Bio Exam 1
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 1-3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
What are the characteristics of living organisms?
Organized and composed of cells
Reproduce, grow, and develop
Respond to changes in their environment
Capture and produce/process energy
Adapt and evolve over time as a population
Have regulatory mechanisms at many different levels (hierarchy of life)
All information is genetically encoded (DNA)
Prokaryotic cells are ______ organisms
singlecelled
Eukaryotic cells can be ______ or ______ organisms.
single-celled or multicelled
The smallest component of life’s hierarchy is _____
molecules
Everything is made of _____, both living and non-living
atoms
Cells are the _______
basic unit of life
The smallest unit of an element that is still able to retain its properties is a(n) _____
atom
What are the elements that make up 96% of the human body? (The Big 4)
Oxygen (65%)
Carbon (18.5%)
Hydrogen (9.5%)
Nitrogen (3%)
The atomic number is equal to….
the number of protons
Protons and neutrons are found in the _____
nucleus
When an element’s electrons change, it is called an ____
ion
When an element’s neutrons change, it is called an _______
isotope
The mass number equals…
the number of protons plus the number of neutrons
Many isotopes are ______, meaning they are radioactive
unstable
_______ can be used in research, medical diagnosis, and treatment because they behave identically in chemical reactions
isotopes
The inner most shell is considered full with __ electrons
2
Outer shells are considered full with __ electrons
8
What does inert mean?
Unavailable/full. An atom won’t bond with other atoms
How are ionic bonds formed?
between charged atoms, and typically with metals and nonmetals
After an ion donates an electron, the two ions are positively and negatively charged, and _____ each other, forming a compound.
attract
Ionic bonds have _____ strength. When they are in dry environments, the bond is ______. When ionic substances are in water, the bond is _____.
moderate; strong, weak
Salts are held together by _____ bonds
ionic
Sugars are held together by _____ bonds
covalent
What is an example of an ionic compound?
sodium chloride
sodium atom + chlorine atom = sodium and chloride ions
sodium ion + chloride ion = sodium chloride
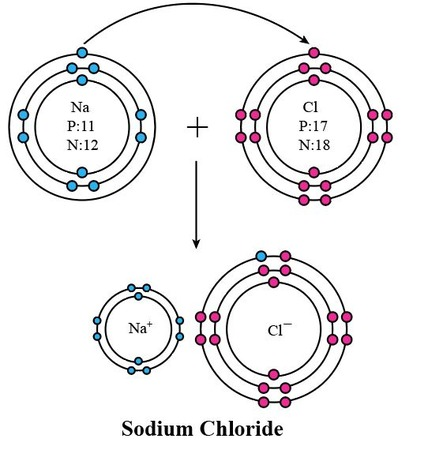
What is represented in this image?
Sodium Chloride
How are covalent bonds formed?
when two atoms share electrons
(co=together, sharing)
Covalent bonds are the _____ bond
strongest
Rather than donate or gain electrons, atoms with covalent bonds ______ electrons
share
Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons. How many bonding partners/covalent bonds can it have?
3
Nonpolar =
shared equally
Polar =
shared unequally
What is it called when an atom is large and tends to grab electrons close to itself?
electronegativity
Water is _____; aka formed by ______ bonds
polar; polar covalent
A dashed line on a model indicates a ________
hydrogen bond
A solid line on a model indicates a _______
covalent bond
What are the properties of water?
High Heat Capacity/Evaporation
Good Solvent
Cohesion and Adhesion
High Surface Tension
Low Density as a Solid
Acids have more ____ ions and less ____ ions
H+ (hydrogen), OH- (hydroxide)
Bases have more ____ ions and less ____ ions
OH- (hydroxide), H+ (hydrogen)
What is an example of a covalent compound?
Water
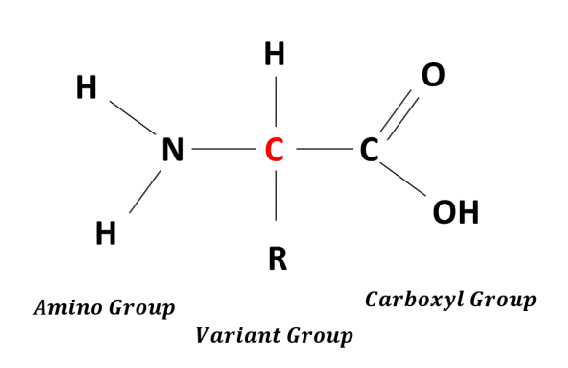
What is this?
Amino acid
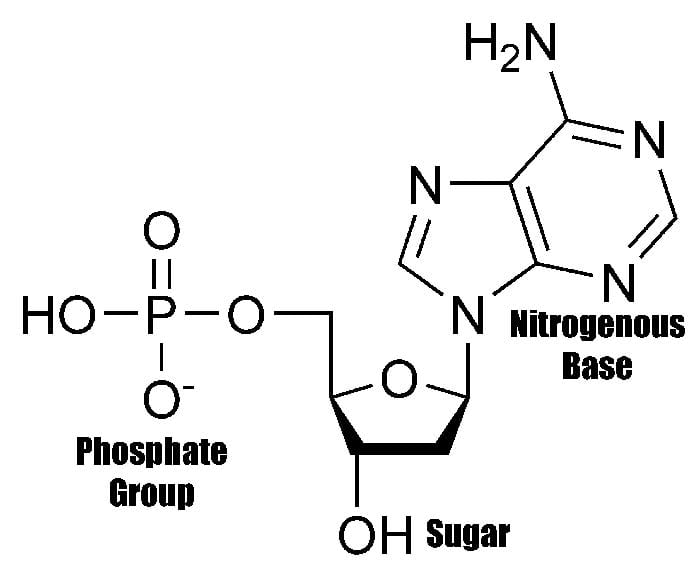
What is this?
Nucleotide
Amino acids are held together by _____
peptide bonds
What is a disease related to misfolded proteins?
Mad Cow Disease
Water has high surface tension because of its _____ ability
cohesion
Why does water have a high heat capacity?
Energy from the sun breaks the hydrogen bonds but they replace themselves quickly
Inorganic molecules have ____ atoms and are held together by _____ bonds
fewer; ionic
Organic Molecules have _____ atoms and are held together by ______ bonds
many; covalent
Inorganic molecules are usually associated with _____ organisms/matter
nonliving
Organic molecules are usually associated with _____ organisms/matter
living
Organic molecules always contain which two elements?
carbon and hydrogen
the tertiary structure of a protein refers to…
the overall three-dimensional structure
How do plants store energy for later?
starch
Hydroxyl group =
—OH
Carbonyl group =
>C=O
Carboxyl group =
— COOH
Amino group =
— NH2
Hydroxyl groups are found in
carbohydrates
Carbonyl groups are found in
lipids
Carboxyl groups are found in
proteins
Amino groups are found in
proteins
Phosphate groups are found in
DNA, ATP
What are isomers?
Compounds that have the same chemical formula but a different shape/function
What is an example of two isomers?
Glucose (6 membered ring) and fructose (5 membered ring)
What monomers make up lipids?
glycerol and fatty acids
What monomers make up carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides (simple sugar monomers)
What monomers make up nucleic acids?
nucleotides
Carbohydrates provide _____ and _____ energy
structure; quick (ex:bread, milk)
Which macromolecule regulates cell processes, forms bones and muscles, and transports materials
proteins (ex: eggs)
Which macromolecule provides long-term energy, forms membranes, and acts as a chemical messenger
Lipids (ex: butter)
What is starch’s function?
An energystorage unit for plants
What is glycogen’s function?
An energy storage unit for animals
What is dextran’s function?
An energy storage for bacteria
What is cellulose’s function?
Provides structure (cell wall of plants)
What is chitin’s function?
exoskeleton of various arthropods and cell walls of fungi
What is peptidoglycan’s function?
cell walls of bacteria
What are protein’s functions?
Structure, protection, regulatory, contractile, transport, storage, and enzymes
What is an example of structural protein?
keratin (fingernails, hair)
What is an example of a protective protein?
the antibodies that our white blood cells secrete
What is an example of a regulatory protein?
insulin
What is an example of a contractile protein?
actin
what is an example of a transport protein?
hemoglobin
What is an example of an enzyme protein?
amylase
what is an example of a storage protein?
albumin
Lipids are fats, ______ (polar/nonpolar), ______ (hydrophobic/hydrophilic)
nonpolar; hydrophobic
What are the components of a triglyceride molecule?
glycerol head, fatty acid tails
Saturated fats are ____ at room temp, while unsaturated fats are ____ at room temp
solid; liquid
What is ATP?
adenine triphosphate
What are sterols?
component of plasma membrane, and sex hormones
what are waxes?
protection, prevent water loss