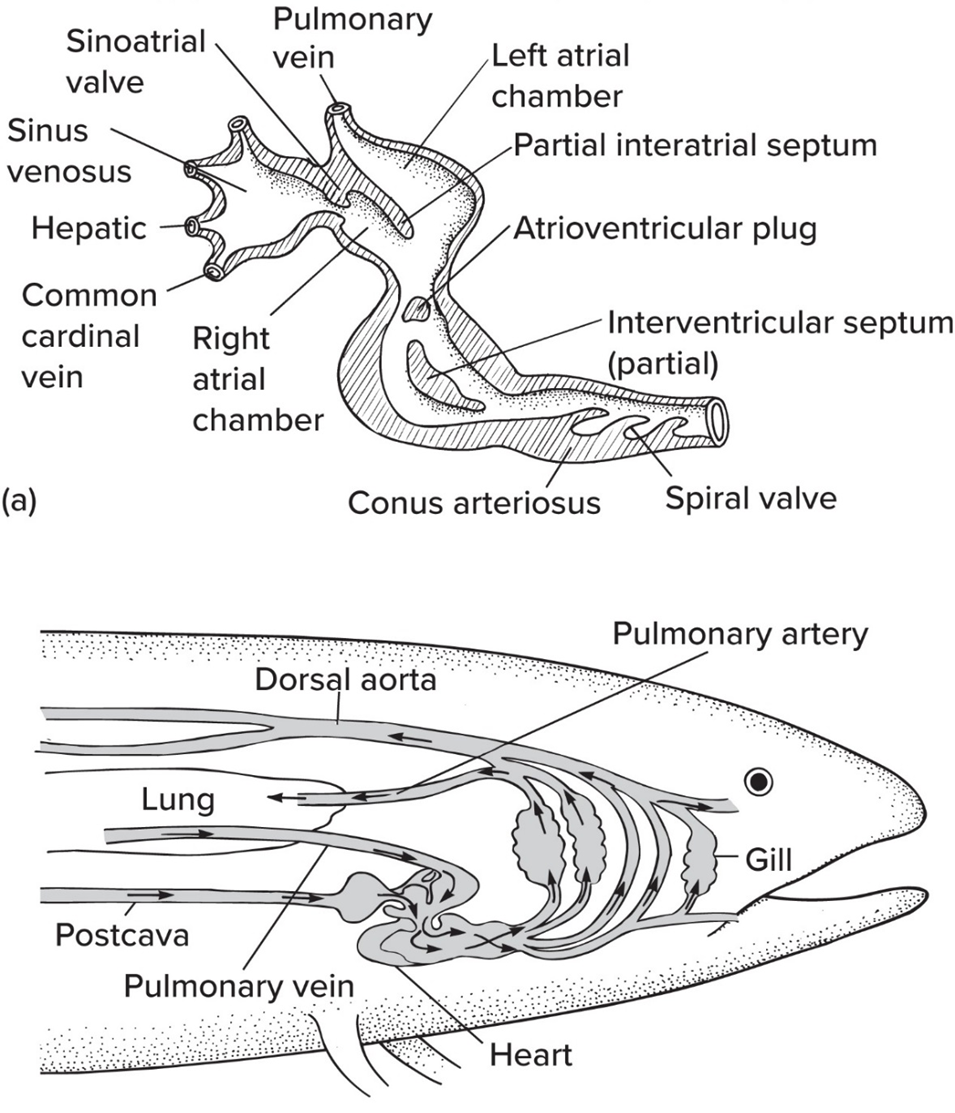
Interatrial and interventricular septum, which partially divide chambers and permits partial separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
When breathing air, left side carries
MORE O2
When breathing air, right side carries
LESS O2
Spiral valve
helps separate O2-rich and O2-poor
MOST amphibian hearts are
3 chambered (2 atria, 1 ventricle)
Amphibians w lungs have
interatrial septum
Amphibian hearts separate O2-rich vs O2-poor via
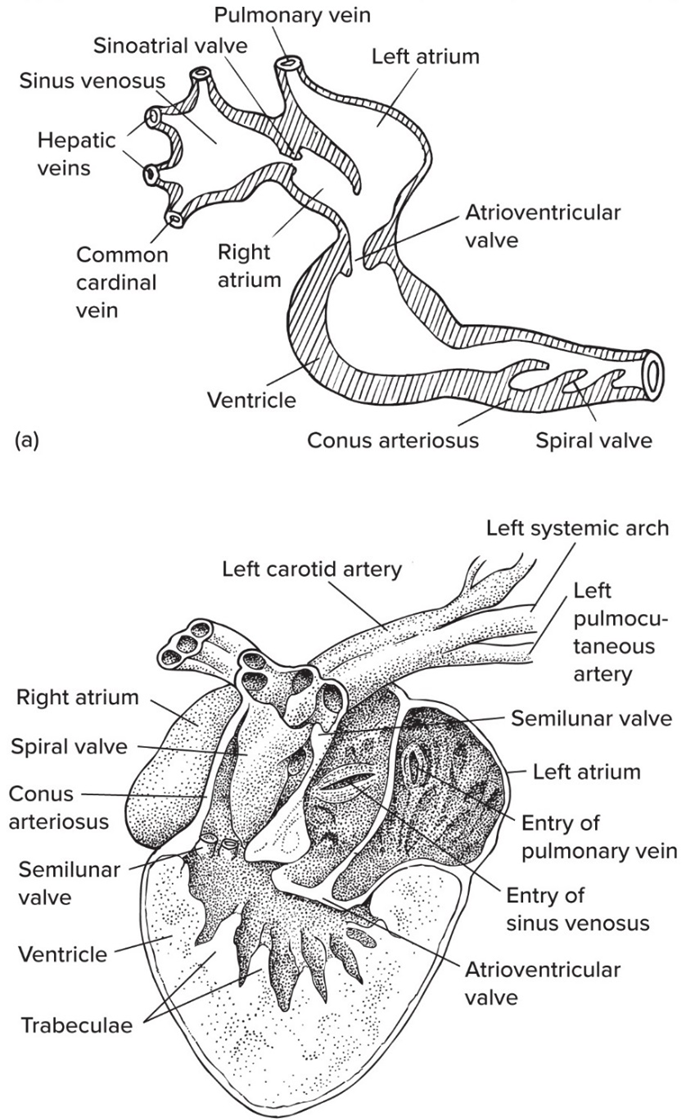
trabeculae w/in ventricle
Turtles and squamates heart consist of
5 chambers: 2 atria, 1 ventricle (3 interconnected compartments);
Ventricle divided by muscular ridge, Cavum pulmonale, Cavum venosum, Cavum ateriosum
Croc hearts are
o4 chambers: 2 atria, 2 ventricles;
Foramen of Panizza connects left and right systemic arches; and VALVES control blood flow, separate O2-rich and O2-poor blood
Turtle and croc have
right-to-left shunt when diving
Birds and mammal hearts are
4 heart chambers: 2 atria + 2 ventricles;
Sinus venosus greatly reduced, especially in mammals; Conus arteriosus splits during development, forms pulmonary trunk and single aortic trunk
Bird and mammal hearts arose
independently…4 chambered hearts are CONVERGENT evolution
For birds and mammals, L/R sides of heart are
completely separated after birth, separating O2-level differing blood
Blood vessels can act as heat blocks or radiators to maintain
body temperatures (vasodilation vs vasoconstriction)
Counter current exchange MAXIMIZES
heat transfer
Carotid rete
Regulates brain temp by cooling incoming blood
Cetaceans
artery-vein networks retain body heat